*NURSING > EXAM > NSG6005 Week 5 Quiz / NSG 6005 Week 5 Quiz (New, 2020): South University (SATISFACTION GUARANTEED) (All)
NSG6005 Week 5 Quiz / NSG 6005 Week 5 Quiz (New, 2020): South University (SATISFACTION GUARANTEED)
Document Content and Description Below
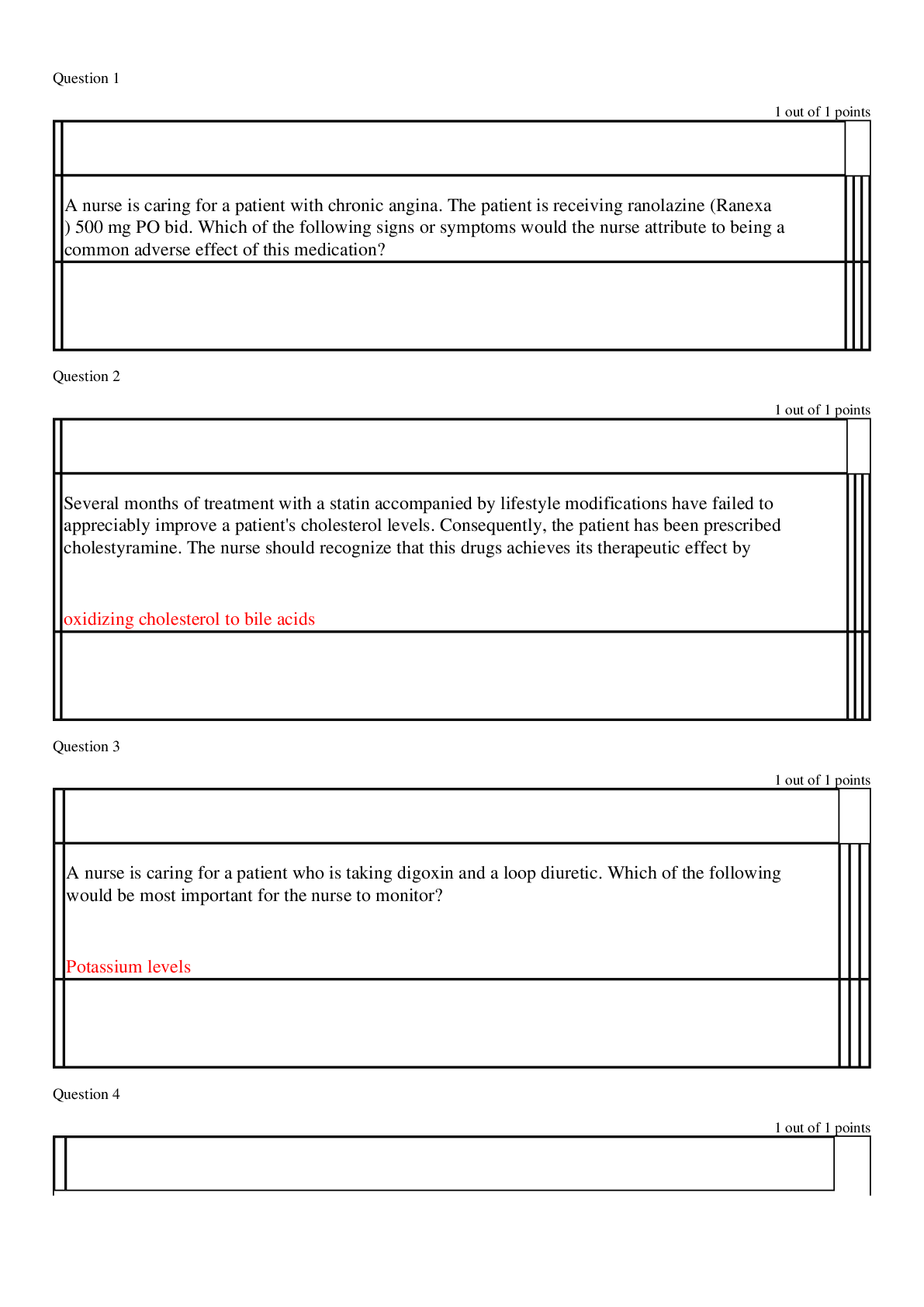
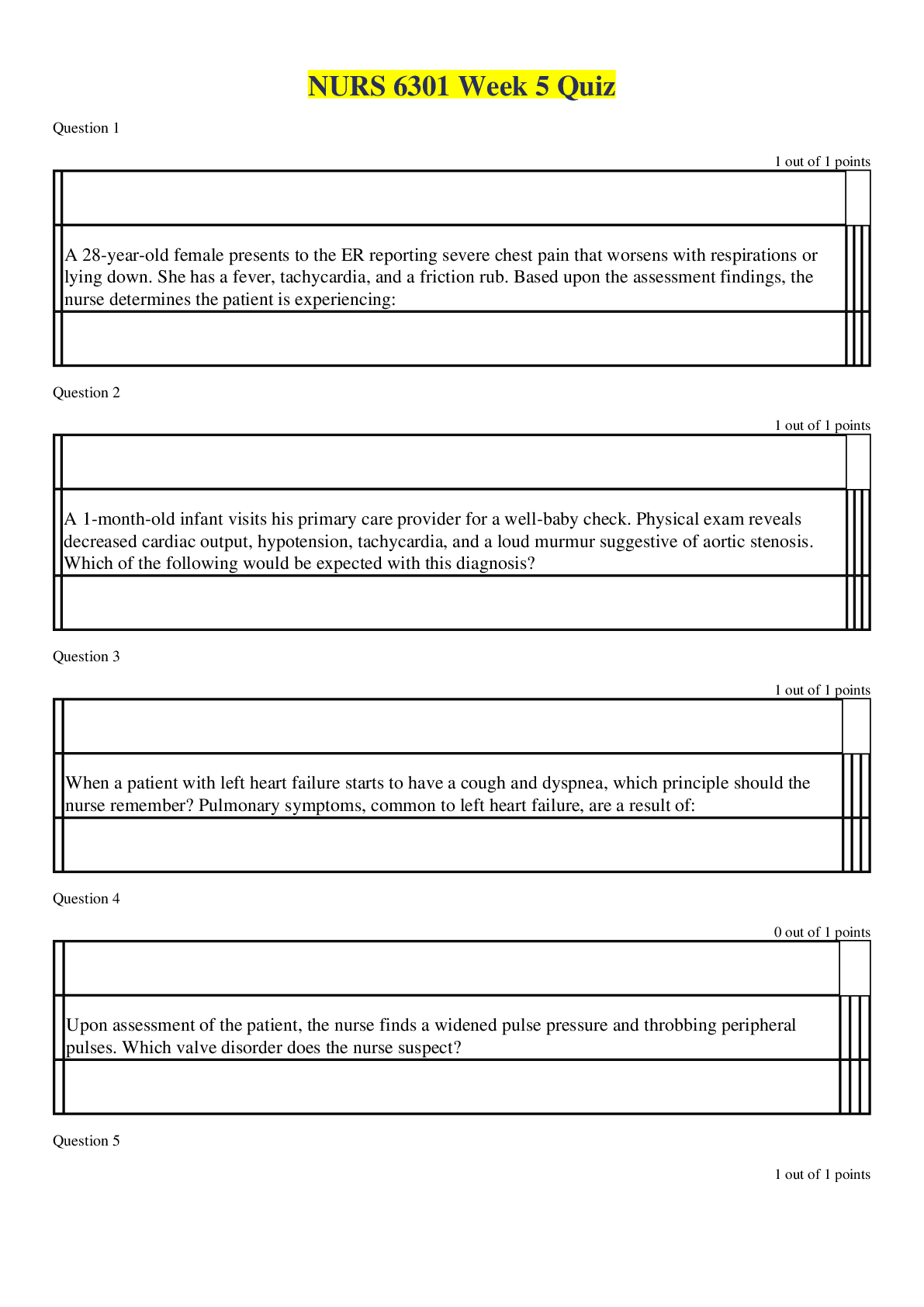
NSG6005 Week 5 Quiz / NSG 6005 Week 5 Quiz (Latest): South University South University NSG 6005 Week 5 Quiz / South University NSG6005 Week 5 Quiz (Latest) Question 1 : A sixty-six-year-old male was p... rescribedphenelzine (Nardil) while in an acute psychiatric unit for recalcitrant depression. The nurse practitioner managing his primary healthcare needs to understand the following regarding phenelzine and other monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs): He should not be prescribed any serotonergic drug such as sumatriptan (Imitrex). MAOIs interact with many common foods, including yogurt, sour cream, and soy sauce. Symptoms of hypertensive crisis (headache, tachycardia, sweating, etc.) require immediate treatment. All the above options are correct. Question 2. Jack, eight years old, has attention deficit disorder (ADD) and is prescribed methylphenidate (Ritalin). He and his parents should be educated about the side effects of methylphenidate, which are: Slurred speech and insomnia Bradycardia and confusion Dizziness and orthostatic hypotension Insomnia and decreased appetite Question 3. Question : Cecilia presents with depression associated with complaints of fatigue, sleeping all the time, and lack of motivation. An appropriate initial antidepressant for her would be: Student Answer: Fluoxetine (Prozac) Paroxetine (Paxil) Amitriptyline (Elavil) Duloxetine (Cymbalta) Question 4. Jake, a forty-five-year-old patient with schizophrenia, was recently hospitalized for acute psychosis due to medication noncompliance. He was treated with intramuscular (IM) long-acting haloperidol. Besides being monitored for his schizophrenia symptoms, the patient should be assessed by his primary care provider: For excessive weight loss With the Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS) for extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) symptoms Monthly for tolerance to the haloperidol Only by the mental health provider as most nurse practitioners in primary care do not care for mentally ill patients Question 5. Monitoring for a child on methylphenidate for ADHD includes: ADHD symptoms Routine height and weight checks Amount of methylphenidate being used All of the above Question 6. An appropriate drug for the treatment of depression with anxiety would be: Alprazolam (Xanax) Escitalopram (Lexapro) Buspirone (Buspar) Amitriptyline (Elavil) Question 7. When prescribing Adderall (amphetamine and dextroamphetamine) to adults with ADHD, the nurse practitioner will need to monitor: The blood pressure Blood glucose levels Urine ketone levels Liver function Question 8. Levetiracetam has known drug interactions with: Oral contraceptives Carbamazepine Warfarin Few, if any, drugs Question 9. Cara is taking levetiracetam (Keppra) to treat seizures. Routine education for levetiracetam includes reminding her: To not abruptly discontinue levetiracetam due to the risk of withdrawal seizures To wear a sunscreen due to photosensitivity from levetiracetam To get an annual eye exam while on levetiracetam To report weight loss if it occurs Question 10. A nineteen-year-old male was started on risperidone. Monitoring for risperidone includes observing for common side effects, including: Bradykinesia, akathisia, and agitation Excessive weight gain Hypertension Potentially fatal agranulocytosis Question 11. An appropriate first-line drug to try for mild to moderate generalized anxiety disorder would be: Alprazolam (Xanax) Diazepam (Valium) Buspirone (Buspar) Amitriptyline (Elavil) Question 12. One major drug used to treat bipolar disease is lithium. Because lithium has a narrow therapeutic range, it is important to recognize symptoms of toxicity, such as: Orthostatic hypotension Agitation and irritability Drowsiness and nausea Painful urination and abdominal distention Question 13. A patient with anxiety and depression may BEST respond to: Duloxetine (Cymbalta) Fluoxetine (Prozac) Oxazepam (Serax) Buspirone (Buspar) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) combined Question 14. Selma, who is overweight, recently started taking topiramate for seizures, and at her follow-up visit, you note she has lost 3 kg. The appropriate action would be: Tell her to increase her caloric intake to counter the effects of the topiramate. Consult with a neurologist as this is not a common adverse effect of topiramate. Decrease her dose of topiramate. Reassure her that this is a normal side effect of topiramate and continue to monitor her weight. Question 15. Sarah, a forty-two-year-old female, requests a prescription for an anorexiant to treat her obesity. A trial of phentermine is prescribed. Prescribing precautions include understanding that: Obesity is a contraindication to prescribing phentermine. Anorexiants may cause tolerance and should only be prescribed for six months. Patients should be monitored for postural hypotension. Renal function should be monitored closely while the patient is on anorexiants. Question 16. Patients should be instructed regarding the rapid onset of zolpidem (Ambien) because: Zolpidem should be taken just before going to bed. Zolpidem may cause a dry mouth and constipation. Patients may need to double the dose for effectiveness. Patients should stop drinking alcohol at least thirty minutes before taking zolpidem. Question 17. In choosing a benzodiazepam to treat anxiety, the prescriber needs to be aware of the possibility of dependence. The benzodiazepam with the greatest likelihood of rapidly developing dependence is: Chlordiazepoxide (Librium) Clonazepam (Klonopin) Alprazolam (Xanax) Oxazepam (Serax) Question 18. Common mistakes practitioners make in treating anxiety disorders include: Switching medications after an eight-week trial to a twelve-week trial Maximizing dosing of antianxiety medications Encouraging exercise and relaxation therapy before starting medication Thinking a partial response to medication is acceptable Question 19. Judy is being prescribed phenytoin for seizures. Monitoring includes: Assessing for phenytoin hypersensitivity syndrome three to eight weeks after starting treatment Assessing for pedal edema throughout therapy Assessing the heart rate at each visit and consider altering therapy if the heart rate is less than 60 bpm Assessing for vision changes, such as red-green blindness, at least annually Question 20. Cynthia is taking valproate (Depakote) for seizures and would like to get pregnant. What advice would you give her? Valproate is safe during all trimesters of pregnancy. She can get pregnant while taking valproate, but she should take adequate folic acid. Valproate is not safe at any time during pregnancy. Valproate is a known teratogen but may be taken after the first trimester if necessary. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 7 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 07, 2020
Number of pages
7
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 07, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
36