*NURSING > ATI MEDICAL SURGICAL > TEST BANK CHAPTER 50: CARE OF SURGICAL PATIENTS QUESTION AND ANSWERS,100% CORRECT (All)
TEST BANK CHAPTER 50: CARE OF SURGICAL PATIENTS QUESTION AND ANSWERS,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
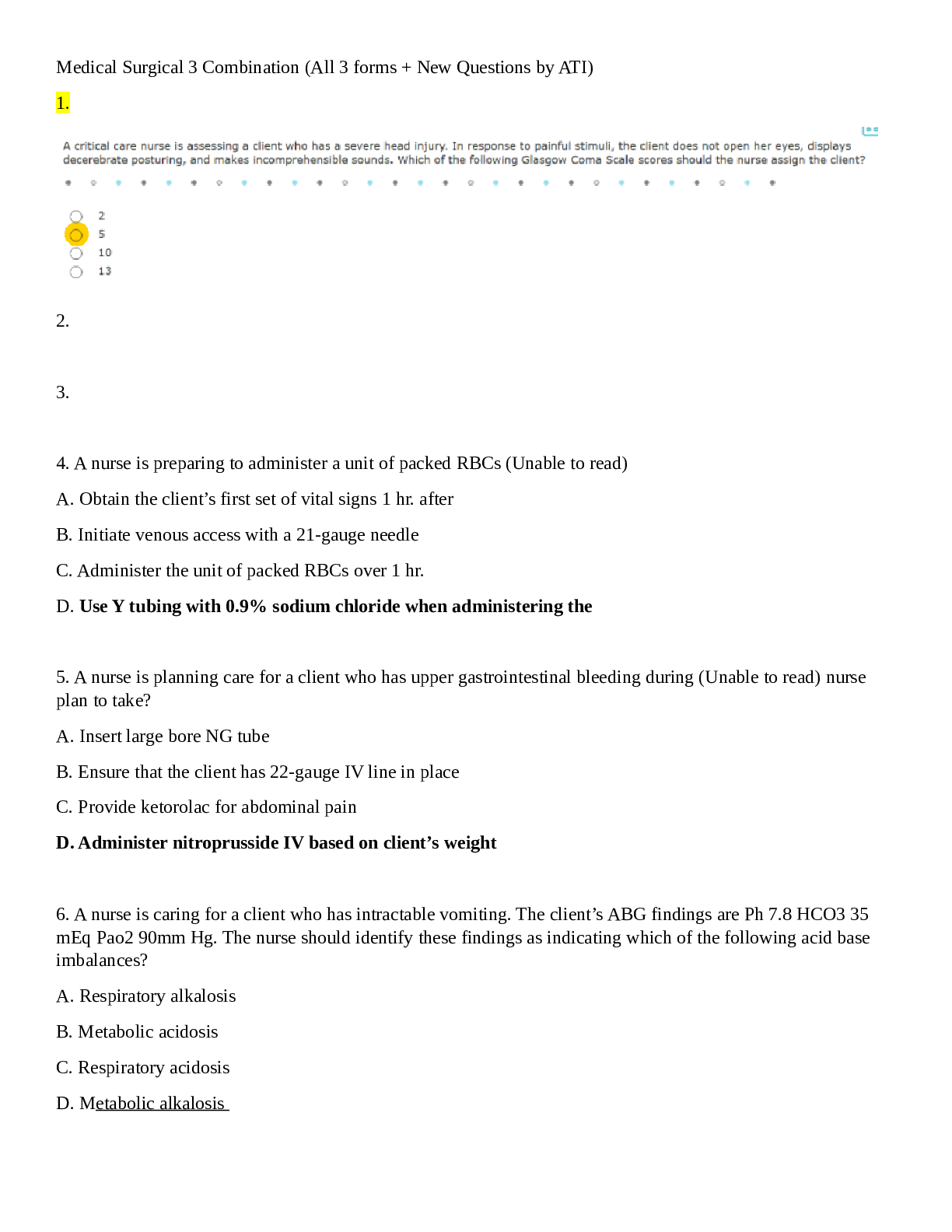
TEST BANK CHAPTER 50: CARE OF SURGICAL PATIENTS QUESTION AND ANSWERS MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The nurse is precepting a student nurse and explains that perioperative nursing care occurs a. Before, duri... ng, and after surgery. b. In preadmission testing. c. During the surgical procedure. d. In the postanesthesia care unit. ANS: A Perioperative nursing care occurs before, during, and after a surgery. Preadmission testing occurs before surgery and is considered preoperative. Nursing care provided during the surgical procedure is considered intraoperative, and in the postanesthesia care unit, it is considered postoperative. All of these are parts of the perioperative phase, but each individual phase does not explain the term completely. DIF: Remember REF: 1254 OBJ: Explain the concept of perioperative nursing care. TOP: Implementation MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 2. The nurse is caring for a patient who is scheduled to undergo a surgical procedure. The nurse is completing an assessment and reviews the patient’s laboratory tests and allergies. In which perioperative nursing phase would this work be completed? a. Perioperative b. Preoperative c. Intraoperative d. Postoperative ANS: B Reviewing the patient’s laboratory tests and allergies is done before surgery in the preoperative phase. Perioperative means before, during, and after surgery. Intraoperative means during the surgical procedure in the operating suite; postoperative means after the surgery and could occur in the postanesthesia care unit, in the ambulatory surgical area, or on the hospital unit. DIF: Understand REF: 1254 OBJ: Explain the concept of perioperative nursing care. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 3. The nurse is caring for a patient in the postanesthesia care unit. The patient has developed profuse bleeding from the surgical site, and the surgeon has determined the need to return to the operative area. This procedure would be classified as a. Elective. b. Urgent. c. Emergency. d. Major. ANS: C An emergency procedure must be done immediately to save life or preserve function of a body part. An example would be repair of a perforated appendix, repair of a traumatic amputation, or control of internal hemorrhaging. An urgent procedure is necessary for a patient’s health and often prevents additional problems form developing. An example would be excision of a cancerous tumor, removal of a gallbladder for stones, or vascular repair for obstructed artery. An elective procedure is performed on the basis of the patient’s choice; it is not essential and is not always necessary for health. An example would be a bunionectomy, plastic surgery, or hernia reconstruction. A major procedure involves extensive reconstruction or alteration in body parts; it poses great risks to well-being. An example would be a coronary artery bypass or colon resection. DIF: Remember REF: 1256 OBJ: Differentiate between classifications of surgery and types of anesthesia. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 4. The nurse is caring for a patient in preadmission testing. The patient has been assigned a physical status classification by the American Society of Anesthesiologist of P3. Which of the following assessments would support this classification? a. Denial of any major illnesses or conditions b. Normal, healthy patient c. History of hypertension, 80 pounds overweight, history of asthma d. History of myocardial infarction that limits activity ANS: C A P3 is a patient with a severe systemic disease. Patients with hypertension, obesity, diabetes mellitus, and asthma fit into this category. A P1 is a normal healthy patient. A P2 is a patient with mild systemic disease. A P4 is a patient with severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life. DIF: Understand REF: 1256 OBJ: Differentiate between classifications of surgery and types of anesthesia. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 5. The patient has presented to the ambulatory surgery center to have a colonoscopy. The patient is scheduled to receive moderate sedation (conscious sedation) during the procedure. Moderate sedation is used routinely for procedures that require a. Performance on an outpatient basis. b. A depressed level of consciousness. c. Loss of sensation in an area of the body. d. The patient to be immobile. ANS: B Moderate sedation (conscious sedation) is used routinely for procedures that do not require complete anesthesia, but rather a depressed level of consciousness. Not all patients who are treated on an outpatient basis receive moderate sedation. Regional anesthesia such as local anesthesia provides loss of sensation in an area of the body. General anesthesia is used for patients who need to be immobile and to not remember the surgical procedure. DIF: Remember REF: 1273-1274 OBJ: Differentiate between classifications of surgery and types of anesthesia. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 6. The nurse is caring for a patient in the postanesthesia care unit who has undergone a left total knee arthroplasty. The anesthesia provider has indicated that the patient received a left femoral peripheral nerve block. Which assessment would be an expected finding for a patient with this type of regional block? a. Decreased pulse at the left posterior tibia b. Left toes cool to touch and slightly cyanotic c. Sensation decreased in the left leg d. Patient report of pain in the left foot ANS: C Induction of regional anesthesia results in loss of sensation in an area of the body. The peripheral nerve block influences the portion of sensory pathways that are anesthetized in the targeted area of the body. Decreased pulse, toes cool to touch, and cyanosis are indications of decreased blood flow and are not expected findings. Reports of pain the in the left foot may indicate that the block is not working or is subsiding and is not an expected finding in the immediate postoperative period. DIF: Understand REF: 1273-1274 OBJ: Differentiate between classifications of surgery and types of anesthesia. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 7. The nurse is preparing a patient for surgery. Aims of assessment before surgery include a. Establishing a patient’s baseline of normal function. b. Planning for care after the procedure. c. Educating the patient and family about the procedure. d. Gathering appropriate equipment for the patient’s needs. ANS: A The aim of assessment of the patient before surgery is to establish the patient’s normal preoperative function to prevent and minimize possible postoperative complications. Gathering appropriate equipment, planning care, and educating the patient and family are all important interventions that must be provided for the surgical patient; they are part of the nursing process but are not the reason for completing an assessment of the surgical patient. DIF: Understand REF: 1369 OBJ: Describe the assessment data to be collected for the surgical patient. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 8. The nurse is completing a medication history for the surgical patient in preadmission testing. Which of the following medications should the nurse instruct the patient to hold in preparation for surgery? a. Ibuprofen b. Acetaminophen c. Vitamin C d. Miconazole ANS: A Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen inhibit platelet aggregation and prolong bleeding time, increasing susceptibility to postoperative bleeding. Acetaminophen is a pain reliever that has no special implications for surgery. Vitamin C actually assists in wound healing and has no special implications for surgery. Miconazole is an antifungal and has no special implications for surgery. DIF: Apply REF: 1261 OBJ: List assessment data for the surgical patient. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 9. The nurse is caring for a potential surgical patient in the preadmission testing unit. The medication history indicates that the patient is currently taking warfarin (Coumadin). Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Consult with the physician regarding a radiological examination of the chest. b. Consult with the physician regarding an international normalized ratio (INR). c. Consult with the physician regarding blood urea nitrogen (BUN). d. Consult with the physician regarding a complete blood count (CBC). ANS: B Warfarin is an anticoagulant that is utilized for different maladies, but its action is to increase the time it takes for the blood to clot. This action can put the surgical patient at risk for bleeding tendencies. Typically, if at all possible, this medication is held several days before a surgical procedure to decrease this risk. INR, PT (prothrombin time), APTT (activated partial thromboplastin time), and platelet counts reveal the clotting ability of the blood. Chest x-ray, BUN, and CBC are diagnostic screening tools for surgery but are not specific to warfarin. DIF: Apply REF: 1261| 1264 OBJ: List assessment data for the surgical patient. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 10. The nurse is encouraging the postoperative patient to utilize diaphragmatic breathing. Reasons for this intervention include a. Management of pain. b. Decreased healing time. c. Prevention of atelectasis. d. Decreased thrombus formation. ANS: C During general anesthesia, the lungs are not fully inflated during surgery and the cough reflex is suppressed, so mucus collects within airway passages. After surgery, patients may have reduced lung volume and may require greater effort to cough and deep breathe; inadequate lung expansion can lead to atelectasis and pneumonia. Purposely utilizing diaphragmatic breathing can decrease this risk. Diaphragmatic breathing, except for the components of distraction, minimal increased level of oxygen, and minimal chest wall movement, does not influence pain, healing time, or thrombus formation. Better, more effective interventions are available for these situations. DIF: Understand REF: 1281 OBJ: Demonstrate postoperative exercises: diaphragmatic breathing, coughing, incentive spirometer use, turning, and leg exercises. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 11. The nurse is caring for a postoperative patient on the medical-surgical floor. To prevent venous stasis and the formation of thrombus after general anesthesia, the nurse encourages a. Coughing. b. Diaphragmatic breathing. c. Incentive spirometry. d. Leg exercises. ANS: D After general anesthesia, circulation slows, and when the rate of blood slows, a greater tendency for clot formation is noted. Immobilization results in decreased muscular contractions in the lower extremities; these promote venous stasis. Coughing, diaphragmatic breathing, and incentive spirometry are utilized to decrease atelectasis. DIF: Remember REF: 1282-1283 OBJ: Demonstrate postoperative exercises: diaphragmatic breathing, coughing, incentive spirometer use, turning, and leg exercises. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 12. The nurse is caring for a preoperative patient. The nurse teaches the principles and demonstrates leg exercises for the patient. The patient is unable to perform leg exercises correctly. What is the nurse’s best next step? a. Assess for the presence of anxiety, pain, or fatigue. b. Ask the patient why he does not want to do the exercises. c. Encourage the patient to practice at a later date. d. Assess the educational methods used to educate the patient. ANS: A If the patient is unable to perform leg exercises after sound educational principles and demonstration are provided, the nurse should look for circumstances that may be impacting the patient’s ability to learn. In this case, the patient can be anticipating the upcoming surgery and may be experiencing anxiety. The patient may also be in pain or may be fatigued; both of these can affect the ability to learn. Assessment of educational methods may be needed, but in this case, sound principles and demonstration are being utilized. Asking anyone why can cause defensiveness and may not help in attaining the answer. In this case, the patient really may want to participate and may not know why he is unable to learn. The nurse is aware that the patient is unable to do the exercises. Moving forward without ascertaining that learning has occurred will not help the patient in meeting goals. DIF: Apply REF: 1292 OBJ: Demonstrate postoperative exercises: diaphragmatic breathing, coughing, incentive spirometer use, turning, and leg exercises. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 13. Which nursing assessment would indicate that the patient is performing diaphragmatic breathing correctly? a. Hands placed on border of rib cage with fingers extended will touch as chest wall contracts. b. Hands placed on chest wall with fingers extended will separate as chest wall contracts. c. The patient will feel upward movement of the diaphragm during inspiration. d. The patient will feel downward movement of the diaphragm during expiration. ANS: A Positioning the hands along the borders of the rib cage allows the patient to feel movement of the chest and abdomen as the diaphragm descends and the lungs expand. As the patient takes a deep breath and slowly exhales, the middle fingers will touch while the chest wall contracts. The fingers will separate as the chest wall expands. The patient will feel normal downward movement of the diaphragm during inspiration and normal upward movement during expiration. DIF: Evaluate REF: 1288 OBJ: Demonstrate postoperative exercises: diaphragmatic breathing, coughing, incentive spirometer use, turning, and leg exercises. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 14. The nurse is caring for a postoperative patient with an abdominal incision. A pillow is used during coughing to provide a. Pain relief. b. Splinting. c. Distraction. d. Anxiety reduction. ANS: B Surgical incisions cut through muscles, tissues, and nerve endings. Deep breathing and coughing exercises place additional stress on the suture line and cause discomfort. Splinting incisions with hands and a pillow provides firm support and reduces incisional pull. Providing a pillow during coughing does not provide distraction or reduce anxiety. Providing a pillow does not provide pain relief. Coughing can increase anxiety because it can cause pain. DIF: Understand REF: 1290 OBJ: Demonstrate postoperative exercises: diaphragmatic breathing, coughing, incentive spirometer use, turning, and leg exercises. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 15. The nurse is encouraging a reluctant postoperative patient to deep breathe and cough. What explanation can the nurse provide that may encourage the patient to cough more effectively? a. “If you don’t deep breathe and cough, you will get pneumonia.” b. “Deep breathing and coughing will clear out the anesthesia.” c. “Coughing will not harm the incision if done correctly.” d. “You will need to cough only a few times during this shift.” ANS: C If coughing is done correctly with proper support of the incision, it will not harm the incision. Deep breathing and coughing help to clear out mucus in the respiratory system that has been caused by the anesthesia. Although it is correct that a patient may experience atelectasis and pneumonia if deep breathing and coughing are not performed, the way this is worded sounds threatening and could be communicated in a more therapeutic manner. Deep breathing and coughing is encouraged every 2 hours while the patient is awake. DIF: Apply REF: 1290 OBJ: Demonstrate postoperative exercises: diaphragmatic breathing, coughing, incentive spirometer use, turning, and leg exercises. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 16. The nurse and the nursing assistant are assisting a postoperative patient to turn in the bed. To assist in minimizing discomfort, which instruction should the nurse provide to the patient? a. “Close your eyes and think about something pleasant.” b. “Hold your breath and count to three.” c. “Hold my shoulders with your hands.” d. “Place your hand over your incision.” ANS: D Instruct the patient to place right hand over incisional area to splint it, providing support and minimizing pulling during turning. Closing one’s eyes, holding one’s breath, and holding the nurse’s shoulders do not help support the incision during a turn. DIF: Apply REF: 1290-1291 OBJ: Demonstrate postoperative exercises: diaphragmatic breathing, coughing, incentive spirometer use, turning, and leg exercises. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 17. The nurse is preparing to assist the patient in using the incentive spirometer. Which nursing intervention should the nurse provide first? a. Perform hand hygiene. b. Place in reverse Trendelenburg position. c. Explain use of the mouthpiece. d. Instruct the patient to inhale slowly. ANS: A Performing hand hygiene reduces microorganisms. Placing the patient in the correct position such as high Fowler’s or reverse Trendelenburg for the bariatric patient would be the next step in the process. Demonstration of use of the mouthpiece followed by the instruction to inhale slowly would be the last step in this scenario. DIF: Apply REF: 1288-1289 OBJ: Demonstrate postoperative exercises: diaphragmatic breathing, coughing, incentive spirometer use, turning, and leg exercises. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 18. The nurse and the nursing assistant are caring for a group of postoperative patients who need turning, coughing, deep breathing, incentive spirometer, and leg exercises. The nurse directs the nursing assistant to a. Teach and demonstrate postoperative exercises. b. Inform the nurse if the patient is unwilling to perform exercises. c. Document in the medical record when exercises are completed. d. Do nothing associated with postoperative exercises. ANS: B The nurse may delegate activities to individuals who are competent, within their scope of practice, and willing to be legally responsible—all while maintaining responsibility for follow-up and outcome. The nurse can delegate to a nursing assistant to encourage patients to practice postoperative exercises regularly after instruction, and to inform the nurse if the patient is unwilling to perform these exercises. The skills of demonstrating and teaching postoperative exercises and documenting are not within the scope of practice for the nursing assistant. Doing nothing is not appropriate. DIF: Apply REF: 1287 OBJ: Demonstrate postoperative exercises: diaphragmatic breathing, coughing, incentive spirometer use, turning, and leg exercises. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 19. The nurse is providing preoperative teaching for the ambulatory surgery patient who will be having a cyst removed from the right arm. Which would be the best explanation for diet progression after surgery? a. “Start with clear liquids, soup, and crackers. Advance to a normal diet as you tolerate.” b. “There is no limitation on your diet. You can have whatever you want.” c. “Stay on clear liquids for 24 hours. Then you can progress to a normal diet.” d. “Start with clear liquids for 2 hours, then full liquids for 2 hours. Then progress to a normal diet.” ANS: A The type of surgery that patients undergo determines how quickly they can resume normal physical activity and regular eating habits. It is normal to progress gradually in activity and eating, and if the patient tolerates activity and diet well, he/she can progress more quickly. A common complication after surgery is nausea and vomiting. This can be caused by the anesthesia, fluid imbalance from being NPO, and pain. The gastrointestinal tract may be hypoactive owing to anesthesia. It is best to start with a clear liquid to see if the patient can tolerate the liquid without vomiting. If so, progressing to soup and crackers and advancing as the patient tolerates is appropriate. Starting with a heavy, greasy meal could cause nausea and vomiting. There is no need to stay on clear liquids for 24 hours after this procedure. Putting a time frame on the progression is too prescriptive. Progression should be adjusted for the patient’s needs. DIF: Apply REF: 1284-1285 OBJ: Design a preoperative teaching plan. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 20. The nurse explains the pain relief measures available after surgery during preoperative teaching for a surgical patient. Which of the following comments from the patient indicates the need for additional education on this topic? a. “I will take the pain medication as the physician prescribes it.” b. “I will be asked to rate my pain on a pain scale.” c. “I will have minimal pain because of the anesthesia.” d. “I will take my pain medications before doing postoperative exercises.” ANS: C Pain after surgery is expected and is one of the patient’s fears. Anesthesia will be provided during the procedure itself, and the patient should not experience pain during the procedure. Pain management is utilized after the postoperative phase. Inform the patient of interventions available for pain relief, including medication, relaxation, and distraction. The patient needs to know and understand how to take the medications that the physician will prescribe postoperatively. During the stay in the facility, the level of pain is frequently assessed by the nurses. Coordinating pain medication with postoperative exercises helps to minimize discomfort and allows the exercises to be more effective. DIF: Evaluate REF: 1283-1284 OBJ: Design a preoperative teaching plan. TOP: Evaluation MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 21. The nurse is making a preoperative education appointment with a patient. The patient asks if he should bring family with him to the appointment. What is the best response by the nurse? a. “There is no need for an additional person at the appointment.” b. “Your family can come and wait with you in the waiting room.” c. “We recommend including family in this appoint to ease everyone’s anxiety.” d. “It is required that you have a family member at this appointment.” ANS: C It is ideal to attempt perioperative education before admission, during the hospital stay, and after discharge. Including family members in perioperative education is advisable. Often a family member is a coach for postoperative exercises when the patient returns from surgery. If anxious relatives do not understand routine postoperative events, it is likely that their anxiety will heighten the patient’s fears and concerns. Perioperative preparation of family members before surgery helps to minimize anxiety and misunderstanding. An additional person is needed at the appointment if at all possible, and he or she needs to be involved in the process, not just waiting in the waiting room; however, it is certainly not a requirement for actually completing the surgery that someone comes to this appointment. DIF: Apply REF: 1267-1268 OBJ: Design a preoperative teaching plan. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 22. The nurse is reviewing the surgical consent with the patient during preoperative education. The patient indicates that he does not understand what procedure will be completed. What is the nurse’s best next step? a. Notify the physician about the patient’s question. b. Explain the procedure that will be completed. c. Ask the patient to sign the form. d. Continue with preoperative education. ANS: A Surgery cannot be legally or ethically performed until the patient understands the need for a procedure, the steps involved, the risks, expected results, and alternative treatments. It is the surgeon’s responsibility to explain the procedure and obtain informed consent. It is important for the nurse to pause to notify the physician of the patient’s questions. It is not within the nurse’s scope to explain the procedure for the first time. The nurse can certainly reinforce what the physician has explained, but the information needs to come from the physician. It is not prudent to ask a patient to sign a form for a procedure that he/she does not understand. DIF: Apply REF: 1267 OBJ: Design a preoperative teaching plan. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 23. During preoperative assessment for a 7:30 case, the patient indicates to the nurse that he had a cup of coffee this morning. The nurse reports this information to the anesthesia provider anticipating a. A delay in or cancellation of surgery. b. Questions regarding components of the coffee. c. Additional questions about why the patient had coffee. d. Instructions to determine what education was provided in the preoperative visit. ANS: A For fatty, fried, and meat sources, the recommended fast is 8 hours. Fasting from intake of a light meal or from nonhuman milk for 6 or more hours, breast milk for 4 or more hours, and clear liquids for 2 to 3 hours before elective procedures requiring general anesthesia, regional anesthesia, or sedation is recommended. A delay in or cancellation of surgery will be in order for this case. Questions regarding components of the coffee (e.g., milk; can determine the length of time for a delay), asking why, and evaluating the preoperative education may all be items to be addressed, especially from a performance improvement perspective, but at this time in caring for this patient, a delay or cancellation is in order. DIF: Understand REF: 1268-1269 OBJ: Prepare a patient for surgery. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 24. The nurse has administered an anxiolytic as a preoperative medication to the patient going to surgery. Which of the following is the best next step? a. Waste any unused medication according to policy. b. Notify the operating suite that the medication has been given. c. Instruct the patient to call for help to go to the restroom. d. Ask the patient to sign the consent for surgery. ANS: C Once a medication has been administered, instruct the patient to call for help when getting out of bed to prevent falls. For patient safety, explain the purpose of a preoperative medication and its effects. Reinforce to the patient to stay in the bed or on the stretcher. Raise the side rails and keep the bed or stretcher in the low position. Place the call light within easy reach of the patient. Notifying the operating suite that the medication has been given may be part of a facilities procedure but is not the best next step. It is important to have the patient sign consents before the patient has received medication that may make him/her drowsy. Wasting unused medication according to policy is important but is not the best next step. DIF: Apply REF: 1270 OBJ: Prepare a patient for surgery. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 25. The nurse has completed a preoperative assessment for a patient going to surgery and gathers assessment data. Of the following, which would be the most important next step? a. Notify the operating suite that the patient has a latex allergy. b. Document that the patient had a bath at home this morning. c. Ask the nursing assistant to obtain vital signs. d. Administer the ordered preoperative intravenous antibiotic. ANS: A Innumerable products that contain latex are used in the operating suite and the postanesthesia care unit (PACU). When preparing for a patient with this allergy, special considerations are required from preparation of the room to the types of tubes, gloves, drapes, and instruments utilized. To ensure that the patient has a safe environment takes time, and if the correct supplies are not available, awaiting their arrival may cancel or delay the case. Obtaining vital signs, documenting, and administering medications are all part of the process and should be done—with the latex allergy in mind. However, making sure that the patient has a safe environment is the first step. DIF: Apply REF: 1272 OBJ: Prepare a patient for surgery. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 26. The nurse is preparing a patient for a surgical procedure on the right great toe. Which of the following actions would be most important to include in this patient’s preparation? a. Ascertain that the surgical site has been correctly marked. b. Ascertain where the family will be located during the procedure. c. Place the patient in a clean surgical gown. d. Ask the patient to remove all hairpins and cosmetics. ANS: A Because errors have occurred in the past with patients undergoing the wrong surgery on the wrong site, the universal protocol has been implemented and is used with all invasive procedures. Part of this protocol includes marking the operative site with indelible ink. Knowing where the family is during a procedure, placing the patient in a clean gown, and asking the patient to remove all hairpins and cosmetics are important but are not most important in this list of items. DIF: Apply REF: 1269-1270 OBJ: Prepare a patient for surgery. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 27. The nurse is caring for a patient intraoperatively. Primary roles of the circulating nurse include a. Establishing and implementing the plan of care. b. Maintaining a sterile field. c. Assisting with applying sterile drapes. d. Handing sterile instruments and supplies to the surgeon. ANS: A The circulating nurse must be a registered nurse and has the responsibilities of preoperative assessment, establishing and implementing the plan of care, evaluating the care provided, and ensuring continuity of care postoperatively. The scrub nurse, who can be a registered nurse, a licensed practical nurse, or a surgical technologist, maintains the sterile field, assists with applying the sterile drapes, and hands sterile instruments and supplies to the surgeon. DIF: Understand REF: 1271 OBJ: Explain the nurse’s role in the operating suite. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 28. The nurse is caring for a patient in the preoperative holding area of an ambulatory surgery center. Which nursing action would be most appropriate for this area? a. Monitor vital signs every 15 minutes. b. Empty the urinary drainage bag. c. Apply a warm blanket. d. Check the surgical dressing. ANS: C The temperature in the preoperative holding area and in adjacent operating suites is usually cool. Offer the patient an extra warm blanket. The main activities in this area include verification of the patient, the surgery to be performed, and physical and emotional readiness for the procedure. The intravenous catheter is usually inserted, and the preoperative checklist is reviewed. Vital signs are not normally monitored unless there is a specific reason, such as a medication being administered. Typically, ambulatory surgery patients will not come to the holding area with a urinary drainage bag or a surgical dressing. These activities if appropriate are performed in the postanesthesia care unit. DIF: Apply REF: 1271 OBJ: Explain the nurse’s role in the operating suite. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 29. The nurse is caring for a patient in the operating suite. Which of the following outcomes would be most appropriate for this patient? a. At the end of the intraoperative phase, the patient will be free of burns at the grounding pad. b. At the end of the intraoperative phase, the patient will be free of infection. c. At the end of the intraoperative phase, the patient will be free of nausea and vomiting. d. At the end of the intraoperative phase, the patient will be free of pain. ANS: A A primary focus of intraoperative care is to prevent injury and complications related to anesthesia, surgery, positioning, and equipment use, including use of the electrical cautery grounding pad for prevention of burns. The perioperative nurse is an advocate for the patient during surgery and protects the patient’s dignity and rights at all times. Evaluation of many goals and outcomes does not occur until after surgery. Signs and symptoms of infection do not have the time to present during the intraoperative phase. During the intraoperative phase, the patient is anesthetized and unconscious and typically has an endotracheal tube that prevents conversation and complaints. These complaints typically begin in the postoperative phase of the experience. DIF: Understand REF: 1272 OBJ: Explain the nurse’s role in the operating suite. TOP: Planning MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 30. The nurse is concerned about the skin integrity of the patient in the intraoperative phase of surgery. Which of the following actions helps to minimize skin breakdown? a. Encouraging the patient to bathe before surgery b. Securing attachments to the operating table with foam padding c. Periodically adjusting the patient during the surgical procedure d. Measuring the time a patient is in one position during surgery ANS: B Although it may be necessary to place a patient in an unusual position, try to maintain correct alignment and protect the patient from pressure, abrasion, and other injuries. Special mattresses, use of foam padding, and attachments to the operating suite table provide protection for the extremities and bony prominences. Bathing before surgery helps to decrease the number of microbes on the skin. Periodically adjusting the patient during the surgical procedure is impractical and can present a safety issue with regard to maintaining sterility of the field and maintaining an airway. Measuring the time the patient is in one position may help with monitoring the situation but does not prevent skin breakdown. DIF: Apply REF: 1272| 1274 OBJ: Explain the nurse’s role in the operating suite. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 31. The nurse is caring for a postoperative patient with a history of obstructive sleep apnea. The nurse monitors for which of the following? a. Choking and noisy, irregular respirations b. Shallow respirations c. Moaning and reports of pain d. Disorientation ANS: A One of the greatest concerns after general anesthesia is airway obstruction. Choking and noisy, irregular respirations are classic signs and symptoms of airway obstruction. A number of factors contribute to obstruction, including a history of obstructive sleep apnea; weak pharyngeal/laryngeal muscle tone from anesthetics; secretions in the pharynx, bronchial tree, or trachea; and laryngeal or subglottic edema. In the postanesthetic patient, the tongue is a major cause of airway obstruction. Shallow respirations are indicative of respiratory depression. Moaning and reports of pain are common in all surgical patients and are an expected event. Disorientation is common when first awakening from anesthesia but can be a sign of hypoxia. DIF: Understand REF: 1277 OBJ: Describe the rationale for nursing interventions designed to prevent postoperative complications. TOP: Planning MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 32. The nurse is caring for a patient in the operating suite who is experiencing hypercarbia, tachypnea, tachycardia, premature ventricular contractions, and muscle rigidity. The nurse suspects that this patient may be experiencing a. Hypoxia. b. Malignant hyperthermia. c. Fluid imbalance. d. Hemorrhage. ANS: B A life-threatening, rare complication of anesthesia is malignant hyperthermia. Malignant hyperthermia causes hypercarbia, tachycardia, tachypnea, premature ventricular contractions, unstable blood pressure, cyanosis, skin mottling, and muscular rigidity. It often occurs during induction. Hypoxia would manifest with decreased oxygen saturation as one of its signs and symptoms. Fluid imbalance would be assessed with intake and output and can manifest with tachycardia and blood pressure fluctuations but does not have muscle rigidity. Hemorrhage can manifest with tachycardia and decreased blood pressure, along with a thread pulse. Usually some sign or symptom of blood loss is noted (e.g., drains incision, orifice, and abdomen). DIF: Evaluate REF: 1278 OBJ: Describe the rationale for nursing interventions designed to prevent postoperative complications. TOP: Evaluation MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 33. The nurse is caring for a postoperative patient who has had a carpel tunnel repair. The patient has a temperature of 97° F and is shivering. Which of the following is the best reason for this condition? a. The patient is dressed only in a gown. b. Anesthesia lowers metabolism. c. The surgical suite has laminar flow. d. The open body cavity contributed to heat loss. ANS: B The operating suite and recovery room environments are cool. The patient’s anesthetically depressed level of body function results in lowering of metabolism and a fall in body temperature. The patient being dressed in a gown and laminar flow in the surgical suite can contribute to a decrease in temperature, but the length of time required for this procedure would minimize this effect. Also, the patient in this type of case does not have a large open body cavity to contribute to heat loss. DIF: Evaluate REF: 1278 OBJ: Describe the rationale for nursing interventions designed to prevent postoperative complications. TOP: Evaluation MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 34. The nurse is monitoring a patient in the postanesthesia care unit (PACU) for postoperative fluid and electrolyte imbalance. Which of the following actions would be most appropriate for this patient? a. Encourage copious amounts of water. b. Weigh the patient and compare with preoperative weight. c. Measure and record all intake and output. d. Start an additional intravenous (IV) line. ANS: C Accurate recording of intake and output assesses renal and circulatory function. Measure and record all sources of intake and output. Encouraging copious amounts of water in a postoperative patient might encourage nausea and vomiting. In the PACU, it is impractical to weigh the patient while waking from surgery, but in the days afterward, it is a good assessment parameter for fluid imbalance. Starting an additional IV is not necessary and is not important at this juncture. DIF: Apply REF: 1278 OBJ: Describe the rationale for nursing interventions designed to prevent postoperative complications. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 35. The nurse is caring for a patient in the postanesthesia care unit. The patient asks for a bedpan and states to the nurse, “I feel like I need to go to the bathroom, but I can’t.” Which of the following nursing interventions would be most appropriate? a. Encourage the patient to wait a minute and try again. b. Call the physician and obtain an order for catheterization. c. Assess the patient’s intake and the patient for bladder distention. d. Inform the patient that everyone feels this way after surgery. ANS: C Depending on the surgery, some patients do not regain voluntary control over urinary function for 6 to 8 hours after anesthesia. Assess the amount of fluid that the patient obtained while in surgery, and palpate the lower abdomen just above the symphysis pubis for bladder distention. If fluid intake is not excessive and the bladder is nondistended, allowing some time might be appropriate. Not everyone feels as if they need to go but can’t after surgery. If the bladder is distended and the patient is unable to void, a catheter might be in order. DIF: Apply REF: 1278 OBJ: Describe the rationale for nursing interventions designed to prevent postoperative complications. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 36. The postanesthesia care unit (PACU) nurse transports the inpatient surgical patient to the medical-surgical floor. Before leaving the floor, the medical-surgical nurse obtains a complete set of vital signs. What is the rationale for this nursing action? a. The first action in a head-to-toe assessment is vital signs. b. This is done to compare and monitor for vital sign variation during transport. c. This is done to ensure that the medical-surgical nurse checks on the postoperative patient. d. This is done to follow hospital policy and procedure for care of the surgical patient. ANS: B The PACU nurse reviews the patient’s information with the medical-surgical nurse, including the surgical and PACU course, physician orders, and the patient’s condition. Before leaving the medical-surgical unit, the PACU nurse waits while the medical-surgical nurse obtains a complete set of vital signs to compare with PACU findings. Minor vital sign variations normally occur after the patient is transported. Vital signs may or may not be the first action in a head-to-toe assessment. Following policy or ascertaining that the floor nurse checks on the patient is not a reason to obtain vital signs. DIF: Understand REF: 1277 OBJ: Explain the differences and similarities in caring for ambulatory versus inpatient surgical patients. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 37. The nurse is caring for a patient who will undergo a coronary artery bypass graft procedure. What level of care will the patient require immediately post procedure? a. Acute care—medical-surgical unit b. Acute care—intensive care unit c. Ambulatory surgery d. Ambulatory surgery—extended stay ANS: B Patients undergoing extensive surgery and requiring anesthesia of longer duration recover more slowly. If a patient is undergoing major surgery such as a procedure on the heart, a stay in the hospital and specifically in the intensive care unit is required to monitor for potential risks to well-being. This patient would require more care than can be provided on a medical- surgical unit. It is not appropriate for this type of patient to go home after the procedure or to stay in an extended stay area of an ambulatory surgery area because of the complexity and associated risks. DIF: Remember REF: 1256 OBJ: Explain the differences and similarities in caring for ambulatory versus inpatient surgical patients. TOP: Planning MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 38. The ambulatory surgical nurse calls to check on the patient at home the morning after surgery. The patient is reporting continued nausea and vomiting. Which of the following discharge education points should be reviewed with the patient? a. Instruct the patient to take deep breaths. b. Instruct the patient to drink ginger ale and eat crackers. c. Instruct and attempt to connect the patient with the physician. d. Instruct the patient to go to the emergency department. ANS: C Postoperative nausea and vomiting sometimes occur once the patient is at home even if symptoms were not present in the surgery center. Options for therapy include medications. Instructing the patient to call the physician and connecting the patient with the physician can help the patient to obtain relief. Taking deep breaths, drinking ginger ale, and eating crackers are interventions that may be helpful, but this patient needs additional help. Instructing the patient to go to the emergency department is an option with continued nausea and vomiting. DIF: Understand REF: 1286 OBJ: Explain the differences and similarities in caring for ambulatory versus inpatient surgical patients. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The nurse is precepting a new nurse in the perioperative area. The nurse explains that perioperative nursing is based on certain principles and includes (Select all that apply.) a. Purchasing the correct equipment. b. Providing high-quality and patient safety–focused care. c. Scheduling the right types of patients. d. Conducting multidisciplinary teamwork. e. Ensuring effective therapeutic communication. f. Providing advocacy for the patient. ANS: B, D, E, F Perioperative nursing is a fast-paced, changing, and challenging field and is based on the nurse’s understanding of several important principles, including high-quality, patient safety– focused care; multidisciplinary teamwork; effective therapeutic communication and collaboration with the patient, the patient’s family, and the surgical team; effective and efficient assessment and intervention in all phases of surgery; advocacy for the patient and the patient’s family; and understanding of cost containment. Purchasing the correct equipment is important in any specialty of nursing. Perioperative nursing cares not only for the “right” types of patients, but for all patients with surgical needs. DIF: Remember REF: 1254 OBJ: Explain the concept of perioperative nursing care. TOP: Planning MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 2. The nurse is caring for an ambulatory surgery patient. To be discharged home, what criteria must the patient meet? (Select all that apply.) a. Able to drink fluids b. Able to eat crackers c. Manageable pain d. Able to void e. Dry and intact dressing f. Able to dress self ANS: A, C, D, E To be discharged home, patients need to meet certain criteria. These criteria include meeting phase 1 criteria of activity, circulation, respiration, consciousness, and O2 saturation, as well as phase 2 criteria of dressing dry and intact, manageable pain, ambulation, able to drink fluids, and voiding. Eating and the ability to dress self are not included in these criteria. DIF: Remember REF: 1286 OBJ: Explain the differences and similarities in caring for ambulatory versus inpatient surgical patients. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 3. The nurse is caring for a postoperative patient with an incision. Which of the following nursing interventions have been found to decrease wound infections? (Select all that apply.) a. Perform hand hygiene before and after contact with the patient. b. Maintain normoglycemia. c. Use hair clippers to remove hair. d. Administer antibiotics within 30 to 60 minutes of incision time. e. Provide bath and linen change daily. f. Perform first dressing change 1 week postoperatively. ANS: A, B, C, D Performing hand hygiene before and after contact with the patient helps to decrease the number of microorganisms and break the chain of infection. Maintaining blood glucose levels at less than 150 mg/dL has resulted in decreased wound infection. Removing unwanted hair by clipping instead of shaving decreases the numbers of nicks and cuts caused by a razor and the potential for the introduction of microbes. Administration of an antibiotic within 30 to 60 minutes of incision time supports the defense against infection. Providing a bath and linen change is positive but is not necessarily important daily for infection control unless copious body fluids are present. The physician usually is the person who changes a dressing the first time to inspect the condition of the site, but this is done well before 7 days postoperatively. DIF: Apply REF: 1278| 1282| 1285 OBJ: Describe the rationale for nursing interventions designed to prevent postoperative complications. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 4. The nurse is preparing for a patient who will be going to surgery. The nurse screens for risk factors that can increase a person’s risks in surgery. What risk factors are included in the nurse’s screening? (Select all that apply.) a. Age b. Nutrition c. Race d. Obesity e. Pregnancy f. Ambulatory surgery ANS: A, B, D, E Very young and old patients are at risk during surgery because of immature or declining physiological status. Normal tissue repair and resistance to infection depend on adequate nutrients. Obesity increases surgical risk by reducing respiratory and cardiac function. During pregnancy, the concern is for the mother and the developing fetus. Because all major systems of the mother are affected during pregnancy, risks for operative complications are increased. Race and ambulatory surgery are not risks associated with a surgical procedure. DIF: Remember REF: 1257-1260 OBJ: List assessment data for the surgical patient. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 5. The nurse is providing preoperative education and reviews with the patient what it will be like to be in the surgical environment. What points should the nurse include? (Select all that apply.) a. The surgical area is cold but warm blankets will be provided. b. The surgical staff will be dressed in special clothing with hats and masks. c. The operative suite will be very dark. d. Families are not allowed in the operating suite. e. The operating table or bed will be comfortable and soft. f. The nurses will be there to assist you through this process. ANS: A, B, D, F The operating suite itself is kept cool to decrease microbial growth, so it can be very cold to patients as they enter the suite, particularly with limited clothing. The surgical staff is dressed in special clothing, hats, and masks—all for infection control. Families are not allowed in the operating suite for several reasons, which include infection control and the emotional effect of seeing a loved one in that condition. The nurse is there as the coordinator and patient advocate during a surgical procedure. The rooms are very bright so everyone can see, and the operating table is very uncomfortable for the patient. DIF: Apply REF: 1267-1268 OBJ: Design a preoperative teaching plan. TOP: Intervention MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 6. The nurse is using a preoperative checklist to assist in preparing a patient on the day of surgery. What will the checklist include? (Select all that apply.) a. Vital signs b. Laboratory data c. Living will d. NPO e. Identification (ID) band on f. Family location ANS: A, B, D, E Vital signs are included in the checklist as a baseline for intraoperative vital signs. Laboratory work is included to assist health care providers in attaining an accurate picture of the patient’s health status. NPO, or nothing by mouth, is important, to decrease risks of vomiting and aspiration during the procedure. An ID band is important for identifying the patient, especially when anesthetized and unable to speak. A living will, although important for the patient’s stay at a facility, is not on the preoperative checklist. Family location, although important for communication, is not part of the list of items that need to be completed for the patient before going to surgery. DIF: Remember REF: 1269-1270 OBJ: Prepare a patient for surgery. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 7. The nurse is caring for a patient in the operating suite. The nurse assists in positioning the patient to (Select all that apply.) a. Gain access to the operative site. b. Sustain adequate circulatory and respiratory function. c. Ensure patient safety and skin integrity. d. Support the use of equipment. e. Maintain neuromuscular structures. f. Provide warmth and comfort. ANS: A, B, C, E Ideally the patient’s position provides good access to the operative site, sustains adequate circulatory and respiratory function, and ensures patient safety and skin integrity. It should not impair neuromuscular structures. Warmth and comfort are always concerns, but the other options are more important because they relate to positioning. Positioning does not support the use of equipment, rather the use of equipment complements the position of the patient to maintain patient safety. DIF: Understand REF: 1274 OBJ: Describe the rationale for nursing interventions designed to prevent postoperative complications. TOP: Planning MSC: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 24 pages
Instant download

Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 21, 2021
Number of pages
24
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 21, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
38
















 – Chamberlain College of Nursing.png)