*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > ATI – NCLEX Predictor Remediation Study Notes 2019/2020 (All)
ATI – NCLEX Predictor Remediation Study Notes 2019/2020
Document Content and Description Below
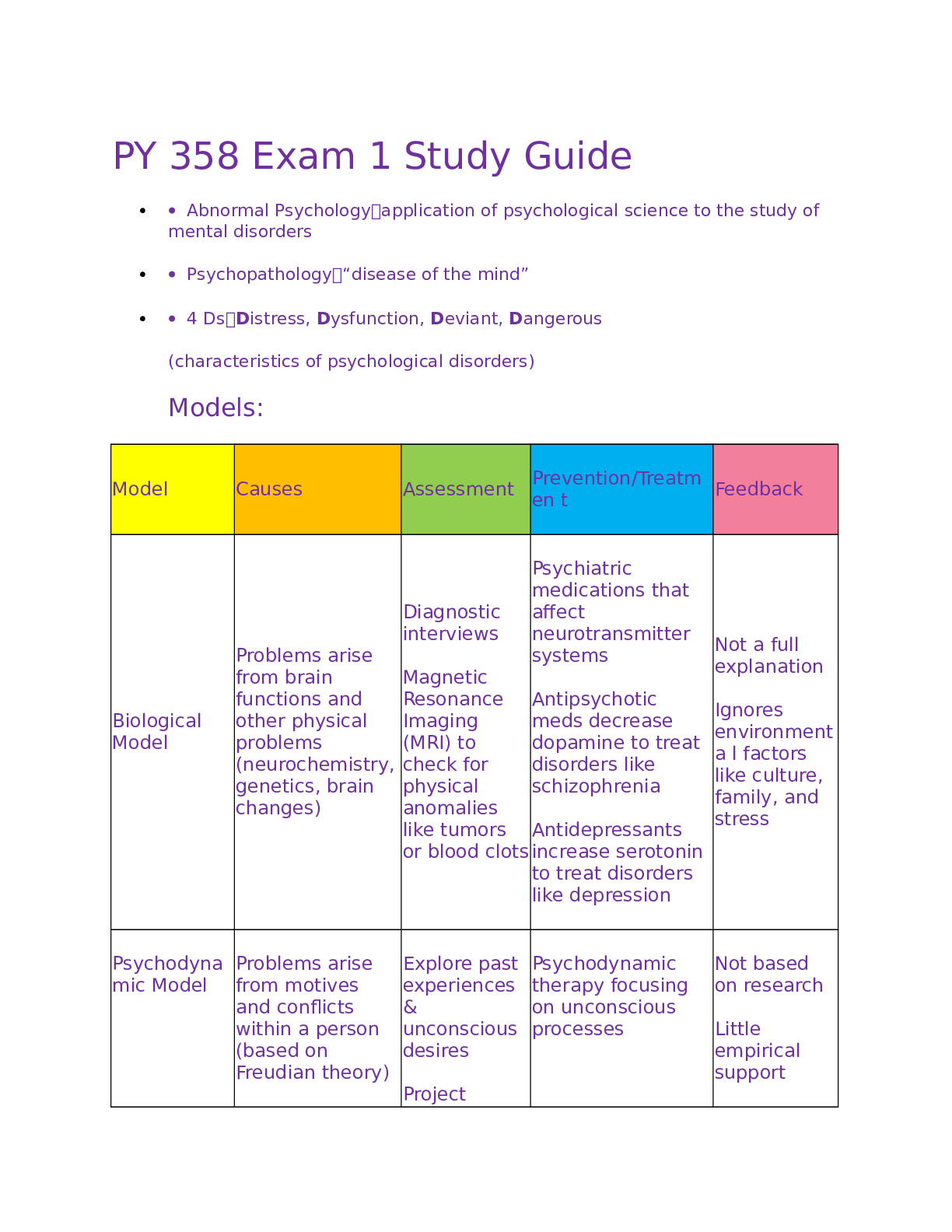
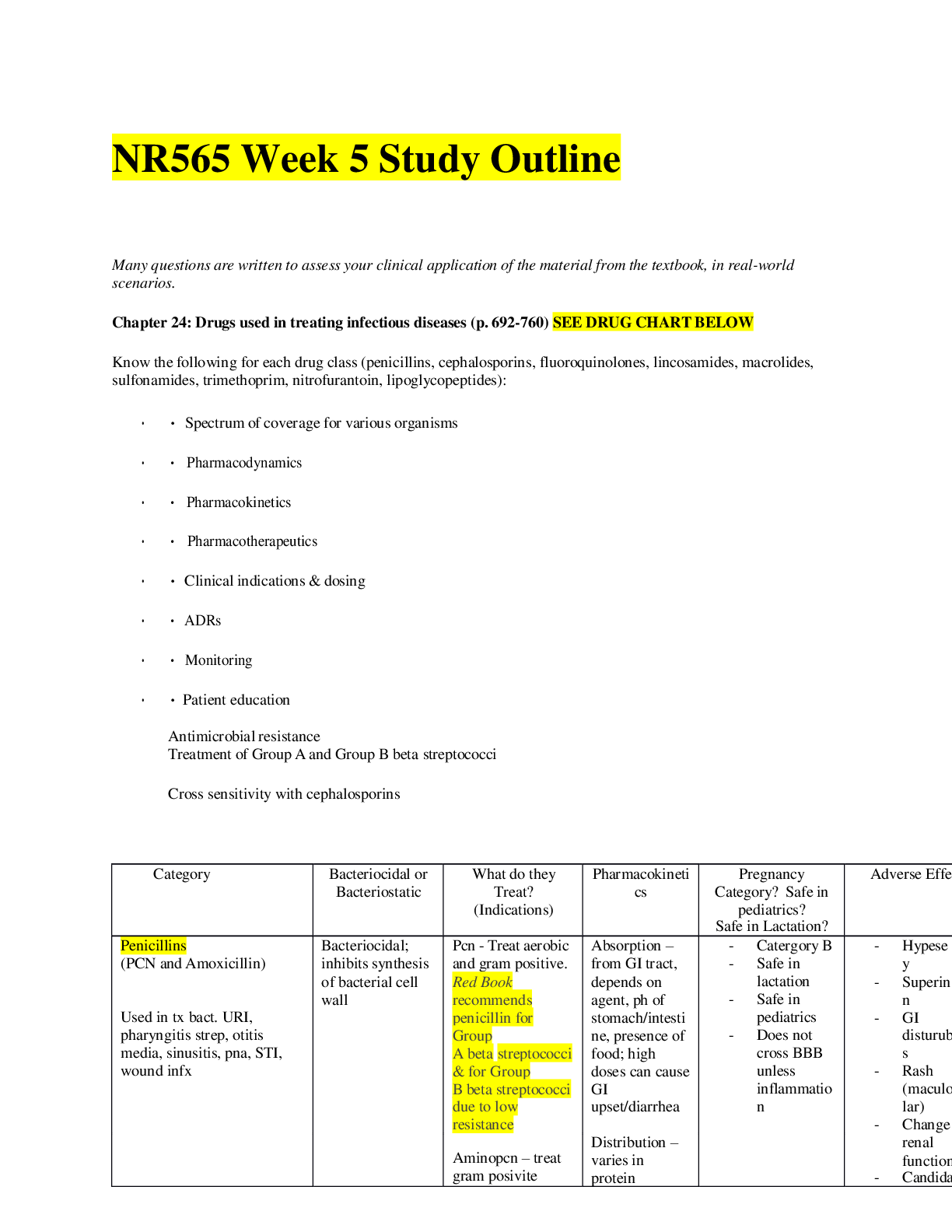
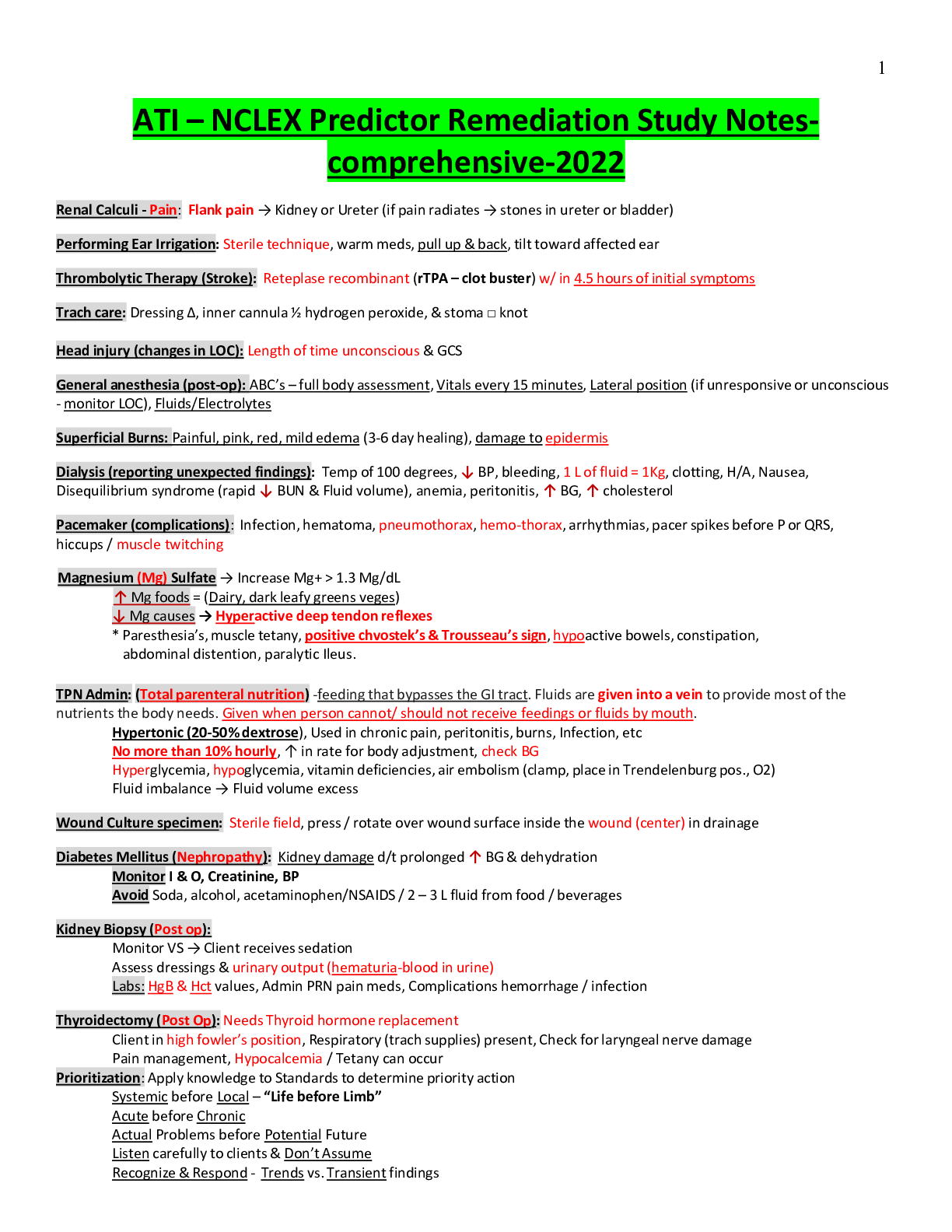
ATI – NCLEX Predictor Remediation Study Notes (PREVIEW the first 10 pages) Renal Calculi - Pain: Flank pain → Kidney or Ureter (if pain radiates → stones in ureter or bladder) Performing Ear Irr... igation: Sterile technique, warm meds, pull up & back, tilt toward affected ear Thrombolytic Therapy ( Stroke): Reteplase recombinant (rTPA – clot buster) w/ in 4.5 hours of initial symptoms Trach care: Dressing ∆, inner cannula ½ hydrogen peroxide, & stoma □ knot Head injury (changes in LOC): Length of time unconscious & GCS General anesthesia (post-op): ABC’s – full body assessment, Vitals every 15 minutes, Lateral position (if unresponsive or unconscious - monitor LOC), Fluids/Electrolytes Superficial Burns: Painful, pink, red, mild edema (3-6 day healing), damage to epidermis Dialysis (reporting unexpected findings): Temp of 100 degrees, ↓ BP, bleeding, 1 L of fluid = 1Kg, clotting, H/A, Nausea, Disequilibrium syndrome (rapid ↓ BUN & Fluid volume), anemia, peritonitis, ↑ BG, ↑ cholesterol Pacemaker (complications): Infection, hematoma, pneumothorax, hemo-thorax, arrhythmias, pacer spikes before P or QRS, hiccups / muscle twitching Magnesium (Mg) Sulfate → Increase Mg > 1.3 Mg/dL ↑ Mg foods = (Dairy, dark leafy greens veges) ↓ Mg causes → Hyperactive deep tendon reflexes * Paresthesia’s, muscle tetany, positive chvostek’s & Trousseau’s sign, hypoactive bowels, constipation, abdominal distention, paralytic Ileus. TPN Admin: (Total parenteral nutrition) -feeding that bypasses the GI tract. Fluids are given into a vein to provide most of the nutrients the body needs. Given when person cannot/ should not receive feedings or fluids by mouth. Hypertonic (20-50% dextrose), Used in chronic pain, peritonitis, burns, Infection, etc No more than 10% hourly, ↑ in rate for body adjustment, check BG Hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, vitamin deficiencies, air embolism (clamp, place in Trendelenburg pos., O2) Fluid imbalance → Fluid volume excess Wound Culture specimen: Sterile field, press / rotate over wound surface inside the wound (center) in drainage Diabetes Mellitus (Nephropathy): Kidney damage d/t prolonged ↑ BG & dehydration Monitor I & O, Creatinine, BP Avoid Soda, alcohol, acetaminophen/NSAIDS / 2 – 3 L fluid from food / beverages Kidney Biopsy (Post op): Monitor VS → Client receives sedation Assess dressings & urinary output (hematuria-blood in urine) Labs: HgB & Hct values, Admin PRN pain meds, Complications hemorrhage / infection Thyroidectomy (Post Op): Needs Thyroid hormone replacement Client in high fowler’s position, Respiratory (trach supplies) present, Check for laryngeal nerve damage Pain management, Hypocalcemia / Tetany can occur Prioritization: Apply knowledge to Standards to determine priority action Systemic before Local – “Life before Limb” Acute before Chronic Actual Problems before Potential Future Listen carefully to clients & Don’t Assume Recognize & Respond - Trends vs. Transient findings Recognize indications - Emergencies vs. Expected Delegate to LPN: Monitoring Findings, Reinforcing teaching, performing trach care, suctioning, checking NG tube patency, administer tube feedings, inserting urinary catheter, administering meds (No IV) Delegate to AP: ADLs, Bathing, Grooming, Dressing, toileting, Ambulating, feeding w/out swallowing precautions, positioning, routine tasks, bed making, specimen collection, I & O, VS for stable clients, monitoring clinical manifestations after initial RN assess/eval. Paracentesis (prep) - take out fluid from belly (peritoneal fluid) Have client VOID Bariatric Surgery: (weight loss surgery) – Semi fowlers, 6 small meals/day, liquid/pureed food for first 6 weeks (not to exceed 1cup), Vitamin / mineral supplements, & 2 servings of protein daily. Ostomy (in small intestine) Avoid odorous & gas foods (dark green veges, dairy, fish, eggs, beans, corn), yogurt ↓ gas Avoid ↑ fiber foods for first 2 months, ↑ fluid intake Dumping Syndrome: Happens within 15mins of eating. Sx: cramps, diarrhea, tachycardia, dizziness, fatigue, hypoglycemia Interventions: small frequent meals, drink liquids 1hr b4/after Parkinson’s disease: Tremor, muscle rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness in movement), postural instability Stages: 1. Unilateral shaking / tremor of one limb 2. Bilateral limb involvement, difficulty walking/balance 3. Slowed physical movements 4. Akinesia & Rigidity make ADL’s difficult 5. Unable to stand/walk, dependent of cares, dementia Assault: threat Battery: touching Hypoglycemia Sx: Shakiness, confusion, sweating, tachycardia, diaphoresis, palpitations, H/A, lack of coordination, blurred vision, seizures, coma Oral Hypoglycemic Agents: promote insulin release from pancreas (Type2 DM) Glipizide (Glucotrol), Chlorpropamide (Diabines), Glyburide (Diabinese), Metformin (Glucophage). * Med for insulin overdose = Glucagon Radiation Adverse Effects: Skin changes, hair loss, debilitating fatigue, 30 minute visits / stays 6ft away / private room Infection control in clients home: good hygiene, avoid crowded areas, avoid raw foods (veges/meats), avoid cleaning litter boxes, clean home and avoid sick family. Client evacuation in response to fire: greatest good for the greatest amount of people Client in seclusion: 18 yo → 4 hours, 9 – 17 yo →2 hours, 8 yo & younger →1 hour Conduct Disorders: lack of remorse, bullies, threatens, low self-esteem, tempers, physical cruelty, destroys property, truant, and shoplifts Manic Phase: ↑ mood, irritable, lasts at least a week, euphoria, agitation, restless, ↑ in talking, flight of ideas, grandiose view of self, impulsive, manipulative, poor judgement, attention seeking. Paranoid: distrust / suspiciousness Schizoid: emotional detachment, disinterest in relationships, indifferent to praise/criticism, uncooperative Schizotypal: odd beliefs, eccentric appearance, magical thinking, perceptual distortions Antisocial: disregard for others, lack of empathy, unlawful, failure to accept responsibility, manipulative, impulsive, seductive Borderline: instability of affect, identity & relationships, splitting behaviors, fear of abandonment, self-injurious, impulsive Histrionic: attention seeking, seductive, flirtatious Narcissist: arrogant, constant admiration, lack of empathy Avoidant: anxious, wants close relationships, fear of rejection Dependent: dependency on another individual OCD: perfectionist, orderly, and control Clozapine (Anti-psychotic Atypical ) Adverse effects: metabolic syndrome, orthostatic hypotension, anti-cholinergic effects, agitation, dizziness, sedation, mild EPS, ↑ prolactin levels(galactorrhea, amenorrhea, gynecomastia), & sexual dysfunction Anti-lipemic Agents: (Statins) – treats high levels of fats/cholesterol in blood -called lipid-lowering drugs Monitor liver enzyme levels (hepatotoxicity) and muscles – monitor CK levels (myopathy & peripheral neuropathy) Med interactions: Fibrates (Genfibrozil) - ↑ myopathy risk, Erythroycin & Ketoconazole, Amiodarone, & Cyclosprine = Grapefruit juice can ↑ statin levels Gentamicin (effects urine output) -causes ototoxicity w/ diuretics, digoxin, lithium, ototoxic meds, NSAIDs, & anti-hypertensives Long term therapy for RA: DMARDs (methotrexate, etanercept, infliximab, adalimubrab, Azathioprine, Cyclosporine) ** Slow joint degradation Glucocorticoids (Prednisone) & NSAIDs provide symptom relief from inflammation & pain Bulb Syringe (for babies): Mouth first, then nose, depress. Then insert into mouth, avoid center of mouth- may stim. gag reflex. Priority action to an allergic response: Mild rashes/hives – Benadryl Anaphylaxis - treat with epi, bronchodilators, and anti-histamines Provide respiratory support & notify HCP Losartan (ARBs -Anti-Hypertensive (HTN) & kidney disease) - Cough & hyperkalemia are for ace inhibitors. Side Effects: Angioedema, hypotension, dizziness Tracheostomy Care: 2 xtra tubes, adequate humidification, oral care every 2 hours, trach care every 8 hours, sterile suctioning, surgical asepsis to remove / clean inner cannula, secure trach ties before removing old, square knot, clean from stoma outward Appropriate Doc.: Subjective/objective data, Accurate/concise, Complete/current, Organized/ date/ time/ blk ink Crutch safety: Support bodyweight at hand grips with elbows at 30 degrees, Position crutches on unaffected side when sitting or rising from a chair Varicella (chicken pox) Transmission: Direct contact, droplet, from person with shingles, 10-21 days, 1-2 days before lesions appear and all lesions have sabs Scoliosis: Lateral curvature of spine & spinal/truncal rotation that causes ribs asymmetry. Curve needs to be at least 10 degrees One leg shorter than the other. Asymmetry in scapula, ribs, flanks, shoulders, hips. Screening for Idiopathic Scoliosis: During pre-adolescence - Observe child from back Bend at waist with arms handing down & observe for asymmetry of ribs and flank Measure truncal rotation with a scolio-meter Use Cobb technique to determine degree of curvature Use riser scale to determine skeletal maturity ↓ Cardiac output (interventions): Maintain bedrest, Semi fowler’s/ fowler’s position while awake, Sleep w/ pillows Cardiac output positioning for optimal output: Left lateral side, Semi fowlers, Supine with wedge under one hip Infant car seat: Position infant in car seat at 45 degree angle, Safety restraints loose and low on abdomen Correct use of Condoms: On erect penis, empty space at tip for sperm reservoir (May be used with spermicidal gel to ↑ effectiveness), Protects against STI’s, only water soluble lube with latex condoms Amnio-infusion for Oligohydramnios: (not enough amniotic fluid around fetus) Infusion or NS or LR into amniotic cavity to reduce severity of variable decelerations caused by cord compression Scant amount or absence of amniotic fluid, Membranes must have ruptured to perform - Warm fluid Rhogam for Clients who are RH-Negative: (Antibodies from human plasma injected into RH mother to protect fetus) Chadwick’s sign – violet/blue color or cervix & vaginal mucosa Goodell’s sign – softening of cervical tip HSV (Herpes simplex virus): direct contact transmission to fetus is greatest during vaginal birth if woman has active lesions, Lesions & tender lymph nodes, Obtain cultures from women who have HSV or are at or near term Urinary frequency Interventions: ↓ fluid intake b-4 bed, Use perineal pads, and Kegel exercises ↓ stress incontinence Buddhist Dietary practices: vegetarian, nuts, legumes (dried peas/cooked beans), No eggs, no milk products Notifiable Communicable diseases: anthrax, botulism, cholera, diphtheria, gonorrhea, hep A/B/C, HIV, legionaries, lymes, malaria, mumps, pertussis, polio, syphilis, tetanus, TSS, TB, Typhoid fever, VRSA, At risk populations, transmissions routes Anterior Pituitary Hormones: Stimulate growth - Caution in DM patients – can cause hyperglycemia (Somatropin) Anti-Convulsants: Tx- seizures (caphe) Petit Mal (Valet) Carbamazepine, valproic acid, ethosuximide, Phenytoin/phenobarbital – adverse effects = yellowing of skin, nystagmus, teratogenicity, osteomalacia, H/A, vertigo, ataxia Ophthalmic Agents: Beta Blockers: ↓ aqueous humor production (betotopic, betaxon, betagan, betimol) Prostaglandin Analogs: ↑ aqueous humor outflow (xalantan, travatan) Alpha Adrenergic Agonists: ↓ aqueous humor & ↑ outflow (Alphagan) Direct Acting Cholinergic Agonist: ↓IOP & ↑ outflow of AH (Pilocarpine) Side effects for Ophthalmic Agents: Blurred vision, angle closure glaucoma, dry eyes, photophobia, ocular pressure, can cause systemic effects, ciliary muscle constriction Mixing Insulin: (Clear before Cloudy) Air into NPH (Cloudy), Air into Regular (Clear), Draw up Regular (Clear), Draw up NPH (Cloudy) * Hypoglycemia is most likely to occur during peak. Obstetric History: (GTPAL) Gravida, Term, Preterm, Abortions, Living Children Pre-Term Infant: Anticipated Problems (TRIES) Temperature regulation (poor), Resistance to infections (poor), Immature Liver, Elimination problems (Necrotizing Enterocolitis), Sensory-Perceptual Functions (Retinopathy) Fetal Heart Rate: (VEAL CHOP) Variable Decels Cord Compression Early Decels Head Compression Accelerations O2 (Baby is well-oxygenated) Late Decels Placental Utero Insufficiency Pregnant Client - Med. Surg Floor: (FETUS) Fetal heart tones (document every shift) Emotional Support Temperature (Measure maternal) Uterine Activity/Contractions (early-low back pain) Sensations of fetal movement Placenta Previa: low implantation of the placenta / Bright red bleeding present that is painless. Place mother on bedrest in side lying position / Weigh perineal pads Abuptio Placenta: Premature separation of the placenta - Dark red bleeding may or may not be present with sharp stabbing pain Start fluid replacement, oxygen by mask, monitor FHR, keep in lateral position, pregnancy must be terminated - birth or C-Section Endocrine Agents: Thyroid Hormones (Hypothyroidism) Synthetic form of thyroxine (T4), ↑ metabolic rate, body temp, oxygen use, renal perfusion, blood volume, & growth processes. (Levothyroxine, Thyroid, Liothronien, Anti-thyroid meds (hyperthyroidism), graves, thyrotoxicosis, propythiouracil (PTU) Cholecystitis: (Inflammation of Gall Bladder) ↓ fat intake, NO - coffee, broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, onions/ legumes Compartment Syndrome: Sx: (5 Ps) Pain, Pallor, Pulse ↓ or absent, ↑ BP, Paresthesia (tingling hands, feet) Acute Renal Failure: Can cause HypoNatremia, HyperKalemia, HypoCalcemia, & HyperPhosphatemia Shock Sx: (Chord Item) Anti-Platelets: Aspirin, Plavix (clopidogrel) Cold, clammy skin, Hypotension, Oliguria, Drowsiness, ↑bleeding risk, prevent MI/stroke, taken PO Rapid/shallow breathing, Irritability, Tachycardia Watch for hemorrhagic stroke (weakness, Dizziness, H/A) Elevated or reduced CVP, Multi-Organ damage Avoid NSAIDs, Heparin, warfarin, corticosteroids Anti-Platelets: Aspirin, Plavix (clopidogrel) ↑bleeding risk, prevent MI/stroke, taken PO Herb/Botanical Therapy Watch for hemorrhagic stroke (weakness, Dizziness, H/A) Echinacea (common cold), Ginger root (↓ nausea, RA) Avoid NSAIDs, Heparin, warfarin, corticosteroids Ginko Biloba (↑ vasodialation, dementia, alzheimers) HypoCalcemia Sx: (CATS) Valarian (↑ GABA to prevent insomnia) – don’t use in MH, Convulsions, Arrhythmias, Tetany, Stridor / Spasms Or pregnancy. Black cohosh (estrogen sub)-↑ anti HTN Nephrotic Syndrome meds& hypoglycemia Serum Proteins in urine, Diet with sufficient protein Peptic Ulcer Disease Diet low in sodium Avoid frequent meals/snacks, alcohol, smoking, NSAIDs, Nephrolithiasis (kidney stones) Coffee, spicy foods, & caffeine ↑ Fluid Consumption is primary intervention Lactose Intolerance HypoKalemia Sx: (6 L’s) Distention, Cramps, Flatus, Diarrhea Lethargy, Leg Cramps, Limp Muscles HypoGlycemia Sx: (TIRED) Low Shallow Respirations Tachycardia, Irritability, Restlessness, Excessive Hunger Lethal Cardiac Dysrhythmias Depression / Diaphoresis Lots of urine (polyuria) End Stage Renal Disease: GFR <25mL/min Pre-End Stage Renal Disease Serum creatinine rises, dialysis or transplant required ↑ in serum creatinine ↑ protein, ↓phosphorus, ↓potassium, ↓sodium Limit protein & phosphorous (meat, dairy, pb, dried peas, Fluid restricted diet Beans, cola, chocolate beer) Protein needs ↑ once dialysis begins Restrict sodium to maintain BP Vitamin D deficiency occurs Arterial occlusion (4 P’s) HTN Care: (Diuretic) Pain, Pulselessness, Pallor, Paresthesia Daily weight, I&O’s, urine output, response of BP, CHF Treatment: (MADD DOG) Electrolytes, take pulse, Ischemic Episodes (TIA’s) Morphine, Aminophylline, Digoxin, Diuretics, Oxygen Complications (CVA, CAD, CHR, CRF) Gases (ABG’s) Labs: Normal Values: Normal Values: Creatinine 0.6-1.2 Males 0.5-1.1 Females RBC 4.7-6.1 Males 4.2-5.4 Females Hematocrit 42-52 Males 37-47 Females Urine Specific Gravity 1.0-1.030 APTT 40 Sec. Digoxin 0.5-2.0 Lithium 0.8-1.4 Anti-Emetics (-tron, -zine): Can cause sedation. Metoclopramide (Reglan)- monitor for EPS PPI’s (-zole): can cause Vit. B12 deficiency Erectile Dysfunction agents (-fil): Can cause H/A, flushing, back pain, muscle aches, & temporary vision changes. * Don’t take if have heart problems, BP issues, or stroke. Anti-Enemics: Liquid iron can cause teeth staining, dilute w/ water or juice. Iron – given IM (Z-track method) Oral Iron – avoid Vit. C. (antacids by 2 hours, empty stomach 1 hr before meals) * Black stools are common. Encourage intake of high iron foods. Anti-Coagulants: prevents of blood coagulation/clotting Heparin Sodium – admin = IV or SQ (Antidote=Protamine Sulfate) - Normal APTT = 60-80 seconds Enoxaparin (Lovenox) – admin = SQ, longer ½ life * Administer with MI or DVT * ↑ bleeding risk Avoid: Corticosteriods, NSAIDs, Vit. K, PO Hypoglycemics. Coumadin – admin = PO (Antidote = Vit. K) Avoid: using with low platelets, foods high in Vit. K, Tylenol, glucocorticoids, aspirin, use while pregnant Monitor: INR & patient HypoNatremia: ↓ Sodium - Sx: confusion, restlessness, lethargy, seizures, coma - Treat: fluid restriction HypoKalemia: ↓ Potassium - Sx: poor muscle strength, slow reflexes, flat T waves (cardiac dysrhythmias) - Treat: PO or IV Potassium supplement HyperNatremia: ↑ Sodium - Sx: Postural hypotension - Treat: Fluids (drink/IV) HyperKalemia: ↑Potassium - Sx: Twitching, contraction, paralysis, peaked T waves (cardiac dysrhythmias) - Treat: Kayexalate, Loop diuretic, Insulin HypoCalcemia: ↓ Calcium - Sx: twitching, muscle cramps, Trousseau/Chvostaks - Treat: dietary supplement, antacids, and vitamins HyperCalcemia: ↑ Calcium - Sx: muscle weakness, fatigue, slow GI - Treat: diuretic, 3-4L fluid daily, weight bearing, and calcitonin Antidotes: Bethanechol/Neostigmine = Atropine Atropine = Phyosostigmine Digoxin = Digibind Warfarin = Vitamin K Heparin = Protamine Sulfate Insulin Induced Hypoglycemia = Glucagon Acetaminophen = Acetylcysteine (mucomyst) Ace Inhibitors (-pril): HF, HTN, MI, and Diabetic Neuropathy Side effects: orthostatic hypotension, dry cough, hyperkalemia, NSAIDs ↓ therapeutic effects Alpha Adrenergic Blockers (-zosin): Dilate Veins/Arteries (Prazosin, Doxazosin) ARBS (-sartan): Produce vasodilation by blocking Angiotensin II. (Losartan) CCB’s (-dipine): Vasodilation by blocking calcium channels. (Nifedipine, Amlodipine, verapamil, Diltiazem) Avoid: drinking grapefruit juice – can lead to toxicity Electrolytes: Sodium: Administer Isotonic IV therapy (NS/LR) Potassium: Maintains electrical excitability of muscle conduction of nerve impulses (NEVER given IV PUSH) Calcium: Muscoskeletal, neuro / cardio function, implement seizure precautions Magnesium: Skeletal muscle contraction & blood coagulation. Monitor: BP, Pulse, Respirations Anti-Gout Meds: Gout is a type of arthritis. Buildup of Uric Acid. First line: NSAIDs / Prednisone, Colchicine (GI distress potential – take with food) Allopurinol: prevents uric acid production Drug interactions: salicylates, loop diuretics, alcohol, warfarin Food interactions: anchovies, yeast, organ meat, legumes, mushroom, spinach, asparagus, cauliflower Anti-Reabsorptives : slow bone removal or improve bone mass. (Menopausal women) Bisphosphonates (Alendronate – Fosamax). Can cause severe esophagitis. Take on empty stomach w/8oz of water & sit upright for 30 minutes. Anti-Neoplastics: Cancer meds Side effects: soreness, difficulty swallowing, diarrhea, stomach pain, low platelets, anemia, sensitive skin, excess tear formation Mental Status Exam: LOC, physical appearance, behavior, & cognitive/intellectual abilities Anxious / depressed: open ended supportive statements Suicidal: direct yes/no questions to assess risk Panicked: use gentle reality orientation Confused: Provide reality orientation Delusions/Hallucinations/Paranoia: Acknowledge, don’t reinforce Obsessive Compulsive Behavior: Communicate after behavior Personality/Cognitive Disorder: Be calm and matter of fact Aggressive/Violent: set boundaries, limits, short simple sentences Psychiatric Meds: SSRI’s: Citalopram, Fluoxetine, Sertraline (avoid St John’s Wort) TCA’s: Amitriptyline (anticholinergic effects “cant’s” – orthostatic Hypotension MAOI’s: Phenelzine, Hypertensive Crisis Atypical: bupropion (appetite suppression, H/A, Dry mouth) SNRI’s: Venlafaxine / Duloxetine (nausea, weight gain, sexual dysfunction) RN delegate surgical asepsis responsibilities to UAP's? Only under RN supervision When should traditional hand washing be used instead of using alcohol-based sanitizer? Hands are visibly soiled, touching bodily fluids, Before/after applying sterile gloves, After using sanitizer 10 times Contradictions of good hand hygiene Nail polish, Long nails, using lotions, Wearing jewelry Potential routes of entry into the body for blood borne pathogens? Mucous membranes, Puncture wounds, Burns on hands, Blood Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is the single most effective way to prevent the transmission of infection Two potential sites for nosocomial infections: hospital & Homecare Causes of nosocomial infections: suppressed immune system, Failure to follow isolation precautions or aseptic technique, Hospital error A physician is preparing to perform a lumbar puncture. The suspected diagnosis is bacterial meningitis. What type of precaution is needed? Standard precautions A 70 y. male develops new diarrhea and a high WBC while in the hospital recovering from MV Replacement surgery which was complicated by a CVA. He is bed bound and incontinent of stool. What do you suspect is the cause for his diarrhea? A bacterial, nosocomial infection Medical abbreviation: CBR, BR complete bedrest, bedrest Frequent bathing for the older client is necessary to prevent skin breakdown. False A bath can be helpful in soaking a client's pelvic area in warm water to decrease inflammation. sitz 3 guidelines for providing patient-centered care when addressing a client's hygiene needs Be respectful to cultural values, Ask the pt in what order they would like to complete their hygiene routine. Provide hygienic care as often as necessary (but not too often) and as gently as necessary. What should be included in documentation of a bath? Date and time, Type of bath, Abnormal findings/pt reaction When might the RN need to collaborate a colleague for personal care? If a patient is not ambulatory and is too heavy to be moved alone What are the components of the Braden scale? Sensory perception, moisture, activity, mobility, nutrition, friction & shear - High score indicates low risk. Trochanter roll -Keeps hips in a neutral position Hemiparesis Weakness on one sign of the body Hemiplegia - Paralysis on one side of the body Prone position - Lying on the abdomen Sim's position - Lying on left side w/ left leg straight and right knee bent Foot drop - Gait w/ drop of the forefoot Fracture pan - A bedpan used for someone w/ a hip fracture Fecal impaction - Dry, hard stool stuck in the rectum Hand roll - Hand placed in the palm to prevent fractures WNL - Within normal limits BRP - bathroom privileges BUS - Bladder ultrasonic scanner Factors to consider when delegating to UAP - Scope of practice, Facility, state regulations, Level of experience, Pt safety Hazards of immobility on CV system & interventions DVT: elastic stockings, SCD's, Orthostatic BP: give pt time between position changes Hazards of immobility on pulmonary system & interventions PE: TED host, Inadequate expansion of the chest: place pt in orthopneic position Pneumonia: clean/sterile technique, pneumovax Intervention for each: early and frequent ambulation Hazards of immobility on renal system & interventions-UTI, problems with continence, altered BP: monitor I/O's, assist w/ voiding as needed Hazards of immobility on integumentary system & interventions Skin breakdown: repositioning, monitor nutrition status, reduce moisture, and provide hygiene care Hazards of immobility on musculoskeletal system & interventions Stiff joints: ROMs/ambulation Muscle atrophy: ROMs/ambulation Ca2 imbalance: nutrition measures Risk factors for skin breakdown Poor nutrition, bedrest, obesity, using an SPM machine, increased friction and shear 4 areas prone to skin breakdown-Tailbone, Heels, Elbows, Hips Intervention most effective in preventing flaccidity in a hospitalized patient? Early ambulation after surgery After application of sequential compression devices (SCDs) on a patient, what assessment finding is essential for the nurse to include in documentation? Lower extremity circulatory status Components of Morse Fall Scale- History of falls, secondary diagnosis, ambulatory aid, IV/hep lock, gait/transferring, mental status Scores: 45 = high risk 25-44 = moderate risk 0-24 = low risk TB Injection - Max amt: 0.1 cc, site: forearm, Angle: 15-20 degrees, Length: 1/4 - 1/2 in, Aspiration? No SQ injections - Max amt: 2 cc, Usual site: Upper arm, stomach, Angle: 45 degrees, Length: 1/2 - 1 in, Aspiration? Yes IM injections - Max amt: 5 cc Usual site: deltoid (1 cc), gluteus med/max or vastus lateralis (5 cc), Angle: 90 degrees, Length: 1 - 1.5 in, Aspiration? Yes What factors affect a BG result? Having fasted or eaten, time of day, level of activity, stress, illness, menstruation client most at risk for hypoglycemia? In the morning before breakfast Considerations for pt's on blood thinners such as warfarin, asprin, heparin, coumadin, etc? Monitor platelet levels (labs) Watch for bleeding/reduce risks of bleeding Monitor vitals (esp. BP) Assess skin Monitor mobility status benzodiazepines to older adults? No, benzo's increase the risk of accidents and mental deficits FUO - fever of unknown origin qhs - at bedtime ac - before meals Contraindications for opening capsules and mixing with food? EC: enteric coated & ER: extended release Rapid acting insulin Generic & brand names: Inslin aspart (NovoLog), insulin glulisine (Apidra), insulin lispro (Humalog) Onset: 15 min Peak: 30 - 90 min Duration: 3-5 hr Short acting insulin - Insulin regular (Humulin R, Novolin R) Onset: 30 - 60 min Peak: 2 - 4 hr Duration: 5 - 8 hr Intermediate-acting insulin- Insulin NPH (Humulin/Novolin N) Onset: 1 - 3 hr Peak: 8 hr Duration: 12 - 16 hr Long-acting insulin- insulin glargine (lantus), insulin detemir (levemir) Onset: 1 hr Peak: no clear peak Duration: 20 - 26 hr Signs of infiltration -Edema, pallor, decreased skin temperature around the site, and pain Signs of phlebitis - Pain, increased skin temperature, and redness along the vein Signs of extravasation (infiltration w/ dislodged IV catheter) - Pain, stinging or burning at the site, swelling, and redness Nursing interventions for infiltration, phlebitis, and extravasation Infiltration: D/C IV, elevate extremity, apply warm compress Phlebitis: D/C IV, apply warm/moist compress Extravasation: D/C IV, apply cool compress, administer antidote if needed, document degree of extravasation INT -intermittent (catheter) The 6 rights of medication administration 1. Right drug 2. Right dose 3. Right route 4. Right pt 5. Right time 6. Right documentation 3 nursing interventions r/t routine care of peripheral IV 1. Check insertion site frequently 2. Change tubing every 96 hr 3. Use good hand hygiene standard precautions Factors to consider when choosing the best IV location Age, condition of veins, circulation status, length of IV therapy What is the smallest gauge IV catheter used to infuse blood? 20-22: RBS' might get crushed when using a smaller cath. 4 techniques to improve the chances of good IV access 1. Trim hair around the area 2. Gently stroke the area from the distal to proximal end 3. Place a warm blanket over the extremity 4. Palpate gently At what range of rate should you administer maintenance fluids? 75-150 [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 53 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 16, 2021
Number of pages
53
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 16, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
41























.png)






