*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NUR 3028 Adult Health Exit HESI-study (100% Verified) Questions and Answers with Rationales. (All)
NUR 3028 Adult Health Exit HESI-study (100% Verified) Questions and Answers with Rationales.
Document Content and Description Below
NUR 3028ENDOCRINE DISORDERS 1. Nurse Ronn is assessing a client with a. Hypotension. 1. Answer C. Because of changes in fat distribution, possible Cushing’s syndrome. In a client wi... t b. Thick, coarse skin. Cushing’s syndrome, the nurse would expectc. Deposits of adipose tissue in the trunk and adipose tissue accumulates in the trunk, face (moonface), and dorsocervical areas (buffalo hump). to find: d. 2. A male client with primary diabetes a. insipidus is ready for discharge on desmopressin (DDAVP). Which instruction should nurse Lina provide? b. 3. Nurse Wayne is aware that a positive a. Chvostek’s sign indicate? a. b. Hypocalcemia b. Hyponatremia d. Hypokalemia d. Hypermagnesemia dorsocervical area. Weight gain in arms and legs. “Administer desmopressin while the suspension is cold.” “Your condition isn’t chronic, so you won’t need to wear a medical identification bracelet.” c. “You may not be able to use desmopressin nasally if you have nasal discharge or blockage.” d. “You won’t need to monitor your fluid intake and output after you start taking desmopressin.” Hypocalcemia Hyponatremia Hypokalemia Hypermagnesemia Hypertension is caused by fluid retention. Skin becomes thin and bruises easily because of a loss of collagen. Muscle wasting causes muscle atrophy and thin extremities. 2. Answer C. Desmopressin may not be absorbed if the intranasal route is compromised. Although diabetes insipidus is treatable, the client should wear medical identification and carry medication at all times to alert medical personnel in an emergency and ensure proper treatment. The client must continue to monitor fluid intake and output and receive adequate fluid replacement. 3. Answer A. Chvostek’s sign is elicited by tapping the client’s face lightly over the facial nerve, just below the temple. If the client’s facial muscles twitch, it indicates hypocalcemia. Hyponatremia is indicated by weight loss, abdominal cramping, muscle weakness, headache, and postural hypotension. Hypokalemia causes paralytic ileus and muscle weakness. Clients with hypermagnesemia exhibit a loss of deep tendon reflexes, coma, or cardiac arrest. a. b. d. mineralization increases. Amenorrhea develops in Cushing’s syndrome. With successful treatment, the client experiences a return of menstrual flow, not a decline in it. 5. A male client has recently undergone a. It decreases cyclic adenosine monophosphate surgical removal of a pituitary tumor. Dr. (cAMP) production and affects the metabolic Wong prescribes corticotropin (Acthar), 20 rate of target organs. units I.M. q.i.d. as a replacement therapy. b. It interacts with plasma membrane receptors to What is the mechanism of action of inhibit enzymatic actions. corticotropin? c. It interacts with plasma membrane receptors to produce enzymatic actions that affect protein, fat, and carbohydrate metabolism. d. It regulates the threshold for water resorption in 5. Answer C. Corticotropin interacts with plasma membrane receptors to produce enzymatic actions that affect protein, fat, and carbohydrate metabolism. It doesn’t decrease cAMP production. The posterior pituitary hormone, antidiuretic hormone, regulates the threshold for water resorption in the kidneys. the kidneys. 6. Capillary glucose monitoring is being a. Onset to be at 2 p.m. and its peak to be at 3 p.m. performed every 4 hours for a female client b. Onset to be at 2:15 p.m. and its peak to be at 3 diagnosed with diabetic ketoacidosis. Insulin p.m. is administered using a scale of regular insulic. Onset to be at 2:30 p.m. and its peak to be at 4 according to glucose results. At 2 p.m., the p.m. client has a capillary glucose level of 250 d. Onset to be at 4 p.m. and its peak to be at 6 p.m. 6. Answer C. Regular insulin, which is a shortacting insulin, has an onset of 15 to 30 minutes and a peak of 2 to 4 hours. Because the nurse gave the insulin at 2 p.m., the expected onset would be from 2:15 p.m. to 2:30 p.m. and the peak from 4 p.m. to 6 p.m. mg/dl for which he receives 8 U of regular insulin. Nurse Vince should expect the dose’s: 7. A female client with Cushing’s syndroma. Depression is admitted to the medical-surgical unit. b. Neuropathy During the admission assessment, nurse Tyzz Hypoglycemia notes that the client is agitated and irritable, d. Hyperthyroidism 7. Answer A. Agitation, irritability, poor memory, loss of appetite, and neglect of one’s appearance may signal depression, which is common in clients with Cushing’s syndrome. Neuropathy affects clients with diabetes mellitus — not Cushing’s syndrome. Although hypoglycemia can cause irritability, it also produces increased appetite, rather than loss of appetite. Hyperthyroidism typically causes such signs as goiter, nervousness, heat intolerance, and weight loss despite increased appetite. has poor memory, reports loss of appetite, and appears disheveled. These findings are consistent with which problem? 8. Nurse Ruth is assessing a client after a a. Tetany thyroidectomy. The assessment reveals b. Hemorrhage 8. Answer A. Tetany may result if the parathyroid glands are excised or damaged during thyroid muscle twitching and tingling, along with Thyroid storm numbness in the fingers, toes, and mouth ared. Laryngeal nerve damage surgery. Hemorrhage is a potential complication after thyroid surgery but is characterized by tachycardia, hypotension, frequent swallowing, feelings of fullness at the incision site, choking, and bleeding. Thyroid storm is another term for severe hyperthyroidism — not a complication of thyroidectomy. Laryngeal nerve damage may occur postoperatively, but its signs include a hoarse voice and, possibly, acute airway obstruction. The nurse should suspect which complication? 9. After undergoing a subtotal a. Primary hypothyroidism thyroidectomy, a female client develops b. Graves’ disease hypothyroidism. Dr. Smith prescribes Thyrotoxicosis levothyroxine (Levothroid), 25 mcg P.O. daid. Euthyroidism 9. Answer A. Levothyroxine is the preferred agent to treat primary hypothyroidism and cretinism, although it also may be used to treat secondary hypothyroidism. It is contraindicated in Graves’ disease and thyrotoxicosis because these conditions are forms of hyperthyroidism. Euthyroidism, a term used to describe normal thyroid function, wouldn’t require any thyroid preparation. For which condition is levothyroxine the preferred agent? 10. Which of these signs suggests that a a. Tetanic contractions male client with the syndrome of b. Neck vein distention inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) Weight loss secretion is experiencing complications? d. Polyuria 10. Answer B. SIADH secretion causes antidiuretic hormone overproduction, which leads to fluid retention. Severe SIADH can cause such complications as vascular fluid overload, signaled by neck vein distention. This syndrome isn’t associated with tetanic contractions. It may cause weight gain and fluid retention (secondary to oliguria). 11. A female client with a history of a. phentolamine (Regitine). pheochromocytoma is admitted to the hospitb. methyldopa (Aldomet). in an acute hypertensive crisis. To reverse mannitol (Osmitrol). hypertensive crisis caused by d. felodipine (Plendil). 11. Answer A. Pheochromocytoma causes excessive production of epinephrine and norepinephrine, natural catecholamines that raise the blood pressure. Phentolamine, an alpha-adrenergic blocking agent given by I.V. bolus or drip, antagonizes the body’s response to circulating epinephrine and norepinephrine, reducing blood pressure quickly and effectively. Although methyldopa is an antihypertensive agent available in parenteral form, it isn’t effective in treating hypertensive emergencies. Mannitol, a diuretic, isn’t used to treat hypertensive emergencies. Felodipine, pheochromocytoma, nurse Lyka expects to administer: an antihypertensive agent, is available only in extended-release tablets and therefore doesn’t reduce blood pressure quickly enough to correct hypertensive crisis. 12. A male client with a history of a. Adrenal cortex hypertension is diagnosed with primary b. Pancreas hyperaldosteronism. This diagnosis indicates Adrenal medulla that the client’s hypertension is caused by d. Parathyroid 12. Answer A. Excessive secretion of aldosterone in the adrenal cortex is responsible for the client’s hypertension. This hormone acts on the renal tubule, where it promotes reabsorption of sodium and excretion of potassium and hydrogen ions. The pancreas mainly secretes hormones involved in fuel metabolism. The adrenal medulla secretes the catecholamines — epinephrine and norepinephrine. The parathyroids secrete parathyroid hormone. excessive hormone secretion from which of the following glands? 13. Nurse Troy is aware that the most a. Risk for infection appropriate for a client with Addison’s b. Excessive fluid volume disease? Urinary retention d. Hypothermia 13. Answer A. Addison’s disease decreases the production of all adrenal hormones, compromising the body’s normal stress response and increasing the risk of infection. Other appropriate nursing diagnoses for a client with Addison’s disease include Deficient fluid volume and Hyperthermia. Urinary retention isn’t appropriate because Addison’s disease causes polyuria. 14. Acarbose (Precose), an alphaglucosidasa. “If I have hypoglycemia, I should eat some inhibitor, is prescribed for a female client with sugar, not dextrose.” type 2 diabetes mellitus. During discharge b. “The drug makes my pancreas release more planning, nurse Pauleen would be aware of the insulin.” client’s need for additional teaching when the client states: c. “I should never take insulin while I’m taking this drug.” d. “It’s best if I take the drug with the first bite of a 14. Answer A. Acarbose delays glucose absorption, so the client should take an oral form of dextrose rather than a product containing table sugar when treating hypoglycemia. The alpha-glucosidase inhibitors work by delaying the carbohydrate digestion and glucose absorption. It’s safe to be on a regimen that includes insulin and an alphaglucosidase inhibitor. The client should take the drug at the start of a meal, not 30 minutes to an hour before. meal.” 15. A female client whose physical finding a. “You must lie flat for 24 hours after surgery.” suggest a hyperpituitary condition undergoesb. “You must avoid coughing, sneezing, and an extensive diagnostic workup. Test results blowing your nose.” reveal a pituitary tumor, which necessitates a transphenoidal hypophysectomy. The evenin c. “You must restrict your fluid intake.” 15. Answer B. After a transsphenoidal hypophysectomy, the client must refrain from coughing, sneezing, and blowing the nose for several days to avoid disturbing the surgical graft used to close the wound. The head of the bed must be before the surgery, nurse Jacob reviews preoperative and postoperative instructions given to the client earlier. Which postoperative instruction should the nurse emphasize? d. “You must report ringing in your ears immediately.” elevated, not kept flat, to prevent tension or pressure on the suture line. Within 24 hours after a hypophysectomy, transient diabetes insipidus commonly occurs; this calls for increased, not restricted, fluid intake. Visual, not auditory, changes are a potential complication of hypophysectomy. 16. Dr. Kennedy prescribes glipizide a. “Be sure to take glipizide 30 minutes before (Glucotrol), an oral antidiabetic agent, for a meals.” male client with type 2 diabetes mellitus who has been having trouble controlling the bl b. “Glipizide may cause a low serum sodium level, ood so make sure you have your sodium level glucose level through diet and exercise. checked monthly.” Which medication instruction should the nurse provide? c. “You won’t need to check your blood glucose 16. Answer A. The client should take glipizide twice a day, 30 minutes before a meal, because food decreases its absorption. The drug doesn’t cause hyponatremia and therefore doesn’t necessitate monthly serum sodium measurement. The client must continue to monitor the blood glucose level during glipizide therapy. level after you start taking glipizide.” d. “Take glipizide after a meal to prevent heartburn.” 17. For a diabetic male client with a foot a. They contain exudate and provide a moist ulcer, the physician orders bed rest, a wet- wound environment. todry dressing change every shift, and blood b. They protect the wound from mechanical trauma glucose monitoring before meals and bedtime. and promote healing. Why are wet-to-dry dressings used for this c. They debride the wound and promote healing by client? secondary intention. d. They prevent the entrance of microorganisms 17. Answer C. For this client, wet-to-dry dressings are most appropriate because they clean the foot ulcer by debriding exudate and necrotic tissue, thus promoting healing by secondary intention. Moist, transparent dressings contain exudate and provide a moist wound environment. Hydrocolloid dressings prevent the entrance of microorganisms and minimize wound discomfort. Dry sterile dressings protect the wound from mechanical trauma and promote healing. and minimize wound discomfort. 18. When instructing the female client a. Restricting fluids diagnosed with hyperparathyroidism about b. Restricting sodium diet, nurse Gina should stress the importance Forcing fluids of which of the following? d. Restricting potassium 18. Answer C. The client should be encouraged to force fluids to prevent renal calculi formation. Sodium should be encouraged to replace losses in urine. Restricting potassium isn’t necessary in hyperparathyroidism. 19. Which nursing diagnosis takes highest a. Risk for imbalanced nutrition: More than body priority for a female client with requirements related to thyroid hormone excess hyperthyroidism? b. Risk for impaired skin integrity related to 19. Answer D. In the client with hyperthyroidism, excessive thyroid hormone production leads to hypermetabolism and increased nutrient metabolism. These conditions may result in a negative nitrogen balance, increased protein synthesis and breakdown, decreased glucose tolerance, and fat mobilization edema, skin fragility, and poor wound healing c. Body image disturbance related to weight gain and edema d. Imbalanced nutrition: Less than body requirements related to thyroid hormone excess and depletion. This puts the client at risk for marked nutrient and calorie deficiency, making Imbalanced nutrition: Less than body requirements the most important nursing diagnosis. Options B and C may be appropriate for a client with hypothyroidism, which slows the metabolic rate. 20. A male client with a tentative diagnosi a. Serum potassium level of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic b. Serum sodium level syndrome (HHNS) has a history of type 2 Arterial blood gas (ABG) values diabetes that is being controlled with an orald. Serum osmolarity 20. Answer D. Serum osmolarity is the most important test for confirming HHNS; it’s also used to guide treatment strategies and determine evaluation criteria. A client with HHNS typically has a serum osmolarity of more than 350 mOsm/L. Serum potassium, serum sodium, and ABG values are also measured, but they aren’t as important as serum osmolarity for confirming a diagnosis of HHNS. A client with HHNS typically has hypernatremia and osmotic diuresis. ABG values reveal acidosis, and the potassium level is variable. diabetic agent, tolazamide (Tolinase). Which of the following is the most important laboratory test for confirming this disorder? 21. A male client has just been diagnosed a. “You’ll need more insulin when you exercise or with type 1 diabetes mellitus. When teaching increase your food intake.” the client and family how diet and exercise b. “You’ll need less insulin when you exercise or affect insulin requirements, Nurse Joy should reduce your food intake.” include which guideline? c. “You’ll need less insulin when you increase your food intake.” d. “You’ll need more insulin when you exercise or 21. Answer B. Exercise, reduced food intake, hypothyroidism, and certain medications decrease the insulin requirements. Growth, pregnancy, greater food intake, stress, surgery, infection, illness, increased insulin antibodies, and certain medications increase the insulin requirements. decrease your food intake.” 22. Nurse Noemi administers glucagon to a. Oral anticoagulants her diabetic client, then monitors the client fb. Anabolic steroids adverse drug reactions and interactions. Whic Beta-adrenergic blockers type of drug interacts adversely with d. Thiazide diuretics 22. Answer A. As a normal body protein, glucagon only interacts adversely with oral anticoagulants, increasing the anticoagulant effects. It doesn’t interact adversely with anabolic steroids, betaadrenergic blockers, or thiazide diuretics. glucagon? 23. Which instruction about insulin administration should nurse Kate give to a client? a. “Always follow the same order when drawing the different insulins into the syringe.” b. “Shake the vials before withdrawing the insulin.” c. “Store unopened vials of insulin in the 23. Answer A. The client should be instructed always to follow the same order when drawing the different insulins into the syringe. Insulin should never be shaken because the resulting froth prevents withdrawal of an accurate dose and may damage the freezer at temperatures well below freezing.” d. “Discard the intermediate-acting insulin if it appears cloudy.” insulin protein molecules. Insulin also should never be frozen because the insulin protein molecules may be damaged. Intermediate-acting insulin is normally cloudy. 24. Nurse Perry is caring for a female cliena. I.M. or subcutaneous glucagon. with type 1 diabetes mellitus who exhibits b. I.V. bolus of dextrose 50%. confusion, light-headedness, and aberrant c. 15 to 20 g of a fast-acting carbohydrate such as behavior. The client is still conscious. The orange juice. nurse should first administer: d. 10 U of fast-acting insulin. 24. Answer C. This client is having a hypoglycemic episode. Because the client is conscious, the nurse should first administer a fastacting carbohydrate, such as orange juice, hard candy, or honey. If the client has lost consciousness, the nurse should administer either I.M. or subcutaneous glucagon or an I.V. bolus of dextrose 50%. The nurse shouldn’t administer insulin to a client who’s hypoglycemic; this action will further compromise the client’s condition. 25. For the first 72 hours after a. Hypocalcemia thyroidectomy surgery, nurse Jamie would b. Hypercalcemia assess the female client for Chvostek’s sign Hypokalemia and Trousseau’s sign because they indicate d. Hyperkalemia 25. Answer A. The client who has undergone a thyroidectomy is at risk for developing hypocalcemia from inadvertent removal or damage to the parathyroid gland. The client with hypocalcemia will exhibit a positive Chvostek’s sign (facial muscle contraction when the facial nerve in front of the ear is tapped) and a positive Trousseau’s sign (carpal spasm when a blood pressure cuff is inflated for a few minutes). These signs aren’t present with hypercalcemia, hypokalemia, or hyperkalemia. which of the following? 1. An agitated, confused female client a. 2 to 5 g of a simple carbohydrate. arrives in the emergency department. Her b. 10 to 15 g of a simple carbohydrate. history includes type 1 diabetes mellitus, 18 to 20 g of a simple carbohydrate. hypertension, and angina pectoris. Assessmed. 25 to 30 g of a simple carbohydrate. 1. Answer B. To reverse hypoglycemia, the American Diabetes Association recommends ingesting 10 to 15 g of a simple carbohydrate, such as three to five pieces of hard candy, two to three packets of sugar (4 to 6 tsp), or 4 oz of fruit juice. If necessary, this treatment can be repeated in 15 minutes. Ingesting only 2 to 5 g of a simple carbohydrate may not raise the blood glucose level sufficiently. Ingesting more than 15 g may raise it above normal, causing hyperglycemia. reveals pallor, diaphoresis, headache, and intense hunger. A stat blood glucose sample measures 42 mg/dl, and the client is treated for an acute hypoglycemic reaction. After recovery, nurse Lily teaches the client to treat hypoglycemia by ingesting: 2. A female adult client with a history of a. Related to bone demineralization resulting in chronic hyperparathyroidism admits to being pathologic fractures noncompliant. Based on initial assessment b. Related to exhaustion secondary to an findings, nurse Julia formulates the nursing accelerated metabolic rate diagnosis of Risk for injury. To complete the c. Related to edema and dry skin secondary to nursing diagnosis statement for this client, fluid infiltration into the interstitial spaces which “related-to” phrase should the nurse d. Related to tetany secondary to a decreased 2. Answer A. Poorly controlled hyperparathyroidism may cause an elevated serum calcium level. This, in turn, may diminish calcium stores in the bone, causing bone demineralization and setting the stage for pathologic fractures and a risk for injury. Hyperparathyroidism doesn’t accelerate the metabolic rate. A decreased thyroid hormone level, not an increased parathyroid hormone level, may cause edema and dry skin secondary to fluid infiltration into the interstitial spaces. Hyperparathyroidism causes hypercalcemia, not hypocalcemia; therefore, it isn’t associated with tetany. add? serum calcium level 3. Nurse John is assigned to care for a a. Encourage the client to ask questions about postoperative male client who has diabetes personal sexuality. mellitus. During the assessment interview, thb. Provide time for privacy. client reports that he’s impotent and says he’ c. Provide support for the spouse or significant concerned about its effect on his marriage. In other. planning this client’s care, the most d. Suggest referral to a sex counselor or other 3. Answer D. The nurse should refer this client to a sex counselor or other professional. Making appropriate referrals is a valid part of planning the client’s care. The nurse doesn’t normally provide sex counseling. appropriate intervention would be to: appropriate professional. 4. During a class on exercise for diabetic a. At least once a week clients, a female client asks the nurse educatb. At least three times a week how often to exercise. The nurse educator At least five times a week advises the clients to exercise how often to d. Every day 4. Answer B. Diabetic clients must exercise at least three times a week to meet the goals of planned exercise — lowering the blood glucose level, reducing or maintaining the proper weight, increasing the serum high-density lipoprotein level, decreasing serum triglyceride levels, reducing blood pressure, and minimizing stress. Exercising once a week wouldn’t achieve these goals. Exercising more than three times a week, although beneficial, would exceed the minimum requirement. meet the goals of planned exercise? 5. Nurse Oliver should expect a client wit a. Increased appetite and weight loss hypothyroidism to report which health b. Puffiness of the face and hands concerns? Nervousness and tremors d. Thyroid gland swelling 5. Answer B. Hypothyroidism (myxedema) causes facial puffiness, extremity edema, and weight gain. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism (Graves’ disease) include an increased appetite, weight loss, nervousness, tremors, and thyroid gland enlargement (goiter). 6. A female client with hypothyroidism a. Dysuria (myxedema) is receiving levothyroxine b. Leg cramps (Synthroid), 25 mcg P.O. daily. Which finding Tachycardia should nurse Hans recognize as an adverse d. Blurred vision 6. Answer C. Levothyroxine, a synthetic thyroid hormone, is given to a client with hypothyroidism to simulate the effects of thyroxine. Adverse effects of this agent include tachycardia. The other options aren’t associated with levothyroxine. drug effect? 7. A 67-year-old male client has been a. Diabetes mellitus complaining of sleeping more, increased b. Diabetes insipidus urination, anorexia, weakness, irritability, Hypoparathyroidism depression, and bone pain that interferes witd. Hyperparathyroidism 7. Answer D. Hyperparathyroidism is most common in older women and is characterized by bone pain and weakness from excess parathyroid hormone (PTH). Clients also exhibit hypercaliuriacausing polyuria. While clients with diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus also have polyuria, they don’t have bone pain and increased sleeping. Hypoparathyroidism is characterized by urinary frequency rather than polyuria. her going outdoors. Based on these assessment findings, nurse Richard would suspect which of the following disorders? 8. When caring for a male client with a. vasopressin (Pitressin Synthetic). diabetes insipidus, nurse Juliet expects to b. furosemide (Lasix). administer: regular insulin. d. 10% dextrose. 8. Answer A. Because diabetes insipidus results from decreased antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) production, the nurse should expect to administer synthetic vasopressin for hormone replacement therapy. Furosemide, a diuretic, is contraindicated because a client with diabetes insipidus experiences polyuria. Insulin and dextrose are used to treat diabetes mellitus and its complications, not diabetes insipidus. 9. The nurse is aware that the following is a. Excessive sodium intake the most common cause of b. A pituitary adenoma hyperaldosteronism? Deficient potassium intake d. An adrenal adenoma 9. Answer D. An autonomous aldosteroneproducing adenoma is the most common cause of hyperaldosteronism. Hyperplasia is the second most frequent cause. Aldosterone secretion is independent of sodium and potassium intake as well as of pituitary stimulation. 10. A male client with type 1 diabetes a. “The test needs to be repeated following a mellitus has a highly elevated glycosylated 12-hour fast.” hemoglobin (Hb) test result. In discussing th b. “It looks like you aren’t following the result with the client, nurse Sharmaine would prescribed diabetic diet.” be most accurate in stating: c. “It tells us about your sugar control for the 10. Answer C. The glycosylated Hb test provides an objective measure of glycemic control over a 3month period. The test helps identify trends or practices that impair glycemic control, and it doesn’t require a fasting period before blood is drawn. The last 3 months.” d. “Your insulin regimen needs to be altered significantly.” nurse can’t conclude that the result occurs from poor dietary management or inadequate insulin coverage. 11. Following a unilateral adrenalectomy, a. Muscle weakness nurse Betty would assess for hyperkalemia b. Tremors shown by which of the following? Diaphoresis d. Constipation 11. Answer A. Muscle weakness, bradycardia, nausea, diarrhea, and paresthesia of the hands, feet, tongue, and face are findings associated with hyperkalemia, which is transient and occurs from transient hypoaldosteronism when the adenoma is removed. Tremors, diaphoresis, and constipation aren’t seen in hyperkalemia. 12. Nurse Louie is developing a teaching a. antidiuretic hormone (ADH). plan for a male client diagnosed with diabet b. thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). insipidus. The nurse should include follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). information about which hormone lacking i d. luteinizing hormone (LH). 12. Answer A. ADH is the hormone clients with diabetes insipidus lack. The client’s TSH, FSH, and LH levels won’t be affected. clients with diabetes insipidus? 13. Early this morning, a female client hada. Diabetic ketoacidosis subtotal thyroidectomy. During evening b. Thyroid crisis rounds, nurse Tina assesses the client, who Hypoglycemia now has nausea, a temperature of 105° F d. Tetany 13. Answer B. Thyroid crisis usually occurs in the first 12 hours after thyroidectomy and causes exaggerated signs of hyperthyroidism, such as high fever, tachycardia, and extreme restlessness. Diabetic ketoacidosis is more likely to produce polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia; hypoglycemia, to produce weakness, tremors, profuse perspiration, and hunger. Tetany typically causes uncontrollable muscle spasms, stridor, cyanosis, and possibly asphyxia. (40.5° C), tachycardia, and extreme restlessness. What is the most likely cause of these signs? 14. For a male client with hyperglycemia, a. Cool, clammy skin which assessment finding best supports a b. Distended neck veins nursing diagnosis of Deficient fluid volume? Increased urine osmolarity d. Decreased serum sodium level 14. Answer C. In hyperglycemia, urine osmolarity (the measurement of dissolved particles in the urine) increases as glucose particles move into the urine. The client experiences glucosuria and polyuria, losing body fluids and experiencing fluid volume deficit. Cool, clammy skin; distended neck veins; and a decreased serum sodium level are signs of fluid volume excess, the opposite imbalance. 15. When assessing a male client with a. a blood pressure of 130/70 mm Hg. pheochromocytoma, a tumor of the adrenal b. a blood glucose level of 130 mg/dl. 15. Answer D. Pheochromocytoma, a tumor of the adrenal medulla that secretes excessive medulla that secretes excessive bradycardia. catecholamine, nurse April is most likely to d. a blood pressure of 176/88 mm Hg. catecholamine, causes hypertension, tachycardia, hyperglycemia, hypermetabolism, and weight loss. It isn’t associated with the other options. detect: 16. A male client is admitted for treatment a. Infusing I.V. fluids rapidly as ordered the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic b. Encouraging increased oral intake hormone (SIADH). Which nursing c. Restricting fluids intervention is appropriate? d. Administering glucose-containing I.V. fluids as 16. Answer C. To reduce water retention in a client with the SIADH, the nurse should restrict fluids. Administering fluids by any route would further increase the client’s already heightened fluid load. ordered 17. A female client has a serum calcium a. Trousseau’s sign. level of 7.2 mg/dl. During the physical b. Homans’ sign. examination, nurse Noah expects to assess: Hegar’s sign. d. Goodell’s sign. 17. Answer A. This client’s serum calcium level indicates hypocalcemia, an electrolyte imbalance that causes Trousseau’s sign (carpopedal spasm induced by inflating the blood pressure cuff above systolic pressure). Homans’ sign (pain on dorsiflexion of the foot) indicates deep vein thrombosis. Hegar’s sign (softening of the uterine isthmus) and Goodell’s sign (cervical softening) are probable signs of pregnancy. 18. Which outcome indicates that treatmen a. Fluid intake is less than 2,500 ml/day. of a male client with diabetes insipidus has b. Urine output measures more than 200 ml/hour. been effective? c. Blood pressure is 90/50 mm Hg. d. The heart rate is 126 beats/minute. 18. Answer A. Diabetes insipidus is characterized by polyuria (up to 8 L/day), constant thirst, and an unusually high oral intake of fluids. Treatment with the appropriate drug should decrease both oral fluid intake and urine output. A urine output of 200 ml/hour indicates continuing polyuria. A blood pressure of 90/50 mm Hg and a heart rate of 126 beats/minute indicate compensation for the continued fluid deficit, suggesting that treatment hasn’t been effective. 19. Jemma, who weighs 210 lb (95 kg) an a. Acromegaly has been diagnosed with hyperglycemia tell b. Type 1 diabetes mellitus the nurse that her husband sleeps in another Hypothyroidism room because her snoring keeps him awake.d. Deficient growth hormone 19. Answer A. Acromegaly, which is caused by a pituitary tumor that releases excessive growth hormone, is associated with hyperglycemia, hypertension, diaphoresis, peripheral neuropathy, and joint pain. Enlarged hands and feet are related to lateral bone growth, which is seen in adults with this disorder. The accompanying soft tissue swelling causes hoarseness and often sleep apnea. Type 1 The nurse notices that she has large hands and a hoarse voice. Which of the following would the nurse suspect as a possible cause of the client’s hyperglycemia? diabetes is usually seen in children, and newly diagnosed persons are usually very ill and thin. Hypothyroidism isn’t associated with hyperglycemia, nor is growth hormone deficiency. 20. Nurse Kate is providing dietary a. Increasing saturated fat intake and fasting in the instructions to a male client with afternoon. hypoglycemia. To control hypoglycemic b. Increasing intake of vitamins B and D and episodes, the nurse should recommend: taking iron supplements. c. Eating a candy bar if light-headedness occurs. d. Consuming a low-carbohydrate, highprotein diet 20. Answer D. To control hypoglycemic episodes, the nurse should instruct the client to consume a lowcarbohydrate, high-protein diet, avoid fasting, and avoid simple sugars. Increasing saturated fat intake and increasing vitamin supplementation wouldn’t help control hypoglycemia. and avoiding fasting. 21. An incoherent female client with a a. Thyroid storm. history of hypothyroidism is brought to the b. Cretinism. emergency department by the rescue squad. myxedema coma. Physical and laboratory findings reveal d. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis 21. Answer C. Severe hypothyroidism may result in myxedema coma, in which a drastic drop in the metabolic rate causes decreased vital signs, hypoventilation (possibly leading to respiratory acidosis), and nonpitting edema. Thyroid storm is an acute complication of hyperthyroidism. Cretinism is a form of hypothyroidism that occurs in infants. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is a common chronic inflammatory disease of the thyroid gland in which autoimmune factors play a prominent role. hypothermia, hypoventilation, respiratory acidosis, bradycardia, hypotension, and nonpitting edema of the face and pretibial area. Knowing that these findings suggest severe hypothyroidism, nurse Libby prepares to take emergency action to prevent the potential complication of:. 22. A male client with type 1 diabetes a. prefers to take insulin orally. mellitus asks the nurse about taking an oral b. has type 2 diabetes. antidiabetic agent. Nurse Jack explains that has type 1 diabetes. these medications are only effective if the d. is pregnant and has type 2 diabetes. 22. Answer B. Oral antidiabetic agents are only effective in adult clients with type 2 diabetes. Oral antidiabetic agents aren’t effective in type 1 diabetes. Pregnant and lactating women aren’t prescribed oral antidiabetic agents because the effect on the fetus is uncertain. client: 23. When caring for a female client with a a. sulfisoxazole (Gantrisin) history of hypoglycemia, nurse Ruby shouldb. mexiletine (Mexitil) avoid administering a drug that may prednisone (Orasone) potentiate hypoglycemia. Which drug fits th d. lithium carbonate (Lithobid) 23. Answer A. Sulfisoxazole and other sulfonamides are chemically related to oral antidiabetic agents and may precipitate hypoglycemia. Mexiletine, an antiarrhythmic, is used to treat refractory ventricular arrhythmias; it doesn’t cause hypoglycemia. Prednisone, a corticosteroid, is associated with hyperglycemia. Lithium may cause description? transient hyperglycemia, not hypoglycemia. 24. After taking glipizide (Glucotrol) for 9 a. Initiate insulin therapy. months, a male client experiences secondary b. Switch the client to a different oral antidiabetic failure. Which of the following would the agent. nurse expect the physician to do? c. Prescribe an additional oral antidiabetic agent. d. Restrict carbohydrate intake to less than 30% of 24. Answer B. Many clients (25% to 60%) with secondary failure respond to a different oral antidiabetic agent. Therefore, it wouldn’t be appropriate to initiate insulin therapy at this time. However, if a new oral antidiabetic agent is unsuccessful in keeping glucose levels at an acceptable level, insulin may be used in addition to the antidiabetic agent. the total caloric intake. 25. During preoperative teaching for a female client who will undergo subtotal a. “The head of your bed must remain flat for 24 hours after surgery.” 25. Answer D. To prevent undue pressure on the surgical incision after subtotal thyroidectomy, the nurse should advise the client to avoid hyperextending the neck. The client may elevate the head of the bed as desired and should perform deep breathing and coughing to help prevent pneumonia. Subtotal thyroidectomy doesn’t affect swallowing. thyroidectomy, the nurse should include whi b. “You should avoid deep breathing and coughing statement? after surgery.” c. “You won’t be able to swallow for the first day or two.” d. “You must avoid hyperextending your neck after surgery.” GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS 1. Nurse Berlinda is assigned to a 41-year a. 45 units/L client who has a diagnosis of chronic b. 100 units/L pancreatitis. The nurse reviews the laboratory 300 units/L result, anticipating a laboratory report that d. 500 units/L 1. Answer C. The normal serum amylase level is 25 to 151 units/L. With chronic cases of pancreatitis indicates a serum amylase level of: 2. A male client who is recovering from a. Tea surgery has been advanced from a clear liq b. Gelatin diet to a full liquid diet. The client is looking Custard forward to the diet change because he has d. Popsicle 2. Answer C. Full liquid food items include items such as plain ice cream been “bored” with the clear liquid diet. The nurse would offer which full liquid item to the client? 3. Nurse Juvy is caring for a client with a. Pork cirrhosis of the liver. To minimize the effect b. Milk of the disorder, the nurse teaches the client Chicken about foods that are high in thiamine. The d. Broccoli 3. Answer A. The client with cirrhosis needs to consume foods high in thiamine. Thiamine is present in a variety of foods of plant and animal origin. Pork products are especially rich in this vitamin. Other good food sources include nuts nurse determines that the client has the best understanding of the dietary measures to follow if the client states an intension to increase the intake of: 4. Nurse Oliver checks for residual before a. Hold the feeding administering a bolus tube feeding to a clientb. Reinstill the amount and continue with with a nasogastric tube and obtains a residual administering the feeding amount of 150 mL. What is appropriate actioc. Elevate the client’s head at least 45 degrees and for the nurse to take? administer the feeding d. Discard the residual amount and proceed with 4. Answer A. Unless specifically indicated administering the feeding 5. A nurse is inserting a nasogastric tube in a. Quickly insert the tube an adult male client. During the procedure, b. Notify the physician immediately the client begins to cough and has difficulty c. Remove the tube and reinsert when the breathing. Which of the following is the respiratory distress subsides appropriate nursing action? d. Pull back on the tube and wait until the 5. Answer D. During the insertion of a nasogastric tube respiratory distress subsides 6. Nurse Ryan is assessing for correct a. 3.5 placement of a nosogartric tube. The nurse b. 7.0 aspirates the stomach contents and check the 7.35 contents for pH. The nurse verifies correct d. 7.5 6. Answer A. If the nasogastric tube is in the stomach tube placement if which pH value is noted? 7. A nurse is preparing to remove a a. Exhale nasogartric tube from a female client. The b. Inhale and exhale quickly nurse should instruct the client to do which of Take and hold a deep breath the following just before the nurse removes d. Perform a Valsalva maneuver 7. Answer C. When the nurse removes a nasogastric tube the tube? 8. Nurse Joy is preparing to administer a. Position the client supine to assist in medication through a nasogastric tube that is medication absorption connected to suction. To administer the b. Aspirate the nasogastric tube after medication 8. Answer C. If a client has a nasogastric tube connected to suction medication, the nurse would: administration to maintain patency c. Clamp the nasogastric tube for 30 minutes following administration of the medication d. Change the suction setting to low intermittent suction for 30 minutes after medication administration 9. A nurse is preparing to care for a femalea. An obturator client with esophageal varices who has just b. Kelly clamp has a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube inserted. An irrigation set The nurse gathers supplies, knowing that d. A pair of scissors 9. Answer C. When the client has a Sengstaken- Blakemore tube which of the following items must be kept at the bedside at all times? 10. Dr. Smith has determined that the cliena. Hepatitis A with hepatitis has contracted the infection b. Hepatitis B form contaminated food. The nurse Hepatitis C understands that this client is most likely d. Hepatitis D 10. Answer A. Hepatitis A is transmitted by the fecal-oral route via contaminated food or infected food handlers. Hepatitis B experiencing what type of hepatitis? 11. A client is suspected of having hepatiti a. Elevated hemoglobin level Which diagnostic test result will assist in b. Elevated serum bilirubin level confirming this diagnosis? Elevated blood urea nitrogen level d. Decreased erythrocycle sedimentation rate 11. Answer B. Laboratory indicators of hepatitis include elevated liver enzyme levels 12. The nurse is reviewing the physician’s a. NPO status orders written for a male client admitted to t b. Nasogastric tube inserted hospital with acute pancreatitis. Which Morphine sulfate for pain physician order should the nurse question if d. An anticholinergic medication 12. Answer C. Meperidine (Demerol) rather than morphine sulfate is the medication of choice to treat pain because morphine sulfate can cause spasms in the sphincter of Oddi. Options A noted on the client’s chart? 13. A female client being seen in a a. Fast for 8 hours before the test physician’s office has just been scheduled fo b. Eat a regular supper and breakfast a barium swallow the next day. The nurse c. Continue to take all oral medications as writes down which instruction for the client to scheduled follow before the test? d. Monitor own bowel movement pattern for 13. Answer A. A barium swallow is an x-ray study that uses a substance called barium for contrast to highlight abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract. The client should fast for 8 to 12 hours before the test constipation 14. The nurse is performing an abdominal a. Palpates the abdomen for size assessment and inspects the skin of the b. Palpates the liver at the right rib margin abdomen. The nurse performs which c. Listens to bowel sounds in all for quadrants assessment technique next? d. Percusses the right lower abdominal quadrant 14. Answer C. The appropriate sequence for abdominal examination is inspection 15. Polyethylene glycol-electrlyte solutiona. Start an IV infusion (GoLYTELY) is prescribed for the female b. Administer an enema client scheduled for a colonoscopy. The client Cancel the diagnostic test 15. Answer D. The solution GoLYTELY is a bowel evacuant used to prepare a client for a colonoscopy by cleansing the bowel. The solution is begins to experience diarrhea following administration of the solution. What action by the nurse is appropriate? d. Explain that diarrhea is expected expected to cause a mild diarrhea and will clear the bowel in 4 to 5 hours. Options A 16. The nurse is caring for a male client w a. Vitamin A a diagnosis of chronic gastritis. The nurse b. Vitamin B12 monitors the client knowing that this client is Vitamin C at risk for which vitamin deficiency? d. Vitamin E 16. Answer B. Chronic gastritis causes deterioration and atrophy of the lining of the stomach 17. The nurse is reviewing the medication a. Digoxin (Lanoxin) record of a female client with acute gastritis.b. Furosemide (Lasix) Which medication, if noted on the client’s Indomethacin (Indocin) record, would the nurse question? d. Propranolol hydrochloride (Inderal) 17. Answer C. Indomethacin (Indocin) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and can cause ulceration of the esophagus 18. The nurse is assessing a male client 24a. Clamp the T tube hours following a cholecystectomy. The nur b. Irrigate the T tube noted that the T tube has drained 750 mL of Notify the physician green-brown drainage since the surgery. d. Document the findings 18. Answer D. Following cholecystectomy Which nursing intervention is appropriate? 19. The nurse is monitoring a female clien a. Bradycardia with a diagnosis of peptic ulcer. Which b. Numbness in the legs assessment findings would most likely Nausea and vomiting indicate perforation of the ulcer? d. A rigid, board-like abdomen 19. Answer D. Perforation of an ulcer is a surgical emergency and is characterized by sudden 20. A male client with a peptic ulcer is a. Halts stress reactions scheduled for a vagotomy and the client ask b. Heals the gastric mucosa the nurse about the purpose of this procedure. Reduces the stimulus to acid secretions Which response by the nurse best describes d. Decreases food absorption in the stomach 20. Answer C. A vagotomy the purpose of a vagotomy? 21. The nurse is caring for a female client a. Leg exercises following a Billroth II procedure. Which b. Early ambulation postoperative order should the nurse question Irrigating the nasogastric tube and verify? d. Coughing and deep-breathing exercises 21. Answer C. In a Billroth II procedure 22. The nurse is providing discharge a. Ambulate following a meal instructions to a male client following b. Eat high carbohydrate foods gastrectomy and instructs the client to take c. Limit the fluid taken with meal which measure to assist in preventing d. Sit in a high-Fowler’s position during meals 22. Answer C. Dumping syndrome is a term that refers to a constellation of vasomotor symptoms that occurs after eating dumping syndrome? 23. The nurse is monitoring a female client a. Sweating and pallor 23. Answer A. Early manifestations of dumping for the early signs and symptoms of dumpin b. Bradycardia and indigestion syndrome. Which of the following indicate Double vision and chest pain this occurrence? d. Abdominal cramping and pain syndrome occur 5 to 30 minutes after eating. Symptoms include vertigo 24. The nurse is preparing a discharge a. Irrigating the drain teaching plan for the male client who had b. Avoiding coughing umbilical hernia repair. What should the nurse Maintaining bed rest include in the plan? d. Restricting pain medication 24. Answer B. Coughing is avoided following umbilical hernia repair to prevent disruption of tissue integrity 25. The nurse is instructing the male clienta. Limit oral fluid who has an inguinal hernia repair how to b. Elevate the scrotum reduce postoperative swelling following the Apply heat to the abdomen procedure. What should the nurse tell the d. Remain in a low-fiber diet 25. Answer B. Following inguinal hernia repair client? 26. The nurse is caring for a hospitalized a. Hypotension female client with a diagnosis of ulcerative b. Bloody diarrhea colitis. Which finding, if noted on assessment Rebound tenderness of the client, would the nurse report to the d. A hemoglobin level of 12 mg/dL 26. Answer C. Rebound tenderness may indicate peritonitis. Bloody diarrhea is expected to occur in ulcerative colitis. Because of the blood loss physician? 27. The nurse is caring for a male client a. Sexual dysfunction postoperatively following creation of a b. Body image, disturbed colostomy. Which nursing diagnosis should c. Fear related to poor prognosis the nurse include in the plan of care? d. Nutrition: more than body requirements, 27. Answer B. Body image imbalanced 28. The nurse is reviewing the record of a a. Diarrhea female client with Crohn’s disease. Which b. Chronic constipation stool characteristics should the nurse expect Constipation alternating with diarrhea to note documented in the client’s record? d. Stools constantly oozing form the rectum 28. Answer A. Crohn’s disease is characterized by nonbloody diarrhea of usually not more than four to five stools daily. Over time 29. The nurse is performing a colostomy a. Notify the physician irrigation on a male client. During the b. Stop the irrigation temporarily irrigation, the client begins to complain of Increase the height of the irrigation abdominal cramps. What is the appropriate d. Medicate for pain and resume the irrigation 29. Answer B. If cramping occurs during a colostomy irrigation nursing action? 30. The nurse is teaching a female client a. Increase fluid intake how to perform a colostomy irrigation. To b. Place heat on the abdomen enhance the effectiveness of the irrigation and Perform the irrigation in the evening fecal returns, what measure should the nursed. Reduce the amount of irrigation solution 30. Answer A. To enhance effectiveness of the irrigation and fecal returns, the client is instructed to increase fluid intake and to take other measures to prevent constipation. Options B, C and D will not instruct the client to do? enhance the effectiveness of this procedure. 1. During preparation for bowel surgery, a a. vitamin A male client receives an antibiotic to reduce b. vitamin D intestinal bacteria. Antibiotic therapy may vitamin E interfere with synthesis of which vitamin an d. vitamin K 1. Answer D. Intestinal bacteria synthesize such nutritional substances as vitamin K, thiamine, riboflavin, vitamin B12, folic acid, biotin, and nicotinic acid. Therefore, antibiotic therapy may interfere with synthesis of these substances, including vitamin K. Intestinal bacteria don’t synthesize vitamins A, D, or E. may lead to hypoprothrombinemia? 2. When evaluating a male client for a. increased intracranial pressure. complications of acute pancreatitis, the nurs b. decreased urine output. would observe for: bradycardia. d. hypertension 2. Answer B. Acute pancreatitis can cause decreased urine output, which results from the renal failure that sometimes accompanies this condition. Intracranial pressure neither increases nor decreases in a client with pancreatitis. Tachycardia, not bradycardia, usually is associated with pulmonary or hypovolemic complications of pancreatitis. Hypotension can be caused by a hypovolemic complication, but hypertension usually isn’t related to acute pancreatitis. 3. A male client with a recent history of a. Lying on the right side with legs straight rectal bleeding is being prepared for a b. Lying on the left side with knees bent colonoscopy. How should the nurse position Prone with the torso elevated the client for this test initially? d. Bent over with hands touching the floor 3. Answer B. For a colonoscopy, the nurse initially should position the client on the left side with knees bent. Placing the client on the right side with legs straight, prone with the torso elevated, or bent over with hands touching the floor wouldn’t allow proper visualization of the large intestine. 4. A male client with extreme weakness, a. “Tell me about your husband’s alcohol usage.” pallor, weak peripheral pulses, and b. “Is your husband being treated for disorientation is admitted to the emergency tuberculosis?” department. His wife reports that he has been “spitting up blood.” A Mallory-Weiss tear is c. “Has your husband recently fallen or injured his suspected, and the nurse begins taking a client chest?” history from the client’s wife. The question d. “Describe spices and condiments your 4. Answer A. A Mallory-Weiss tear is associated with massive bleeding after a tear occurs in the mucous membrane at the junction of the esophagus and stomach. There is a strong relationship between ethanol usage, resultant vomiting, and a MalloryWeiss tear. The bleeding is coming from the stomach, not from the lungs as would be true in by the nurse that demonstrates her understanding of Mallory-Weiss tearing is: husband uses on food.” some cases of tuberculosis. A Mallory-Weiss tear doesn’t occur from chest injuries or falls and isn’t associated with eating spicy foods. 5. Which of the following nursing a. Change the tube feeding solutions and tubing at interventions should the nurse perform for a least every 24 hours. female client receiving enteral feedings b. Maintain the head of the bed at a 15-degree through a gastrostomy tube? elevation continuously. c. Check the gastrostomy tube for position every 2 days. d. Maintain the client on bed rest during the 5. Answer A. Tube feeding solutions and tubing should be changed every 24 hours, or more frequently if the feeding requires it. Doing so prevents contamination and bacterial growth. The head of the bed should be elevated 30 to 45 degrees continuously to prevent aspiration. Checking for gastrostomy tube placement is performed before initiating the feedings and every 4 hours during continuous feedings. Clients may ambulate during feedings. feedings. 6. A male client is recovering from a a. 5 to 10 minutes smallbowel resection. To relieve pain, the b. 15 to 30 minutes physician prescribes meperidine (Demerol), 30 to 60 minutes 75 mg I.M. every 4 hours. How soon after d. 2 to 4 hours 6. Answer B. Meperidine’s onset of action is 15 to 30 minutes. It peaks between 30 and 60 minutes and has a duration of action of 2 to 4 hours. administration should meperidine’s onset of action occur? 7. The nurse is caring for a male client wita. Dyspnea and fatigue cirrhosis. Which assessment findings indicatb. Ascites and orthopnea that the client has deficient vitamin K Purpura and petechiae absorption caused by this hepatic disease? d. Gynecomastia and testicular atrophy 7. Answer C. A hepatic disorder, such as cirrhosis, may disrupt the liver’s normal use of vitamin K to produce prothrombin (a clotting factor). Consequently, the nurse should monitor the client for signs of bleeding, including purpura and petechiae. Dyspnea and fatigue suggest anemia. Ascites and orthopnea are unrelated to vitamin K absorption. Gynecomastia and testicular atrophy result from decreased estrogen metabolism by the diseased liver. 8. Which condition is most likely to have a. Appendicitis nursing diagnosis of fluid volume deficit? b. Pancreatitis Cholecystitis d. Gastric ulcer 8. Answer B. Hypovolemic shock from fluid shifts is a major factor in acute pancreatitis. The other conditions are less likely to exhibit fluid volume deficit. 9. While a female client is being prepared a. Irrigate the tube with cola. for discharge, the nasogastric (NG) feeding b. Advance the tube into the intestine. tube becomes clogged. To remedy this c. Apply intermittent suction to the tube. problem and teach the client’s family how to d. Withdraw the obstruction with a 30-ml syringe. 9. Answer A. The nurse should irrigate the tube with cola because its effervescence and acidity are suited to the purpose, it’s inexpensive, and it’s readily available in most homes. Advancing the NG tube is inappropriate because the tube is designed to stay in the stomach and isn’t long enough to reach the intestines. Applying intermittent suction or using a syringe for aspiration is unlikely to dislodge the material clogging the tube but may create excess pressure. Intermittent suction may even collapse the tube. deal with it at home, what should the nurse do? 10. A male client with pancreatitis complai a. meperidine provides a better, more prolonged of pain. The nurse expects the physician to analgesic effect. prescribe meperidine (Demerol) instead of b. morphine may cause spasms of Oddi’s sphincter. morphine to relieve pain because: c. meperidine is less addictive than morphine. d. morphine may cause hepatic dysfunction. 10. Answer B. For a client with pancreatitis, the physician will probably avoid prescribing morphine because this drug may trigger spasms of the sphincter of Oddi (a sphincter at the end of the pancreatic duct), causing irritation of the pancreas. Meperidine has a somewhat shorter duration of action than morphine. The two drugs are equally addictive. Morphine isn’t associated with hepatic dysfunction. 11. Mandy, an adolescent girl is admitted ta. Hopelessness an acute care facility with severe malnutritiob. Powerlessness After a thorough examination, the physician Chronic low self esteem diagnoses anorexia nervosa. When developind. Deficient knowledge 11. Answer C. Young women with Chronic low self esteem — are at highest risk for anorexia nervosa because they perceive being thin as a way to improve their self-confidence. Hopelessness and Powerlessness are inappropriate nursing diagnoses because clients with anorexia nervosa seldom feel hopeless or powerless; instead, they use food to control their desire to be thin and hope that restricting food intake will achieve this goal. Anorexia nervosa doesn’t result from a knowledge deficit, such as one regarding good nutrition. the plan of care for this client, the nurse is most likely to include which nursing diagnosis? 12. Which diagnostic test would be used fia. Endoscopy to evaluate a client with upper GI b. Upper GI series 12. Answer A. Endoscopy permits direct evaluation of the upper GI tract and can detect 90% bleeding? Hemoglobin (Hb) levels and hematocrit (HCT) d. Arteriography of bleeding lesions. An upper GI series, or barium study, usually isn’t the diagnostic method of choice, especially in a client with acute active bleeding who’s vomiting and unstable. An upper GI series is also less accurate than endoscopy. Although an upper GI series might confirm the presence of a lesion, it wouldn’t necessarily reveal whether the lesion is bleeding. Hb levels and HCT, which indicate loss of blood volume, aren’t always reliable indicators of GI bleeding because a decrease in these values may not be seen for several hours. Arteriography is an invasive study associated with life-threatening complications and wouldn’t be used for an initial evaluation. 13. A female client who has just been a. “You may have eaten contaminated restaurant diagnosed with hepatitis A asks, “How could I food.” have gotten this disease?” What is the nurse’ b. “You could have gotten it by using I.V. best response? drugs.” c. “You must have received an infected blood transfusion.” d. “You probably got it by engaging in unprotected 13. Answer A. Hepatitis A virus typically is transmitted by the oral-fecal route — commonly by consuming food contaminated by infected food handlers. The virus isn’t transmitted by the I.V. route, blood transfusions, or unprotected sex. Hepatitis B can be transmitted by I.V. drug use or blood transfusion. Hepatitis C can be transmitted by unprotected sex. sex.” 14. When preparing a male client, age 51, a. Obstruction of the appendix may increase for surgery to treat appendicitis, the nurse venous drainage and cause the appendix to formulates a nursing diagnosis of Risk for rupture. infection related to inflammation, perforatio b. Obstruction of the appendix reduces arterial and surgery. What is the rationale for choosing flow, leading to ischemia, inflammation, and this nursing diagnosis? rupture of the appendix. c. The appendix may develop gangrene and 14. Answer B. A client with appendicitis is at risk for infection related to inflammation, perforation, and surgery because obstruction of the appendix causes mucus fluid to build up, increasing pressure in the appendix and compressing venous outflow drainage. The pressure continues to rise with venous obstruction; arterial blood flow then decreases, leading to ischemia from lack of perfusion. Inflammation and bacterial growth follow, and swelling continues to raise pressure within the appendix, resulting in gangrene and rupture. Geriatric, not middle-aged, clients are especially rupture, especially in a middle-aged client. d. Infection of the appendix diminishes necrotic arterial blood flow and increases venous drainage. susceptible to appendix rupture. 15. A female client with hepatitis C develoa. whole blood and albumin. liver failure and GI hemorrhage. The blood b. platelets and packed red blood cells. products that would most likely bring about fresh frozen plasma and whole blood. hemostasis in the client are: d. cryoprecipitate and fresh frozen plasma. 15. Answer D. The liver is vital in the synthesis of clotting factors, so when it’s diseased or dysfunctional, as in hepatitis C, bleeding occurs. Treatment consists of administering blood products that aid clotting. These include fresh frozen plasma containing fibrinogen and cryoprecipitate, which have most of the clotting factors. Although administering whole blood, albumin, and packed cells will contribute to hemostasis, those products aren’t specifically used to treat hemostasis. Platelets are helpful, but the best answer is cryoprecipitate and fresh frozen plasma. 16. To prevent gastroesophageal reflux in aa. “Lie down after meals to promote digestion.” male client with hiatal hernia, the nurse b. “Avoid coffee and alcoholic beverages.” should provide which discharge instruction? c. “Take antacids with meals.” d. “Limit fluid intake with meals.” 16. Answer B. To prevent reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus, the nurse should advise the client to avoid foods and beverages that increase stomach acid, such as coffee and alcohol. The nurse also should teach the client to avoid lying down after meals, which can aggravate reflux, and to take antacids after eating. The client need not limit fluid intake with meals as long as the fluids aren’t gastric irritants. 17. The nurse caring for a client with a. Administering pain medication smallbowel obstruction would plan to b. Obtaining a blood sample for laboratory studies implement which nursing intervention first? c. Preparing to insert a nasogastric (NG) tube d. Administering I.V. fluids 17. Answer D. I.V. infusions containing normal saline solution and potassium should be given first to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance. For the client’s comfort and to assist in bowel decompression, the nurse should prepare to insert an NG tube next. A blood sample is then obtained for laboratory studies to aid in the diagnosis of bowel obstruction and guide treatment. Blood studies usually include a complete blood count, serum electrolyte levels, and blood urea nitrogen level. Pain medication often is withheld until obstruction is diagnosed because analgesics can decrease intestinal motility. 18. A female client with dysphagia is beinga. The client doesn’t exhibit rectal tenesmus. prepared for discharge. Which outcome b. The client is free from esophagitis and achalasia. indicates that the client is ready for dischargec. The client reports diminished duodenal inflammation. d. The client has normal gastric structures. 18. Answer B. Dysphagia may be the reason why a client with esophagitis or achalasia seeks treatment. Dysphagia isn’t associated with rectal tenesmus, duodenal inflammation, or abnormal gastric structures. 19. A male client undergoes total a. Notify the physician gastrectomy. Several hours after surgery, theb. Reposition the tube nurse notes that the client’s nasogastric (NG) Irrigate the tube tube has stopped draining. How should the d. Increase the suction level 19. Answer A. An NG tube that fails to drain during the postoperative period should be reported to the physician immediately. It may be clogged, which could increase pressure on the suture site because fluid isn’t draining adequately. Repositioning or irrigating an NG tube in a client who has undergone gastric surgery can disrupt the anastomosis. Increasing the level of suction may cause trauma to GI mucosa or the suture line. nurse respond? 20. What laboratory finding is the primarya. Elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) diagnostic indicator for pancreatitis? b. Elevated serum lipase Elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST) d. Increased lactate dehydrogenase (LD) 20. Answer B. Elevation of serum lipase is the most reliable indicator of pancreatitis because this enzyme is produced solely by the pancreas. A client’s BUN is typically elevated in relation to renal dysfunction; the AST, in relation to liver dysfunction; and LD, in relation to damaged cardiac muscle. 21. A male client with cholelithiasis has a a. yellow sclerae. gallstone lodged in the common bile duct. b. light amber urine. When assessing this client, the nurse expects circumoral pallor. to note: d. black, tarry stools. 21. Answer A. Yellow sclerae may be the first sign of jaundice, which occurs when the common bile duct is obstructed. Urine normally is light amber. Circumoral pallor and black, tarry stools don’t occur in common bile duct obstruction; they are signs of hypoxia and GI bleeding, respectively. 22. Nurse Hannah is teaching a group of a. a sedentary lifestyle and smoking. middle-aged men about peptic ulcers. When b. a history of hemorrhoids and smoking. 22. Answer D. Risk factors for peptic (gastric and duodenal) ulcers include alcohol abuse, smoking, discussing risk factors for peptic ulcers, the c. alcohol abuse and a history of acute renal nurse should mention: failure. d. alcohol abuse and smoking. and stress. A sedentary lifestyle and a history of hemorrhoids aren’t risk factors for peptic ulcers. Chronic renal failure, not acute renal failure, is associated with duodenal ulcers. 23. While palpating a female client’s right a. Sigmoid colon upper quadrant (RUQ), the nurse would b. Appendix expect to find which of the following Spleen structures? d. Liver 23. Answer D. The RUQ contains the liver, gallbladder, duodenum, head of the pancreas, hepatic flexure of the colon, portions of the ascending and transverse colon, and a portion of the right kidney. The sigmoid colon is located in the left lower quadrant; the appendix, in the right lower quadrant; and the spleen, in the left upper quadrant. 24. A male client has undergone a colon a. call the physician. resection. While turning him, wound b. place saline-soaked sterile dressings on the dehiscence with evisceration occurs. The wound. nurse’s first response is to: c. take a blood pressure and pulse. d. pull the dehiscence closed. 24. Answer B. The nurse should first place salinesoaked sterile dressings on the open wound to prevent tissue drying and possible infection. Then the nurse should call the physician and take the client’s vital signs. The dehiscence needs to be surgically closed, so the nurse should never try to close it. 25. The nurse is monitoring a female clien a. Antiarrhythmic drugs receiving paregoric to treat diarrhea for drugb. Anticholinergic drugs interactions. Which drugs can produce Anticoagulant drugs additive constipation when given with an d. Antihypertensive drugs 25. Answer B. Paregoric has an additive effect of constipation when used with anticholinergic drugs. Antiarrhythmics, anticoagulants, and antihypertensives aren’t known to interact with paregoric. opium preparation? 26. A male client is recovering from an a. increasing fluid intake to prevent dehydration. ileostomy that was performed to treat b. wearing an appliance pouch only at bedtime. inflammatory bowel disease. During c. consuming a low-protein, high-fiber diet. discharge teaching, the nurse should stress thd. taking only enteric-coated medications. 26. Answer A. Because stool forms in the large intestine, an ileostomy typically drains liquid waste. To avoid fluid loss through ileostomy drainage, the nurse should instruct the client to increase fluid intake. The nurse should teach the client to wear a collection appliance at all times because ileostomy drainage is incontinent, to avoid high-fiber foods because they may irritate the intestines, and to avoid enteric-coated medications because the body can’t importance of: absorb them after an ileostomy 27. The nurse is caring for a female client a. Regular diet with active upper GI bleeding. What is the b. Skim milk appropriate diet for this client during the first Nothing by mouth 24 hours after admission? d. Clear liquids 27. Answer C. Shock and bleeding must be controlled before oral intake, so the client should receive nothing by mouth. A regular diet is incorrect. When the bleeding is controlled, the diet is gradually increased, starting with ice chips and then clear liquids. Skim milk shouldn’t be given because it increases gastric acid production, which could prolong bleeding. A liquid diet is the first diet offered after bleeding and shock are controlled. 28. A male client has just been diagnosed a. severe abdominal pain radiating to the shoulder. with hepatitis A. On assessment, the nurse b. anorexia, nausea, and vomiting. expects to note: c. eructation and constipation. d. abdominal ascites. 28. Answer B. Hallmark signs and symptoms of hepatitis A include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and weakness. Abdominal pain may occur but doesn’t radiate to the shoulder. Eructation and constipation are common in gallbladder disease, not hepatitis A. Abdominal ascites is a sign of advanced hepatic disease, not an early sign of hepatitis A. 29. A female client with viral hepatitis A is a. place the client in a private room. being treated in an acute care facility. Becausb. wear a mask when handling the client’s bedpan. the client requires enteric precautions, the c. wash the hands after touching the client. nurse should: d. wear a gown when providing personal care for 29. Answer C. To maintain enteric precautions, the nurse must wash the hands after touching the client or potentially contaminated articles and before caring for another client. A private room is warranted only if the client has poor hygiene — for instance, if the client is unlikely to wash the hands after touching infective material or is likely to share contaminated articles with other clients. For enteric precautions, the nurse need not wear a mask and must wear a gown only if soiling from fecal matter is likely. the client. 30. Which of the following factors can a. Contact with infected blood cause hepatitis A? b. Blood transfusions with infected blood Eating contaminated shellfish d. Sexual contact with an infected person 30. Answer C. Hepatitis A can be caused by consuming contaminated water, milk, or food — especially shellfish from contaminated water. Hepatitis B is caused by blood and sexual contact with an infected person. Hepatitis C is usually caused by contact with infected blood, including receiving blood transfusions. GENITOURINARY SYSTEM 1. The nurse is aware that the following a. A low-riding prostate findings would be further evidence of a b. The presence of a boggy mass urethral injury in a male client during rectal Absent sphincter tone examination? d. A positive Hemoccult 1. Answer B. When the urethra is ruptured, a hematoma or collection of blood separates the two sections of urethra. This may feel like a boggy mass on rectal examination. Because of the rupture and hematoma, the prostate becomes high riding. A palpable prostate gland usually indicates a nonurethral injury. Absent sphincter tone would refer to a spinal cord injury. The presence of blood would probably correlate with GI bleeding or a colon injury. 2. When a female client with an indwellinga. The client sets the drainage bag on the floor urinary (Foley) catheter insists on walking to while sitting down. the hospital lobby to visit with family b. The client keeps the drainage bag below the members, nurse Rose teaches how to do this bladder at all times. without compromising the catheter. Which c. The client clamps the catheter drainage tubing client action indicates an accurate while visiting with the family. understanding of this information? d. The client loops the drainage tubing below its 2. Answer B. To maintain effective drainage, the client should keep the drainage bag below the bladder; this allows the urine to flow by gravity from the bladder to the drainage bag. The client shouldn’t lay the drainage bag on the floor because it could become grossly contaminated. The client shouldn’t clamp the catheter drainage tubing because this impedes the flow of urine. To promote drainage, the client may loop the drainage tubing above — not below — its point of entry into the drainage bag. point of entry into the drainage bag. 3. A female client has just been diagnosed with condylomata acuminata (genital warts). What information is appropriate to tell this client? a. This condition puts her at a higher risk for cervical cancer; therefore, she should have a Papanicolaou (Pap) smear annually. b. The most common treatment is metronidazole (Flagyl), which should eradicate the problem within 7 to 10 days. 3. Answer A. Women with condylomata acuminata are at risk for cancer of the cervix and vulva. Yearly Pap smears are very important for early detection. Because condylomata acuminata is a virus, there is no permanent cure. Because condylomata acuminata can occur on the vulva, a condom won’t protect sexual partners. HPV can be transmitted to other parts of the body, such as the mouth, oropharynx, and larynx. c. The potential for transmission to her sexual partner will be eliminated if condoms are used every time they have sexual intercourse. d. The human papillomavirus (HPV), which causes condylomata acuminata, can’t be transmitted during oral sex. 4. A male client with bladder cancer has haa. The skin wasn’t lubricated before the pouch was the bladder removed and an ileal conduit applied. created for urine diversion. While changing b. The pouch faceplate doesn’t fit the stoma. this client’s pouch, the nurse observes that thc. A skin barrier was applied properly. area around the stoma is red, weeping, and painful. What should nurse Katrina concluded. Stoma dilation wasn’t performed. 4. Answer B. If the pouch faceplate doesn’t fit the stoma properly, the skin around the stoma will be exposed to continuous urine flow from the stoma, causing excoriation and red, weeping, and painful skin. A lubricant shouldn’t be used because it would prevent the pouch from adhering to the skin. When properly applied, a skin barrier prevents skin excoriation. Stoma dilation isn’t performed with an ileal conduit, although it may be done with a colostomy if ordered. 5. The nurse is aware that the following a. Myoglobinuria laboratory values supports a diagnosis of b. Ketonuria pyelonephritis? Pyuria d. Low white blood cell (WBC) count 5. Answer C. Pyelonephritis is diagnosed by the presence of leukocytosis, hematuria, pyuria, and bacteriuria. The client exhibits fever, chills, and flank pain. Because there is often a septic picture, the WBC count is more likely to be high rather than low, as indicated in option D. Ketonuria indicates a diabetic state. 6. A female client with chronic renal failura. hematuria. (CRF) is receiving a hemodialysis treatmentb. weight loss. After hemodialysis, nurse Sarah knows that increased urine output. the client is most likely to experience: d. increased blood pressure. 6. Answer B. Because CRF causes loss of renal function, the client with this disorder retains fluid. Hemodialysis removes this fluid, causing weight loss. Hematuria is unlikely to follow hemodialysis because the client with CRF usually forms little or no urine. Hemodialysis doesn’t increase urine output because it doesn’t correct the loss of kidney function, which severely decreases urine production in this disorder. By removing fluids, hemodialysis decreases rather than increases the blood pressure. 7. Nurse Lea is assessing a male client a. Rashes on the palms of the hands and soles of diagnosed with gonorrhea. Which symptom the feet most likely prompted the client to seek b. Cauliflower-like warts on the penis medical attention? c. Painful red papules on the shaft of the penis d. Foul-smelling discharge from the penis 7. Answer D. Symptoms of gonorrhea in men include purulent, foul-smelling drainage from the penis and painful urination. Rashes on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet are symptoms of the secondary stage of syphilis. Cauliflower-like warts on the penis are a sign of human papillomavirus. Painful red papules on the shaft of the penis may be a sign of the first stage of genital herpes. 8. Nurse Agnes is reviewing the report of a a. Specific gravity of 1.03 8. Answer B. Normal urine pH is 4.5 to 8; client’s routine urinalysis. Which value sho b. Urine pH of 3.0 the nurse consider abnormal? Absence of protein d. Absence of glucose therefore, a urine pH of 3.0 is abnormal. Urine specific gravity normally ranges from 1.002 to 1.035, making this client’s value normal. Normally, urine contains no protein, glucose, ketones, bilirubin, bacteria, casts, or crystals. Red blood cells should measure 0 to 3 per high-power field; white blood cells, 0 to 4 per high-power field. Urine should be clear, its color ranging from pale yellow to deep amber. 9. A male client is scheduled for a renal a. 1 minute. clearance test. Nurse Maureen should explaib. 30 minutes. that this test is done to assess the kidneys’ 1 hour. ability to remove a substance from the plas d. 24 hours. 9. Answer A. The renal clearance test determines the kidneys’ ability to remove a substance from the plasma in 1 minute. It doesn’t measure the kidneys’ ability to remove a substance over a longer period. in: 10. A male client in the short-procedure unia. keep the client’s knee on the affected side bent is recovering from renal angiography in for 6 hours. which a femoral puncture site was used. b. apply pressure to the puncture site for 30 When providing postprocedure care, the nurse minutes. should: c. check the client’s pedal pulses frequently. d. remove the dressing on the puncture site after 10. Answer C. After renal angiography involving a femoral puncture site, the nurse should check the client’s pedal pulses frequently to detect reduced circulation to the feet caused by vascular injury. The nurse also should monitor vital signs for evidence of internal hemorrhage and should observe the puncture site frequently for fresh bleeding. The client should be kept on bed rest for several hours so the puncture site can seal completely. Keeping the client’s knee bent is unnecessary. By the time the client returns to the short-procedure unit, manual pressure over the puncture site is no longer needed because a pressure dressing is in place. The nurse shouldn’t remove this dressing for several hours — and only if instructed to do so. vital signs stabilize. 11. A female client is admitted for treatment of chronic renal failure (CRF). Nurse Juliet knows that this disorder increases the client’s risk of: a. water and sodium retention secondary to a severe decrease in the glomerular filtration rate. b. a decreased serum phosphate level secondary to kidney failure. c. an increased serum calcium level secondary to kidney failure. 11. Answer A. A client with CRF is at risk for fluid imbalance — dehydration if the kidneys fail to concentrate urine, or fluid retention if the kidneys fail to produce urine. Electrolyte imbalances associated with this disorder result from the kidneys’ inability to excrete phosphorus; such imbalances d. metabolic alkalosis secondary to retention of hydrogen ions. may lead to hyperphosphatemia with reciprocal hypocalcemia. CRF may cause metabolic acidosis, not metabolic alkalosis, secondary to inability of the kidneys to excrete hydrogen ions. 12. Because of difficulties with a. Potassium level of 3.5 mEq/L hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis is initiated b. Hematocrit (HCT) of 35% treat a female client’s uremia. Which finding Blood glucose level of 200 mg/dl signals a significant problem during this d. White blood cell (WBC) count of 12. Answer D. An increased WBC count indicates infection, probably resulting from peritonitis, which may have been caused by insertion of the peritoneal catheter into the peritoneal cavity. Peritonitis can cause the peritoneal membrane to lose its ability to filter solutes; therefore, peritoneal dialysis would no longer be a treatment option for this client. Hyperglycemia occurs during peritoneal dialysis because of the high glucose content of the dialysate; it’s readily treatable with sliding-scale insulin. A potassium level of 3.5 mEq/L can be treated by adding potassium to the dialysate solution. An HCT of 35% is lower than normal. However, in this client, the value isn’t abnormally low because of the daily blood samplings. A lower HCT is common in clients with chronic renal failure because of the lack of erythropoietin. procedure? 20,000/mm3 13. For a male client in the oliguric phase a. Encouraging coughing and deep breathing acute renal failure (ARF), which nursing b. Promoting carbohydrate intake intervention is most important? Limiting fluid intake d. Providing pain-relief measures 13. Answer C. During the oliguric phase of ARF, urine output decreases markedly, possibly leading to fluid overload. Limiting oral and I.V. fluid intake can prevent fluid overload and its complications, such as heart failure and pulmonary edema. Encouraging coughing and deep breathing is important for clients with various respiratory disorders. Promoting carbohydrate intake may be helpful in ARF but doesn’t take precedence over fluid limitation. Controlling pain isn’t important because ARF rarely causes pain. 14. A female client requires hemodialysis. a. Phosphate binders Which of the following drugs should be b. Insulin withheld before this procedure? Antibiotics d. Cardiac glycosides 14. Answer D. Cardiac glycosides such as digoxin should be withheld before hemodialysis. Hypokalemia is one of the electrolyte shifts that occur during dialysis, and a hypokalemic client is at risk for arrhythmias secondary to digitalis toxicity. Phosphate binders and insulin can be administered because they aren’t removed from the blood by dialysis. Some antibiotics are removed by dialysis and should be administered after the procedure to ensure their therapeutic effects. The nurse should check a formulary to determine whether a particular antibiotic should be administered before or after dialysis. 15. A client comes to the outpatient a. Chlamydia department complaining of vaginal discharg b. Gonorrhea dysuria, and genital irritation. Suspecting a Genital herpes sexually transmitted disease (STD), Dr. Smi d. Human papillomavirus infection 15. Answer B. Gonorrhea must be reported to the public health department. Chlamydia, genital herpes, and human papillomavirus infection aren’t reportable diseases. orders diagnostic tests of the vaginal discharge. Which STD must be reported to the public health department? 16. A male client with acute pyelonephritisa. Urine output increases to 2,000 ml/day. receives a prescription for co-trimoxazole b. Flank and abdominal discomfort decrease. (Septra) P.O. twice daily for 10 days. Which Bacteria are absent on urine culture. finding best demonstrates that the client has d. The red blood cell (RBC) count is normal. 16. Answer C. Co-trimoxazole is a sulfonamide antibiotic used to treat urinary tract infections. Therefore, absence of bacteria on urine culture indicates that the drug has achieved its desired effect. Although flank pain may decrease as the infection resolves, this isn’t a reliable indicator of the drug’s effectiveness. Co-trimoxazole doesn’t affect urine output or the RBC count. followed the prescribed regimen? 17. A 26-year-old female client seeks care a. nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin) for a possible infection. Her symptoms b. ibuprofen (Motrin) include burning on urination and frequent, acetaminophen with codeine urgent voiding of small amounts of urine. d. phenazopyridine (Pyridium) 17. Answer D. Phenazopyridine may be prescribed in conjunction with an antibiotic for painful bladder infections to promote comfort. Because of its local anesthetic action on the urinary mucosa, phenazopyridine specifically relieves bladder pain. Nitrofurantoin is a urinary antiseptic with no analgesic properties. While ibuprofen and acetaminophen with codeine are analgesics, they don’t exert a direct effect on the urinary mucosa. She’s placed on trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole (Bactrim) to treat possible infection. Another medication is prescribed to decrease the pain and frequency. Which of the following is the most likely medication prescribed? 18. A triple-lumen indwelling urinary a. Continuous inflow and outflow of irrigation catheter is inserted for continuous bladder solution. irrigation following a transurethral resection b. Intermittent inflow and continuous outflow of of the prostate. In addition to balloon inflation, irrigation solution. the nurse is aware that the functions of the c. Continuous inflow and intermittent outflow of three lumens include: irrigation solution. d. Intermittent flow of irrigation solution and 18. Answer A. When preparing for continuous bladder irrigation, a triple-lumen indwelling urinary catheter is inserted. The three lumens provide for balloon inflation and continuous inflow and outflow of irrigation solution. prevention of hemorrhage. 19. Nurse Claudine is reviewing a client’s a. Fluid intake should be double the urine output. fluid intake and output record. Fluid intake b. Fluid intake should be approximately equal to and urine output should relate in which way? the urine output. c. Fluid intake should be half the urine output. d. Fluid intake should be inversely proportional to 19. Answer B. Normally, fluid intake is approximately equal to the urine output. Any other relationship signals an abnormality. For example, fluid intake that is double the urine output indicates fluid retention; fluid intake that is half the urine output indicates dehydration. Normally, fluid intake isn’t inversely proportional to the urine output. the urine output. 20. After trying to conceive for a year, a a. Chickenpox couple consults an infertility specialist. Wheb. Measles obtaining a history from the husband, nurse Mumps Jenny inquires about childhood infectious d. Scarlet fever 20. Answer C. Mumps is the most significant childhood infectious disease affecting male fertility. Chickenpox, measles, and scarlet fever don’t affect male fertility. diseases. Which childhood infectious disease most significantly affects male fertility? 21. A male client comes to the emergency a. Kidney department complaining of sudden onset of b. Ureter sharp, severe pain in the lumbar region, which Bladder radiates around the side and toward the d. Urethra 21. Answer A. The most common site of renal calculi formation is the kidney. Calculi may travel down the urinary tract with or without causing damage and may lodge anywhere along the tract or may stay within the kidney. The ureter, bladder, and urethra are less common sites of renal calculi formation. bladder. The client also reports nausea and vomiting and appears pale, diaphoretic, and anxious. The physician tentatively diagnoses renal calculi and orders flat-plate abdominal X-rays. Renal calculi can form anywhere in the urinary tract. What is their most common formation site? 22. A female client with acute renal failurea. confusion, headache, and seizures. undergoing dialysis for the first time. The b. acute bone pain and confusion. 22. Answer A. Dialysis equilibrium syndrome causes confusion, a decreasing level of nurse in charge monitors the client closely f c. weakness, tingling, and cardiac arrhythmias. dialysis equilibrium syndrome, a complicatiod. hypotension, tachycardia, and tachypnea. consciousness, headache, and seizures. These findings, which may last several days, probably result from a relative excess of interstitial or intracellular solutes caused by rapid solute removal from the blood. The resultant organ swelling interferes with normal physiologic functions. To prevent this syndrome, many dialysis centers keep first-time sessions short and use a reduced blood flow rate. Acute bone pain and confusion are associated with aluminum intoxication, another potential complication of dialysis. Weakness, tingling, and cardiac arrhythmias suggest hyperkalemia, which is associated with renal failure. Hypotension, tachycardia, and tachypnea signal hemorrhage, another dialysis complication. that is most common during the first few dialysis sessions. Typically, dialysis equilibrium syndrome causes: 23. Dr. Marquez prescribes norfloxacin a. 3 to 5 days. (Noroxin), 400 mg P.O. twice daily, for a b. 7 to 10 days. client with a urinary tract infection (UTI). The 12 to 14 days. client asks the nurse how long to continue d. 10 to 21 days. 23. Answer B. For an uncomplicated UTI, norfloxacin therapy usually lasts 7 to 10 days. Taking the drug for less than 7 days wouldn’t eradicate such an infection. Taking it for more than 10 days isn’t necessary. Only a client with a complicated UTI must take norfloxacin for 10 to 21 days. taking the drug. For an uncomplicated UTI, the usual duration of norfloxacin therapy is: 24. Nurse Joy is providing postprocedure a. limit oral fluid intake for 1 to 2 weeks. care for a client who underwent percutaneou b. report the presence of fine, sandlike particles lithotripsy. In this procedure, an ultrasonic through the nephrostomy tube. probe inserted through a nephrostomy tube c. notify the physician about cloudy or into the renal pelvis generates ultra– foulsmelling urine. highfrequency sound waves to shatter renal d. report bright pink urine within 24 hours after the 24. Answer C. The client should report the presence of foul-smelling or cloudy urine. Unless contraindicated, the client should be instructed to drink large quantities of fluid each day to flush the kidneys. Sandlike debris is normal due to residual stone products. Hematuria is common after lithotripsy. calculi. The nurse should instruct the client to: procedure. 25. A client is frustrated and embarrassed ba. Establishing a predetermined fluid intake pattern urinary incontinence. Which of the following for the client measures should nurse Bea include in a b. Encouraging the client to increase the time bladder retraining program? between voidings c. Restricting fluid intake to reduce the need to 25. Answer D. The guidelines for initiating bladder retraining include assessing the client’s intake patterns, voiding patterns, and reasons for each accidental voiding. Lowering the client’s fluid intake won’t reduce or prevent incontinence. The client should actually be encouraged to drink 1.5 to 2 L of void d. Assessing present elimination patterns water per day. A voiding schedule should be established after assessment. 1. After having transurethral resection of tha. The urine in the drainage bag appears red to prostate (TURP), a Mr. Locke returns to the pink. unit with a three-way indwelling urinary b. The client reports bladder spasms and the urge catheter and continuous closed bladder to void. irrigation. Which finding suggests that the c. The normal saline irrigant is infusing at a rate of client’s catheter is occluded? 50 drops/minute. d. About 1,000 ml of irrigant have been instilled; 1. Answer B. Reports of bladder spasms and the urge to void suggest that a blood clot may be occluding the catheter. After TURP, urine normally appears red to pink, and normal saline irrigant usually is infused at a rate of 40 to 60 drops/minute or according to facility protocol. The amount of returned fluid (1,200 ml) should correspond to the amount of instilled fluid, plus the client’s urine output (1,000 ml + 200 ml), which reflects catheter patency. 1,200 ml of drainage have been returned. 2. Nurse Myrna is inserting a urinary a. initiate a stream of urine. catheter into a client who is extremely b. breathe deeply. anxious about the procedure. The nurse can turn to the side. facilitate the insertion by asking the client tod. hold the labia or shaft of penis. 2. Answer B. When inserting a urinary catheter, facilitate insertion by asking the client to breathe deeply. Doing this will relax the urinary sphincter. Initiating a stream of urine isn’t recommended during catheter insertion. Turning to the side or holding the labia or penis won’t ease insertion, and doing so may contaminate the sterile field. 3. A female adult client admitted with a a. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level of 22 mg/dl gunshot wound to the abdomen is transferredb. Serum creatinine level of 1.2 mg/dl to the intensive care unit after an exploratoryc. Serum creatinine level of 1.2 mg/dl laparotomy. Which assessment finding d. Urine output of 400 ml/24 hours 3. Answer D. ARF, characterized by abrupt loss of kidney function, commonly causes oliguria, which is demonstrated by a urine output of 400 ml/24 hours. A serum creatinine level of 1.2 mg/dl isn’t diagnostic of ARF. A BUN level of 22 mg/dl or a temperature of 100.2° F (37.8° C) wouldn’t result from this disorder. suggests that the client is experiencing acute renal failure (ARF)? 4. A 55-year old client with benign prostat a. Transurethral resection of the prostate hyperplasia doesn’t respond to medical (TURP) treatment and is admitted to the facility for b. Suprapubic prostatectomy prostate gland removal. Before providing Retropubic prostatectomy preoperative and postoperative instructions td. Transurethral laser incision of the prostate 4. Answer A. TURP is the most widely used procedure for prostate gland removal. Because it requires no incision, TURP is especially suitable for men with relatively minor prostatic enlargements and for those who are poor surgical risks. Suprapubic prostatectomy, retropubic prostatectomy, and transurethral laser incision of the prostate are less common procedures; they all require an incision. the client, nurse Gail asks the surgeon which prostatectomy procedure will be done. What is the most widely used procedure for prostate gland removal? 5. A female client with suspected renal a. Cystic fibrosis dysfunction is scheduled for excretory b. Multiple myeloma urography. Nurse July reviews the history for Gout conditions that may warrant changes in cliend. Myasthenia gravis 5. Answer B. Fluid depletion before excretory urography is contraindicated in clients with multiple myeloma, severe diabetes mellitus, and uric acid nephropathy — conditions that can seriously compromise renal function in fluid-depleted clients with reduced renal perfusion. If these clients must undergo excretory urography, they should be well hydrated before the test. Cystic fibrosis, gout, and myasthenia gravis don’t necessitate changes in client preparation for excretory urography. preparation. Normally, a client should be mildly hypovolemic (fluid depleted) before excretory urography. Which history finding would call for the client to be well hydrated instead? 6. Nurse Kim is caring for a client who ha a. Encouraging intake of at least 2 L of fluid daily a cerebrovascular accident (CVA). Which b. Giving the client a glass of soda before bedtime nursing intervention promotes urinary c. Taking the client to the bathroom twice per day continence? d. Consulting with a dietitian 6. Answer A. By encouraging a daily fluid intake of at least 2 L, the nurse helps fill the client’s bladder, thereby promoting bladder retraining by stimulating the urge to void. The nurse shouldn’t give the client soda before bedtime; soda acts as a diuretic and may make the client incontinent. The nurse should take the client to the bathroom or offer the bedpan at least every 2 hours throughout the day; twice per day is insufficient. Consultation with a dietitian won’t address the problem of urinary incontinence. 7. When examining a female client’s a. A flat sound genitourinary system, nurse Sally assesses fb. A dull sound tenderness at the costovertebral angle by Hyperresonance placing the left hand over this area and d. Tympany 7. Answer B. Percussion over the costovertebral angle normally produces a dull, thudding sound, which is soft to moderately loud with a moderate pitch and duration. This sound occurs over less dense, mostly fluid-filled matter, such as the kidneys, liver, and spleen. In contrast, a flat sound occurs over highly dense matter such as muscle; hyperresonance occurs over the air-filled, overinflated lungs of a client with pulmonary emphysema or the lungs of a child (because of a thin chest wall); and tympany occurs over enclosed structures containing air, such as the stomach and bowel. striking it with the right fist. Normally, this percussion technique produces which sound? 8. A male client with chronic renal failure a. Blood pressure has a serum potassium level of 6.8 mEq/L. b. Respirations 8. Answer D. An elevated serum potassium level may lead to a life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia, What should nurse Olivia assess first? Temperature d. Pulse which the nurse can detect immediately by palpating the pulse. The client’s blood pressure may change, but only as a result of the arrhythmia. Therefore, the nurse should assess blood pressure later. The nurse also can delay assessing respirations and temperature because these aren’t affected by the serum potassium level. 9. Nurse Hazel is ware that the following ia. Ineffective tissue perfusion an appropriate nursing diagnosis for a client b. Functional urinary incontinence with renal calculi? Risk for infection d. Decreased cardiac output 9. Answer C. Infection can occur with renal calculi from urine stasis caused by obstruction. Options A and D aren’t appropriate for this diagnosis, and retention of urine usually occurs, rather than incontinence. 10. A male client develops acute renal a. cardiac arrhythmia. failure (ARF) after receiving I.V. therapy wib. paresthesia. a nephrotoxic antibiotic. Because the client’s dehydration. 24-hour urine output totals 240 ml, nurse d. pruritus. 10. Answer A. As urine output decreases, the serum potassium level rises; if it rises sufficiently, hyperkalemia may occur, possibly triggering a cardiac arrhythmia. Hyperkalemia doesn’t cause paresthesia (sensations of numbness and tingling). Dehydration doesn’t occur during this oliguric phase of ARF, although typically it does arise during the diuretic phase. In a client with ARF, pruritus results from increased phosphates and isn’t associated with hyperkalemia. Andy suspects that the client is at risk for: 11. After undergoing transurethral resectio a. Increase the I.V. flow rate. of the prostate to treat benign prostatic b. Notify the physician immediately. hyperplasia, a male client returns to the roomc. Assess the irrigation catheter for patency and with continuous bladder irrigation. On the drainage. first day after surgery, the client reports d. Administer meperidine (Demerol), 50 mg I.M., 11. Answer C. Although postoperative pain is expected, the nurse should make sure that other factors, such as an obstructed irrigation catheter, aren’t the cause of the pain. After assessing catheter patency, the nurse should administer an analgesic, such as meperidine, as prescribed. Increasing the I.V. flow rate may worsen the pain. Notifying the physician isn’t necessary unless the pain is severe or unrelieved by the prescribed medication. bladder pain. What should nurse Andrew do first? as prescribed. 12. When performing a scrotal examinatio a. Notify the physician. nurse Paul finds a nodule. What should the b. Change the client’s position and repeat the nurse do next? examination. c. Perform a rectal examination. d. Transilluminate the scrotum. 12. Answer D. A nurse who discovers a nodule, swelling, or other abnormal finding during a scrotal examination should transilluminate the scrotum by darkening the room and shining a flashlight through the scrotum behind the mass. A scrotum filled with serous fluid transilluminates as a red glow; a more solid lesion, such as a hematoma or mass, doesn’t transilluminate and may appear as a dark shadow. Although the nurse should notify the physician of the abnormal finding, performing transillumination first provides additional information. The nurse can’t uncover more information about a scrotal mass by changing the client’s position and repeating the examination or by performing a rectal examination. 13. A male client who has been treated fora. “Be sure to eat meat at every meal.” chronic renal failure (CRF) is ready forb. “Monitor your fruit intake, and eat plenty of discharge. Nurse Bea should reinforce which bananas.” dietary instruction? c. “Increase your carbohydrate intake.” d. “Drink plenty of fluids, and use a salt 13. Answer C. In a client with CRF, unrestricted intake of sodium, protein, potassium, and fluid may lead to a dangerous accumulation of electrolytes and protein metabolic products, such as amino acids and ammonia. Therefore, the client must limit intake of sodium; meat, which is high in protein; bananas, which are high in potassium; and fluid, because the failing kidneys can’t secrete adequate urine. Salt substitutes are high in potassium and should be avoided. Extra carbohydrates are needed to prevent protein catabolism. substitute.” 14. Nurse Wayne is aware that the followina. Urinary incontinence is a normal part of aging. statements describing urinary incontinence i b. Urinary incontinence isn’t a disease. the elderly is true? c. Urinary incontinence in the elderly can’t be treated. d. Urinary incontinence is a disease. 14. Answer B. Urinary incontinence isn’t a normal part of aging nor is it a disease. It may be caused by confusion, dehydration, fecal impaction, restricted mobility, or other causes. Certain medications, including diuretics, hypnotics, sedatives, anticholinergics, and antihypertensives, may trigger urinary incontinence. Most clients with urinary incontinence can be treated; some can be cured. 15. The client underwent a transurethral a. Tell the client to try to urinate around the resection of the prostate gland 24 hours ago catheter to remove blood clots. and is on continuous bladder irrigation. Nurs b. Restrict fluids to prevent the client’s bladder Yoly is aware that the following nursing from becoming distended. interventions is appropriate? c. Prepare to remove the catheter. d. Use aseptic technique when irrigating the 15. Answer D. If the catheter is blocked by blood clots, it may be irrigated according to physician’s orders or facility protocol. The nurse should use sterile technique to reduce the risk of infection. Urinating around the catheter can cause painful bladder spasms. Encourage the client to drink fluids to dilute the urine and maintain urine output. The catheter remains in place for 2 to 4 days after surgery catheter. and is only removed with a physician’s order. 16. A female client with a urinary tract a. “Take the medication with food.” infection is prescribed co-trimoxazole b. “Drink at least eight 8-oz glasses of fluid daily.” (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole). Nurse Do c. “Avoid taking antacids during cotrimoxazole should provide which medication instruction? therapy.” d. “Don’t be afraid to go out in the sun.” 16. Answer B. When receiving a sulfonamide such as co-trimoxazole, the client should drink at least eight 8-oz glasses of fluid daily to maintain a urine output of at least 1,500 ml/day. Otherwise, inadequate urine output may lead to crystalluria or tubular deposits. For maximum absorption, the client should take this drug at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals. No evidence indicates that antacids interfere with the effects of sulfonamides. To prevent a photosensitivity reaction, the client should avoid direct sunlight during co-trimoxazole therapy. 17. A male client is admitted for treatment a. generalized edema, especially of the face and glomerulonephritis. On initial assessment, periorbital area. Nurse Rose detects one of the classic signs o b. green-tinged urine. acute glomerulonephritis of sudden onset. c. moderate to severe hypotension. Such signs include: d. polyuria. 17. Answer A. Generalized edema, especially of the face and periorbital area, is a classic sign of acute glomerulonephritis of sudden onset. Other classic signs and symptoms of this disorder include hematuria (not green-tinged urine), proteinuria, fever, chills, weakness, pallor, anorexia, nausea, and vomiting. The client also may have moderate to severe hypertension (not hypotension), oliguria or anuria (not polyuria), headache, reduced visual acuity, and abdominal or flank pain. 18. A client reports experiencing vulvar a. Cottage cheese–like discharge pruritus. Which assessment factor may b. Yellow-green discharge indicate that the client has an infection caused Gray-white discharge by Candida albicans? d. Discharge with a fishy odor 18. Answer A. The symptoms of C. albicans include itching and a scant white discharge that has the consistency of cottage cheese. Yellow-green discharge is a sign of Trichomonas vaginalis. Graywhite discharge and a fishy odor are signs of Gardnerella vaginalis. 19. A 24-year old female client has just been diagnosed with condylomata acuminata (genital warts). What information is appropriate to tell this client? a. This condition puts her at a higher risk for cervical cancer; therefore, she should have a Papanicolaou (Pap) smear annually. b. The most common treatment is metronidazole (Flagyl), which should eradicate the problem within 7 to 10 days. c. The potential for transmission to her sexual partner will be eliminated if condoms are used 19. Answer A. Women with condylomata acuminata are at risk for cancer of the cervix and vulva. Yearly Pap smears are very important for early detection. Because condylomata acuminata is a virus, there is no permanent cure. Because condylomata acuminata can occur on the vulva, a condom won’t protect sexual partners. HPV can be transmitted to other parts of the body, such as the every time they have sexual intercourse. d. The human papillomavirus (HPV), which causes condylomata acuminata, can’t be transmitted during oral sex. mouth, oropharynx, and larynx. 20. Nurse Vic is monitoring the fluid intak a. Maintaining a closed indwelling urinary catheter and output of a female client recovering from system and securing the catheter to the leg an exploratory laparotomy. Which nursing b. Limiting fluid intake to 1 L/day intervention would help the client avoid a c. Encouraging the client to use a feminine urinary tract infection (UTI)? deodorant after bathing d. Encouraging the client to douche once a day 20. Answer A. Maintaining a closed indwelling urinary catheter system helps prevent introduction of bacteria; securing the catheter to the client’s leg also decreases the risk of infection by helping to prevent urethral trauma. To flush bacteria from the urinary tract, the nurse should encourage the client to drink at least 10 glasses of fluid daily, if possible. Douching and feminine deodorants may irritate the urinary tract and should be discouraged. after removal of the indwelling urinary catheter 21. Nurse Eve is caring for a client who ha a. Encouraging intake of at least 2 L of fluid daily a cerebrovascular accident (CVA). Which b. Giving the client a glass of soda before bedtime nursing intervention promotes urinary c. Taking the client to the bathroom twice per day continence? d. Consulting with a dietitian 21. Answer A. By encouraging a daily fluid intake of at least 2 L, the nurse helps fill the client’s bladder, thereby promoting bladder retraining by stimulating the urge to void. The nurse shouldn’t give the client soda before bedtime; soda acts as a diuretic and may make the client incontinent. The nurse should take the client to the bathroom or offer the bedpan at least every 2 hours throughout the day; twice per day is insufficient. Consultation with a dietitian won’t address the problem of urinary incontinence. 22. A female client with an indwelling a. disconnecting the tubing from the urinary urinary catheter is suspected of having a catheter and letting the urine flow into a sterile urinary tract infection. Nurse Angel should container. collect a urine specimen for culture and b. wiping the self-sealing aspiration port with sensitivity by: antiseptic solution and aspirating urine with a sterile needle. c. draining urine from the drainage bag into a sterile container. d. clamping the tubing for 60 minutes and inserting 22. Answer B. Most catheters have a self-sealing port for obtaining a urine specimen. Antiseptic solution is used to reduce the risk of introducing microorganisms into the catheter. Tubing shouldn’t be disconnected from the urinary catheter. Any break in the closed urine drainage system may allow the entry of microorganisms. Urine in urine drainage bags may not be fresh and may contain bacteria, giving false test results. When there is no urine in the tubing, the catheter may be clamped for no more than 30 minutes to allow urine to collect. a sterile needle into the tubing above the clamp to aspirate urine. 23. Nurse Grace is assessing a male client a. Rashes on the palms of the hands and soles 23. Answer D. Symptoms of gonorrhea in men diagnosed with gonorrhea. Which symptom of the feet include purulent, foul-smelling drainage from the penis and painful urination. Rashes on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet are symptoms of the secondary stage of syphilis. Cauliflower-like warts on the penis are a sign of human papillomavirus. Painful red papules on the shaft of the penis may be a sign of the first stage of genital herpes. most likely prompted the client to seek b. Cauliflower-like warts on the penis medical attention? Painful red papules on the shaft of the penis d. Foul-smelling discharge from the penis 24. Nurse Ethel is planning to administer a a. retain the enema for 30 minutes to allow for sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) sodium exchange; afterward, the client should enema to a client with a potassium level of have diarrhea. 5.9 mEq/L. Correct administration and the b. retain the enema for 30 minutes to allow for effects of this enema would include having glucose exchange; afterward, the client should the client: have diarrhea. c. retain the enema for 60 minutes to allow for sodium exchange; diarrhea isn’t necessary to reduce the potassium level. d. retain the enema for 60 minutes to allow for 24. Answer A. Kayexalate is a sodium exchange resin. Thus the client will gain sodium as potassium is lost in the bowel. For the exchange to occur, Kayexalate must be in contact with the bowel for at least 30 minutes. Sorbitol in the Kayexalate enema causes diarrhea, which increases potassium loss and decreases the potential for Kayexalate retention. glucose exchange; diarrhea isn’t necessary to reduce the potassium level. 25. When caring for a male client with acua. acetaminophen (Tylenol) renal failure (ARF), Nurse Fatima expects t b. gentamicin sulfate (Garamycin) adjust the dosage or dosing schedule of cyclosporine (Sandimmune) certain drugs. Which of the following drugs d. ticarcillin disodium (Ticar) 25. Answer A. Because acetaminophen is metabolized in the liver, its dosage and dosing schedule need not be adjusted for a client with ARF. In contrast, the dosages and schedules for gentamicin and ticarcillin, which are metabolized and excreted by the kidney, should be adjusted. Because cyclosporine may cause nephrotoxicity, the nurse must monitor both the dosage and blood drug level in a client receiving this drug. would not require such adjustment? SKIN AND INTEGUMENTARY DISEASES 1. When planning care for a male client with burns on the upper torso, which nursing diagnosis should take the highest priority? a. Ineffective airway clearance related to edema of the respiratory passages b. Impaired physical mobility related to the disease process c. Disturbed sleep pattern related to facility environment d. Risk for infection related to breaks in the skin life-threatening problems. 2. In a female client with burns on the legs,a. Applying knee splints which nursing intervention helps prevent b. Elevating the foot of the bed contractures? c. Hyperextending the client’s palms d. Performing shoulder range-of-motion exercises 2. Answer A. Applying knee splints prevents leg contractures by holding the joints in a position of function. Elevating the foot of the bed can’t prevent contractures because this action doesn’t hold the joints in a position of function. Hyperextending a body part for an extended time is inappropriate because it can cause contractures. Performing shoulder range-of-motion exercises can prevent contractures in the shoulders, but not in the legs. 3. A male client comes to the physician’s a. “Minimize sun exposure from 1 to 4 p.m. when office for treatment of severe sunburn. The the sun is strongest.” nurse takes this opportunity to discuss the b. “Use a sunscreen with a sun protection factor of importance of protecting the skin from the 6 or higher.” sun’s damaging rays. Which instruction would best prevent skin damage? c. “Apply sunscreen even on overcast days.” d. “When at the beach, sit in the shade to prevent 3. Answer C. Sunscreen should be applied even on overcast days, because the sun’s rays are as damaging then as on sunny days. The sun is strongest from 10 a.m. to 2 p.m. (11 a.m. to 3 p.m. daylight saving time) — not from 1 to 4 p.m. Sun exposure should be minimized during these hours. The nurse should recommend sunscreen with a sun protection factor of at least 15. Sitting in the shade when at the beach doesn’t guarantee protection against sunburn because sand, concrete, and water can reflect more than half the sun’s rays onto the skin. sunburn.” 4. A female client is brought to the emergency department with second- and third-degree burns on the left arm, left anterior leg, and anterior trunk. Using the a. b. d. 18% 27% 30% 36% 4. Answer D. The Rule of Nines divides body surface area into percentages that, when totaled, equal 100%. According to the Rule of Nines, the arms account for 9% each, the anterior legs account for 9% each, and the anterior trunk accounts for 18%. Therefore, this client’s burns cover 36% of the body surface area. Rule of Nines, what is the total body surface area that has been burned? 5. Which nursing intervention can help a client maintain healthy skin? a. b. Keep the client well hydrated. Avoid bathing the client with mild soap. Remove adhesive tape quickly from the 5. Answer A. Keeping the client well hydrated helps prevent skin cracking and infection because intact healthy skin is the body’s first line of defense. skin. d. Recommend wearing tight-fitting clothes in hot weather. To help a client maintain healthy skin, the nurse should avoid strong or harsh detergents and should use mild soap. The nurse shouldn’t remove adhesive tape quickly because this action can strip or scrape the skin. The nurse should recommend wearing loose-fitting — not tight-fitting — clothes in hot weather to promote heat loss by evaporation. 6. A male client with psoriasis visits the a. Scale dermatology clinic. When inspecting the b. Crust affected areas, the nurse expects to see which Ulcer type of secondary lesion? d. Scar 6. Answer A. A scale is the characteristic secondary lesion occurring in psoriasis. Although crusts, ulcers, and scars also are secondary lesions in skin disorders, they don’t accompany psoriasis. 7. A female adult client with atopic a. Related to potential interactions between the dermatitis is prescribed a potent topical topical corticosteroid and other prescribed drugs corticosteroid, to be covered with an b. Related to vasodilatory effects of the topical occlusive dressing. To address a potential corticosteroid client problem associated with this treatment c. Related to percutaneous absorption of the the nurse formulates the nursing diagnosis of topical corticosteroid Risk for injury. To complete the nursing d. Related to topical corticosteroid application to 7. Answer C. A potent topical corticosteroid may increase the client’s risk for injury because it may be absorbed percutaneously, causing the same adverse effects as systemic corticosteroids. Topical corticosteroids aren’t involved in significant drug interactions. These preparations cause vasoconstriction, not vasodilation. A potent topical corticosteroid rarely is prescribed for use on the face, neck, or intertriginous sites because application on these areas may lead to increased adverse effects. diagnosis statement, the nurse should add which “related-to” phrase? the face, neck, and intertriginous sites 8. A male client is diagnosed with herpes a. During early pregnancy, herpes simplex simplex. Which statement about herpes infection may cause spontaneous abortion or simplex infection is true? premature delivery. b. Genital herpes simplex lesions are painless, fluid-filled vesicles that ulcerate and heal in 3 to 7 days c. Herpetic keratoconjunctivitis usually is bilateral and causes systemic symptoms. d. A client with genital herpes lesions can have 8. Answer A. Herpes simplex may be passed to the fetus transplacentally and, during early pregnancy, may cause spontaneous abortion or premature delivery. Genital herpes simplex lesions typically are painful, fluid-filled vesicles that ulcerate and heal within 1 to 2 weeks. Herpetic keratoconjunctivitis usually is unilateral and causes localized symptoms, such as conjunctivitis. A client with genital herpes lesions should avoid all sexual contact to prevent spreading the disease. sexual contact but must use a condom. 9. A female client with a severe a. Aplastic anemia 9. Answer B. The most significant adverse staphylococcal infection is receiving the b. Ototoxicity aminoglycoside gentamicin sulfate Cardiac arrhythmias (Garamycin) by the I.V. route. The nurse d. Seizures reactions to gentamicin and other aminoglycosides are ototoxicity (indicated by vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss) and nephrotoxicity (indicated by urinary cells or casts, oliguria, proteinuria, and reduced creatinine clearance). These adverse reactions are most common in elderly and dehydrated clients, those with renal impairment, and those receiving concomitant therapy with another potentially ototoxic or nephrotoxic drug. Gentamicin isn’t associated with aplastic anemia, cardiac arrhythmias, or seizures. should assess the client for which adverse reaction to this drug? 10. A male client is diagnosed with primar a. “Apply one applicator of terconazole herpes genitalis. Which instruction should the intravaginally at bedtime for 7 days.” nurse provide? b. “Apply one applicator of tioconazole intravaginally at bedtime for 7 days.” c. “Apply acyclovir ointment to the lesions every 3 hours, six times a day for 7 days.” d. “Apply sulconazole nitrate twice daily by 10. Answer C. A client with primary herpes genitalis should apply topical acyclovir ointment in sufficient quantities to cover the lesions every 3 hours, six times a day for 7 days. Terconazole and tioconazole are used to treat vulvovaginal candidiasis. Sulconazole nitrate is used to treat tinea versicolor. massaging it gently into the lesions.” 11. Nurse Bea plans to administer a. With a circular motion, to enhance absorption dexamethasone cream to a client who has b. With an upward motion, to increase blood dermatitis over the anterior chest How should supply to the affected area the nurse apply this topical agent? c. In long, even, outward, and downward strokes in the direction of hair growth d. In long, even, outward, and upward strokes in 11. Answer C. When applying a topical agent, the nurse should begin at the midline and use long, even, outward, and downward strokes in the direction of hair growth. This application pattern reduces the risk of follicle irritation and skin inflammation. the direction opposite hair growth 12. Nurse Meredith is caring for a a. Polyurethane foam mattress wheelchair-bound client. Which piece of b. Ring or donut equipment impedes circulation to the area it’s Gel flotation pad meant to protect? d. Water bed 12. Answer B. Rings or donuts aren’t to be used because they restrict circulation. Foam mattresses evenly distribute pressure. Gel pads redistribute with the client’s weight. The water bed also distributes pressure over the entire surface. 13. Nurse Rudolf documents the presence a. Inflammatory a scab on a client’s deep wound. The nurse b. Migratory 13. Answer B. The scab formation is found in the migratory phase. It is accompanied by migration of identifies this as which phase of wound Proliferative healing? d. Maturation epithelial cells, synthesis of scar tissue by fibroblasts, and development of new cells that grow across the wound. In the inflammatory phase, a blood clot forms, epidermis thickens, and an inflammatory reaction occurs in the subcutaneous tissue. During the proliferative phase, the actions of the migratory phase continue and intensify, and granulation tissue fills the wound. In the maturation phase, cells and vessels return to normal and the scab sloughs off. 14. In an industrial accident, a male client a. A urine output consistently above 100 ml/hour that weighs 155 lb (70 kg) sustained b. A weight gain of 4 lb (2 kg) in 24 hours fullthickness burns over 40% of his body. Hec. Body temperature readings all within normal in the burn unit receiving fluid resuscitation. limits Which observation shows that the fluid d. An electrocardiogram (ECG) showing no 14. Answer A. In a client with burns, the goal of fluid resuscitation is to maintain a mean arterial blood pressure that provides adequate perfusion of vital structures. If the kidneys are adequately perfused, they will produce an acceptable urine output of at least 0.5 ml/kg/hour. Thus, the expected urine output of a 155-lb client is 35 ml/hour, and a urine output consistently above 100 ml/hour is more than adequate. Weight gain from fluid resuscitation isn’t a goal. In fact, a 4-lb weight gain in 24 hours suggests third spacing. Body temperature readings and ECG interpretations may demonstrate secondary benefits of fluid resuscitation but aren’t primary indicators. resuscitation is benefiting the client? arrhythmias 15. A female client with herpes zoster is a. palpitations. prescribed acyclovir (Zovirax), 200 mg P.O. b. dizziness. every 4 hours while awake. The nurse should diarrhea. inform the client that this drug may cause: d. metallic taste. 15. Answer C. Oral acyclovir may cause such adverse GI effects as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. It isn’t associated with palpitations, dizziness, or a metallic taste. 16. A female client sees a dermatologist f a. palpitations. skin problem. Later, the nurse reviews the b. dizziness. client’s chart and notes that the chief diarrhea. complaint was intertrigo. This term refers to d. metallic taste. 16. Answer D. Intertrigo refers to irritation of opposing skin surfaces caused by friction. Spontaneously occurring wheals occur in hives. A fungus that enters the skin surface and causes infection is a dermatophyte. Inflammation of a hair which condition? follicle is called folliculitis. 17. A male client who has suffered a a. turn him frequently. cerebrovascular accident (CVA) is too weak b. perform passive range-of-motion (ROM) to move on his own. To help the client avoid exercises. pressure ulcers, the nurse should: c. reduce the client’s fluid intake. d. encourage the client to use a footboard. 17. Answer A. The most important intervention to prevent pressure ulcers is frequent position changes, which relieve pressure on the skin and underlying tissues. If pressure isn’t relieved, capillaries become occluded, reducing circulation and oxygenation of the tissues and resulting in cell death and ulcer formation. During passive ROM exercises, the nurse moves each joint through its range of movement, which improves joint mobility and circulation to the affected area but doesn’t prevent pressure ulcers. Adequate hydration is necessary to maintain healthy skin and ensure tissue repair. A footboard prevents plantar flexion and footdrop by maintaining the foot in a dorsiflexed position. 18. A male client visits the physician’s a. an I.V. corticosteroid. office for treatment of a skin disorder. As a b. an I.V. antibiotic. primary treatment, the nurse expects the an oral antibiotic. physician to prescribe: d. a topical agent. 18. Answer D. Although many drugs are used to treat skin disorders, topical agents — not I.V. or oral agents — are the mainstay of treatment. 19. While in a skilled nursing facility, a a. “All family members will need to be treated.” male client contracted scabies, which is b. “If someone develops symptoms, tell him to see diagnosed the day after discharge. The client a physician right away.” is living at her daughter’s home, where six other persons are living. During her visit to c. “Just be careful not to share linens and towels the clinic, she asks a staff nurse, “What with family members.” should my family do?” The most accurate d. “After you’re treated, family members won’t be 19. Answer A. When someone in a group of persons sharing a home contracts scabies, each individual in the home needs prompt treatment whether he’s symptomatic or not. Towels and linens should be washed in hot water. Scabies can be transmitted from one person to another before symptoms develop. response from the nurse is: at risk for contracting scabies.” 20. When caring for a male client with a. Placing mitts on the client’s hands severe impetigo, the nurse should include b. Administering systemic antibiotics as which intervention in the plan of care? prescribed c. Applying topical antibiotics as prescribed d. Continuing to administer antibiotics for 21 20. Answer B. Impetigo is a contagious, superficial skin infection caused by beta-hemolytic streptococci. If the condition is severe, the physician typically prescribes systemic antibiotics for 7 to 10 days to prevent glomerulonephritis, a dangerous days as prescribed complication. The client’s nails should be kept trimmed to avoid scratching; however, mitts aren’t necessary. Topical antibiotics are less effective than systemic antibiotics in treating impetigo. 21. A female client with second- and a. dislodge the autografts. thirddegree burns on the arms receives b. increase edema in the arms. autografts. Two days later, the nurse finds the increase the amount of scarring. client doing arm exercises. The nurse knowsd. decrease circulation to the fingers. 21. Answer A. Because exercising the autograft sites may dislodge the grafted tissue, the nurse should advise the client to keep the grafted extremity in a neutral position. None of the other options results from exercise that this client should avoid exercise because it may: 22. Nurse Troy discovers scabies when a. dislodge the autografts. assessing a client who has just been b. increase edema in the arms. transferred to the medical-surgical unit from increase the amount of scarring. the day surgery unit. To prevent scabies d. decrease circulation to the fingers. 22. Answer B. To prevent the spread of scabies in other hospitalized clients, the nurse should isolate the client’s bed linens until the client is no longer infectious — usually 24 hours after treatment begins. Other required precautions include using good handwashing technique and wearing gloves when applying the pediculicide and during all contact with the client. Although the nurse should notify the nurse in the day surgery unit of the client’s condition, a scabies epidemic is unlikely because scabies is spread through skin or sexual contact. This client doesn’t require enteric precautions because the mites aren’t found on feces. infection in other clients, the nurse should: 23. Dr. Smith prescribes an emollient for a a. “This makes the skin feel soft.” client with pruritus of recent onset. The clienb. “This prevents evaporation of water from the asks why the emollient should be applied hydrated epidermis.” immediately after a bath or shower. How should the nurse respond? c. “This minimizes cracking of the dermis.” d. “This prevents inflammation of the skin.” 23. Answer B. Applying an emollient immediately after taking a bath or shower prevents evaporation of water from the hydrated epidermis, the skin’s upper layer. Although emollients make the skin feel soft, this effect occurs whether or not the client has just bathed or showered. An emollient minimizes cracking of the epidermis, not the dermis (the layer beneath the epidermis). An emollient doesn’t prevent skin inflammation. 24. Following a full-thickness (third-degrea. range of motion. burn of his left arm, a female client is treate b. protein intake. with artificial skin. The client understands going outdoors. postoperative care of artificial skin when he d. fluid ingestion. 24. Answer A. To prevent disruption of the artificial skin’s adherence to the wound bed, the client should restrict range of motion of the involved limb. Protein intake and fluid intake are important for healing and regeneration and shouldn’t be restricted. Going outdoors is acceptable as long as the left arm is protected from direct sunlight. states that during the first 7 days after the procedure, he will restrict: 25. A male client with a solar burn of the a. fluid resuscitation. chest, back, face, and arms is seen in urgent b. infection. care. The nurse’s primary concern should be: body image. d. pain management. 25. Answer D. With a superficial partial thickness burn such as a solar burn (sunburn), the nurse’s main concern is pain management. Fluid resuscitation and infection become concerns if the burn extends to the dermal and subcutaneous skin layers. Body image disturbance is a concern that has lower priority than pain management. 26. The nurse is providing home care a. use cosmetic camouflage techniques. instructions to a client who has recently had b. protect the graft from direct sunlight. skin graft. It’s most important that the client continue physical therapy. remember to: d. apply lubricating lotion to the graft site. 26. Answer B. To avoid burning and sloughing, the client must protect the graft from direct sunlight. The other three interventions are helpful to the client and his recovery but are less important. 27. A male client is diagnosed with a. “Avoid sexual intercourse until you’ve gonorrhea. When teaching the client about this completed treatment, which takes 14 to 21 disease, the nurse should include which days.” instruction? b. “Wash your hands thoroughly to avoid transferring the infection to your eyes.” c. “If you have intercourse before treatment ends, tell sexual partners of your status and have them wash well after intercourse.” d. “If you don’t get treatment, you may develop 27. Answer B. Adults and children with gonorrhea may develop gonococcal conjunctivitis by touching the eyes with contaminated hands. The client should avoid sexual intercourse until treatment is completed, which usually takes 4 to 7 days, and a follow-up culture confirms that the infection has been eradicated. A client who doesn’t refrain from intercourse before treatment is completed should use a condom in addition to informing sex partners of the client’s health status and instructing them to wash well after intercourse. Meningitis and widespread CNS damage are potential complications of untreated syphilis, not gonorrhea. meningitis and suffer widespread central nervous system (CNS) damage.” 28. A female client with atopic dermatitis is a. 4 hours. 28. Answer D. To prevent eye discomfort, the prescribed medication for photochemothera b.. 8 hours. The nurse teaches the client about the 24 hours. importance of protecting the skin from d. 48 hours. client must protect the eyes for 48 hours after taking medication for photochemotherapy. Protecting the eyes for a shorter period increases the risk of eye injury. ultraviolet light before drug administration and for 8 hours afterward and stresses the need to protect the eyes. After administering medication for photochemotherapy, the client must protect the eyes for: 29. A female client with genital herpes a. cancer of the ovaries. simplex is being treated in the outpatient b. cancer of the uterus. department. The nurse teaches her about cancer of the cervix. measures that may prevent herpes recurrenc d. cancer of the vagina. 29. Answer C. A female client with genital herpes simplex is at increased risk for cervical cancer. Genital herpes simplex isn’t a risk factor for cancer of the ovaries, uterus, or vagina. and emphasizes the need for prompt treatment if complications arise. Genital herpes simplex increases the risk of: 30. Which of the following is the initial a. Elevation of the extremity intervention for a male client with external b. Pressure point control bleeding? Direct pressure d. Application of a tourniquet 30. Answer C. Applying direct pressure to an injury is the initial step in controlling bleeding. For severe or arterial bleeding, pressure point control can be used. Pressure points are those areas where large blood vessels can be compressed against bone: femoral, brachial, facial, carotid, and temporal artery sites. Elevation reduces the force of flow, but direct pressure is the first step. A tourniquet may further damage the injured extremity and should be avoided unless all other measures have failed. 1. Nurse Jay is performing wound care. a. Holding sterile objects above the waist Which of the following practices violates b. Considering a 1″ edge around the sterile field as surgical asepsis? being contaminated c. Pouring solution onto a sterile field cloth d. Opening the outermost flap of a sterile package 1. Answer C. Pouring solution onto a sterile field cloth violates surgical asepsis because moisture penetrating the cloth can carry microorganisms to the sterile field via capillary action. The other options are practices that help ensure surgical asepsis. away from the body following? Tobacco use d. Circulatory status respiratory status, vital signs, fluid intake and output, ability to move, bowel sounds, wounds, and mental status. Information about the client’s lifestyle and alcohol and tobacco use may be obtained later when the client’s condition has stabilized. 3. Nurse Kate is changing a dressing and a. Assess the drainage in the dressing. providing wound care. Which activity shoul b. Slowly remove the soiled dressing she perform first? Wash hands thoroughly. d. Put on latex gloves. 3. Answer C. When caring for a client, the nurse must first wash her hands. Putting on gloves, removing the dressing, and observing the drainage are all parts of performing a dressing change after hand washing is completed. 4. Nurse May is caring for an elderly a. Turn and reposition the client at least once every bedridden adult. To prevent pressure ulcers, 8 hours. which intervention should the nurse include ib. Vigorously massage lotion into bony the plan of care? prominences. c. Post a turning schedule at the client’s bedside. d. Slide the client, rather than lifting, when 4. Answer C. A turning schedule with a signing sheet will help ensure that the client gets turned and, thus, help prevent pressure ulcers. Turning should occur every 1 to 2 hours — not every 8 hours — for clients who are in bed for prolonged periods. The nurse should apply lotion to keep the skin moist but should avoid vigorous massage, which could damage capillaries. When moving the client, the nurse should lift — rather than slide — the client to avoid shearing. turning. 5. Nurse Jane formulates a nursing a. Related to fat emboli diagnosis of Impaired physical mobility for b. Related to infection client with third-degree burns on the lower Related to femoral artery occlusion portions of both legs. To complete the nursind. Related to circumferential eschar 5. Answer D. As edema develops on circumferential burns, eschar forms a tight, constricting band, compromising circulation to the extremity distal to the circumferential site and impairing physical mobility. This client isn’t likely to develop fat emboli unless long bone or pelvic fractures are present. Infection doesn’t alter physical mobility. A client with burns on the lower portions of both legs isn’t likely to have femoral artery occlusion. diagnosis statement, the nurse should add which “related-to” phrase? 6. The nurse is assessing for the presence oa. Lips cyanosis in a male dark-skinned client. The b. Sacrum 6. Answer A. In a dark-skinned client, the nurse examines the lips, tongue, nail beds, conjunctivae, nurse understands that which body area would Earlobes provide the best assessment? d. Back of the hands and palms of the hands and soles of the feet at regular intervals for subtle color changes. In a client with cyanosis, the lips and tongue are gray; the palms, soles, conjunctivae, and nail beds have a bluish tinge. 7. Which of the following individuals is leaa. A 32 year-old-African American likely to be at risk of developing psoriasis? b. A woman experiencing menopause c. A client with a family history of the disorder d. An individual who has experienced a significant 7. Answer A. Psoriasis occurs equally among women and men, although the incidence is lower in darker skinned races and ethnic groups. A genetic predisposition has been recognized in some cases. Emotional distress, trauma, systemic illness, seasonal changes, and hormonal changes are linked to exacerbations. amount of emotional distress 8. Which of the following clients would leaa. A client incontinent of urine feces likely be at risk of developing skin b. A client with chronic nutritional deficiencies breakdown? c. A client with decreased sensory perception d. A client who is unable to move about and is 8. Answer C. Bed or chair confinement, inability to move, loss of bowel or bladder control, poor nutrition, absent or inconsistent caregiving, and decreased sensory perception can contribute to the development of skin breakdown. The least likely risk, as presented in the options, is the decreased sensory perception. Options A, B, and D identify physiological conditions, which are the risk priorities. confined to bed 9. The nurse prepares to care for a male a. Cold compress to the affected area client with acute cellulites of the lower leg. b. Warm compress to the affected area The nurse anticipates that which of the c. Intermittent heat lamp treatments four times following will be prescribed for the client? daily d. Alternating hot and cold compresses 9. Answer B. Cellulitis is a skin infection into deeper dermal and subcutaneous tissues that results in a deep red erythema without sharp borders and spreads widely throughout tissue spaces. Warm compresses may be used to decrease the discomfort, erythema, and edema. After tissue and blood cultures are obtained, antibiotics will be initiated. The nurse should provide supportive care as prescribed to manage symptoms such as fatigue, fever, chills, headache, and myalgia. Heat lamps can cause more disruption to already inflamed tissue. Cold compresses and alternating cold and hot compresses continuously are not the best measures. 10. The clinic nurse assesses the skin of a a. Clear, thin nail beds white characteristic is associated with this b. Red-purplish scaly lesions skin disorder? c. Oily skin and no episodes of pruritus d. Silvery-white scaly patches on the scalp, elbow, 10. Answer D. Cellulitis is a skin infection into deeper dermal and subcutaneous tissues that results in a deep red erythema without sharp borders and spreads widely throughout tissue spaces. Warm compresses may be used to decrease the discomfort, erythema, and edema. After tissue and blood cultures are obtained, antibiotics will be initiated. The nurse should provide supportive care as prescribed to manage symptoms such as fatigue, fever, chills, headache, and myalgia. Heat lamps can cause more disruption to already inflamed tissue. Cold compresses and alternating cold and hot compresses are not the best measures. knees, and sacral regions 11. The clinic nurse notes that the physiciaa. Patch test has documented a diagnosis of herpes zosterb. Skin biopsy (shingles) in the male client’s chart. Based on Culture of the lesion an understanding of the cause of this disorded. Woo’s light examination 11. Answer C. With the classic presentation of herpes zoster, the clinical examination is diagnostic. A viral culture of the lesion provides the definitive diagnosis. Herpes zoster (shingles) is caused by a reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, the virus that causes chickenpox. A patch test is a skin test that involves the administration of an allergen to the surface of the skin to identify specific allergies. A biopsy would provide a cytological examination of tissue. In a Wood’s light examination, the skin is viewed under ultraviolet light to identify superficial infections of the skin. the nurse determines that this definitive diagnosis was made following which diagnostic test? 12. The nurse is assigned to care for a a. Clustered skin vesicles female client with herpes zoster (Shingles). b. A generalized body rash Which of the following characteristics would Small blue-white spots with a red base the nurse expect to note when assessing the d. A fiery red, edematous rash on the cheeks 12. Answer A. The primary lesion of herpes zoster is a vesicle. The classic presentation is grouped vesicles on an erythematous base along a dermatome. Because the lesions follow nerve pathways, they do not cross the midline of the body. Options B, C, and D are incorrect descriptions of herpes zoster. lesions of this infection? 13. When assessing a lesion diagnosed as a. An irregular shaped lesion malignant melanoma, the nurse in-charge b. A small papule with a dry, rough scale most likely expects to note which of the c. A firm, nodular lesion topped with crust following? d. A pearly papule with a central crater and a waxy 13. Answer A. A melanoma is an irregularly shaped pigmented papule or plaque with a red-, white-, or blue-toned color. Basal cell carcinoma appears as a pearly papule with a central crater and rolled waxy border. Squamous cell carcinoma is a firm, nodular lesion topped with a crust or a central area of ulceration. Actinic keratosis, a premalignant lesion, appears as a small macule or papule with a dry, rough, adherent yellow or brown scale. border 14. The nurse prepares discharge a. Avoid showering for 7 to 10 days instructions for a male client following b. Apply ice to the site to prevent discomfort cryosurgery for the treatment of a malignant c. Apply alcohol-soaked dressing twice a day skin lesion. Which of the following should thd. Clean the site with hydrogen peroxide to prevent 14. Answer D. Cryosurgery involves the local application of liquid nitrogen to isolated lesions and causes cell death and tissue destruction. The nurse informs the client that swelling and increased tenderness of the treated area can occur when the skin thaws. Tissue freezing is followed by hemorrhagic blister formation in 1 to 2 days. The nurse instructs the client to clean the treatment site with hydrogen peroxide to prevent secondary infection. A topical antibiotic also may be prescribed. Application of a warm, damp washcloth intermittently to the site will provide relief from any discomfort. Alcohol-soaked dressings will cause irritation. The client does not need to avoid showering. nurse include in the instruction? infection 15. Nurse Carl reviews the client’s chart ana. Red shiny skin around the nail bed notes that the physician has documented a b. White taut skin in the popliteal area diagnosis of paronychia. Based on this White silvery patches on the elbows diagnosis, which of the following would the d. Swelling of the skin near the parotid gland 15. Answer A. Paronychia, or infection around the nail, is characterized by red, shiny skin, often associated with painful swelling. These infections frequently result from trauma, picking at the nail, or disorders such as dermatitis. Often, these become secondarily infected with bacteria or fungus, which later involves the nail. Warm soaks three or four times a day may reduce pain and pressure; however, incision and drainage of the inflamed site frequently nurse expect to note during the assessment? are required. Options B, C, and D are incorrect. 16. A male client arrives at the emergency a. A pink, edematous hand room and has experienced frostbites to the b. A fiery red skin with edema in the nail beds right hand. Which of the following would th c. Black fingertips surrounded by an erythematous nurse note on assessment of the client’s hand? rash d. A white color to the skin, which is insensitive to 16. Answer D. Assessment findings in frostbite include a white or blue color; the skin will be hard, cold, and insensitive to touch. As thawing occurs, flushing of the skin, the development of blisters or blebs, or tissue edema appears. Options A, B, and C are incorrect. touch 17. The evening nurse reviews the nursinga. Intact skin documentation in the male client’s chart andb. Full-thickness skin loss notes that the day nurse has documented that Exposed bone, tendon, or muscle the client has a stage II pressure ulcer in the d. Partial-thickness skin loss of the dermis 17. Answer D. In a stage II pressure ulcer, the skin is not intact. Partial-thickness skin loss of the dermis has occurred. It presents as a shallow open ulcer with a red-pink wound bed, without slough. It may also present as an intact, open or ruptured, serum-filled blister. The skin is intact in stage I. Full-thickness skin loss occurs in stage 3. Exposed bone, tendon, or muscle is present in stage 4. sacral area. Which of the following would the nurse expect to note on assessment of the client’s sacral area? 18. Nurse Ivy is implementing a teaching a. “Acne is caused by oily skin” plan to a group of adolescents regarding the b. “The actual cause is not known” causes of acne. Which of the following is an c. “Acne is caused by eating chocolate” appropriate nursing statement regarding the d. “Acne is caused as a result of exposure to heat 18. Answer B. The actual cause of acne is unknown. Oily skin or the consumption of foods such as chocolate, nuts, or fatty foods are not causes of acne. Exacerbations that coincide with the menstrual cycle result from hormonal activity. Heat, humidity, and excessive perspiration may play a role in exacerbating acne but does not cause it. cause of this disorder? and humidity” 19. The nurse is reviewing the health care a. An adolescent record of a male clients scheduled to be seenb. An older female at the health care clinic. The nurse determines A physical education teacher that which of the following individuals is at d. An outdoor construction worker 19. Answer D. Prolonged exposure to the sun, unusual cold, or other conditions can damage the skin. The outdoor construction worker would fit into a high-risk category for the development of an integumentary disorder. An adolescent may be prone to the development of acne, but this does not occur in all adolescents. Immobility and lack of nutrition would increase the older person’s risk but the older client is not at as high a risk as the outdoor construction worker. The physical education teacher the greatest risk for development of an integumentary disorder? is at low or no risk of developing an integumentary problem. 20. A male client schedule for a skin biops a. “There is no pain associated with this is concerned and asks the nurse how painful procedure” the procedure is. The appropriate response b b. “The local anesthetic may cause a burning or the nurse is: stinging sensation” c. A preoperative medication will be given so you 20. Answer B. Depending on the size and location of the lesion, a biopsy is usually a quick and almost painless procedure. The most common source of pain is the initial local anesthetic, which can produce a burning or stinging sensation. Preoperative medication is not necessary with this procedure. will be sleeping and will not feel any pain” d. “There is some pain, but the physician will prescribe an opioid analgesic following the procedure” 21. The nurse is teaching a female client a. “I’ll limit my intake of protein.” with a leg ulcer about tissue repair and wou b. “I’ll make sure that the bandage is wrapped healing. Which of the following statements by tightly.” the client indicates effective teaching? c. “My foot should feel cold.” d. “I’ll eat plenty of fruits and vegetables.” 21. Answer D. For effective tissue healing, adequate intake of protein, vitamin A, B complex, C, D, E, and K are needed. Therefore, the client should eat a high protein diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables to provide these nutrients. The bandage should be secure but not too tight to impede circulation to the area (needed for tissue repair). If the client’s foot feels cold, circulation is impaired, thus inhibiting wound healing. 22. Following a full-thickness (third-degrea. range of motion. burn of his left arm, a male client is treated b. protein intake. with artificial skin. The client understands going outdoors. postoperative care of artificial skin when he d. fluid ingestion. 22. Answer A. To prevent disruption of the artificial skin’s adherence to the wound bed, the client should restrict range of motion of the involved limb. Protein intake and fluid intake are important for healing and regeneration and shouldn’t be restricted. Going outdoors is acceptable as long as the left arm is protected from direct sunlight. states that during the first 7 days after the procedure, he will restrict: 23. Following a small-bowel resection, a a. erythema. male client develops fever and anemia. The b. leukocytosis. surface surrounding the surgical wound is pressurelike pain. warm to the touch and necrotizing fasciitis i d. swelling. 23. Answer C. Severe pressure like pain out of proportion to visible signs distinguishes necrotizing fasciitis from cellulitis. Erythema, leukocytosis, and swelling are present in both cellulitis and necrotizing fasciitis. suspected. Another manifestation that would most suggest necrotizing fasciitis is: 24. While in a skilled nursing facility, a a. “All family members will need to be treated.” female client contracted scabies, which is b. “If someone develops symptoms, tell him to see diagnosed the day after discharge. The client a physician right away.” is living at her daughter’s home, where six other persons are living. During her visit to c. “Just be careful not to share linens and towels the clinic, she asks a staff nurse, “What should with family members.” my family do?” The most accurate response d. “After you’re treated, family members won’t be 24. Answer A. When someone in a group of persons sharing a home contracts scabies, each individual in the home needs prompt treatment whether he’s symptomatic or not. Towels and linens should be washed in hot water. Scabies can be transmitted from one person to another before symptoms develop. from the nurse is: at risk for contracting scabies.” 25. The nurse is assessing a male client a. Partial pressure of arterial oxygen (PaO2) value admitted with second- and third-degree burns of 80 mm Hg on the face, arms, and chest. Which finding b. Urine output of 20 ml/hour indicates a potential problem? c. White pulmonary secretions d. Rectal temperature of 100.6° F (38° C) 25. Answer B. A urine output of less than 40 ml/hour in a client with burns indicates a fluid volume deficit. This client’s PaO2 value falls within the normal range (80 to 100 mm Hg). White pulmonary secretions also are normal. The client’s rectal temperature isn’t significantly elevated and probably results from the fluid volume deficit. 26. A female client exhibits s purplish bruia. Purpura to the skin after a fall. The nurse would b. Petechiae document this finding most accurately using Ecchymosis which of the following terms? d. Erythema 26. Answer C. Ecchymosis is a type of purpuric lesion and also is known as a bruise. Purpura is an umbrella term that incorporates ecchymoses and petechiae. Petechiae are pinpoint hemorrhages and are another form of purpura. Erythema is an area of redness on the skin. 27. An older client’s physical examination a. Cherry angioma reveals the presence of a number of bright r b. Spider angioma colored lesions scattered on the trunk and Venous star tights. The nurse interprets that this indicate d. Purpura 27. Answer A. Cherry angioma occurs with increasing age and has no clinical significance. It appears as a small, round, bright red–colored lesion on the trunk or extremities. Spider angiomas have a bright red center with legs that radiate outward. These lesions commonly are seen in liver disease and vitamin B deficiency, although they occasionally can occur without underlying pathology. A venous star results from increased pressure in veins, usually in the lower legs, and has an irregularly shaped bluish center with radiating branches. Purpura results which of the following lesions due to alterations in blood vessels of the skin? from hemorrhage into the skin. 28. A nurse is reviewing the medical reco a. Ring-shaped of a male client to be admitted to the nursin b. Linear unit and notes documentation of reticular skin Shaped like an arc lesions. The nurse expects that these lesions d. Net-like appearance 28. Answer D. Reticular skin lesions resemble a net in appearance. Annular lesions are ring-shaped, whereas linear lesions appear in a straight line. Arciform lesions are shaped like an arc. will appear to be: 29. A male client seen in an ambulatory a. Hyperthyroidism clinic has a butterfly rash across the nose. Thb. Perncious anemia nurse interprets that this finding is consistent Cardiopulmonary disorders with early manifestations of which of the d. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) 29. Answer D. An early sign of SLE is the appearance of a butterfly rash across the nose. Hyperthyroidism often leads to moist skin and increased perspiration. Pernicious anemia would be manifested by pallor of the skin. Cardiopulmonary disorders may lead to clubbing of the fingers. following disorders? 30. A female client with cellulites of the a. Staphylococcus epidermidis lower leg has had cultures done on the b. Staphylococcus aureus affected area. The nurse reading the culture Escherichia coli (E. coli) report understands that which of the followind. Candida albicans 30. Answer C. E. coli normally is found in the intestines and constitutes a common source of infection of wounds and the urinary system. The other microbes listed are part of the normal flora of the skin. organisms is not part of the normal flora of the skin? RESPIRATORY 1. A male client who takes theophylline for 10 mcg/mL chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is seen 12 mcg/mL in the urgent care center for respiratory 15 mcg/mL distress. Once the client is stabilized, the 18mcg/mL 1. Answer A. The therapeutic range for the serum theophylline level is 10 to 20 mcg/mL. If the level is below the therapeutic range, the client may experience frequent exacerbations of the disorder. Although all the options identify values within the therapeutic range, option A is the option that reflects a need for compliance with medication. nurse begins discharge teaching. The nurse would be especially vigilant to include information about complying with medication therapy if the client’s baseline theophylline level was: 2. Nurse Kim is caring for a client with a a. Do nothing, because this is an expected finding. pneumothorax and who has had a chest tube b. Immediately clamp the chest tube and 2. Answer A. Continuous gentle bubbling should be noted in the suction control chamber. Option B is incorrect. Chest tubes should only be clamped to inserted notes continuous gentle bubbling in the suction control chamber. What action is notify the physician. check for an air leak or when changing drainage devices (according to agency policy). Option C is incorrect. Bubbling should be continuous and not intermittent. Option D is incorrect because bubbling should be gentle. Increasing the suction pressure only increases the rate of evaporation of water in the drainage system. appropriate? c. Check for an air leak because the bubbling should be intermittent. d. Increase the suction pressure so that bubbling becomes vigorous. 3. A nurse has assisted a physician with th a. Inform the physician. insertion of a chest tube. The nurse monitorsb. Continue to monitor the client. the adult client and notes fluctuation of the Reinforce the occlusive dressing. fluid level in the water seal chamber after th d. Encourage the client to deep-breathe. 3. Answer B. The presence of fluctuation of the fluid level in the water seal chamber indicates a patent drainage system. With normal breathing, the water level rises with inspiration and falls with expiration. Fluctuation stops if the tube is obstructed, if a dependent loop exists, if the suction is not working properly, or if the lung has reexpanded. Options A, C, and D are incorrect. tube is inserted. Based on this assessment, which action would be appropriate? 4. The nurse caring for a male client with aa. Call the physician. chest tube turns the client to the side, and theb. Place the tube in a bottle of sterile water. chest tube accidentally disconnects. The initi c. Immediately replace the chest tube system. nursing action is to: d. Place the sterile dressing over the disconnection 4. Answer B. If the chest drainage system is disconnected, the end of the tube is placed in a bottle of sterile water held below the level of the chest. The system is replaced if it breaks or cracks or if the collection chamber is full. Placing a sterile dressing over the disconnection site will not prevent complications resulting from the disconnection. The physician may need to be notified, but this is not the initial action. site. 5. Nurse Paul is assisting a physician with a. Exhale slowly. the removal of a chest tube. The nurse shoulb. Stay very still. instruct the client to:. Inhale and exhale quickly. d. Perform the Valsalva maneuver 5. Answer D. When the chest tube is removed, the client is asked to perform the Valsalva maneuver (take a deep breath, exhale, and bear down). The tube is quickly withdrawn, and an airtight dressing is taped in place. An alternative instruction is to ask the client to take a deep breath and hold the breath while the tube is removed. Options A, B, and C are incorrect client instructions. 6. While changing the tapes on a a. Call the physician to reinsert the tube. tracheostomy tube, the male client coughs anb. Grasp the retention sutures to spread the the tube is dislodged. The initial nursing action opening. is to: c. Call the respiratory therapy department to reinsert the tracheotomy. d. Cover the tracheostomy site with a sterile 6. Answer B. If the tube is dislodged accidentally, the initial nursing action is to grasp the retention sutures and spread the opening. If agency policy permits, the nurse then attempts immediately to replace the tube. Covering the tracheostomy site will block the airway. Options 1 and 3 will delay treatment in this emergency situation. dressing to prevent infection. 7. A nurse is caring for a male client a. Stridor immediately after removal of the endotracheb. Occasional pink-tinged sputum tube. The nurse reports which of the followin A few basilar lung crackles on the right signs immediately if experienced by the d. Respiratory rate of 24 breaths/min 7. Answer A. The nurse reports stridor to the physician immediately. This is a high-pitched, coarse sound that is heard with the stethoscope over the trachea. Stridor indicates airway edema and places the client at risk for airway obstruction. Options B, C, and D are not signs that require immediate notification of the physician. client? 8. An emergency room nurse is assessing a. A low respiratory female client who has sustained a blunt injurb. Diminished breathe sounds to the chest wall. Which of these signs would The presence of a barrel chest indicate the presence of a pneumothorax in d. A sucking sound at the site of injury 8. Answer B. This client has sustained a blunt or a closed chest injury. Basic symptoms of a closed pneumothorax are shortness of breath and chest pain. A larger pneumothorax may cause tachypnea, cyanosis, diminished breath sounds, and subcutaneous emphysema. Hyperresonance also may occur on the affected side. A sucking sound at the site of injury would be noted with an open chest injury. this client? 9. A nurse is caring for a male client a. Hypocapnia hospitalized with acute exacerbation of b. A hyperinflated chest noted on the chest xray chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Whicc. Increase oxygen saturation with exercise of the following would the nurse expect to d. A widened diaphragm noted on the chest xray 9. Answer B. Clinical manifestations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) include hypoxemia, hypercapnia, dyspnea on exertion and at rest, oxygen desaturation with exercise, and the use of accessory muscles of respiration. Chest x-rays reveal a hyperinflated chest and a flattened diaphragm if the disease is advanced. note on assessment of this client? 10. A community health nurse is conductina. Dyspnea an educational session with community b. Chest pain 10. Answer D. One of the first pulmonary symptoms is a slight cough with the expectoration of members regarding tuberculosis. The nurse c. A bloody, productive cough tells the group that one of the first symptoms d. A cough with the expectoration of mucoid mucoid sputum. Options A, B, and C are late symptoms and signify cavitation and extensive lung involvement. associated with tuberculosis is: sputum 11. A nurse performs an admission a. Bronchoscopy assessment on a female client with a diagno b. Sputum culture of tuberculosis. The nurse reviews the results Chest x-ray of which diagnostic test that will confirm thid. Tuberculin skin test 11. Answer B. Tuberculosis is definitively diagnosed through culture and isolation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A presumptive diagnosis is made based on a tuberculin skin test, a sputum smear that is positive for acid-fast bacteria, a chest x-ray, and histological evidence of granulomatous disease on biopsy. diagnosis? 12. The nursing instructor asks a nursing a. Hand and mouth student to describe the route of transmission b. The airborne route of tuberculosis. The instructor concludes that The fecal-oral route the student understands this information if thd. Blood and body fluids 12. Answer B. Tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by the bacillus Mycobacterium tuberculosis and is spread primarily by the airborne route. Options A, C, and D are incorrect. student states that the tuberculosis is transmitted by: 13. A nurse is caring for a male client witha. 1 L/min emphysema who is receiving oxygen. The b. 2 L/min nurse assesses the oxygen flow rate to ensure 6 L/min that it does not exceed: d. 10 L/min 13. Answer B. Oxygen is used cautiously and should not exceed 2 L/min. Because of the longstanding hypercapnia that occurs in emphysema, the respiratory drive is triggered by low oxygen levels rather than increased carbon dioxide levels, as is the case in a normal respiratory system. 14. A nurse instructs a female client to use a. Promote oxygen intake. the pursed-lip method of breathing and the b. Strengthen the diaphragm. client asks the nurse about the purpose of this Strengthen the intercostal muscles. type of breathing. The nurse responds, d. Promote carbon dioxide elimination. 14. Answer D. Pursed-lip breathing facilitates maximal expiration for clients with obstructive lung disease. This type of breathing allows better expiration by increasing airway pressure that keeps air passages open during exhalation. Options A, B, and C are not the purposes of this type of breathing. knowing that the primary purpose of pursedlip breathing is to: 15. Nurse Hannah is preparing to obtain a a. Limiting fluids sputum specimen from a client. Which of th b. Having the clients take three deep breaths following nursing actions will facilitate Asking the client to split into the collection 15. Answer B. To obtain a sputum specimen, the client should rinse the mouth to reduce contamination, breathe deeply, and then cough into a obtaining the specimen? container d. Asking the client to obtain the specimen after eating sputum specimen container. The client should be encouraged to cough and not spit so as to obtain sputum. Sputum can be thinned by fluids or by a respiratory treatment such as inhalation of nebulized saline or water. The optimal time to obtain a specimen is on arising in the morning. 16. A nurse is caring for a female client afta. Dry cough a bronchoscope and biopsy. Which of the b. Hematuria following signs, if noted in the client, should Bronchospasm be reported immediately to the physicians? d. Blood-streaked sputum 16. Answer C. If a biopsy was performed during a bronchoscopy, blood-streaked sputum is expected for several hours. Frank blood indicates hemorrhage. A dry cough may be expected. The client should be assessed for signs of complications, which would include cyanosis, dyspnea, stridor, bronchospasm, hemoptysis, hypotension, tachycardia, and dysrhythmias. Hematuria is unrelated to this procedure. 17. A nurse is suctioning fluids from a mala. 1 minute client via a tracheostomy tube. When b. 5 seconds suctioning, the nurse must limit the suctioning 10 seconds time to a maximum of: d. 30 seconds 17. Answer C. Hypoxemia can be caused by prolonged suctioning, which stimulates the pacemaker cells in the heart. A vasovagal response may occur, causing bradycardia. The nurse must preoxygenate the client before suctioning and limit the suctioning pass to 10 seconds. 18. A nurse is suctioning fluids from a a. Continue to suction. female client through an endotracheal tube. b. Notify the physician immediately. During the suctioning procedure, the nurse c. Stop the procedure and reoxygenate the client. notes on the monitor that the heart rate is d. Ensure that the suction is limited to 15 seconds. 18. Answer C. During suctioning, the nurse should monitor the client closely for side effects, including hypoxemia, cardiac irregularities such as a decrease in heart rate resulting from vagal stimulation, mucosal trauma, hypotension, and paroxysmal coughing. If side effects develop, especially cardiac irregularities, the procedure is stopped and the client is reoxygenated. decreasing. Which of the following is the appropriate nursing intervention? 19. An unconscious male client is admitte a. Metabolic acidosis to an emergency room. Arterial blood gas b. Respiratory acidosis measurements reveal a pH of 7.30, a low Overcompensated respiratory acidosis 19. Answer A. In an acidotic condition, the pH would be low, indicating the acidosis. In addition, a low bicarbonate level along with the low pH would bicarbonate level, a normal carbon dioxide level, a normal oxygen level, and an elevated potassium level. These results indicate the presence of: d. Combined respiratory and metabolic acidosis indicate a metabolic state. Therefore, options B, C, and D are incorrect. 20. A female client is suspected of having a. Dyspnea pulmonary embolus. A nurse assesses the b. Bradypnea client, knowing that which of the following is Bradycardia a common clinical manifestation of pulmon d. Decreased respiratory 20. Answer A. The common clinical manifestations of pulmonary embolism are tachypnea, tachycardia, dyspnea, and chest pain. embolism? 21. A nurse teaches a male client about the a. Inhales the mist and quickly exhales use of a respiratory inhaler. Which action by b. Removes the cap and shakes the inhaler well the client indicates a need for further before use teaching? c. Presses the canister down with the finger as he breathes in d. Waits 1 to 2 minutes between puffs if more than 21. Answer A. The client should be instructed to hold his or her breath for at least 10 to 15 seconds before exhaling the mist. Options B, C, and D are accurate instructions regarding the use of the inhaler. one puff has been prescribed 22. A female client has just returned to a a. Administering atropine intravenously nursing unit following bronchoscopy. A nursb. Administering small doses of midazolam would implement which of the following (Versed) nursing interventions for this client? Encouraging additional fluids for the next 22. Answer D. After bronchoscopy, the nurse keeps the client on NPO status until the gag reflex returns because the preoperative sedation and local anesthesia impair swallowing and the protective laryngeal reflexes for a number of hours. Additional fluids are unnecessary because no contrast dye is used that would need flushing from the system. Atropine and midazolam would be administered before the procedure, not after. 24 hours d. Ensuring the return of the gag reflex before offering food or fluids 23. A nurse is assessing the respiratory stata. Slow deep respirations of a male client who has suffered a fracturedb. Rapid deep respirations rib. The nurse would expect to note which of Paradoxical respirations the following? d. Pain, especially with inspiration 23. Answer D. Rib fractures are a common injury, especially in the older client, and result from a blunt injury or a fall. Typical signs and symptoms include pain and tenderness localized at the fracture site and exacerbated by inspiration and palpation, shallow respirations, splinting or guarding the chest protectively to minimize chest movement, and possible bruising at the fracture site. Paradoxical respirations are seen with flail chest. 24. A female client with chest injury has a. Cyanosis suffered flail chest. A nurse assesses the clie b. Hypotension for which most distinctive sign of flail chest? Paradoxical chest movement d. Dyspnea, especially on exhalation 24. Answer C. Flail chest results from fracture of two or more ribs in at least two places each. This results in a “floating” section of ribs. Because this section is unattached to the rest of the bony rib cage, this segment results in paradoxical chest movement. This means that the force of inspiration pulls the fractured segment inward, while the rest of the chest expands. Similarly, during exhalation, the segment balloons outward while the rest of the chest moves inward. This is a telltale sign of flail chest. 25. A male client has been admitted with a. Right pneumothorax chest trauma after a motor vehicle accident b. Pulmonary embolism and has undergone subsequent intubation. A Displaced endotracheal tube nurse checks the client when the highpressu d. Acute respiratory distress syndrome 25. Answer A. Pneumothorax is characterized by restlessness, tachycardia, dyspnea, pain with respiration, asymmetrical chest expansion, and diminished or absent breath sounds on the affected side. Pneumothorax can cause increased airway pressure because of resistance to lung inflation. Acute respiratory distress syndrome and pulmonary embolism are not characterized by absent breath sounds. An endotracheal tube that is inserted too far can cause absent breath sounds, but the lack of breath sounds most likely would be on the left side because of the degree of curvature of the right and left main stem bronchi. alarm on the ventilator sounds, and notes that the client has absence of breathe sounds in right upper lobe of the lung. The nurse immediately assesses for other signs of: 26. A nurse is teaching a male client with a. Inhale quickly chronic respiratory failure how to use a b. Inhale through the nose metered-dose inhaler correctly. The nurse Hold the breath after inhalation instructs the client to: d. Take two inhalations during one breath 26. Answer C. Instructions for using a metereddose inhaler include shaking the canister, holding it right side up, inhaling slowly and evenly through the mouth, delivering one spray per breath, and holding the breath after inhalation. 27. A nurse is assessing a female client wita. Bilateral wheezing multiple trauma who is at risk for developin b. Inspiratory crackles acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Intercostal retractions 27. Answer D. The earliest detectable sign of acute respiratory distress syndrome is an increased respiratory rate, which can begin from 1 to 96 hours nurse assesses for which earliest sign of acute respiratory distress syndrome? d. Increased respiratory rate after the initial insult to the body. This is followed by increasing dyspnea, air hunger, retraction of accessory muscles, and cyanosis. Breath sounds may be clear or consist of fine inspiratory crackles or diffuse coarse crackles. 28. A nurse is taking pulmonary artery a. High and expected catheter measurements of a male client with b. Low and unexpected acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Normal and expected pulmonary capillary wedge pressure readingd. Uncertain and unexpected 28. Answer C. The normal pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) is 8 to 13 mm Hg, and the client is considered to have high readings if they exceed 18 to 20 mm Hg. The client with acute respiratory distress syndrome has a normal PCWP, which is an expected finding because the edema is in the interstitium of the lung and is noncardiac. is 12mm Hg. The nurse interprets that this readings is: 29. A nurse is assessing a male client with a. Emphysema chronic airflow limitations and notes that th b. Bronchial asthma client has a “barrel chest.” The nurse Chronic obstructive bronchitis interprets that this client has which of the d. Bronchial asthma and bronchitis 29. Answer A. The client with emphysema has hyperinflation of the alveoli and flattening of the diaphragm. These lead to increased anteroposterior diameter, referred to as “barrel chest.” The client also has dyspnea with prolonged expiration and has hyperresonant lungs to percussion. following forms of chronic airflow limitations? 30. A nurse is caring for a female client a. Cough diagnosed with tuberculosis. Which b. High-grade fever assessment, if made by the nurse, is Chills and night sweats inconsistent with the usual clinical d. Anorexia and weight loss 30. Answer B. The client with tuberculosis usually experiences cough (productive or nonproductive), fatigue, anorexia, weight loss, dyspnea, hemoptysis, chest discomfort or pain, chills and sweats (which may occur at night), and a low-grade fever. presentation of tuberculosis and may indicate the development of a concurrent problem? 1. The nurse is caring for a male client wit a. Place the end of the chest tube in a container of a chest tube. If the chest drainage system is sterile saline. accidentally disconnected, what should the b. Apply an occlusive dressing and notify the nurse plan to do? physician. c. Clamp the chest tube immediately. d. Secure the chest tube with tape. 1. Answer A. If a chest drainage system is disconnected, the nurse may place the end of the chest tube in a container of sterile saline or water to prevent air from entering the chest tube, thereby preventing negative respiratory pressure. The nurse should apply an occlusive dressing if the chest tube is pulled out — not if the system is disconnected. The nurse shouldn’t clamp the chest tube because clamping increases the risk of tension pneumothorax. The nurse should tape the chest tube securely to prevent it from being disconnected, rather than taping it after it has been disconnected. 2. A male elderly client is admitted to an a. Septicemia acute care facility with influenza. The nurse b. Pneumonia monitors the client closely for complications. Meningitis What is the most common complication of d. Pulmonary edema 2. Answer B. Pneumonia is the most common complication of influenza. It may be either primary influenza viral pneumonia or pneumonia secondary to a bacterial infection. Other complications of influenza include myositis, exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and Reye’s syndrome. Myocarditis, pericarditis, transverse myelitis, and encephalitis are rare complications of influenza. Although septicemia may arise when any infection becomes overwhelming, it rarely results from influenza. Meningitis and pulmonary edema aren’t associated with influenza. influenza? 3. A female client has a tracheostomy but a. 15 to 60 seconds. doesn’t require continuous mechanical b. 5 to 20 minutes. ventilation. When weaning the client from the 30 to 40 minutes. tracheostomy tube, the nurse initially shouldd. 45 to 60 minutes. 3. Answer B. Initially, the nurse should plug the opening in the tracheostomy tube for 5 to 20 minutes, and then gradually lengthen this interval according to the client’s respiratory status. A client who doesn’t require continuous mechanical ventilation already is breathing without assistance, at least for short periods; therefore, plugging the opening of the tube for only 15 to 60 seconds wouldn’t be long enough to reveal the client’s true tolerance to the procedure. Plugging the opening for more than 20 minutes would increase the risk of acute respiratory distress because the client requires an adjustment period to start breathing normally. plug the opening in the tube for: of 10 breaths/minute. These signs are associated with which condition? characterized by disorientation to time and place. Hyperventilation (respiratory rate greater than that metabolically necessary for gas exchange) is marked by an increased respiratory rate or tidal volume, or both. Semiconsciousness is a state of impaired consciousness characterized by limited motor and verbal responses and decreased orientation. 5. A male client with Guillain-Barré a. pH, 5.0; PaCO2 30 mm Hg syndrome develops respiratory acidosis as a b. pH, 7.40; PaCO2 35 mm Hg result of reduced alveolar ventilation. Which pH, 7.35; PaCO2 40 mm Hg combination of arterial blood gas (ABG) d. pH, 7.25; PaCO2 50 mm Hg 5. Answer D. In respiratory acidosis, ABG analysis reveals an arterial pH below 7.35 and partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide (PaCO2) above 45 mm Hg. Therefore, the combination of a pH value of 7.25 and a PaCO2 value of 50 mm Hg confirms respiratory acidosis. A pH value of 5.0 with a PaCO2 value of 30 mm Hg indicates respiratory alkalosis. Options B and C represent normal ABG values, reflecting normal gas exchange in the lungs. values confirms respiratory acidosis? 6. A female client with interstitial lung a. hyperglycemia and glycosuria. disease is prescribed prednisone (Deltasone)b. acute adrenocortical insufficiency. to control inflammation. During client GI bleeding. teaching, the nurse stresses the importance od. restlessness and seizures. 6. Answer B. Administration of a corticosteroid such as prednisone suppresses the body’s natural cortisol secretion, which may take weeks or months to normalize after drug discontinuation. Abruptly discontinuing such therapy may cause the serum cortisol level to drop low enough to trigger acute adrenocortical insufficiency. Hyperglycemia, glycosuria, GI bleeding, restlessness, and seizures are common adverse effects of corticosteroid therapy, not its sudden cessation. taking prednisone exactly as prescribed and cautions against discontinuing the drug abruptly. A client who discontinues prednisone abruptly may experience: 7. A male client is admitted to the health caa. Activity intolerance related to fatigue facility for treatment of chronic obstructive b. Anxiety related to actual threat to health status pulmonary disease. Which nursing diagnosis c. Risk for infection related to retained secretions most important for this client? d. Impaired gas exchange related to airflow 7. Answer D. A patent airway and an adequate breathing pattern are the top priority for any client, making impaired gas exchange related to airflow obstruction the most important nursing diagnosis. The other options also may apply to this client but are less important. obstruction 8. A male client abruptly sits up in bed, a. Simple mask reports having difficulty breathing and has ab. Non-rebreather mask arterial oxygen saturation of 88%. Which Face tent mode of oxygen delivery would most likely d. Nasal cannula 8. Answer B. A non-rebreather mask can deliver levels of the fraction of inspired oxygen (FIO2) as high as 100%. Other modes — simple mask, face tent and nasal cannula — deliver lower levels of FIO2. reverse the manifestations? 9. A male adult client with cystic fibrosis ia. Immediately before a meal admitted to an acute care facility with an b. At least 2 hours after a meal acute respiratory infection. Prescribed When bronchospasms occur respiratory treatment includes chest d. When secretions have mobilized 9. Answer B. The nurse should perform chest physiotherapy at least 2 hours after a meal to reduce the risk of vomiting and aspiration. Performing it immediately before a meal may tire the client and impair the ability to eat. Percussion and vibration, components of chest physiotherapy, may worsen bronchospasms; therefore, the procedure is contraindicated in clients with bronchospasms. Secretions that have mobilized (especially when suction equipment isn’t available) are a contraindication for postural drainage, another component of chest physiotherapy. physiotherapy. When should the nurse perform this procedure? 10. On arrival at the intensive care unit, a a. Fever critically ill female client suffers respiratory b. Tachypnea arrest and is placed on mechanical ventilation. Tachycardia The physician orders pulse oximetry to d. Hypotension 10. Answer D. Hypotension, hypothermia, and vasoconstriction may alter pulse oximetry values by reducing arterial blood flow. Likewise, movement of the finger to which the oximeter is applied may interfere with interpretation of SaO2. All of these conditions limit the usefulness of pulse oximetry. Fever, tachypnea, and tachycardia don’t affect pulse oximetry values directly. monitor the client’s arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) noninvasively. Which vital sign abnormality may alter pulse oximetry values? 11. The nurse is caring for a male clienta. helping him communicate. who recently underwent a tracheostomy. Theb. keeping his airway patent. first priority when caring for a client with ac. encouraging him to perform activities of daily tracheostomy is: living. d. preventing him from developing an infection. 11. Answer B. Maintaining a patent airway is the most basic and critical human need. All other interventions are important to the client’s well-being but not as important as having sufficient oxygen to breathe. 12. For a male client with chronic a. Restricting fluid intake to 1,000 ml/day obstructive pulmonary disease, which nursinb. Enforcing absolute bed rest 12. Answer C. Controlled coughing helps maintain a patent airway by helping to mobilize and remove intervention would help maintain a patent c. Teaching the client how to perform controlled airway? coughing d. Administering prescribed sedatives regularly secretions. A moderate fluid intake (usually 2 L or more daily) and moderate activity help liquefy and mobilize secretions. Bed rest and sedatives may limit the client’s ability to maintain a patent airway, causing a high risk of infection from pooled secretions. and in large amounts 13. The amount of air inspired and expireda. tidal volume. with each breath is called: b. residual volume. vital capacity. d. dead-space volume. 13. Answer A. Tidal volume is the amount of air inspired and expired with each breath. Residual volume is the amount of air remaining in the lungs after forcibly exhaling. Vital capacity is the maximum amount of air that can be moved out of the lungs after maximal inspiration and expiration. Dead- space volume is the amount of air remaining in the upper airways that never reaches the alveoli. In pathologic conditions, dead space may also exist in the lower airways. 14. A male client with pneumonia develo a. 0.21 respiratory failure and has a partial pressure b. 0.35 of arterial oxygen of 55 mm Hg. He’s placed 0.5 on mechanical ventilation with a fraction of d. 0.7 14. Answer C. An FO2 greater than 0.5 for as little as 16 to 24 hours can be toxic and can lead to decreased gas diffusion and surfactant activity. The ideal oxygen source is room air F IO 2 0.18 to 0.21. inspired oxygen (FIO2) of 0.9. The nursing goal should be to reduce the FIO2 to no greater than: 15. Nurse Mickey is administering a a. A positive reaction indicates that the client has purified protein derivative (PPD) test to a active tuberculosis (TB). homeless client. Which of the following b. A positive reaction indicates that the client has statements concerning PPD testing is true? been exposed to the disease. c. A negative reaction always excludes the diagnosis of TB. d. The PPD can be read within 12 hours after the 15. Answer B. A positive reaction means the client has been exposed to TB; it isn’t conclusive of the presence of active disease. A positive reaction consists of palpable swelling and induration of 5 to 15 mm. It can be read 48 to 72 hours after the injection. In clients with positive reactions, further studies are usually done to rule out active disease. In immunosuppressed clients, a negative reaction doesn’t exclude the presence of active disease. injection. 16. Nurse Murphy administers albuterol a. Respiratory rate of 22 breaths/minute (Proventil), as prescribed, to a client with b. Dilated and reactive pupils emphysema. Which finding indicates that the Urine output of 40 ml/hour drug is producing a therapeutic effect? d. Heart rate of 100 beats/minute 16. Answer A. In a client with emphysema, albuterol is used as a bronchodilator. A respiratory rate of 22 breaths/minute indicates that the drug has achieved its therapeutic effect because fewer respirations are required to achieve oxygenation. Albuterol has no effect on pupil reaction or urine output. It may cause a change in the heart rate, but this is an adverse, not therapeutic, effect. 17. What is the normal pH range for arteri a. 7 to 7.49 blood? b. 7.35 to 7.45 7.50 to 7.60 d. 7.55 to 7.65 17. Answer B. A pH less than 7.35 is indicative of acidosis; a pH above 7.45 indicates alkalosis. 18. Before weaning a male client from a a. Fluid intake for the last 24 hours ventilator, which assessment parameter is m b. Baseline arterial blood gas (ABG) levels important for the nurse to review? Prior outcomes of weaning d. Electrocardiogram (ECG) results 18. Answer B. Before weaning a client from mechanical ventilation, it’s most important to have baseline ABG levels. During the weaning process, ABG levels will be checked to assess how the client is tolerating the procedure. Other assessment parameters are less critical. Measuring fluid volume intake and output is always important when a client is being mechanically ventilated. Prior attempts at weaning and ECG results are documented on the client’s record, and the nurse can refer to them before the weaning process begins. 19. Which of the following would be most a. Administer a prescribed decongestant. appropriate for a male client with an arterial b. Instruct the client to breathe into a paper bag. blood gas (ABG) of pH 7.5, PaCO2 26 mm c. Offer the client fluids frequently. Hg, O2 saturation 96%, HCO3 24 mEq/L, and. Administer prescribed supplemental oxygen. 19. Answer B. The ABG results reveal respiratory alkalosis. The best intervention to raise the PaCO2 level would be to have the client breathe into a paper bag. All of the other options — such as administering a decongestant, offering fluids frequently, and administering supplemental oxygen — wouldn’t raise the lowered PaCO2 level. PaO2 94 mm Hg? 20. A female client is receiving a. pH supplemental oxygen. When determining th b. Bicarbonate (HCO3–) effectiveness of oxygen therapy, which Partial pressure of arterial oxygen (PaO2) 20. Answer C. The most significant and direct indicator of the effectiveness of oxygen therapy is the PaO2 value. Based on the PaO2 value, the nurse arterial blood gas value is most important? d. Partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide (PaCO2) may adjust the type of oxygen delivery (cannula, venturi mask, or mechanical ventilator), flow rate, and oxygen percentage. The other options reflect the client’s ventilation status, not oxygenation. 21. Nurse Julia is caring for a client who ha. Endotracheal suctioning a tracheostomy and temperature of 103° F b. Encouragement of coughing (39.4° C). Which of the following Use of cooling blanket interventions will most likely lower the d. Incentive spirometry 21. Answer A. Endotracheal suctioning removes secretions as well as gases from the airway and lowers the arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) level. Coughing and incentive spirometry improves oxygenation and should raise or maintain oxygen saturation. Because of superficial vasoconstriction, using a cooling blanket can lower peripheral oxygen saturation readings, but SaO2 levels wouldn’t be affected. client’s arterial blood oxygen saturation? 22. For a male client who has a chest tube a. Measuring and documenting the drainage in the connected to a closed water-seal drainage collection chamber system, the nurse should include which actio b. Maintaining continuous bubbling in the water- in the plan of care? seal chamber c. Keeping the collection chamber at chest level d. Stripping the chest tube every hour 22. Answer A. The nurse should measure and document the amount of chest tube drainage regularly to detect abnormal drainage patterns, such as may occur with a hemorrhage (if excessive) or a blockage (if decreased). Continuous bubbling in the water-seal chamber indicates a leak in the closed chest drainage system, which must be corrected. The nurse should keep the collection chamber below chest level to allow fluids to drain into it. The nurse should not strip chest tubes because doing so may traumatize the tissue or dislodge the tube. 23. Nurse Eve formulates a nursing a. drinking more than 1,500 ml of fluid daily. diagnosis of Activity intolerance related to b. being overweight. inadequate oxygenation and dyspnea for a eating a high-protein snack at bedtime. client with chronic bronchitis. To minimize d. eating more than three large meals a day. 23. Answer B. Conditions that increase oxygen demands include obesity, smoking, exposure to temperature extremes, and stress. A client with chronic bronchitis should drink at least 2,000 ml of fluid daily to thin mucus secretions; restricting fluid intake may be harmful. The nurse should encourage the client to eat a high-protein snack at bedtime because protein digestion produces an amino acid with sedating effects that may ease the insomnia this problem, the nurse instructs the client to avoid conditions that increase oxygen demands. Such conditions include: associated with chronic bronchitis. Eating more than three large meals a day may cause fullness, making breathing uncomfortable and difficult; however, it doesn’t increase oxygen demands. To help maintain adequate nutritional intake, the client with chronic bronchitis should eat small, frequent meals (up to six a day). 24. A black male client with asthma seeks a. lips. emergency care for acute respiratory distres b. mucous membranes. Because of this client’s dark skin, the nurse nail beds. should assess for cyanosis by inspecting the:d. earlobes. 24. Answer B. Skin color doesn’t affect the mucous membranes. The lips, nail beds, and earlobes are less reliable indicators of cyanosis because they’re affected by skin color. 25. A female client with asthma is receivina. 1 to 2 mcg/ml a theophylline preparation to promote b. 2 to 5 mcg/ml bronchodilation. Because of the risk of drug 5 to 10 mcg/ml toxicity, the nurse must monitor the client’s d. 10 to 20 mcg/ml 25. Answer D. The therapeutic serum theophylline concentration ranges from 10 to 20 mcg/ml. Values below 10 mcg/ml aren’t therapeutic. serum theophylline level closely. The nurse knows that the therapeutic theophylline concentration falls within which range? 26. A male client is to receive I.V. a. vancomycin should be infused over 60 to 90 vancomycin (Vancocin). When preparing to minutes in a large volume of fluid. administer this drug, the nurse should keep i b. vancomycin may cause irreversible neutropenia. mind that: c. vancomycin should be administered rapidly in a large volume of fluid. d. vancomycin should be administered over 1 to 2 26. Answer A. To avoid a hypotensive reaction from rapid I.V. administration, the nurse should infuse vancomycin slowly, over 60 to 90 minutes, in a large volume of fluid. Although neutropenia may occur in approximately 5% to 10% of clients receiving vancomycin, this adverse effect reverses rapidly when the drug is discontinued. minutes as an I.V. bolus. 27. Before seeing a newly assigned femalea. Myasthenia gravis client with respiratory alkalosis, the nurse b. Type 1 diabetes mellitus quickly reviews the client’s medical history. Extreme anxiety Which condition is a predisposing factor for d. Narcotic overdose 27. Answer C. Extreme anxiety may lead to respiratory alkalosis by causing hyperventilation, which results in excessive carbon dioxide (CO2) loss. Other conditions that may set the stage for respiratory alkalosis include fever, heart failure, and injury to the brain’s respiratory center, overventilation with a mechanical ventilator, respiratory alkalosis? pulmonary embolism, and early salicylate intoxication. Type 1 diabetes mellitus may lead to diabetic ketoacidosis; the deep, rapid respirations occurring in this disorder (Kussmaul’s respirations) don’t cause excessive CO2 loss. Myasthenia gravis and narcotic overdose suppress the respiratory drive, causing CO2 retention, not CO2 loss; this may lead to respiratory acidosis, not alkalosis. 28. At 11 p.m., a male client is admitted toa. alprazolam (Xanax). the emergency department. He has a b. propranolol (Inderal) respiratory rate of 44 breaths/minute. He’s morphine. anxious, and wheezes are audible. The clientd. albuterol (Proventil). 28. Answer D. The client is hypoxemic because of bronchoconstriction as evidenced by wheezes and a subnormal arterial oxygen saturation level. The client’s greatest need is bronchodilation, which can be accomplished by administering bronchodilators. Albuterol is a beta2 adrenergic agonist, which causes dilation of the bronchioles. It’s given by nebulization or metered-dose inhalation and may be given as often as every 30 to 60 minutes until relief is accomplished. Alprazolam is an anxiolytic and central nervous system depressant, which could suppress the client’s breathing. Propranolol is contraindicated in a client who’s wheezing because it’s a beta2 adrenergic antagonist. Morphine is a respiratory center depressant and is contraindicated in this situation. is immediately given oxygen by face mask and methylprednisolone (Depo-medrol) I.V. At 11:30 p.m., the client’s arterial blood oxygen saturation is 86% and he’s still wheezing. The nurse should plan to administer: 29. Pulmonary disease (COPD), which a. Encouraging the client to drink three glasses of nursing action best promotes adequate gas fluid daily exchange? b. Keeping the client in semi-Fowler’s position c. Using a high-flow Venturi mask to deliver oxygen as prescribed d. Administering a sedative as prescribed 29. Answer C. The client with COPD retains carbon dioxide, which inhibits stimulation of breathing by the medullary center in the brain. As a result, low oxygen levels in the blood stimulate respiration, and administering unspecified, unmonitored amounts of oxygen may depress ventilation. To promote adequate gas exchange, the nurse should use a Venturi mask to deliver a specified, controlled amount of oxygen consistently and accurately. Drinking three glasses of fluid daily wouldn’t affect gas exchange or be sufficient to liquefy secretions, which are common in COPD. Clients with COPD and respiratory distress should be placed in high Fowler’s position and shouldn’t receive sedatives or other drugs that may further depress the respiratory center. 30. Nurse Joana is teaching a client with a. It helps prevent early airway collapse. emphysema how to perform pursed-lip b. It increases inspiratory muscle strength breathing. The client asks the nurse to explai c. It decreases use of accessory breathing muscles. the purpose of this breathing technique. d. It prolongs the inspiratory phase of respiration. 30. Answer A. Pursed-lip breathing helps prevent early airway collapse. Learning this technique helps the client control respiration during periods of excitement, anxiety, exercise, and respiratory distress. To increase inspiratory muscle strength and endurance, the client may need to learn inspiratory resistive breathing. To decrease accessory muscle use and thus reduce the work of breathing, the client may need to learn diaphragmatic (abdominal) breathing. In pursed-lip breathing, the client mimics a normal inspiratory-expiratory (I:E) ratio of 1:2. (A client with emphysema may have an I:E ratio as high as 1:4.) Which explanation should the nurse provide? NEUROLOGY 1. A white female client is admitted to an a. Caucasian race acute care facility with a diagnosis of b. Female sex cerebrovascular accident (CVA). Her history Obesity reveals bronchial asthma, exogenous obesityd. Bronchial asthma 1. Answer C. Obesity is a risk factor for CVA. Other risk factors include a history of ischemic episodes, cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis of the cranial vessels, hypertension, polycythemia, smoking, hypercholesterolemia, oral contraceptive use, emotional stress, family history of CVA, and advancing age. The client’s race, sex, and bronchial asthma aren’t risk factors for CVA. and iron deficiency anemia. Which history finding is a risk factor for CVA? 2. The nurse is teaching a female client wia. take a hot bath. multiple sclerosis. When teaching the client b. rest in an air-conditioned room how to reduce fatigue, the nurse should tell increase the dose of muscle relaxants. the client to: d. avoid naps during the day 2. Answer B. Fatigue is a common symptom in clients with multiple sclerosis. Lowering the body temperature by resting in an air-conditioned room may relieve fatigue; however, extreme cold should be avoided. A hot bath or shower can increase body temperature, producing fatigue. Muscle relaxants, prescribed to reduce spasticity, can cause drowsiness and fatigue. Planning for frequent rest periods and naps can relieve fatigue. Other measures to reduce fatigue in the client with multiple sclerosis include treating depression, using occupational therapy to learn energy conservation techniques, and reducing spasticity. 3. A male client is having a tonic-clonic a. Elevate the head of the bed. seizures. What should the nurse do first? b. Restrain the client’s arms and legs. Place a tongue blade in the client’s mouth. d. Take measures to prevent injury. 3. Answer D. Protecting the client from injury is the immediate priority during a seizure. Elevating the head of the bed would have no effect on the client’s condition or safety. Restraining the client’s arms and legs could cause injury. Placing a tongue blade or other object in the client’s mouth could damage the teeth. 4. A female client with Guillain-Barré a. “You may have difficulty believing this, but the syndrome has paralysis affecting the paralysis caused by this disease is temporary.” respiratory muscles and requires mechanical b. “You’ll have to accept the fact that you’re ventilation. When the client asks the nurse permanently paralyzed. However, you won’t about the paralysis, how should the nurse have any sensory loss.” respond? c. “It must be hard to accept the permanency of your paralysis.” d. “You’ll first regain use of your legs and then 4. Answer A. The nurse should inform the client that the paralysis that accompanies Guillain-Barré syndrome is only temporary. Return of motor function begins proximally and extends distally in the legs. your arms.” 5. The nurse is working on a surgical floora. laminectomy. The nurse must logroll a male client followib. thoracotomy. a: hemorrhoidectomy. d. cystectomy. 5. Answer A. The client who has had spinal surgery, such as laminectomy, must be logrolled to keep the spinal column straight when turning. The client who has had a thoracotomy or cystectomy may turn himself or may be assisted into a comfortable position. Under normal circumstances, hemorrhoidectomy is an outpatient procedure, and the client may resume normal activities immediately after surgery. 6. A female client with a suspected brain a. Immobilize the neck before the client is moved tumor is scheduled for computed tomography onto a stretcher. (CT). What should the nurse do when b. Determine whether the client is allergic to 6. Answer B. Because CT commonly involves use of a contrast agent, the nurse should determine whether the client is allergic to iodine, contrast dyes, or shellfish. Neck immobilization is necessary only preparing the client for this test? iodine, contrast dyes, or shellfish. Place a cap over the client’s head. d. Administer a sedative as ordered. if the client has a suspected spinal cord injury. Placing a cap over the client’s head may lead to misinterpretation of test results; instead, the hair should be combed smoothly. The physician orders a sedative only if the client can’t be expected to remain still during the CT scan. 7. During a routine physical examination t a. use the pointed end of the reflex hammer when assess a male client’s deep tendon reflexes, the striking the Achilles tendon. nurse should make sure to: b. support the joint where the tendon is being tested. c. tap the tendon slowly and softly d. hold the reflex hammer tightly. 7. Answer B. To prevent the attached muscle from contracting, the nurse should support the joint where the tendon is being tested. The nurse should use the flat, not pointed, end of the reflex hammer when striking the Achilles tendon. (The pointed end is used to strike over small areas, such as the thumb placed over the biceps tendon.) Tapping the tendon slowly and softly wouldn’t provoke a deep tendon reflex response. The nurse should hold the reflex hammer loosely, not tightly, between the thumb and fingers so it can swing in an arc. 8. A female client is admitted in a a. Disturbed sensory perception (visual) disoriented and restless state after sustainingb. Self-care deficient: Dressing/grooming concussion during a car accident. Which Impaired verbal communication nursing diagnosis takes highest priority in thd. Risk for injury 8. Answer D. Because the client is disoriented and restless, the most important nursing diagnosis is risk for injury. Although the other options may be appropriate, they’re secondary because they don’t immediately affect the client’s health or safety. client’s plan of care? 9. A female client with amyotrophic laterala. Anxiety sclerosis (ALS) tells the nurse, “Sometimes b. Powerlessness feel so frustrated. I can’t do anything without Ineffective denial help!” This comment best supports which d. Risk for disuse syndrome 9. Answer B. This comment best supports a nursing diagnosis of Powerlessness because ALS may lead to locked-in syndrome, characterized by an active and functioning mind locked in a body that can’t perform even simple daily tasks. Although Anxiety and Risk for disuse syndrome may be diagnoses associated with ALS, the client’s comment specifically refers to an inability to act autonomously. A diagnosis of Ineffective denial would be indicated if the client didn’t seem to perceive the personal relevance of symptoms or danger. nursing diagnosis? 10. For a male client with suspected a. prevent respiratory alkalosis. 10. Answer C. The goal of treatment is to prevent increased intracranial pressure (ICP), a mostb. lower arterial pH. appropriate respiratory goal is to: promote carbon dioxide elimination. d. maintain partial pressure of arterial oxygen acidemia by eliminating carbon dioxide. That is because an acid environment in the brain causes cerebral vessels to dilate and therefore increases ICP. Preventing respiratory alkalosis and lowering arterial pH may bring about acidosis, an undesirable condition in this case. It isn’t necessary to maintain a PaO2 as high as 80 mm Hg; 60 mm Hg will adequately oxygenate most clients. (PaO2) above 80 mm Hg 11. Nurse Maureen witnesses a neighbor’s a. Flexed position husband sustain a fall from the roof of his b. Head tilt-chin lift house. The nurse rushes to the victim and Jaw thrust maneuver determines the need to opens the airway in thd. Modified head tilt-chin lift 11. Answer C. If a neck injury is suspected, the jaw thrust maneuver is used to open the airway. The head tilt–chin lift maneuver produces hyperextension of the neck and could cause complications if a neck injury is present. A flexed position is an inappropriate position for opening the airway. victim by using which method? 12. The nurse is assessing the motor functioa. Sternal rub of an unconscious male client. The nurse b. Nail bed pressure would plan to use which plan to use which o c. Pressure on the orbital rim the following to test the client’s peripheral d. Squeezing of the sternocleidomastoid muscle 12. Answer B. Motor testing in the unconscious client can be done only by testing response to painful stimuli. Nail bed pressure tests a basic peripheral response. Cerebral responses to pain are tested using sternal rub, placing upward pressure on the orbital rim, or squeezing the clavicle or sternocleidomastoid muscle. response to pain? 13. A female client admitted to the hospitaa. Hypertension with a neurological problem asks the nurse b. Heart failure whether magnetic resonance imaging may be Prosthetic valve replacement done. The nurse interprets that the client ma d. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder 13. Answer C. The client having a magnetic resonance imaging scan has all metallic objects removed because of the magnetic field generated by the device. A careful history is obtained to determine whether any metal objects are inside the client, such as orthopedic hardware, pacemakers, artificial heart valves, aneurysm clips, or intrauterine devices. These may heat up, become dislodged, or malfunction during this procedure. The client may be ineligible if significant risk exists. be ineligible for this diagnostic procedure based on the client’s history of: 14. A male client is having a lumbar a. Side-lying, with a pillow under the hip puncture performed. The nurse would plan tob. Prone, with a pillow under the abdomen place the client in which position? c. Prone, in slight-Trendelenburg’s position d. Side-lying, with the legs pulled up and head 14. Answer D. The client undergoing lumbar puncture is positioned lying on the side, with the legs pulled up to the abdomen and the head bent down onto the chest. This position helps open the spaces between the vertebrae. bent down onto chest. 15. The nurse is positioning the female a. Head mildline client with increased intracranial pressure. b. Head turned to the side Which of the following positions would the Neck in neutral position nurse avoid? d. Head of bed elevated 30 to 45 degrees 15. Answer B. The head of the client with increased intracranial pressure should be positioned so the head is in a neutral midline position. The nurse should avoid flexing or extending the client’s neck or turning the head side to side. The head of the bed should be raised to 30 to 45 degrees. Use of proper positions promotes venous drainage from the cranium to keep intracranial pressure down. 16. A female client has clear fluid leaking a. Is clear and tests negative for glucose from the nose following a basilar skull b. Is grossly bloody in appearance and has a pH of fracture. The nurse assesses that this is 6 cerebrospinal fluid if the fluid: c. Clumps together on the dressing and has a pH of 7 d. Separates into concentric rings and test positive 16. Answer D. Leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the ears or nose may accompany basilar skull fracture. CSF can be distinguished from other body fluids because the drainage will separate into bloody and yellow concentric rings on dressing material, called a halo sign. The fluid also tests positive for glucose. of glucose 17. A male client with a spinal cord injury a. Strict adherence to a bowel retraining program is prone to experiencing automatic b. Keeping the linen wrinkle-free under the client dysreflexia. The nurse would avoid which of c. Preventing unnecessary pressure on the lower the following measures to minimize the risk limbs of recurrence? d. Limiting bladder catheterization to once every 17. Answer D. The most frequent cause of autonomic dysreflexia is a distended bladder. Straight catheterization should be done every 4 to 6 hours, and foley catheters should be checked frequently to prevent kinks in the tubing. Constipation and fecal impaction are other causes, so maintaining bowel regularity is important. Other causes include stimulation of the skin from tactile, thermal, or painful stimuli. The nurse administers care to minimize risk in these areas. 12 hours 18. The nurse is caring for the male client a. Loosening restrictive clothing who begins to experience seizure activity b. Restraining the client’s limbs while in bed. Which of the following actions c. Removing the pillow and raising padded side by the nurse would be contraindicated? rails d. Positioning the client to side, if possible, with 18. Answer B. Nursing actions during a seizure include providing for privacy, loosening restrictive clothing, removing the pillow and raising side rails in the bed, and placing the client on one side with the head flexed forward, if possible, to allow the tongue to fall forward and facilitate drainage. The limbs are never restrained because the strong muscle contractions could cause the client harm. If the client is not in bed when seizure activity begins, the nurse lowers the client to the floor, if possible, protects the head from injury, and moves furniture that may the head flexed forward injure the client. Other aspects of care are as described for the client who is in bed. 19. The nurse is assigned to care for a a. The client has complete bilateral paralysis of the female client with complete right-sided arms and legs. hemiparesis. The nurse plans care knowing b. The client has weakness on the right side of the that this condition: body, including the face and tongue. c. The client has lost the ability to move the right arm but is able to walk independently. d. The client has lost the ability to move the right 19. Answer B. Hemiparesis is a weakness of one side of the body that may occur after a stroke. Complete hemiparesis is weakness of the face and tongue, arm, and leg on one side. Complete bilateral paralysis does not occur in this condition. The client with right-sided hemiparesis has weakness of the right arm and leg and needs assistance with feeding, bathing, and ambulating. arm but is able to walk independently. 20. The client with a brain attack (stroke) a. Giving the client thin liquids has residual dysphagia. When a diet order is b. Thickening liquids to the consistency of oatmeal initiated, the nurse avoids doing which of thec. Placing food on the unaffected side of the mouth following? d. Allowing plenty of time for chewing and 20. Answer A. Before the client with dysphagia is started on a diet, the gag and swallow reflexes must have returned. The client is assisted with meals as needed and is given ample time to chew and swallow. Food is placed on the unaffected side of the mouth. Liquids are thickened to avoid aspiration. swallowing 21. The nurse is assessing the adaptation oa. Gets angry with family if they interrupt a task the female client to changes in functional b. Experiences bouts of depression and irritability status after a brain attack (stroke). The nurse c. Has difficulty with using modified feeding assesses that the client is adapting most utensils successfully if the client: d. Consistently uses adaptive equipment in 21. Answer D. Clients are evaluated as coping successfully with lifestyle changes after a brain attack (stroke) if they make appropriate lifestyle alterations, use the assistance of others, and have appropriate social interactions. Options A, B, and C are not adaptive behaviors. dressing self 22. Nurse Kristine is trying to communicata. Speaking to the client at a slower rate with a client with brain attack (stroke) and b. Allowing plenty of time for the client to respond aphasia. Which of the following actions by thc. Completing the sentences that the client cannot nurse would be least helpful to the client? finish d. Looking directly at the client during 22. Answer C. Clients with aphasia after brain attack (stroke) often fatigue easily and have a short attention span. General guidelines when trying to communicate with the aphasic client include speaking more slowly and allowing adequate response time, listening to and watching attempts to communicate, and trying to put the client at ease with a caring and understanding manner. The nurse would avoid shouting (because the client is not deaf), appearing rushed for a response, and letting family members provide all the responses for the client. attempts at speech 23. A female client has experienced an a. Getting too little exercise episode of myasthenic crisis. The nurse wo b. Taking excess medication assess whether the client has precipitating Omitting doses of medication factors such as: d. Increasing intake of fatty foods 23. Answer C. Myasthenic crisis often is caused by undermedication and responds to the administration of cholinergic medications, such as neostigmine (Prostigmin) and pyridostigmine (Mestinon). Cholinergic crisis (the opposite problem) is caused by excess medication and responds to withholding of medications. Too little exercise and fatty food intake are incorrect. Overexertion and overeating possibly could trigger myasthenic crisis. 24. The nurse is teaching the female client a. Eating large, well-balanced meals with myasthenia gravis about the prevention b. Doing muscle-strengthening exercises of myasthenic and cholinergic crises. The c. Doing all chores early in the day while less nurse tells the client that this is most fatigued effectively done by: d. Taking medications on time to maintain 24. Answer D. Clients with myasthenia gravis are taught to space out activities over the day to conserve energy and restore muscle strength. Taking medications correctly to maintain blood levels that are not too low or too high is important. Musclestrengthening exercises are not helpful and can fatigue the client. Overeating is a cause of exacerbation of symptoms, as is exposure to heat, crowds, erratic sleep habits, and emotional stress. therapeutic blood levels 25. A male client with Bell’s palsy asks th a. Unknown, but possibly includes ischemia, viral nurse what has caused this problem. The infection, or an autoimmune problem nurse’s response is based on an understandin b. Unknown, but possibly includes long-term that the cause is: tissue malnutrition and cellular hypoxia c. Primary genetic in origin, triggered by exposure to meningitis d. Primarily genetic in origin, triggered by 25. Answer A. Bell’s palsy is a one-sided facial paralysis from compression of the facial nerve. The exact cause is unknown, but may include vascular ischemia, infection, exposure to viruses such as herpes zoster or herpes simplex, autoimmune disease, or a combination of these factors. exposure to neurotoxins 26. The nurse has given the male client wia. Exposure to cold and drafts Bell’s palsy instructions on preserving musclb. Massage the face with a gentle upward motion tone in the face and preventing denervation. c. Perform facial exercises The nurse determines that the client needs d. Wrinkle the forehead, blow out the cheeks, and 26. Answer A. Prevention of muscle atrophy with Bell’s palsy is accomplished with facial massage, facial exercises, and electrical stimulation of the nerves. Exposure to cold or drafts is avoided. Local application of heat to the face may improve blood flow and provide comfort. additional information if the client states that he or she will: whistle 27. Female client is admitted to the a. Seizures or trauma to the brain hospital with a diagnosis of Guillain-Barre b. Meningitis during the last 5 years syndrome. The nurse inquires during the Back injury or trauma to the spinal cord 27. Answer D. Guillain-Barré syndrome is a clinical syndrome of unknown origin that involves cranial and peripheral nerves. Many clients report a nursing admission interview if the client has history of: d. Respiratory or gastrointestinal infection during the previous month. history of respiratory or gastrointestinal infection in the 1 to 4 weeks before the onset of neurological deficits. Occasionally, the syndrome can be triggered by vaccination or surgery. 28. A female client with Guillian-Barre a. Giving client full control over care decisions syndrome has ascending paralysis and is and restricting visitors intubated and receiving mechanical b. Providing positive feedback and encouraging ventilation. Which of the following strategies active range of motion would the nurse incorporate in the plan of c. Providing information, giving positive feedback, care to help the client cope with this illness? and encouraging relaxation d. Providing intravaneously administered 28. Answer C. The client with Guillain-Barré syndrome experiences fear and anxiety from the ascending paralysis and sudden onset of the disorder. The nurse can alleviate these fears by providing accurate information about the client’s condition, giving expert care and positive feedback to the client, and encouraging relaxation and distraction. The family can become involved with selected care activities and provide diversion for the client as well. sedatives, reducing distractions and limiting visitors 29. A male client has an impairment of a. Speak loudly to the client cranial nerve II. Specific to this impairment, b. Test the temperature of the shower water the nurse would plan to do which of the c. Check the temperature of the food on the following to ensure client to ensure client delivery tray. safety? d. Provide a clear path for ambulation without 29. Answer D. Cranial nerve II is the optic nerve, which governs vision. The nurse can provide safety for the visually impaired client by clearing the path of obstacles when ambulating. Testing the shower water temperature would be useful if there were an impairment of peripheral nerves. Speaking loudly may help overcome a deficit of cranial nerve VIII (vestibulocochlear). Cranial nerve VII (facial) and IX (glossopharyngeal) control taste from the anterior two thirds and posterior third of the tongue, respectively. obstacles 30. A female client has a neurological a. Is disoriented to person, place, and time deficit involving the limbic system. Specific b. Affect is flat, with periods of emotional lability to this type of deficit, the nurse would c. Cannot recall what was eaten for breakfast today document which of the following informatio d. Demonstrate inability to add and subtract; does 30. Answer B. The limbic system is responsible for feelings (affect) and emotions. Calculation ability and knowledge of current events relates to function of the frontal lobe. The cerebral hemispheres, with specific regional functions, control orientation. Recall of recent events is controlled by the hippocampus. related to the client’s behavior. not know who is president 1. If a male client experienced a a. body temperature control. cerebrovascular accident (CVA) that damag b. balance and equilibrium. the hypothalamus, the nurse would anticipate visual acuity. that the client has problems with: d. thinking and reasoning. 1. Answer A. The body’s thermostat is located in the hypothalamus; therefore, injury to that area can cause problems of body temperature control. Balance and equilibrium problems are related to cerebellar damage. Visual acuity problems would occur following occipital or optic nerve injury. Thinking and reasoning problems are the result of injury to the cerebrum. 2. A female client admitted to an acute car a. phenytoin (Dilantin) facility after a car accident develops signs anb. mannitol (Osmitrol) symptoms of increased intracranial pressure lidocaine (Xylocaine) (ICP). The client is intubated and placed on d. furosemide (Lasix) 2. Answer C. Administering lidocaine via an endotracheal tube may minimize elevations in ICP caused by suctioning. Although mannitol and furosemide may be given to reduce ICP, they’re administered parenterally, not endotracheally. Phenytoin doesn’t reduce ICP directly but may be used to abolish seizures, which can increase ICP. However, phenytoin isn’t administered endotracheally. mechanical ventilation to help reduce ICP. To prevent a further rise in ICP caused by suctioning, the nurse anticipates administering which drug endotracheally before suctioning? 3. After striking his head on a tree while a. Give him a barbiturate. falling from a ladder, a young man age 18 is b. Place him on mechanical ventilation. admitted to the emergency department. He’s Perform a lumbar puncture. unconscious and his pupils are nonreactive. d. Elevate the head of his bed. 3. Answer C. The client’s history and assessment suggest that he may have increased intracranial pressure (ICP). If this is the case, lumbar puncture shouldn’t be done because it can quickly decompress the central nervous system and, thereby, cause additional damage. After a head injury, barbiturates may be given to prevent seizures; mechanical ventilation may be required if breathing deteriorates; and elevating the head of the bed may be used to reduce ICP. Which intervention would be the most dangerous for the client? 4. When obtaining the health history from a. light flashes and floaters in front of the eye. male client with retinal detachment, the nurs b. a recent driving accident while changing lanes. expects the client to report: c. headaches, nausea, and redness of the eyes. d. frequent episodes of double vision. 4. Answer A. The sudden appearance of light flashes and floaters in front of the affected eye is characteristic of retinal detachment. Difficulty seeing cars in another driving lane suggests gradual loss of peripheral vision, which may indicate glaucoma. Headache, nausea, and redness of the eyes are signs of acute (angle-closure) glaucoma. Double vision is common in clients with cataracts. 5. Which nursing diagnosis takes highest a. Imbalanced nutrition: Less than body priority for a client with Parkinson’s crisis? requirements b. Ineffective airway clearance c. Impaired urinary elimination d. Risk for injury 5. Answer B. In Parkinson’s crisis, dopaminerelated symptoms are severely exacerbated, virtually immobilizing the client. A client confined to bed during such a crisis is at risk for aspiration and pneumonia. Also, excessive drooling increases the risk of airway obstruction. Because of these concerns, the nursing diagnosis of Ineffective airway clearance takes highest priority. Although the other options also are appropriate, they aren’t immediately life-threatening. 6. To encourage adequate nutritional intakea. stay with the client and encourage him to eat. for a female client with Alzheimer’s disease, b. help the client fill out his menu. the nurse should: c. give the client privacy during meals. d. fill out the menu for the client. 6. Answer A. Staying with the client and encouraging him to feed himself will ensure adequate food intake. A client with Alzheimer’s disease can forget how to eat. Allowing privacy during meals, filling out the menu, or helping the client to complete the menu doesn’t ensure adequate nutritional intake. 7. The nurse is performing a mental status a. Cerebellar function examination on a male client diagnosed withb. Intellectual function subdural hematoma. This test assesses which Cerebral function of the following? d. Sensory function 7. Answer C. The mental status examination assesses functions governed by the cerebrum. Some of these are orientation, attention span, judgment, and abstract reasoning. Intellectual functioning isn’t the only cerebral activity. Cerebellar function testing assesses coordination, equilibrium, and fine motor movement. Sensory function testing involves assessment of pain, light-touch sensation, and temperature discrimination. 8. Shortly after admission to an acute care a. In 30 to 45 seconds facility, a male client with a seizure disorderb. In 10 to 15 minutes develops status epilepticus. The physician In 30 to 45 minutes orders diazepam (Valium) 10 mg I.V. stat. d. In 1 to 2 hours 8. Answer B. When used to treat status epilepticus, diazepam may be given every 10 to 15 minutes, as needed, to a maximum dose of 30 mg. The nurse can repeat the regimen in 2 to 4 hours, if necessary, but the total dose shouldn’t exceed 100 mg in 24 hours. The nurse must not administer I.V. diazepam faster than 5 mg/minute. Therefore, the dose can’t be repeated in 30 to 45 seconds because the first dose wouldn’t have been administered completely by that time. Waiting longer than 15 minutes to repeat the dose would increase the client’s risk of complications associated with status epilepticus. How soon can the nurse administer a second dose of diazepam, if needed and prescribed? 9. A female client complains of periorbital a. Parasympathomimetic agent aching, tearing, blurred vision, and b. Sympatholytic agent photophobia in her right eye. Ophthalmologic Adrenergic blocker examination reveals a small, irregular, d. Cholinergic blocker 9. Answer D. Atropine sulfate is a cholinergic blocker. It isn’t a parasympathomimetic agent, a sympatholytic agent, or an adrenergic blocker. nonreactive pupil — a condition resulting from acute iris inflammation (iritis). As part of the client’s therapeutic regimen, the physician prescribes atropine sulfate (Atropisol), two drops of 0.5% solution in the right eye twice daily. Atropine sulfate belongs to which drug classification? 10. Emergency medical technicians transp a. Assessing the left leg a 27-year-old iron worker to the emergency b. Assessing the pupils department. They tell the nurse, “He fell fro c. Placing the client in Trendelenburg’s position a two-story building. He has a large contusio d. Assessing level of consciousness 10. Answer A. In the scenario, airway and breathing are established so the nurse’s next priority should be circulation. With a compound fracture of the femur, there is a high risk of profuse bleeding; therefore, the nurse should assess the site. Neurologic assessment is a secondary concern to airway, breathing, and circulation. The nurse doesn’t have enough data to warrant putting the client in Trendelenburg’s position. on his left chest and a hematoma in the left parietal area. He has a compound fracture of his left femur and he’s comatose. We intubated him and he’s maintaining an arterial oxygen saturation of 92% by pulse oximeter with a manualresuscitation bag.” Which intervention by the nurse has the highest priority? 11. An auto mechanic accidentally has a. increasing the exudative reaction of ocular battery acid splashed in his eyes. His tissue. coworkers irrigate his eyes with water for 20 b. decreasing leukocyte infiltration at the site of minutes, and then take him to the emergency ocular inflammation. department of a nearby hospital, where he c. inhibiting the action of carbonic anhydrase. receives emergency care for corneal injury. d. producing a miotic reaction by stimulating and 11. Answer B. Dexamethasone exerts its therapeutic effect by decreasing leukocyte infiltration at the site of ocular inflammation. This reduces the exudative reaction of diseased tissue, lessening edema, redness, and scarring. Dexamethasone and other anti-inflammatory agents don’t inhibit the action of carbonic anhydrase or produce any type of miotic reaction. The physician prescribes dexamethasone (Maxidex Ophthalmic Suspension), two drops of 0.1% solution to be instilled initially into the conjunctival sacs of both eyes every hour; and polymyxin B sulfate (Neosporin Ophthalmic), 0.5% ointment to be placed in the conjunctival sacs of both eyes every 3 hours. Dexamethasone exerts its therapeutic effect by: contracting the sphincter muscles of the iris. 12. Nurse April is caring for a client who a. More back pain than the first postoperative day underwent a lumbar laminectomy 2 days ag b. Paresthesia in the dermatomes near the wounds Which of the following findings should the c. Urine retention or incontinence nurse consider abnormal? d. Temperature of 99.2° F (37.3° C) 12. Answer C. Urine retention or incontinence may indicate cauda equina syndrome, which requires immediate surgery. An increase in pain on the second postoperative day is common because the long- acting local anesthetic, which may have been injected during surgery, will wear off. While paresthesia is common after surgery, progressive weakness or paralysis may indicate spinal nerve compression. A mild fever is also common after surgery but is considered significant only if it reaches 101° F (38.3° C). 13. After an eye examination, a male clienta. instilling one drop of pilocarpine 0.25% into is diagnosed with open-angle glaucoma. The both eyes daily. physician prescribes pilocarpine ophthalmic b. instilling one drop of pilocarpine 0.25% into solution (Pilocar), 0.25% gtt i, OU q.i.d. both eyes four times daily. Based on this prescription, the nurse should c. instilling one drop of pilocarpine 0.25% into the teach the client or a family member to right eye daily. administer the drug by: d. instilling one drop of pilocarpine 0.25% into the 13. Answer B. The abbreviation "gtt" stands for drop, "i" is the apothecary symbol for the number 1, OU signifies both eyes, and "q.i.d." means four times a day. Therefore, one drop of pilocarpine 0.25% should be instilled into both eyes four times daily. left eye four times daily. 14. A female client who’s paralyzed on the a. left side has been receiving physical therapy b. and attending teaching sessions about safety. c. Which behavior indicates that the client accurately understands safety measures d. The client leaves the side rails down. The client uses a mirror to inspect the skin. The client repositions only after being reminded to do so. The client hangs the left arm over the side of the 14. Answer B. Using a mirror enables the client to inspect all areas of the skin for signs of breakdown without the help of staff or family members. The client should keep the side rails up to help with repositioning and to prevent falls. The paralyzed client should take responsibility for repositioning or for reminding the staff to assist with it, if needed. A client with left-side paralysis may not realize that the left arm is hanging over the side of the wheelchair. However, the nurse should call this to the client’s attention because the arm can get caught in the wheel spokes or develop impaired circulation from being in a dependent position for too long. related to paralysis? wheelchair. 15. A male client in the emergency a. Ataxic 15. Answer C. A helicopod gait is an abnormal gait department has a suspected neurologic b. Dystrophic in which the client’s feet make a half circle with each disorder. To assess gait, the nurse asks the Helicopod step. An ataxic gait is staggering and unsteady. client to take a few steps; with each step, the client’s feet make a half circle. To document the client’s gait, the nurse should use which term? d. Steppage In a dystrophic gait, the client waddles with the legs far apart. In a steppage gait, the feet and toes raise high off the floor and the heel comes down heavily with each step. 16. A client, age 22, is admitted with a. A private room down the hall from the nurses’ bacterial meningitis. Which hospital room station would be the best choice for this client? b. An isolation room three doors from the nurses’ station c. A semiprivate room with a 32-year-old client who has viral meningitis d. A two-bed room with a client who previously 16. Answer B. A client with bacterial meningitis should be kept in isolation for at least 24 hours after admission and, during the initial acute phase, should be as close to the nurses’ station as possible to allow maximal observation. Placing the client in a room with a client who has viral meningitis may cause harm to both clients because the organisms causing viral and bacterial meningitis differ; either client may contract the other’s disease. Immunity to bacterial meningitis can’t be acquired; therefore, a client who previously had bacterial meningitis shouldn’t be put at risk by rooming with a client who has just been diagnosed with this disease. had bacterial meningitis 17. A physician diagnoses a client with a. Ulcerative colitis myasthenia gravis, prescribing pyridostigminb. Blood dyscrasia (Mestinon), 60 mg P.O. every 3 hours. Before Intestinal obstruction administering this anticholinesterase agent, d. Spinal cord injury 17. Answer C. Anticholinesterase agents such as pyridostigmine are contraindicated in a client with a mechanical obstruction of the intestines or urinary tract, peritonitis, or hypersensitivity to anticholinesterase agents. Ulcerative colitis, blood dyscrasia, and spinal cord injury don’t contraindicate use of the drug. the nurse reviews the client’s history. Which preexisting condition would contraindicate the use of pyridostigmine? 18. A female client is admitted to the facilia. vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss. for investigation of balance and coordinatio b. vertigo, vomiting, and nystagmus problems, including possible Ménière’s vertigo, pain, and hearing impairment. disease. When assessing this client, the nurs d. vertigo, blurred vision, and fever. 18. Answer A. Ménière’s disease, an inner ear disease, is characterized by the symptom triad of vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss. The combination of vertigo, vomiting, and nystagmus suggests labyrinthitis. Ménière’s disease rarely causes pain, blurred vision, or fever. expects to note: 19. A male client with a conductive hearinga. “Lie in bed with your head elevated, and refrain disorder caused by ankylosis of the stapes in from blowing your nose for 24 hours.” the oval window undergoes a stapedectomy tb. “Try to ambulate independently after about 24 19. Answer D. For 30 days after a stapedectomy, the client should avoid air travel, sudden movements that may cause trauma, and exposure to loud sounds and pressure changes (such as from high altitudes). remove the stapes and replace the impaired hours.” bone with a prosthesis. After the c. “Shampoo your hair every day for 10 days to stapedectomy, the nurse should provide which help prevent ear infection.” client instruction? d. “Don’t fly in an airplane, climb to high altitudes, Immediately after surgery, the client should lie flat with the surgical ear facing upward; nose blowing is permitted but should be done gently and on one side at a time. The client’s first attempt at postoperative ambulation should be supervised to prevent falls caused by vertigo and light-headedness. The client must avoid shampooing and swimming to keep the dressing and the ear dry. make sudden movements, or expose yourself to loud sounds for 30 days.” 20. Nurse Oliver is monitoring a client for a. Excessive tearing adverse reactions to dantrolene (Dantrium). b. Urine retention Which adverse reaction is most common? Muscle weakness d. Slurred speech 20. Answer C. The most common adverse reaction to dantrolene is muscle weakness. The drug also may depress liver function or cause idiosyncratic hepatitis. Muscle weakness is rarely severe enough to cause slurring of speech, drooling, and enuresis. Although excessive tearing and urine retention are adverse reactions associated with dantrolene use, they aren’t as common as muscle weakness 21. The nurse is monitoring a male client fa. Tachycardia adverse reactions to atropine sulfate (Atropi b. Increased salivation Care) eyedrops. Systemic absorption of Hypotension atropine sulfate through the conjunctiva can d. Apnea 21. Answer A. Systemic absorption of atropine sulfate can cause tachycardia, palpitations, flushing, dry skin, ataxia, and confusion. To minimize systemic absorption, the client should apply digital pressure over the punctum at the inner canthus for 2 to 3 minutes after instilling the drops. The drug also may cause dry mouth. It isn’t known to cause hypotension or apnea. cause which adverse reaction? 22. A male client is admitted with a cervic a. Impaired physical mobility spine injury sustained during a diving b. Ineffective breathing pattern accident. When planning this client’s care, the Disturbed sensory perception (tactile) nurse should assign highest priority to whic d. Self-care deficient: Dressing/grooming 22. Answer B. Because a cervical spine injury can cause respiratory distress, the nurse should take immediate action to maintain a patent airway and provide adequate oxygenation. The other options may be appropriate for a client with a spinal cord injury — particularly during the course of recovery — but don’t take precedence over a diagnosis of Ineffective breathing pattern. nursing diagnosis? 23. A male client has a history of painful, a. long-term treatment of epilepsy. continuous muscle spasms. He has taken b. postoperative pain management of laminectomy several skeletal muscle relaxants without clients. experiencing relief. His physician prescribes c. postoperative pain management of 23. Answer D. In addition to relieving painful muscle spasms, diazepam also is recommended for treatment of spasticity associated with spinal cord lesions. Diazepam’s use is limited by its central diazepam (Valium), 2 mg P.O. twice daily. In addition to being used to relieve painful muscle spasms, diazepam also is recommended for: diskectomy clients d. treatment of spasticity associated with spinal cord lesions. nervous system effects and the tolerance that develops with prolonged use. The parenteral form of diazepam can treat status epilepticus, but the drug’s sedating properties make it an unsuitable choice for long-term management of epilepsy. Diazepam isn’t an analgesic agent. 24. A female client who was found a. introducing ice water into the external auditory unconscious at home is brought to the hospital canal. by a rescue squad. In the intensive care unit, b. touching the cornea with a wisp of cotton. the nurse checks the client’s oculocephalic c. turning the client’s head suddenly while holding (doll’s eye) response by: the eyelids open. d. shining a bright light into the pupil. 24. Answer C. To elicit the oculocephalic response, which detects cranial nerve compression, the nurse turns the client’s head suddenly while holding the eyelids open. Normally, the eyes move from side to side when the head is turned; in an abnormal response, the eyes remain fixed. The nurse introduces ice water into the external auditory canal when testing the oculovestibular response; normally, the client’s eyes deviate to the side of ice water introduction. The nurse touches the client’s cornea with a wisp of cotton to elicit the corneal reflex response, which reveals brain stem function; blinking is the normal response. Shining a bright light into the client’s pupil helps evaluate brain stem and cranial nerve III functions; normally, the pupil responds by constricting. 25. While reviewing a client’s chart, the nurse notices that the female client has myasthenia gravis. Which of the following statements about neuromuscular blocking agents is true for a client with this condition? a. The client may be less sensitive to the effects of a neuromuscular blocking agent. b. Succinylcholine shouldn’t be used; pancuronium may be used in a lower dosage. c. Pancuronium shouldn’t be used; succinylcholine may be used in a lower dosage. d. Pancuronium and succinylcholine both require cautious administration. 25. Answer D. The nurse must cautiously administer pancuronium, succinylcholine, and any other neuromuscular blocking agent to a client with myasthenia gravis. Such a client isn’t less sensitive to the effects of a neuromuscular blocking agent. Either succinylcholine or pancuronium can be administered in the usual adult dosage to a client with myasthenia gravis. 26. A male client is color blind. The nurse a. rods. understands that this client has a problem b. cones. with: lens. d. aqueous humor. 26. Answer B. Cones provide daylight color vision, and their stimulation is interpreted as color. If one or more types of cones are absent or defective, color blindness occurs. Rods are sensitive to low levels of illumination but can’t discriminate color. The lens is responsible for focusing images. Aqueous humor is a clear watery fluid and isn’t involved with color perception. 27. A female client who was trapped insid a. Diencephalon car for hours after a head-on collision is b. Medulla rushed to the emergency department with Midbrain multiple injuries. During the neurologic d. Cortex 27. Answer C. Decerebrate posturing, characterized by abnormal extension in response to painful stimuli, indicates damage to the midbrain. With damage to the diencephalon or cortex, abnormal flexion (decorticate posturing) occurs when a painful stimulus is applied. Damage to the medulla results in flaccidity. examination, the client responds to painful stimuli with decerebrate posturing. This finding indicates damage to which part of the brain? 28. The nurse is assessing a 37-year-old a. Vision changes client diagnosed with multiple sclerosis. b. Absent deep tendon reflexes Which of the following symptoms would the Tremors at rest nurse expect to find? d. Flaccid muscles 28. Answer A. Vision changes, such as diplopia, nystagmus, and blurred vision, are symptoms of multiple sclerosis. Deep tendon reflexes may be increased or hyperactive — not absent. Babinski’s sign may be positive. Tremors at rest aren’t characteristic of multiple sclerosis; however, intentional tremors, or those occurring with purposeful voluntary movement, are common in clients with multiple sclerosis. Affected muscles are spastic, rather than flaccid. 29. The nurse is caring for a male client a. Sit with the client for a few minutes. diagnosed with a cerebral aneurysm who b. Administer an analgesic. reports a severe headache. Which action Inform the nurse manager. should the nurse perform? d. Call the physician immediately. 29. Answer D. The headache may be an indication that the aneurysm is leaking. The nurse should notify the physician immediately. Sitting with the client is appropriate but only after the physician has been notified of the change in the client’s condition. The physician will decide whether or not administration of an analgesic is indicated. Informing the nurse manager isn’t necessary. 30. During recovery from a cerebrovascul a. cranial nerves I and II. accident (CVA), a female client is given b. cranial nerves III and V. nothing by mouth, to help prevent aspiration. cranial nerves VI and VIII. To determine when the client is ready for a d. cranial nerves IX and X. 30. Answer D. Swallowing is a motor function of cranial nerves IX and X. Cranial nerves I, II, and VIII don’t possess motor functions. The motor functions of cranial nerve III include extraocular eye movement, eyelid elevation, and pupil constriction. The motor function of cranial nerve V is chewing. Cranial nerve VI controls lateral eye movement. liquid diet, the nurse assesses the client’s swallowing ability once each shift. This assessment evaluates: BASIC CARE AND COMFORT 1. Nurse Jessie is caring for an elderly a. arranging for the wheelchair woman who has had a fractured hip repairedb. asking her family to visit In the first few days following the surgical assisting her to sit out of bed in a chair qid repair, which of the following nursing d. encouraging the use of an overhead trapeze 1. Answer D. Exercise is important to keep the joints and muscles functioning and to prevent secondary complications. Using the overhead trapeze prevents hazards of immobility by permitting movement in bed and strengthening of the upper extremities in preparation for ambulation. Sitting in a wheelchair would require too great hip flexion initially. Asking her family to visit would not facilitate the resumption of activities. Sitting in a chair would cause too much hip flexion. The client initially needs to be in a low Fowler’s position or taking a few steps (as ordered) with the aid of a walker. measures will best facilitate the resumption of activities for this client? 2. What do you think is the most important measure intake and output. nursing order in a client with major head check albumin level. trauma who is about to receive bolus enteral monitor glucose levels. feeding? increase enteral feeding. 2. Answer A. It is important to measure intake and output, which should equal. Enteral feeding are hyperosmotic agents pulling fluid from cells into vascular bed. Water given before feeding will present a hyperosmotic diuresis. I and O measures assess fluid balance. 3. What is the pathological process causin a. ascites and edema. esophageal varices is b. systemic hypertension. portal hypertension. d. dilated veins and varicesitis. 3. Answer C. Esophageal varices results from increased portal hypertension. In portal hypertension, the liver cannot accept all of the fluid from the portal vein. The excess fluid will back flow to the vessels with lesser pressure, such as esophageal veins or rectal veins causing esophageal varices or hemorrhoids. 4. Which of the following interventions a. Elevate the head of the bed on 4-6 inch blocks. will help lessen the effect of GERD (acid b. Lie down after eating. reflux)? c. Increase fluid intake just before bedtime. d. Wear a girdle. 4. Answer A. Elevation of the head of the bed allows gravity to assist in decreasing the backflow of acid into the esophagus. Fluid does not flow uphill. The other three options all increase fluid backflow into the esophagus through position or increasing abdominal pressure. 5. What is the main benefit of therapeutic a. to help a person with swollen legs to decrease massages is: the fluid retention. b. to help a person with duodenal ulcers feel better. c. to help damaged tissue in a diabetic to heal. d. to improve circulation and muscles tone. 5. Answer D. Particularly in the elderly adults, therapeutic massage will help improve circulation and muscle tone as well as the personal attention and social interaction that a good massage provides. A massage is contraindicated in any condition where massage to damaged tissue can dislodge a blood clot. 6. Which of the following foods should be a. Lettuce avoided by clients who are prone to developb. Eggs heartburn as a result of gastroesophgeal reflux Chocolate disease (GERD)? d. Butterscotch 6. Answer C. Ingestion of chocolate can reduce lower esophageal sphincter (LES) pressure leading to reflux and clinical symptoms of GERD. All of the other foods do not affect LES pressure. 7. Which of the following should be a. Withhold medications while the TPN is infusing. included in a plan of care for a client b. Change TPN solution every 24 hours. receiving total parenteral nutrition (TPN)? c. Flush the TPN line with water prior to initiating nutritional support. d. Keep client on complete bed rest during TPN 7. Answer B. TPN solutions should be changed every 24 hours in order to prevent bacterial overgrowth due to hypertonicity of the solution. Option 1 is incorrect; medication therapy can continue during TPN therapy. Option 3 is incorrect; flushing is not required because the initiation of TPN does not require a client to remain on bed rest during therapy. However, other clinical conditions of the client may affect mobility issues and warrant the client’s being on bed rest. therapy. 8. Which of the following should be includa. Remove all dairy products from the diet. in a plan of care for a client who is lactose b. Frozen yogurt can be included in the diet. intolerant? c. Drink small amounts of milk on an empty stomach. d. Spread out selection of dairy products 8. Answer B. Clients who are lactose intolerant can digest frozen yogurt. Yogurt products are formed by bacterial action, and this action assists in the digestion of lactose. The freezing process further stops bacterial action so that limited lactase activity remains. Option 1 is incorrect; elimination of all dairy products can lead to significant clinical deficiencies of other nutrients. Option 3 is incorrect because drinking milk on an empty stomach can exacerbate clinical symptoms. Drinking milk with a meal may benefit the client because other foods, throughout the day. (especially fat) may decrease transit time and allow for increased lactase activity. Option 4 is incorrect because although individual tolerance should be acknowledged, spreading out the use of known dairy products will usually exacerbate clinical symptoms. 9. Pain tolerance in an elderly patient witha. stay the same. cancer would: b. be lowered. be increased. d. no effect on pain tolerance. 9. Answer B. There is potential for a lowered pain tolerance to exist with diminished adaptative capacity. 10. What is the main advantage of a. costs less. cutaneous stimulation in managing paint: b. restricts movement and decreases. c. gives client control over pain syndrome. d. allows the family to care for the patient at 10. Answer C. Cutaneous stimulation allows the patient to have control over his pain and allows him to be in his own environment. Cutaneous stimulation increases movement and decreases pain. home. 11. The nurse is instructing a 65 year-old a. exercise doing weight bearing activities female client diagnosed with osteoporosis. b. exercise to reduce weight The most important instruction regarding c. avoid exercise activities that increase the risk of exercise would be to fracture d. exercise to strengthen muscles and thereby 11. Answer A. Weight bearing exercises are beneficial in the treatment of osteoporosis. Although loss of bone cannot be substantially reversed, further loss can be greatly reduced if the client includes weight bearing exercises along with estrogen replacement and calcium supplements in their treatment protocol. protect bones 12. A client in a long term care facility a. have the client identify coping methods complains of pain. The nurse collects data b. get the description of the location and intensity about the client’s pain. The first step in pain of the pain assessment is for the nurse to c. accept the client’s report of pain d. determine the client’s status of pain 12. Answer C. Although all of the options above are correct, the first and most important piece of information in this client’s pain assessment is what the client is telling you about the pain –“the client’s report.” 13. Which statement best describes the effects of immobility in children? a. Immobility prevents the progression of language and fine motor development b. Immobility in children has similar physical effects to those found in adults c. Children are more susceptible to the effects of immobility than are adults d. Children are likely to have prolonged immobility with subsequent complications 14. After a myocardial infarction, a client i a. 3 oz. broiled fish, 1 baked potato, ½ cup canned placed on a sodium restricted diet. When the beets, 1 orange, and milk nurse is teaching the client about the diet, b. 3 oz. canned salmon, fresh broccoli, 1 biscuit, which meal plan would be the most tea, and 1 apple appropriate to suggest? c. A bologna sandwich, fresh eggplant, 2 oz fresh fruit, tea, and apple juice d. 3 oz. turkey, 1 fresh sweet potato, 1/2 cup 14. Answer D. Canned fish and vegetables and cured meats are high in sodium. This meal does not contain any canned fish and/or vegetables or cured meats fresh green beans, milk, and 1 orange 15. A nurse is assessing several clients in a a. A 79 year-old malnourished client on bed rest long term health care facility. Which client isb. An obese client who uses a wheelchair at highest risk for development of decubitus c. An incontinent client who has had 3 diarrhea ulcers? stools d. An 80 year-old ambulatory diabetic client 15. Answer A. Weighing significantly less than ideal body weight increases the number and surface area of bony prominences which are susceptible to pressure ulcers. Thus, malnutrition is a major risk factor for decubiti, due in part to poor hydration and inadequate protein intake. 16. Ms. Kelly. has had a CVA a. Holding the cane in her left hand, Ms. Kelly. (cerebrovascular accident) and has severe moves the cane forward first, then her right leg, right-sided weakness. She has been taught to and finally her left leg walk with a cane. The nurse is evaluating herb. Holding the cane in her right hand, Ms. Kelly. use of the cane prior to discharge. Which of moves the cane forward first, then her left leg, the following reflects correct use of the cane? and finally her right leg c. Holding the cane in her right hand, Ms. Kelly. moves the cane and her right leg forward, then moves her left leg forward. d. Holding the cane in her left hand, Ms. Kelly. 16. Answer A. When a person with weakness on one side uses a cane, there should always be two points of contact with the floor. When Ms. Kelly. moves the cane forward, she has both feet on the floor, providing stability. As she moves the weak leg, the cane and the strong leg provide support. Finally, the cane, which is even with the weak leg, provides stability while she moves the strong leg. She should not hold the cane with her weak arm. The use of the cane requires arm strength to ensure that the cane provides adequate stability when standing on the weak leg. The cane should be held in the left hand, the hand opposite the affected leg. If Ms. Kelly. moved the cane and her strong foot at the same time, she would be left standing on her weak leg at one point. This would be unstable at best; at worse, impossible moves the cane and her left leg forward, then moves her right leg forward 17. The nurse is instructing a woman in a low-fat, high-fiber diet. Which of the a. Tuna salad sandwich on whole wheat bread. 17. Answer B. Mayonnaise in tuna salad is high in fat. The whole wheat bread has some fiber. This following food choices, if selected by the b. Vegetable soup made with vegetable stock, client, indicate an understanding of a low-fat, carrots, celery, and legumes served with toasted high-fiber diet? oat bread c. Chef’s salad with hard boiled eggs and fatfree dressing d. Broiled chicken stuffed with chopped apples and choice shows a low-fat soup (which would have been higher in fat if made with chicken or beef stock) and high-fiber bread and soup contents (both the vegetables and the legumes). Salad is high in fiber, but hard boiled eggs are high in fat. There is some fiber in the apples and walnuts. The walnuts are high in fat, as is the chicken. walnuts 18. An 85-year-old male patient has been a. Stiffness of the right ankle joint bedridden for two weeks. Which of the b. Soreness of the gums following complaints by the patient indicates Short-term memory loss. to the nurse that he is developing a d. Decreased appetite. 18. Answer A. Stiffness of a joint may indicate the beginning of a contracture and/or early muscle atrophy. Soreness of the gums is not related to immobility. Short-term memory loss is not related to immobility. Decreased appetite is unlikely to be related to immobility. complication of immobility? 19. An eleven-month-old infant is brought a. Normal dietary intake. c the pediatric clinic. The nurse suspects that thb. Relevant sociocultural, economic, and child has iron deficiency anemia. Because iron educational background of the family. deficiency anemia is suspected, which of the c. Any evidence of blood in the stools following is the most important information td. A history of maternal anemia during pregnancy 19. Answer A. Iron deficiency anemia occurs commonly in children 6 to 24 months of age. For the first 4 to 5 months of infancy iron stores laid down for the baby during pregnancy are adequate. When fetal iron stores are depleted, supplemental dietary obtain from the infant’s parents? iron needs to be supplied to meet the infant’s rapid growth needs. Iron deficiency may occur in the infant who drinks mostly milk, which contains no iron, and does not receive adequate dietary iron or supplemental iron. Daily dietary intake is much more related to the diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia than is sociocultural, economic, and educational background of the family. Iron deficiency anemia in an infant is very unlikely to be related to gastrointestinal bleeding. Anemia during pregnancy is unlikely to be the cause of the infant’s iron deficiency anemia. Fetal iron stores are drawn from the mother even if she is anemic. 20. A 46-year-old female with chronic constipation is assessed by the nurse for a a. The client’s dietary habits include foods high in bulk. 20. Answer D. Foods high in bulk are appropriate. Exercise should be a part of a bowel training bowel training regimen. Which factor indicates further information is needed by the b. The client’s fluid intake is between 2500- 3000 ml per day regimen. To assess the client for a bowel training program the factors causing the bowel alteration should be assessed. A routine for bowel elimination should be based on the client’s previous bowel habits and alterations in bowel habits that have occurred because of illness or trauma. The client and the family should assist in the planning of the program which should include foods high in bulk, adequate exercise, and fluid intake of 2500-3000 ml nurse? c. The client engages in moderate exercise each day d. The client’s bowel habits were not discussed. HEALTH PROMOTION AND MAINTENANCE 1. Nurse Tristan is assigned to care for a a. A client with a colostomy group of clients. On review of the clients’ b. A client with congestive heart failure medical records, the nurse determines that c. A client with decreased kidney function which client is at risk for deficient fluid d. A client receiving frequent wound irrigation 1. Answer A. Causes of deficient fluid volume include vomiting, diarrhea, conditions that cause increased respirations or increased urinary output, insufficient IV fluid replacement, draining fistulas, and the presence of an ileostomy or colostomy. A client with congestive heart failure or decreased kidney function, or a client receiving frequent wound irrigations, is at risk for excess fluid volume. volume? 2. Nurse Lorena caring for a client who haa. Lung congestion been receiving intravenous diuretics suspectb. Decrease hematocrit that the client is experiencing a deficient fluid Increased blood pressure volume. Which assessment finding would thd. Decrease central venous pressure (CVP) 2. Answer D. Assessment findings in a client with a deficient fluid volume include increased respirations and heart rate, decreased central venous pressure (CVP), weight loss, poor skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, decreased urine volume, increased specific gravity of the urine, increased hematocrit, and altered level of consciousness. The normal CVP is between 4 and 11 cm H2O. A client with dehydration has a low CVP. nurse note in a client with this condition? 3. Nurse George is assigned to care for a a. The client taking diuretics group of clients. On review of the clients’ b. The client with renal failure medical records, the nurse determines that c. The client with an ileostomy which client is at risk for excess fluid d. The client who requires gastrointestinal 3. Answer B. The causes of excess fluid volume include decreased kidney function, congestive heart failure, the use of hypotonic fluids to replace isotonic fluid losses, excessive irrigation of wounds and body cavities, and excessive ingestion of sodium. The client taking diuretics, the client with an ileostomy, and the client who requires gastrointestinal suctioning are at risk for deficient fluid volume. volume? suctioning 4. Nurse Levy is caring for a client with a. Weight loss 4. Answer C. Assessment findings associated with congestive heart failure. On assessment the b. Flat neck and hand veins nurse notes that the client is dyspneic and that An increase in blood pressure crackles are audible on auscultation. The nu d. A decreased central venous pressure (CVP) excess fluid volume include cough, dyspnea, crackles, tachypnea, tachycardia, an elevated blood pressure and a bounding pulse, an elevated CVP, weight gain, edema, neck and hand vein distention, altered level of consciousness, and a decreased hematocrit. suspects excess fluid volume. What additional signs would the nurse expect to note in this client if excess fluid volume is present? 5. Nurse Faye is preparing to care for a a. Has renal failure client with a potassium deficit. The nurse b. Requires nasogastric suction reviews the client was at risk for developing Has a history of Addison’s disease the potassium deficit because the client: d. Is taking a potassium-sparing diuretic 5. Answer B. Potassium-rich gastrointestinal fluids are lost through gastrointestinal suction, placing the client at risk for hypokalemia. The client with renal failure or Addison’s disease and the client taking a potassium-sparing diuretic are at risk for hyperkalemia. 6. Nurse Jessica reviews a client’s a. U waves electrolyte laboratory report and notes that thb. Absent P waves potassium level is 3.2 mEq/L. which of the Elevated T waves following would the nurse note on the d. Elevated ST segment 6. Answer A. A serum potassium level lower than 3.5 mEq/L indicates hypokalemia. Potassium deficit is a common electrolyte imbalance and is potentially life threatening. Electrocardiographic changes include inverted T waves, ST segment depression, and prominent U waves. Absent P waves are not a characteristic of hypokalemia. electrocardiogram as a result of the laboratory value? 7. Tanya, a nursing student needs to a. Obtaining a cotrolled IV infusion pump administer potassium chloride intravenously b. Monitoring urine output during administration as prescribed to a client with hypokalemia. c. Diluting in appropriate amount of normal saline The nursing instructor determines that the d. Preparing the medication for bolus 7. Answer D. Potassium chloride administered intravenously must always be diluted in IV fluid and infused via a pump or controller. The usual concentration of IV potassium chloride is 20 to 40 mEq/L. Potassium chloride is never given by bolus (IV push). Giving potassium chloride by IV push can result in cardiac arrest. Dilution in normal saline is recommended, but dextrose solution is avoided because this type of solution increases intracellular potassium shifting. The IV bag containing the potassium chloride is always gently agitated before hanging. The IV site is monitored closely because potassium chloride is irritating to the veins and the risk of phlebitis exists. The nurse monitors urinary output during administration and contacts the student is unprepared for this procedure if the student states that which of the following is part of the plan for preparation and administration of the potassium? administration physician if the urinary output is less than 30 mL/hr. 8. Nurse Kim caring for a group of clients a. The client with colitis reviews the electrolyte laboratory results andb. The client with Cushing’s syndrome notes a potassium level og 5.5 mEq/L on onec. The client who has been overusing laxatives client’s laboratory report. The nurse d. The client who has sustained a traumatic burn 8. Answer D. A serum potassium level higher than 5.1 mEq/L indicates hyperkalemia. Clients who experience cellular shifting of potassium in the early stages of massive cell destruction, such as with trauma, burns, sepsis, or metabolic or respiratory acidosis, are at risk for hyperkalemia. The client with Cushing’s syndrome or colitis and the client who has been overusing laxatives are at risk for hypokalemia. understands that which client is at highest risk for the development of a potassium value at this level? 9. Nurse Nerissa reviews the electrolyte a. ST depression results of an assigned client and notes that thb. Inverted T wave potassium level is 5.4 mEq/L. which of the Prominent U wave following would the nurse expect to note on d. Tall peaked T waves 9. Answer D. A serum potassium level higher than 5.1 mEq/L indicates hyperkalemia. Electrocardiographic changes include flat P waves, prolonged PR intervals, widened QRS complexes, and tall peaked T waves. the electrocardiogram as a result of the laboratory value? 10. Nurse Noemi caring for a group of a. The client with renal failure clients reviews the electrolyte laboratory b. The client who is taking diuretics results and notes a sodium level of 130 mEq/ The client with hyperaldosteronism on one client’s laboratory report. The nurse d. The client who is taking corticosteroids 10. Answer B. Hyponatremia is evidenced by a serum sodium level lower than 135 mEq/L. Hyponatremia can occur in the client taking diuretics. The client taking corticosteroids and the client with renal failure or hyperaldosteronism are at risk for hypernatremia. understands that which client is at highest risk for the development of a sodium value at this level? 11. Nurse Princess is caring for a client wia. Dry skin acute congestive heart failure who is b. Decrease urinary output receiving high doses of a diuretic. On Hyperactive bowel sounds assessment, the nurse notes that the client had. Increased specific gravity of the urine 11. Answer C. Hyperactive bowel sounds indicate hyponatremia. Options A, B, and D are signs of hypernatremia. In hyponatremia, increased urinary output and decreased specific gravity of the urine would be noted. Dry skin occurs in deficient fluid volume. flat neck veins, generalized muscles weakness, and diminished deep tendon reflexes. The nurse suspects hyponatremia. What additional signs would the nurse expect to note in this client if hyponatremia were present? 12. Nurse Andrew is reviewing a client’s a. Prolonged bed rest 12. Answer A. The normal serum calcium level is laboratory report and notes that the serum b. Renal insufficiency calcium level is 4.0 mg/dL. The nurse Hyperparathyroidism understands that which condition most likel d. Excessive ingestion of vitamin D 8.6 to 10.0 mg/dL. A client with a serum calcium level of 4.0 mg/dL is experiencing hypocalcemia. The excessive ingestion of vitamin D and hyperparathyroidism are causative factors associated with hypercalcemia. End-stage renal disease, rather than renal insufficiency, is a cause of hypocalcemia. Prolonged bed rest is a cause of hypocalcemia. Although immobilization initially can cause hypercalcemia, the long-term effect of prolonged bed rest is hypocalcemia. caused this serum calcium level? 13. Nurse Editha is assessing a client with a. Twitching suspected diagnosis of hypocalcemia. Whic b. Negative Trousseau’s sign of the following clinical manifestations would Hypoactive bowel sounds the nurse expect to note in the client? d. Hypoactive deep tendon reflexes 13. Answer A. Signs of hypocalcemia include paresthesias followed by numbness, hyperactive deep tendon reflexes, and a positive Trousseau’s or Chvostek’s sign. Additional signs of hypocalcemia include increased neuromuscular excitability, muscle cramps, twitching, tetany, seizures, irritability, and anxiety. Gastrointestinal symptoms include increased gastric motility, hyperactive bowel sounds, abdominal cramping, and diarrhea. 14. Nurse Sally caring for a client with a. Widened T wave hypocalcemia would expect to note which o b. Prominent U wave the following changes on the Prolonged QT interval electrocardiogram? d. Shortened ST segment 14. Answer C. Electrocardiographic changes that occur in a client with hypocalcemia include a prolonged ST or QT interval. A shortened ST segment and a widened T wave occur with hypercalcemia. Prominent U waves occur with hypokalemia. 15. Nurse Sam caring for a client with a. Prominent U waves severe malnutrition reviews the laboratory b. Prolonged PR interval results and notes a magnesium level of 1.0 Depressed ST segment mg/dL. Which electrocardiographic changesd. Widened QRS complexes 15. Answer C. The normal magnesium level is 1.6 to 2.6 mg/dL. A magnesium level of 1.0 mg/dL indicates hypomagnesemia. In hypomagnesemia, the nurse would note tall T waves and a depressed ST segment. Options 2 and 4 would be noted in a client experiencing hypermagnesemia. Prominent U waves occur with hypokalemia. would the nurse expects to note based on the magnesium level? 16. Nurse Danny reviews a client’s a. Alcoholism laboratory report and notes that the client’s b. Renal insufficiency serum phosphorus level is 2.0 mg/dL. Which Hypoparathyroidism condition most likely caused this serum d. Tumor lysis syndrome 16. Answer A. The normal serum phosphorus level is 2.7 to 4.5 mg/dL. The client is experiencing hypophosphatemia. Causative factors relate to malnutrition or starvation and the use of aluminum phosphorus level? hydroxide–based or magnesium-based antacids. Malnutrition is associated with alcoholism. Hypoparathyroidism, tumor lysis syndrome, and renal insufficiency are causative factors of hyperphosphatemia. 17. A client with a 3-day history of nausea a. A decreased pH and an increased CO2 and vomiting presents to the emergency b. An increased pH and a decreased CO2 department. The client is hypoventilating and A decreased pH and a decreased HCO3 has a respiratory rete of 6 breaths/min. The d. An increased pH with an increased HCO3 17. Answer D. Clients experiencing nausea and vomiting would most likely present with metabolic alkalosis resulting from loss of gastric acid, thus causing the pH and HCO3– to increase. Symptoms experienced by the client would include hypoventilation and tachycardia. electrocardiogram (ECG) monitor displays tachycardia, with a heart rate of 120 beats/min. Arterial blood gases are drawn and nurse Gio reviews the results, expecting to note which of the following? 18. Nurse Venus is assigned to a 40-yearola. 45 units/L client who has a diagnosis of chronic b. 100 units/L pancreatitis. The nurse reviews the laboratory 300 units/L result, anticipating a laboratory report that d. 500 units/L 18. Answer C. The normal serum amylase level is 25 to 151 units/L. With chronic cases of pancreatitis, the rise in serum amylase levels usually does not exceed three times the normal value. In acute pancreatitis, the value may exceed five times the normal value. indicating a laboratory report that indicates a serum amylase level of: 19. A client has been admitted to the a. 3 mg/dL hospital for urinary tract infection and b. 15 mg/dL dehydration. Nurse Veronica determines that 29 mg/dL the client has received adequate volume d. 35 mg/dL 19. Answer B. The normal blood urea nitrogen level is 8 to 25 mg/dL. Values such as those in options C and D reflect continued dehydration. Option A reflects a lower than normal value, which may occur with fluid volume overload, among other conditions. replacement if the blood urea nitrogen level drops to: 20. A maleclient arrives in the emergency a. Normal level room complaining of chest pain that began 4 b. Low value that indicates possible gastritis hours ago. A troponin T blood specimen is c. Level that indicates a myocardial infraction obtained, and the results indicate a level of d. Level that indicates the presence of possible 20. Answer C. Troponin is a regulatory protein found in striated muscle. The troponins function together in the contractile apparatus for striated muscle in skeletal muscle and in the myocardium. Increased amounts of troponins are released into the bloodstream when an infarction causes damage to the myocardium. A troponin T value that is higher 0.6 ng/mL. Nurse Celeste interprets that this result indicates a: angina than 0.1 to 0.2 ng/mL is consistent with a myocardial infarction. A normal troponin I level is lower than 0.6 ng/mL. 21. An adult client has had laboratory wor a. 0.2 mg/dL done as part of a routine physical b. 0.5 mg/dL examination. Nurse Amy interprets that the 1.9 mg/dL client may have a mild degree of renal d. 3.5 mg/dl 21. Answer C. The normal serum creatinine level for adults is 0.6 to 1.3 mg/dL. The client with a mild degree of renal insufficiency would have a slightly elevated level. A creatinine level of 0.2 mg/dL is low, and a level of 0.5 mg/dL is just below normal. A creatinine level of 3.5 mg/dL may be associated with acute or chronic renal failure. insufficiency if which of the following serum creatinine levels is noted? 22. A female client with atrial fibrillation a. Adding a dose of heparin sodium who is receiving maintenance therapy of b. Holding the next dose of warfarin warfarin sodium (Coumadin) has a Increasing the next dose of warfarin prothrombin time of 35 seconds. Based on thd. Administering the next dose of warfarin 22. Answer B. The normal prothrombin time (PT) is 9.6 to 11.8 seconds (male adult) or 9.5 to 11.3 seconds (female adult). A therapeutic PT level is 1.5 to 2.0 times higher than the normal level. Because the value of 35 seconds is high (and perhaps near the critical range), the nurse should anticipate that the client would not receive further doses at this time. prothrombin time, nurse Daniel anticipates which of the following orders? 23. A client is receiving a continuous a. Discontinuing the heparin infusion intravenous infusion of heparin sodium to b. Increasing the rate of the heparin infusion treat deep vein thrombosis. The client’s Decreasing the rate of the heparin infusion activated partial thromboplastin (aPTT) timed. Leaving the rate of the heparin infusion as 23. Answer D. The normal activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) varies between 20 and 36 seconds, depending on the type of activator used in testing. The therapeutic dose of heparin for treatment of deep vein thrombosis is to keep the aPTT between 1.5 and 2.5 times normal. Thus, the client’s aPTT is within the therapeutic range, and the dose should remain unchanged. is 65 seconds. Nurse Jessie anticipates that which action is needed? is 24. An adult client was diagnosed with acute pancreatitis 9 days ago. The nurse interprets that the client is recovering from this episode if the serum lipase level a. b. d. 20 units/L 80 units/L 135 units/L 350 units/L 24. Answer C. The normal serum lipase level is 10 to 140 units/L. The client who is recovering from acute pancreatitis usually has elevated lipase levels for about 10 days after the onset of symptoms. This makes lipase a valuable test in monitoring the decreases to which of the following values, which is just below the upper limit of normal? client’s pancreatic function because serum amylase levels usually return to normal 3 days after the onset of symptoms. Option C is the only option that contains a value just below the upper limit of normal. 25. An adult female has a hemoglobin level a. Dehydration 25. Answer C. The normal hemoglobin level for an of 10.8 g/dL. Nurse Gemma interprets that b. Heart failure this result is most likely caused by which of Iron deficiency anemia the following conditions noted in the client’ d. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease adult female client is 12 to 15 g/dL. Iron deficiency anemia can result in lower hemoglobin levels. Dehydration may increase the hemoglobin level by hemoconcentration. Heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease may increase the hemoglobin level as a result of the body’s need for more oxygen-carrying capacity. history? GEN. Misc. MED/SURG NURSING I/II 1. Following surgery, Mario complains of mild A. “Pain will become less each day.” incisional pain while performing deep- breathing B. “This is a normal reaction after surgery.” and coughing exercises. The nurse’s best response C. “With a pillow, apply pressure against the incision.” D. “I 1. Answer: (C) “With a pillow, apply pressure against the incision.” Applying pressure against the incision with a pillow will help lessen the intra-abdominal pressure created by coughing which causes tension on the incision that leads to pain. would be: will give you the pain medication the physician ordered.” 2. The nurse needs to carefully assess the complaint A. are expected to experience chronic pain of pain of the elderly because older people B. have a decreased pain threshold C. experience reduced sensory perception D. have altered mental function 2. Answer: (C) experience reduced sensory perception Degenerative changes occur in the elderly. The response to pain in the elderly maybe lessened because of reduced acuity of touch, alterations in neural pathways and diminished processing of sensory data. 3. Mary received AtropineSO4 as a pre-medication A. The patient is having an allergic reaction to the drug. 30 minutes ago and is now complaining of dry B. The patient needs a higher dose of this drug mouth and her PR is higher, than before the C. This is normal side-effect of AtSO4 medication was administered. The nurse’s best D. The patient is anxious about upcoming surgery 3. Answer: (C) This is normal side-effect of AtSO4 Atropine sulfate is a vagolytic drug that decreases oropharyngeal secretions and increases the heart rate. 4. Ana’s postoperative vital signs are a blood A.Put the client in modified Trendelenberg’s position. 4. Answer: (D) Administer Demerol 50mg IM q4h Administering Demerol, which is a narcotic analgesic, can depress respiratory and cardiac function and thus not given to a patient in shock. What is needed is promotion for adequate oxygenation and perfusion. All the other interventions can be expected to be done by the nurse. pressure of 80/50 mm Hg, a pulse of 140, and B. Administer oxygen at 100%. respirations of 32. Suspecting shock, which of the C. Monitor urine output every hour. following orders would the nurse question? D. Administer Demerol 50mg IM q4h 5. Mr. Pablo, diagnosed with Bladder Cancer, is A. "Good evening, Mr. Pablo. Wasn’t it a pleasant day, scheduled for a cystectomy with the creation of an today?" ileal conduit in the morning. He is wringing his B. "Mr, Pablo, you must be so worried, I’ll leave you alone hands and pacing the floor when the nurse enters with your thoughts. his room. What is the best approach? C. “Mr. Pablo, you’ll wear out the hospital floors and yourself at this rate." D. "Mr. Pablo, you appear anxious to me. How are you 5. Answer: (D) "Mr. Pablo, you appear anxious to me. How are you feeling about tomorrow’s surgery?" The client is showing signs of anxiety reaction to a stressful event. Recognizing the client’s anxiety conveys acceptance of his behavior and will allow for verbalization of feelings and concerns. feeling about tomorrow’s surgery?" 6. After surgery, Gina returns from the A. Call the physician immediately. Postanesthesia Care Unit (Recovery Room) with a B. Administer the prescribed antiemetic. nasogastric tube in place following a gall bladder C. Check the patency of the nasogastric tube for any surgery. She continues to complain of nausea. obstruction. Which action would the nurse take? D. Change the patient’s position. 6. Answer: (C) Check the patency of the nasogastric tube for any obstruction. Nausea is one of the common complaints of a patient after receiving general anesthesia. But this complaint could be aggravated by gastric distention especially in a patient who has undergone abdominal surgery. Insertion of the NGT helps relieve the problem. Checking on the patency of the NGT for any obstruction will help the nurse determine the cause of the problem and institute the necessary intervention. 7. Mr. Perez is in continuous pain from cancer thatA. Reassure him that the nurses will not hurt him has metastasized to the bone. Pain medication B. Let him perform his own activities of daily living provides little relief and he refuses to move. The C. Handle him gently when assisting with required care D. 7. Answer: (C) Handle him gently when assisting with required care Patients with cancer and bone metastasis experience severe pain especially when moving. Bone tumors weaken the bone to appoint at which normal activities and even position changes can lead to fracture. During nursing care, the patient needs to be supported and handled gently. nurse should plan to: Complete A.M. care quickly as possible when necessary 8. A client returns from the recovery room at 9AM A. Notify his physician. alert and oriented, with an IV infusing. His pulse is B. Take his vital signs again in 15 minutes. 82, blood pressure is 120/80, respirations are 20, andC. Take his vital signs again in an hour. all are within normal range. At 10 am and at 11 am, D. Place the patient in shock position. 8. Answer: (B) Take his vital signs again in 15 minutes. Monitoring the client’s vital signs following surgery gives the nurse a sound information about the client’s condition. Complications can occur during this period as a result of the surgery or the anesthesia or both. Keeping close track of changes in the VS and validating them will help the nurse initiate interventions to prevent complications from occurring. his vital signs are stable. At noon, however, his pulse rate is 94, blood pressure is 116/74, and respirations are 24. What nursing action is most appropriate? 9. A 56 year old construction worker is brought to A. Reactive pupils the hospital unconscious after falling from a 2-story B. A depressed fontanel building. When assessing the client, the nurse wouldC. Bleeding from ears be most concerned if the assessment revealed: D. An elevated temperature 9. Answer: (C) Bleeding from ears The nurse needs to perform a thorough assessment that could indicate alterations in cerebral function, increased intracranial pressures, fractures and bleeding. Bleeding from the ears occurs only with basal skull fractures that can easily contribute to increased intracranial pressure and brain herniation 10. Which of the ff. statements by the client to the A. “I exercise every other day.” nurse indicates a risk factor for CAD? B. “My father died of Myasthenia Gravis.” C. “My cholesterol is 180.” D. “I smoke 1 1/2 packs of cigarettes per day.” 10. Answer: (D) “I smoke 1 1/2 packs of cigarettes per day.” Smoking has been considered as one of the major modifiable risk factors for coronary artery disease. Exercise and maintaining normal serum cholesterol levels help in its prevention. 11. Mr. Braga was ordered Digoxin 0.25 mg. OD. A. It has positive inotropic and negative chronotropic effects Which is poor knowledge regarding this drug? B. The positive inotropic effect will decrease urine output C. 11. Answer: (B) The positive inotropic effect will decrease urine output Inotropic effect of drugs on the heart causes increase force of its contraction. This increases cardiac output that improves renal perfusion resulting in an improved urine output. Toxixity can occur more easily in the presence of hypokalemia, liver and renal problems D. Do not give the drug if the apical rate is less than 60 beats per minute. 12. Valsalva maneuver can result in bradycardia. A. Use of stool softeners. Which of the following activities will not stimulate B. Enema administration Valsalva’s maneuver? C. Gagging while toothbrushing. D. Lifting heavy objects 12. Answer: (A) Use of stool softeners. Straining or bearing down activities can cause vagal stimulation that leads to bradycardia. Use of stool softeners promote easy bowel evacuation that prevents straining or the valsalva maneuver. 13. The nurse is teaching the patient regarding his permanent artificial pacemaker. Which information A. take the pulse rate once a day, in the morning upon awakening 13. Answer: (D) may engage in contact sports The client should be advised by the nurse to avoid contact given by the nurse shows her knowledge deficit B. may be allowed to use electrical appliances about the artificial cardiac pacemaker? C. have regular follow up care D. may engage in contact sports sports. This will prevent trauma to the area of the pacemaker generator. 14. A patient with angina pectoris is being A. “When your chest pain begins, lie down, and place one discharged home with nitroglycerine tablets. Which tablet under your tongue. If the pain continues, take of the following instructions does the nurse include another tablet in 5 minutes.” in the teaching? B. “Place one tablet under your tongue. If the pain is not relieved in 15 minutes, go to the hospital.” C. “Continue your activity, and if the pain does not go away 14. Answer: (D) “Place one Nitroglycerine tablet under the tongue every five minutes for three doses. Go to the hospital if the pain is unrelieved. Angina pectoris is caused by myocardial ischemia related to decreased coronary blood supply. Giving nitroglycerine will produce coronary vasodilation that improves the coronary blood flow in 3 – 5 mins. If the chest pain is unrelieved, after three tablets, there is a possibility of acute coronary occlusion that requires immediate medical attention. in 10 minutes, begin taking the nitro tablets one every 5 minutes for 15 minutes, then go lie down.” D. “Place one Nitroglycerine tablet under the tongue every five minutes for three doses. Go to the hospital if the pain is unrelieved. 15. A client with chronic heart failure has been A. Whole milk placed on a diet restricted to 2000mg. of sodium per B. Canned sardines day. The client demonstrates adequate knowledge if C. Plain nuts behaviors are evident such as not salting food and D. Eggs 15. Answer: (B) Canned sardines Canned foods are generally rich in sodium content as salt is used as the main preservative. avoidance of which food? 16. A student nurse is assigned to a client who has A. Apply a heating pad to the involved site. diagnosis of thrombophlebitis. Which action by thiB. Elevate the client’s legs 90 degrees. team member is most appropriate? C. Instruct the client about the need for bed rest. D. Provide active range-of-motion exercises to both legs at 16. Answer: (C) Instruct the client about the need for bed rest. In a client with thrombophlebitis, bedrest will prevent the dislodgment of the clot in the extremity which can lead to pulmonary embolism. least twice every shift. 17. A client receiving heparin sodium asks the nursA. It dissolves existing thrombi. how the drug works. Which of the following pointsB. It prevents conversion of factors that are needed in the would the nurse include in the explanation to the formation of clots. client? C. It inactivates thrombin that forms and dissolves existing thrombi. D. It interferes with vitamin K absorption. 17. Answer: (B) It prevents conversion of factors that are needed in the formation of clots. Heparin is an anticoagulant. It prevents the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. It does not dissolve a clot. 18. The nurse is conducting an education session for A. Dyspnea on exertion a group of smokers in a “stop smoking” class. B. Foamy, blood-tinged sputum Which finding would the nurse state as a common C. Wheezing sound on inspiration symptom of lung cancer? : D. Cough or change in a chronic cough 18. Answer: (D) Cough or change in a chronic cough Cigarette smoke is a carcinogen that irritates and damages the respiratory epithelium. The irritation causes the cough which initially maybe dry, persistent and unproductive. As the tumor enlarges, obstruction of the airways occurs and the cough may become productive due to infection. 19. Which is the most relevant knowledge about A. Oxygen at 1-2L/min is given to maintain the hypoxic oxygen administration to a client with COPD? stimulus for breathing. B. Hypoxia stimulates the central chemoreceptors in the medulla that makes the client breath. C. Oxygen is administered best using a non-rebreathing mask D. Blood gases are monitored using a pulse oximeter. 19. Answer: (A) Oxygen at 1-2L/min is given to maintain the hypoxic stimulus for breathing. COPD causes a chronic CO2 retention that renders the medulla insensitive to the CO2 stimulation for breathing. The hypoxic state of the client then becomes the stimulus for breathing. Giving the clientoxygen in low concentrations will maintain the client’s hypoxic drive. 20. When suctioning mucus from a client’s lungs, A. Lubricate the catheter tip with sterile saline before 20. Answer: (C) Suction until the client indicates to stop which nursing action would be least appropriate? insertion. B. Use sterile technique with a two-gloved approach C. Suction until the client indicates to stop or no longer than 20 second D. Hyperoxygenate the client before and after suctioning or no longer than 20 second One hazard encountered when suctioning a client is the development of hypoxia. Suctioning sucks not only the secretions but also the gases found in the airways. This can be prevented by suctioning the client for an average time of 5-10 seconds and not more than 15 seconds and hyperoxygenating the client before and after suctioning. 21. Dr. Santos prescribes oral rifampin (RimactaneA. Cause less irritation to the gastrointestinal tract and isoniazid (INH) for a client with a positive B. Destroy resistant organisms and promote proper blood Tuberculin skin test. When informing the client of levels of the drugs this decision, the nurse knows that the purpose of C. Gain a more rapid systemic effect this choice of treatment is to D. Delay resistance and increase the tuberculostatic effect 21. Answer: (D) Delay resistance and increase the tuberculostatic effect Pulmonary TB is treated primarily with chemotherapeutic agents for 6-12 mons. A prolonged treatment duration is necessary to ensure eradication of the organisms and to prevent relapse. The increasing prevalence of drug resistance points to the need to begin the treatment with drugs in combination. Using drugs in combination can delay the drug resistance. 22. Mario undergoes a left thoracotomy and a A. Reduce incisional pain. partial pneumonectomy. Chest tubes are inserted, B. Facilitate ventilation of the left lung. and one-bottle water-seal drainage is instituted in C. Equalize pressure in the pleural space. the operating room. In the postanesthesia care unit D. Increase venous return 22. Answer: (B) Facilitate ventilation of the left lung. Since only a partial pneumonectomy is done, there is a need to promote expansion of this remaining Left lung by positioning the client on the opposite unoperated side. Mario is placed in Fowler’s position on either his right side or on his back to 23. A client with COPD is being prepared for A. Breath in and out as fully as possible before placing the discharge. The following are relevant instructions to mouthpiece inside the mouth. the client regarding the use of an oral inhaler B. Inhale slowly through the mouth as the canister is pressed EXCEPT down C. Hold his breath for about 10 seconds before exhaling D. 23. Answer: (D) Slowly breath out through the mouth with pursed lips after inhaling the drug. If the client breathes out through the mouth with pursed lips, this can easily force the just inhaled drug out of the respiratory tract that will lessen its effectiveness. Slowly breath out through the mouth with pursed lips after inhaling the drug. 24. A client is scheduled for a bronchoscopy. When A. Food and fluids will be withheld for at least 2 hours. teaching the client what to expect afterward, the B. Warm saline gargles will be done q 2h. nurse’s highest priority of information would be C. Coughing and deep-breathing exercises will be done q2h. D. Only ice chips and cold liquids will be allowed initially. 24. Answer: (A) Food and fluids will be withheld for at least 2 hours. Prior to bronchoscopy, the doctors sprays the back of the throat with anesthetic to minimize the gag reflex and thus facilitate the insertion of the bronchoscope. Giving the client food and drink after the procedure without checking on the return of the gag reflex can cause the client to aspirate. The gag reflex usually returns after two hours. 25. The nurse enters the room of a client with chroniA. Take heart rate and blood pressure. obstructive pulmonary disease. The client’s nasal B. Call the physician. cannula oxygen is running at a rate of 6 L per C. Lower the oxygen rate. minute, the skin color is pink, and the respirations D. Position the client in a Fowler’s position. 25. Answer: (C) Lower the oxygen rate. The client with COPD is suffering from chronic CO2 retention. The hypoxic drive is his chief stimulus for breathing. Giving O2 inhalation at a rate that is more than 2-3L/min can make the client lose his hypoxic drive which can be assessed as decreasing RR. are 9 per minute and shallow. What is the nurse’s best initial action? 26. The nurse is preparing her plan of care for her A. Fluid volume deficit 26. Answer: (C) Impaired gas exchange. patient diagnosed with pneumonia. Which is the B. Decreased tissue perfusion. most appropriate nursing diagnosis for this patient?C. Impaired gas exchange. D. Risk for infection Pneumonia, which is an infection, causes lobar consolidation thus impairing gas exchange between the alveoli and the blood. Because the patient would require adequate hydration, this makes him prone to fluid volume excess. 27. A nurse at the weight loss clinic assesses a client A. large thighs and upper arms who has a large abdomen and a rounded face. Whic B. pendulous abdomen and large hips additional assessment finding would lead the nurse C. abdominal striae and ankle enlargement to suspect that the client has Cushing’s syndrome D. posterior neck fat pad and thin extremities 27. Answer: (D) posterior neck fat pad and thin extremities “ Buffalo hump” is the accumulation of fat pads over the upper back and neck. Fat may also accumulate on the face. There is truncal obesity but the extremities are thin. All these are noted in a client with Cushing’s syndrome. rather than obesity? 28. Which statement by the client indicates A. “I should limit my potassium intake because hyperkalemia understanding of the possible side effects of is a side-effect of this drug.” Prednisone therapy? B. “I must take this medicine exactly as my doctor ordered it. I shouldn’t skip doses.” C. “This medicine will protect me from getting any colds or infection.” D. “My incision will heal much faster because of this drug.” 28. Answer: (B) “I must take this medicine exactly as my doctor ordered it. I shouldn’t skip doses.” The possible side effects of steroid administration are hypokalemia, increase tendency to infection and poor wound healing. Clients on the drug must follow strictly the doctor’s order since skipping the drug can lower the drug level in the blood that can trigger acute adrenal insufficiency or Addisonian Crisis 29. A client, who is suspected of having A. Pupil reaction Pheochromocytoma, complains of sweating, B. Hand grips palpitation and headache. Which assessment is C. Blood pressure essential for the nurse to make first? D. Blood glucose 29. Answer: (C) Blood pressure Pheochromocytoma is a tumor of the adrenal medulla that causes an increase secretion of catecholamines that can elevate the blood pressure. 30. The nurse is attending a bridal shower for a A. Encourage the guest to eat some baked macaroni friend when another guest, who happens to be a B. Call the guest’s personal physician diabetic, starts to tremble and complains of C. Offer the guest a cup of coffee dizziness. The next best action for the nurse to take iD. Give the guest a glass of orange juice 30. Answer: (D) Give the guest a glass of orange juice In diabetic patients, the nurse should watch out for signs of hypoglycemia manifested by dizziness, tremors, weakness, pallor diaphoresis and tachycardia. When this occurs in a conscious client, he should be given immediately carbohydrates in the form of fruit juice, hard candy, honey or, if unconscious, glucagons or dextrose per IV. to: 31. An adult, who is newly diagnosed with Graves A. “The medication will limit thyroid hormone secretion.” disease, asks the nurse, “Why do I need to take B. “The medication limit synthesis of the thyroid hormones.” Propanolol (Inderal)?” Based on the nurse’s C. “The medication will block the cardiovascular symptoms understanding of the medication and Grave’s of Grave’s disease.” disease, the best response would be: D. “The medication will increase the synthesis of thyroid 31. Answer: (C) “The medication will block the cardiovascular symptoms of Grave’s disease.” Propranolol (Inderal) is a beta-adrenergic blocker that controls the cardiovascular manifestations brought about by increased secretion of the thyroid hormone in Grave’s disease. hormones.” 32. During the first 24 hours after thyroid surgery, the nurse should include in her care: A. Checking the back and sides of the operative dressing B. Supporting the head during mild range of motion exercise 32. Answer: (A) Checking the back and sides of the operative dressing Following surgery of the thyroid gland, bleeding is a potential complication. This can best be assessed by checking the back and the sides of the operative dressing as the blood may flow towards the side and back leaving the front dry and clear of drainage. C. Encouraging the client to ventilate her feelings about the surgery D. Advising the client that she can resume her normal activities immediately 33. On discharge, the nurse teaches the patient to A. Intolerance to heat observe for signs of surgically induced B. Dry skin and fatigue hypothyroidism. The nurse would know that the C. Progressive weight gain patient understands the teaching when she states D. Insomnia and excitability 33. Answer: (C) Progressive weight gain Hypothyroidism, a decrease in thyroid hormone production, is characterized by hypometabolism that manifests itself with weight gain. she should notify the MD if she develops: 34. What is the best reason for the nurse in instructing the client to rotate injection sites for insulin? A. Lipodystrophy can result and is extremely painful B. Poor rotation technique can cause superficial hemorrhaging 34. Answer: (C) Lipodystrophic areas can result, causing erratic insulin absorption rates from these Lipodystrophy is the development of fibrofatty masses at the injection site caused by repeated use of an injection site. Injecting insulin into these scarred areas can cause the insulin to be poorly absorbed and lead to erratic reactions. C. Lipodystrophic areas can result, causing erratic insulin absorption rates from these D. Injection sites can never be reused 35. Which of the following would be inappropriate A. Change position hourly to increase circulation to include in a diabetic teaching plan? B. Inspect feet and legs daily for any changes C. Keep legs elevated on 2 pillows while sleeping D. Keep the insulin not in use in the refrigerator 35. Answer: (C) Keep legs elevated on 2 pillows while sleeping The client with DM has decreased peripheral circulation caused by microangiopathy. Keeping the legs elevated during sleep will further cause circulatory impairment. 36. Included in the plan of care for the immediate A. Maintain NGT to intermittent suction post-gastroscopy period will be: B. Assess gag reflex prior to administration of fluids C. Assess for pain and medicate as ordered D. Measure abdominal girth every 4 hours 36. Answer: (B) Assess gag reflex prior to administration of fluids The client, after gastroscopy, has temporary impairment of the gag reflex due to the anesthetic that has been sprayed into his throat prior to the procedure. Giving fluids and food at this time can lead to aspiration. 37. Which description of pain would be most A. Gnawing, dull, aching, hungerlike pain in the epigastric characteristic of a duodenal ulcer? area that is relieved by food intake B. RUQ pain that increases after meal C. Sharp pain in the epigastric area that radiates to the right shoulder D. A sensation of painful pressure in the midsternal area 37. Answer: (A) Gnawing, dull, aching, hungerlike pain in the epigastric area that is relieved by food intake Duodenal ulcer is related to an increase in the secretion of HCl. This can be buffered by food intake thus the relief of the pain that is brought about by food intake. 38. The client underwent Billroth surgery for gastricA. Reposition the NGT by advancing it gently NSS ulcer. Post-operatively, the drainage from his NGT B. Notify the MD of your findings is thick and the volume of secretions has C. Irrigate the NGT with 50 cc of sterile dramatically reduced in the last 2 hours and the D. Discontinue the low-intermittent suction 38. Answer: (B) Notify the MD of your findings The client’s feeling of vomiting and the reduction in the volume of NGT drainage that is thick are signs of possible abdominal distention caused by obstruction of the NGT. This should be reported immediately to the MD to prevent tension and rupture on the site of anastomosis caused by gastric distention. client feels like vomiting. The most appropriate nursing action is to: 39. After Billroth II Surgery, the client developed A. Sit upright for at least 30 minutes after meals dumping syndrome. Which of the following should B. Take only sips of H2O between bites of solid food the nurse exclude in the plan of care? C. Eat small meals every 2-3 hours D. Reduce the amount of simple carbohydrate in the diet 39. Answer: (A) Sit upright for at least 30 minutes after meals The dumping syndrome occurs within 30 mins after a meal due to rapid gastric emptying, causing distention of the duodenum or jejunum produced by a bolus of food. To delay the emptying, the client has to lie down after meals. Sitting up after meals will promote the dumping syndrome. 40. The laboratory of a male patient with Peptic ulcer revealed an elevated titer of Helicobacter A. Treatment will include Ranitidine and Antibiotics B. No treatment is necessary at this time 40. Answer: (A) Treatment will include Ranitidine and Antibiotics pylori. Which of the following statements indicate C. This result indicates gastric cancer caused by the an understanding of this data? organism D. Surgical treatment is necessary One of the causes of peptic ulcer is H. Pylori infection. It releases toxin that destroys the gastric and duodenal mucosa which decreases the gastric epithelium’s resistance to acid digestion. Giving antibiotics will control the infection and Ranitidine, which is a histamine-2 blocker, will reduce acid secretion that can lead to ulcer. 41. What instructions should the client be given A. NPO 12 hours before procedure before undergoing a paracentesis? B. Empty bladder before procedure C. Strict bed rest following procedure D. Empty bowel before procedure 41. Answer: (B) Empty bladder before procedure Paracentesis involves the removal of ascitic fluid from the peritoneal cavity through a puncture made below the umbilicus. The client needs to void before the procedure to prevent accidental puncture of a distended bladder during the procedure. 42. The husband of a client asks the nurse about thA. “The liver cannot rid the body of ammonia that is made protein-restricted diet ordered because of advanced by the breakdown of protein in the digestive system.” liver disease. What statement by the nurse would B. “The liver heals better with a high carbohydrates diet best explain the purpose of the diet? rather than protein.” C. “Most people have too much protein in their diets. The 42. Answer: (A) “The liver cannot rid the body of ammonia that is made by the breakdown of protein in the digestive system.” The largest source of ammonia is the enzymatic and bacterial digestion of dietary and blood proteins in the GI tract. A protein- restricted diet will therefore decrease ammonia production. amount of this diet is better for liver healing.” D. “Because of portal hyperemesis, the blood flows around the liver and ammonia made from protein collects in the brain causing hallucinations.” 43. Which of the drug of choice for pain controls theA. Morphine patient with acute pancreatitis? B. NSAIDS C. Meperidine D. Codeine 43. Answer: (C) Meperidine Pain in acute pancreatitis is caused by irritation and edema of the inflamed pancreas as well as spasm due to obstruction of the pancreatic ducts. Demerol is the drug of choice because it is less likely to cause spasm of the Sphincter of Oddi unlike Morphine which is spasmogenic. 44. Immediately after cholecystectomy, the nursingA. encouraging the client to take adequate deep breaths by action that should assume the highest priority is: mouth B. encouraging the client to cough and deep breathe C. changing the dressing at least BID D. irrigate the T-tube frequently 44. Answer: (B) encouraging the client to cough and deep breathe Cholecystectomy requires a subcostal incision. To minimize pain, clients have a tendency to take shallow breaths which can lead to respiratory complications like pneumonia and atelectasis. Deep breathing and coughing exercises can help prevent such complications. 45. A Sengstaken-Blakemore tube is inserted in t he A. Deflate the esophageal balloon effort to stop the bleeding esophageal varices in a B. Monitor VS patient with complicated liver cirrhosis. Upon C. Encourage him to take deep breaths insertion of the tube, the client complains of D. Notify the MD 45. Answer: (A) Deflate the esophageal balloon When a client with a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube develops difficulty of breathing, it means the tube is displaced and the inflated balloon is in the oropharynx causing airway obstruction difficulty of breathing. The first action of the nurse is to: 46. The client presents with severe rectal bleeding, A. Chrons disease 16 diarrheal stools a day, severe abdominal pain, B. Ulcerative colitis tenesmus and dehydration. Because of these C. Diverticulitis 46. Answer: (B) Ulcerative colitis Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory condition producing edema and ulceration affecting the entire colon. symptoms the nurse should be alert for other problems associated with what disease? D. Peritonitis Ulcerations lead to sloughing that causes stools as many as 1020 times a day that is filled with blood, pus and mucus. The other symptoms mentioned accompany the problem. 47. A client is being evaluated for cancer of the A. Give laxative the night before and a cleansing enema in colon. In preparing the client for barium enema, the morning before the test the nurse should: B. Render an oil retention enema and give laxative the night before C. Instruct the client to swallow 6 radiopaque tablets the evening before the study D. Place the client on CBR a day before the study 47. Answer: (A) Give laxative the night before and a cleansing enema in the morning before the test Barium enema is the radiologic visualization of the colon using a die. To obtain accurate results in this procedure, the bowels must be emptied of fecal material thus the need for laxative and enema. 48. The client has a good understanding of the A. “I will exercise daily.” means to reduce the chances of colon cancer when B. “I will include more red meat in my diet.” he states: C. “I will have an annual chest x-ray.” D. “I will include more fresh fruits and vegetables in my 48. Answer: (D) “I will include more fresh fruits and vegetables in my diet.” Numerous aspects of diet and nutrition may contribute to the development of cancer. A low-fiber diet, such as when fresh fruits and vegetables are minimal or lacking in the diet, slows transport of materials through the gut which has been linked to colorectal cancer. diet.” 49. Days after abdominal surgery, the client’s A. Cover the wound with sterile, moist saline dressing wound dehisces. The safest nursing intervention B. Approximate the wound edges with tapes when this occurs is to C. Irrigate the wound with sterile saline D. Hold the abdominal contents in place with a sterile gloved 49. Answer: (A) Cover the wound with sterile, moist saline dressing Dehiscence is the partial or complete separation of the surgical wound edges. When this occurs, the client is placed in low Fowler’s position and instructed to lie quietly. The wound should be covered to protect it from exposure and the dressing must be sterile to protect it from infection and moist to prevent the dressing from sticking to the wound which can disturb the healing process. hand 50. An intravenous pyelogram reveals that Paulo, A. Strain all urine. age 35, has a renal calculus. He is believed to have B. Ambulate. a small stone that will pass spontaneously. To C. Remain on bed rest. increase the chance of the stone passing, the nurse D. Ask for medications to relax him. 50. Answer: (B) Ambulate. Free unattached stones in the urinary tract can be passed out with the urine by ambulation which can mobilize the stone and by increased fluid intake which will flush out the stone during urination. would instruct the client to force fluids and to The nurse is performing her admission assessment of a patient. When grading arterial pulses, a 1+ pulse indicates: a. Above normal perfusion. b. Absent perfusion. c. Normal perfusion. d. Diminished perfusion. 1. Answer: D A 1+ pulse indicates weak pulses and is associated with diminished perfusion. A 4+ is bounding perfusion, a 3+ is increased perfusion, a 2+ is normal perfusion, and 0 is absent perfusion. Murmurs that indicate heart disease are often accompanied by other symptoms such as: a. Dyspnea on exertion. b. Subcutaneous emphysema. c. Thoracic petechiae. 2. Answer: A A murmur that indicates heart disease is often accompanied by dyspnea on exertion, which is a hallmark of heart failure. Other indicators are d. Periorbital edema. tachycardia, syncope, and chest pain. Subcutaneous emphysema, thoracic petechiae, and perior-bital edema aren’t associated with murmurs and heart disease. Which pregnancy-related physiologic change would place the patient with a history of cardiac disease at the greatest risk of developing severe cardiac problems? a. Decrease heart rate b. Decreased cardiac output c. Increased plasma volume d. Increased blood pressure 3. Answer: C Pregnancy increase plasma volume and expands the uterine vascular bed, possibly increasing both the heart rate and cardiac output. These changes may cause cardiac stress, especially during the second trimester. Blood pressure during early pregnancy may decrease, but it gradually returns to prepregnancy levels. The priority nursing diagnosis for the patient with cardiomyopathy is: a. Anxiety related to risk of declining health b. status. Ineffective individual coping related to fear of debilitating illness c. Fluid volume excess related to altered compensatory mechanisms. d. Decreased cardiac output related to reduced myocardial contractility. 4. Answer: D Decreased cardiac output related to reduced myocardial contractility is the greatest threat to the survival of a patient with cardiomyopathy. The other options can be addressed once cardiac output and myocardial contractility have been restored. A patient with thrombophlebitis reached her expected outcomes of care. Her affected leg appears pink and warm. Her pedal pulse is palpable and there is no edema present. Which step in the nursing process is described above? a. Planning b. Implementation c. Analysis d. Evaluation 5. Answer: D Evaluation assesses the effectiveness of the treatment plan by determining if the patient has met the expected treatment outcome. Planning refers to designing a plan of action that will help the nurse deliver quality patient care. Implementation refers to all of the nursing interventions directed toward solving the patient’s nursing problems. Analysis is the process of identifying the patient’s nursing problems. An elderly patient may have sustained a basilar skull fracture after slipping and falling on an icy sidewalk. The nurse knows that basilar skull factures: a. Are the least significant type of skull fracture. b. May have cause cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks from the nose or ears. c. Have no characteristic findings. d. Are always surgically repaired. 6. Answer: B A basilar skull fracture carries the risk of complications of dural tear, causing CSF leakage and damage to cranial nerves I, II, VII, and VIII. Classic findings in this type of fracture may include otorrhea, rhinorrhea, Battle’s signs, and raccoon eyes. Surgical treatment isn’t always required. Which of the following types of drugs might be given to control increased intracranial pressure (ICP)? a. Barbiturates b. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors c. Anticholinergics 7. Answer: A Barbiturates may be used to induce a coma in a patient with increased ICP. This decreases cortical activity d. Histamine receptor blockers and cerebral metabolism, reduces cerebral blood volume, decreases cerebral edema, and reduces the brain’s need for glucose and oxygen. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are used to decrease ocular pressure or to decrease the serum pH in a patient with metabolic alkalosis. Anticholinergics have many uses including reducing GI spasms. Histamine receptor blockers are used to decrease stomach acidity. The nurse is teaching family members of a patient with a concussion about the early signs of increased intracranial pressure (ICP). Which of the following would she cite as an early sign of increased ICP? a. Decreased systolic blood pressure b. Headache and vomiting c. Inability to wake the patient with noxious stimuli d. Dilated pupils that don’t react to light 8. Answer: B Headache and projectile vomiting are early signs of increased ICP. Decreased systolic blood pressure, unconsciousness, and dilated pupils that don’t reac to light are considered late signs. Jessie James is diagnosed with retinal detachment. Which intervention is the most important for this patient? a. Admitting him to the hospital on strict bed rest b. Patching both of his eyes c. Referring him to an ophthalmologist d. Preparing him for surgery 9. Answer: A Immediate bed rest is necessary to prevent further injury. Both eyes should be patched to avoid consensual eye movement and the patient should receive early referral to an ophthalmologist should treat the condition immediately. Retinal reattachment can be accomplished by surgery only. If the macula is detached or threatened, surgery is urgent; prolonged detachment of the macula results in permanent loss of central vision. Dr. Bruce Owen, a chemist, sustained a chemical burn to one eye. Which intervention takes priority for a patient with a chemical burn of the eye? a. Patch the affected eye and call the ophthalmologist. b. Administer a cycloplegic agent to reduce ciliary spasm. c. Immediately instill a tropical anesthetic, then irrigate the eye with saline solution. d. Administer antibiotics to reduce the risk of infection 10. Answer: C A chemical burn to the eye requires immediate instillation of a topical anesthetic followed by irrigation with copious amounts of saline solution. Irrigation should be done for 5 to 10 minutes, and then the pH of the eye should be checked. Irrigation should be continued until the pH of the eye is restored to neutral (pH 7.0): Double eversion of the eyelids should be performed to look for and remove ciliary spasm, and an antibiotic ointment can be administered to reduce the risk of infection. Then the eye should be patched. Parenteral narcotic analgesia is often required for pain relief. An ophthalmologist should also be consulted. The nurse is assessing a patient and notes a a. Cerebrovascular accident (CVA) 11. Answer: B Brudzinski’s sign and Kernig’s sign. These are two classic signs of which of the following disorders? b. Meningitis c. Seizure disorder d. Parkinson’s disease A positive response to one or both tests indicates meningeal irritation that is present with meningitis. Brudzinski’s and Kernig’s signs don’t occur in CVA, seizure disorder, or Parkinson’s disease. A patient is admitted to the hospital for a brain biopsy. The nurse knows that the most common type of primary brain tumor is: a. Meningioma. b. Angioma. c. Hemangioblastoma. d. Glioma. 12. Answer: D Gliomas account for approximately 45% of all brain tumors. Meningiomas are the second most common, with 15%. Angiomas and hemangioblastomas are types of cerebral vascular tumors that account for 3% of brain tumors. The nurse should instruct the patient with Parkinson’s disease to avoid which of the following? a. Walking in an indoor shopping mall b. Sitting on the deck on a cool summer evening c. Walking to the car on a cold winter day d. Sitting on the beach in the sun on a summer day 13. Answer: D The patient with Parkinson’s disease may be hypersensitive to heat, which increases the risk of hyperthermia, and he should be instructed to avoid sun exposure during hot weather. Gary Jordan suffered a cerebrovascular accident that left her unable to comprehend speech and unable to speak. This type of aphasia is known as: a. Receptive aphasia b. Expressive aphasia c. Global aphasia d. Conduction aphasia 14. Answer: C Global aphasia occurs when all language functions are affected. Receptive aphasia, also known as Wernicke’s aphasia, affects the ability to comprehend written or spoken words. Expressive aphasia, also known as Broca’s aphasia, affected the patient’s ability to form language and express thoughts. Conduction aphasia refers to abnormalities in speech repetition. Kelly Smith complains that her headaches are occurring more frequently despite medications. Patients with a history of headaches should be taught to avoid: a. Freshly prepared meats. b. Citrus fruits. c. Skim milk d. Chocolate 15. Answer: D Patients with a history of headaches, especially migraines, should be taught to keep a food diary to identify potential food triggers. Typical headache triggers include alcohol, aged cheeses, processed meats, and chocolate and caffeine-containing products. Immediately following cerebral aneurysm rupture, the patient usually complains of: a. Photophobia b. Explosive headache c. Seizures d. Hemiparesis 16. Answer: B An explosive headache or “the worst headache I’ve ever had” is typically the first presenting symptom of a bleeding cerebral aneurysm. Photophobia, seizures, and hemiparesis may occur later. Which of the following is a cause of embolic brain injury? a. Persistent hypertension b. Subarachnoid hemorrhage 17. Answer: C An embolic injury, caused by a traveling clot, may c. Atrial fibrillation d. Skull fracture result from atrial fibrillation. Blood may pool in the fibrillating atrium and be released to travel up the cerebral artery to the brain. Persistent hypertension may place the patient at risk for a thrombotic injury to the brain. Subarachnoid hemorrhage and skull fractures aren’t associated with emboli. Although Ms. Priestly has a spinal cord injury, she can still have sexual intercourse. Discharge teaching should make her aware that: a. She must remove indwelling urinary catheter prior to intercourse. b. She can no longer achieve orgasm. c. Positioning may be awkward. d. She can still get pregnant. 18. Answer: D Women with spinal cord injuries who were sexually active may continue having sexual intercourse and must be reminded that they can still become pregnant. She may be fully capable of achieving orgasm. An indwelling urinary catheter may be left in place during sexual intercourse. Positioning will need to be adjusted to fit the patient’s needs. Ivy Hopkins, age 25, suffered a cervical fracture requiring immobilization with halo traction. When caring for the patient in halo traction, the nurse must: a. Keep a wrench taped to the halo vest for quick removal if cardiopulmonary resuscitation is necessary. b. Remove the brace once a day to allow the c. patient to rest. Encourage the patient to use a pillow under the d. ring. Remove the brace so that the patient can shower. 19. Answer: A The nurse must have a wrench taped on the vest at all times for quick halo removal in emergent situations. The brace isn’t to be removed for any other reason until the cervical fracture is healed. Placing a pillow under the patient’s head may alter the stability of the brace. The nurse asks a patient’s husband if he understands why his wife is receiving nimodipine (Nimotop), since she suffered a cerebral aneurysm rupture. Which response by the husband indicates that he understands the drug’s use? a. Nimodipine replaces calcium.” b. “Nimodipine promotes growth of blood vessels in the brain.” c. “Nimodipine reduces the brain’s demand for b. oxygen.” “Nimodipine reduces vasospasm in the brain.” 20. Answer: D Nimodipine is a calcium channel blocker that acts on cerebral blood vessels to reduce vasospasm. The drug doesn’t increase the amount of calcium, affect cerebral vasculature growth, or reduce cerebral oxygen demand. Many men who suffer spinal injuries continue to be sexually active. The teaching plan for a man with a spinal cord injury should include sexually concerns. Which of the following injuries would most likely prevent erection and ejaculation? a. C5 b. C7 c. T4d. S4 21. Answer: D Men with spinal cord injury should be taught that the higher the level of the lesion, the better their sexual function will be. The sacral region is the lowest area on the spinal column and injury to this area will cause more erectile dysfunction. Cathy Bates, age 36, is a homemaker who frequently forgets to take her carbamazepine (Tegretol). As a result, she has been experiencing seizures. How can the a. Tell her take her medication at bedtime. b. Instruct her to take her medication after one of her favorite television shows. 22. Answer: C Tegretol should be taken with food to minimize GI distress. Taking it at meals will also establish a regular nurse best help the patient remember to take her medication? c. Explain that she should take her medication with breakfast. d. Tell her to buy an alarm watch to remind her. routine, which should help compliance. Richard Barnes was diagnosed with pneumococcal meningitis. What response by the patient indicates that he understands the precautions necessary with this diagnosis? a. “I’m so depressed because I can’t have any visitors for a week.” b. “Thank goodness, I’ll only be in isolation for c. 24 hours.” “The nurse told me that my urine and stool are d. also sources of meningitis bacteria.” “The doctor is a good friend of mine and won’t keep me in isolation.” 23. Answer: B Patient with pneumococcal meningitis require respiratory isolation for the first 24 hours after treatment is initiated. An early symptom associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) includes: a. Fatigue while talking b. Change in mental status c. Numbness of the hands and feet d. Spontaneous fractures 24. Answer: A Early symptoms of ALS include fatigue while talking, dysphagia, and weakness of the hands and arms. ALS doesn’t cause a change in mental status, paresthesia, or fractures. When caring for a patient with esophageal varices, the nurse knows that bleeding in this disorder usually stems from: a. Esophageal perforation b. Pulmonary hypertension c. Portal hypertension d. Peptic ulcers 25. Answer: C Increased pressure within the portal veins causes them to bulge, leading to rupture and bleeding into the lower esophagus. Bleeding associated with esophageal varices doesn’t stem from esophageal perforation, pulmonary hypertension, or peptic ulcers. Tiffany Black is diagnosed with type A hepatitis. What special precautions should the nurse take when caring for this patient? a. Put on a mask and gown before entering the patient’s room. b. Wear gloves and a gown when removing the c. patient’s bedpan. d. Prevent the droplet spread of the organism. Use caution when bringing food to the patient. 26. Answer: B The nurse should wear gloves and a gown when removing the patient’s bedpan because the type A hepatitis virus occurs in stools. It may also occur in blood, nasotracheal secretions, and urine. Type A hepatitis isn’t transmitted through the air by way of droplets. Special precautions aren’t needed when feeding the patient, but disposable utensils should be used. Discharge instructions for a patient who has been operated on for colorectal cancer include irrigating the colostomy. The nurse knows her teaching is effective when the patient states he’ll contact the doctor if: a. He experiences abdominal cramping while the irrigant is infusing b. He has difficulty inserting the irrigation tube into the stoma c. He expels flatus while the return is running out 27. Answer: B The patient should notify the doctor if he has difficulty inserting the irrigation tube into the stoma. Difficulty with insertion may indicate stenosis of the bowel. Abdominal cramping and expulsion of flatus may d. He’s unable to complete the procedure in 1 hour normally occur with irrigation. The procedure will often take an hour to complete. The nurse explains to the patient who has an abdominal perineal resection that an indwelling urinary catheter must be kept in place for several days afterward because: a. It prevents urinary tract infection following surgery b. It prevents urine retention and resulting pressure on the perineal wound c. It minimizes the risk of wound contamination d. by the urine It determines whether the surgery caused bladder trauma 28. Answer: B An indwelling urinary catheter is kept in place several days after this surgery to prevent urine retention that could place pressure on the perineal wound. An indwelling urinary catheter may be a source of postoperative urinary tract infection. Urine won’t contaminate the wound. An indwelling urinary catheter won’t necessarily show bladder trauma. The first day after, surgery the nurse finds no measurable fecal drainage from a patient’s colostomy stoma. What is the most appropriate nursing intervention? a. Call the doctor immediately. b. Obtain an order to irrigate the stoma. c. Place the patient on bed rest and call the doctor. d. Continue the current plan of care. 29. Answer: D The colostomy may not function for 2 days or more (48 to 72 hours) after surgery. Therefore, the normal plan of care can be followed. Since no fecal drainage is expected for 48 to 72 hours after a colostomy (only mucous and serosanguineous), the doctor doesn’t have to be notified and the stoma shouldn’t be irrigated at this time. If a patient’s GI tract is functioning but he’s unable to take foods by mouth, the preferred method of feeding is: a. Total parenteral nutrition b. Peripheral parenteral nutrition c. Enteral nutrition d. Oral liquid supplements 30. Answer: C If the patient’s GI tract is functioning, enteral nutrition via a feeding tube is the preferred method. Peripheral and total parenteral nutrition places the patient at risk for infection. If the patient is unable to consume foods by mouth, oral liquid supplements are contraindicated. Which type of solution causes water to shift from the cells into the plasma? a. Hypertonic b. Hypotonic c. Isotonic d. Alkaline 31. Answer: A A hypertonic solution causes water to shift from the cells into the plasma because the hypertonic solution has a greater osmotic pressure than the cells. A hypotonic solution has a lower osmotic pressure than that of the cells. It causes fluid to shift into the cells, possibly resulting in rupture. An isotonic solution, which has the same osmotic pressure as the cells, wouldn’t cause any shift. A solution’s alkalinity is related to the hydrogen ion concentration, not its osmotic effect. Particles move from an area of greater osmelarity to one of lesser osmolarity through: a. Active transport b. Osmosis 32. Answer: C Particles move from an area of greater osmolarity to c. Diffusion d. Filtration one of lesser osmolarity through diffusion. Active transport is the movement of particles though energy expenditure from other sources such as enzymes. Osmosis is the movement of a pure solvent through a semipermeable membrane from an area of greater osmolarity to one of lesser osmolarity until equalization occurs. The membrane is impermeable to the solute but permeable to the solvent. Filtration is the process by which fluid is forced through a membrane by a difference in pressure; small molecules pass through, but large ones don’t. Which assessment finding indicates dehydration? a. Tenting of chest skin when pinched b. Rapid filling of hand veins c. A pulse that isn’t easily obliterated d. Neck vein distention 33. Answer: A Tenting of chest skin when pinched indicates decreased skin elasticity due to dehydration. Hand veins fill slowly with dehydration, not rapidly. A pulse that isn’t easily obliterated and neck vein distention indicate fluid overload, not dehydration. Which nursing intervention would most likely lead to a hypo-osmolar state? a. Performing nasogastric tube irrigation with normal saline solution Weighing the b. patient daily c. Administering tap water enema until the return is clear d. Encouraging the patient with excessive perspiration to dink broth 34. Answer: C Administering a tap water enema until return is clear would most likely contribute to a hypo-osmolar state. Because tap water is hypotonic, it would be absorbed by the body, diluting the body fluid concentration and lowering osmolarity. Weighing the patient is the easiest, most accurate method to determine fluid changes. Therefore, it helps identify rather than contribute to fluid imbalance. Nasogastric tube irrigation with normal saline solution wouldn’t cause a shift in fluid balance. Drinking broth wouldn’t contribute to a hypo-osmolar state because it doesn’t replace sodium and water lost through excessive perspiration. Which assessment finding would indicate an extracellular fluid volume deficit? a. Bradycardia b. A central venous pressure of 6 mm Hg c. Pitting edema d. An orthostatic blood pressure change 35. Answer: D An orthostatic blood pressure indicates an extracellular fluid volume deficit. (The extracellular compartment consists of both the intravascular compartment and interstitial space.) A fluid volume deficit within the intravascular compartment would cause tachycardia, not bradycardia or orthostatic blood pressure change. A central venous pressure of 6 mm Hg is in the high normal range, indicating adequate hydration. Pitting edema indicates fluid volume overload. A patient with metabolic acidosis has a preexisting problem with the kidneys. Which other organ helps regulate blood pH? a. Liver b. Pancreas c. Lungs d. heart 36. Answer: C The respiratory and renal systems act as compensatory mechanisms to counteract-base imbalances. The lungs alter the carbon dioxide levels in the blood by increasing or decreasing the rate and depth of respirations, thereby increasing or decreasing carbon dioxide elimination. The liver, pancreas, and heart play no part in compensating for acid-base imbalances. The nurse considers the patient anuric if the patient; a. Voids during the nighttime hours b. Has a urine output of less than 100 ml in 24 hours c. Has a urine output of at least 100 ml in 2 hours d. Has pain and burning on urination 37. Answer: B Anuria refers to a urine output of less than 100 ml in 24 hours. The baseline for urine output and renal function is 30 ml of urine per hour. A urine output of at least 100 ml in 2 hours is within normal limits. Voiding at night is called nocturia. Pain and burning on urination is called dysuria. Which nursing action is appropriate to prevent infection when obtaining a sterile urine specimen from an indwelling urinary catheter? a. Aspirate urine from the tubing port using a sterile syringe and needle b. Disconnect the catheter from the tubing and obtain urine c. Open the drainage bag and pour out some urine d. Wear sterile gloves when obtaining urine 38. Answer: A To obtain urine properly, the nurse should aspirate it from a port, using a sterile syringe after cleaning the port. Opening a closed urine drainage system increases the risk of urinary tract infection. Standard precautions specify the use of gloves during contract with body fluids; however, sterile gloves aren’t necessary. After undergoing a transurethral resection of the prostate to treat benign prostatic hypertrophy, a patient is retuned to the room with continuous bladder irrigation in place. One day later, the patient reports bladder pain. What should the nurse do first? a. Increase the I.V. flow rate b. Notify the doctor immediately c. Assess the irrigation catheter for patency and drainage d. Administer meperidine (Demerol) as prescribed 39. Answer: C Although postoperative pain is expected, the nurse should ensure that other factors, such as an obstructed irrigation catheter, aren’t the cause of the pain. After assessing catheter patency, the nurse should administer an analgesic such as meperidine as prescribed. Increasing the I.V. flow rate may worse the pain. Notifying the doctor isn’t necessary unless the pain is severe or unrelieved by the prescribed medication. A patient comes to the hospital complaining of sudden onset of sharp, severe pain originating in the lumbar region and radiating around the side and toward the bladder. The patient also reports nausea and vomiting and appears pale, diaphoretic, and anxious. The doctor tentatively diagnoses renal calculi and orders flat-plate a. Kidney b. Ureter c. Bladder d. Urethra 40. Answer: A Renal calculi most commonly from in the kidney. They may remain there or become lodged anywhere along the urinary tract. The ureter, bladder, and urethra abdominal X-rays. Renal calculi can form anywhere in the urinary tract. What is their most common formation site? are less common sites of renal calculi formation. A patient comes to the hospital complaining of severe pain in the right flank, nausea, and vomiting. The doctor tentatively diagnoses right ureter-olithiasis (renal calculi). When planning this patient’s care, the nurse should assign highest priority to which nursing diagnosis? a. Pain b. Risk of infection c. Altered urinary elimination d. Altered nutrition: less than body requirements 41. Answer: A Ureterolithiasis typically causes such acute, severe pain that the patient can’t rest and becomes increasingly anxious. Therefore, the nursing diagnosis of pain takes highest priority. Risk for infection and altered urinary elimination are appropriate once the patient’s pain is controlled. Altered nutrition: less than body requirements isn’t appropriate at this time. The nurse is reviewing the report of a patient’s routine urinalysis. Which of the following values should the nurse consider abnormal? a. Specific gravity of 1.002 b. Urine pH of 3 c. Absence of protein d. Absence of glucose 42. Answer: B Normal urine pH is 4.5 to 8; therefore, a urine pH of 3 is abnormal and may indicate such conditions as renal tuberculosis, pyrexia, phenylketonuria, alkaptonuria, and acidosis. Urine specific gravity normally ranges from 1.002 to 1.032, making the patient’s value normal. Normally, urine contains no protein, glucose, ketones, bilirubin, bacteria, casts, or crystals. A patient with suspected renal insufficiency is scheduled for a comprehensive diagnostic work-up. After the nurse explains the diagnostic tests, the patient asks which part of the kidney “does the work.” Which answer is correct? a. The glomerulus b. Bowman’s capsule c. The nephron d. The tubular system 43. Answer: C The nephron is the kidney’s functioning unit. The glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, and tubular system are components of the nephron. During a shock state, t he renin-angiotensin- aldosterone system exerts which of the following effects on renal function? a. Decreased urine output, increased reabsorption of sodium and water b. Decreased urine output, decreased reabsorption of sodium and water c. Increased urine output, increased reabsorption d. of sodium and water Increased urine output, decreased reabsorption of sodium and water 44. Answer: A As a response to shock, the renin- angiotensinaldosterone system alters renal function by decreasing urine output and increasing reabsorption of sodium and water. Reduced renal perfusion stimulates the renin-angiotensin- aldosterone system in an effort to conserve circulating volume. While assessing a patient who complained of lower abdominal pressure, the nurse notes a firm mass extending above the symphysis pubis. The nurse suspects: a. A urinary tract infection b. Renal calculi c. An enlarged kidney d. A distended bladder 45. Answer: D The bladder isn’t usually palpable unless it is distended. The feeling of pressure is usually relieved with urination. Reduced bladder tone due to general anesthesia is a common postoperative complication that causes difficulty in voiding. A urinary tract infection and renal calculi aren’t palpable. The kidneys aren’t palpable above the symphysis pubis. Gregg Lohan, age 75, is admitted to the medicalsurgical floor with weakness and left-sided chest pain. The symptoms have been present for several weeks after a viral illness. Which assessment finding is most symptomatic of pericarditis? a. Pericardial friction rub b. Bilateral crackles auscultated at the lung bases c. Pain unrelieved by a change in position d. Third heart sound (S3) 46. Answer: A A pericardial friction rub may be present with the pericardial effusion of pericarditis. The lungs are typically clear when auscultated. Sitting up and leaning forward often relieves pericarditis pain. An S3 indicates left-sided heart failure and isn’t usually present with pericarditis. James King is admitted to the hospital with right- sideheart failure. When assessing him for jugular vein distention, the nurse should position him: a. Lying on his side with the head of the bed flat. b. Sitting upright. c. Flat on his back. d. Lying on his back with the head of the bed elevated 30 to 45 degrees. 47. Answer: D Assessing jugular vein distention should be done when the patient is in semi-Fowler’s position (head of the bed elevated 30 to 45 degrees). If the patient lies flat, the veins will be more distended; if he sits upright, the veins will be flat. The nurse is interviewing a slightly overweight 43year-old man with mild emphysema and borderline hypertension. He admits to smoking a pack of cigarettes per day. When developing a teaching plan, which of the following should receive highest priority to help decrease respiratory complications? a. Weight reduction b. Decreasing salt intake c. Smoking cessation d. Decreasing caffeine intake 48. Answer: C Smoking should receive highest priority when trying to reduce risk factors for with respiratory complications. Losing weight and decreasing salt and caffeine intake can help to decrease risk factors for hypertension. What is the ratio of chest compressions to ventilations when one rescuer performs cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) on an adult? a. 15:1 b. 15:2 c. 12:1 d. 12:2 49. Answer: B The correct ratio of compressions to ventilations when one rescuer performs CPR is 15:2 When assessing a patient for fluid and electrolyte balance, the nurse is aware that the organs most important in maintaining this balance are the: a. Pituitary gland and pancreas b. Liver and gallbladder. c. Brain stem and heart. d. Lungs and kidneys. 50. Answer: D The lungs and kidneys are the body’s regulators of homeostasis. The lungs are responsible for removing fluid and carbon dioxide; the kidneys maintain a balance of fluid and electrolytes. The other organs play secondary roles in maintaining homeostasis. 1. A female client is admitted with a diagnosis of A. Hyponatremia acute renal failure. She is awake, alert, oriented, B. Hyperkalemia and complaining of severe back pain, nausea and C. Hyperphosphatemia vomiting and abdominal cramps. Her vital signs D. Hypercalcemia 1. Answer: (A) Hyponatremia The normal serum sodium level is 135 – 145 mEq/L. The client’s serum sodium is below normal. Hyponatremia also manifests itself with abdominal cramps and nausea and are blood pressure 100/70 mm Hg, pulse 110, respirations 30, and oral temperature 100.4°F (38°C). Her electrolytes are sodium 120 mEq/L, potassium 5.2 mEq/L; her urinary output for the first 8 hours is 50 ml. The client is displaying signs of which electrolyte imbalance? vomiting 2. Assessing the laboratory findings, which result A. would the nurse most likely expect to find in a BUN 10 to 30 mg/dl, potassium 4.0 mEq/L, creatinine 0.5 to 1.5 mg/dl 2. Answer: (B) Decreased serum calcium, blood pH 7.2, potassium 6.5 mEq/L Chronic renal failure is usually the end result of gradual tissue destruction and loss of renal function. With the loss of renal function, the kidneys ability to regulate fluid and electrolyte and acid base balance results. The serum Ca decreases as the kidneys fail to excrete phosphate, potassium and hydrogen ions are retained. client with chronic renal failure? B. Decreased serum calcium, blood pH 7.2, potassium 6.5 mEq/L C. BUN 15 mg/dl, increased serum calcium, creatinine l.0 D. mg/dl BUN 35 to 40 mg/dl, potassium 3.5 mEq/L, pH 7.35, decreased serum calcium 3. Treatment with hemodialysis is ordered for a client and an external shunt is created. Which nursing action would be of highest priority with regard to the external shunt? A. Heparinize it daily. B. Avoid taking blood pressure measurements or blood samples from the affected arm. C. Change the Silastic tube daily. D. Instruct the client not to use the affected arm. 3. Answer: (B) Avoid taking blood pressure measurements or blood samples from the affected arm. In the client with an external shunt, don’t use the arm with the vascular access site to take blood pressure readings, draw blood, insert IV lines, or give injections because these procedures may rupture the shunt or occlude blood flow causing damage and obstructions in the shunt. 4. Romeo Diaz, age 78, is admitted to the hospital with the diagnosis of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). He is scheduled for a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). It would be inappropriate to include which of the following points in the preoperative teaching? A. TURP is the most common operation for BPH. B. Explain the purpose and function of a twoway irrigation system. C. Expect bloody urine, which will clear as healing takes place. D. He will be pain free. 4. Answer: (D) He will be pain free. Surgical interventions involve an experience of pain for the client which can come in varying degrees. Telling the pain that he will be pain free is giving him false reassurance. 5. Roxy is admitted to the hospital with a possible A. left lower quadrant diagnosis of appendicitis. On physical examination, B. left upper quadrant the nurse should be looking for tenderness on C. right lower quadrant palpation at McBurney’s point, which is located in D. right upper quadrant 5. Answer: (C) right lower quadrant To be exact, the appendix is anatomically located at the Mc Burney’s point at the right iliac area of the right lower quadrant. the 6. Mr. Valdez has undergone surgical repair of his inguinal hernia. Discharge teaching should include A. telling him to avoid heavy lifting for 4 to 6 weeks B. instructing him to have a soft bland diet for two weeks C. telling him to resume his previous daily activities without limitations D. recommending him to drink eight glasses of 6. Answer: (A) telling him to avoid heavy lifting for 4 to 6 weeks The client should avoid lifting heavy objects and any strenuous activity for 4-6 weeks after surgery to prevent stress on the inguinal area. There is no special diet required. The fluid intake of eight glasses a day is good advice but is not a priority in this case. water daily 7. A 30-year-old homemaker fell asleep while A. 18% smoking a cigarette. She sustained severe burns of B. 22% the face,neck, anterior chest, and both arms and C. 31% hands. Using the rule of nines, which is the best D. 40% 7. Answer: (C) 31% Using the Rule of Nine in the estimation of total body surface burned, we allot the following: 9% – head; 9% – each upper extremity; 18%- front chest and abdomen; 18% – entire back; 18% – each lower extremity and 1% – perineum. estimate of total body-surface area burned? 8. Nursing care planning is based on the knowledge that the first 24-48 hours post-burn are characterized by: A. An increase in the total volume of intracranial plasma B. Excessive renal perfusion with diuresis C. Fluid shift from interstitial space D. Fluid shift from intravascular space to the interstitial space 8. Answer: (D) Fluid shift from intravascular space to the interstitial space This period is the burn shock stage or the hypovolemic phase. Tissue injury causes vasodilation that results in increase capillary permeability making fluids shift from the intravascular to the interstitial space. This can lead to a decrease in circulating blood volume or hypovolemia which decreases renal perfusion and urine output. 9. If a client has severe bums on the upper torso, which item would be a primary concern? A. Debriding and covering the wounds B. Administering antibiotics C. Frequently observing for hoarseness, stridor, and dyspnea D. Establishing a patent IV line for fluid replacement 9. Answer: (C) Frequently observing for hoarseness, stridor, and dyspnea Burns located in the upper torso, especially resulting from thermal injury related to fires can lead to inhalation burns. This causes swelling of the respiratory mucosa and blistering which can lead to airway obstruction manifested by hoarseness, noisy and difficult breathing. Maintaining a patent airway is a primary concern. 10. Contractures are among the most serious longterm complications of severe burns. If a burn is located on the upper torso, which nursing measure would be least effective to help prevent contractures? A. Changing the location of the bed or the TV set, or both, daily B. Encouraging the client to chew gum and blow up balloons C. Avoiding the use of a pillow for sleep, or placing the head in a position of hyperextension D. Helping the client to rest in the position of maximal comfort 10. Answer: (D) Helping the client to rest in the position of maximal comfort Mobility and placing the burned areas in their functional position can help prevent contracture deformities related to burns. Pain can immobilize a client as he seeks the position where he finds less pain and provides maximal comfort. But this approach can lead to contracture deformities and other complications. 11. An adult is receiving Total Parenteral Nutrition A. evaluation of the peripheral IV site (TPN). Which of the following assessment is B. confirmation that the tube is in the stomach essential? C. assess the bowel sound D. fluid and electrolyte monitoring 11. Answer: (D) fluid and electrolyte monitoring Total parenteral nutrition is a method of providing nutrients to the body by an IV route. The admixture is made up of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, electrolytes, vitamins, trace minerals and sterile water based on individual client needs. It is intended to improve the clients nutritional status. Because of its composition, it is important to monitor the clients fluid intake and output including electrolytes, blood glucose and weight. 12. Which drug would be least effective in lowering A. Glucose and insulin a client’s serum potassium level? B. Polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) C. Calcium glucomite 12. Answer: (D) Aluminum hydroxide Aluminum hydroxide binds dietary phosphorus in the GI tract and helps treat hyperphosphatemia. All the other medications D. Aluminum hydroxide mentioned help treat hyperkalemia and its effects. 13. A nurse is directed to administer a hypotonic A. 0.45% NaCl intravenous solution. Looking at the following B. 0.9% NaCl labeled solutions, she should choose C. D5W D. D5NSS 13. Answer: (A) 0.45% NaCl Hypotonic solutions like 0.45% NaCl has a lower tonicity that the blood; 0.9% NaCl and D5W are isotonic solutions with same tonicity as the blood; and D5NSS is hypertonic with a higher tonicity thab the blood. 14. A patient is hemorrhaging from multiple traumaA. hypertension sites. The nurse expects that compensatory B. oliguria mechanisms associated with hypovolemia would C. tachycardia cause all of the following symptoms EXCEPT D. tachypnea 14. Answer: (A) hypertension In hypovolemia, one of the compenasatory mechanisms is activation of the sympathetic nervous system that increases the RR & PR and helps restore the BP to maintain tissue perfusion but not cause a hypertension. The SNS stimulation constricts renal arterioles that increases release of aldosterone, decreases glomerular filtration and increases sodium & water reabsorption that leads to oliguria. 15. Maria Sison, 40 years old, single, was admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of Breast Cancer. She was scheduled for radical mastectomy. Nursing care during the preoperative period should consist of A. assuring Maria that she will be cured of cancer B. assessing Maria’s expectations and doubts C. maintaining a cheerful and optimistic environment D. keeping Maria’s visitors to a minimum so she can have time for herself 15. Answer: (B) assessing Maria’s expectations and doubts Assessing the client’s expectations and doubts will help lessen her fears and anxieties. The nurse needs to encourage the client to verbalize and to listen and correctly provide explanations when needed. 16. Maria refuses to acknowledge that her breast was removed. She believes that her breast is intact under the dressing. The nurse should A. call the MD to change the dressing so Kathy can see the incision B. recognize that Kathy is experiencing denial, a normal stage of the grieving process C. reinforce Kathy’s belief for several days until her body can adjust to stress of surgery. D. remind Kathy that she needs to accept her diagnosis so that she can begin rehabilitation exercises. 16. Answer: (B) recognize that Kathy is experiencing denial, a normal stage of the grieving process A person grieves to a loss of a significant object. The initial stage in the grieving process is denial, then anger, followed by bargaining, depression and last acceptance. The nurse should show acceptance of the patient’s feelings and encourage verbalization. 17. A chemotherapeutic agent 5FU is ordered as an adjunct measure to surgery. Which of the ff. statements about chemotherapy is true? A. it is a local treatment affecting only tumor cells B. it affects both normal and tumor cells C. it has been proven as a complete cure for cancer D. it is often used as a palliative measure. 17. Answer: (B) it affects both normal and tumor cells Chemotherapeutic agents are given to destroy the actively proliferating cancer cells. But these agents cannot differentiate the abnormal actively proliferating cancer cells from those that are actively proliferating normal cells like the cells of the bone marrow, thus the effect of bone marrow depression. 18. Which is an incorrect statement pertaining to the following procedures for cancer diagnostics? A. Biopsy is the removal of suspicious tissue and the only definitive method to diagnose cancer B. Ultrasonography detects tissue density changes difficult to observe by X-ray via sound waves. C. CTscanning uses magnetic fields and radio 18. Answer: (C) CTscanning uses magnetic fields and radio frequencies to provide cross-sectional view of tumor CT scan uses narrow beam x-ray to provide cross-sectional view. MRI uses magnetic fields and radio frequencies to detect tumors. frequencies to provide cross-sectional view of tumor D. Endoscopy provides direct view of a body cavity to detect abnormality. 19. A post-operative complication of mastectomy is lymphedema. This can be prevented by A. ensuring patency of wound drainage tube B. placing the arm on the affected side in a dependent position C. restricting movement of the affected arm D. frequently elevating the arm of the affected side above the level of the heart. 19. Answer: (D) frequently elevating the arm of the affected side above the level of the heart. Elevating the arm above the level of the heart promotes good venous return to the heart and good lymphatic drainage thus preventing swelling. 20. Which statement by the client indicates to the nurse that the patient understands precautions necessary during internal radiation therapy for cancer of the cervix? A. “I should get out of bed and walk around in my room.” B. “My 7 year old twins should not come to visit me while I’m receiving treatment.” C. “I will try not to cough, because the force might make me expel the application.” D. “I know that my primary nurse has to wear one of those badges like the people in the x-ray department, but they are not necessary for anyone else who comes in here.” 20. Answer: (B) “My 7 year old twins should not come to visit me while I’m receiving treatment.” Children have cells that are normally actively dividing in the process of growth. Radiation acts not only against the abnormally actively dividing cells of cancer but also on the normally dividing cells thus affecting the growth and development of the child and even causing cancer itself. 21. High uric acid levels may develop in clients who are receiving chemotherapy. This is caused by: A. The inability of the kidneys to excrete the drug metabolites B. Rapid cell catabolism C. Toxic effect of the antibiotic that are given concurrently D. The altered blood ph from the acid medium of the drugs 21. Answer: (B) Rapid cell catabolism One of the oncologic emergencies, the tumor lysis syndrome, is caused by the rapid destruction of large number of tumor cells. . Intracellular contents are released, including potassium and purines, into the bloodstream faster than the body can eliminate them. The purines are converted in the liver to uric acid and released into the blood causing hyperuricemia. They can precipitate in the kidneys and block the tubules causing acute renal failure. 22. Which of the following interventions would be A. Frequent ambulation included in the care of plan in a client with cervical B. Unlimited visitors implant? C. Low residue diet D. Vaginal irrigation every shift 22. Answer: (C) Low residue diet It is important for the nurse to remember that the implant be kept intact in the cervix during therapy. Mobility and vaginal irrigations are not done. A low residue diet will prevent bowel movement that could lead to dislodgement of the implant. Patient is also strictly isolated to protect other people from the radiation emissions 23. Which nursing measure would avoid constriction on the affected arm immediately after mastectomy? A. Avoid BP measurement and constricting clothing on the affected arm B. Active range of motion exercises of the arms once a day. C. Discourage feeding, washing or combing with the affected arm 23. Answer: (A) Avoid BP measurement and constricting clothing on the affected arm A BP cuff constricts the blood vessels where it is applied. BP measurements should be done on the unaffected arm to ensure adequate circulation and venous and lymph drainage in the affected arm D. Place The affected arm in a dependent position, below the level of the heart 24. A client suffering from acute renal failure has an unexpected increase in urinary output to 150ml/hr. The nurse assesses that the client has entered the second phase of acute renal failure. Nursing actions throughout this phase include observation for signs and symptoms of A. Hypervolemia, hypokalemia, and hypernatremia. B. Hypervolemia, hyperkalemia, and hypernatremia. C. Hypovolemia, wide fluctuations in serum sodium and potassium levels. D. Hypovolemia, no fluctuation in serum sodium and potassium levels. 24. Answer: (C) Hypovolemia, wide fluctuations in serum sodium and potassium levels. The second phase of ARF is the diuretic phase or high output phase. The diuresis can result in an output of up to 10L/day of dilute urine. Loss of fluids and electrolytes occur. 25. An adult has just been brought in by ambulance A. A rapid pulse and increased RR after a motor vehicle accident. When assessing the B. Decreased physiologic functioning client, the nurse would expect which of the followingC. Rigid posture and altered perceptual focus manifestations could have resulted from D. Increased awareness and attention 25. Answer: (A) A rapid pulse and increased RR The fight or flight reaction of the sympathetic nervous system occurs during stress like in a motor vehicular accident. This is manifested by increased in cardiovascular function and RR to provide the immediate needs of the body for survival. sympathetic nervous system stimulation? 26. Ms. Sy undergoes surgery and the abdominal aortic aneurysm is resected and replaced with a graft. When she arrives in the RR she is still in shock. The nurse’s priority should be A. placing her in a trendeleburg position B. putting several warm blankets on her C. monitoring her hourly urine output D. assessing her VS especially her RR 26. Answer: (D) assessing her VS especially her RR Shock is characterized by reduced tissue and organ perfusion and eventual organ dysfunction and failure. Checking on the VS especially the RR, which detects need for oxygenation, is a priority to help detect its progress and provide for prompt management before the occurrence of complications. 27. A major goal for the client during the first 48 hours after a severe bum is to prevent hypovolemic shock. The best indicator of adequate fluid balance during this period is A. Elevated hematocrit levels. B. Urine output of 30 to 50 ml/hr. C. Change in level of consciousness. D. Estimate of fluid loss through the burn eschar. 27. Answer: (B) Urine output of 30 to 50 ml/hr. Hypovolemia is a decreased in circulatory volume. This causes a decrease in tissue perfusion to the different organs of the body. Measuring the hourly urine output is the most quantifiable way of measuring tissue perfusion to the organs. Normal renal perfusion should produce 1ml/kg of BW/min. An output of 30-50 ml/hr is considered adequate and indicates good fluid balance. 28. A thoracentesis is performed on a chest-injured A. Spontaneous pneumothorax client, and no fluid or air is found. Blood and fluids B. Ruptured diaphragm is administered intravenously (IV), but the client’s C. Hemothorax vital signs do not improve. A central venous pressur D. Pericardial tamponade 28. Answer: (D) Pericardial tamponade Pericardial tamponade occurs when there is presence of fluid accumulation in the pericardial space that compresses on the ventricles causing a decrease in ventricular filling and stretching during diastole with a decrease in cardiac output. . This leads to right atrial and venous congestion manifested by a CVP reading above normal. line is inserted, and the initial reading is 20 cm H^O. The most likely cause of these findings is which of the following? 29. Intervention for a pt. who has swallowed a A. administering an irritant that will stimulate 29. Answer: (A) administering an irritant that will Muriatic Acid includes all of the following except vomiting B. aspirating secretions from the pharynx if respirations are affected C. neutralizing the chemical D. washing the esophagus with large volumes of water via gastric lavage stimulate vomiting Swallowing of corrosive substances causes severe irritation and tissue destruction of the mucous membrane of the GI tract. Measures are taken to immediately remove the toxin or reduce its absorption. For corrosive poison ingestion, such as in muriatic acid where burn or perforation of the mucosa may occur, gastric emptying procedure is immediately instituted, This includes gastric lavage and the administration of activated charcoal to absorb the poison. Administering an irritant with the concomitant vomiting to remove the swallowed poison will further cause irritation and damage to the mucosal lining of the digestive tract. Vomiting is only indicated when non-corrosive poison is swallowed. 30. Which initial nursing assessment finding would A. Skin warm and dry best indicate that a client has been successfully B. Pupils equal and react to light resuscitated after a cardio-respiratory arrest? C. Palpable carotid pulse D. Positive Babinski’s reflex 30. Answer: (C) Palpable carotid pulse Presence of a palpable carotid pulse indicates the return of cardiac function which, together with the return of breathing, is the primary goal of CPR. Pulsations in arteries indicates blood flowing in the blood vessels with each cardiac contraction. Signs of effective tissue perfusion will be noted after. 31. Chemical burn of the eye are treated with A. local anesthetics and antibacterial drops for 24 – 36 hrs. B. hot compresses applied at 15-minute intervals C. Flushing of the lids, conjunctiva and cornea with tap or preferably sterile water D. cleansing the conjunctiva with a small cottontipped applicator 31. Answer: (C) Flushing of the lids, conjunctiva and cornea with tap or preferably sterile water Prompt treatment of ocular chemical burns is important to prevent further damage. Immediate tap-water eye irrigation should be started on site even before transporting the patient to the nearest hospital facility. In the hospital, copious irrigation with normal saline, instillation of local anesthetic and antibiotic is done. 32. The Heimlich maneuver (abdominal thrust), for A. Force air out of the lungs acute airway obstruction, attempts to: B. Increase systemic circulation C. Induce emptying of the stomach D. Put pressure on the apex of the heart 32. Answer: (A) Force air out of the lungs The Heimlich maneuver is used to assist a person choking on a foreign object. The pressure from the thrusts lifts the diaphragm, forces air out of the lungs and creates an artificial cough that expels the aspirated material. 33. John, 16 years old, is brought to the ER after a vehicular accident. He is pronounced dead on arrival. When his parents arrive at the hospital, the nurse should: A. ask them to stay in the waiting area until she can spend time alone with them B. speak to both parents together and encourage them to support each other and express their emotions freely C. Speak to one parent at a time so that each can ventilate feelings of loss without upsetting the other D. ask the MD to medicate the parents so they can stay calm to deal with their son’s death. 33. Answer: (B) speak to both parents together and encourage them to support each other and express their emotions freely Sudden death of a family member creates a state of shock on the family. They go into a stage of denial and anger in their grieving. Assisting them with information they need to know, answering their questions and listening to them will provide the needed support for them to move on and be of support to one another. 34. An emergency treatment for an acute asthmatic A. increase BP attack is Adrenaline 1:1000 given hypodermically. B. decrease mucosal swelling 34. Answer: (C) relax the bronchial smooth muscle Acute asthmatic attack is characterized by severe This is given to: C. relax the bronchial smooth muscle D. decrease bronchial secretions bronchospasm which can be relieved by the immediate administration of bronchodilators. Adrenaline or Epinephrine is an adrenergic agent that causes bronchial dilation by relaxing the bronchial smooth muscles. 35. A nurse is performing CPR on an adult patient. A. upper half of the sternum When performing chest compressions, the nurse B. upper third of the sternum understands the correct hand placement is located C. lower half of the sternum over the D. lower third of the sternum 35. Answer: (C) lower half of the sternum The exact and safe location to do cardiac compression is the lower half of the sternum. Doing it at the lower third of the sternum may cause gastric compression which can lead to a possible aspiration. 36. The nurse is performing an eye examination on an elderly client. The client states ‘My vision is blurred, and I don’t easily see clearly when I get into a dark room.” The nurse best response is: A. “You should be grateful you are not blind.” B. “As one ages, visual changes are noted as part of degenerative changes. This is normal.” C. “You should rest your eyes frequently.” D. “You maybe able to improve you vision if you move slowly.” 36. Answer: (B) “As one ages, visual changes are noted as part of degenerative changes. This is normal.” Aging causes less elasticity of the lens affecting accommodation leading to blurred vision. The muscles of the iris increase in stiffness and the pupils dilate slowly and less completely so that it takes the older person to adjust when going to and from light and dark environment and needs brighter light for close vision. 37. Which of the following activities is not A. sneezing, coughing and blowing the nose encouraged in a patient after an eye surgery? B. straining to have a bowel movement C. wearing tight shirt collars D. sexual intercourse 37. Answer: (D) sexual intercourse To reduce increases in IOP, teach the client and family about activity restrictions. Sexual intercourse can cause a sudden rise in IOP. 38. Which of the following indicates poor practice in communicating with a hearing-impaired client? A. Use appropriate hand motions B. Keep hands and other objects away from your mouth when talking to the client C. Speak clearly in a loud voice or shout to be heard D. Converse in a quiet room with minimal distractions 38. Answer: (C) Speak clearly in a loud voice or shout to be heard Shouting raises the frequency of the sound and often makes understanding the spoken words difficult. It is enough for the nurse to speak clearly and slowly. 39. A client is to undergo lumbar puncture. Which is least important information about LP? A. Specimens obtained should be labeled in their proper sequence. B. It may be used to inject air, dye or drugs into the spinal canal. C. Assess movements and sensation in the lower extremities after the D. Force fluids before and after the procedure. 39. Answer: (D) Force fluids before and after the procedure. LP involves the removal of some amount of spinal fluid. To facilitate CSF production, the client is instructed to increase fluid intake to 3L, unless contraindicated, for 24 to 48 hrs after the procedure. 40. A client diagnosed with cerebral thrombosis is scheduled for cerebral angiography. Nursing care of the client includes the following EXCEPT A. Inform the client that a warm, flushed feeling and a salty taste may be B. Maintain pressure dressing over the site of puncture and check for C. Check pulse, color and temperature of the extremity distal to the site of D. Kept the extremity used as puncture site 40. Answer: (D) Kept the extremity used as puncture site flexed to prevent bleeding. Angiography involves the threading of a catheter through an artery which can cause trauma to the endothelial lining of the blood vessel. The platelets are attracted to the area causing thrombi formation. This is further enhanced by the slowing of blood flow caused by flexion of the affected extremity. The flexed to prevent bleeding. affected extremity must be kept straight and immobilized during the duration of the bedrest after the procedure. Ice bag can be applied intermittently to the puncture site. 41. Which is considered as the earliest sign of increased ICP that the nurse should closely observed for? A. abnormal respiratory pattern B. rising systolic and widening pulse pressure C. contralateral hemiparesis and ipsilateral dilation of the pupils D. progression from restlessness to confusion and disorientation to lethargy 41. Answer: (D) progression from restlessness to confusion and disorientation to lethargy The first major effect of increasing ICP is a decrease in cerebral perfusion causing hypoxia that produces a progressive alteration in the LOC. This is initially manifested by restlessness. 42. Which is irrelevant in the pharmacologic management of a client with CVA? A. Osmotic diuretics and corticosteroids are given to decrease cerebral edema B. Anticonvulsants are given to prevent seizures C. Thrombolytics are most useful within three hours of an occlusive CVA D. Aspirin is used in the acute management of a completed stroke. 42. Answer: (D) Aspirin is used in the acute management of a completed stroke. The primary goal in the management of CVA is to improve cerebral tissue perfusion. Aspirin is a platelet deaggregator used in the prevention of recurrent or embolic stroke but is not used in the acute management of a completed stroke as it may lead to bleeding. 43. What would be the MOST therapeutic nursing action when a client’s expressive aphasia is severe? A. Anticipate the client wishes so she will not need to talk B. Communicate by means of questions that can be answered by the client shaking the head C. Keep us a steady flow rank to minimize silence D. Encourage the client to speak at every possible opportunity. 43. Answer: (D) Encourage the client to speak at every possible opportunity. Expressive or motor aphasia is a result of damage in the Broca’s area of the frontal lobe. It is amotor speech problem in which the client generally understands what is said but is unable to communicate verbally. The patient can best he helped therefore by encouraging him to communicate and reinforce this behavior positively. 44. A client with head injury is confused, drowsy an A. altered level of cognitive function has unequal pupils. Which of the following nursing B. high risk for injury diagnosis is most important at this time? C. altered cerebral tissue perfusion D. sensory perceptual alteration 44. Answer: (C) altered cerebral tissue perfusion The observations made by the nurse clearly indicate a problem of decrease cerebral perfusion. Restoring cerebral perfusion is most important to maintain cerebral functioning and prevent further brain damage. 45. Which nursing diagnosis is of the highest priority when caring for a client with myasthenia gravis? A. Pain B. High risk for injury related to muscle weakness C. Ineffective coping related to illness D. Ineffective airway clearance related to muscle weakness 45. Answer: (D) Ineffective airway clearance related to muscle weakness Myasthenia gravis causes a failure in the transmission of nerve impulses at the neuromuscular junction which may be due to a weakening or decrease in acetylcholine receptor sites. This leads to sporadic, progressive weakness or abnormal fatigability of striated muscles that eventually causes loss of function. The respiratory muscles can become weak with decreased tidal volume and vital capacity making breathing and clearing the airway through coughing difficult. The respiratory muscle weakness may be severe enough to require and emergency airway and mechanical ventilation. 46. The client has clear drainage from the nose and A. Measure the ph of the fluid ears after a head injury. How can the nurse B. Measure the specific gravity of the fluid 46. Answer: (C) Test for glucose The CSF contains a large amount of glucose which can be determine if the drainage is CSF? C. Test for glucose D. Test for chlorides detected by using glucostix. A positive result with the drainage indicate CSF leakage. 47. The nurse includes the important measures for stump care in the teaching plan for a client with an amputation. Which measure would be excluded from the teaching plan? A. Wash, dry, and inspect the stump daily. B. Treat superficial abrasions and blisters promptly. C. Apply a "shrinker" bandage with tighter arms around the proximal end of the affected limb. D. Toughen the stump by pushing it against a progressively harder substance (e.g., pillow on a foot-stool). 47. Answer: (C) Apply a "shrinker" bandage with tighter arms around the proximal end of the affected limb. The “shrinker” bandage is applied to prevent swelling of the stump. It should be applied with the distal end with the tighter arms. Applying the tighter arms at the proximal end will impair circulation and cause swelling by reducing venous flow. 48. A 70-year-old female comes to the clinic for a routine checkup. She is 5 feet 4 inches tall and weighs 180 pounds. Her major complaint is pain in her joints. She is retired and has had to give up her volunteer work because of her discomfort. She was told her diagnosis was osteoarthritis about 5 years ago. Which would be excluded from the clinical pathway for this client? A. Decrease the calorie count of her daily diet. B. Take warm baths when arising. C. Slide items across the floor rather than lift them. D. Place items so that it is necessary to bend or stretch to reach them. 48. Answer: (D) Place items so that it is necessary to bend or stretch to reach them. Patients with osteoarthritis have decreased mobility caused by joint pain. Over-reaching and stretching to get an object are to be avoided as this can cause more pain and can even lead to falls. The nurse should see to it therefore that objects are within easy reach of the patient. 49. A client is admitted from the emergency department with severe-pain and edema in the right foot. His diagnosis is gouty arthritis. When developing a plan of care, which action would have the highest priority? A. Apply hot compresses to the affected joints. B. Stress the importance of maintaining good posture to prevent deformities. C. Administer salicylates to minimize the inflammatory reaction. D. Ensure an intake of at least 3000 ml of fluid per day. 49. Answer: (D) Ensure an intake of at least 3000 ml of fluid per day. Gouty arthritis is a metabolic disease marked by urate deposits that cause painful arthritic joints. The patient should be urged to increase his fluid intake to prevent the development of urinary uric acid stones. 50. A client had a laminectomy and spinal fusion yesterday. Which statement is to be excluded from your plan of care? A. Before log rolling, place a pillow under the client’s head and a pillow between the client’s legs. B. Before log rolling, remove the pillow from under the client’s head and use no pillows between the client’s legs. C. Keep the knees slightly flexed while the client is lying in a semi-Fowler’s position in bed. D. Keep a pillow under the client’s head as needed for comfort. 50. Answer: (B) Before log rolling, remove the pillow from under the client’s head and use no pillows between the client’s legs. Following a laminectomy and spinal fusion, it is important that the back of the patient be maintained in straight alignment and to support the entire vertebral column to promote complete healing. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 141 pages
Instant download

Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 31, 2021
Number of pages
141
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 31, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
38





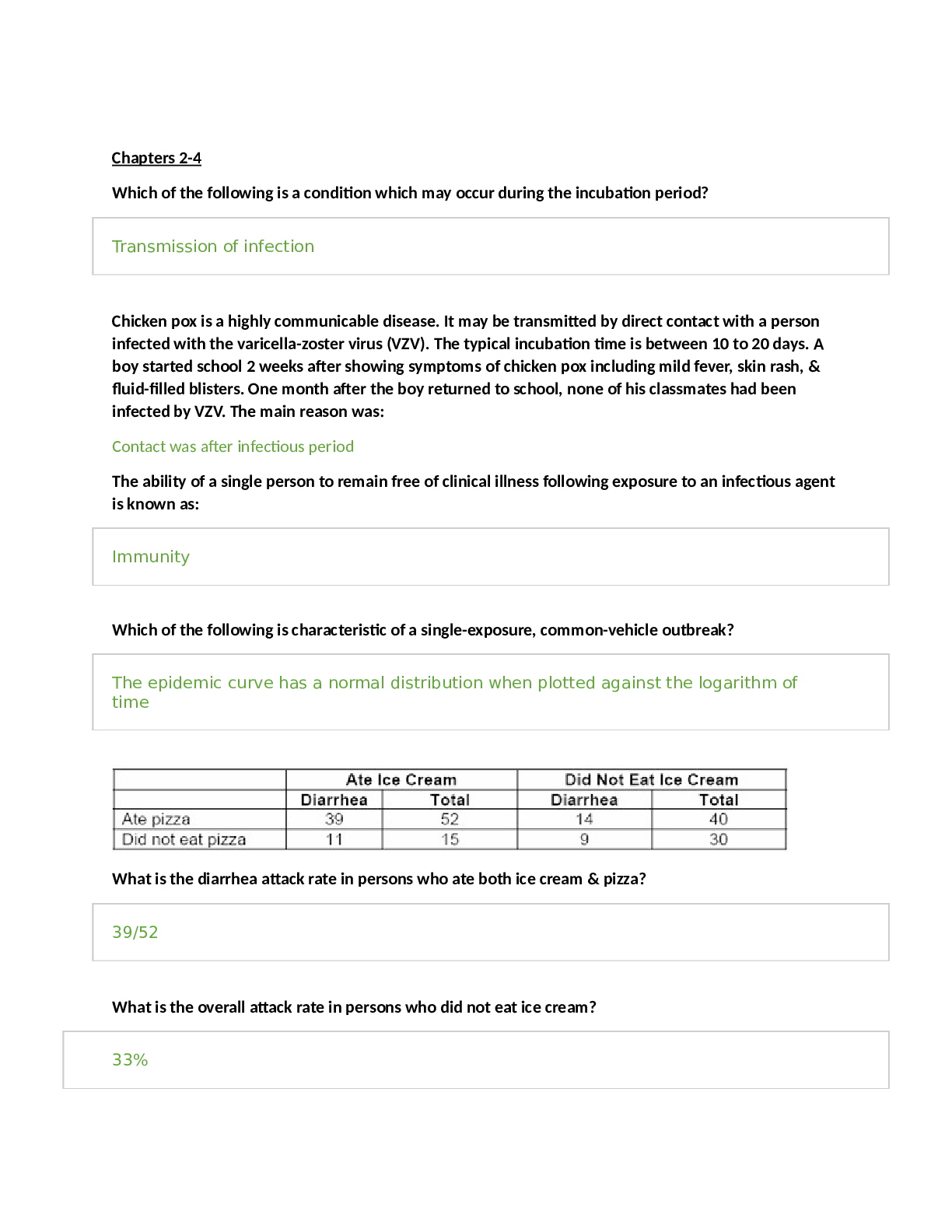


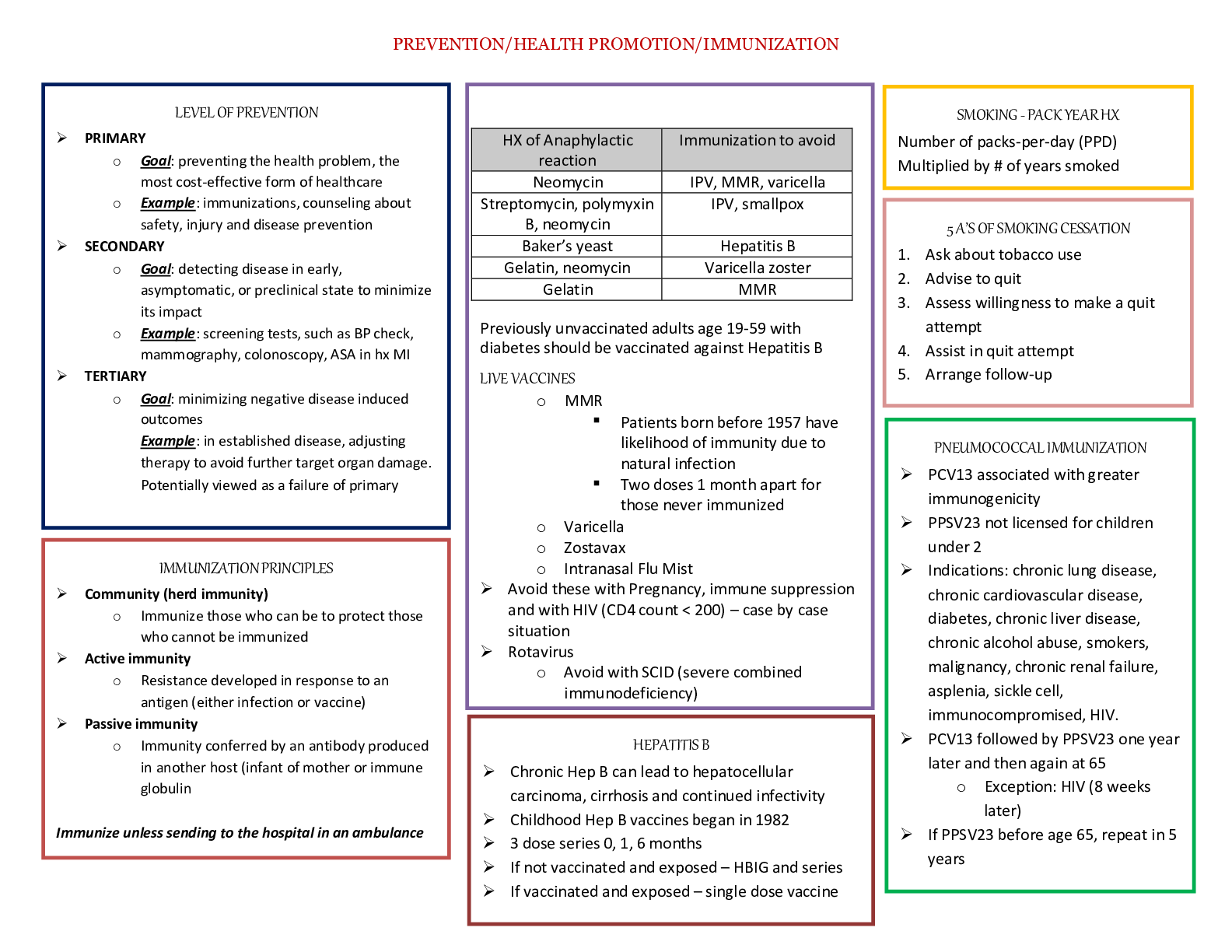





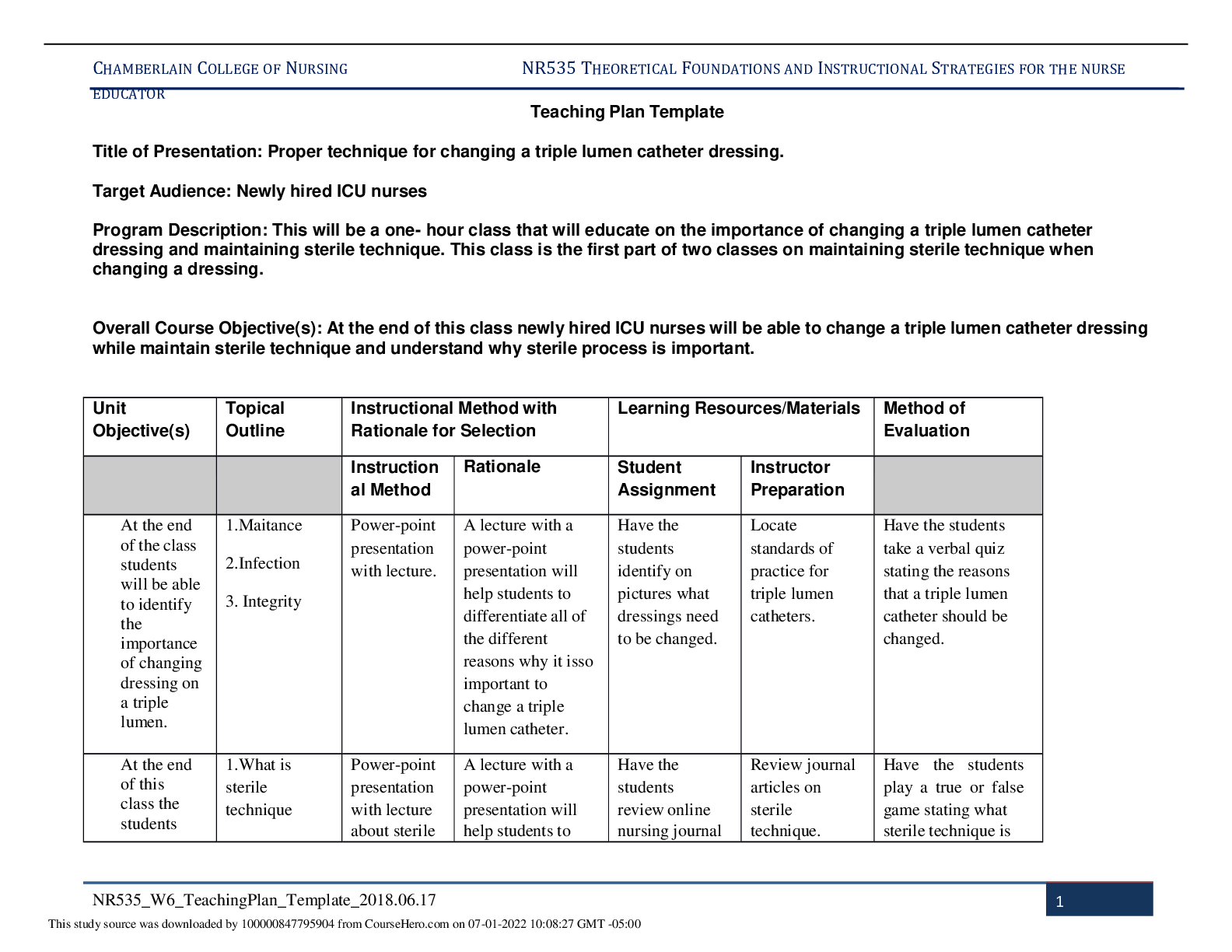

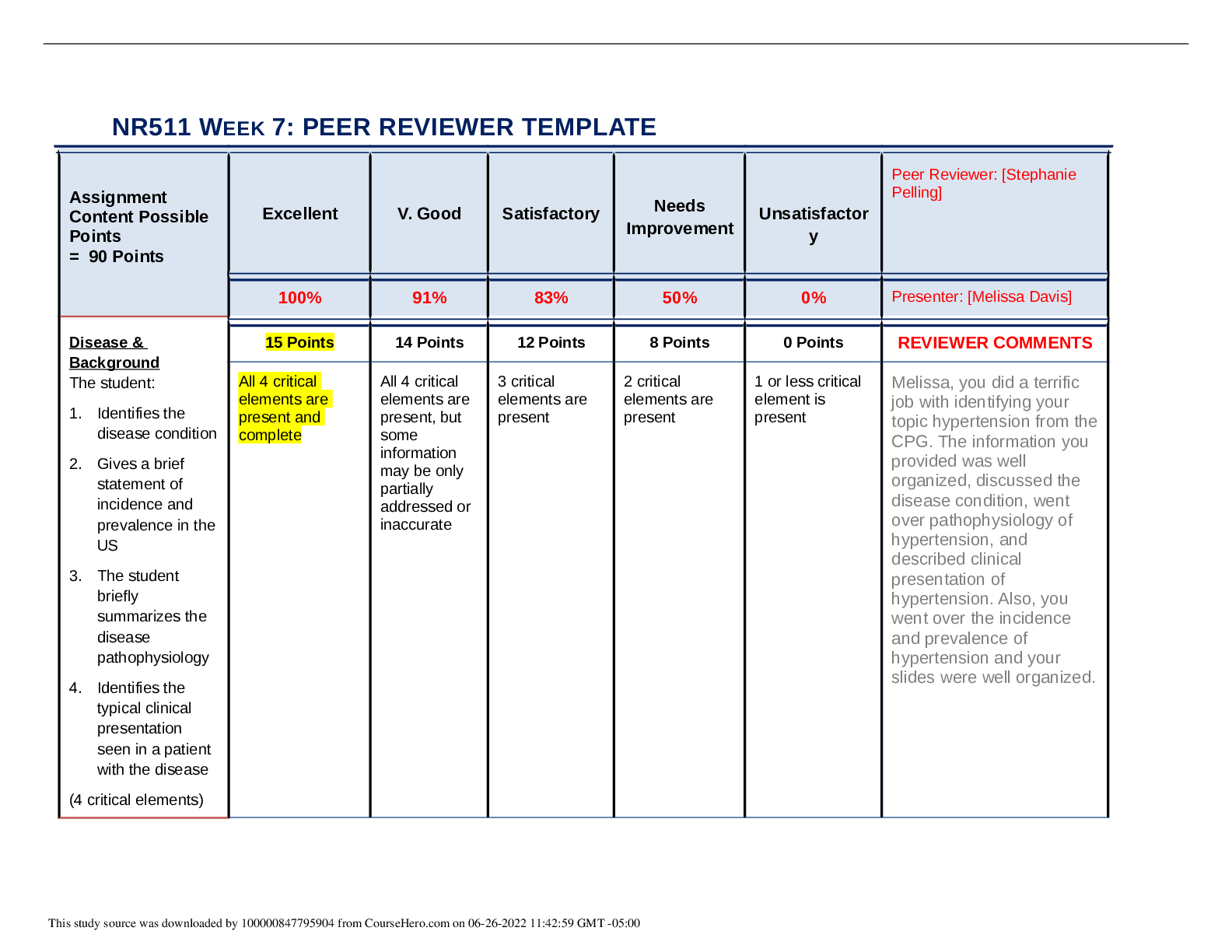






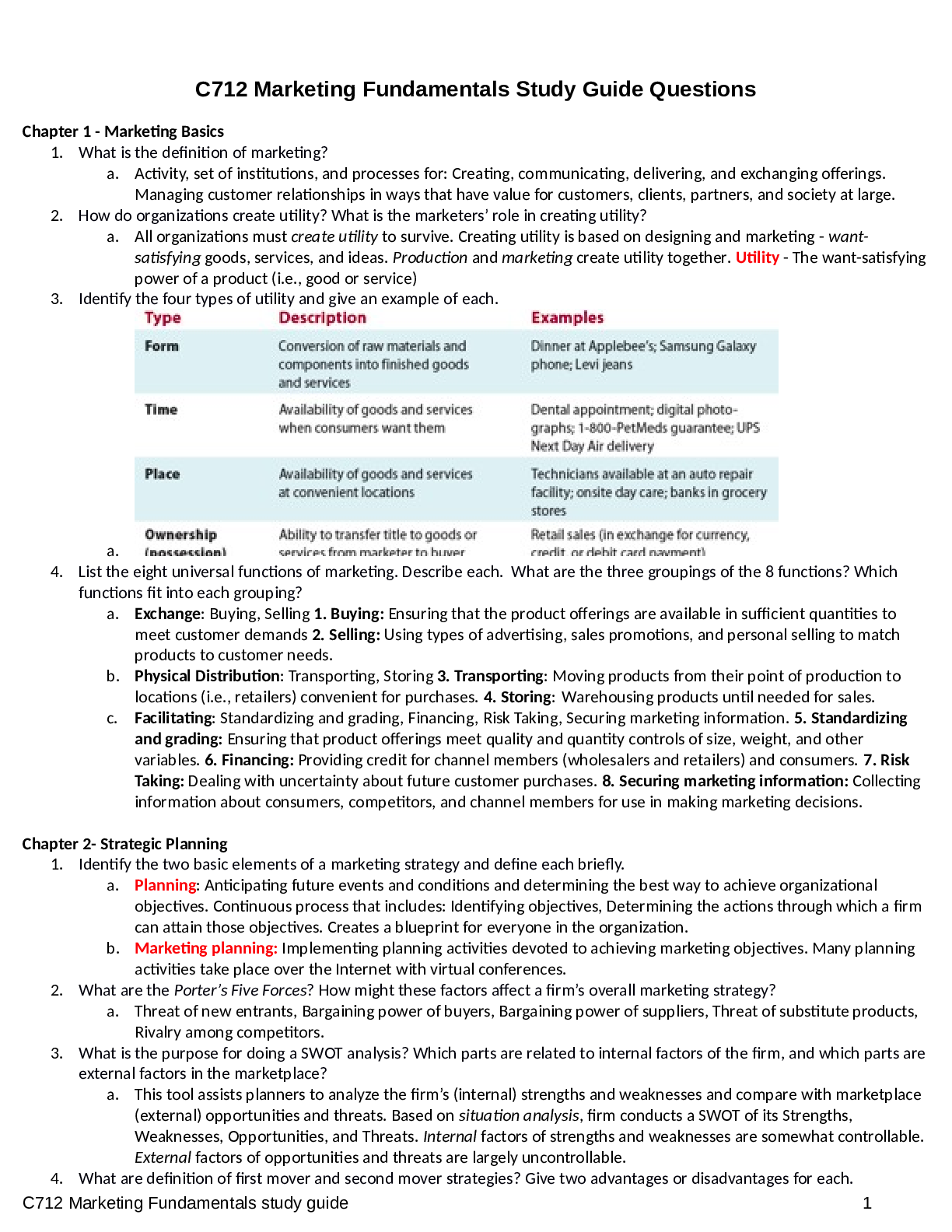



.png)







