*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NR 601 Midterm Study guide questions & answers, verified A+ grade. (All)
NR 601 Midterm Study guide questions & answers, verified A+ grade.
Document Content and Description Below
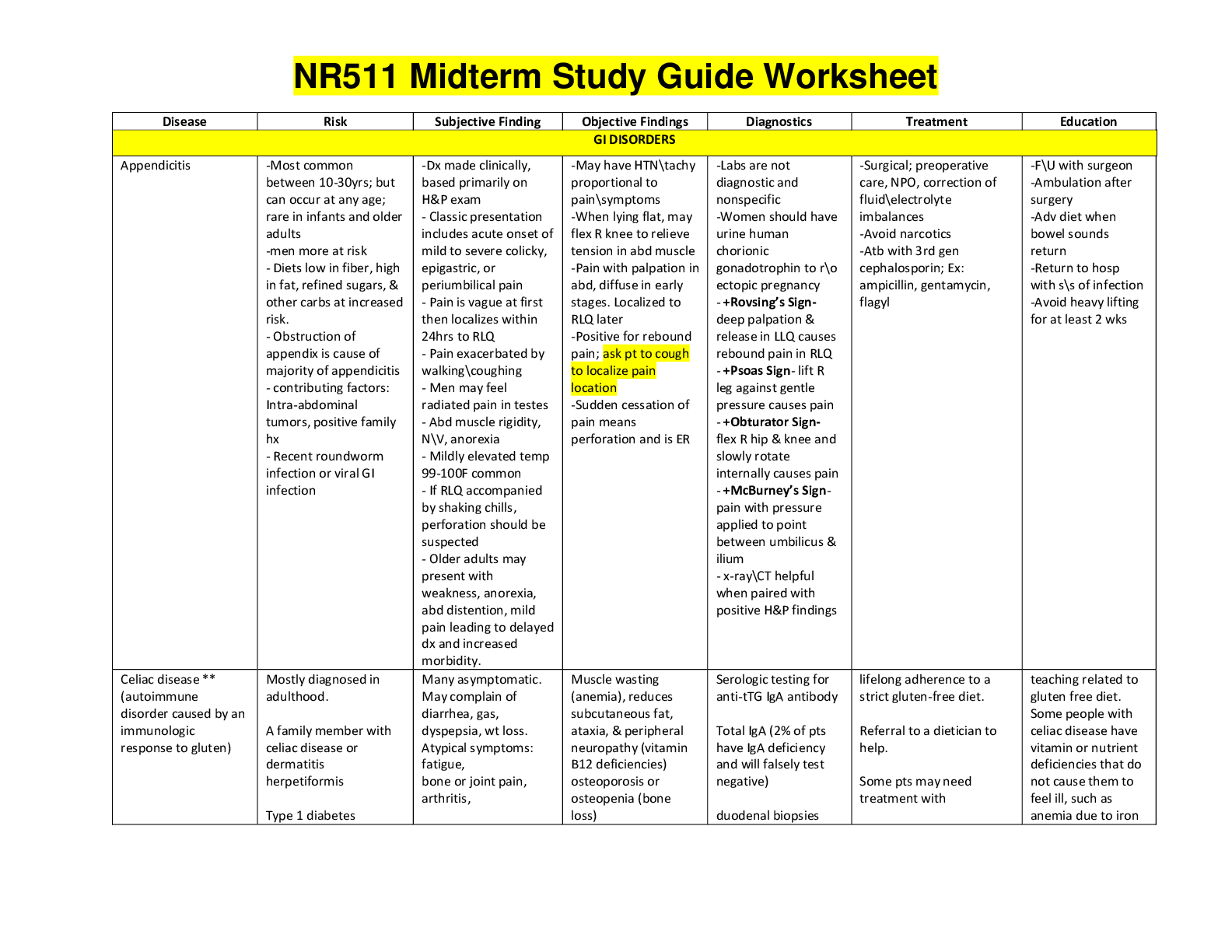
NR 601 Midterm Study guide. Chapter 1: Changes with Aging Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The major impact of the physiologic... al changes that occur with aging is: A. Reduced physiological reserve B. Reduced homeostatic mechanisms C. Impaired immunological response D. All of the above 2. The strongest evidence regarding normal physiological aging is available through: A. Randomized controlled clinical trials B. Cross-sectional studies C. Longitudinal studies D. Case control studies 3. All of the following statements are true about laboratory values in older adults except: A. Reference ranges are preferable B. Abnormal findings are often due to physiological aging C. Normal ranges may not be applicable for older adults D. Reference values are not necessarily acceptable values 4. Biochemical individuality is best described as: A. Each individual’s variation is often much greater than that of a larger group B. The unique biochemical profile of a selected population C. The truly “normal” individual—falling within average range D. Each individual’s variation is often much smaller than that of a larger group 5. Polypharmacy is best described as taking: A. More than nine medications per day B. More than five medications per day C. Even a single medication if there is not a clear indication for its use D. When a drug is given to treat the side effect of another drug 6. Pharmacokinetic changes with aging is reflective of: A. What the drug does to the body B. What the body does to the drug C. The effect at the site of action and the time and intensity of the drug D. The side effects commonly associated with the drug 7. All the following statements are false about drug absorption except: A. Antacids increase the bioavailability of digitalis B. Gastric acidity decreases with age C. Anticholinergics increase colonic motility D. Underlying chronic disease has little impact on drug absorption 8. All of the following statements are true about drug distribution in the elderly except: A. Drugs distributed in water have lower concentration B. Drugs distributed in fat have less intense, more prolonged effect C. Drugs highly protein bound have greater potential to cause an adverse drug reaction D. The fastest way to deliver a drug to the action site is by inhalation 9. Men have faster and more efficient biotransformation of drugs and this is thought to be due to: A. Less obesity rates than women B. Prostate enlargement C. Testosterone D. Less estrogen than women 10. The cytochrome p system involves enzymes that are generally: A. Inhibited by drugs B. Induced by drugs C. Inhibited or induced by drugs D. Associated with decreased liver perfusion 11. A statement not shown to be true about pharmacodynamics changes with aging is: A. Decreased sensitivity to oral anticoagulants B. Enhanced sensitivity to central nervous system drugs C. Drug responsiveness can be influenced by patient activity level D. There is a decreased sensitivity to beta blockers 12. Atypical presentation of disease in the elderly is reflected by all the following except: A. Infection without fever B. Depression without dysphoric mood C. Myocardial infarction with chest pain and diaphoresis D. Cardiac manifestations of thyroid disease 13. Functional abilities are best assessed by: A. Self-report of function B. Observed assessment of function C. A comprehensive head-to-toe examination D. Family report of function Chapter 2: Health Promotion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The leading cause of death in elderly travelers worldwide is: A. Cardiovascular disease B. Infections C. Accidents D. Malaria 2. Which of the following should be avoided in countries where food and water precautions are to be observed? A. Hot coffee B. Bottled water C. Salad buffet D. Unpeeled bananas 3. What insect precautions are not necessary to prevent insect-borne diseases in the tropics? A. Using 100% DEET on skin to prevent bites B. Treating clothes with permetherin C. Covering up exposed skin to lessen biting surface D. Taking malaria pills as directed for areas at risk for malaria 4. An example of secondary prevention you could recommend/order for older adults would be to: A. Check for fecal occult blood B. Wear seat belts in the car C. Provide foot care for a diabetic patient D. Administer a tetanus shot 5. Ali is a 72-year-old man who recently came to the U.S. from Nigeria. He reports having BCG (bacille Calmette-Guerin) vaccination as a child. Which of the following is correct regarding a tuberculin skin test? A. It should not be done at all. B. It should be read as smaller than it really is. C. Vaccination history is irrelevant; read as usual. -D. It should be read as larger than it really is. 6. A 72-year-old woman and her husband are on a cross-country driving vacation. After a long day of driving, they stop for dinner. Midway through the meal, the woman becomes very short of breath, with chest pain and a feeling of panic. Which of the following problems is most likely? A. Pulmonary edema B. Heart failure C. Pulmonary embolism D. Pneumonia 7. Ivan W. is a 65-year-old man who is new to your practice. He has a history of COPD, CAD, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. He has had no immunizations since his discharge from the military at age 25. Childhood diseases included chickenpox, measles, mumps, and “German measles.” He presents for a disease management visit. Which of the following immunizations would you recommend for Ivan? A. MMR, influenza, pneumococcal, Zostavax B. Influenza, pneumococcal, PPD, Hepatitis B C. Tdap, pneumococcal, influenza, Zostavax D. Hepatitis B, influenza, pneumococcal, Hepatitis A 8. Leo L. is a 62-year-old African American male who comes for an initial visit to your practice. Personal health history includes smoking 1 pack/day since age 11, consuming a case of beer (24 bottles) every weekend, and working as an assembler (sedentary job) for the past 10 years. Family history in first-degree relatives includes hypertension, high cholesterol, heart attack, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Leo’s BMI is 32; BP today is 130/86. You order a fasting glucose, lipid profile, and return visit for BP check. This is an example of: A. Primary prevention B. Secondary prevention C. Tertiary prevention D. Health profiling 9. A local chapter of a nurse practitioner organization has begun planning a community-based screening for hypertension at a local congregate living facility. This population was selected on the basis of: A. A predicted decreased incidence of high blood pressure in this population B. A recognized element of high risk within this group C. Readily available treatment measures D. Achieving an administrative goal for the congregate living facility 10. Performing range of motion exercises on a client who has had a stroke is an example of which level of prevention? A. Primary prevention B. Tertiary prevention C. Secondary prevention D. Rehabilitation prevention 11. The nurse practitioner demonstrates an understanding of primary prevention of falling among the elderly through which management plan? A. Evaluate a need for assistive devices for ambulation after the client has been injured from a fall. B. Provide resources to correct hazards contributing to falls in the home environment. C. Reinforce the need to use prescribed eyeglasses to prevent further injury from falls. D. Provide information about medications, side effects, and interactions. 12. An example of an active strategy of health promotion for an individual to accomplish would be: A. Maintaining clean water in the local environment B. Introducing fluoride into the water C. Beginning a stress management program D. Maintaining a sanitary sewage system 13. You are working with an older male adult with a long history of alcohol abuse and a 30-year history of smoking. In recommending an intervention for this client, your responsibility is to: A. Make the individual abandon his own health practices and follow your recommendations B. Register the patient for a local intervention program and secure payments C. Promote positive change in lifestyle choices D. Identify the barriers that the client will encounter 14. The four main domains of clinical preventive services that the practitioner will provide are: A. Counseling interventions, screening tests, immunizations, and chemoprophylaxis B. Counseling intervention, screening tests, immunizations, and education C. Counseling interventions, transportation, screening tests, and immunizations D. Screening tests, brief psychotherapy, immunizations, and chemoprophylaxis 15. Which organism that can be prevented by immunization is most often responsible for an infectious “outbreak” in the nursing home setting? A. Haemophilus influenza B. Streptococcus C. Influenza A D. Mycobacterium tuberculosis 16. What is the appropriate method for tuberculosis screening of an older adult entering a nursing home? A. 5 tuberculin units intramuscular PPD injection and if negative repeat with same dose one week later B. 5 tuberculin units intradermal PPD injection and if negative repeat with same dose one week later C. Chest x-ray at the same time of PPD testing D. 5 tuberculin units intradermal PPD injection and if positive repeat same dose in one week Chapter 3: Exercise in Older Adults Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Exercise recommended for older adults should include activities that: A. Conserve energy B. Restrict flexibility C. Strengthen muscles D. Are anaerobic in nature 2. Preferred amount of exercise for older adults is: A. 10 minutes of physical activity each morning B. 30 minutes per day of aerobic activity five times a week C. Any increase in physical activity over a sedentary lifestyle D. 60 minutes per day that includes 30 minutes of aerobic activity and 30 minutes of weight training five times a week 3. Which of the following medical conditions is not considered restrictive for engaging in physical activity? A. Unstable angina B. Dehydration C. Depression D. Uncontrolled tachycardia 4. The best recommendation for a patient who states they have no equipment to exercise would be: A. Sign a contract for a year’s membership to a local gym B. Borrow free weights from grandchildren C. Have a personal trainer come to the home three times a week D. Improvise with recommended objects at home that can be used 5. When the nurse practitioner recommends exercise for a sedentary older adult, which of the following pieces of advice should be considered for all types of exercise? A. Only use equipment recommended by physical trainers B. Start low and go slow C. Only group exercise is beneficial to someone who has not been active in a long time D. Focus only on one type of exercise for the first few months Chapter 5: Symptoms and Syndromes Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The term “geriatric syndrome” is best described as: A. A condition that has multiple underlying factors and involves multiple systems B. A condition that has a discreet etiology that is difficult to pinpoint C. Significant progress has been made in understanding geriatric syndromes, especially falls and delirium D. Therapeutic management of a geriatric syndrome can be accomplished once a specific diagnosis is made 2. The anal wink reflex is used to test: A. Rectal prolapse B. Sensation and pudental nerve function C. Baseline and squeeze sphincter tone D. Fissures and fistulas 3. Atypical presentation of acute coronary syndrome is: A. Most common in Hispanic females B. More common in men C. Most common in African American men D. More common in females 4. What disease can mimic and often co-exists with myocardial infarctions in elders with coronary artery disease? A. Hypertension B. Esophageal disease C. Diabetic gastroparesis D. Vascular disease 5. Thoracic aortic dissection presents typically as: A. Sharp stabbing pain in the mid thorax B. Pleuretic chest pain and dyspnea C. Severe retrosternal chest pain that radiates to the back and both arms D. Unilateral pleuretic chest pain and dyspnea 6. Medications known to contribute to constipation include all of the following except: A. Stimulant laxatives B. Anticholinergic drugs C. Broad-spectrum antibiotics D. Iron 7. Bordetella pertussis is best characterized by: A. Sub-acute cough lasting greater than two weeks B. Acute cough associated with a coryzal symptom C. Chronic cough with post-nasal drip D. Non-productive acute cough 8. The routine testing of tuberculosis should occur in all of the following vulnerable populations except: A. Nursing home residents B. Prison inmates C. Hospitalized elderly D. Immune-compromised patients 9. Which of the following statements about fluid balance in the elderly is false? A. Total body water decreases with age. B. Thirst response decreases as a person ages. C. African Americans have higher rates of dehydration than white Americans. D. Assessment of skin turgor at the sternum is a reliable indicator of dehydration in the elderly. 10. Distinguishing delirium from dementia can be problematic since they may co-exist. The primary consideration in the differential is: A. Performance on the Mini Mental Status Exam B. The Confusion Assessment is negative C. Rapid change and fluctuating course of cognitive function D. The presence of behavioral symptoms with cognitive impairment 11. Presbystasis is best described as: A. Impairment in vestibular apparatus that causes dizziness B. Age-related disequilibrium of unknown pathology characterized by a gradual onset of difficulty walking C. The loss of high frequency tones with aging that can impair sensation D. A disorder of the inner ear characterized by vertigo 12. If dizziness has a predictable pattern associated with it, the clinician should first consider: A. Hypoglycemia B. Psychogenic etiology C. Cardiovascular cause D. Neurogenic cause 13. All of the following are considered as contributors to dysphagia except: A. Anticholinergics B. Drugs that increase reflux symptoms C. Inadequate intake of fluids with medications and meals D. Smooth muscle relaxants 14. Evidence shows that the most important predictor of a fall is: A. Prior history of a fall B. Cognitive impairment C. Gait and balance disturbance D. Proximal muscle weakness 15. The most cost-effective interventions used to prevent falls are: A. Use of sitters B. Use of alarms (bed, chair, monitors) C. Tai Chi exercises D. Home modifications and vitamin D supplements 16. Chronic fatigue syndrome is best described as: A. Fatigue that is constant, lasting more than three months B. Fatigue lasting longer than six months and not relieved by rest C. Fatigue that waxes and wanes over a period of three months D. Total exhaustion with inability to get out of bed 17. Which form of headache is bilateral? A. Cluster B. Tension C. Migraine D. Acute angle closure glaucoma 18. Microscopic hematuria is defined as: A. Twenty or more RBCs on a urine sample B. Three or more RBCs on a urine sample C. Twenty or more RBCs on three or more samples of urine D. Three or more RBCs on three or more samples of urine 19. Risk factors associated with the finding of a malignancy in a patient with hemoptysis include all of the following except: A. Male sex B. Smoking history C. Over age 40 D. Childhood asthma 20. Recent weight loss is defined as: A. loss of >10 pounds over the past 3-6 months B. loss of >2 pounds a week C. 5% weight loss in three months D. 10% weight loss in one year 21. The most common cause of disability in the elderly is due to: A. Diabetes B. Arthritis C. Heart disease D. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 22. Lipedema is best described as: A. Bilateral accumulation of interstitial fluid B. Bilateral distribution of fat in the lower extremities C. Fluid retention caused by a compromised lymphatic system D. Lipid molecules that break down and cause fluid retention 23. Drug-induced pruritus is distinguished because it: A. Occurs soon after a new drug is taken B. Usually is a generalized rash C. May occur right after the drug is taken or months later D. Usually involves localized circumscribed lesions 24. A form of syncope that is more common in the elderly than younger adults is: A. Vasovagal B. Carotid sinus sensitivity C. Orthostatic hypotension D. Arrhythmias 25. All of the following statements about tremor are true except: A. The most common tremor is the Parkinson tremor B. Most individuals with tremor do not seek medical attention C. Psychogenic tremor is uncommon D. Tremor is more prevalent in whites than blacks 26. Overflow incontinence is usually associated with: A. Loss of urine that occurs with urgency B. Cognitive impairment C. Weak pelvic floor muscles D. Bladder outlet obstruction 27. Wandering is best described as: A. Aimless excessive ambulatory behavior B. Purposeful excessive ambulatory behavior C. Risk-seeking behavior in the cognitively impaired D. A result of boredom in those with dementia Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In mitral stenosis, p waves may suggest: A. Left atrial enlargement B. Right atrial enlargement C. Left ventricle enlargement D. Right ventricle enlargement 2. Aortic regurgitation requires medical treatment for early signs of CHF with: A. Beta blockers B. ACE inhibitors C. Surgery D. Hospitalization 3. A key symptom of ischemic heart disease is chest pain. However, angina equivalents may include exertional dyspnea. Angina equivalents are important because: A. Women with ischemic heart disease many times do not present with chest pain B. Some patients may have no symptoms or atypical symptoms. Diagnosis may only be made at the time of an actual myocardial infarction C. Elderly patients have the most severe symptoms D. A & B only 4. The best evidence rating drugs to consider in a post myocardial infarction patient include: A. ASA, ACE/ARB, beta-blocker, aldosterone blockade B. Ace, ARB, Calcium channel blocker, ASA C. Long-acting nitrates, warfarin, ACE, and ARB D. ASA, clopidogrel, nitrates 5. A 55-year-old post-menopausal woman with a history of hypertension complains of jaw pain on heavy exertion. There were no complaints of chest pain. Her ECG indicates normal sinus rhythm without ST segment abnormalities. Your plan may include: A. Echocardiogram B. Exercise stress test C. Cardiac catheterization D. Myocardial perfusion imaging 6. Preceding a stress test, the following lab work might include: A. CBC and differential to differentiate ischemic heart disease from anemia B. Liver enzymes to rule out underlying gall bladder disease C. Thyroid studies to rule out hyperthyroidism D. A & C only 7. Which test is the clinical standard for the assessment of aortic stenosis? A. Cardiac catheterization B. Stress test C. Chest x-ray D. Echocardiography 8. What is the most common valvular heart disease in the older adult? A. Aortic regurgitation B. Aortic stenosis C. Mitral regurgitation D. Mitral stenosis 9. On examination, what type of murmur can be auscultated with aortic regurgitation? A. Austin flint B. Systolic ejection C. Soft S1 and a Loud S2 D. Loud S1 10. Ischemic heart disease is: A. Defined as imbalance between oxygen supply and demand. B. Frequently is manifested as angina. C. Leading cause of death in the elderly. D. All of the above. 11. Which test is the clinical standard for the assessment of aortic stenosis? A. Cardiac catheterization B. Stress test C. Chest x-ray D. Echocardiography 12. The aging process causes what normal physiological changes in the heart? A. The heart valve thickens and becomes rigid, secondary to fibrosis and sclerosis B. Cardiology occurs along with prolapse of the mitral valve and regurgitation C. Dilation of the right ventricle occurs with sclerosis of pulmonic and tricuspid valves D. Hypertrophy of the right ventricle 13. An older adult may present with atypical clinical signs of pneumonia. The nurse practitioner needs to be aware that the clustering of all of the following signs and symptoms may be indicative of pneumonia in an older person except: A. Bradycardia B. Malaise C. Anorexia D. Confusion 14. Which of the following statements is true concerning anti-arrhythmic drugs? A. Amiodarone is the only one not associated with increased mortality and it has a very favorable side effect profile. B. Both long-acting and short-acting calcium channel blockers are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. C. Most anti-arrhythmics have a low toxic/therapeutic ratio and some are exceedingly toxic. D. Anti-arrhythmic therapy should be initiated in the hospital for all patients. 15. Dan G., a 65-year-old man, presents to your primary care office for the evaluation of chest pain and left-sided shoulder pain. Pain begins after strenuous activity, including walking. Pain is characterized as dull, aching; 8/10 during activity, otherwise 0/10. Began a few months ago, intermittent, aggravated by exercise, and relieved by rest. Has occasional nausea. Pain is retrosternal, radiating to left shoulder, definitely affects quality of life by limiting activity. Pain is worse today; did not go away after he stopped walking. BP 120/80. Pulse 72 and regular. Normal heart sounds, S1 and S2, no murmurs. Which of the following differential diagnoses would be most likely? A. Musculoskeletal chest wall syndrome with radiation B. Esophageal motor disorder with radiation C. Acute cholecystitis with cholelithiasis D. Coronary artery disease with angina pectoris 16. Jose M. is a 68-year-old man who presents to your primary care practice for a physical. Jose has had type 2 diabetes mellitus for 5 years, diet controlled. His BMI is 32. Smoker, pack per day for 25 years. He denies other medical problems. Family history includes CAD, CABG x4 for father, now deceased; CHF, type 2 diabetes mellitus, HT for mother. According to the AHA/ACC guidelines, what stage is Jose? A. Stage A B. Stage B C. Stage C D. Stage D 17. Susan P., a 60-year-old woman with a 30 pack year history, presents to your primary care practice for evaluation of a persistent, daily cough with increased sputum production, worse in the morning, occurring over the past three months. She tells you, “I have the same thing, year after year.” Which of the following choices would you consider strongly in your critical thinking process? A. Seasonal allergies B. Acute bronchitis C. Bronchial asthma D. Chronic bronchitis 18. The best way to diagnose structural heart disease/dysfunction non-invasively is: A. Chest x-ray B. EKG C. Echocardiogram D. Heart catheterization 19. A common auscultatory finding in advanced CHF is: A. Systolic ejection murmur B. S3 gallop rhythm C. Friction rub D. Bradycardia 20. The organism most commonly responsible for community-acquired pneumonia in older adults is: A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa B. Staphylococcus aureus C. Proteus mirabilis D. Streptococcus pneumonia 21. A 72-year-old woman and her husband are on a cross-country driving vacation. After a long day of driving, they stop for dinner. Midway through the meal, the woman becomes very short of breath, with chest pain and a feeling of panic. Which of the following problems is most likely? A. Pulmonary edema B. Heart failure C. Pulmonary embolism D. Pneumonia Chapter 12: Musculoskeletal Disorders Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Osteoarthritis of the cervical and lumbar spine causes pain that is related to all of the following except: A. Bone spur formation B. Pressure of the ligaments C. Reactive muscle spasm D. Crystal deposition 2. In differentiating osteoarthritis from chronic gout, pseudogout, or septic arthritis, the most valuable diagnostic study would be: A. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) B. Synovial fluid analysis C. C-reactive protein analysis D. Complete blood cell count 3. Patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and knee often have a distinguishable gait described as: A. Ataxic B. Festinating C. Antalgic D. Steppage 4. Which of the following best describes the pain associated with osteoarthritis? A. Constant, burning, and throbbing with an acute onset? B. Dull and primarily affected by exposure to cold and barometric pressure C. Begins upon arising and after prolonged weight bearing and/or use of the joint D. Begins in the morning but decreases with activity 5. Joint effusions typically occur later in the course of OA, especially in the: A. Knee B. Elbow C. DIP joints D. Hips 6. You have ordered a CBC for your patient you suspect has polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR). Which two clinical findings are common in patients with PMR? A. Neutropenia and hypochromic, normocytic anemia B. Normochromic, normocytic anemia and thrombocytosis C. Microcytic, hypochromic anemia and reticulocytopenia D. Macrocytic, hyperchromic anemia and leukocytopenia 7. You suspect that your patient has polymyalgia rheumatica and now are concerned that the patient may also have Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA). Which of the following two symptoms are most indicative of GCA and PMR? A. Jaw pain and heart murmur B. Joint swelling and sudden loss of central vision bilaterally C. Hoarseness and the total inability to grasp small objects D. Scalp tenderness and aching in shoulder and pelvic girdle 8. Your 63-year-old Caucasian woman with polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) will begin treatment with corticosteroids until the condition has resolved. You look over her records and it has been 2 years since her last physical examination and any laboratory or diagnostic tests as she relocated and had not yet identified a health-care provider. In prioritizing your management plan, your first orders should include: A. Recommending she increase her dietary intake of Calcium and Vitamin D B. Ordering once a year bisphosphonate and a proton pump inhibitor C. Participate in a fall prevention program D. Dual-energy x-ray (DEXA) scan and updating immunizations 9. Which of the following differential diagnosis for patients presenting with polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) can be ruled out with a muscle biopsy? A. Parkinson’s disease B. Polymyositis C. Late onset rheumatoid arthritis D. Giant Cell Arteritis 10. In reviewing laboratory results for patients suspected with polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR), you realize that there is no definitive test to diagnosis PRM, rather clinical response to treatment. Results you would expect to see include: A. Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) greater than 50mm per hour B. Elevated rheumatoid factor and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (RF and ACPA) C. Decreased C-reactive protein level (CR-P) D. Elevated thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) 11. Which of the following is the most appropriate laboratory test for monitoring gout therapy over the long-term? A. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) B. Completer blood count (CBC) C. Serum urate level D. Serum albumin 12. In providing health teaching related to dietary restrictions, the nurse practitioner should advise a patient with gout to avoid which of the following dietary items: A. Green leafy vegetables B. Beer, sausage, fried seafood C. Sugar D. Gluten and bread items 13. The best method of verifying a diagnosis of gout in a joint is which of the following: A. Radiographic examination of the joint with two views B. Ultrasound C. Palpation D. Joint aspiration and polarized-light microscopy 14. The most appropriate first-line treatment for an acute gout flare is (assuming no kidney disease or elevated bleeding risk): A. Indomethacin 50 mg TID for 2 days; then 25 mg TID for 3 days B. Doxycycline 100 mg BID for 5 days C. Prednisolone 35 mg QD for 5 days D. Ice therapy 15. The nurse practitioner orders bilateral wrist X-rays on a 69-year-old gentleman complaining of pain in both wrists for the past 6 weeks not related to any known trauma. The nurse practitioner suspects elderly onset rheumatoid arthritis. The initial radiographic finding in a patient with elderly onset rheumatoid arthritis would be: A. Symmetric joint space narrowing B. Soft tissue swelling C. Subluxations of the joints D. Joint erosions 16. The nurse practitioner is examining the hands of a 55-year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis and notes bilateral spindle shaped deformities on the middle interphalangeal joints. These are known as: A. Haygarth’s nodes B. Heberden’s nodes C. Bouchard’s nodes D. Benediction hands 17. A 72-year-old female patient has been diagnosed with gout. She also has a long history of chronic congestive heart failure. The most likely contributing factor to the development of gout in this older female is: A. Lead intoxication B. Illegal whiskey C. Binge-eating D. Thiazide diuretics 18. Which of the following statements about osteoarthritis is true? A. It affects primarily weight-bearing joints B. It is a systemic inflammatory illness C. The metacarpal phalangeal joints are commonly involved D. Prolonged morning stiffness is common 19. In considering the specificity of laboratory data, the most reliable diagnostic test listed below would be: A. Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) to rule out inflammation B. CBC to rule out infection C. Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) test to rule out a collagen disease D. Synovial fluid analysis to differentiate between an infectious versus an inflammatory infusion 20. When examining the spine of an older adult you notice a curvature with a sharp angle. This is referred to as a: A. Gibbus B. Scoliosis C. Kyphosis D. Lordosis Chapter 14: Endocrine, Metabolic, and Nutritional Disorders Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An elderly client presents with a new onset of feeling her heart race and fatigue. An EKG reveals atrial fibrillation with rate >110. The patient also has a new fine tremor of both hands. Which of the following would the nurse practitioner suspect? A. Hypothyroidism B. Hyperthyroidism C. Congestive heart failure D. Type 2 diabetes mellitus 2. A 62-year-old female complains of fatigue and lack of energy. Constipation has increased and the patient has gained ten pounds in the past 3 months. Depression is denied although the patient reports a lack of interest in usual hobbies. Vital signs are within normal limits and the patient’s skin is dry and cool. Which of the following must be included in the differential? A. Hyperthyroidism B. Hypothyroidism C. Hyperparathyroidism D. Grave’s disease 3. Mrs. Black, an 87-year-old patient, has been taking 100 mcg of Synthroid for 10 years. She comes to your office for a routine follow-up, feeling well. Her heart rate is 90. Your first response is to: A. Increase the Synthroid B. Order TSH C. Start a beta-blocker D. Order thyroid scan 4. Which patient is most likely to have osteoporosis? A. An 80-year-old underweight male who smokes and has been on steroids for psoriasis B. A 90-year-old female with no family history of osteoporosis who is on hormone replacement therapy C. A 68-year-old overweight female who drinks 1-2 drinks alcohol/day D. An 82-year-old female with a normal BMI takes calcium and performs weight-bearing exercise daily 5. When evaluating the expected outcome for a hypothyroid elderly patient placed on levothyroxine, the nurse practitioner will: A. Assess a weekly TSH B. Assess the TSH in 4-6 weeks C. Ask the patient if the symptoms have subsided and adjust dosage accordingly D. Decrease the dosage should a cardiac event occur 6. A postmenopausal woman with osteoporosis is taking a bisphosphonate daily by mouth. What action information statement would indicate the patient understood the nurse practitioner’s instructions regarding this medication? A. Takes medication at bedtime with a full glass of water B. Takes medication with a full glass of water when up in a.m. 30 minutes prior to other food and medications C. Takes medication when up in a.m. with a glass of orange juice to increase absorption D. Takes medication sitting up and with a meal to avoid gastrointestinal distress 7. The primary reason levothyroxine sodium is initiated at a low dose in an elderly patient with hypothyroidism is to prevent which of the following untoward effects? A. Angina and arrhythmia B. Nausea and diarrhea C. Confusion and delirium D. Osteoporosis and muscle weakness 8. Six months ago an elderly patient was diagnosed with subclinical hypothyroidism. Today the patient returns and has a TSH of 11.0 and complains of fatigue. He has taken Synthroid 25 mcg daily as prescribed. What is the best course of action for the nurse practitioner? A. Assess further for a cause of fatigue B. Double the dose of Synthroid C. Discontinue the Synthroid D. Prescribe Liotrix (T3 & T4 combination) 9. A fluoroquinolone (Ciprofloxin) is prescribed for a male patient with a UTI. What should the nurse practitioner teach the patient regarding taking this medication? A. It must be taken on an empty stomach B. Its effectiveness is decreased by antacids, iron, or caffeine ingestion C. It may cause a metallic aftertaste D. Its effectiveness is not a concern and it can be taken with any medications 10. A patient has been prescribed metformin (Glucophage). One week later he returns with lowered blood sugars but complains of some loose stools during the week. How should the nurse practitioner respond? A. Discontinue the medication immediately B. Reassure the patient that this is an anticipated side effect C. Double the dosage of medication and have patient return in 1 week D. Order a chem. 7 to check for lactic acidosis 11. Which of the following signs of hyperthyroidism commonly manifest in younger populations, but is notably lacking in the elderly? A. Weight gain B. Constipation C. Bradycardia D. Exophthalmos 12. A 60-year-old obese male client has type 2 diabetes mellitus and a lipid panel of TC = 250, HDL = 32, LDL = 165. The nurse practitioner teaches the patient about his modifiable cardiac risk factors, which include: A. Advancing age, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and male gender B. Diabetes, obesity, and hyperlipidemia C. Hyperlipidemia, smoking, and family history of heart disease D. Male with age > 45, diabetes mellitus, and hyperlipidemia 13. A diabetic patient presents with the complaint of right foot pain but denies any recent known injury. He states it has gotten progressively worse over the past few months. On exam, vibratory sense, as well as sensation tested with a monofilament, was abnormal. The patient’s foot is warm, edematous, and misshapen. The nurse practitioner suspects Charcot foot. What intervention is indicated? A. Warm soaks and return for follow-up in 1 week B. Referral to a pain management clinic C. Referral to an orthopedist D. Referral to a cardiologist for evaluation of peripheral vascular disease 14. What is a sign of insulin resistance that can present in African American patients? A. Acanthosis Nigricans B. Psoriasis Nigricans C. Seborrheic Nigricans D. Bullemic Nigricans 15. During a routine physical examination of a 62-year-old female patient, the nurse practitioner identifies xanthelasma around both his eyes. What is the significance of this finding? A. High potential for future blindness and requires immediate referral B. None, normal variant of aging process C. Abnormal lipid metabolism requiring medical management D. Hereditary variant that is of no consequence but requires watchful waiting 16. Mr. White is 62 years old and has chronic kidney disease that has been relatively stable. He also has a history of hyperlipidemia, osteoarthritis, and hypertension. He is compliant with his medications, and his BP has been well controlled on a calcium channel blocker. His last lipid panel showed: TC = 201, HDL = 40, TG = 180, LDL = 98. He currently takes Crestor 20 mg daily. In the office today, his BP is 188/90, and his urine dip now shows significant proteinuria. He denies any changes in his dietary habits or medication regimen. What would be the best medication change for Mr. White at this point? A. No change—have him return in 4 weeks for a re-check of his blood pressure and urine B. Increase the dose of the calcium channel blocker for his hypertension C. Change the calcium channel blocker to an ACE-I D. Increase the dose of his Crestor and have him return in 3 months for a re-check of his BP 17. You are working as a nurse practitioner in the Fast Track of the emergency room. A 76-year-old male presents with left upper quadrant abdominal pain. There can be many conditions that present as left upper quadrant pain, but which of the following is least likely to cause pain in the left upper quadrant? A. Splenic abscess B. Left pyelonephritis C. Splenic rupture D. Acute pancreatitis 18. Which is a “cardinal feature” of failure to thrive? A. Decline in toileting ability B. Gait disturbance C. Poor nutritional status D. Spiritual distress 19. Feeding gastrostomy tubes at end-of-life Alzheimer’s disease patients have been associated with: A. Prolongation of life B. Aspirational pneumonia C. Increase in skin infections D. Reversal of any clinical signs of failure to thrive 20. Which of the following nutritional indicators is not an indication of poor nutritional status in an older person? A. Albumin of < 3.5 g/dl B. Body mass index of 25 C. Total cholesterol < 150 mg/dl D. Loss of 10% body weight in 180 days Chapter 16: Psychological Disorders Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The prevalence of depression in nursing home residents is greater than adults living in the community. A. 1-2 times B. 2-3 times C. 3-4 times D. 5 times 2. The majority of depressed older adults remain untreated because of: A. Misdiagnosis B. Social stigma C. Environmental barriers D. All of the above 3. Symptoms of depression distinct to the elderly include: A. Flat affect B. Loss of pleasure in usual activities C. Appetite and weight disturbances D. Lack of emotions 4. The justification for ordering a CBC, TSH, and serum B12 for a patient you suspect may have clinical depression is: A. To determine the cause of sadness B. Because of overlapping symptoms with anemia, thyroid dysfunction, and nutritional deficiencies C. To differentiate between depression and metabolic disorders D. To rule out vascular disease 5. One major difference that is useful in the differential diagnosis of dementia versus delirium is that: A. Dementia develops slowly and delirium develops quickly B. The initial symptoms of dementia are more severe than the symptoms of delirium C. Dementia symptoms are not associated with underlying medical conditions and delirium symptoms usually result from underlying medical conditions D. Symptoms of delirium involve memory and attention and symptoms of dementia involve only memory 6. Which of the following is the most appropriate screening tool for delirium? A. Lawton Scale of Instrumental Activities of Daily Living B. Confusion Assessment Method C. Folstein’s Mini-Mental Status Examination D. Montreal Cognitive Assessment 7. The proposed mechanism by which diphenhydramine causes delirium is: A. Serotinergic effects B. Dopaminergic effects C. Gabanergic effects D. Anticholinergic effects 8. The elderly are at high risk for delirium because of: A. Multisensory declines B. Polypharmacy C. Multiple medical problems D. All of the above 9. A consistent finding in delirium, regardless of cause, is: A. Dopamine deficiency B. Serotinergic toxicity C. Acetylcholine deficiency D. Reduction in regional cerebral perfusion 10. Older adults with dementia sometimes suffer from agnosia, which is defined as the inability to: A. Use language B. Understand language C. Recognize objects D. Remember events and places 11. In late stages of dementia, a phenomenon called “sun downing” occurs, in which cognitive disturbances tend to: A. Improve as the day goes on B. Become worse toward the evening C. Fluctuate during the course of the day D. Peak mid-day 12. Of the following, which one is the most useful clinical evaluation tool to assist in the diagnosis of dementia? A. Folstein’s Mini-Mental Status Exam (MMSE) B. St. Louis University Mental Status Exam (SLUMS) C. Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) D. Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) 13. The cornerstone of pharmacotherapy in treating Alzheimer’s disease is: A. Cholinesterase inhibitors B. NMDA receptor antagonist C. Psychotropic medications D. Anxiolytics 14. The comorbid psychiatric problem with the highest frequency in dementia is: A. Anxiety B. Depression C. Agitation and aggression D. Psychosis 15. When treating depression associated with dementia, which of the following would be a poor choice and should not be prescribed? A. Fluoxetine B. Desipramine C. Amitriptyline D. Mirtazapine Chapter 18: Chronic Illness and the Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All of the following statements are true about chronic disease/illness except: A. Chronic disease is defined as a condition that requires both modification by the patient along with interaction with the provider B. The meaning of chronic illness includes the experience of the patient and family and provider C. Chronic illness is reversible if diagnosed and treated early D. Chronic conditions are those that last a year or longer 2. The highest number of people with multiple chronic conditions are those that are: A. Over age 85 B. Diagnosed with type 2 diabetes C. African American women over age 65 D. Diagnosed with COPD 3. Long durations of a chronic illness that are most commonly associated in both women and men are: A. Heart disease and obesity B. Diabetes and COPD C. Arthritis and dementia D. Dyslipidemia and eye disease 4. The percentage of non-institutionalized elderly over age 75 with limitations in activity due to a chronic condition is: A. 25% B. Nearly 50% C. Over 75% D. Less than 15% 5. Which of the following statements are true? A. Most Medicare participants have a single care provider B. Chronic kidney disease patients have better outcomes due to the dialysis benefit C. Nearly half of Medicare participants have five or more chronic diseases D. Nearly half of Medicare participants have three or more chronic diseases 6. Which statement about chronic mental disorders is false? A. The numbers are projected to increase in the next decade B. Individuals with mental health problems actually have a decreased risk of medical problems C. The number of older adults with addiction problems is projected to increase in the next decade D. Nearly half of individuals with dementia are not diagnosed prior to hospitalization 7. All of the following criteria define frailty except: A. Unintentional weight loss >10 pounds in the past year B. Slow walking speed C. Stooped posture D. Self-reported exhaustion 8. All of the following are health consequences of obesity except: A. Mortality of aging B. Hypertension C. Coronary artery disease D. Sleep apnea 9. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines may have limited applicability in the older population because: A. They often are disease specific B. They often have complex comorbid conditions C. Both A and B D. None of the above evidence-based clinical practice guidelines are always the standard 10. Inter-professional care is distinguished from other models of team-based care in that: A. Independent providers share information B. Expert advice is shared from one provider to another C. Different disciplines work under one leader D. Shared leadership and accountability is a primary focus 11. All of the following statements about the Chronic Care Model are true except: A. It was developed with Robert Wood Johnson Foundation funding B. It focuses exclusively on a self-management model C. It is an evidence-based policy response designed to meet the needs of the chronically ill D. It directs quality improvement and system change for patients with chronic disease 12. The legislation signed in March 2010 with provisions for addressing chronic disease was: A. Accountable Care Organization Act B. Independence at Home Act C. Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act D. Patient Centered Medical Home Act 13. Reported outcome measures for the Patient Centered Medical Home include all of the following except: A. Emergency room use B. Hospitalizations C. Patient/family satisfaction D. Number of primary care visits 14. Transitional care is best described as: A. A set of actions to ensure the coordination and continuity of care across sites/settings B. The care received in transit from one site of care to another C. A discharge-planning model D. Long-term acute care that provides the transition from hospital to long-term care or home [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 31 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 25, 2020
Number of pages
31
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 25, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
48