*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NURS C475 STUDY GUIDE for Care of Older Adult Objective Assessment. | Western Governors University (All)
NURS C475 STUDY GUIDE for Care of Older Adult Objective Assessment. | Western Governors University
Document Content and Description Below
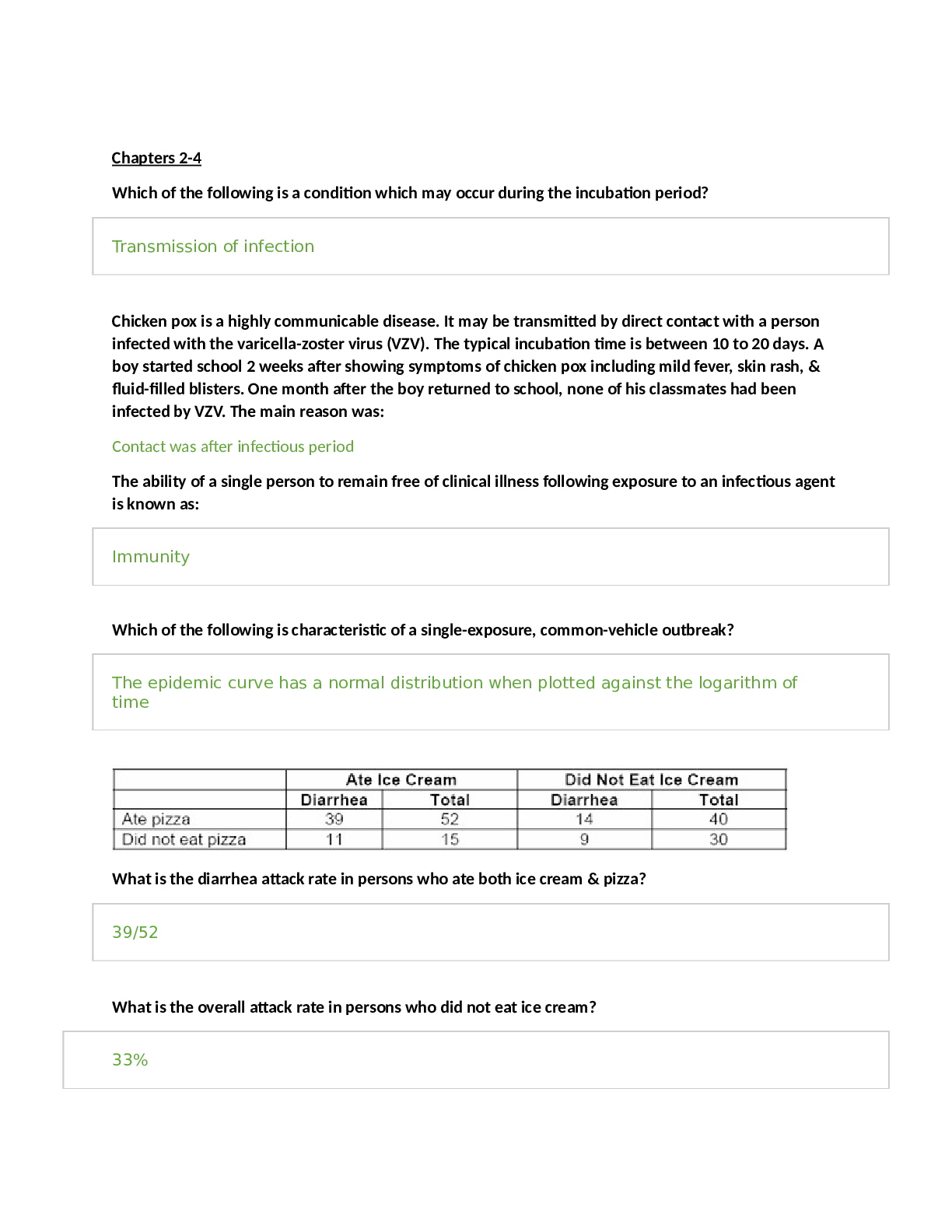
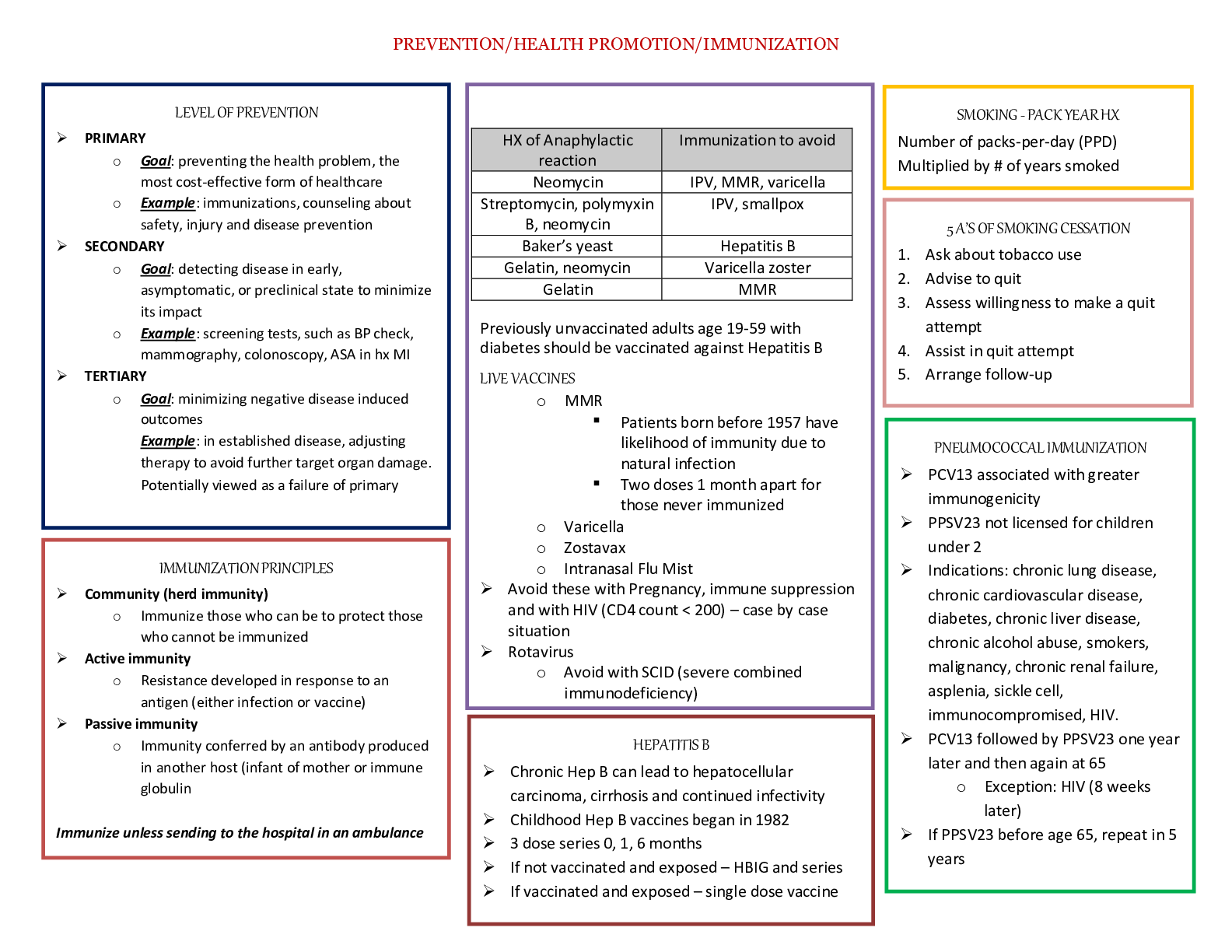
STUDY GUIDE for Care of Older Adult Objective Assessment Exam questions are taken from the Learning Objectives under the 9 Competencies: #1 Competency 742.1.1: Compassionate and Respectful Care of... Older Adults The graduate integrates principles of compassion and respect for patients and their families into the planning and delivery of care to a diverse population of older adults and into advocacy for vulnerable older adults. This topic addresses the following learning objectives: • Recognize the impact of attitudes, values, and expectations about aging. • Describe how the RN’s personal beliefs and values may impact the care of older adults. • Articulate the concept of individualized care as the standard of practice with older adults, considering the right care, at the right time, in the right place and by the right provider of care. o Define Baby Boomers o What are the five racial groups listed in your text? o How would you perform discharge teaching to an Hispanic patient • Apply effective and respectful communication strategies in the care of older adults and their families. o List some of the changes of aging that could affect therapeutic communication o Note the ways to communicate or assist a patient with disabilities such as hearing deficits, vision impairments, or aphasia and dysarthria. Be familiar with the types of hearing devices. How should you address the older adult during therapeutic communication? o Know the abbreviations or acronyms, such as AAC. Know which hearing aids cover the widest range of hearing loss. See the box on Types of Hearing Aids in chapter 5. Both hearing aids and AAC will be mentioned again in Chapter 16. ▪ Make sure you understand what patients could benefit from the use of the AAC. ▪ Understand what things can occur to make it difficult to communicate ▪ Which type of hearing aid covers the entire range of hearing loss? o What factors in a diverse aging population affect communication? • Support individual health goals that range from healthy activities to simply achieving comfort. • Illustrate compassionate and individualized care for older adults with chronic illness that reduces symptom burden and seeks to preserve quality of life. #2 Competency 742.1.2: Health Promotion/Maintenance and Living Environments of Older Adults The graduate evaluates the older adults' lifeworld with special awareness of the diversity among the health status of older adults, individualizing care according to the physical, mental/cognitive, functional, and psychosocial well-being of an elder patient, along with support systems in place. *You will notice that Competencies two through five overlap one another. Some of the information for one topic may be found in another topic or another competency. Don’t become frustrated. It will all come together. This topic addresses the following learning objectives: • Identify functional and physical changes in the aging adult that would necessitate changes to the living environment. • Identify cognitive, psychological, and social changes common to the aging adult that would necessitate changes to the living environment. • Recognize steps to mitigate common physical safety issues. • Analyze the living environment of a given older adult with special awareness of the functional, physical, cognitive, psychological, and social changes of aging. • What are the five A’s to tobacco cessation? • What are the Five R’s to tobacco cessation? • What is the criterion for the pneumococcal vaccine? • In most cases of elder abuse who is the perpetrator? • What 5 areas do Healthy People 2010 and the USPSTF suggest that nurses focus on to promote health & prevent disability in the older adult? (see page 356 in text) • Describe the difference between ADLs and IADLs (instrumental activities of daily living) • List the nutritional assessment tests to determine risk for diet-related chronic illness (see text page 359) • Review the USPSTF Screening Recommendations for Older Adults, Table 12-1 on page 376 in text. • Review the I HATE FALLING risk assessment tool, Box 12-4 on page 361. What can the nurse recommend to reduce risk of falling? #3 Competency 742.1.3: Health Needs of Older Adults The graduate effectively collaborates with patients, families and inter-professional team members in planning primary, secondary, tertiary and end-of-life care that addresses older adults' physical, mental, psychosocial and spiritual needs and preferences and responses to changes in health status and related treatments. This topic addresses the following learning objectives: • Identify how the physiological changes of aging affect the organs involved in absorption and excretion of medications • Recognize functional changes and mobility issues that may threaten independence in the older adult. • Identify factors that may contribute to alterations in nutrition, metabolism, and elimination in older adults. • Recognize the signs and symptoms of geriatric syndromes and the subsequent frailty that may result. • Apply knowledge of the aging process and associated risk factors; skills in history-taking and assessment; and respect for the dignity of older adults in a comprehensive, individualized assessment. • Identify and use valid and reliable standardized tools of functional assessment in older adults. • Identify and use valid and reliable standardized tools of cognitive assessment in older adults. • Observe for risks or the presence of the five most common geriatric syndromes (pressure ulcers, incontinence, falls, functional decline, and delirium, including hypokinetic delirium). • Describe how to use evidence-based assessment tools and methods to conduct a comprehensive assessment of an older adult. • Promote quality outcomes through the application of evidence-based practices specific to the care needs of older adults. • Promote evidence-based practice by utilizing the Beer list of potentially unsafe medications for the elderly. • Contribute to interdisciplinary plans of care to promote health, reduce risk, and prevent disease in older adults. • Contribute to interdisciplinary care plans that address common acute and chronic health conditions, such as arthritis, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases that may lead to congestive heart failure, and dementia. • Consider potential drug side effects in assessing adverse symptoms in older adults. o There are three types of assessments: Physical, Cognitive and Functional. ▪ Physical assessment is assessing the patient’s physical health. It included vital signs, assessing for pain, blood pressure problems, irregular heartbeat, abnormal breath sounds, etc. you know these because as a nurse you are always assessing the patient. In addition, for older adults you want to assess cognitive function. ▪ Functional assessment is assessing what the older adult can still for themselves. Bathing, eating, getting dress, brushing their teeth and more are functional abilities. Functional abilities can be altered due to physical impairment and illness. Dr. Katz and Dr. Barthel developed ADL/IADL indexes to measure the patients functional abilities. You should have noticed that ADL is used throughout the book. This is because the ADL's can determine the patient's care plan. It determines whether they are safe in the current environment. It impacts their ability to participate in health promotion and disease prevention. ▪ Cognitive- thought processing, thinking and reasoning skills. Know the normal cognitive changes as a result of aging. Dementia is not normal. You will need to understand the difference between delirium and dementia. • There are special tools to assess the older adult that have been proven to produce accurate results. You must be familiar with those tools specific for the older adult. The exam will use the acronyms for the tools. For example, CAM, MMSE, CDT, SPICES. Make sure you know what these stand for and can answer when they are to be used or what the results of these assessment tools will tell you. • Be familiar with the pain assessment tools, and how unrelieved pain can lead to prolonged hospitalization. • Know Katz Index of ADL and Barthel Index both are in chapter 7. You will see ADL and IADL throughout the rest of the entire book. • The Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) is the most extensively used cognitive assessment tool (page 246). The Mini-Cog can be done in 5 minutes see also www.consultgerirn.org. • They may also mention CDT (Clock Drawing Test) which is commonly done with the Mini-Cog evaluation. • Be familiar with ConsultGeriRn.org web videos: Katz Index of Independence in Activities of Daily Living and Administering and Interpreting the Mini-Cog, The Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) Short Form Assessment, Delirium: The under-recognized Medical Emergency, The Modified Caregiver Strain Index (CSI) • You have to know the physiological changes that occur which make the older adult more susceptible to adverse drug reactions. • Five Rights of Medication Administration • The most common drugs that alter lab results • Polypharmacy- why is the older adult more apt to polypharmacy. • Beers’ List of Inappropriate drugs for Older Adults- this is in the e-text and www.consultgerirn.org. Make sure you are familiar with this. Benzodiazepines are mentioned quite a bit • MAP- this means medication assistance program and it will be mentioned in a later chapter. Make sure you understand what it is. This is a choice you can offer your patient who cannot pay for their medication. • You want to advise your patients to become very familiar with their pharmacist. Only use one pharmacy for all their medications, including over the counter (OTC) and herbal remedies. The pharmacist can alert the patient to potential drug reactions. • Know the common classes cause ADR: antipsychotics, antihistamines, benzodiazepine (Atarax, restoril, florazepam, diazepam, Librium, Xanax, Restyl, Paxil), Muscle relaxants, anti-anxiety drugs, anticonvulsants, antiemetics, analgesics #4 Competency 742.1.4: Promoting Independence and Autonomy While Reducing Risk Factors in Older Adults The graduate recommends techniques to co-create health and illness management practices with older adults and their families (caregivers) that ensure safety and optimal maintenance of functional ability, taking into account patient characteristics and needs and patient and caregiver vulnerabilities as well as strengths. This topic addresses the following learning objectives: • Identify ethical principles for preserving autonomy while reducing risk in the care of older adults. • Describe strategies for preventing morbidity and mortality associated with the use of physical and chemical restraints in older adults. • Determine appropriate best practices to co-create a plan of care with the patient, family and other caregivers. • Explain how you would assist older adults, families, and caregivers to balance the need for autonomy and safety when making everyday decisions. • Apply ethical and legal principles to the complex issues that arise in the care of older adults. • Identify appropriate principles of care commensurate with older adults' vulnerabilities and the frequency and intensity of care needs. • Assess the effectiveness of various steps taken to assist health professionals in recognizing and reporting suspected mistreatment of older adults or abuse of resources. • Recommend appropriate individualized care practices to eliminate the use of physical and chemical restraints in older adults. • Recommend techniques to cocreate health practices of a given older adult and family to address identified patient vulnerabilities. o Define autonomy and self-determination. o What is frailty? o What are the characteristics? o What is the Kohlman Evaluation of Living Skills (KELS)? o What are the factors that influence the quality of life of an older adult? o What is the one of the most common role changes faced by the aging person? List all. o What is role reversal for the older adult? o List and describe the care options for the older adult? o What is the Borg Category Rating Scale? o What are the common signs of abuse in an older adult and who is mostly to be the abuser? o List common tools used to assess abuse in the older adult? o Describe the Framingham Heart Study. What did it look at and what were the findings? o What are the risk factors for stroke? Describe the statistical data in regards to strokes and the older adult. o What are other disease processes the older adult is at risk for? Explain the prevalence and how to prevent or control the illness o Instruct the patient to obtain all medications (prescription and nonprescription) at one pharmacy so that pharmacists can check for potentially dangerous interactions. The pharmacist can serve as the central figure who maintains a list of medications and screens for drug-drug interactions to avoid harmful situations. #5 Competency 742.1.5: Promoting Health and Independence in Older Adults The graduate selects appropriate evidence-based standards of health promotion, risk reduction, and disease prevention in older adult populations. This topic addresses the following learning objectives: • Explain how to facilitate older adults' active engagement and participation in their own healthcare. • After discussing evidence-based health promotion activities, facilitate the development of health promotion goals with a given older adult. • Analyze evidence-based research regarding risk reduction and disease prevention in older adults. • Describe strategies to enhance the physical and mental function of older adults. • Identify common risk factors that contribute to functional decline in older adults. • Identify the principles for improving functional ability and quality of life for the older adult. • Articulate psychosocial interventions for maximizing a given older adult’s quality of life. o What is the definition of a fall? And what can happen to an older adult after a fall? What are the risks for falls? (Past history of falls is a major risk factor!) o What are intrinsic risk factors? What are extrinsic risk factors? o Among older adults living in the community, when and where do most falls occur? o What can you do to prevent falls? o What are the types of restraints used? o What are the effects of restraint use on the elderly? o What are alternatives techniques (instead of restraints) to deal with wandering, combative or confused patients? • Identify ways to promote healthy living among the elderly • What are the two most widely publicized components of health promotion? • What are some of the preventive care services covered under Medicare? • Describe a health contract. • Explain Bailey's Bull's eyes • Discuss Healthy People 2010 and 2000. • Define health promotion versus. health screening. • What are the three types of prevention and provide an explanation and example of each. • What is the chronic disease self-management program (CDSMP)? • What are the barriers to physical activity for the older adult? • What is the risk for a sedentary lifestyle? • What are the four leading causes of death in the US? • Are older adults at risk for poor nutrition? If so, why? Explain the barriers for older adults in regards to good nutrition? • What is a healthy weight or BMI and when should we be concerned? • What are the lab values that could show malnutrition in the older adult? • Explain the general guidelines to dietary counseling. • What are the environmental risk factors that be dangerous for an older adult? Can you explain ways to modify the environment to address these safety issues? • Some of the risk factors are client related. What changes of aging can make the patient at risk? • Are older adults at risk for alcohol abuse? If they are, what can be done to re-educate them and prevent harm? #6 Competency 742.1.6: Technology-Assisted Care of Older Adults The graduate collaborates with patients, families and the inter-professional team to select the appropriate application of technology to enhance older adults' safety and independence. This topic addresses the following learning objectives: • Recognize the value of electronic health records to care coordination among older adults across various health care settings and providers. • Identify the major types of assistive technology commonly used to enhance older adults’ function, independence, and safety. • Explain the teaching methods for introducing an older adult patient to a new technology. • Select appropriate communication technology to promote optimal transitions of care for older adults. • Select cost-effective assistive technology to promote quality of life for older adults. • Select strategies for collaborating with older adults, families, and caregivers on applying technology to enhance function, independence, and safety. • Recommend steps to successfully introduce a new technology to an older adult in a given situation. • Evaluate an older adult’s response to a newly introduced assistive technology. o Assistive technology is designed to fill the patient’s gap in functional ability. This goes back to the ADLs and IADLs. What can they do and what can they not do. Can we put something in place to help them? o Chapter 16 is the technology chapter. There is a loss of strength, balance, visual and auditory, cognitive, and/or memory changes that occur as we age. Assistive technology is designed to help us with these losses & bridge the gap between capabilities and care needs. o It is anything that can enhance the function of some physical or mental ability that is impaired. It can be a cane, walker, glasses, hearing aids, wheelchair, bath bench, elevated toilet seat. All of this is assistive technology. It is filling the functional gap. o How do you teach an older adult about the assistive technology? Chapter 9- How older adults learn. Focus on the practical application and benefits of using them. Which type of patients are more likely to use assistive devices? o Review Box 16-1 on page 564: Guidelines for Introducing Technology & Teaching the Elderly about its Use o Briefly discuss assistive robots and sensor-based monitoring systems that we may see used in the future and why they may be useful #7 Competency 742.1.7: Health Care Systems and Reform The graduate evaluates the effectiveness of the healthcare environment and the influence of health policy in providing care that maximizes the function and independence of older adults in accordance with individual patient characteristics and patient and family needs. This topic addresses the following learning objectives: • Explain the implications of an aging population for health policy. • Compare the foundational principles, goals, and methods of identified government programs and other community health initiatives available to older adults. • Identify community resources for older adults that facilitate autonomy and quality of life for a given scenario. • Compare the opportunities and constraints of supportive living arrangements on the function and independence of older adults. • Analyze health care trends related to the independence and autonomy of older adults. • Analyze a given policy or legislative act that promotes or hinders the independence and autonomy of older adults. • Compare the benefits and limitations of the major forms of reimbursement on the delivery of healthcare services to older adults, differentiating the roles of Medicare and Medicaid. • Explain the elements of the triple aim of healthcare reform as reflected in the care of older adults. • Evaluate the influence of payer systems on access, quality, and affordability of healthcare for older adults. o The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act was signed into law in 2010. The intention: ▪ Eliminate lifetime limits for health insurance coverage for essential services ▪ Eliminate the ability of insurance companies to rescind coverage ▪ Free Preventative care ▪ Development of a prevention and public health fund. ▪ Increase access to affordable care, including a provision for pre existing ▪ Quality improvement and risk reduction ▪ The Independence at Home Demonstration: NP’s worked with patients to help them experience a higher level of independence through better management of their chronic illnesses • Provisions that have already taken effect: ▪ Improved drug discounts for Medicare recipients ▪ Coverage for young adults through parental health insurance until age 26. ▪ Expanding coverage for early retirees ▪ National pre existing-condition insurance plan to assist those individuals without coverage for at least 6 months due to a prior condition. ▪ 2012 mandate The US Supreme Court upheld provisions to expand Medicaid and Medicare coverage ▪ The Medicare expansion program requires participating states to expand coverage to most individuals under the age of 65 with income below poverty levels outlined in the Act. • The intent of PPACA in terms of Medicare is to reduce overall cost while maintaining coverage to those entitled to Medicare. • A national Medicare pilot program will be developed to provide Medicare recipients with more options for long-term care, including primary care services in their homes rather than institutional care. • Increase services that will impact the older population include providing wellness and prevention programs at no cost to the individual and prescription drug discounts. • Need to know what Part A and Part B of Medicare covers • What is Medicaid---what does it cover and who is eligible? • What is Triple Aim of healthcare reform? #8 Competency: Care Transitions The graduate determines the needs of older adults and their families & caregivers in coordinating patient-centered, safe transitions of care that aim to assure the least restrictive environment relative to strengths and vulnerabilities, and reduce unnecessary hospitalizations. This topic addresses the following learning objectives: • Recognize common errors related to the transition of care for older adults, such as inaccurate or absent medication reconciliation. • Identify effective communication strategies to promote a safe transition of care for the older adult. • Apply appropriate methods to evaluate the transition of an older adult to a new care environment. • Determine the receiving caregiver’s knowledge of a given patient’s care needs when transitioning care. • Apply multiple communication techniques that promote safe transition of care. • Analyze the effectiveness of a transition in protecting older adults from harm in a given scenario. o Review each of the transitions models provided in the Course of Study. What do they attempt to accomplish? o What are the problems associated with patient transfers o What is the importance of discharge med reconciliation? o What can be done to eliminate the problems? o Cover the interdisciplinary team. Who is usually on the team? Who is most likely not going to be at a meeting? What is the team’s purpose and what is the role of the Nurse? #9 Competency 742.1.9: Palliative and End-of-life Care The graduate collaborates with patients and families to support palliative care needs in order to reduce symptom burden and treatment fatigue and enhance quality of life, as well as end-of-life care that is compassionate, respectful, patient centered, and family supported. This topic addresses the following learning objectives: • Identify fundamentals of pain and symptom management in the palliative care of patients with chronic illness. • Determine the needs and wishes of patients and families related to palliative care. • Recognize aspects of care, including pain and symptom management, as priorities that contribute to a dignified end-of-life experience. • Identify legal and ethical standards related to end-of-life care. • Describe effects of grief and mourning on older adults and their families. • Determine the needs and wishes of patients nearing the end of life. • Assess the availability of services and resources to provide comprehensive end-of-life care. • Recommend appropriate interventions to facilitate the wishes of the dying and their families. o You must be able to explain the differences between curative, palliative, and end of life or hospice care. o Make sure you understand what advance directives and living wills are as well as DNR and AND request. What is the nurse’s role in this? What are the steps to initiating and carrying out the patients request especially when family disagrees/ o What are the signs of impending death? o What are they 2 main categories of pain? Nociceptive pain and Neuropathic pain. What types of medications works best with these types? o Should an older adult in pain and receiving palliative care be concerned with addiction? o Recognize aspects of care, including pain and symptom management as priorities, that contribute to a dignified end-of-life experience. o How is quality of life influenced by burden of symptoms? o Identify legal and ethical standards related to end-of-life care. o Describe effects of grief and mourning on older adults and their families. o Determine the needs and wishes of patients nearing the end of life. o Assess the availability of services and resources to provide comprehensive end- of-life care. o Recommend appropriate interventions to facilitate the wishes of the dying and their families. o What are “5 Wishes”? [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 19, 2021
Number of pages
15
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 19, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
32



















.png)

.png)

