*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NR-507 Mid-Term latest Study Guide to booste your grades (All)
NR-507 Mid-Term latest Study Guide to booste your grades
Document Content and Description Below
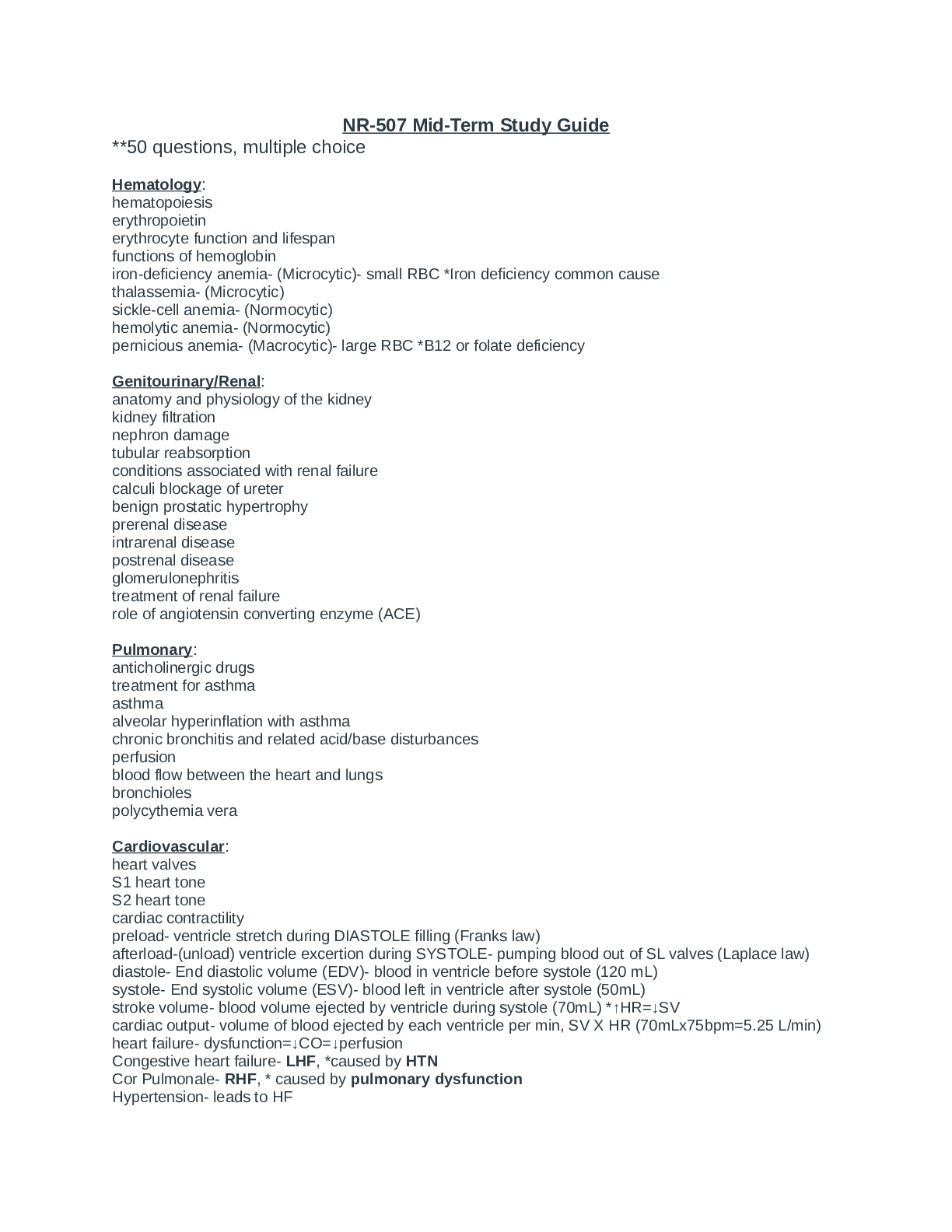
NR-507 Mid-Term Study Guide **50 questions, multiple choice Hematology: hematopoiesis erythropoietin erythrocyte function and lifespan functions of hemoglobin iron-deficiency anemia- (Microcytic)... - small RBC *Iron deficiency common cause thalassemia- (Microcytic) sickle-cell anemia- (Normocytic) hemolytic anemia- (Normocytic) pernicious anemia- (Macrocytic)- large RBC *B12 or folate deficiency Genitourinary/Renal: anatomy and physiology of the kidney kidney filtration nephron damage tubular reabsorption conditions associated with renal failure calculi blockage of ureter benign prostatic hypertrophy prerenal disease intrarenal disease postrenal disease glomerulonephritis treatment of renal failure role of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) Pulmonary: anticholinergic drugs treatment for asthma asthma alveolar hyperinflation with asthma chronic bronchitis and related acid/base disturbances perfusion blood flow between the heart and lungs bronchioles polycythemia vera Cardiovascular: heart valves S1 heart tone S2 heart tone cardiac contractility preload- ventricle stretch during DIASTOLE filling (Franks law) afterload-(unload) ventricle excertion during SYSTOLE- pumping blood out of SL valves (Laplace law) diastole- End diastolic volume (EDV)- blood in ventricle before systole (120 mL) systole- End systolic volume (ESV)- blood left in ventricle after systole (50mL) stroke volume- blood volume ejected by ventricle during systole (70mL) *↑HR=↓SV cardiac output- volume of blood ejected by each ventricle per min, SV X HR (70mLx75bpm=5.25 L/min) heart failure- dysfunction=↓CO=↓perfusion Congestive heart failure- LHF, *caused by HTN Cor Pulmonale- RHF, * caused by pulmonary dysfunction Hypertension- leads to HF MIDTERM PATHO READINGS WEEK 1: 1, 2, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 Cell/Caner/Immunity WEEK 2: 3, 34, 35, 36 Acid-Base/F&E/Pulmonary WEEK 3: 27, 28, 29, 30, 32, 33 Hematology/Cardiovascular WEEK 4: 37, 38, 39 Renal Hematology Hematopoiesis (Hemato=blood Poiesis= to form or make) (blood = 7% BW) ● Process of creating new blood cells. All blood cells are made in the bone marrow. Stimulated by androgens (testosterone) & erythropoietin made by the kidney & liver in response to tissue hypoxia ● Stimulated by infiltration of yellow (fatty) bone marrow with red marrow cells ● All blood is created from hematopoietic stem cells (HSC)-(Hemocytoblast) o Proliferate & differentiate by growth factors & cytokines to form RBC, WBC, & platelets o 4 groups ▪ Lymphoid: T-cell (T-lymphocyte) & B-cell (B-lymphocyte) ▪ Myeloid: Monocyte & Granulocytes (WBC) ▪ Erythrocyte (RBC) ▪ Megakaryocyte (platelets), ● Site of formation: o 3rd week gestation, yolk sac, o 8th week gestation, liver & spleen o 5th month gestation, bone marrow o Birth-5yrs, red marrow o 20+ years, larger bones (ilium, vertebrae, cranium, jaw, sternum, ribs, femur, humerus) ● Erythrocyte (RBC) o Normal RBC level = 4.2-6.2 million mm = 45% of our blood volume o Contains hemoglobin molecules: Oxygen carrying molecule, which regulate diffusion through a cell’s plasma membrane, to cells (Hgb can carry up to 4 molecules of oxygen) ▪ Carry oxygen to lungs & exchange it for carbon dioxide in the tissues ▪ Responsible for blood’s ruby-red color ▪ As many as 300 million Hgb molecules/RBC (90% dry weight RBC) ▪ Hbg= polypeptide chains (2alpha & 2 beta), 4 heme molecules, & 4 iron o Oxyhemoglobin: Oxygen binds to iron in heme molecule, RED o Deoxyhemoglobin: CO2 binds Hgb, released in lungs, BLUE o Mature erythrocytes lack a nucleus & organelles, so it cannot synthesize protein or carry out oxidative reactions. Cannot divide = limited life span *Anaerobic metabolism only o Biconcave, spherical disk, reversible o Lifespan: 100-120 days, 1% circulating RBC replenished every 24 hours (2.5million RBC’s/second) o Stages: (7-day process) ▪ Hemocytoblast (stem cell) binds with erythropoietin ▪ Proerythroblast- committed to morph into RBC ▪ Erythroblast- ribosome synthesis (2 phases) ▪ Normoblast- Hgb accumulation & nucleus ejection ▪ Reticulocyte – released into circulation, no nucleus, ribosome, or mitochondria ▪ RBC (once in bone marrow 1-2 days) o Size: microcytic, normocytic, macrocytic o Color: hypochromic, normorchromic, hyperchromic (due to Hgb level) o Variability: Anisocytosis (size), poikilocytosis (shape) ................................................................CONTINUED......................................................................... [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 38 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$13.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 12, 2021
Number of pages
38
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 12, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
34


.png)