PEDIATRIC NURSING TEST BANK
Document Content and Description Below
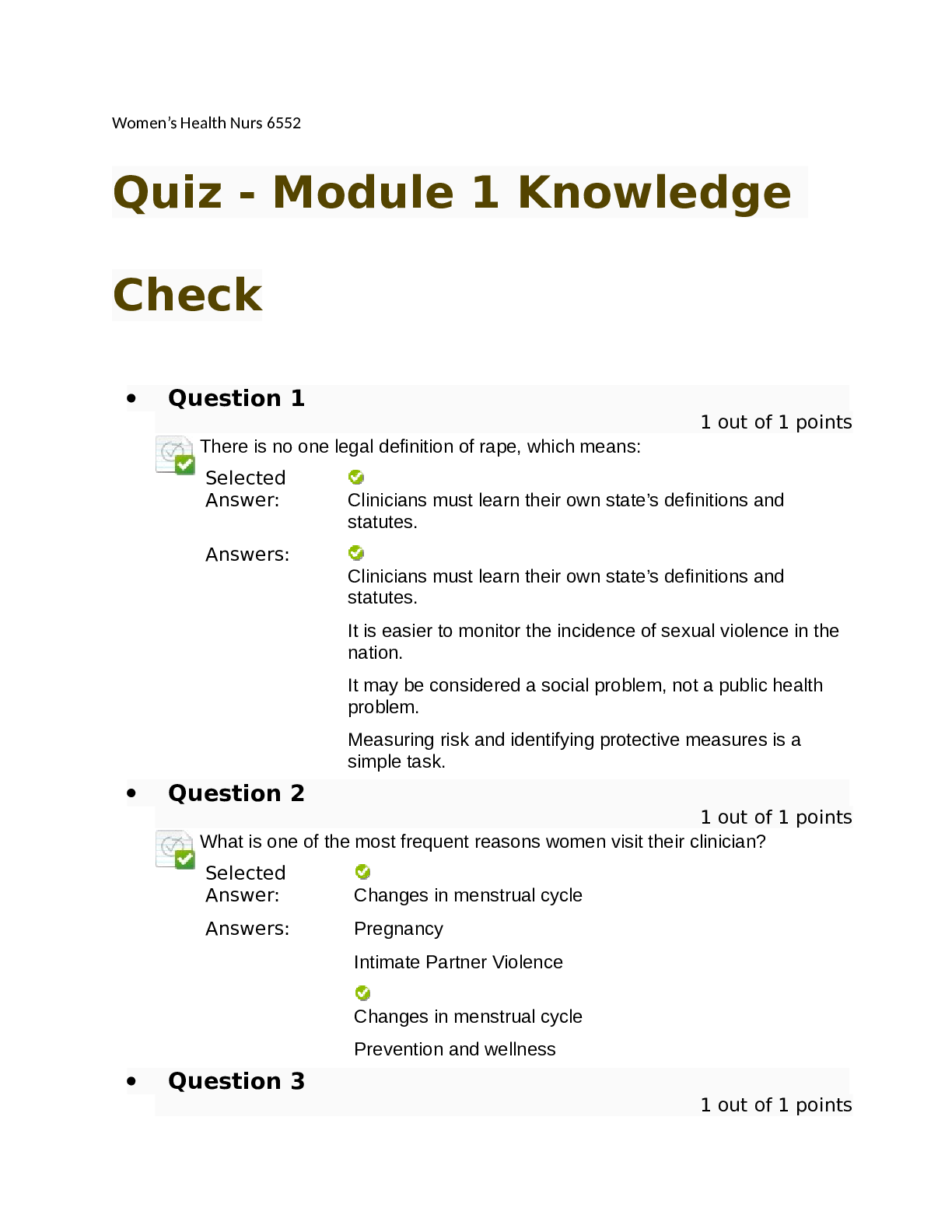
Chapter 1: Bronchiolitis 1. Which intervention is appropriate for the infant hospitalized with bronchiolitis? a. Position on the side with neck slightly flexed. b. Administer antibiotics as ordered... . c. Restrict oral and parenteral fluids if tachypneic. d. Give cool, humidified oxygen. ANS: D Cool, humidified oxygen is given to relieve dyspnea, hypoxemia, and insensible fluid loss from tachypnea. The infant should be positioned with the head and chest elevated at a 30- to 40-degree angle and the neck slightly extended to maintain an open airway and decrease pressure on the diaphragm. The etiology of bronchiolitis is viral. Antibiotics are given only if there is a secondary bacterial infection. Tachypnea increases insensible fluid loss. If the infant is tachypneic, fluids are given parenterally to prevent dehydration. 2. An infant with bronchiolitis is hospitalized. The causative organism is respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). The nurse knows that a child infected with this virus requires what type of isolation? a. Reverse isolation b. Airborne isolation c. Contact Precautions d. Standard Precautions ANS: C RSV is transmitted through droplets. In addition to Standard Precautions and hand washing, Contact Precautions are required. Caregivers must use gloves and gowns when entering the room. Care is taken not to touch their own eyes or mucous membranes with a contaminated gloved hand. Children are placed in a private room or in a room with other children with RSV infections. Reverse isolation focuses on keeping bacteria away from the infant. With RSV, other children need to be protected from exposure to the virus. The virus is not airborne. 3. A child has a chronic cough and diffuse wheezing during the expiratory phase of respiration. This suggests what condition? a. Asthma b. Pneumonia c. Bronchiolitis d. Foreign body in trachea ANS: A Asthma may have these chronic signs and symptoms. Pneumonia appears with an acute onset, fever, and general malaise. Bronchiolitis is an acute condition caused by respiratory syncytial virus. Foreign body in the trachea occurs with acute respiratory distress or failure and maybe stridor. 4. Which nursing diagnosis is most appropriate for an infant with acute bronchiolitis due to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)? a. Activity Intolerance b. Decreased Cardiac Output c. Pain, Acute d. Tissue Perfusion, Ineffective (peripheral) ANS. A Rationale 1: Activity intolerance is a problem because of the imbalance between oxygen supply and demand. Cardiac output is not compromised during an acute phase of bronchiolitis. Pain is not usually associated with acute bronchiolitis. Tissue perfusion (peripheral) is not affected by this respiratory-disease process. Rationale 2: Activity intolerance is a problem because of the imbalance between oxygen supply and demand. Cardiac output is not compromised during an acute phase of bronchiolitis. Pain is not usually associated with acute bronchiolitis. Tissue perfusion (peripheral) is not affected by this respiratory-disease process. Rationale 3: Activity intolerance is a problem because of the imbalance between oxygen supply and demand. Cardiac output is not compromised during an acute phase of bronchiolitis. Pain is not usually associated with acute bronchiolitis. Tissue perfusion (peripheral) is not affected by this respiratory-disease process. Rationale 4: Activity intolerance is a problem because of the imbalance between oxygen supply and demand. Cardiac output is not compromised during an acute phase of bronchiolitis. Pain is not usually associated with acute bronchiolitis. Tissue perfusion (peripheral) is not affected by this respiratory-disease process. Global Rationale: Activity intolerance is a problem because of the imbalance between oxygen supply and demand. Cardiac output is not compromised during an acute phase of bronchiolitis. Pain is not usually associated with acute bronchiolitis. Tissue perfusion (peripheral) is not affected by this respiratory-disease process. Chapter 2: Asthma 1. The nurse is caring for a child hospitalized for status asthmaticus. Which assessment finding suggests that the child’s condition is worsening? a. Hypoventilation b. Thirst c. Bradycardia d. Clubbing ANS: A The nurse would assess the child for signs of hypoxia, including restlessness, fatigue, irritability, and increased heart and respiratory rate. As the child tires from the increased work of breathing hypoventilation occurs leading to increased carbon dioxide levels. The nurse would be alert for signs of hypoxia. Thirst would reflect the childs hydration status. Bradycardia is not a sign of hypoxia; tachycardia is. Clubbing develops over a period of months in response to hypoxia. The presence of clubbing does not indicate the childs condition is worsening. 2. Which finding is expected when assessing a child hospitalized for asthma? a. Inspiratory stridor b. Harsh, barky cough c. Wheezing d. Rhinorrhea ANS: C Wheezing is a classic manifestation of asthma. Inspiratory stridor is a clinical manifestation of croup. A harsh, barky cough is characteristic of croup. Rhinorrhea is not associated with asthma. 3. A child has had cold symptoms for more than 2 weeks, a headache, nasal congestion with purulent nasal drainage, facial tenderness, and a cough that increases during sleep. The nurse recognizes these symptoms are characteristic of which respiratory condition? a. Allergic rhinitis b. Bronchitis c. Asthma d. Sinusitis ANS: D Sinusitis is characterized by signs and symptoms of a cold that do not improve after 14 days, a low-grade fever, nasal congestion and purulent nasal discharge, headache, tenderness, a feeling of fullness over the affected sinuses, halitosis, and a cough that increases when the child is lying down. The classic symptoms of allergic rhinitis are watery rhinorrhea, itchy nose, eyes, ears, and palate, and sneezing. Symptoms occur as long as the child is exposed to the allergen. Bronchitis is characterized by a gradual onset of rhinitis and a cough that is initially nonproductive but may change to a loose cough. The manifestations of asthma may vary, with wheezing being a classic sign. The symptoms presented in the question do not suggest asthma. 4. What is a common trigger for asthma attacks in children? a. Febrile episodes b. Dehydration c. Exercise d. Seizures ANS: C Exercise is one of the most common triggers for asthma attacks, particularly in school-age children. Febrile episodes are consistent with other problems, for example, seizures. Dehydration occurs as a result of diarrhea; it does not trigger asthma attacks. Viral infections are triggers for asthma. Seizures can result from a too-rapid intravenous infusion of theophyllinea therapy for asthma. 5.The practitioner changes the medications for the child with asthma to salmeterol (Serevent). The mother asks the nurse what this drug will do. The nurse explains that salmeterol (Serevent) is used to treat asthma because the drug produces which characteristic? 1. Decreases inflammation 2. Decreases mucous production 3. Controls allergic rhinitis 4. Dilates the bronchioles Correct Answer: 4 Rationale 1: Salmeterol (Serevent) is a long-acting beta2-agonist that acts by bronchodilating. Steroids are anti-inflammatory, anticholinergics decrease mucous production, and antihistamines control allergic rhinitis. Rationale 2: Salmeterol (Serevent) is a long-acting beta2-agonist that acts by bronchodilating. Steroids are anti-inflammatory, anticholinergics decrease mucous production, and antihistamines control allergic rhinitis. Rationale 3: Salmeterol (Serevent) is a long-acting beta2-agonist that acts by bronchodilating. Steroids are anti-inflammatory, anticholinergics decrease mucous production, and antihistamines control allergic rhinitis. Rationale 4: Salmeterol (Serevent) is a long-acting beta2-agonist that acts by bronchodilating. Steroids are anti-inflammatory, anticholinergics decrease mucous production, and antihistamines control allergic rhinitis. Global Rationale: Salmeterol (Serevent) is a long-acting beta2-agonist that acts by bronchodilating. Steroids are anti-inflammatory, anticholinergics decrease mucous production, and antihistamines control allergic rhinitis. Cognitive Level: Analyzing Client Need: Physiological Integrity Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation Learning Outcome: LO 20.6 Create a nursing care plan for a child with a common acute respiratory condition. 6.Following parental teaching, the nurse is evaluating the parents understanding of environmental control for their childs asthma management. Which statement by the parents indicates appropriate understanding of the teaching? 1. We will replace the carpet in our childs bedroom with tile. 2. Were glad the dog can continue to sleep in our childs room. 3. Well be sure to use the fireplace often to keep the house warm in the winter. 4. Well keep the plants in our childs room dusted. Correct Answer: 1 Rationale 1: Control of dust in the childs bedroom is an important aspect of environmental control for asthma management. When possible, pets and plants should not be kept in the home. Smoke from fireplaces should be eliminated. Rationale 2: Control of dust in the childs bedroom is an important aspect of environmental control for asthma management. When possible, pets and plants should not be kept in the home. Smoke from fireplaces should be eliminated. Rationale 3: Control of dust in the childs bedroom is an important aspect of environmental control for asthma management. When possible, pets and plants should not be kept in the home. Smoke from fireplaces should be eliminated. Rationale 4: Control of dust in the childs bedroom is an important aspect of environmental control for asthma management. When possible, pets and plants should not be kept in the home. Smoke from fireplaces should be eliminated. Global Rationale: Control of dust in the childs bedroom is an important aspect of environmental control for asthma management. When possible, pets and plants should not be kept in the home. Smoke from fireplaces should be eliminated. 7.A child with asthma will be receiving an oral dose of prednisone. The order reads prednisone 2 mg/kg per day. The child weighs 50 lbs. The child will receive milligrams daily. (Round the answer.) Standard Text: Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Correct Answer: 45.5 = 46 Rationale: 22.7 2 = 45.5 (46) Global Rationale: 22.7 2 = 45.5 (46) Cognitive Level: Analyzing Client Need: Physiological Integrity Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation Learning Outcome: LO 07. Plan the nursing care for the child with a chronic respiratory condition. 8.Parents of a child admitted with respiratory distress are concerned because the child wont lie down and wants to sit in a chair leaning forward. Which response by the nurse is the most appropriate? 1. This helps the child feel in control of his situation. 2. The child needs to be encouraged to lie flat in bed. 3. This position helps keep the airway open. 4. This confirms the child has asthma. Correct Answer: 3 Rationale 1: Leaning forward helps keep the airway open. The child is not in control just because he is leaning forward. Lying flat in bed will increase the respiratory distress. This position does not confirm asthma. Rationale 2: Leaning forward helps keep the airway open. The child is not in control just because he is leaning forward. Lying flat in bed will increase the respiratory distress. This position does not confirm asthma. Rationale 3: Leaning forward helps keep the airway open. The child is not in control just because he is leaning forward. Lying flat in bed will increase the respiratory distress. This position does not confirm asthma. Rationale 4: Leaning forward helps keep the airway open. The child is not in control just because he is leaning forward. Lying flat in bed will increase the respiratory distress. This position does not confirm asthma. Global Rationale: Leaning forward helps keep the airway open. The child is not in control just because he is leaning forward. Lying flat in bed will increase the respiratory distress. This position does not confirm asthma. 9.A school nurse is planning care for a school-age child recently diagnosed with asthma. Which items will the school nurse include in the plan of care at the school? Standard Text: Select all that apply. 1. Maintain a log of quick-relief medication administration. 2. Call the parents if quick-relief medications work appropriately. 3. Assess for symptoms of exercise-induced bronchospasm. 4. Coordinate education of the childs teachers. 5. Conduct a support group for all children with asthma. Correct Answer: 1,3,4,5 Rationale 1: Appropriate interventions for the school nurse to include in the plan of care include: keeping a log of the quick-relief medications administered; assessing the child for exercise-induced bronchospasms and reporting, if needed; coordinating education of the childs teachers; and conducting a support group for all children in the school with asthma. The nurse would only call the parents if the quick-relief mediation was not effective in treating the childs symptoms. Rationale 2: Appropriate interventions for the school nurse to include in the plan of care include: keeping a log of the quick-relief medications administered; assessing the child for exercise-induced bronchospasms and reporting, if needed; coordinating education of the childs teachers; and conducting a support group for all children in the school with asthma. The nurse would only call the parents if the quick-relief mediation was not effective in treating the childs symptoms. Rationale 3: Appropriate interventions for the school nurse to include in the plan of care include: keeping a log of the quick-relief medications administered; assessing the child for exercise-induced bronchospasms and reporting, if needed; coordinating education of the childs teachers; and conducting a support group for all children in the school with asthma. The nurse would only call the parents if the quick-relief mediation was not effective in treating the childs symptoms. Rationale 4: Appropriate interventions for the school nurse to include in the plan of care include: keeping a log of the quick-relief medications administered; assessing the child for exercise-induced bronchospasms and reporting, if needed; coordinating education of the childs teachers; and conducting a support group for all children in the school with asthma. The nurse would only call the parents if the quick-relief mediation was not effective in treating the childs symptoms. Rationale 5: Appropriate interventions for the school nurse to include in the plan of care include: keeping a log of the quick-relief medications administered; assessing the child for exercise-induced bronchospasms and reporting, if needed; coordinating education of the childs teachers; and conducting a support group for all children in the school with asthma. The nurse would only call the parents if the quick-relief mediation was not effective in treating the childs symptoms. Global Rationale: Appropriate interventions for the school nurse to include in the plan of care include: keeping a log of the quick-relief medications administered; assessing the child for exercise-induced bronchospasms and reporting, if needed; coordinating education of the childs teachers; and conducting a support group for all children in the school with asthma. The nurse would only call the parents if the quick-relief mediation was not effective in treating the childs symptoms. Chapter 3: Ulnar Fracture 1. Which is an accurate statement concerning a childs musculoskeletal system and how it may be different from adults? a. Growth occurs in children as a result of an increase in the number of muscle fibers. b. Infants are at greater risk for fractures because their epiphyseal plates are not fused. Because soft tissues are resilient in children, dislocations and sprains are less common than in c. adults. d. Their bones have less blood flow. ANS: C Because soft tissues are resilient in children, dislocations and sprains are less common than in adults. A childs growth occurs because of an increase in size rather than an increase in the number of the muscle fibers. Fractures in children younger than 1 year are unusual because a large amount of force is necessary to fracture their bones. A childs bones have greater blood flow than an adults bones. 2. When infants are seen for fractures, which nursing intervention is a priority? a. No intervention is necessary. It is not uncommon for infants to fracture bones. b. Assess the familys safety practices. Fractures in infants usually result from falls. c. Assess for child abuse. Fractures in infants are often nonaccidental. d. Assess for genetic factors. ANS: C Fractures in infants warrant further investigation to rule out child abuse. Fractures in children younger than 1 year are not common because of the cartilaginous quality of the skeleton; a large amount of force is necessary to fracture their bones. Infants should be cared for in a safe environment and should not be falling. Fractures in infancy are usually nonaccidental rather than related to a genetic factor. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 248 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 04, 2023
Number of pages
248
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 04, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
42