*NURSING > EXAM > NURS 3481 Theories_and_Therapies_Chapter_3 (latest 2020) – University of Texas | NURS 3481 Theorie (All)
NURS 3481 Theories_and_Therapies_Chapter_3 (latest 2020) – University of Texas | NURS 3481 Theories_and_Therapies_Chapter_3 (latest 2020)
Document Content and Description Below
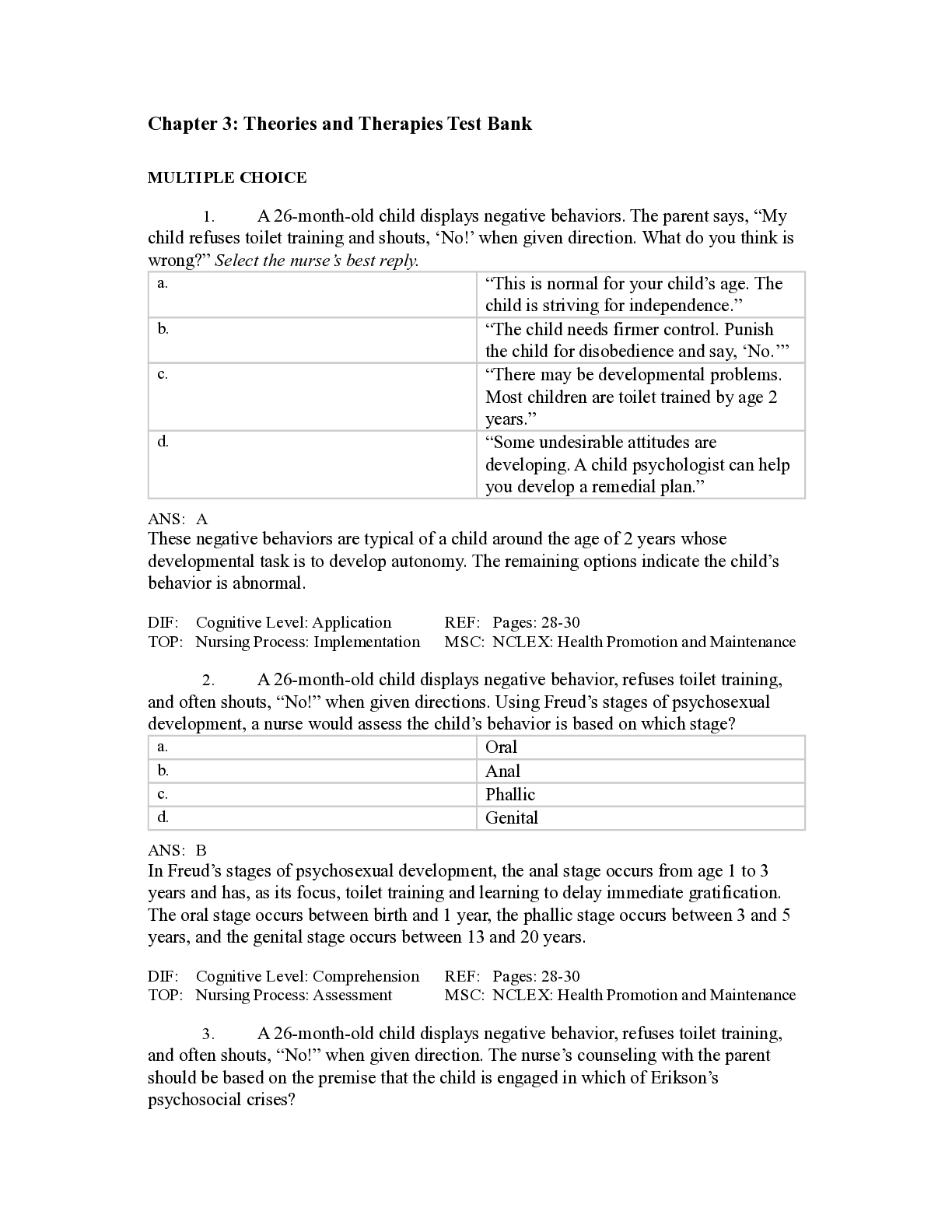
Chapter 3: Theories and Therapies Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A 26-month-old child displays negative behaviors. The parent says, “My child refuses toilet training and shouts, ‘No!’ when g... iven direction. What do you think is wrong?” Select the nurse’s best reply. a. “This is normal for your child’s age. The child is striving for independence.” b. “The child needs firmer control. Punish the child for disobedience and say, ‘No.’” c. “There may be developmental problems. Most children are toilet trained by age 2 years.” d. “Some undesirable attitudes are developing. A child psychologist can help you develop a remedial plan.” 2. A 26-month-old child displays negative behavior, refuses toilet training, and often shouts, “No!” when given directions. Using Freud’s stages of psychosexual development, a nurse would assess the child’s behavior is based on which stage? a. Oral b. Anal c. Phallic d. Genital 3. A 26-month-old child displays negative behavior, refuses toilet training, and often shouts, “No!” when given direction. The nurse’s counseling with the parent should be based on the premise that the child is engaged in which of Erikson’s psychosocial crises? a. Trust versus Mistrust b. Initiative versus Guilt c. Industry versus Inferiority d. Autonomy versus Shame and Doubt 4. A 4-year-old child grabs toys from siblings, saying, “I want that toy now!” The siblings cry, and the child’s parent becomes upset with the behavior. Using the Freudian theory, a nurse can interpret the child’s behavior as a product of impulses originating in the: a. id. b. ego. c. superego. d. preconscious. 5. The parent of a 4-year-old rewards and praises the child for helping a younger sibling, being polite, and using good manners. A nurse supports the use of praise because according to the Freudian theory, these qualities will likely be internalized and become part of the child’s: a. id. b. ego. c. superego. d. preconscious. 6. A nurse supports parental praise of a child who is behaving in a helpful way. When the individual behaves with politeness and helpfulness in adulthood, which feeling will most likely result? a. Guilt b. Anxiety c. Loneliness d. Self-esteem 7. A patient comments, “I never know the right answer” and “My opinion is not important.” Using Erikson’s theory, which psychosocial crisis did the patient have difficulty resolving? a. Initiative versus Guilt b. Trust versus Mistrust c. Autonomy versus Shame and Doubt d. Generativity versus Self-Absorption 8. Which patient statement would lead a nurse to suspect that the developmental task of infancy was not successfully completed? a. “I have very warm and close friendships.” b. “I’m afraid to let anyone really get to know me.” c. “I am always right, so don’t bother saying more.” d. “I’m ashamed that I didn’t do it correctly in the first place.” 9. A nurse assesses that a patient is suspicious and frequently manipulates others. Using the Freudian theory, these traits are related to which psychosexual stage? a. Oral b. Anal c. Phallic d. Genital 10. An adult expresses the wish to be taken care of and often behaves in a helpless fashion. This adult has needs related to which of Freud’s stages of psychosexual development? a. Latency b. Phallic c. Anal d. Oral 11. A nurse listens to a group of recent retirees. One says, “I volunteer with Meals on Wheels, coach teen sports, and do church visitation.” Another laughs and says, “I’m too busy taking care of myself to volunteer. I don’t have time to help others.” These comments contrast which developmental tasks? a. Trust versus Mistrust b. Industry versus Inferiority c. Intimacy versus Isolation d. Generativity versus Self-Absorption 12. Cognitive therapy was provided for a patient who frequently said, “I’m stupid.” Which statement by the patient indicates the therapy was effective? a. “I’m disappointed in my lack of ability.” b. “I always fail when I try new things.” c. “Things always go wrong for me.” d. “Sometimes I do stupid things.” 13. A student nurse tells the instructor, “I don’t need to interact with my patients. I learn what I need to know by observation.” The instructor can best interpret the nursing implications of Sullivan’s theory to the student by responding: a. “nurses cannot be isolated. We must interact to provide patients with opportunities to practice interpersonal skills.” b. “observing patient interactions can help you formulate priority nursing diagnoses and appropriate interventions.” c. “I wonder how accurate your assessment of the patient’s needs can be if you do not interact with the patient.” d. “noting patient behavioral changes is important because these signify changes in personality.” 14. A psychiatric technician says, “Little of what takes place on the behavioral health unit seems to be theory based.” A nurse educates the technician by identifying which common use of Sullivan’s theory? a. Structure of the therapeutic milieu of most behavioral health units b. Frequent use of restraint and seclusion as behavior management tools c. Assessment tools based on age- appropriate versus arrested behaviors d. Method nurses use to determine the best sequence for nursing actions TOP: Nursing Process: Implementation MSC: NCLEX: Safe, Effective Care Environment 15. A nurse uses Maslow’s hierarchy of needs to plan care for a psychotic patient. Which problem will receive priority? The patient: a. refuses to eat or bathe. b. reports feelings of alienation from family. c. is reluctant to participate in unit social activities. d. needs to be taught about medication action and side effects. 16. Operant conditioning will be used to encourage speech in a child who is nearly mute. Which technique would a nurse include in the treatment plan? a. Ignore the child for using silence. b. Have the child observe others talking. c. Give the child a small treat for speaking. d. Teach the child relaxation techniques, then coax speech. 17. The parent of a child who has schizophrenia tearfully asks a nurse, “What could I have done differently to prevent this illness?” Select the nurse’s most caring response. a. “Although schizophrenia is caused by impaired family relationships, try not to feel guilty. No one can predict how a child will respond to parental guidance.” b. “Most of the damage is done, but there is still hope. Changing your parenting style can help your child learn to cope more effectively with the environment.” c. “Schizophrenia is a biological illness with similarities to diabetes and heart disease. You are not to blame for your child’s illness.” d. “Most mental illnesses result from genetic inheritance. Your genes are more at fault than your parenting.” 18. A nurse uses Peplau’s interpersonal therapy while working with an anxious, withdrawn patient. Interventions should focus on: a. changing the patient’s perceptions about self b. improving the patient’s interactional skills c. using medications to relieve anxiety d. reinforcing specific behaviors 19. A patient underwent psychotherapy weekly for 3 years. The therapist used free association, dream analysis, and facilitated transference to help the patient understand unconscious processes and foster personality changes. Which type of therapy was used? a. Short-term dynamic psychotherapy b. Transactional analysis c. Cognitive therapy d. Psychoanalysis 20. An advanced practice nurse determines a group of patients would benefit from therapy in which peers and interdisciplinary staff all have a voice in determining the level of the patients’ privileges. The nurse would arrange for: a. milieu therapy b. cognitive therapy c. short-term dynamic therapy d. systematic desensitization 21. A nurse psychotherapist works with an anxious, dependent patient. The therapeutic strategy most consistent with the framework of psychoanalytic psychotherapy is: a. emphasizing medication compliance b. identifying the patient’s strengths and assets c. offering psychoeducational materials and groups d. focusing on feelings developed by the patient toward the nurse 22. A person tells a nurse, “I was the only survivor in a small plane crash, but three business associates died. I got anxious and depressed and saw a counselor three times a week for a month. We talked about my feelings related to being a survivor, and now I’m fine, back to my old self.” Which type of therapy was used? a. Milieu therapy b. Psychoanalysis c. Behavior modification d. Interpersonal therapy 23. A cognitive strategy a nurse could use to assist a very dependent patient would be to help the patient: a. reveal dream content. b. take prescribed medications. c. examine thoughts about being independent. d. role model ways to ask for help from others. 24. A single parent is experiencing feelings of inadequacy related to work and family since one teenaged child ran away several weeks ago. The parent seeks the help of a therapist specializing in cognitive therapy. The psychotherapist who uses cognitive therapy will treat the patient by: a. discussing ego states b. focusing on unconscious mental processes c. negatively reinforcing an undesirable behavior d. helping the patient identify and change faulty thinking 25. A person received an invitation to be in the wedding of a friend who lives across the country. The individual is afraid of flying. What type of therapy should the nurse recommend? a. Psychoanalysis b. Milieu therapy c. Systematic desensitization d. Short-term dynamic therapy MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. A basic level registered nurse works with patients in a community setting. Which groups should this nurse expect to lead? Select all that apply. a. Symptom management b. Medication education c. Family therapy d. Psychotherapy e. Self-care 2. A patient states, “I’m starting cognitive behavioral therapy. What can I expect from the sessions?” Which responses by the nurse are appropriate? Select all that apply. a. “The therapist will be active and questioning.” b. “You may be given homework assignments.” c. “The therapist will ask you to describe your dreams.” d. “The therapist will help you look at ideas and beliefs you have about yourself.” e. “The goal is to increase your subjectivity about thoughts that govern your behavior.” [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages
Instant download
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 05, 2020
Number of pages
12
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 05, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
39