*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > AANP Study Guide UPDATED 2021 GUARANTEED GRADES Chamberlain College of Nursing (All)
AANP Study Guide UPDATED 2021 GUARANTEED GRADES Chamberlain College of Nursing
Document Content and Description Below
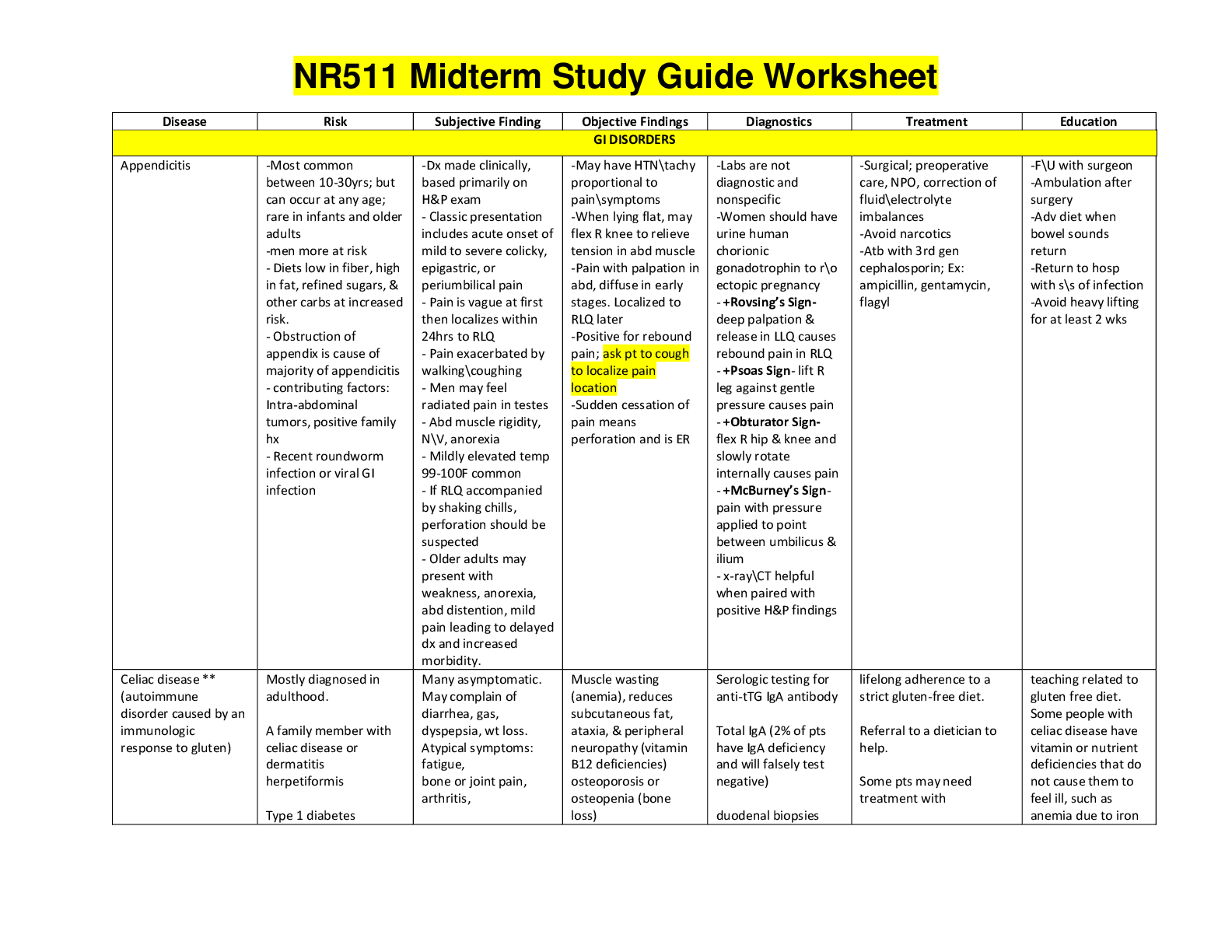
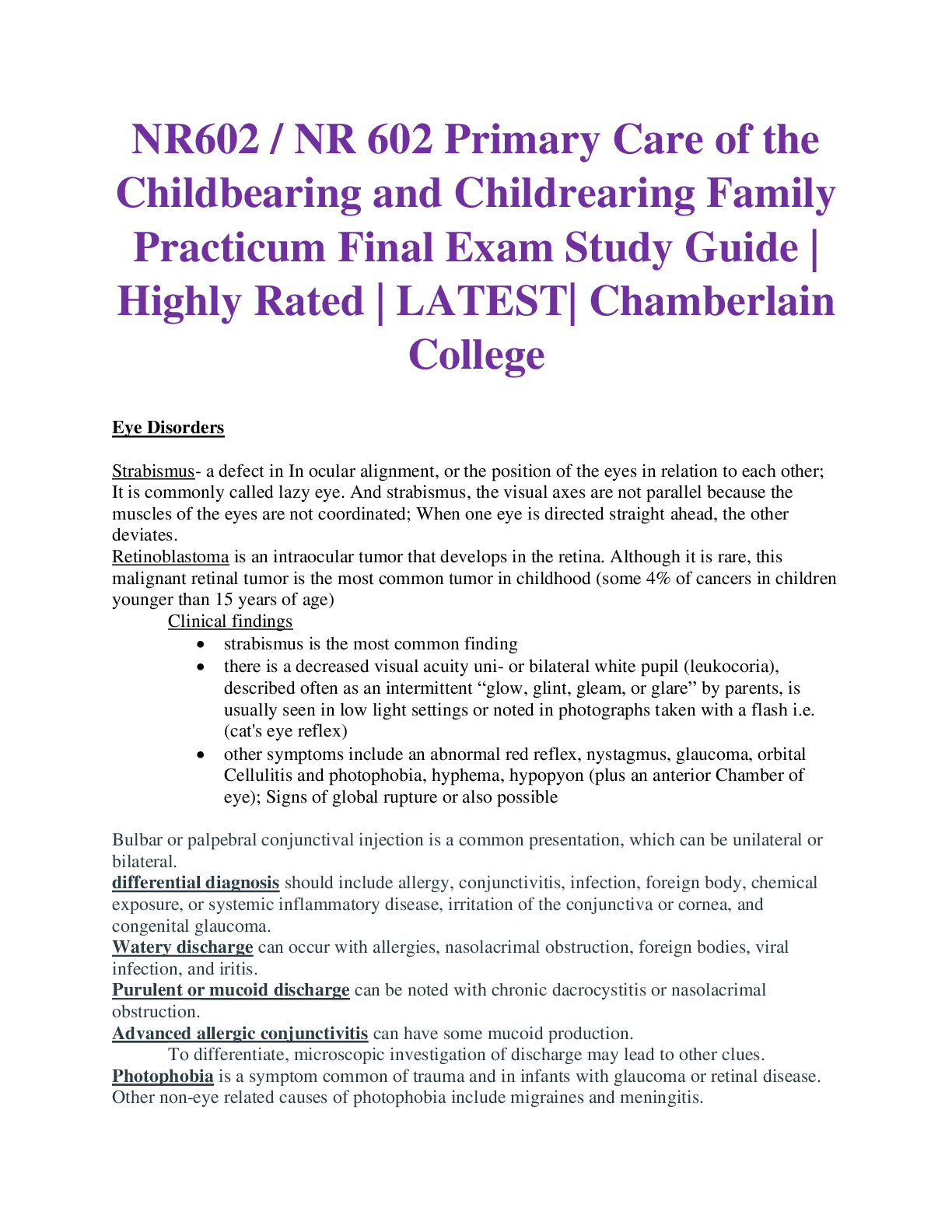
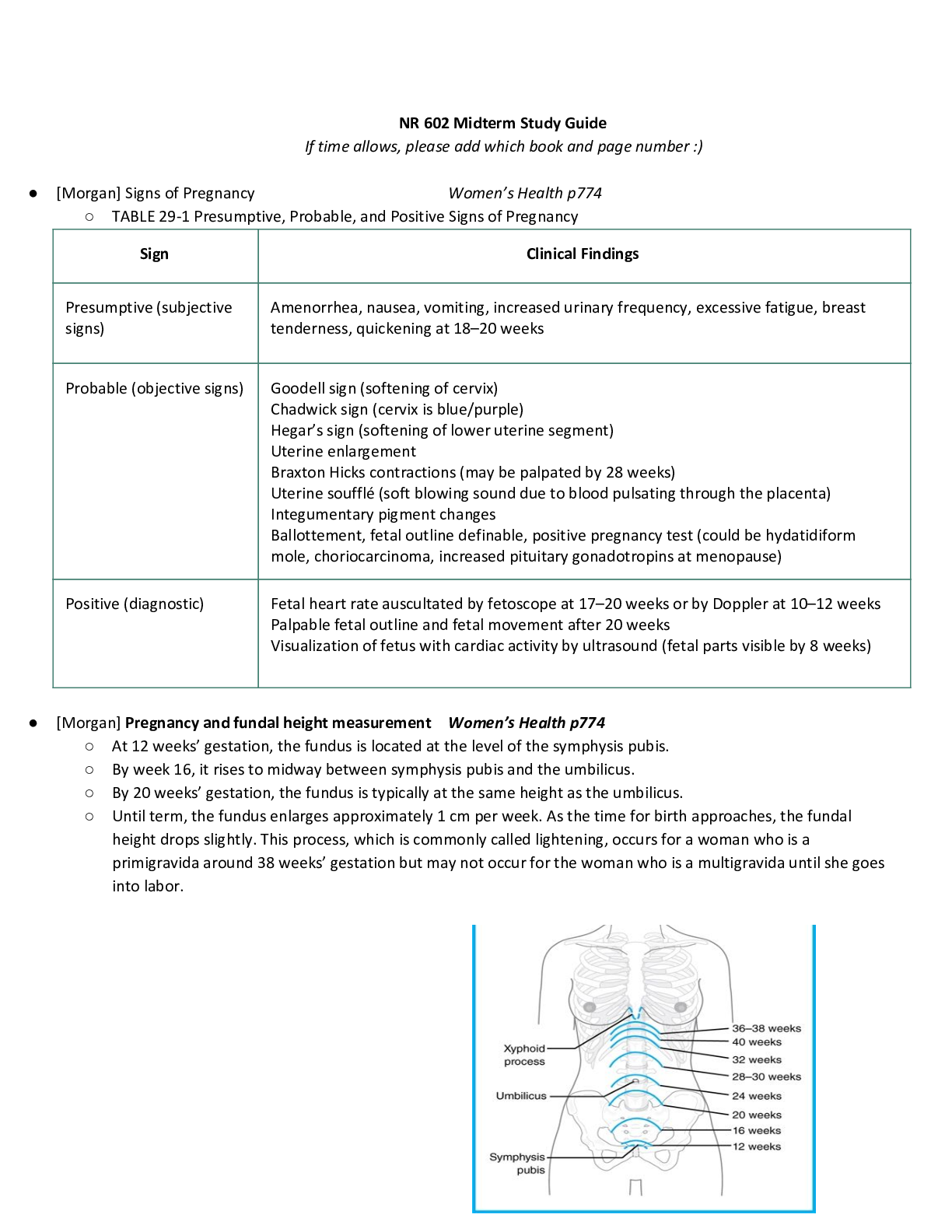
ENT Allergies to PCN - use macrolides, fluoroquinolones Blepharitis- inflammation of eyelids TX baby shampoo, warm compresses Baby with normal exam except yellow discharge from eyes how... to you treat. Sialolithiasis – Stones within the salivary glands or the salivary gland ducts. Painful lump on jaw that comes and goes, Sialolithiasis typically presents with pain and swelling in the involved gland; these symptoms are usually aggravated by eating or by anticipation of eating. Otitis media- inflammation of middle ear/inner, erythema, decreased tympanic membrane mobility, distorted landmarks, displaced light reflex, moderate to severe bulging, mastoid pain, Dx pneumatic otoscopy TX analgesics acetaminophen, ibuprofen, narcotic with codeine, amoxicillin, Augmentin, omnicef, ceftin, otic drops ciprofloxacin with dexamethasone Otitis externa- swimmers ear, P. aeruginosa, external canal producing inflammation, itching, pain, tragal/pinna pain, otorrhea, Dx culture, TX fluoroquinolone and polymyxin B cortisporin drops! Sensorineural loss Weber test(top of head)no laterization, normal finding, does not lateralize to either ear, bilateral hearing loss, if hear better in left ear, right sensorineural loss Conductive loss Rinne test (behind pinna)–normal finding if AC last longer than bone conduction, good ear= air conduction> bone conduction, bad ear BC>AC Sjogren’s syndrome- chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by decrease function of lacrimal and salivary glands Bacterial conjunctivitis- purulent (pus) exudate, initially unilateral, then often bilateral, self-limiting 5-7 days, delay treatment till 3rd day, TX eye drops or ointment polytrim, trimethoprim, polymyxin, macrolide Viral conjunctivitis- profuse tearing, mucus discharge, burning, concurrent URI, enlarged preauricular node TX antihistamine, decongestant drops, Trifluridine in herpes conjunctivitis Nystagmus- eye makes repetitive uncontrolled movements, decrease vision, depth perception, balance Fluorescein strips- check for corneal abrasions, keratitis Horizontal nystagmus- normal for eye to return to midline Cover/uncover test- strabismus Hirschberg test- screening test for strabismus, compare corneal light reflex Visual field by confrontation test- test peripheral vision Ishihara- color vision test Fovea of macula- responsible for sharpest vision Cones- responsible for color vision Rods- responsible for night vision Mononucleosis- (Epstein Barr virus) normally lymphocytosis, maculopapular rash, fever, fatigue, pharyngitis, cervical lymphadenopathy, limit sports/activity, monitor forsplenomegaly hepatomegaly, Dx monospot screen for heterophil antibodies, TX ibuprofen/Tylenol, no virus infection, no Abx treatment, rehydrate, if with strep add Ceftin for 5 days Hairy leukoplakia- caused by Epstein Barr virus Pathognomonic for HIV infection Strep pharyngitis- strep pyongenes, cause of scarlet fever affects heart valves and kidneys, Criteria for strep tonsillar exudates, anterior cervical adenopathy, fever, sore throat, fatigue, NO cough TX PCN, amoxicillin, macrolide cephalosporin, Dx rapid strep test, CNC, monspot if mono suspected, increases mortality in community acquired pneumonia Allergic rhinitis- clear discharge, blue tinged or pale and swollen (boggy) turbinate’s, sneezing itching nasal stuffiness TX single most effective treatment intranasal glucocorticosteroids, antihistamines, decongestants (raises BP) Acute rhinosinusitis- inflammation of paranasal sinuses due to bacteria, viral fungal or allergic infection, Goal to promote drainage, Sx facial pain, tooth pain, purulent discharge, nasal congestion, TX wait 10 days then amoxicillin or Augmentin, if allergy, fluoroquinolones/ tetracyclines Kiesselbachs plexus- epistaxis commonly occurs anterior, posterior nasal bleeds may hemorrhage, refer to ER Herpes keratitis- eye pain, photophobia, blurred vision in affected eye, DX fluorescein stain, , may result in blindness, refer to ED, ophthalmology stat Pterygium- surfers eye, yellow triangular thickening of conjunctiva, web in eye, avoid light, glasses Cataracts- opacity in lens, difficulty with glare, halos around light, blurred vision, gradual onset of decreased night vision, red reflex disappears (Red reflex is now opaque gray instead of orange red glow) Macular degeneration- loss of center vision, loss of visual acuity, contrast sensitivity but still have peripheral vision, may find Drusen bodies, Dx Amsler grid to evaluate central vision changes Retinal detachment- sudden onset of shower floaters with looking thru curtain with sudden flashes of light, refer to ED Epiglottis- life threatening infection of epiglottis and surrounding tissue, cellulitis of the epiglottis, drooling, stridor, hoarseness, head is leaned back, can’t swallow because it hurts, big eyes scared, thumbs sign enlarged epiglottis protruding from anterior wall Cholesteatoma- affected ear hearing loss, cauliflower like mass inside middle ear, can erode bones in face, damage facial nerve CN 7 Retinoblastoma- white reflection in child’s pupil Vertigo- spinning or rotating common characteristic TX antivertSKIN Prevalent Cancer males- prostate Prevalent cancer in females- breast Highest mortality from cancer – Lung Highest mortality of skin cancer-melanoma Gynecological cancer most common- uterine/endometrial Gynecological cancer second most common- ovarian Kolpik spots- are a prodromic viral enanthem of measles manifesting two to three days before the measles rash itself. They are characterized as clustered, white lesions on the buccal mucosa (opposite the lower 1st & 2nd molars) and are pathognomonic for measles/rubeola. Scarlet fever, scaralatina- sandpaper textured pink rash with sore throat strawberry tongue Fifth disease- Parvovirus B19, stages of rash, slap cheek syndrome, erythema infection, A common and highly contagious childhood ailment causing a distinctive face rash, blanches Roseola infantum- Sixth disease, viral infection, young children, high fever rash, rash, TX bedrest, fluids, Tylenol Kawasaki disease- high fever enlarged lymph nodes red rash in groin are, conjunctivitis, dry cracked lips, strawberry tongue, swollen hands/feet, skin peels form hands/feet, TX high dose aspirin, gamma globulin Hand foot mouth disease- Coxsackie virus, direct contact, with nasal discharge, saliva, blister fluid, or stool, most contagious for first week, fever, severe sore throat, headache anorexia, blisters on the hands and feet, diaper area, ulcers mouth throat tonsils and tongue, pain with acidic foods, TX symptomatic treatment ibuprofen or Tylenol saltwater gargle, cold fluids Molluscum contagiosum- poxvirus, smooth wax like, round, (dome shaped) papules 5 mm size, central umbilication with white plug, viral skin infection results in round firm painless bumps, contagious, TX resolve on own, wart medication (if near genitals in kids, suspects sexual abuse) Acanthosis nigricans- thickening of the skin, skin pigmentation disorder (darkening) related to diabetes, colon cancer and obesity Intertrigo –candidiasis, burning malodorous odor, maceration, located in folds, under breasts, scrotum, inner thigh, between toes TX nystatin Urticaria- hives TX with Benadryl or Zyrtec Actinic keratosis- rough flat, dry, erythematous papules or plaques, scaly patch of red or brown skin caused by years of sun exposure, evolving carcinoma, precursor to squamous cell carcinoma, Dx biopsy, refer to dermatology, TX topical 5 fluoracil 5-FU, cryotherapy, Basal cell- most prevalent skin cancer, pearly domed nodule with overlying telangiectatic vessels, maybe plaque, maybe papule, may see central ulceration and crusting, deepest layer of the epidermis, Dx gold standard biopsy, TX chemo or immunotherapy ABCDE- asymmetry, border is irregular, color variegation, diameter .6mm size greater than pencil eraser, elevation above skin level Squamous cell- skin cancer develops in the outer layer of the skin, lower lip common location, nodule, indistinct margins, surface is firm, scaly, irregular, and may bleed easily, may metastasize Atopic dermatitis- (eczema) itchy inflammation of the skin TX topical steroids, emollients linear formation Contact dermatitis- allergy to something Seborrheic dermatitis- chronic, superficial disorder, scaly patches and red skin mainly on scalp, TX rotation of prescription/nonprescription (scalpketoconazole/metronidazole(antifungal) shampoo, capitrol shampoo, selenium sulfide Selsun blue(adults/children) shampoo ciclopirox shampoo, topical steroid gel hydrocortisone) face hydrocortisone, ears-hydrocortisone cream, eyelids- baby shampoo, Sebhorric keratoses- soft wart like lesion appears pasted on, seen on back and trunk, (elderly) BENIGN Lentigines- liver spots, tan to brown colored macules on dorsum of the hands/forearms, caused by sun damage, BENIGN Stasis dermatitis- affects lower legs and ankles due to chronic edema (PVD) Rocky spotted mountain fever- rash on ankles/wrists, spreads to trunk, hi fever, headache, myalgia, nausea, TX doxycycline refer to ED Cheilitis- chapped lips, lip fissures Moderate acne- TX oral abx + topical retinoid +/- benzoyl peroxide (tetracycline + tazarotene +/- Benz Pero ….Retin topical, oral tetracycline then Accutane (isotretinoin) Hidradenitis suppurativa – acne inversa, the skin lesions develop as a result of inflammation and infection of sweat glands. This condition features pea- to marble-sized lumps under the skin that can be painful and tend to enlarge and drain pus. They usually occur where skin rubs together, such as in the armpits, groin, and buttocks. TX doxycycline, topical abx Postherpetic neuralgia PHN- prophylaxis is TCA-Elavil Subungual hematoma- collection of blood underneath toenail or fingernail, TX make hole and drain the blood (trephination) Petechia- tiny round brown/purple spots due to bleeding under skin Cellulitis- deep tissue, gram positive, gradual course over days, TX PCN, macrolide Erysipelas-(strept infection)- acute onset, well demarcated and above the skin, TX pcn or macrolide MRSA- TX Bactrim or tetracyclines Papule – solid elevated mass up to 1 cm Macule- flat small like a freckle Vesicle – filled with serous fluid and less than 1 cm Bullae- fluid filled and larger than 1 cm Xerosis- dry skin, use petroleum-based product, not lotions Psoriasis- pruritic erythematous plaque covered with fine silvery white scales, scalp and elbows TX topical steroids Auspitz sign – appearance of bleeding spots when scales are scraped off from psoriasis plaque Shingles- chicken pox, reactivation of varicella zoster virus involves single dermatome, less likely several dermatomes, finding prodrome- itching burning photophobia fever headache malaise, acute phase dermatomal rash 3-4 days, unilateral, pain, possible severe, macupapular rash progresses to vesicles then pustules 3-4 days, may appear for a week, convalescent phase- 2-3 week rash resolves, pain Dx viral culture, polymerase chain reaction PCR, TX acyclovir, zostrix cream, gabapentin amitriptyline Spider bite- TX abx on wound, cold packs nsaids Dog bite- treat with analgesia (Tylenol, nsaids, Demerol), Augmentin/doxycycline/Bactrim, wound cleaning with soap and water, betadine, local anesthesia (lidocaine), irrigated with 2000ml normal saline, betadine, wound debridement, facial bites should be closed with sutures only, pack wound, tetanus immunization, antibiotic therapy, I had cat, man with scratches know tx. Lyme disease- erythema migrans, bulls eye rash, start within 72 hours of exposure, TX with doxycycline or amoxicillin, or azithromycin Dx two step test EIA and then western blot Lupus- multisystem autoimmune disease, characterized by remission and exacerbations, affects organs, skin kidney, heart, and blood vessels, face butterfly rash, avoid sunlight exposure, photosensitivity TX refer to rheumatologist, topical and oral steroids, avoid sun and cover skin Less seen in Caucasians Pityriasis rosea- Christmas tree pattern rash, herald patch, normally on trunk Anthrax- TX doxycycline/ fluoroquinolones (Cipro) Tinea versicolor- trunk and extremities sun spots Tinea corporis-(ringworm) arms/legs or body Tinea cruris- jock itch Tinea capitas- skin or scalp Tinea pedis-athletes foot [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 54 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 04, 2021
Number of pages
54
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 04, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
40






.png)