Health Care > EXAM > Adult Health Exam 5_Test Prep Exam Elaborations Verified Questions and Answers With Explanations (20 (All)
Adult Health Exam 5_Test Prep Exam Elaborations Verified Questions and Answers With Explanations (2021) Study Guide
Document Content and Description Below
Adult Health Exam 5-Musculoskeletal, Neurological, Cognitive & Perceptual, & Endocrine Disorders Review Questions & Answers Musculoskeletal Disorders 1. A patient is suspected of having rheumatoid ... arthritis and her diagnostic regimen includes aspiration of synovial fluid from the knee for a definitive diagnosis. The nurse knows that which of the following procedures will be involved? A. Angiography B. Myelography C. Paracentesis D. Arthrocentesis Ans: D. Arthrocentesis involves needle aspiration of synovial fluid. Angiography is an x-ray study of circulation with a contrast agent injected into a selected artery. Myelography is an x-ray of the spinal subarachnoid space taken after the injection of a contrast agent into the spinal subarachnoid space through a lumbar puncture. Paracentesis is removal of fluid (ascites) from the peritoneal cavity through a small surgical incision or puncture made through the abdominal wall under sterile conditions. 2. A nurse is providing care for a patient who has just been diagnosed as being in the early stage of rheumatoid arthritis. The nurse should anticipate the administration of which of the following? A. Hydromorphone (Dilaudid) B. Methotrexate (Rheumatrex) C. Allopurinol (Zyloprim) D. Prednisone Ans: B. In the past, a step-wise approach starting with NSAIDs was standard of care. However, evidence clearly documenting the benefits of early DMARD (methotrexate [Rheumatrex], antimalarials, leflunomide [Arava], or sulfasalazine [Azulfidine]) treatment has changed national guidelines for management. Now it is recommended that treatment with the non-biologic DMARDs begin within 3 months of disease onset. Allopurinol is used to treat gout. Opioids are not indicated in early RA. Prednisone is used in unremitting RA. 3. A nurse is performing the initial assessment of a patient who has a recent diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). What skin manifestation would the nurse expect to observe on inspection? A. Petechiae B. Butterfly rash C. Jaundice D. Skin sloughing Ans: B. An acute cutaneous lesion consisting of a butterfly-shaped rash across the bridge of the nose and cheeks occurs in SLE. Petechiae are pinpoint skin hemorrhages, which are not a clinical manifestation of SLE. Patients with SLE do not typically experience jaundice or skin sloughing. 4. A clinic nurse is caring for a patient with suspected gout. While explaining the pathophysiology of gout to the patient, the nurse should describe which of the following? A. Autoimmune processes in the joints B. Chronic metabolic acidosis C. Increased uric acid levels D. Unstable serum calcium levels Ans: C. Gout is caused by hyperuricemia (increased serum uric acid). Gout is not categorized as an autoimmune disease and it does not result from metabolic acidosis or unstable serum calcium levels. 5. A patients decreased mobility is ultimately the result of an autoimmune reaction originating in the synovial tissue, which caused the formation of pannus. This patient has been diagnosed with what health problem? A. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) B. Systemic lupus erythematosus C. Osteoporosis D. Polymyositis Ans: A. In RA, the autoimmune reaction results in phagocytosis, producing enzymes within the joint that break down collagen, cause edema and proliferation of the synovial membrane, and ultimately form pannus. Pannus destroys cartilage and bone. SLE, osteoporosis, and polymyositis do not involve pannus formation. 6. A nurse is performing the health history and physical assessment of a patient who has a diagnosis of 1Adult Health Exam 5 rheumatoid arthritis (RA). What assessment finding is most consistent with the clinical presentation of RA? A. Cool joints with decreased range of motion B. Signs of systemic infection C. Joint stiffness, especially in the morning D. Visible atrophy of the knee and shoulder joints Ans: C. In addition to joint pain and swelling, another classic sign of RA is joint stiffness, especially in the morning. Joints are typically swollen, not atrophied, and systemic infection does not accompany the disease. Joints are often warm rather than cool. 7. A patient has a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis and the primary care provider has now prescribed cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan). The nurses subsequent assessments should address what potential adverse effect? A. Infection B. Acute confusion C. Sedation D. Malignant hyperthermia Ans: A. When administering immunosuppressives such as Cytoxan, the nurse should be alert to manifestations of bone marrow suppression and infection. Confusion and sedation are atypical adverse effects. Malignant hyperthermia is a surgical complication and not a possible adverse effect. 8. A nurse is assessing a patient for risk factors known to contribute to osteoarthritis. What assessment finding would the nurse interpret as a risk factor? A. The patient has a 30 pack-year smoking history. B. The patients body mass index is 34 (obese). C. The patient has primary hypertension. D. The patient is 58 years old. Ans: B. Risk factors for osteoarthritis include obesity and previous joint damage. Risk factors of OA do not include smoking or hypertension. Incidence increases with age, but a patient who is 58 would not yet face a significantly heightened risk. 9. A patient is undergoing diagnostic testing to determine the etiology of recent joint pain. The patient asks the nurse about the difference between osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). What is the best response by the nurse? A. OA is a considered a noninflammatory joint disease. RA is characterized by inflamed, swollen joints. B. OA and RA are very similar. OA affects the smaller joints such as the fingers, and RA affects the larger, weight-bearing joints like the knees. C. OA originates with an infection. RA is a result of your body's cells attacking one another. D. OA is associated with impaired immune function; RA is a consequence of physical damage. Ans: A. OA is a degenerative arthritis with a noninflammatory etiology, characterized by the loss of cartilage on the articular surfaces of weight-bearing joints, with spur development. RA is characterized by inflammation of synovial membranes and surrounding structures. The diseases are not distinguished by the joints affected and neither has an infectious etiology. 10.A patient with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is preparing for discharge. The nurse knows that the patient has understood health education when the patient makes what statement? A. Ill make sure I get enough exposure to sunlight to keep up my vitamin D levels. B. Ill try to be as physically active as possible between flare-ups. C. Ill make sure to monitor my body temperature on a regular basis. D. Ill stop taking my steroids when I get relief from my symptoms. Ans: C. Fever can signal an exacerbation and should be reported to the physician. Sunlight and other sources of ultraviolet light may precipitate severe skin reactions and exacerbate the disease. Fatigue can cause a flare-up of SLE. Patients should be encouraged to pace activities and plan rest periods. Corticosteroids must be gradually tapered because they can suppress the function of the adrenal gland. As well, these drugs should not be independently adjusted by the patient. 11.A nurse is caring for a 78-year-old patient with a history of osteoarthritis (OA). When planning the patients 2Adult Health Exam 5 care, what goal should the nurse include? A. The patient will express satisfaction with her ability to perform ADLs. B. The patient will recover from OA within 6 months. C. The patient will adhere to the prescribed plan of care. D. The patient will deny signs or symptoms of OA. Ans: A. Pain management and optimal functional ability are major goals of nursing interventions for OA. Cure is not a possibility and it is unrealistic to expect a complete absence of signs and symptoms. Adherence to the plan of care is highly beneficial, but this is not the priority goal of care. 12.Allopurinol (Zyloprim) has been ordered for a patient receiving treatment for gout. The nurse caring for this patient knows to assess the patient for bone marrow suppression, which may be manifested by which of the following diagnostic findings? A. Hyperuricemia B. Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate C. Elevated serum creatinine D. Decreased platelets Ans: D. Thrombocytopenia occurs in bone marrow suppression. Hyperuricemia occurs in gout, but is not caused by bone marrow suppression. Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate may occur from inflammation associated with gout, but is not related to bone marrow suppression. An elevated serum creatinine level may indicate renal damage, but this is not associated with the use of allopurinol. 13.A patient with rheumatic disease is complaining of stomatitis. The nurse caring for the patient should further assess the patient for the adverse effects of what medications? A. Corticosteroids B. Gold-containing compounds C. Antimalarials D. Salicylate therapy Ans: B. Stomatitis is an adverse effect that is associated with gold therapy. Steroids, antimalarials, and salicylates do not normally have this adverse effect. 14.A nurse is planning patient education for a patient being discharged home with a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. The patient has been prescribed antimalarials for treatment, so the nurse knows to teach the patient to self-monitor for what adverse effect? A. Tinnitus B. Visual changes C. Stomatitis D. Hirsutism Ans: B. Antimalarials may cause visual changes; regular ophthalmologic examinations are necessary. Tinnitus is associated with salicylate therapy, stomatitis is associated with gold therapy, and hirsutism is associated with corticosteroid therapy. 15.A nurse is working with a patient with rheumatic disease who is being treated with salicylate therapy. What statement would indicate that the patient is experiencing adverse effects of this drug? A. I have this ringing in my ears that just wont go away. B. I feel so foggy in the mornings and it takes me so long to wake up. C. When I eat a meal thats high in fat, I get really nauseous. D. I seem to have lost my appetite, which is unusual for me. Ans: A. Tinnitus is associated with salicylate therapy. Salicylates do not normally cause drowsiness, intolerance of high-fat meals, or anorexia. 16.A nurse is educating a patient with gout about lifestyle modifications that can help control the signs and 3Adult Health Exam 5 symptoms of the disease. What recommendation should the nurse make? A. Ensuring adequate rest B. Limiting exposure to sunlight C. Limiting intake of alcohol D. Smoking cessation Ans: C. Alcohol and red meat can precipitate an acute exacerbation of gout. Each of the other listed actions is consistent with good health, but none directly addresses the factors that exacerbate gout. 17.A patients rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has failed to respond appreciably to first-line treatments and the primary care provider has added prednisone to the patients drug regimen. What principle will guide this aspect of the patients treatment? A. The patient will need daily blood testing for the duration of treatment. B. The patient must stop all other drugs 72 hours before starting prednisone. C. The drug should be used at the highest dose the patient can tolerate. D. The drug should be used for as short a time as possible. Ans: D. Corticosteroids are used for shortest duration and at lowest dose possible to minimize adverse effects. Daily blood work is not necessary and the patient does not need to stop other drugs prior to using corticosteroids. 18.A patient with SLE has come to the clinic for a routine check-up. When auscultating the patients apical heart rate, the nurse notes the presence of a distinct scratching sound. What is the nurses most appropriate action? A. Reposition the patient and auscultate posteriorly. B. Document the presence of S3 and monitor the patient closely. C. Inform the primary care provider that a friction rub may be present. D. Inform the primary care provider that the patient may have pneumonia. Ans: C. Patients with SLE are susceptible to developing a pericardial friction rub, possibly associated with myocarditis and accompanying pleural effusions; this warrants prompt medical follow-up. This finding is not characteristic of pneumonia and does not constitute S3. Posterior auscultation is unlikely to yield additional meaningful data. 19.A community health nurse is performing a visit to the home of a patient who has a history of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). On what aspect of the patients health should the nurse focus most closely during the visit? A. The patients understanding of rheumatoid arthritis B. The patients risk for cardiopulmonary complications C. The patients social support system D. The patients functional status Ans: D. The patients functional status is a central focus of home assessment of the patient with RA. The nurse may also address the patients understanding of the disease, complications, and social support, but the patients level of function and quality of life is a primary concern. 20.A 21-year-old male has just been diagnosed with a spondyloarthropathy. What will be a priority nursing intervention for this patient? A. Referral for assistive devices B. Teaching about symptom management C. Referral to classes to stop smoking D. Setting up an exercise program Ans: B. Major nursing interventions in the spondyloarthropathies are related to symptom management and maintenance of optimal functioning. This is a priority over the use of assistive devices, smoking cessation, and exercise programs, though these topics may be of importance for some patients. 21.A patient with SLE asks the nurse why she has to come to the office so often for check-ups. What would be 4Adult Health Exam 5 the nurses best response? A. Taking care of you in the best way involves seeing you face to face. B. Taking care of you in the best way involves making sure you are taking your medication the way it is ordered. C. Taking care of you in the best way involves monitoring your disease activity and how well the prescribed treatment is working. D. Taking care of you in the best way involves drawing blood work every month. Ans: C. The goals of treatment include preventing progressive loss of organ function, reducing the likelihood of acute disease, minimizing disease-related disabilities, and preventing complications from therapy.Management of SLE involves regular monitoring to assess disease activity and therapeutic effectiveness. Stating the benefit of face-toface interaction does not answer the patients question. Blood work is not necessarily drawn monthly and assessing medication adherence is not the sole purpose of visits. 22.A patient with rheumatoid arthritis comes to the clinic complaining of pain in the joint of his right great toe and is eventually diagnosed with gout. When planning teaching for this patient, what management technique should the nurse emphasize? A. Take OTC calcium supplements consistently. B. Restrict consumption of foods high in purines. C. Ensure fluid intake of at least 4 liters per day. D. Restrict weight-bearing on right foot. Ans: B. Although severe dietary restriction is not necessary, the nurse should encourage the patient to restrict consumption of foods high in purines, especially organ meats. Calcium supplementation is not necessary and activity should be maintained as tolerated. Increased fluid intake is beneficial, but it is not necessary for the patient to consume more than 4 liters daily. 23.A nurses plan of care for a patient with rheumatoid arthritis includes several exercise-based interventions. Exercises for patients with rheumatoid disorders should have which of the following goals? A. Maximize range of motion while minimizing exertion B. Increase joint size and strength C. Limit energy output in order to preserve strength for healing D. Preserve and increase range of motion while limiting joint stress Ans: D. Exercise is vital to the management of rheumatic disorders. Goals should be preserving and promoting mobility and joint function while limiting stress on the joint and possible damage. Cardiovascular exertion should remain within age-based limits and individual ability, but it is not a goal to minimize exertion. Increasing joint size is not a valid goal. 24.A nurse is providing care for a patient who has a rheumatic disorder. The nurses comprehensive assessment includes the patients mood, behavior, LOC, and neurologic status. What is this patients most likely diagnosis? A. Osteoarthritis (OA) B. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) C. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) D. Gout Ans: B. SLE has a high degree of neurologic involvement, and can result in central nervous system changes. The patient and family members are asked about any behavioral changes, including manifestations of neurosis or psychosis. Signs of depression are noted, as are reports of seizures, chorea, or other central nervous system manifestations. OA, RA, and gout lack this dimension. 25.A patient with rheumatoid arthritis comes into the clinic for a routine check-up. On assessment the nurse notes that the patient appears to have lost some of her ability to function since her last office visit. Which of the following is the most appropriate action? A. Arrange a family meeting in order to explore assisted living options. B. Refer the patient to a support group. C. Arrange for the patient to be assessed in her home environment. D. Refer the patient to social work. Ans: C. Assessment in the patients home setting can often reveal more meaningful data than an assessment in the 5Adult Health Exam 5 health care setting. There is no indication that assisted living is a pressing need or that the patient would benefit from social work or a support group. 26.A nurse is assessing a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. The patient expresses his intent to pursue complementary and alternative therapies. What fact should underlie the nurses response to the patient? A. New evidence shows CAM to be as effective as medical treatment. B. CAM therapies negate many of the benefits of medications. C. CAM therapies typically do more harm than good. D. Evidence shows minimal benefits from most CAM therapies. Ans: D. A recent systematic review of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) examined the efficacy of herbal medicine, acupuncture, Tai chi and biofeedback for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Although acupuncture treatment for pain management showed some promise, in all modalities the evidence was ambiguous. There is not enough evidence of the effectiveness of CAM and more rigorous research is needed. 27.A nurse is providing care for a patient whose pattern of laboratory testing reveals longstanding hypocalcemia. What other laboratory result is most consistent with this finding? A. An elevated parathyroid hormone level B. An increased calcitonin level C. An elevated potassium level D. A decreased vitamin D level Ans: A. In the response to low calcium levels in the blood, increased levels of parathyroid hormone prompt the mobilization of calcium and the demineralization of bone. Increased calcitonin levels would exacerbate hypocalcemia. Vitamin D levels do not increase in response to low calcium levels. Potassium levels would likely be unaffected. 28.A nurse is caring for a patient whose cancer metastasis has resulted in bone pain. Which of the following are typical characteristics of bone pain? A. A dull, deep ache that is boring in nature B. Soreness or aching that may include cramping C. Sharp, piercing pain that is relieved by immobilization D. Spastic or sharp pain that radiates Ans: A. Bone pain is characteristically described as a dull, deep ache that is boring in nature, whereas muscular pain is described as soreness or aching and is referred to as muscle cramps. Fracture pain is sharp and piercing and is relieved by immobilization. Sharp pain may also result from bone infection with muscle spasm or pressure on a sensory nerve. 29.A nurse is assessing a patient who is experiencing peripheral neurovascular dysfunction. What assessment findings are most consistent with this diagnosis? A. Hot skin with a capillary refill of 1 to 2 seconds B. Absence of feeling, capillary refill of 4 to 5 seconds, and cool skin C. Pain, diaphoresis, and erythema D. Jaundiced skin, weakness, and capillary refill of 3 seconds Ans: B. Indicators of peripheral neurovascular dysfunction include pale, cyanotic, or mottled skin with a cool temperature; capillary refill greater than 3 seconds; weakness or paralysis with motion; and paresthesia, unrelenting pain, pain on passive stretch, or absence of feeling. Jaundice, diaphoresis, and warmth are inconsistent with peripheral neurovascular dysfunction. 30.An older adult patient has symptoms of osteoporosis and is being assessed during her annual physical examination. The assessment shows that the patient will require further testing related to a possible exacerbation of her osteoporosis. The nurse should anticipate what diagnostic test? A. Bone densitometry B. Hip bone radiography C. Computed tomography (CT) D. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Ans: A. Bone densitometry is considered the most accurate test for osteoporosis and for predicting a fracture. As such, it is more likely to be used than CT, MRI, or x-rays. 31.An older adult patient has come to the clinic for a regular check-up. The nurses initial inspection reveals an 6Adult Health Exam 5 increased thoracic curvature of the patients spine. The nurse should document the presence of which of the following? A. Scoliosis B. Epiphyses C. Lordosis D. Kyphosis Ans: D. Kyphosis is the increase in thoracic curvature of the spine. Scoliosis is a deviation in the lateral curvature of the spine. Epiphyses are the ends of the long bones. Lordosis is the exaggerated curvature of the lumbar spine. 32. The results of a nurses musculoskeletal examination show an increase in the lumbar curvature of the spine. The nurse should recognize the presence of what health problem? A. Osteoporosis B. Kyphosis C. Lordosis D. Scoliosis Ans: C. The nurse documents the spinal abnormality as lordosis. Lordosis is an increase in lumbar curvature of the spine. Kyphosis is an increase in the convex curvature of the spine. Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine. Osteoporosis is the significant loss of bone mass and strength with an increased risk for fracture. 33.The human body is designed to protect its vital parts. A fracture of what type of bone may interfere with the protection of vital organs? A. Long bones B. Short bones C. Flat bones D. Irregular bones Ans: C. Flat bones, such as the sternum, provide vital organ protection. Fractures of the flat bones may lead to puncturing of the vital organs or may interfere with the protection of the vital organs. Long, short, and irregular bones do not usually have this physiologic function. 34.A patient has just had an arthroscopy performed to assess a knee injury. What nursing intervention should the nurse implement following this procedure? A. Wrap the joint in a compression dressing. B. Perform passive range of motion exercises. C. Maintain the knee in flexion for up to 30 minutes. D. Apply heat to the knee. Ans: A. Interventions to perform following an arthroscopy include wrapping the joint in a compression dressing, extending and elevating the joint, and applying ice or cold packs. Passive ROM exercises, static flexion, and heat are not indicated. 35.While assessing a patient, the patient tells the nurse that she is experiencing rhythmic muscle contractions when the nurse performs passive extension of her wrist. What is this pattern of muscle contraction referred to as? A. Fasciculations B. Contractures C. Effusion D. Clonus Ans: D. Clonus may occur when the ankle is dorsiflexed or the wrist is extended. It is characterized as rhythmic contractions of the muscle. Fasciculation is involuntary twitching of muscle fiber groups. Contractures are prolonged tightening of muscle groups and an effusion is the pathologic escape of body fluid. 36. A nurse is caring for an older adult who has been diagnosed with geriatric failure to thrive. This patients prolonged immobility creates a risk for what complication? A. Muscle clonus B. Muscle atrophy C. Rheumatoid arthritis D. Muscle fasciculations Ans: B. If a muscle is in disuse for an extended period of time, it is at risk of developing atrophy, which is the decrease 7Adult Health Exam 5 in size. Clonus is a pattern of rhythmic muscle contractions and fasciculation is the involuntary twitch of muscle fibers; neither results from immobility. Lack of exercise is a risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis. 37.A clinic nurse is caring for a patient with a history of osteoporosis. Which of the following diagnostic tests best allows the care team to assess the patients risk of fracture? A. Arthrography B. Bone scan C. Bone densitometry D. Arthroscopy Ans: C. Bone densitometry is used to detect bone density and can be used to assess the risk of fracture in osteoporosis. Arthrography is used to detect acute or chronic tears of joint capsule or supporting ligaments. Bone scans can be used to detect metastatic and primary bone tumors, osteomyelitis, certain fractures, and aseptic necrosis. Arthroscopy is used to visualize a joint. 38.A nurse is performing a musculoskeletal assessment of a patient with arthritis. During passive range-ofmotion exercises, the nurse hears an audible grating sound. The nurse should document the presence of which of the following? A. Fasciculations B. Clonus C. Effusion D. Crepitus Ans: D. Crepitus is a grating, crackling sound or sensation that occurs as the irregular joint surfaces move across one another, as in arthritic conditions. Fasciculations are involuntary twitching of muscle fiber groups. Clonus is the rhythmic contractions of a muscle. Effusion is the collection of excessive fluid within the capsule of a joint. 39.A child is growing at a rate appropriate for his age. What cells are responsible for the secretion of bone matrix that eventually results in bone growth? A. Osteoblasts B. Osteocytes C. Osteoclasts D. Lamellae Ans: A. Osteoblasts function in bone formation by secreting bone matrix. Osteocytes are mature bone cells and osteoclasts are multinuclear cells involved in dissolving and resorbing bone. Lamellae are circles of mineralized bone matrix. 40.A nurse is explaining a patients decreasing bone density in terms of the balance between bone resorption and formation. What dietary nutrients and hormones play a role in the resorption and formation of adult bones? Select all that apply. A. Thyroid hormone B. Growth hormone C. Estrogen D. Vitamin B12 E. Luteinizing hormone Ans: A, B, C. The balance between bone resorption and formation is influenced by the following factors: physical activity; dietary intake of certain nutrients, especially calcium; and several hormones, including calcitriol (i.e., activated vitamin D), parathyroid hormone (PTH), calcitonin, thyroid hormone, cortisol, growth hormone, and the sex hormones estrogen and testosterone. Luteinizing hormone and vitamin B12 do not play a role in bone formation or resorption. 41.Diagnostic tests show that a patients bone density has decreased over the past several years. The patient asks the nurse what factors contribute to bone density decreasing. What would be the nurses best response? A. For many people, lack of nutrition can cause a loss of bone density. B. Progressive loss of bone density is mostly related to your genes. C. Stress is known to have many unhealthy effects, including reduced bone density. D. Bone density decreases with age, but scientists are not exactly sure why this is the case. Ans: A. Nutrition has a profound effect on bone density, especially later life. Genetics are also an important factor, 8Adult Health Exam 5 but nutrition has a more pronounced effect. The pathophysiology of bone density is well understood and psychosocial stress has a minimal effect. 42.The nurse is assessing a patient for dietary factors that may influence her risk for osteoporosis. The nurse should question the patient about her intake of what nutrients? Select all that apply. A. Calcium B. Simple carbohydrates C. Vitamin D D. Protein E. Soluble fiber Ans: A, C. A patients risk for osteoporosis is strongly influenced by vitamin D and calcium intake. Carbohydrate, protein, and fiber intake do not have direct effect on the development of osteoporosis. 43.A nurse is performing a nursing assessment of a patient suspected of having a musculoskeletal disorder. What is the primary focus of the nursing assessment with a patient who has a musculoskeletal disorder? A. Range of motion B. Activities of daily living C. Gait D. Strength Ans: B. The nursing assessment is primarily a functional evaluation, focusing on the patients ability to perform activities of daily living. The nurse also assesses strength, gait, and ROM, but these are assessed to identify their effect on functional status rather than to identify a medical diagnosis. 44.A nurses assessment of a teenage girl reveals that her shoulders are not level and that she has one prominent scapula that is accentuated by bending forward. The nurse should expect to read about what health problem in the patients electronic health record? A. Lordosis B. Kyphosis C. Scoliosis D. Muscular dystrophy Ans: C. Scoliosis is evidenced by an abnormal lateral curve in the spine, shoulders that are not level, an asymmetric waistline, and a prominent scapula, accentuated by bending forward. Lordosis is the curvature in the lower back; kyphosis is an exaggerated curvature of the upper back. This finding is not suggestive of muscular dystrophy. 45.A nurse is caring for a patient who has just had an arthroscopy as an outpatient and is getting ready to go home. The nurse should teach the patient to monitor closely for what post-procedure complication? A. Fever B. Crepitus C. Fasciculations D. Synovial fluid leakage Ans: A. Following arthroscopy, the patient and family are informed of complications to watch for, including fever. Synovial fluid leakage is unlikely and crepitus would not develop as a post-procedure complication. Fasciculations are muscle twitches and do not involve joint integrity or function. 46.A patient has had a cast placed for the treatment of a humeral fracture. The nurses most recent assessment shows signs and symptoms of compartment syndrome. What is the nurses most appropriate action? A. Arrange for a STAT assessment of the patients serum calcium levels. B. Perform active range of motion exercises. C. Assess the patients joint function symmetrically. D. Contact the primary care provider immediately. Ans: D. This major neurovascular problem is caused by pressure within a muscle compartment that increases to such an extent that microcirculation diminishes, leading to nerve and muscle anoxia and necrosis. Function can be permanently lost if the anoxic situation continues for longer than 6 hours. Therefore, immediate medical care is a priority over further nursing assessment. Assessment of calcium levels is unnecessary. 47.A patient has been experiencing an unexplained decline in knee function and has consequently been 9Adult Health Exam 5 scheduled for arthrography. The nurse should teach the patient about what process? A. Injection of a contrast agent into the knee joint prior to ROM exercises B. Aspiration of synovial fluid for serologic testing C. Injection of corticosteroids into the patients knee joint to facilitate ROM D. Replacement of the patients synovial fluid with a synthetic substitute Ans: A. During arthrography, a radiopaque contrast agent or air is injected into the joint cavity to visualize the joint structures such as the ligaments, cartilage, tendons, and joint capsule. The joint is put through its range of motion to distribute the contrast agent while a series of x-rays are obtained. Synovial fluid is not aspirated or replaced and corticosteroids are not administered. 48.The nurses musculoskeletal assessment of a patient reveals involuntary twitching of muscle groups. How would the nurse document this observation in the patients chart? A. Tetany B. Atony C. Clonus D. Fasciculations Ans: D. Fasciculation is involuntary twitching of muscle fiber groups. Clonus is a series of involuntary, rhythmic, muscular contractions and tetany is involuntary muscle contraction, but neither is characterized as twitching. Atony is a loss of muscle strength. 49.A patient has been experiencing progressive increases in knee pain and diagnostic imaging reveals a worsening effusion in the synovial capsule. The nurse should anticipate which of the following? A. Arthrography B. Knee biopsy C. Arthrocentesis D. Electromyography Ans: C. Arthrocentesis (joint aspiration) is carried out to obtain synovial fluid for purposes of examination or to relieve pain due to effusion. Arthrography, biopsy, and electromyography would not remove fluid and relieve pressure. 50.A nurse is caring for a patient who has had a plaster arm cast applied. Immediately postapplication, the nurse should provide what teaching to the patient? A. The cast will feel cool to touch for the first 30 minutes. B. The cast should be wrapped snuggly with a towel until the patient gets home. C. The cast should be supported on a board while drying. D. The cast will only have full strength when dry. Ans: D. A cast requires approximately 24 to 72 hours to dry, and until dry, it does not have full strength. While drying, the cast should not be placed on a hard surface. The cast will exude heat while it dries and should not be wrapped. 51.A patient broke his arm in a sports accident and required the application of a cast. Shortly following application, the patient complained of an inability to straighten his fingers and was subsequently diagnosed with Volkmann contracture. What pathophysiologic process caused this complication? A. Obstructed arterial blood flow to the forearm and hand B. Simultaneous pressure on the ulnar and radial nerves C. Irritation of Merkel cells in the patients skin surfaces D. Uncontrolled muscle spasms in the patients forearm Ans: A. Volkmann contracture occurs when arterial blood flow is restricted to the forearm and hand and results in contractures of the fingers and wrist. It does not result from nerve pressure, skin irritation, or spasms. 52.A patient is admitted to the unit in traction for a fractured proximal femur and requires traction prior to surgery. What is the most appropriate type of traction to apply to a fractured proximal femur? A. Russells traction B. Dunlops traction C. Bucks extension traction D. Cervical head halter Ans: C. Bucks extension is used for fractures of the proximal femur. Russells traction is used for lower leg fractures. 10Adult Health Exam 5 Dunlops traction is applied to the upper extremity for supracondylar fractures of the elbow and humerus. Cervical head halters are used to stabilize the neck. 53.A nurse is caring for a patient who is in skeletal traction. To prevent the complication of skin breakdown in a patient with skeletal traction, what action should be included in the plan of care? A. Apply occlusive dressings to the pin sites. B. Encourage the patient to push up with the elbows when repositioning. C. Encourage the patient to perform isometric exercises once a shift. D. Assess the pin insertion site every 8 hours. Ans: D. The pin insertion site should be assessed every 8 hours for inflammation and infection. Loose cover dressings should be applied to pin sites. The patient should be encouraged to use the overhead trapeze to shift weight for repositioning. Isometric exercises should be done 10 times an hour while awake. 54.A nurse is caring for a patient who is postoperative day 1 right hip replacement. How should the nurse position the patient? A. Keep the patients hips in abduction at all times. B. Keep hips flexed at no less than 90 degrees. C. Elevate the head of the bed to high Fowlers. D. Seat the patient in a low chair as soon as possible. Ans: A. The hips should be kept in abduction by an abductor pillow. Hips should not be flexed more than 90 degrees, and the head of bed should not be elevated more than 60 degrees. The patients hips should be higher than the knees; as such, high seat chairs should be used. 55.While assessing a patient who has had knee replacement surgery, the nurse notes that the patient has developed a hematoma at the surgical site. The affected leg has a decreased pedal pulse. What would be the priority nursing diagnosis for this patient? A. Risk for Infection B. Risk for Peripheral Neurovascular Dysfunction C. Unilateral Neglect D. Disturbed Kinesthetic Sensory Perception Ans: B. The hematoma may cause an interruption of tissue perfusion, so the most appropriate nursing diagnosis is Risk of Peripheral Neurovascular Dysfunction. There is also an associated risk for infection because of the hematoma, but impaired neurovascular function is a more acute threat. Unilateral neglect and impaired sensation are lower priorities than neurovascular status. 56.A patient was brought to the emergency department after a fall. The patient is taken to the operating room to receive a right hip prosthesis. In the immediate postoperative period, what health education should the nurse emphasize? A. Make sure you dont bring your knees close together. B. Try to lie as still as possible for the first few days. C. Try to avoid bending your knees until next week. D. Keep your legs higher than your chest whenever you can. Ans: A. After receiving a hip prosthesis, the affected leg should be kept abducted. Mobility should be encouraged within safe limits. There is no need to avoid knee flexion and the patients legs do not need to be higher than the level of the chest. 57.A patient with a fractured femur is in balanced suspension traction. The patient needs to be repositioned toward the head of the bed. During repositioning, what should the nurse do? A. Place slight additional tension on the traction cords. B. Release the weights and replace them immediately after positioning. C. Reposition the bed instead of repositioning the patient. D. Maintain consistent traction tension while repositioning. Ans: D. Traction is used to reduce the fracture and must be maintained at all times, including during repositioning. It would be inappropriate to add tension or release the weights. Moving the bed instead of the patient is not feasible. 58.A patient with a total hip replacement is progressing well and expects to be discharged tomorrow. On 11Adult Health Exam 5 returning to bed after ambulating, he complains of a new onset of pain at the surgical site. What is the nurses best action? A. Administer pain medication as ordered. B. Assess the surgical site and the affected extremity. C. Reassure the patient that pain is a direct result of increased activity. D. Assess the patient for signs and symptoms of systemic infection. Ans: B. Worsening pain after a total hip replacement may indicate dislocation of the prosthesis. Assessment of pain should include evaluation of the wound and the affected extremity. Assuming he is anxious about discharge and administering pain medication do not address the cause of the pain. Sudden severe pain is not considered normal after hip replacement. Sudden pain is rarely indicative of a systemic infection. 59.The nurse is caring for a patient who underwent a total hip replacement yesterday. What should the nurse do to prevent dislocation of the new prosthesis? A. Keep the affected leg in a position of adduction. B. Have the patient reposition himself independently. C. Protect the affected leg from internal rotation. D. Keep the hip flexed by placing pillows under the patients knee. Ans:C. Abduction of the hip helps to prevent dislocation of a new hip joint. Rotation and adduction should be avoided. While the hip may be flexed slightly, it shouldnt exceed 90 degrees and maintenance of flexion isnt necessary. The patient may not be capable of safe independent repositioning at this early stage of recovery. 60.A patient is complaining of pain in her casted leg. The nurse has administered analgesics and elevated the limb. Thirty minutes after administering the analgesics, the patient states the pain is unrelieved. The nurse should identify the warning signs of what complication? A. Subcutaneous emphysema B. Skin breakdown C. Compartment syndrome D. Disuse syndrome Ans: C. Compartment syndrome may manifest as unrelenting, uncontrollable pain. This presentation of pain is not suggestive of disuse syndrome or skin breakdown. Subcutaneous emphysema is not a complication of casting. 61.The nurse educator on an orthopedic trauma unit is reviewing the safe and effective use of traction with some recent nursing graduates. What principle should the educator promote? A. Knots in the rope should not be resting against pulleys. B. Weights should rest against the bed rails. C. The end of the limb in traction should be braced by the footboard of the bed. D. Skeletal traction may be removed for brief periods to facilitate the patients independence. Ans: A. Knots in the rope should not rest against pulleys, because this interferes with traction. Weights are used to apply the vector of force necessary to achieve effective traction and should hang freely at all times. To avoid interrupting traction, the limb in traction should not rest against anything. Skeletal traction is never interrupted. 62.The orthopedic surgeon has prescribed balanced skeletal traction for a patient. What advantage is conferred by balanced traction? A. Balanced traction can be applied at night and removed during the day. B. Balanced traction allows for greater patient movement and independence than other forms of traction. C. Balanced traction is portable and may accompany the patients movements. D. Balanced traction facilitates bone remodeling in as little as 4 days. Ans: B. Often, skeletal traction is balanced traction, which supports the affected extremity, allows for some patient movement, and facilitates patient independence and nursing care while maintaining effective traction. It is not portable, however, and it cannot be removed. Bone remodeling takes longer than 4 days. 63.The nursing care plan for a patient in traction specifies regular assessments for venous thromboembolism 12Adult Health Exam 5 (VTE). When assessing a patients lower limbs, what sign or symptom is suggestive of deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? A. Increased warmth of the calf B. Decreased circumference of the calf C. Loss of sensation to the calf D. Pale-appearing calf Ans: A. Signs of DVT include increased warmth, redness, swelling, and calf tenderness. These findings are promptly reported to the physician for definitive evaluation and therapy. Signs and symptoms of a DVT do not include a decreased circumference of the calf, a loss of sensation in the calf, or a pale-appearing calf. 64.An elderly patients hip joint is immobilized prior to surgery to correct a femoral head fracture. What is the nurses priority assessment? A. The presence of leg shortening B. The patients complaints of pain C. Signs of neurovascular compromise D. The presence of internal or external rotation Ans: C. Because impaired circulation can cause permanent damage, neurovascular assessment of the affected leg is always a priority assessment. Leg shortening and internal or external rotation are common findings with a fractured hip. Pain, especially on movement, is also common after a hip fracture. 65. A nurse is caring for a patient who has had a total hip replacement. The nurse is reviewing health education prior to discharge. Which of the patients statements would indicate to the nurse that the patient requires further teaching? A. Ill need to keep several pillows between my legs at night. B. I need to remember not to cross my legs. Its such a habit. C. The occupational therapist is showing me how to use a sock puller to help me get dressed. D. I will need my husband to assist me in getting off the low toilet seat at home. Ans: D. To prevent hip dislocation after a total hip replacement, the patient must avoid bending the hips beyond 90 degrees. Assistive devices, such as a raised toilet seat, should be used to prevent severe hip flexion. Using an abduction pillow or placing several pillows between the legs reduces the risk of hip dislocation by preventing adduction and internal rotation of the legs. Likewise, teaching the patient to avoid crossing the legs also reduces the risk of hip dislocation. A sock puller helps a patient get dressed without flexing the hips beyond 90 degrees. 66.A nurse is admitting a patient to the unit who presented with a lower extremity fracture. What signs and symptoms would suggest to the nurse that the patient may have aperoneal nerve injury? A. Numbness and burning of the foot B. Pallor to the dorsal surface of the foot C. Visible cyanosis in the toes D. Inadequate capillary refill to the toes Ans: A. Peroneal nerve injury may result in numbness, tingling, and burning in the feet. Cyanosis, pallor, and decreased capillary refill are signs of inadequate circulation. 67.A patient has suffered a muscle strain and is complaining of pain that she rates at 6 on a 10-point scale. The nurse should recommend what action? A. Taking an opioid analgesic as ordered B. Applying a cold pack to the injured site C. Performing passive ROM exercises D. Applying a heating pad to the affected muscle Ans: B. Most pain can be relieved by elevating the involved part, applying cold packs, and administering analgesics as prescribed. Heat may exacerbate the pain by increasing blood circulation, and ROM exercises would likely be painful. Analgesia is likely necessary, but NSAIDs would be more appropriate than opioids. 68.A patient has had a brace prescribed to facilitate recovery from a knee injury. What are the potential 13Adult Health Exam 5 therapeutic benefits of a brace? Select all that apply. A. Preventing additional injury B. Immobilizing prior to surgery C. Providing support D. Controlling movement E. Promoting bone remodeling Ans: A, C, D. Braces (i.e., orthoses) are used to provide support, control movement, and prevent additional injury. They are not used to immobilize body parts or to facilitate bone remodeling. 69.A physician writes an order to discontinue skeletal traction on an orthopedic patient. The nurse should anticipate what subsequent intervention? A. Application of a walking boot B. Application of a cast C. Education on how to use crutches D. Passive range of motion exercises Ans: B. After skeletal traction is discontinued, internal fixation, casts, or splints are then used to immobilize and support the healing bone. The use of a walking boot, crutches, or ROM exercises could easily damage delicate, remodeled bone. 70.A patient has just begun been receiving skeletal traction and the nurse is aware that muscles in the patients affected limb are spastic. How does this change in muscle tone affect the patients traction prescription? A. Traction must temporarily be aligned in a slightly different direction. B. Extra weight is needed initially to keep the limb in proper alignment. C. A lighter weight should be initially used. D. Weight will temporarily alternate between heavier and lighter weights. Ans: B. The traction weights applied initially must overcome the shortening spasms of the affected muscles. As the muscles relax, the traction weight is reduced to prevent fracture dislocation and to promote healing. Weights never alternate between heavy and light. 71.A nurse is caring for a patient receiving skeletal traction. Due to the patients severe limits on mobility, the nurse has identified a risk for atelectasis or pneumonia. What intervention should the nurse provide in order to prevent these complications? A. Perform chest physiotherapy once per shift and as needed. B. Teach the patient to perform deep breathing and coughing exercises. C. Administer prophylactic antibiotics as ordered. D. Administer nebulized bronchodilators and corticosteroids as ordered. Ans: B. To prevent these complications, the nurse should educate the patient about performing deep-breathing and coughing exercises to aid in fully expanding the lungs and clearing pulmonary secretions. Antibiotics, bronchodilators, and steroids are not used on a preventative basis and chest physiotherapy is unnecessary and implausible for a patient in traction. 72.A patient is scheduled for a total hip replacement and the surgeon has explained the risks of blood loss associated with orthopedic surgery. The risk of blood loss is the indication for which of the following actions? A. Use of a cardiopulmonary bypass machine B. Postoperative blood salvage C. Prophylactic blood transfusion D. Autologous blood donation Ans: D. Many patients donate their own blood during the weeks preceding their surgery. Autologous blood donations are cost effective and eliminate many of the risks of transfusion therapy. Orthopedic surgery does not necessitate cardiopulmonary bypass and blood is not salvaged postoperatively. Transfusions are not given prophylactically. 73.The nurse is helping to set up Bucks traction on an orthopedic patient. How often should the nurse assess 14Adult Health Exam 5 circulation to the affected leg? A. Within 30 minutes, then every 1 to 2 hours B. Within 30 minutes, then every 4 hours C. Within 30 minutes, then every 8 hours D. Within 30 minutes, then every shift Ans: A. After skin traction is applied, the nurse assesses circulation of the foot or hand within 15 to 30 minutes and then every 1 to 2 hours. 74.A nurse is caring for a patient in skeletal traction. In order to prevent bony fragments from moving against one another, the nurse should caution the patient against which of the following actions? A. Shifting ones weight in bed B. Bearing down while having a bowel movement C. Turning from side to side D. Coughing without splinting Ans: C. To prevent bony fragments from moving against one another, the patient should not turn from side to side; however, the patient may shift position slightly with assistance. Bearing down and coughing do not pose a threat to bone union. 75.A nurse is caring for an older adult patient who is preparing for discharge following recovery from a total hip replacement. Which of the following outcomes must be met prior to discharge? A. Patient is able to perform ADLs independently. B. Patient is able to perform transfers safely. C. Patient is able to weight-bear equally on both legs. D. Patient is able to demonstrate full ROM of the affected hip. Ans: B. The patient must be able to perform transfers and to use mobility aids safely. Each of the other listed goals is unrealistic for the patient who has undergone recent hip replacement. 76.A patient has recently been admitted to the orthopedic unit following total hip arthroplasty. The patient has a closed suction device in place and the nurse has determined that there were 320 mL of output in the first 24 hours. How should the nurse best respond to this assessment finding? A. Inform the primary care provider promptly. B. Document this as an expected assessment finding. C. Limit the patients fluid intake to 2 liters for the next 24 hours. D. Administer a loop diuretic as ordered. Ans: B. Drainage of 200 to 500 mL in the first 24 hours is expected. Consequently, the nurse does not need to inform the physician. Fluid restriction and medication administration are not indicated. 77.A 91-year-old patient is slated for orthopedic surgery and the nurse is integrated gerontologic considerations into the patients plan of care. What intervention is most justified in the care of this patient? A. Administration of prophylactic antibiotics B. Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) C. Use of a pressure-relieving mattress D. Use of a Foley catheter until discharge Ans: C. Older adults have a heightened risk of skin breakdown; use of a pressure-reducing mattress addresses this risk. Older adults do not necessarily need TPN and the Foley catheter should be discontinued as soon as possible to prevent urinary tract infections. Prophylactic antibiotics are not a standard infection prevention measure. 78.A nurse is providing a class on osteoporosis at the local seniors center. Which of the following statements related to osteoporosis is most accurate? A. Osteoporosis is categorized as a disease of the elderly. B. A nonmodifiable risk factor for osteoporosis is a persons level of activity. C. Secondary osteoporosis occurs in women after menopause. D. Slow discontinuation of corticosteroid therapy can halt the progression of the osteoporosis. Ans: D. When corticosteroid therapy is discontinued, the progression of osteoporosis is halted, but restoration of lost 15Adult Health Exam 5 bone mass does not occur. Osteoporosis is not a disease of the elderly because its onset occurs earlier in life, when bone mass peaks and then begins to decline. A persons level of physical activity is a modifiable factor that influences peak bone mass. Lack of activity increases the risk for the development of osteoporosis. Primary osteoporosis occurs in women after menopause. 79.A nurse is reviewing the pathophysiology that may underlie a patients decreased bone density. What hormone should the nurse identify as inhibiting bone resorption and promoting bone formation? A. Estrogen B. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) C. Calcitonin D. Progesterone Ans: C. Calcitonin inhibits bone resorption and promotes bone formation, estrogen inhibits bone breakdown, and parathyroid increases bone resorption. Estrogen, which inhibits bone breakdown, decreases with aging. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) increases with aging, increasing bone turnover and resorption. Progesterone is the major naturally occurring human progestogen and plays a role in the female menstrual cycle. 80.An older adult womans current medication regimen includes alendronate (Fosamax). What outcome would indicate successful therapy? A. Increased bone mass B. Resolution of infection C. Relief of bone pain D. Absence of tumor spread Ans: A. Bisphosphonates such as Fosamax increase bone mass and decrease bone loss by inhibiting osteoclast function. These drugs do not treat infection, pain, or tumors. 81.A nursing educator is reviewing the risk factors for osteoporosis with a group of recent graduates. What risk factor of the following should the educator describe? A. Recurrent infections and prolonged use of NSAIDs B. High alcohol intake and low body mass index C. Small frame, female gender, and Caucasian ethnicity D. Male gender, diabetes, and high protein intake Ans: C. Small-framed, nonobese Caucasian women are at greatest risk for osteoporosis. Diabetes, high protein intake, alcohol use, and infections are not among the most salient risk factors for osteoporosis. 82.An elderly female with osteoporosis has been hospitalized. Prior to discharge, when teaching the patient, the nurse should include information about which major complication of osteoporosis? A. Bone fracture B. Loss of estrogen C. Negative calcium balance D. Dowagers hump Ans: A. Bone fracture is a major complication of osteoporosis that results when loss of calcium and phosphate increases the fragility of bones. Estrogen deficiencies result from menopause, not osteoporosis. Calcium and vitamin D supplements may be used to support normal bone metabolism, but a negative calcium balance is not a complication of osteoporosis. Dowagers hump results from bone fractures. It develops when repeated vertebral fractures increase spinal curvature. 83.A nurse admits a patient who has a fracture of the nose that has resulted in a skin tear and involvement of the mucous membranes of the nasal passages. The orthopedic nurse is aware that this description likely indicates which type of fracture? A. Compression B. Compound C. Impacted D. Transverse Ans: B. A compound fracture involves damage to the skin or mucous membranes and is also called an open fracture. A compression fracture involves compression of bone and is seen in vertebral fractures. An impacted fracture occurs when a bone fragment is driven into another bone fragment. A transverse fracture occurs straight across the bone. 84.A patient has sustained a long bone fracture and the nurse is preparing the patients care plan. Which of 16Adult Health Exam 5 the following should the nurse include in the care plan? A. Administer vitamin D and calcium supplements as ordered. B. Monitor temperature and pulses of the affected extremity. C. Perform passive range of motion exercises as tolerated. D. Administer corticosteroids as ordered. Ans: B. The nurse should include monitoring for sufficient blood supply by assessing the color, temperature, and pulses of the affected extremity. Weight-bearing exercises are encouraged, but passive ROM exercises have the potential to cause pain and inhibit healing. Corticosteroids, vitamin D, and calcium are not normally administered. 85.A nurse is writing a care plan for a patient admitted to the emergency department (ED) with an open fracture. The nurse will assign priority to what nursing diagnosis for a patient with an open fracture of the radius? A. Risk for Infection B. Risk for Ineffective Role Performance C. Risk for Perioperative Positioning Injury D. Risk for Powerlessness Ans: A. The patient has a significant risk for osteomyelitis and tetanus due to the fact that the fracture is open. Powerlessness and ineffective role performance are psychosocial diagnoses that may or may not apply, and which would be superseded by immediate physiologic threats such as infection. Surgical positioning injury is not plausible, since surgery is not likely indicated. 86.A nurse is caring for a patient who has suffered an unstable thoracolumbar fracture. Which of the following is the priority during nursing care? A. Preventing infection B. Maintaining spinal alignment C. Maximizing function D. Preventing increased intracranial pressure Ans: B. Patients with an unstable fracture must have their spine in alignment at all times in order to prevent neurologic damage. This is a greater threat, and higher priority, than promoting function and preventing infection, even though these are both valid considerations. Increased ICP is not a high risk. 87.Six weeks after an above-the-knee amputation (AKA), a patient returns to the outpatient office for a routine postoperative checkup. During the nurses assessment, the patient reports symptoms of phantom pain. What should the nurse tell the patient to do to reduce the discomfort of the phantom pain? A. Apply intermittent hot compresses to the area of the amputation. B. Avoid activity until the pain subsides. C. Take opioid analgesics as ordered. D. Elevate the level of the amputation site. Ans: C. Opioid analgesics may be effective in relieving phantom pain. Heat, immobility, and elevation are not noted to relieve this form of pain. 88.The orthopedic nurse should assess for signs and symptoms of Volkmanns contracture if a patient has fractured which of the following bones? A. Femur B. Humerus C. Radial head D. Clavicle Ans: B. The most serious complication of a supracondylar fracture of the humerus is Volkmanns ischemic contracture, which results from antecubital swelling or damage to the brachial artery. This complication is specific to humeral fractures. 89.A nurse is performing a shift assessment on an elderly patient who is recovering after surgery for a hip fracture. The nurse notes that the patient is complaining of chest pain, has an increased heart rate, and increased respiratory rate. The nurse further notes that the patient is febrile and hypoxic, coughing, and 17Adult Health Exam 5 producing large amounts of thick, white sputum. The nurse recognizes that this is a medical emergency and calls for assistance, recognizing that this patient is likely demonstrating symptoms of what complication? A. Avascular necrosis of bone B. Compartment syndrome C. Fat embolism syndrome D. Complex regional pain syndrome Ans: C. Fat embolism syndrome occurs most frequently in young adults and elderly patients who experience fractures of the proximal femur (i.e., hip fracture). Presenting features of fat embolism syndrome include hypoxia, tachypnea, tachycardia, and pyrexia. The respiratory distress response includes tachypnea, dyspnea, wheezes, precordial chest pain, cough, large amounts of thick, white sputum, and tachycardia. Avascular necrosis (AVN) occurs when the bone loses its blood supply and dies. This does not cause coughing. Complex regional pain syndrome does not have cardiopulmonary involvement. 90.A young patient is being treated for a femoral fracture suffered in a snowboarding accident. The nurses most recent assessment reveals that the patient is uncharacteristically confused. What diagnostic test should be performed on this patient? A. Electrolyte assessment B. Electrocardiogram C. Arterial blood gases D. Abdominal ultrasound Ans: C. Subtle personality changes, restlessness, irritability, or confusion in a patient who has sustained a fracture are indications for immediate arterial blood gas studies due to the possibility of fat embolism syndrome. This assessment finding does not indicate an immediate need for electrolyte levels, an ECG, or abdominal ultrasound. 91.Which of the following is the most appropriate nursing intervention to facilitate healing in a patient who has suffered a hip fracture? A. Administer analgesics as required. B. Place a pillow between the patients legs when turning. C. Maintain prone positioning at all times. D. Encourage internal and external rotation of the affected leg. Ans: B. Placing a pillow between the patients legs when turning prevents adduction and supports the patients legs. Administering analgesics addresses pain but does not directly protect bone remodeling and promote healing. Rotation of the affected leg can cause dislocation and must be avoided. Prone positioning does not need to be maintained at all times. 92.A nurse is planning the care of an older adult patient who will soon be discharged home after treatment for a fractured hip. In an effort to prevent future fractures, the nurse should encourage which of the following? Select all that apply. A. Regular bone density testing B. A high-calcium diet C. Use of falls prevention precautions D. Use of corticosteroids as ordered E. Weight-bearing exercise Ans: A, B, C, E. Health promotion measures after an older adults hip fracture include weight-bearing exercise, promotion of a healthy diet, falls prevention, and bone density testing. Corticosteroids have the potential to reduce bone density and increase the risk for fractures. 93.An emergency department patient is diagnosed with a hip dislocation. The patients family is relieved that the patient has not suffered a hip fracture, but the nurse explains that this is still considered to be a medical emergency. What is the rationale for the nurses statement? 18Adult Health Exam 5 A. The longer the joint is displaced, the more difficult it is to get it back in place. B. The patients pain will increase until the joint is realigned. C. Dislocation can become permanent if the process of bone remodeling begins. D. Avascular necrosis may develop at the site of the dislocation if it is not promptly resolved. Ans: D. If a dislocation or subluxation is not reduced immediately, avascular necrosis (AVN) may develop. Bone remodeling does not take place because a fracture has not occurred. Realignment does not become more difficult with time and pain would subside with time, not become worse. 94.The surgical nurse is admitting a patient from postanesthetic recovery following the patients below-theknee amputation. The nurse recognizes the patients high risk for postoperative hemorrhage and should keep which of the following at the bedside? A. A tourniquet B. A syringe preloaded with vitamin K C. A unit of packed red blood cells, placed on ice D. A dose of protamine sulfate Ans: A. Immediate postoperative bleeding may develop slowly or may take the form of massive hemorrhage resulting from a loosened suture. A large tourniquet should be in plain sight at the patients bedside so that, if severe bleeding occurs, it can be applied to the residual limb to control the hemorrhage. PRBCs cannot be kept at the bedside. Vitamin K and protamine sulfate are antidotes to warfarin and heparin, but are not administered to treat active postsurgical bleeding. 95.A 25-year-old man is involved in a motorcycle accident and injures his arm. The physician diagnoses the man with an intra-articular fracture and splints the injury. The nurse implements the teaching plan developed for this patient. What sequela of intra-articular fractures should the nurse describe regarding this patient? A. Post-traumatic arthritis B. Fat embolism syndrome (FES) C. Osteomyelitis D. Compartment syndrome Ans: A. Intra-articular fractures often lead to post-traumatic arthritis. Research does not indicate a correlation between intra-articular fractures and FES, osteomyelitis, or compartment syndrome. 96.A patient is admitted to the orthopedic unit with a fractured femur after a motorcycle accident. The patient has been placed in traction until his femur can be rodded in surgery. For what early complications should the nurse monitor this patient? Select all that apply. A. Systemic infection B. Complex regional pain syndrome C. Deep vein thrombosis D. Compartment syndrome E. Fat embolism Ans: C, D, E. Early complications include shock, fat embolism, compartment syndrome, and venous thromboemboli (deep vein thrombosis [DVT], pulmonary embolism [PE]). Infection and CRPS are later complications of fractures. 97.A patient has come to the orthopedic clinic for a follow-up appointment 6 weeks after fracturing his ankle. Diagnostic imaging reveals that bone union is not taking place. What factor may have contributed to this complication? A. Inadequate vitamin D intake B. Bleeding at the injury site C. Inadequate immobilization D. Venous thromboembolism Ans: C. Inadequate fracture immobilization can delay or prevent union. A short-term vitamin D deficiency would not likely prevent bone union. VTE is a serious complication but would not be a cause of nonunion. Similarly, bleeding would not likely delay union. 98.An older adult patient has fallen in her home and is brought to the emergency department by ambulance with a suspected fractured hip. X-rays confirm a fracture of the left femoral neck. When planning assessments during the patients presurgical care, the nurse should be aware of the patients heightened risk of what complication? 19Adult Health Exam 5 A. Osteomyelitis B. Avascular necrosis C. Phantom pain D. Septicemia Ans: B. Fractures of the neck of the femur may damage the vascular system that supplies blood to the head and the neck of the femur, and the bone may become ischemic. For this reason, AVN is common in patients with femoral neck fractures. Infections are not immediate complications and phantom pain applies to patients with amputations, not hip fractures. 99.A patient is being treated for a fractured hip and the nurse is aware of the need to implement interventions to prevent muscle wasting and other complications of immobility. What intervention best addresses the patients need for exercise? A. Performing gentle leg lifts with both legs B. Performing massage to stimulate circulation C. Encouraging frequent use of the overbed trapeze D. Encouraging the patient to log roll side to side once per hour Ans: C. The patient is encouraged to exercise as much as possible by means of the overbed trapeze. This device helps strengthen the arms and shoulders in preparation for protected ambulation. Independent logrolling may result in injury due to the location of the fracture. Leg lifts would be contraindicated for the same reason. Massage by the nurse is not a substitute for exercise. 100. A patient who has had an amputation is being cared for by a multidisciplinary rehabilitation team. What is the primary goal of this multidisciplinary team? A. Maximize the efficiency of care B. Ensure that the patients health care is holistic C. Facilitate the patients adjustment to a new body image D. Promote the patients highest possible level of function Ans: D. The multidisciplinary rehabilitation team helps the patient achieve the highest possible level of function and participation in life activities. The team is not primarily motivated by efficiency, the need for holistic care, or the need to foster the patients body image, despite the fact that each of these are valid goals. 101. The nurse is providing care for a patient who has had a below-the-knee amputation. The nurse enters the patients room and finds him resting in bed with his residual limb supported on pillow. What is the nurses most appropriate action? A. Inform the surgeon of this finding. B. Explain the risks of flexion contracture to the patient. C. Transfer the patient to a sitting position. D. Encourage the patient to perform active ROM exercises with the residual limb. Ans: B. The residual limb should not be placed on a pillow, because a flexion contracture of the hip may result. There is no acute need to contact the patients surgeon. Encouraging exercise or transferring the patient does not address the risk of flexion contracture. 102. A patient has returned to the postsurgical unit from the PACU after an above-the-knee amputation of the right leg. Results of the nurses initial postsurgical assessment were unremarkable but the patient has called out. The nurse enters the room and observes copious quantities of blood at the surgical site. What should be the nurses initial action? A. Apply a tourniquet. B. Elevate the residual limb. C. Apply sterile gauze. D. Call the surgeon. Ans: A. The nurse should apply a tourniquet in the event of postsurgical hemorrhage. Elevating the limb and applying sterile gauze are likely insufficient to stop the hemorrhage. The nurse should attempt to control the immediate bleeding before contacting the surgeon. 103. A patient who has undergone a lower limb amputation is preparing to be discharged home. What outcome is necessary prior to discharge? A. Patient can demonstrate safe use of assistive devices. B. Patient has a healed, nontender, nonadherent scar. 20Adult Health Exam 5 C. Patient can perform activities of daily living independently. D. Patient is free of pain. Ans: A. A patient should be able to use assistive devices appropriately and safely prior to discharge. Scar formation will not be complete at the time of hospital discharge. It is anticipated that the patient will require some assistance with ADLs postdischarge. Pain should be well managed, but may or may not be wholly absent. 104. An older adult patient experienced a fall and required treatment for a fractured hip on the orthopedic unit. Which of the following are contributory factors to the incidence of falls and fractured hips among the older adult population? Select all that apply. A. Loss of visual acuity B. Adverse medication effects C. Slowed reflexes D. Hearing loss E. Muscle weakness Ans: A, B, C, E. Older adults are generally vulnerable to falls and have a high incidence of hip fracture. Weak quadriceps muscles, medication effects, vision loss, and slowed reflexes are among the factors that contribute to the incidence of falls. Decreased hearing is not noted to contribute to the incidence of falls. 105. The nurse is conducting health screening for osteoporosis. Which client is at greatest risk of developing this disorder? A. A 36-year-old man who has asthma B. A 25-year-old woman who runs C. A 70-year-old man who consumes excess alcohol D. A sedentary 65-year-old woman who smokes cigarettes Ans: D. Risk factors for osteoporosis include female gender, being postmenopausal, advanced age, a low-calcium diet, excessive alcohol intake, being sedentary, and smoking cigarettes. Long-term use of corticosteroids, anticonvulsants, and/or furosemide also increases the risk. 106. The nurse is evaluating a client in skeletal traction. When evaluating the pin sites, the nurse would be most concerned with which finding? A. Redness around the pin sites B. Pain on palpation at the pin sites C. Thick, yellow drainage from the pin sites D. Clear, watery drainage from the pin sites Ans: C. The nurse should monitor for signs of infection such as inflammation, purulent drainage, and pain at the pin site. However, some degree of inflammation, pain at the pin site, and serous drainage would be expected; the nurse should correlate assessment findings with other clinical findings, such as fever, elevated white blood cell count, and changes in vital signs. Additionally, the nurse should compare any findings to baseline findings to determine if there were any changes. 107. The nurse is assessing the casted extremity of a client. Which sign is indicative of infection? A. Dependent edema B. Diminished distal pulse C. Presence of a “hot spot” on the cast D. Coolness and pallor of the extremity Ans: C. Signs of infection under a casted area include odor or purulent drainage from the cast or the presence of "hot spots," which are areas of the cast that are warmer than others. The health care provider should be notified if any of these occur. Signs of impaired circulation in the distal limb include coolness and pallor of the skin, diminished distal pulse, and edema. 108. A client has sustained a closed fracture and has just had a cast applied to the affected arm. The client is complaining of intense pain. The nurse elevates the limb, applies an ice bag, and administers an analgesic, with little relief. Which problem may be causing this pain? A. Infection under the cast 21Adult Health Exam 5 B. Anxiety of the client C. Impaired tissue perfusion D. Recent occurrence of the fracture Ans: C. Most pain associated with fractures can be minimized with rest, elevation, application of cold, and administration of analgesics. Pain that is not relieved by these measures should be reported to the health care provider because pain unrelieved by medications and other measures may indicate neurovascular compromise. Because this is a new closed fracture and cast, infection would not have had time to set in. Intense pain after casting is normally not associated with anxiety or the recent occurrence of the injury. Treatment following the fracture should assist in relieving the pain associated with the injury. 109. The nurse is caring for a client being treated for fat embolus after multiple fractures. Which data would the nurse evaluate as the most favorable indication of resolution of the fat embolus? A. Clear mental status B. Minimal dyspnea C. Oxygen saturation of 85% D. Arterial oxygen level of 78mmHg Ans: A. An altered mental state is an early indication of fat emboli; therefore, clear mentation is a good indicator that a fat embolus is resolving. Eupnea, not minimal dyspnea, is a normal sign. Arterial oxygen levels should be 80–100 mm Hg (10.6–13.33 kPa). Oxygen saturation should be higher than 95%. 110. The nurse has conducted teaching with a client in an arm cast about the signs and symptoms of compartment syndrome. The nurse determines that the client understands the information if the client states that he or she should report which early symptom of compartment syndrome? A. Cold, bluish-colored fingers B. Numbness and tingling in the fingers C. Pain that increases when the arm is dependent D. Pain that is out of proportion to the severity of the fracture Ans: B. The earliest symptom of compartment syndrome is paresthesia (numbness and tingling in the fingers). Other symptoms include pain unrelieved by opioids, pain that increases with limb elevation, and pallor and coolness to the distal limb. Cyanosis is a late sign. Pain that is out of proportion to the severity of the fracture, along with other symptoms associated with the pain, is not an early manifestation. 111. A client is complaining of low back pain that radiates down the left posterior thigh. The nurse should ask the client if the pain is worsened or aggravated by which factor? A. Bed rest B. Ibuprofen C. Bending or lifting D. Application of heat Ans: C. Low back pain that radiates into 1 leg (sciatica) is consistent with herniated lumbar disk. The nurse assesses the client to see whether the pain is aggravated by events that increase intraspinal pressure, such as bending, lifting, sneezing, and coughing, or by lifting the leg straight up while supine (straight leg-raising test). Bed rest, heat (or sometimes ice), and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) usually relieve back pain. 112. The nurse is caring for a client who has had spinal fusion, with insertion of hardware. The nurse would be most concerned with which assessment finding? A. Temperature of 101.6°F (38.7°C) orally B. Complaints of discomfort during repositioning C. Old bloody drainage outlined on the surgical dressing D. Discomfort during coughing and deep-breathing exercises Ans: A. The nursing assessment conducted after spinal surgery is similar to that done after other surgical procedures. For this specific type of surgery, the nurse assesses the neurovascular status of the lower extremities, watches for signs and symptoms of infection, and inspects the surgical site for evidence of cerebrospinal fluid leakage (drainage is clear and tests positive for glucose). A mild temperature is expected but a high temperature should be reported. 113. The nurse is caring for a client with a diagnosis of gout. Which laboratory value would the nurse expect to note in the client? A. Calcium level of 9.0 mg/dL B. Uric acid level of 9.0 mg/dL 22Adult Health Exam 5 C. Potassium level of 4.1 mEq/L D. Phosphorus level of 3.1 mg/dL Ans: B. In addition to the presence of clinical manifestations, gout is diagnosed by the presence of persistent hyperuricemia, with a uric acid level higher than 8 mg/dL (0.48 mmol/L); a normal value for a male ranges from 4.0 to 8.5 mg/dL (0.24 to 0.51 mmol/L) and for a female, from 2.7 to 7.3 mg/dL (0.16 to 0.43 mmol/L). Options 1, 3, and 4 indicate normal laboratory values. In addition, the presence of uric acid in an aspirated sample of synovial fluid confirms the diagnosis. 114. A client with a hip fracture asks the nurse about Buck's (extension) traction that is being applied before surgery and what is involved. The nurse should provide which information to the client? A. Allows bony healing to begin before surgery and involves pins and screws B. Provides rigid immobilization of the fracture site and involves pulleys and wheels C. Lengthens the fractured leg to prevent severing of blood vessels and involves pins and screws D. Provides comfort by reducing muscle spasms, provides fracture immobilization, and involves pulleys and wheels Ans: D. Buck's (extension) traction is a type of skin traction often applied after hip fracture before the fracture is reduced in surgery. Traction reduces muscle spasms and helps to immobilize the fracture. Traction does not allow for bony healing to begin or provide rigid immobilization. Traction does not lengthen the leg for the purpose of preventing blood vessel severance. This type of traction involves pulleys and wheels, not pins and screws. 115. The nurse is assigned to care for a client in traction. The nurse creates a plan of care for the client and should include which action in the plan? A. Ensure that the knots are at the pulleys. B. Check the weights to ensure that they are off of the floor. C. Ensure that the head of the bed is kept at a 45- to 90-degree angle. D. Monitor the weights to ensure that they are resting on a firm surface. Ans: B. To achieve proper traction, weights need to be free-hanging, with knots kept away from the pulleys. Weights should not be kept resting on a firm surface. The head of the bed is usually kept low to provide countertraction. 116. The nurse is creating a plan of care for a client in skin traction. The nurse should monitor for which priority finding in this client? A. Urinary incontinence B. Signs of skin breakdown C. Presence of bowel sounds D. Signs of infection around pin sites Ans: B. Skin traction is achieved by Ace wraps, boots, or slings that apply a direct force on the client's skin. Traction is maintained with 5 to 8 lb (2.3 to 3.6 kg) of weight, and this type of traction can cause skin breakdown. Urinary incontinence is not related to the use of skin traction. Although constipation can occur as a result of immobility and monitoring bowel sounds may be a component of the assessment, this intervention is not the priority assessment. There are no pin sites with skin traction. 117. The nurse is caring for a client in skeletal leg traction with an overbed frame. Which nursing intervention will best assist the client with self-positioning in bed? A. Use the assistance of four nurses to reposition the client. B. Place a draw sheet on the mattress for pulling the client up in bed. C. Place a trapeze on the bed frame to provide a means for the client to lift the hips off the bed. D. Encourage the client to push with the unaffected leg on the bed mattress to help with repositioning. Ans: C. The nurse can best assist the client in skeletal traction with repositioning by providing a trapeze on the bed frame for the client's use. Although a draw sheet is helpful and client movement may be more easily facilitated with four nurses, these actions will not promote repositioning by the client. Encouraging the client to push with the unaffected leg on the bed mattress for repositioning may cause skin breakdown on the unaffected heel area. 118. The nurse is caring for the client who has skeletal traction applied to the left leg. The client complains of severe left leg pain. The nurse checks the client's alignment in bed and notes that proper alignment is maintained. Which is the priority nursing action? A. Provide pin care 23Adult Health Exam 5 B. Medicate the client C. Call HCP D. Remove weight of traction system Ans: C. Severe pain in a client in skeletal traction may indicate a need for realignment, or the traction weights applied to the limb may be too heavy. The nurse realigns the client. If this measure is ineffective, the nurse then calls the health care provider. Severe leg pain once traction has been established indicates a problem. Providing pin care is unrelated to the problem as described. Medicating the client should be done after trying to determine and treat the cause. The nurse should never remove the weights from the traction system without a specific prescription to do so. 119. A client who has been taking high doses of acetylsalicylic acid to relieve pain from osteoarthritis now has more generalized joint pain and an elevated temperature. The nurse should assess for which complication to determine whether the client has other signs of aspirin toxicity? A. Diarrhea B. Constipation C. Double vision D. Ringing of the ears Ans: D. Mild intoxication with acetylsalicylic acid, called salicylism, commonly occurs when the daily dosage is more than 4 g. Tinnitus (ringing in the ears) is the most frequent effect noted with intoxication. Hyperventilation also may occur because a salicylate stimulates the respiratory center. Fever may result because a salicylate interferes with the metabolic pathways coupling oxygen consumption and heat production. The remaining options are not signs of aspirin toxicity. 120. The nurse is developing a plan of care for a client in Buck's traction. The plan of care should include assessing the client for which finding indicating a complication associated with the use of this type of traction? A. Hypotension B. Weak pedal pulses C. Redness at pin sites D. Drainage at pin sites Ans: B. Weak pedal pulses are a sign of vascular compromise, which can be caused by pressure on the tissues of the leg by the elastic bandage used to secure the traction system. This type of traction does not use pins; rather, elastic bandages or a prefabricated boot is worn by the client. Therefore, redness and/or drainage at the pin sites are incorrect. Hypotension is not directly associated with the use of this type of traction. 121. The nurse is caring for a client with a radius fractured across the shaft and bone splintered into fragments. Information about which type of fracture should be included by the nurse in the client's education? A. Simple fracture B. Greenstick fracture C. Compound fracture D. Comminuted fracture Ans: D. A comminuted fracture is a complete fracture across the shaft of a bone, with splintering of the bone into fragments. A simple fracture is a fracture of the bone across its entire shaft with some possible displacement but without breaking the skin. A greenstick fracture is an incomplete fracture, which occurs through part of the cross section of a bone: one side of the bone is fractured, and the other side is bent. A compound fracture, also called an open or complex fracture, is one in which the skin or mucous membrane has been broken and the resulting wound extends to the depth of the fractured bone. 122. A male client arrives in the hospital emergency department and tells the nurse that he twisted his ankle while jogging. The client is seen by the health care provider and is diagnosed with a sprained ankle. The nurse provides instructions to the client regarding home care for the injury. Which statement, if made by the client, would indicate an understanding of appropriate care measures for the next 24 hours? A. "I should place hot packs on my ankle." 24Adult Health Exam 5 B. "I should wrap my ankle with blankets." C. "I should elevate my foot above the level of the heart." D. “I should try to ambulate at least 10 minutes out of every hour." Ans: C. Soft tissue injuries such as sprains are treated with RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) for the first 24 to 48 hours after the injury, depending on health care provider prescription. Ice is applied intermittently for 20 to 30 minutes at a time. Heat is not used for the first 24 hours because this could cause venous congestion, thereby increasing edema and pain. Blankets would produce heat to the affected area. The client should rest and not walk around, and the foot should be elevated and not placed in a dependent position. 123. The nurse is performing a neurovascular assessment on a client with a cast on the left lower leg. The nurse notes the presence of edema in the foot below the cast. The nurse should make which interpretation about this finding? A. Arterial insufficiency B. Impaired venous return C. Impaired arterial circulation D. Presence of an infection Ans: B. Edema in the extremity indicates impaired venous return. Signs of impaired arterial circulation in the limb include coolness and pallor of the skin and a diminished arterial pulse. Signs of infection under a cast area would include odor or purulent drainage from the cast and the presence of "hot spots," which are areas of the cast that feel warmer to the touch than the rest of the cast. 124. The nurse is caring for a client with a long bone fracture at risk for fat embolism. The nurse specifically monitors for the earliest signs of this complication by performing an assessment of which item(s)? A. Client’s mobility status B. Renal and endocrine systems C. Cardiovascular and renal systems D. Neurological and respiratory systems Ans: D. The early signs of the complication of fat embolism include changes in the client's mental status and signs of impaired respiratory function as a result of impaired perfusion distal to the site of the embolus. Cardiovascular and renal impairments are likely to be secondary to impaired respiratory function. Effects on the endocrine system usually are not seen. The client's mobility status is unrelated to the signs of fat embolism. 125. The nurse is caring for a client who was just admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of a fractured right hip sustained from a fall 5 hours earlier. The nurse creates a plan of care for the client and includes interventions related to monitoring for signs of fat embolism. Which findings should be listed in the care plan as a sign/symptom of fat embolism? A. Fever and chills B. Dyspnea and chest pain C. External rotation of the right leg D. Pallor, paresthesia, pulselessness of right lower leg Ans: B. The signs of fat embolism are associated with alterations in respiratory status or neurological status. Dyspnea, petechiae, and chest pain are signs of fat embolism. External rotation of the leg is indicative of the hip fracture itself. Fever and chills indicate signs of infection, and pallor, paresthesia, and pulselessness indicate signs of severe circulatory impairment. 126. Which assessment findings should the nurse identify as early signs of possible fat embolism? A. Decreased heart rate and increased restlessness B. Decreased heart rate and decreased respiratory rate C. Increased heart rate and adventitious breath sounds D. Increased heart rate and increased oxygen saturation Ans: C. Fat embolism commonly causes signs and symptoms related to respiratory or neurological impairment. Because the client is unable to speak, it may be difficult to immediately assess early changes in neurological status. However, adventitious breath sounds and an increased heart rate may be easily and quickly observed, even before the client demonstrates labored breathing. The remaining options are incorrect. 25Adult Health Exam 5 127. The nurse should suspect impairment with the neurovascular status of the client's casted extremity if which findings are noted? Select all that apply. A. Capillary refill is less than 3 seconds B. Pulses present and with swollen, pink fingers. C. Client reports severe, deep, unrelenting pain D. Client reports pain as nurse assess finger movement E. Client reports numbness and tingling sensations in the fingers. Ans: C, D, E. The pressure in compartment syndrome, if unrelieved, will cause permanent damage to nerve and muscle tissue distal to the pressure. Circulatory damage may result in necrosis. Nerve and muscle damage may result in permanent contractures, deformity of the extremity, and functional impairment. Normal capillary refill time is 3 seconds or less. Pink appearance and a pulse indicate adequate blood flow; swelling is expected after a fracture. Client report of severe, deep, unrelenting pain; client report of numbness and tingling sensation; and client report of pain as the nurse assesses finger movement are indicative of development of compartment syndrome. 128. A client has had surgery to repair a fractured left hip. When repositioning the client from side to side in the bed, what should the nurse plan to use as the most important item for this maneuver? A. Bed pillow B. Abductor splint C. Adductor splint D. Overhead trapeze Ans: B. After surgery to repair a fractured hip, an abductor splint is used to maintain the affected extremity in good alignment. A bed pillow and an overhead trapeze also are used, but neither is the priority item to be used in repositioning the client from side to side. 129. A client with a 4-day-old lumbar vertebral fracture is experiencing muscle spasms. Which are interventions to aid the client in relieving the spasm? Select all that apply. A. Ice B. Heat C. Analgesics D. Muscle relaxers E. Intermittent traction Ans: B,C,D,E. Heat, analgesics, muscle relaxers, and traction all may be used to relieve the pain of muscle spasm in the client with a vertebral fracture. Ice is applied to a painful site only for the first 48 to 72 hours (depending on the health care provider's preference) after an injury. Application of ice to the spine of a client could be uncomfortable and could result in feelings of being chilled. 130. The nurse is planning discharge teaching for a client diagnosed and treated for compartment syndrome. Which information should the nurse include in the teaching? A. "A bone fragment has injured the nerve supply in the area." B. "An injured artery caused impaired arterial perfusion through the compartment." C. "Bleeding and swelling caused increased pressure in an area that couldn't expand." D. "The fascia expanded with injury, causing pressure on underlying nerves and muscles." Ans: C. Compartment syndrome is caused by bleeding and swelling within a tissue compartment that is lined by fascia, which does not expand. The bleeding and swelling put pressure on the nerves, muscles, and blood vessels in the compartment, triggering the symptoms. The remaining options are inaccurate descriptions of compartment syndrome. 131. The nurse is repositioning a client who has been returned to the nursing unit after internal fixation of a fractured right hip with a femoral head replacement. The nurse should use which method to reposition the client? A. A trochanter roll to prevent abduction during turning B. A pillow to keep the right leg abducted during turning 26Adult Health Exam 5 C. A pillow to keep the right leg adducted during turning D. A trochanter roll to prevent external rotation during turning Ans: B. After femoral head replacement for a fractured hip with an intracapsular fracture, the client is turned to the affected side or the unaffected side as prescribed by the surgeon. Before moving the client, the nurse places a pillow between the client's legs to keep the affected leg in abduction. The nurse then repositions the client while maintaining proper alignment and abduction. A trochanter roll is useful in preventing external rotation, but it is used after the client has been repositioned. A trochanter roll is not used while the client is being turned. 132. A client has been placed in Buck's extension traction. The nurse can provide for countertraction to reduce shear and friction by performing which action? A. Using a footboard B. Providing an overhead trapeze C. Slightly elevating the foot of the bed D. Slightly elevating the head of the bed 133. The nurse is reviewing the postprocedure plan of care formulated by a nursing student for a client scheduled for a bone biopsy. The nurse determines that the student needs additional information about postprocedure care if which inaccurate intervention is documented? A. Elevating the limb B. Monitoring vital signs every 4 hours C. Administering opioid analgesics intramuscularly D. Monitoring the biopsy site for swelling, bleeding, or hematoma Ans: C. Nursing care after bone biopsy includes monitoring the site for swelling, bleeding, and hematoma formation. The biopsy site is elevated for 24 hours or as prescribed to reduce edema. The vital signs are monitored every 4 hours for 24 hours for signs of complications such as infection and bleeding. The client usually requires mild analgesics. More severe pain usually indicates that complications are arising. 134. A client seeks treatment in the hospital emergency department for a lower leg injury. Deformity of the lower portion of the leg is evident, and the injured leg appears shorter than the other. The area is painful, swollen, and beginning to become ecchymotic. The nurse interprets that this client has experienced which injury? A. Strain B. Sprain C. Fracture D. Contusion Ans: C. Typical signs and symptoms of fracture include pain, loss of function in the area, deformity, shortening of the extremity, crepitus, swelling, and ecchymosis. Not all fractures lead to the development of every sign or symptom. A strain results from a pulling force on the muscle, resulting in soreness and pain with muscle use. A sprain is an injury to a ligament caused by a wrenching or twisting motion and is manifested by pain, swelling, and inability to use the joint or bear weight normally. A contusion results from a blow to soft tissue and causes pain, swelling, and ecchymosis. 135. A client is admitted to the nursing unit after a left below-the-knee amputation after a crush injury to the foot and lower leg. The client tells the nurse, "I think I'm going crazy. I can feel my left foot itching." How should the nurse interpret this client statement? A. A normal response that indicates the presence of phantom limb pain B. A normal response that indicates the presence of phantom limb sensation C. An abnormal response that indicates that the client is in denial about the limb loss D. An abnormal response that indicates that the client needs more psychological support Ans: B. Phantom limb sensations are felt in the area of the amputated limb. These sensations can include itching, warmth, and cold. The sensations are caused by intact peripheral nerves in the area of the amputation. Whenever possible, the client should be prepared for these sensations. The client also may feel painful sensations in the amputated limb, called phantom limb pain. The origin of the pain is less well understood, but the client should be prepared for this, too, whenever possible. 27Adult Health Exam 5 136. A hospitalized client has been diagnosed with osteomyelitis of the left tibia. The nurse determines that this condition is most likely a result of which event in the client's recent history? A. Sprained left ankle B. Decreased calcium intake C. Open trauma to the left leg D. Starting to smoke cigarettes Ans: C. Osteomyelitis is a bone infection and may be caused by direct contamination of bone through an open wound. Bacteria invade the bone tissue and produce inflammation. Ischemia and necrosis of the bone tissue may follow if not treated. The remaining options are unrelated to the cause of osteomyelitis. 137. An older client is diagnosed with osteoporosis. The nurse teaches the client about self-care measures, knowing that the client is most at risk for which problem as a result of this disorder of the bones? A. Anemia B. Fractures C. Infection D. Muscle spasms Ans: B. The client is most at risk for fractures as a result of osteoporosis. Although other complications can occur, fracture is the greatest concern. Anemia and infection can occur with bone marrow disorders, and muscle sprains are unrelated to osteoporosis. 138. A client has been diagnosed with osteomalacia, or adult rickets. The nurse should anticipate that the health care provider will include a new prescription for which vitamin supplement? A. Vitamin A B. Vitamin D C. Vitamin E D. Vitamin K Ans: B. Osteomalacia technically refers to bone softening that results from demineralization of bone matrix and failure to calcify. A common cause is vitamin D deficiency in the diet. Other causes are inadequate exposure to sunlight (to synthesize vitamin D) and disorders that interfere with absorption and metabolism of vitamin D. Deficiencies of the vitamins noted in the remaining options are not associated with osteomalacia. 139. A client is complaining of knee pain. The knee is swollen, reddened, and warm to the touch. The nurse interprets that the client's signs and symptoms are compatible with which conditions? Select all that apply. A. Infection B. Recent injury C. Inflammation D. Degenerative disease E. Developmental retardation Ans: A,B,C. Redness and heat are associated with musculoskeletal inflammation, infection, or a recent injury. Degenerative disease is accompanied by pain, but there is no redness. Swelling may or may not occur. These symptoms are not specifically associated with developmental retardation. 140. A client has undergone fasciotomy to treat compartment syndrome of the leg. The nurse should anticipate that which type of wound care to the fasciotomy site will be prescribed? A. Dry sterile dressings B. Hydrocolloid dressings C. Moist sterile saline dressings D. One-half strength povidone-iodine dressings Ans: C. The fasciotomy site is not sutured but is left open to relieve pressure and edema. The site is covered with moist sterile saline dressings. After 3 to 5 days, when perfusion is adequate and edema subsides, the wound is debrided and closed. Because this is an open wound, dry dressings should not be used. A hydrocolloid dressing is not indicated for use with clean, open incisions. The incision is clean, not dirty, so povidone-iodine should not be required. Also, this agent is irritating to tissues. 28Adult Health Exam 5 141. The nurse is assessing a client with a shortened, adducted, and externally rotated left leg. On the basis of this finding, which condition should the nurse anticipate? A. Fractured knee B. Dislocated knee C. Fracture of the femoral neck D. Fracture of the midshaft of the femur Ans: C. Typical signs after femoral neck fracture include shortening of the affected leg, adduction, and external rotation. The client may report slight groin pain or pain in the medial side of the knee. Moving the fractured extremity increases the pain significantly. The signs noted in the question are not associated with a fractured or dislocated knee or a fractured femur. 142. A client who has had a total knee arthroplasty tells the nurse that there is pain with extension of the knee. The nurse should perform which action? A. Administer an analgesic. B. Notify the health care provider. C. Immobilize the knee temporarily. D. Put the client's knee through full passive range of motion. Ans: A. Pain with knee extension is a common complaint of clients after knee arthroplasty; therefore, administering an analgesic would be the appropriate action. Immobilizing the knee will not help. The pain may be the result of a flexion contracture that developed preoperatively as the client tried to reduce the pain by keeping the knee partially flexed much of the time. The nurse should encourage the client to keep the knee extended and administer analgesics as needed. Pain is expected postoperatively, so there is no need to notify the health care provider based on the symptom described. Full passive range of motion can be harmful to the knee replacement. 143. The nurse is caring for a client admitted for a herniated intervertebral lumbar disk who is complaining about stabbing pain radiating to the lower back and the right buttock. The nurse determines that the client's signs/symptoms are most likely due to which condition? A. Pressure on the spinal cord B. Pressure on the spinal nerve root C. Muscle spasm in the area of the herniated disk D. Excess cerebrospinal fluid production in the area Ans: C. Compression of a nerve results in inflammation, which then irritates adjacent muscles, putting them into spasm. The pain of muscle spasm is continuous, knife-like, and localized in the affected area. Pressure on the spinal cord itself could result in a variety of manifestations, depending on the area involved. Pressure on a spinal nerve root causes the symptoms of sciatica. 144. The nurse has a prescription to place a client with a herniated lumbar intervertebral disk on bed rest in Williams' position to minimize the pain. The nurse should put the bed in what position? A. Flat with the knees raised B. In high Fowler's position, with the foot of the bed flat C. In semi Fowler's position, with the foot of the bed flat D. In semi Fowler's position, with the knees slightly flexed Ans: D. Clients with low back pain often are more comfortable when placed in Williams' position. The bed is placed in semi Fowler's position with the knee gatch raised sufficiently to flex the knees. This relaxes the muscles of the lower back and relieves pressure on the spinal nerve root. The remaining positions will not minimize the pain and may make the pain worse. 145. The nurse in the hospital emergency department is assessing a client with an open leg fracture. The nurse should inquire about the last time the client had which done? A. Tuberculin test B. Tetanus vaccine C. Chest radiograph 29Adult Health Exam 5 D. Physical examination Ans: B. With an open fracture, the client is at risk for the development of osteomyelitis, gas gangrene, and tetanus. The nurse assesses for the date of the last tetanus immunization to ensure that the client has tetanus prophylaxis. The remaining options are unrelated to the current situation identified in the question. 146. A client has just been admitted to the hospital with a fractured femur and pelvic fractures. The nurse should plan to carefully monitor the client for which signs/symptoms? A. Fever and bradycardia B. Fever and hypertension C. Tachycardia and hypotension D. Bradycardia and hypertension Ans: C. Clients who experience fractures of the femur, pelvis, thorax, and spine are at risk for hypovolemic shock. Bone fragments can damage blood vessels, leading to hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity and the thigh. This can occur with closed fractures as well as open fractures. Signs of hypovolemic shock include tachycardia and hypotension. 147. The nurse is obtaining a health history from a client and is assessing for risk factors associated with osteoporosis. The nurse would be most concerned if which data were obtained? Select all that apply. A. The client reports that she doesn't exercise much at all. B. The client reports that she smokes a few cigarettes a day C. The client reports that she is taking phenytoin to treat a seizure disorder D. The client reports that she consumes calcium and vitamin foods and supplements daily. E. The client reports that she takes a daily low dose of prednisone to treat a chronic respiratory condition. Ans: A,B,C,E. Risk factors associated with osteoporosis include a sedentary lifestyle, cigarette smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, chronic illness, and long-term use of anticonvulsants and furosemide. Another risk factor associated with osteoporosis includes a diet that is deficient in calcium. 148. The home health nurse visits a client who is having an acute attack of gout. The nurse determines that the client needs further instruction regarding the treatment of gout if the client states to take which action? A. Restricting fluids B. Maintaining bed rest C. Eating a low-purine diet D. Taking NSAIDs Ans: A. Ample fluid intake is encouraged to promote the excretion of uric acid. The client is placed on bed rest during an acute attack until the pain subsides. A diet low in purine normally is prescribed. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to reduce pain and inflammation. Colchicine, which also may be prescribed, reduces the migration of leukocytes to the synovial fluid. 149. The clinic nurse is performing an assessment on a client with a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The nurse checks for which assessment finding that is associated with RA? A. Age of onset is generally 65 years of age or older B. Complaints of pain that is more severe after activity C. Systemic symptoms such as fatigue, anorexia, and weight loss D. Joint pain is asymmetrical and associated with past injuries to the joint Ans: C. In clients diagnosed with RA, systemic symptoms such as fatigue, anorexia, weight loss, and nonspecific aching and stiffness may appear before joint manifestations. RA is characterized by chronic joint pain of variable intensity, which is more severe on rising in the morning. The age of onset for RA is most commonly between 30 and 50 years of age. Complaints of pain that is more severe after activity and asymmetrical joint pain associated with past injuries to the joint are more commonly seen in osteoarthritis. 150. The nurse is performing an assessment on a client after a closed reduction of a fractured right humerus and application of a plaster cast. To assess for signs of compartment syndrome, the nurse should perform which action? A. Assess the client's cognitive level. B. Assess the temperature of the cast. 30Adult Health Exam 5 C. Monitor for the presence of drainage or odors on or beneath the cast. D. Assess capillary refill, temperature, color, and amount of pain in the right hand. Ans: D. The major signs and symptoms of compartment syndrome include pallor or cyanosis; pain, even following the administration of opioid analgesics; vascular compromise demonstrated by weakened or absent pulses and poor capillary refill; and edema of the extremity distal to the area of the fracture. Cognitive level, temperature of the cast, and the presence of drainage or odors on or beneath the cast are not related to compartment syndrome. 151. The nurse is caring for a client admitted for a fractured hip status post fall at home. On assessment of the client's affected lower extremity, which signs/symptoms would most likely be noted? A. Shortening and abduction B. Abduction and internal rotation C. Shortening and internal rotation D. Shortening and external rotation Ans: D. Signs of a hip fracture include shortening and deformity. The affected leg externally rotates as a result of discontinuation of the femur and loss of alignment and muscle control. The remaining options are not findings associated with a fractured hip. 152. The nurse is preparing a plan of care for a client who is scheduled to return from the recovery room after a left total knee arthroplasty. The nurse includes in the plan of care to assess the client's neurovascular status the monitoring of which parameter? A. The pain level of the client B. Blood pressure and respiratory rate C. Capillary refill, sensation, color, and pulse of the left foot D. The range of motion of the left knee when a continuous passive motion machine is used Ans: C. The nurse would check capillary refill, sensation, color, and pulse of the affected extremity in a neurovascular assessment. Monitoring the pain level may be a component of the assessment but is not specifically related to neurovascular status. Blood pressure and respiratory rate may also be components of the nursing assessment but are not specific to neurovascular status. Range of motion is related to musculoskeletal status, not neurovascular status. 153. The nurse is preparing instructions for a client who is diagnosed with osteomalacia. Which information should the nurse include in the teaching? A. "Avoid exposure to sunlight." B. "Avoid weight-bearing exercise." C. "Ensure adequate intake of vitamin D fortified foods. D. "Osteomalacia and osteoporosis are interchangeable terms." Ans: C. A common cause of osteomalacia is vitamin D deficiency, so the client should include adequate dietary intake of vitamin D–fortified foods. Other causes include inadequate exposure to sunlight (to synthesize vitamin D) and disorders that interfere with the absorption and metabolism of vitamin D. Osteomalacia technically refers to bone softening, which results from demineralization of bone matrix and its failure to calcify. This is different from osteoporosis, which is a metabolic bone disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to increased bone fragility and pathologic fractures. Weight-bearing exercises are appropriate. 154. The nurse provides instructions to a client diagnosed with osteoporosis. Education about prevention of which complication is the most important? A. Fractures B. Weight loss C. Hypocalcemia D. Muscle atrophy Ans: A. Osteoporosis is a chronic, progressive metabolic bone disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to increased bone fragility. The woman is most likely to suffer fractures as a result of this disorder. The remaining options are not directly related to this disorder. 155. The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with osteomyelitis. Which mechanism of the disease process can result in necrosis of the bone? A. Devascularization B. Infection of the bone C. Decreased bone mass 31Adult Health Exam 5 D. Decreased bone density Ans: A. Osteomyelitis is an infectious process affecting the bone, bone marrow, and surrounding soft tissue. A microorganism gains entry into the blood and grows, causing increased pressure on the bone, leading to ischemia and ultimately necrosis as a result of devascularization. Infection of the bone occurs but is not specifically related to necrosis of the bone. Decreased bone mass and decreased bone density are also not related to necrosis of the bone. 156. The nurse is gathering subjective and objective data from a client with a diagnosis of suspected rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The nurse would expect to note which early signs and symptoms of RA? Select all that apply. A. Fatigue B. Weight gain C. Restlessness D. Morning stiffness E. Pain with movement only Ans: A, D. Early signs and symptoms of RA include fatigue, weight loss, fever, malaise, morning stiffness, pain at rest and with movement, and complaints of night pain. The involved joints appear edematous. 157. The nurse is performing a musculoskeletal assessment of an immobile client for disuse osteoporosis. Which should the nurse assess to obtain the best information about the bone remodeling process? A. Vitamin C B. Vitamin A C. Calcitonin D. Thyroid hormone Ans: C. Bone remodeling is the result of osteoblastic and osteoclastic activities, which are influenced by the degree of stress that is placed on the bone. The three substances that play an important role in this process are parathyroid hormone (which regulates calcium levels and bone resorption), vitamin D (which is active in bone formation and calcium resorption from bone), and calcitonin (which antagonizes parathyroid hormone and inhibits bone resorption). The other substances listed do not play a role in this process. 158. The nurse is planning discharge teaching for a client admitted with a fracture of the leg that does not extend all the way through the bone. The nurse should include information about which types of fractures? A. Open B. Displaced C. Complete D. Incomplete Ans: D. An incomplete fracture is one that extends through only part of the thickness of the bone. These fractures usually are nondisplaced, meaning that the bone remains in the normal position. An open (or compound) fracture is one in which the fractured bone protrudes through the skin, disrupting soft tissue. A complete fracture is one that extends through the full thickness of bone and often is displaced, meaning that the bone moves out of normal position. 159. A client has been diagnosed with subluxation of the shoulder. The nurse explains to the client that which injury has occurred to the joint? A. It is strained B. It is contused C. It is completely dislocated D. It is incompletely dislocated. Ans: D. A dislocation is the disruption of a joint to the extent that the articulating surfaces are no longer in contact. A subluxation is an incomplete dislocation of the joint surfaces. Because the disruption is less severe, healing time is less prolonged. A strain occurs when a muscle or ligament is used beyond the limit of its functional ability. It is characterized by overstretching of the muscle or ligament and also could involve tearing if the strain is more severe (i.e., second- or third-degree strain versus first-degree strain). A contusion is a soft tissue injury that results in hemorrhage into the involved tissue. 160. A client who suffered a contusion after being hit on the thigh with a racquetball has been told that it is acceptable to apply heat to the area 72 hours after the injury. The nurse explains the rationale for this treatment to the client, stating that which is the physiological benefit of heat in this case? 32Adult Health Exam 5 A. It induces muscle relaxation B. It prevents abscess formation. C. It reduces the likelihood of strain as a complication. D. It promotes reabsorption of blood from the injured tissue. Ans: D. The primary benefit from applying heat to a contusion is to speed up the rate of absorption of blood that has hemorrhaged into the affected soft tissue. Although heat also promotes muscle relaxation, this is not the intended benefit of this therapy in treating a contusion. Heat is not applied to reduce abscess formation or prevent muscle strain. 161. The nurse is caring for a client with a swollen left ankle who has difficulty bearing weight on this leg and states that he twisted his ankle. Based on these findings, which condition does the nurse determine the client has most likely experienced? A. Strain B. Sprain C. Fracture D. Contusion Ans: B. A sprain is an injury to a ligament caused by a wrenching or twisting motion. Signs and symptoms include pain, swelling, and inability to use the joint or bear weight normally. A strain results from a pulling force on a muscle. Manifestations include soreness and pain with muscle use. Typical signs and symptoms of fracture are variable but include pain, loss of function in the affected area, deformity, shortening of the extremity, crepitus, swelling, and ecchymosis. A contusion results from a blow to soft tissue and causes pain, swelling, and ecchymosis. 162. Which tests can be used to diagnose gout? Select all that apply. A. Renal ultrasound B. Serum uric acid level C. Bone marrow biopsy D. Urinalysis with culture E. Synovial fluid aspiration F. 24-hour urine uric acid level Ans: B,E,F. Diagnostic tests for gout include serum uric acid level and 24-hour urine uric acid level, as well as synovial fluid aspiration and x-ray of the affected areas. Renal ultrasound, bone marrow biopsy, and urinalysis with culture are not specifically associated with gout; they test for a variety of other conditions. 163. The nurse is preparing a client for an arthroscopy of the knee. When providing teaching, which information is essential for the nurse to include? A. It will drain fluid that has accumulated below the knee. B. It is used to obtain a muscle biopsy for pathology studies C. It will determine the degree of range of motion of the joint. D. It will identify if there is joint injury and provide a route for surgical repair if indicated Ans: D. Arthroscopy is used to diagnose acute and chronic conditions of the joint. In addition, surgical repairs can be done during this procedure. This procedure does not quantitate the degree of range of motion of the joint. Obtaining a muscle biopsy is not performed through an arthroscope, nor is this invasive procedure necessary to remove fluid from below the knee. 164. The nurse is creating a plan of care for a client in skin traction. Which frequent assessment should the nurse include in the plan as a priority intervention? A. Urinary incontinence B. Signs of skin breakdown C. Presence of bowel sounds D. Signs of infection around the pin sites Ans: B. Skin traction is achieved by Ace wraps, boots, and slings that apply a direct force on the client's skin. Skin traction is usually removed and reapplied once a day. Traction is maintained with 5 to 8 lb (2.3 to 3.6 kg) of weight, and this type of traction can cause skin breakdown. Urinary incontinence is not related to the use of skin traction. Although constipation can result from immobility, and although monitoring bowel sounds may be a component of the assessment, this intervention is not the priority assessment. There are no pin sites with skin traction. 33Adult Health Exam 5 165. The nurse is caring for a client with osteoarthritis. The nurse performs an assessment knowing that which clinical manifestations are associated with the disorder? Select all that apply. A. Elevated white blood cell count B. A decreased sedimentation rate C. Joint pain that diminishes after rest D. Elevated antinuclear antibody levels E. Joint pain that intensifies with activity Ans: C, E. The stiffness and joint pain that occur in osteoarthritis diminish after rest and intensify with activity. No specific laboratory findings are useful in diagnosing osteoarthritis. The client may have a normal or slightly elevated sedimentation rate. Morning stiffness lasting longer than 30 minutes occurs in rheumatoid arthritis. Elevated white blood cell counts, platelet counts, and antinuclear antibody levels occur in rheumatoid arthritis. 166. The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with osteomyelitis. Which data noted in the client's record are supportive of this diagnosis? Select all that apply.t A. Pyrexia B. Elevated potassium level C. Elevated white blood cell count D. Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate E. Bone scan impression indicative of infection Ans: A,C,D,E. Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone, bone marrow, and surrounding tissue. Clinical data indicative of osteomyelitis include pyrexia, elevated white blood cell count, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and a bone scan, computed tomography scan, or magnetic resonance imaging scan indicative of infection. Elevated potassium level is not specifically associated with osteomyelitis. 167. A client was admitted to the hospital 2 hours ago following multiple fractures to the pelvis and soft tissue injury to the abdomen. Diagnostic studies have ruled out perforation of abdominal organs. The nurse places highest priority on monitoring this client for which changes in vital signs? A. Fever, bradycardia B. Fever, hypertension C. Tachycardia, hypotension D. Bradycardia, hypertension Ans: C. Clients who experience fractures of the femur, pelvis, thorax, and spine are at risk for hypovolemic shock. Bone fragments can damage blood vessels, leading to hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity and, in the case of a fractured femur, into the thigh. This can occur with closed fractures as well as open fractures. Signs of hypovolemic shock include tachycardia and hypotension. 168. The nurse is caring for a client who had surgery to repair a fractured left-sided hip using a posterior approach. In implementing hip precautions, which action should the nurse teach the client to avoid? A. Crossing legs at the ankle B. Using an elevated toilet seat C. Placing a pillow between the legs D. Keeping the legs abducted from the midline Ans: A. Following surgery to repair a fractured hip using a posterior approach, client education should include the following: avoiding crossing the legs at the ankle or the knee, using an elevated toilet seat, placing a pillow between the legs while lying down for the first 6 weeks, keeping the legs abducted from the midline, and keeping the hip in a neutral position at all times. Neurological & Cognitive-Perceptual Disorders 1. The clinic nurse caring for a patient with Parkinson's disease notes that the patient has been taking levodopa and carbidopa (Sinemet) for 7 years. For what common side effect of Sinemet would the nurse assesses this patient? A. Pruritus B. Dyskinesia C. Lactose intolerance 34Adult Health Exam 5 D. Diarrhea Ans: B. Within 5 to 10 years of taking levodopa, most patients develop a response to the medication characterized by dyskinesia (abnormal involuntary movements). Another potential complication of long- term dopaminergic medication use is neuroleptic malignant syndrome characterized by severe rigidity, stupor, and hyperthermia. Side effects of long-term Sinemet therapy are not pruritus, lactose intolerance, or diarrhea. 2. The nurse is caring for a boy who has muscular dystrophy. When planning assistance with the patients ADLs, what goal should the nurse prioritize? A. Promoting the patients recovery from the disease B. Maximizing the patients level of function C. Ensuring the patients adherence to treatment D. Fostering the family’s’ participation in care Ans: B. Priority for the care of the child with muscular dystrophy is the need to maximize the patients level of function. Family participation is also important, but should be guided by this goal. Adherence is not a central goal, even though it is highly beneficial, and the disease is not curable. 3. A patient with Parkinson’s disease is undergoing a swallowing assessment because she has recently developed adventitious lung sounds. The patients nutritional needs should be met by what method? A. Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) B. Provision of a low-residue diet C. Semisolid food with thick liquids D. Minced foods and a fluid restriction Ans: C. A semisolid diet with thick liquids is easier for a patient with swallowing difficulties to consume than is a solid diet. Low-residue foods and fluid restriction are unnecessary and counterproductive to the patients nutritional status. The patients status does not warrant TPN. 4. While assessing the patient at the beginning of the shift, the nurse inspects a surgical dressing covering the operative site after the patients cervical discectomy. The nurse notes that the drainage is 75% saturated with serosanguineous discharge. What is the nurses most appropriate action? A. Page the physician and report this sign of infection. B. Reinforce the dressing and reassess in 1 to 2 hours. C. Reposition the patient to prevent further hemorrhage. D. Inform the surgeon of the possibility of a dural leak. Ans: D. After a cervical diskectomy, the nurse will monitor the operative site and dressing covering this site. Serosanguineous drainage may indicate a dural leak. This constitutes a risk for meningitis, but is not a direct sign of infection. This should be reported to the surgeon, not just reinforced and observed. 5. A patient has just been diagnosed with Parkinson's disease and the nurse is planning the patients subsequent care for the home setting. What nursing diagnosis should the nurse address when educating the patients family? A. Risk for infection B. Impaired spontaneous ventilation C. Unilateral neglect D. Risk for injury Ans: D. Individuals with Parkinson's disease face a significant risk for injury related to the effects of dyskinesia. Unilateral neglect is not characteristic of the disease, which affects both sides of the body. Parkinson's disease does not directly constitute a risk for infection or impaired respiration. 6. A male patient with a metastatic brain tumor is having a generalized seizure and begins vomiting. What should the nurse do first? A. Perform oral suctioning. B. Page the physician. C. Insert a tongue depressor into the patients mouth. D. Turn the patient on his side. Ans: D. The nurses first response should be to place the patient on his side to prevent him from aspirating emesis. Inserting something into the seizing patients mouth is no longer part of a seizure protocol. Obtaining supplies to 35Adult Health Exam 5 suction the patient would be a delegated task. Paging or calling the physician would only be necessary if this is the patients first seizure. 7. A patient newly diagnosed with a cervical disk herniation is receiving health education from the clinic nurse. What conservative management measures should the nurse teach the patient to implement? A. Perform active ROM exercises three times daily. B. Sleep on a firm mattress. C. Apply cool compresses to the back of the neck daily. D. Wear the cervical collar for at least 2 hours at a time. Ans: B. Proper positioning on a firm mattress and bed rest for 1 to 2 days may bring dramatic relief from pain. The patient may need to wear a cervical collar 24 hours a day during the acute phase of pain from a cervical disk herniation. Hot, moist compresses applied to the back of the neck will increase blood flow to the muscles and help relax the spastic muscles. 8. A patient has just returned to the unit from the PACU after surgery for a tumor within the spine. The patient complains of pain. When positioning the patient for comfort and to reduce injury to the surgical site, the nurse will position to patient in what position? A. In the high Fowlers position B. In a flat side-lying position C. In the Trendelenberg position D. In the reverse Trendelenberg position Ans: B. After spinal surgery, the bed is usually kept flat initially. The side-lying position is usually the most comfortable because this position imposes the least pressure on the surgical site. The Fowlers position, Trendelenberg position, and reverse Trendelenberg position are inappropriate for this patient because they would result in increased pain and complications. 9. An older adult has encouraged her husband to visit their primary care provider, stating that she is concerned that he may have Parkinson's disease. Which of the wifes descriptions of her husbands health and function is most suggestive of Parkinson's disease? A. Lately he seems to move far more slowly than he ever has in the past. B. He often complains that his joints are terribly stiff when he wakes up in the morning. C. He is forgotten the names of some people that weve known for years. D. He is losing weight even though he has a ravenous appetite. Ans: A. Parkinson's disease is characterized by bradykinesia. It does not manifest as memory loss, increased appetite, or joint stiffness. 10.A patient who was diagnosed with Parkinson's disease several months ago recently began treatment with levodopa-carbidopa. The patient and his family are excited that he has experienced significant symptom relief. The nurse should be aware of what implication of the patients medication regimen? A. The patient is in a honeymoon period when adverse effects of levodopa-carbidopa are not yet evident. B. Benefits of levodopa-carbidopa do not peak until 6 to 9 months after the initiation of treatment. C. The patients temporary improvement in status is likely unrelated to levodopa-carbidopa. D. Benefits of levodopa-carbidopa often diminish after 1 or 2 years of treatment. Ans: D. The beneficial effects of levodopa therapy are most pronounced in the first year or two of treatment. Benefits begin to wane and adverse effects become more severe over time. However, a honeymoon period of treatment is not known. 11.The nurse caring for a patient diagnosed with Parkinson's disease has prepared a plan of care that would include what goal? A. Promoting effective communication B. Controlling diarrhea C. Preventing cognitive decline D. Managing choreiform movements Ans: A. The goals for the patient may include improving functional mobility, maintaining independence in ADLs, achieving adequate bowel elimination, attaining and maintaining acceptable nutritional status, achieving 36Adult Health Exam 5 effective communication, and developing positive coping mechanisms. Constipation is more likely than diarrhea and cognition largely remains intact. Choreiform movements are related to Huntington disease. 12.The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with Parkinson's disease. The patient is having increasing problems with rising from the sitting to the standing position. What should the nurse suggest to the patient to use that will aid in getting from the sitting to the standing position as well as aid in improving bowel elimination? A. Use of a bedpan B. Use of a raised toilet seat C. Sitting quietly on the toilet every 2 hours D. Following the outlined bowel program Ans: B. A raised toilet seat is useful, because the patient has difficulty in moving from a standing to a sitting position. A handicapped toilet is not high enough and will not aid in improving bowel elimination. Sitting quietly on the toilet every 2 hours will not aid in getting from the sitting to standing position; neither will following the outlined bowel program. 13.A patient with Parkinson's disease is experiencing episodes of constipation that are becoming increasingly frequent and severe. The patient states that he has been achieving relief for the past few weeks by using OTC laxatives. How should the nurse respond? A. Its important to drink plenty of fluids while you're taking laxatives. B. Make sure that you supplement your laxatives with a nutritious diet. C. Lets explore other options, because laxatives can have side effects and create dependency. D. You should ideally be using herbal remedies rather than medications to promote bowel function. Ans: C. Laxatives should be avoided in patients with Parkinson's disease due to the risk of adverse effects and dependence. Herbal bowel remedies are not necessarily less risky. 14.The nurse is caring for a patient who is scheduled for a cervical discectomy the following day. During health education, the patient should be made aware of what potential complications? A. Vertebral fracture B. Hematoma at the surgical site C. Scoliosis D. Renal trauma Ans: B. Based on all the assessment data, the potential complications of diskectomy may include hematoma at the surgical site, resulting in cord compression and neurologic deficit and recurrent or persistent pain after surgery. Renal trauma and fractures are unlikely; scoliosis is a congenital malformation of the spine. 15.The nurse responds to the call light of a patient who has had a cervical diskectomy earlier in the day. The patient states that she is having severe pain that had a sudden onset. What is the nurses most appropriate action? A. Palpate the surgical site. B. Remove the dressing to assess the surgical site. C. Call the surgeon to report the patients pain. D. Administer a dose of an NSAID. Ans: C. If the patient experiences a sudden increase in pain, extrusion of the graft may have occurred, requiring reoperation. A sudden increase in pain should be promptly reported to the surgeon. Administration of an NSAID would be an insufficient response and the dressing should not be removed without an order. Palpation could cause further damage. 16.A nurse is planning discharge education for a patient who underwent a cervical diskectomy. What strategies would the nurse assess that would aid in planning discharge teaching? A. Care of the cervical collar B. Technique for performing neck ROM exercises C. Home assessment of ABGs D. Techniques for restoring nerve function Ans: A. Prior to discharge, the nurse should assess the patients use and care of the cervical collar. Neck ROM exercises would be contraindicated and ABGs cannot be assessed in the home. Nerve function is not 37Adult Health Exam 5 compromised by a diskectomy. 17.A patient is receiving ongoing nursing care for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. When assessing this patients gait, what finding is most closely associated with this health problem? A. Spastic hemiparesis gait B. Shuffling gait C. Rapid gait D. Steppage gait Ans: B. A variety of neurologic conditions are associated with abnormal gaits, such as a spastic hemiparesis gait (stroke), steppage gait (lower motor neuron disease), and shuffling gait (Parkinsons disease). A rapid gait is not associated with Parkinson's disease. 18. A patient is being admitted to the neurologic ICU following an acute head injury that has resulted in cerebral edema. When planning this patients care, the nurse would expect to administer what priority medication? A. Hydrochlorothiazide (HydroDIURIL) B. Furosemide (Lasix) C. Mannitol (Osmitrol) D. Spirolactone (Aldactone) Ans:C. The osmotic diuretic mannitol is given to dehydrate the brain tissue and reduce cerebral edema. This drug acts by reducing the volume of brain and extracellular fluid. Spirolactone, furosemide, and hydrochlorothiazide are diuretics that are not typically used in the treatment of increased ICP resulting from cerebral edema. 19. The nurse is providing care for a patient who is unconscious. What nursing intervention takes highest priority? A. Maintaining accurate records of intake and output B. Maintaining a patent airway C. Inserting a nasogastric (NG) tube as ordered D. Providing appropriate pain control Ans: B. Maintaining a patent airway always takes top priority, even though each of the other listed actions is . necessary and appropriate. 20. The nurse is caring for a patient in the ICU who has a brain stem herniation and who is exhibiting an altered level of consciousness. Monitoring reveals that the patients mean arterial pressure (MAP) is 60 mm Hg with an intracranial pressure (ICP) reading of 5 mm Hg. What is the nurses most appropriate action? A. Position the patient in the high Fowlers position as tolerated. B. Administer osmotic diuretics as ordered. C. Participate in interventions to increase cerebral perfusion pressure. D. Prepare the patient for craniotomy. Ans: C. The cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) is 55 mm Hg, which is considered low. The normal CPP is 70 to 100 mm Hg. Patients with a CPP of less than 50 mm Hg experience irreversible neurologic damage. As a result, interventions are necessary. A craniotomy is not directly indicated. Diuretics and increased height of bed would exacerbate the patients condition. 21. The nurse is caring for a patient who is postoperative following a craniotomy. When writing the plan of care, the nurse identifies a diagnosis of deficient fluid volume related to fluid restriction and osmotic diuretic use. What would be an appropriate intervention for this diagnosis? A. Change the patients position as indicated. B. Monitor serum electrolytes. C. Maintain NPO status. D. Monitor arterial blood gas (ABG) values. Ans: B. The postoperative fluid regimen depends on the type of neurosurgical procedure and is determined on an 38Adult Health Exam 5 individual basis. The volume and composition of fluids are adjusted based on daily serum electrolyte values, along with fluid intake and output. Fluids may have to be restricted in patients with cerebral edema. Changing the patients position, maintaining an NPO status, and monitoring ABG values do not relate to the nursing diagnosis of deficient fluid volume. 22. A patient with a documented history of seizure disorder experiences a generalized seizure. What nursing action is most appropriate? A. Restrain the patient to prevent injury. B. Open the patients jaws to insert an oral airway. C. Place patient in high Fowlers position. D. Loosen the patients restrictive clothing. Ans:D. An appropriate nursing intervention would include loosening any restrictive clothing on the patient. No attempt should be made to restrain the patient during the seizure because muscular contractions are strong and restraint can produce injury. Do not attempt to pry open jaws that are clenched in a spasm to insert anything. Broken teeth and injury to the lips and tongue may result from such an action. If possible, place the patient on one side with head flexed forward, which allows the tongue to fall forward and facilitates drainage of saliva and mucus. 23. A patient who has been on long-term phenytoin (Dilantin) therapy is admitted to the unit. In light of the adverse of effects of this medication, the nurse should prioritize which of the following in the patients plan of care? A. Monitoring of pulse oximetry B. Administration of a low-protein diet C. Administration of thorough oral hygiene D. Fluid restriction as ordered Ans: C. Gingival hyperplasia (swollen and tender gums) can be associated with long-term phenytoin (Dilantin) use. Thorough oral hygiene should be provided consistently and encouraged after discharge. Fluid and protein restriction are contraindicated and there is no particular need for constant oxygen saturation monitoring. 24. While completing a health history on a patient who has recently experienced a seizure, the nurse would assess for what characteristic associated with the postictal state? A. Epileptic cry B. Confusion C. Urinary incontinence D. Body rigidity Ans: B. In the postictal state (after the seizure), the patient is often confused and hard to arouse and may sleep for hours. The epileptic cry occurs from the simultaneous contractions of the diaphragm and chest muscles that occur during the seizure. Urinary incontinence and intense rigidity of the entire body are followed by alternating muscle relaxation and contraction (generalized tonic-clonic contraction) during the seizure. 25. A patient with increased ICP has a ventriculostomy for monitoring ICP. The nurses most recent assessment reveals that the patient is now exhibiting nuchal rigidity and photophobia. The nurse would be correct in suspecting the presence of what complication? A. Encephalitis B. CSF leak C. Meningitis D. Catheter occlusion Ans: C. Complications of a ventriculostomy include ventricular infectious meningitis and problems with the monitoring system. Nuchal rigidity and photophobia are clinical manifestations of meningitis, but are not suggestive of encephalitis, a CSF leak, or an occluded catheter. 26. The nurse is participating in the care of a patient with increased ICP. What diagnostic test is contraindicated in this patients treatment? A. Computed tomography (CT) scan B. Lumbar puncture C. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) D. Venous Doppler studies Ans: B. A lumbar puncture in a patient with increased ICP may cause the brain to herniate from the withdrawal of fluid and change in pressure during the lumbar puncture. Herniation of the brain is a dire and frequently fatal event. 39Adult Health Exam 5 CT, MRI, and venous Doppler are considered noninvasive procedures and they would not affect the ICP itself. 27. The nurse is caring for a patient who is in status epilepticus. What medication does the nurse know may be given to halt the seizure immediately? A. Intravenous phenobarbital (Luminal) B. Intravenous diazepam (Valium) C. Oral lorazepam (Ativan) D. Oral phenytoin (Dilantin Ans:B. Medical management of status epilepticus includes IV diazepam (Valium) and IV lorazepam (Ativan) given slowly in an attempt to halt seizures immediately. Other medications (phenytoin, phenobarbital) are given later to maintain a seizure-free state. Oral medications are not given during status epilepticus. 28. The nurse has created a plan of care for a patient who is at risk for increased ICP. The patients care plan should specify monitoring for what early sign of increased ICP? A. Disorientation and restlessness B. Decreased pulse and respirations C. Projectile vomiting D. Loss of corneal reflex Ans: A. Early indicators of ICP include disorientation and restlessness. Later signs include decreased pulse and respirations, projectile vomiting, and loss of brain stem reflexes, such as the corneal reflex. 29. The neurologic ICU nurse is admitting a patient following a craniotomy using the supratentorial approach. How should the nurse best position the patient? A. Position the patient supine. B. Maintain head of bed (HOB) elevated at 30 to 45 degrees. C. Position patient in prone position. D. Maintain bed in Trendelenberg position. Ans:B. The patient undergoing a craniotomy with a supratentorial (above the tentorium) approach should be placed with the HOB elevated 30 to 45 degrees, with the neck in neutral alignment. Each of the other listed positions would cause a dangerous elevation in ICP. 30. A clinic nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with migraine headaches. During the patient teaching session, the patient questions the nurse regarding alcohol consumption. What would the nurse be correct in telling the patient about the effects of alcohol? A. Alcohol causes hormone fluctuations. B. Alcohol causes vasodilation of the blood vessels. C. Alcohol has an excitatory effect on the CNS. D. Alcohol diminishes endorphins in the brain. Ans: B. Alcohol causes vasodilation of the blood vessels and may exacerbate migraine headaches. Alcohol has a depressant effect on the CNS. Alcohol does not cause hormone fluctuations, nor does it decrease endorphins (morphine-like substances produced by the body) in the brain. 31. A patient has developed diabetes insipidus after having increased ICP following head trauma. What nursing assessment best addresses this complication? A. Vigilant monitoring of fluid balance B. Continuous BP monitoring C. Serial arterial blood gases (ABGs) D. Monitoring of the patients airway for patency Ans: A. Diabetes insipidus requires fluid and electrolyte replacement, along with the administration of vasopressin, to replace and slow the urine output. Because of these alterations in fluid balance, careful monitoring is necessary. None of the other listed assessments directly addresses the major manifestations of diabetes insipidus. 32. What should the nurse suspect when hourly assessment of urine output on a patient post-craniotomy exhibits a urine output from a catheter of 1,500 mL for two consecutive hours? A. Cushing syndrome B. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) C. Adrenal crisis 40Adult Health Exam 5 D. Diabetes insipidus Ans: D. Diabetes insipidus is an abrupt onset of extreme polyuria that commonly occurs in patients after brain surgery. Cushing syndrome is excessive glucocorticoid secretion resulting in sodium and water retention. SIADH is the result of increased secretion of ADH; the patient becomes volume-overloaded, urine output diminishes, and serum sodium concentration becomes dilute. Adrenal crisis is undersecretion of glucocorticoids resulting in profound hypoglycemia, hypovolemia, and hypotension. 33. During the examination of an unconscious patient, the nurse observes that the patients pupils are fixed and dilated. What is the most plausible clinical significance of the nurses finding? A. It suggests onset of metabolic problems. B. It indicates paralysis on the right side of the body. C. It indicates paralysis of cranial nerve X. D. It indicates an injury at the midbrain level. Ans: D. Pupils that are fixed and dilated indicate injury at the midbrain level. This finding is not suggestive of unilateral paralysis, metabolic deficits, or damage to CN X. 34. The nurse caring for a patient in a persistent vegetative state is regularly assessing for potential complications. Complications of neurologic dysfunction for which the nurse should assess include which of the following? Select all that apply. A. Contractures B. Hemorrhage C. Pressure ulcers D. Venous thromboembolism E. Pneumonia Ans: A, C, D, E. Based on the assessment data, potential complications may include respiratory distress or failure, pneumonia, aspiration, pressure ulcer, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and contractures. The pathophysiology of decreased LOC does not normally create a heightened risk for hemorrhage. 35. The nurse is caring for a patient with a brain tumor. What drug would the nurse expect to be ordered to reduce the edema surrounding the tumor? A. Solumedrol B. Dextromethorphan C. Dexamethasone D. Furosemide Ans: C. If a brain tumor is the cause of the increased ICP, corticosteroids (e.g., dexamethasone) help reduce the edema surrounding the tumor. Solumedrol, a steroid, and furosemide, a loop diuretic, are not the drugs of choice in this instance. Dextromethorphan is used in cough medicines. 36. The nurse is caring for a patient who sustained a moderate head injury following a bicycle accident. The nurses most recent assessment reveals that the patients respiratory effort has increased. What is the nurses most appropriate response? A. Inform the care team and assess for further signs of possible increased ICP. B. Administer bronchodilators as ordered and monitor the patients LOC. C. Increase the patients bed height and reassess in 30 minutes. D. Administer a bolus of normal saline as ordered. Ans: A. Increased respiratory effort can be suggestive of increasing ICP, and the care team should be promptly informed. A bolus of IV fluid will not address the problem. Repositioning the patient and administering bronchodilators are insufficient responses, even though these actions may later be ordered. 37. A patient has experienced a seizure in which she became rigid and then experienced alternating muscle relaxation and contraction. What type of seizure does the nurse recognize? A. Unclassified seizure B. Absence seizure C. Generalized seizure D. Focal seizure Ans: C. Generalized seizures often involve both hemispheres of the brain, causing both sides of the body to react. Intense rigidity of the entire body may occur, followed by alternating muscle relaxation and contraction (generalized 41Adult Health Exam 5 tonicclonic contraction). This pattern of rigidity does not occur in patients who experience unclassified, absence, or focal seizures. 38. When caring for a patient with increased ICP the nurse knows the importance of monitoring for possible secondary complications, including syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH). What nursing interventions would the nurse most likely initiate if the patient developed SIADH? A. Fluid restriction B. Transfusion of platelets C. Transfusion of fresh frozen plasma (FFP) D. Electrolyte restriction Ans: A. The nurse also assesses for complications of increased ICP, including diabetes insipidus, and SIADH. SIADH requires fluid restriction and monitoring of serum electrolyte levels. Transfusions are unnecessary. 39. A patient is recovering from intracranial surgery that was performed using the transsphenoidal approach. The nurse should be aware that the patient may have required surgery on what neurologic structure? A. Cerebellum B. Hypothalamus C. Pituitary gland D. Pineal gland Ans: C. The transsphenoidal approach (through the mouth and nasal sinuses) is often used to gain access to the pituitary gland. This surgical approach would not allow for access to the pineal gland, cerebellum, or hypothalamus. 40. A school nurse is called to the playground where a 6-year-old girl has been found unresponsive and staring into space, according to the playground supervisor. How would the nurse document the girls activity in her chart at school? A. Generalized seizure B. Absence seizure C. Focal seizure D. Unclassified seizure Ans:B. Staring episodes characterize an absence seizure, whereas focal seizures, generalized seizures, and unclassified seizures involve uncontrolled motor activity. 41. A neurologic nurse is reviewing seizures with a group of staff nurses. How should this nurse best describe the cause of a seizure? A. Sudden electrolyte changes throughout the brain B. A dysrhythmia in the peripheral nervous system C. A dysrhythmia in the nerve cells in one section of the brain D. Sudden disruptions in the blood flow throughout the brain Ans: C. The underlying cause of a seizure is an electrical disturbance (dysrhythmia) in the nerve cells in one section of the brain; these cells emit abnormal, recurring, uncontrolled electrical discharges. Seizures are not caused by changes in blood flow or electrolytes. 42. The nurse is caring for a patient who has undergone supratentorial removal of a pituitary mass. What medication would the nurse expect to administer prophylactically to prevent seizures in this patient? A. Prednisone B. Dexamethasone C. Cafergot D. Phenytoin Ans: D. Antiseizure medication (phenytoin, diazepam) is often prescribed prophylactically for patients who have undergone supratentorial craniotomy because of the high risk of seizures after this procedure. Prednisone and dexamethasone are steroids and do not prevent seizures. Cafergot is used in the treatment of migraines. 43. A patient has had an ischemic stroke and has been admitted to the medical unit. What action should the nurse perform to best prevent joint deformities? A. Place the patient in the prone position for 30 minutes/day. B. Assist the patient in acutely flexing the thigh to promote movement. 42Adult Health Exam 5 C. Place a pillow in the axilla when there is limited external rotation. D. Place patients hand in pronation. Ans: C. A pillow in the axilla prevents adduction of the affected shoulder and keeps the arm away from the chest. The prone position with a pillow under the pelvis, not flat, promotes hyperextension of the hip joints, essential for normal gait. To promote venous return and prevent edema, the upper thigh should not be flexed acutely. The hand is placed in slight supination, not pronation, which is its most functional position. 44. When caring for a patient who had a hemorrhagic stroke, close monitoring of vital signs and neurologic changes is imperative. What is the earliest sign of deterioration in a patient with a hemorrhagic stroke of which the nurse should be aware? A. Generalized pain B. Alteration in level of consciousness (LOC) C. Tonic-clonic seizures D. Shortness of breath Ans: B. Alteration in LOC is the earliest sign of deterioration in a patient after a hemorrhagic stroke, such as mild drowsiness, slight slurring of speech, and sluggish papillary reaction. Sudden headache may occur, but generalized pain is less common. Seizures and shortness of breath are not identified as early signs of hemorrhagic stroke. 45. The nurse is performing stroke risk screenings at a hospital open house. The nurse has identified four patients who might be at risk for a stroke. Which patient is likely at the highest risk for a hemorrhagic stroke? A. White female, age 60, with history of excessive alcohol intake B. White male, age 60, with history of uncontrolled hypertension C. Black male, age 60, with history of diabetes D. Black male, age 50, with history of smoking Ans: B. Uncontrolled hypertension is the primary cause of a hemorrhagic stroke. Control of hypertension, especially in individuals over 55 years of age, clearly reduces the risk for hemorrhagic stroke. Additional risk factors are increased age, male gender, and excessive alcohol intake. Another high-risk group includes African Americans, where the incidence of first stroke is almost twice that as in Caucasians. 46. A patient who just suffered a suspected ischemic stroke is brought to the ED by ambulance. On what should the nurses primary assessment focus? A. Cardiac and respiratory status B. Seizure activity C. Pain D. Fluid and electrolyte balance Ans: A. Acute care begins with managing ABCs. Patients may have difficulty keeping an open and clear airway secondary to decreased LOC. Neurologic assessment with close monitoring for signs of increased neurologic deficit and seizure activity occurs next. Fluid and electrolyte balance must be controlled carefully with the goal of adequate hydration to promote perfusion and decrease further brain activity. 47. A patient with a cerebral aneurysm exhibits signs and symptoms of an increase in intracranial pressure (ICP). What nursing intervention would be most appropriate for this patient? A. Range-of-motion exercises to prevent contractures B. Encouraging independence with ADLs to promote recovery C. Early initiation of physical therapy D. Absolute bed rest in a quiet, nonstimulating environment Ans:D. The patient is placed on immediate and absolute bed rest in a quiet, nonstressful environment because activity, pain, and anxiety elevate BP, which increases the risk for bleeding. Visitors are restricted. The nurse administers all personal care. The patient is fed and bathed to prevent any exertion that might raise BP. 48. The nurse is assessing a patient with a suspected stroke. What assessment finding is most suggestive of a stroke? A. Facial droop B. Dysrhythmias C. Periorbital edema 43Adult Health Exam 5 D. Projectile vomiting Ans: A. Facial drooping or asymmetry is a classic abnormal finding on a physical assessment that may be associated with a stroke. Facial edema is not suggestive of a stroke and patients less commonly experience dysrhythmias or vomiting. 49. The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with an ischemic stroke and knows that effective positioning of the patient is important. Which of the following should be integrated into the patients plan of care? A. The patients hip joint should be maintained in a flexed position. B. The patient should be in a supine position unless ambulating. C. The patient should be placed in a prone position for 15 to 30 minutes several times a day. D. The patient should be placed in a Trendelenberg position two to three times daily to promote cerebral perfusion. Ans: C. If possible, the patient is placed in a prone position for 15 to 30 minutes several times a day. A small pillow or a support is placed under the pelvis, extending from the level of the umbilicus to the upper third of the thigh. This helps to promote hyperextension of the hip joints, which is essential for normal gait, and helps prevent knee and hip flexion contractures. The hip joints should not be maintained in flexion and the Trendelenberg position is not indicated. 50. The nurse is preparing health education for a patient who is being discharged after hospitalization for a hemorrhagic stroke. What content should the nurse include in this education? A. Mild, intermittent seizures can be expected. B. Take ibuprofen for complaints of a serious headache. C. Take antihypertensive medication as ordered. D. Drowsiness is normal for the first week after discharge. Ans: C. The patient and family are provided with information that will enable them to cooperate with the care and restrictions required during the acute phase of hemorrhagic stroke and to prepare the patient to return home. Patient and family teaching includes information about the causes of hemorrhagic stroke and its possible consequences. Symptoms of hydrocephalus include gradual onset of drowsiness and behavioral changes. Hypertension is the most serious risk factor, suggesting that appropriate antihypertensive treatment is essential for a patient being discharged. Seizure activity is not normal; complaints of a serious headache should be reported to the physician before any medication is taken. Drowsiness is not normal or expected. 51. A patient is brought by ambulance to the ED after suffering what the family thinks is a stroke. The nurse caring for this patient is aware that an absolute contraindication for thrombolytic therapy is what? A. Evidence of hemorrhagic stroke B. Blood pressure of 180/110 mm Hg C. Evidence of stroke evolution D. Previous thrombolytic therapy within the past 12 months Ans: A. Thrombolytic therapy would exacerbate a hemorrhagic stroke with potentially fatal consequences. Stroke evolution, high BP, or previous thrombolytic therapy does not contraindicate its safe and effective use. 52. When caring for a patient who has had a stroke, a priority is reduction of ICP. What patient position is most consistent with this goal? A. Head turned slightly to the right side B. Elevation of the head of the bed C. Position changes every 15 minutes while awake D. Extension of the neck Ans: B. Elevation of the head of the bed promotes venous drainage and lowers ICP; the nurse should avoid flexing or extending the neck or turning the head side to side. The head should be in a neutral midline position. Excessively frequent position changes are unnecessary. 53. A patient who suffered an ischemic stroke now has disturbed sensory perception. What principle should guide the nurses care of this patient? A. The patient should be approached on the side where visual perception is intact. B. Attention to the affected side should be minimized in order to decrease anxiety. C. The patient should avoid turning in the direction of the defective visual field to minimize shoulder subluxation. D. The patient should be approached on the opposite side of where the visual perception is intact to promote recovery. 44Adult Health Exam 5 Ans: A. Patients with decreased field of vision should first be approached on the side where visual perception is intact. All visual stimuli should be placed on this side. The patient can and should be taught to turn the head in the direction of the defective visual field to compensate for this loss. The nurse should constantly remind the patient of the other side of the body and should later stand at a position that encourages the patient to move or turn to visualize who and what is in the room. 54. A patient who has experienced an ischemic stroke has been admitted to the medical unit. The patients family in adamant that she remain on bed rest to hasten her recovery and to conserve energy. What principle of care should inform the nurses response to the family? A. The patient should mobilize as soon as she is physically able. B. To prevent contractures and muscle atrophy, bed rest should not exceed 4 weeks. C. The patient should remain on bed rest until she expresses a desire to mobilize. D. Lack of mobility will greatly increase the patients risk of stroke recurrence. Ans: A. As soon as possible, the patient is assisted out of bed and an active rehabilitation program is started. Delaying mobility causes complications, but not necessarily stroke recurrence. Mobility should not be withheld until the patient initiates. 55. A patient has recently begun mobilizing during the recovery from an ischemic stroke. To protect the patients safety during mobilization, the nurse should perform what action? A. Support the patients full body weight with a waist belt during ambulation. B. Have a colleague follow the patient closely with a wheelchair. C. Avoid mobilizing the patient in the early morning or late evening. D. Ensure that the patients family members do not participate in mobilization. Ans: B. During mobilization, a chair or wheelchair should be readily available in case the patient suddenly becomes fatigued or feels dizzy. The family should be encouraged to participate, as appropriate, and the nurse should not have to support the patients full body weight. Morning and evening activity are not necessarily problematic. 56. After a subarachnoid hemorrhage, the patients laboratory results indicate a serum sodium level of less than 126 mEq/L. What is the nurses most appropriate action? A. Administer a bolus of normal saline as ordered. B. Prepare the patient for thrombolytic therapy as ordered. C. Facilitate testing for hypothalamic dysfunction. D. Prepare to administer 3% NaCl by IV as ordered. Ans: D. The patient may be experiencing syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) or cerebral saltwasting syndrome. The treatment most often is the use of IV hypertonic 3% saline. A normal saline bolus would exacerbate the problem and there is no indication for tests of hypothalamic function or thrombolytic therapy. 57. The nurse is reviewing the medication administration record of a female patient who possesses numerous risk factors for stroke. Which of the womans medications carries the greatest potential for reducing her risk of stroke? A. Naproxen 250 PO b.i.d. B. Calcium carbonate 1,000 mg PO b.i.d. C. Aspirin 81 mg PO o.d. D. Lorazepam 1 mg SL b.i.d. PRN Ans: C. Research findings suggest that low-dose aspirin may lower the risk of stroke in women who are at risk. Naproxen, lorazepam, and calcium supplements do not have this effect. 58. A preceptor is discussing stroke with a new nurse on the unit. The preceptor would tell the new nurse which cardiac dysrhythmia is associated with cardiogenic embolic strokes? A. Ventricular tachycardia B. Atrial fibrillation C. Supraventricular tachycardia D. Bundle branch block Ans: B. Cardiogenic embolic strokes are associated with cardiac dysrhythmias, usually atrial fibrillation. The other listed dysrhythmias are less commonly associated with this type of stroke. 45Adult Health Exam 5 59. After a major ischemic stroke, a possible complication is cerebral edema. Nursing care during the immediate recovery period from an ischemic stroke should include which of the following? A. Positioning to avoid hypoxia B. Maximizing PaCO2 C. Administering hypertonic IV solution D. Initiating early mobilization Ans: A. Interventions during this period include measures to reduce ICP, such as administering an osmotic diuretic (e.g., mannitol), maintaining the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) within the range of 30 to 35 mm Hg, and positioning to avoid hypoxia. Hypertonic IV solutions are not used unless sodium depletion is evident. Mobilization would take place after the immediate threat of increased ICP has past. 60. The nurse is caring for a patient recovering from an ischemic stroke. What intervention best addresses a potential complication after an ischemic stroke? A. Providing frequent small meals rather than three larger meals B. Teaching the patient to perform deep breathing and coughing exercises C. Keeping a urinary catheter in situ for the full duration of recovery D. Limiting intake of insoluble fiber Ans: B. Because pneumonia is a potential complication of stroke, deep breathing and coughing exercises should be encouraged unless contraindicated. No particular need exists to provide frequent meals and normally fiber intake should not be restricted. Urinary catheters should be discontinued as soon as possible. 61. A patient with a new diagnosis of ischemic stroke is deemed to be a candidate for treatment with tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) and has been admitted to the ICU. In addition to closely monitoring the patients cardiac and neurologic status, the nurse monitors the patient for signs of what complication? A. Acute pain B. Septicemia C. Bleeding D. Seizures Ans: C. Bleeding is the most common side effect of t-PA administration, and the patient is closely monitored for any bleeding. Septicemia, pain, and seizures are much less likely to result from thrombolytic therapy. 62. A nurse is caring for a critically ill patient with autonomic dysreflexia. What clinical manifestations would the nurse expect in this patient? A. Respiratory distress and projectile vomiting B. Bradycardia and hypertension C. Tachycardia and agitation D. Third-spacing and hyperthermia Ans: B. Autonomic dysreflexia is characterized by a pounding headache, profuse sweating, nasal congestion, piloerection (goose bumps), bradycardia, and hypertension. It occurs in cord lesions above T6 after spinal shock has resolved; it does not result in vomiting, tachycardia, or third-spacing. 63. The nurse is caring for a patient with increased intracranial pressure (ICP) caused by a traumatic brain injury. Which of the following clinical manifestations would suggest that the patient may be experiencing increased brain compression causing brain stem damage? A. Hyperthermia B. Tachycardia C. Hypertension D. Bradypnea Ans: A. Signs of increasing ICP include slowing of the heart rate (bradycardia), increasing systolic BP, and widening pulse pressure. As brain compression increases, respirations become rapid, BP may decrease, and the pulse slows further. A rapid rise in body temperature is regarded as unfavorable. Hyperthermia increases the metabolic demands of the brain and may indicate brain stem damage. 64. A patient is brought to the ED by her family after falling off the roof. A family member tells the nurse that when the patient fell she was knocked out, but came to and seemed okay. Now she is complaining of a severe headache and not feeling well. The care team suspects an epidural hematoma, prompting the nurse 46Adult Health Exam 5 to prepare for which priority intervention? A. Insertion of an intracranial monitoring device B. Treatment with antihypertensives C. Emergency craniotomy D. Administration of anticoagulant therapy Ans: C. An epidural hematoma is considered an extreme emergency. Marked neurologic deficit or respiratory arrest can occur within minutes. Treatment consists of making an opening through the skull to decrease ICP emergently, remove the clot, and control the bleeding. Antihypertensive medications would not be a priority. Anticoagulant therapy should not be ordered for a patient who has a cranial bleed. This could further increase bleeding activity. Insertion of an intracranial monitoring device may be done during the surgery, but is not priority for this patient. 65. The staff educator is precepting a nurse new to the critical care unit when a patient with a T2 spinal cord injury is admitted. The patient is soon exhibiting manifestations of neurogenic shock. In addition to monitoring the patient closely, what would be the nurses most appropriate action? A. Prepare to transfuse packed red blood cells. B. Prepare for interventions to increase the patients BP. C. Place the patient in the Trendelenberg position. D. Prepare an ice bath to lower core body temperature. Ans: B. Manifestations of neurogenic shock include decreased BP and heart rate. Cardiac markers would be expected to rise in cardiogenic shock. Transfusion, repositioning, and ice baths are not indicated interventions. 66. An ED nurse has just received a call from EMS that they are transporting a 17-year-old man who has just sustained a spinal cord injury (SCI). The nurse recognizes that the most common cause of this type of injury is what? A. Sports-related injuries B. Acts of violence C. Injuries due to a fall D. Motor vehicle accidents Ans: D. The most common causes of SCIs are motor vehicle crashes (46%), falls (22%), violence (16%), and sports (12%). 67. A patient with spinal cord injury has a nursing diagnosis of altered mobility and the nurse recognizes the increased the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Which of the following would be included as an appropriate nursing intervention to prevent a DVT from occurring? A. Placing the patient on a fluid restriction as ordered B. Applying thigh-high elastic stockings C. Administering an antifibrinolyic agent D. Assisting the patient with passive range of motion (PROM) exercises Ans: B. It is important to promote venous return to the heart and prevent venous stasis in a patient with altered mobility. Applying elastic stockings will aid in the prevention of a DVT. The patient should not be placed on fluid restriction because a dehydrated state will increase the risk of clotting throughout the body. Antifibrinolytic agents cause the blood to clot, which is absolutely contraindicated in this situation. PROM exercises are not an effective protection against the development of DVT. 68. Paramedics have brought an intubated patient to the RD following a head injury due to accelerationdeceleration motor vehicle accident. Increased ICP is suspected. Appropriate nursing interventions would include which of the following? A. Keep the head of the bed (HOB) flat at all times. B. Teach the patient to perform the Valsalva maneuver. C. Administer benzodiazepines on a PRN basis. D. Perform endotracheal suctioning every hour. Ans: C. If the patient with a brain injury is very agitated, benzodiazepines are the most commonly used sedatives and 47Adult Health Exam 5 do not affect cerebral blood flow or ICP. The HOB should be elevated 30 degrees. Suctioning should be done a limited basis, due to increasing the pressure in the cranium. The Valsalva maneuver is to be avoided. This also causes increased ICP. 69. A patient who suffered a spinal cord injury is experiencing an exaggerated autonomic response. What aspect of the patients current health status is most likely to have precipitated this event? A. The patient received a blood transfusion. B. The patients analgesia regimen was recent changed. C. The patient was not repositioned during the night shift. D. The patients urinary catheter became occluded Ans: D. A distended bladder is the most common cause of autonomic dysreflexia. Infrequent positioning is a less likely cause, although pressure ulcers or tactile stimulation can cause it. Changes in mediations or blood transfusions are unlikely causes. 70. A patient with a C5 spinal cord injury is tetraplegic. After being moved out of the ICU, the patient complains of a severe throbbing headache. What should the nurse do first? A. Check the patients indwelling urinary catheter for kinks to ensure patency. B. Lower the HOB to improve perfusion. C. Administer analgesia. D. Reassure the patient that headaches are expected after spinal cord injuries. Ans: A. A severe throbbing headache is a common symptom of autonomic dysreflexia, which occurs after injuries to the spinal cord above T6. The syndrome is usually brought on by sympathetic stimulation, such as bowel and bladder distention. Lowering the HOB can increase ICP. Before administering analgesia, the nurse should check the patients catheter, record vital signs, and perform an abdominal assessment. A severe throbbing headache is a dangerous symptom in this patient and is not expected. 71. A patient is admitted to the neurologic ICU with a spinal cord injury. When assessing the patient the nurse notes there is a sudden depression of reflex activity in the spinal cord below the level of injury. What should the nurse suspect? A. Epidural hemorrhage B. Hypertensive emergency C. Spinal shock D. Hypovolemia Ans: C. In spinal shock, the reflexes are absent, BP and heart rate fall, and respiratory failure can occur. Hypovolemia, hemorrhage, and hypertension do not cause this sudden change in neurologic function. 72. An elderly woman found with a head injury on the floor of her home is subsequently admitted to the neurologic ICU. What is the best rationale for the following physician orders: elevate the HOB; keep the head in neutral alignment with no neck flexion or head rotation; avoid sharp hip flexion? A. To decrease cerebral arterial pressure B. To avoid impeding venous outflow C. To prevent flexion contractures D. To prevent aspiration of stomach contents Ans: B. Any activity or position that impedes venous outflow from the head may contribute to increased volume inside the skull and possibly increase ICP. Cerebral arterial pressure will be affected by the balance between oxygen and carbon dioxide. Flexion contractures are not a priority at this time. Stomach contents could still be aspirated in this position. 73. A patient with a T2 injury is in spinal shock. The nurse will expect to observe what assessment finding? A. Absence of reflexes along with flaccid extremities B. Positive Babinskis reflex along with spastic extremities C. Hyperreflexia along with spastic extremities D. Spasticity of all four extremities Ans: A. During the period immediately following a spinal cord injury, spinal shock occurs. In spinal shock, all reflexes are absent and the extremities are flaccid. When spinal shock subsides, the patient demonstrates a positive Babinskis reflex, hyperreflexia, and spasticity of all four extremities. 48Adult Health Exam 5 74. A nurse is reviewing the trend of a patients scores on the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS). This allows the nurse to gauge what aspect of the patients status? A. Reflex activity B. Level of consciousness C. Cognitive ability D. Sensory involvement Ans: B. The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) examines three responses related to LOC: eye opening, best verbal response, and best motor response. 75. The nurse is caring for a patient who is rapidly progressing toward brain death. The nurse should be aware of what cardinal signs of brain death? Select all that apply. A. Absence of pain response B. Apnea C. Coma D. Absence of brain stem reflexes E. Absence of deep tendon reflexes Ans: B, C, D. The three cardinal signs of brain death upon clinical examination are coma, the absence of brain stem reflexes, and apnea. Absences of pain response and deep tendon reflexes are not necessarily indicative of brain death. 76. An 82-year-old man is admitted for observation after a fall. Due to his age, the nurse knows that the patient is at increased risk for what complication of his injury? A. Hematoma B. Skull fracture C. Embolus D. Stroke Ans: A. Two major factors place older adults at increased risk for hematomas. First, the dura becomes more adherent to the skull with increasing age. Second, many older adults take aspirin and anticoagulants as part of routine management of chronic conditions. Because of these factors, the patients risk of a hematoma is likely greater than that of stroke, embolism, or skull fracture. 77. The school nurse is giving a presentation on preventing spinal cord injuries (SCI). What should the nurse identify as prominent risk factors for SCI? Select all that apply. A. Young age B. Frequent travel C. African American race D. Male gender E. Alcohol or drug use Ans: A, D, E. The predominant risk factors for SCI include young age, male gender, and alcohol and drug use. Ethnicity and travel are not risk factors. 78. The nurse is caring for a patient whose spinal cord injury has caused recent muscle spasticity. What medication should the nurse expect to be ordered to control this? A. Baclofen (Lioresal) B. Dexamethasone (Decadron) C. Mannitol (Osmitrol) D. Phenobarbital (Luminal) Ans: A. Baclofen is classified as an antispasmodic agent in the treatment of muscles spasms related to spinal cord injury. Decadron is an anti-inflammatory medication used to decrease inflammation in both SCI and head injury. Mannitol is used to decrease cerebral edema in patients with head injury. Phenobarbital is an anticonvulsant that is used in the treatment of seizure activity. 79. A patient with a spinal cord injury has experienced several hypotensive episodes. How can the nurse best address the patients risk for orthostatic hypotension? A. Administer an IV bolus of normal saline prior to repositioning. B. Maintain bed rest until normal BP regulation returns. 49Adult Health Exam 5 C. Monitor the patients BP before and during position changes. D. Allow the patient to initiate repositioning. Ans: C. To prevent hypotensive episodes, close monitoring of vital signs before and during position changes is essential. Prolonged bed rest carries numerous risks and it is not possible to provide a bolus before each position change. Following the patients lead may or may not help regulate BP. 80. A nurse on the neurologic unit is providing care for a patient who has spinal cord injury at the level of C4. When planning the patients care, what aspect of the patients neurologic and functional status should the nurse consider? A. The patient will be unable to use a wheelchair. B. The patient will be unable to swallow food. C. The patient will be continent of urine, but incontinent of bowel. D. The patient will require full assistance for all aspects of elimination. Ans: D. Patients with a lesion at C4 are fully dependent for elimination. The patient is dependent for feeding, but is able to swallow. The patient will be capable of using an electric wheelchair. 81. The nurse is providing health education to a patient who has a C6 spinal cord injury. The patient asks why autonomic dysreflexia is considered an emergency. What would be the nurses best answer? A. The sudden increase in BP can raise the ICP or rupture a cerebral blood vessel. B. The suddenness of the onset of the syndrome tells us the body is struggling to maintain its normal state. C. Autonomic dysreflexia causes permanent damage to delicate nerve fibers that are healing. D. The sudden, severe headache increases muscle tone and can cause further nerve damage. Ans: A. The sudden increase in BP may cause a rupture of one or more cerebral blood vessels or lead to increased ICP. Autonomic dysreflexia does not directly cause nerve damage. 82. The nurse caring for a patient with a spinal cord injury notes that the patient is exhibiting early signs and symptoms of disuse syndrome. Which of the following is the most appropriate nursing action? A. Limit the amount of assistance provided with ADLs. B. Collaborate with the physical therapist and immobilize the patients extremities temporarily. C. Increase the frequency of ROM exercises. D. Educate the patient about the importance of frequent position changes. Ans: C. To prevent disuse syndrome, ROM exercises must be provided at least four times a day, and care is taken to stretch the Achilles tendon with exercises. The patient is repositioned frequently and is maintained in proper body alignment whether in bed or in a wheelchair. The patient must be repositioned by caregivers, not just taught about repositioning. It is inappropriate to limit assistance for the sole purpose of preventing disuse syndrome. 83. A patient who is being treated in the hospital for a spinal cord injury is advocating for the removal of his urinary catheter, stating that he wants to try to resume normal elimination. What principle should guide the care teams decision regarding this intervention? A. Urinary retention can have serious consequences in patients with SCIs. B. Urinary function is permanently lost following an SCI. C. Urinary catheters should not remain in place for more than 7 days. D. Overuse of urinary catheters can exacerbate nerve damage. Ans: A. Bladder distention, a major cause of autonomic dysreflexia, can also cause trauma. For this reason, removal of a urinary catheter must be considered with caution. Extended use of urinary catheterization is often necessary following SCI. The effect of a spinal cord lesion on urinary function depends on the level of the injury. Catheter use does not cause nerve damage, although it is a major risk factor for UTIs. 84. A patient with spinal cord injury is ready to be discharged home. A family member asks the nurse to review potential complications one more time. What are the potential complications that should be monitored for in this patient? Select all that apply. A. Orthostatic hypotension B. Autonomic dysreflexia C. DVT D. Salt-wasting syndrome E. Increased ICP 50Adult Health Exam 5 Ans: A, B, C. For a spinal cord-injured patient, based on the assessment data, potential complications that may develop include DVT, orthostatic hypotension, and autonomic dysreflexia. Salt-wasting syndrome or increased ICP are not typical complications following the immediate recovery period. 85. The nurse recognizes that a patient with a SCI is at risk for muscle spasticity. How can the nurse best prevent this complication of an SCI? A. Position the patient in a high Fowlers position when in bed. B. Support the knees with a pillow when the patient is in bed. C. Perform passive ROM exercises as ordered. D. Administer NSAIDs as ordered. Ans: C. Passive ROM exercises can prevent muscle spasticity following SCI. NSAIDs are not used for this purpose. Pillows and sitting upright do not directly address the patients risk of muscle spasticity. 86. A patient is admitted to the neurologic ICU with a C4 spinal cord injury. When writing the plan of care for this patient, which of the following nursing diagnoses would the nurse prioritize in the immediate care of this patient? A. Risk for impaired skin integrity related to immobility and sensory loss B. Impaired physical mobility related to loss of motor function C. Ineffective breathing patterns related to weakness of the intercostal muscles D. Urinary retention related to inability to void spontaneously Ans: C. A nursing diagnosis related to breathing pattern would be the priority for this patient. A C4 spinal cord injury will require ventilatory support, due to the diaphragm and intercostals being affected. The other nursing diagnoses would be used in the care plan, but not designated as a higher priority than ineffective breathing patterns. 87. The nurse is caring for the client with increased intracranial pressure. The nurse would note which trend in vital signs if the intracranial pressure is rising? A. Increasing temperature, increasing pulse, increasing respirations, decreasing blood pressure B. Increasing temperature, decreasing pulse, decreasing respirations, increasing blood pressure C. Decreasing temperature, decreasing pulse, increasing respirations, decreasing blood pressure D. Decreasing temperature, increasing pulse, decreasing respirations, increasing blood pressure Ans: B. A change in vital signs may be a late sign of increased intracranial pressure. Trends include increasing temperature and blood pressure and decreasing pulse and respirations. Respiratory irregularities also may occur. 88. A client recovering from a head injury is participating in care. The nurse determines that the client understands measures to prevent elevations in intracranial pressure if the nurse observes the client doing which activity? A. Blowing the nose B. Isometric exercises C. Laughing vigorously D. Exhaling during repositioning Ans: D. Activities that increase intrathoracic and intraabdominal pressures cause an indirect elevation of the intracranial pressure. Some of these activities include isometric exercises, Valsalva's maneuver, coughing, sneezing, and blowing the nose. Exhaling during activities such as repositioning or pulling up in bed opens the glottis, which prevents intrathoracic pressure from rising. 89. A client has clear fluid leaking from the nose following a basilar skull fracture. Which finding would alert the nurse that cerebrospinal fluid is present? A. Fluid is clear and tests negative for glucose. B. Fluid is grossly bloody in appearance and has a pH of 6. C. Fluid clumps together on the dressing and has a pH of 7 D. Fluid separates into concentric rings and tests positive for glucose. Ans: D. Leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the ears or nose may accompany basilar skull fracture. CSF can be distinguished from other body fluids because the drainage will separate into bloody and yellow concentric rings on 51Adult Health Exam 5 dressing material, called a halo sign. The fluid also tests positive for glucose. 90. A client with a spinal cord injury is prone to experiencing autonomic dysreflexia. The nurse should include which measures in the plan of care to minimize the risk of occurrence? Select all that apply. A. Keeping the linens wrinkle-free under the client B. Preventing unnecessary pressure on the lower limbs C. Limiting bladder catheterization to once every 12 hours D. Turning and repositioning the client at least every 2 hours E. Ensuring that the client has a bowel movement at least once a week Ans: A,B,D. The most frequent cause of autonomic dysreflexia is a distended bladder. Straight catheterization should be done every 4 to 6 hours (catheterization every 12 hours is too infrequent), and urinary catheters should be checked frequently to prevent kinks in the tubing. Constipation and fecal impaction are other causes, so maintaining bowel regularity is important. Ensuring a bowel movement once a week is much too infrequent. Other causes include stimulation of the skin from tactile, thermal, or painful stimuli. The nurse administers care to minimize risk in these areas. 91. The nurse is evaluating the neurological signs of a client in spinal shock following spinal cord injury. Which observation indicates that spinal shock persists? A. Hyperreflexia B. Positive reflexes C. Flaccid paralysis D. Reflex emptying of the bladder Ans: C. Resolution of spinal shock is occurring when there is return of reflexes (especially flexors to noxious cutaneous stimuli), a state of hyperreflexia rather than flaccidity, and reflex emptying of the bladder. 92. The nurse is assigned to care for a client with complete right-sided hemiparesis from a stroke (brain attack). Which characteristics are associated with this condition? Select all that apply. A. The client is aphasic. B. The client has weakness on the right side of the body. C. The client has complete bilateral paralysis of the arms and legs. D. The client has weakness on the right side of the face and tongue. E. The client has lost the ability to move the right arm but is able to walk independently. F. The client has lost the ability to ambulate independently but is able to feed and bathe himself or herself without assistance. Ans: A,B,D. Hemiparesis is a weakness of one side of the body that may occur after a stroke. It involves weakness of the face and tongue, arm, and leg on one side. These clients are also aphasic: unable to discriminate words and letters. They are generally very cautious and get anxious when attempting a new task. Complete bilateral paralysis does not occur in hemiparesis. The client with right-sided hemiparesis has weakness of the right arm and leg and needs assistance with feeding, bathing, and ambulating. 93. The nurse is assessing the adaptation of a client to changes in functional status after a stroke (brain attack). Which observation indicates to the nurse that the client is adapting most successfully? A. Gets angry with family if they interrupt a task B. Experiences bouts of depression and irritability C. Has difficulty with using modified feeding utensils D. Consistently uses adaptive equipment in dressing self Ans: D. Clients are evaluated as coping successfully with lifestyle changes after a stroke if they make appropriate lifestyle alterations, use the assistance of others, and have appropriate social interactions. Options 1 and 2 are not adaptive behaviors; option 3 indicates a not yet successful attempt to adapt. 94. The nurse is evaluating the status of a client who had a craniotomy 3 days ago. Which assessment finding would indicate that the client is developing meningitis as a complication of surgery? A. A negative Kernig's sign B. Absence of nuchal rigidity C. A positive Brudzinski's sign D. A Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 Ans: C. Signs of meningeal irritation compatible with meningitis include nuchal rigidity, a positive Brudzinski's sign, and positive Kernig's sign. Nuchal rigidity is characterized by a stiff neck and soreness, which is especially noticeable 52Adult Health Exam 5 when the neck is flexed. Kernig's sign is positive when the client feels pain and spasm of the hamstring muscles when the leg is fully flexed at the knee and hip. Brudzinski's sign is positive when the client flexes the hips and knees in response to the nurse gently flexing the head and neck onto the chest. A Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 is a perfect score and indicates that the client is awake and alert, with no neurological deficits. 95. The nurse has just admitted to the nursing unit a client with a basilar skull fracture who is at risk for increased intracranial pressure. Pending specific health care provider prescriptions, the nurse should safely place the client in which positions? Select all that apply. A. Head in midline B. Neck in neutral position C. HOB at 30-45 degrees D. Head turned to the side when flat in bed E. Neck and jaw flexed forward when opening the mouth Ans: A,B,C. Use of proper positions promotes venous drainage from the cranium to keep intracranial pressure from elevating. The head of the client at risk for or with increased intracranial pressure should be positioned so that it is in a neutral, midline position. The head of the bed should be raised to 30 to 45 degrees. The nurse should avoid flexing or extending the client's neck or turning the client's head from side to side. 96. The nurse in the neurological unit is caring for a client who was in a motor vehicle crash and sustained a blunt head injury. On assessment of the client, the nurse notes the presence of bloody drainage from the nose. Which nursing action is most appropriate? A. Insert nasal packing B. Document the findings C. Contact the HCP D. Monitor the client's blood pressure and check for signs of increased intracranial pressure. Ans: C. Bloody or clear drainage from either the nasal or the auditory canal after head trauma could indicate a cerebrospinal fluid leak. The appropriate nursing action is to notify the HCP, because this finding requires immediate intervention. The remaining options are inappropriate nursing actions in this situation. 97. The nurse is caring for a client who has undergone a craniotomy and has a supratentorial incision. The nurse should place the client in which position postoperatively? A. HOB, head and neck midline B. HOB flat, head turned to the non-operative side C. HOB elevated 30 to 45 degrees, head and neck midline D. HOB elevated 3- to 45, head turned to the operative side Ans: C. After supratentorial surgery, the head is kept at a 30- to 45-degree angle. The head and neck should not be angled either anteriorly or laterally but rather should be kept in a neutral (midline) position. This promotes venous return through the jugular veins, which will help prevent a rise in intracranial pressure. 98. The nurse is assessing fluid balance in a client who has undergone a craniotomy. The nurse should assess for which finding as a sign of overhydration, which would aggravate cerebral edema? A. Unchanged weight B. Shift intake 950mL, output 900mL C. BUN 10mg/dL D. Serum osmolarity 280mOsm/kg H2O Ans: D. After craniotomy the goal is to keep the serum osmolality on the high side of normal to minimize excess body water and control cerebral edema. The normal serum osmolality is 285 to 295 mOsm/kg H2O (285 to 295 mmol/kg). A higher value indicates dehydration; a lower value indicates overhydration. Stable weight indicates that there is neither fluid excess nor fluid deficit. A difference of 50 mL in intake and output for an 8-hour shift is insignificant. The BUN of 10 mg/dL (3.6 mmol/L) is within normal range and does not indicate overhydration or underhydration. 99. A client with a spinal cord injury at the level of C5 has a weakened respiratory effort and ineffective cough and is using accessory neck muscles in breathing. The nurse carefully monitors the client and suspects the presence of which problem? A. Altered breathing pattern B. Increased likelihood of injury C. Ineffective oxygen consumption 53Adult Health Exam 5 D. Increased susceptibility to aspiration Ans: A. Altered breathing pattern indicates that the respiratory rate, depth, rhythm, timing, or chest wall movements are insufficient for optimal ventilation of the client. This is a risk for clients with spinal cord injury in the lower cervical area. Ineffective oxygen consumption occurs when oxygenation or carbon dioxide elimination is altered at the alveolar-capillary membrane. Increased susceptibility to aspiration and increased likelihood of injury are unrelated to the subject of the question. 100. The nurse is assessing the client's gait and notes it is unsteady and staggering. Which description should the nurse use when documenting the assessment finding? A. Spastic B. Ataxic C. Festinating D. Dystrophic or broad-based Ans: B. An ataxic gait is characterized by unsteadiness and staggering. A spastic gait is characterized by stiff, short steps with the legs held together, hip and knees flexed, and toes that catch and drag. A festinating gait is best described as walking on the toes with an accelerating pace. A dystrophic or broad-based gait is seen as waddling, with the weight shifting from side to side and the legs far apart 101. Which intervention should the nurse include in a postoperative teaching plan for a client who underwent a spinal fusion and will be wearing a brace? A. Tell the client to inspect the environment for safety hazards B. Inform the client about the importance of sitting as much as possible. C. Inform the client that lotions and body powders can be used for skin breakdown. D. Instruct the client to tighten the brace during meals and to loosen it for the first 30 minutes after each meal. Ans: A. The client must inspect the environment for safety hazards. The client is instructed in the importance of avoiding prolonged sitting and standing. Powders and lotions should not be used because they may irritate the skin. The client should be taught to loosen the brace during meals and for 30 minutes after each meal. The client may have difficulty eating if the brace is too tight. Loosening the brace after each meal will allow adequate nutritional intake and promote comfort. 102. The nurse is preparing to care for a client after a lumbar puncture. The nurse should plan to place the client in which best position following the procedure? A. Prone in semi Fowler's position B. Supine in semi Fowler's position C. Prone with a small pillow under the abdomen D. Lateral with the head slightly lower than the rest of the body Ans: C. After the procedure, the client assumes a flat position. If the client is able, a prone position with a pillow under the abdomen is the best position. This position helps reduce cerebrospinal fluid leakage and decreases the likelihood of post–lumbar puncture headache. The remaining options are incorrect. 103. The student nurse develops a plan of care for a client after a lumbar puncture. The nursing instructor corrects the student if the student documents which incorrect intervention in the plan? A. Maintain the client in a flat position. B. Restrict fluid intake for a period of 2 hours. C. Assess the client's ability to void and move the extremities. D. Inspect the puncture site for swelling, redness, and drainage. Ans: B. After the lumbar puncture the client remains flat in bed for at least 2 hours, depending on the health care provider's prescriptions. A liberal fluid intake is encouraged to replace the cerebrospinal fluid removed during the procedure, unless contraindicated by the client's condition. The nurse checks the puncture site for redness and drainage and assesses the client's ability to void and move the extremities. 104. The nurse is monitoring a client who has returned to the nursing unit after a myelogram. Which client complaint would indicate the need to notify the health care provider (HCP)? A. Backache 54Adult Health Exam 5 B. Headache C. Neck stiffness D. Feelings of fatigue Ans: C. Headache is relatively common after the procedure, but neck stiffness, especially on flexion, and pain should be reported because they signal meningeal irritation. The client also is monitored for evidence of allergic reactions to the dye such as confusion, dizziness, tremors, and hallucinations. Feelings of fatigue may be normal, and back discomfort may occur because of the positions required for the procedure. 105. The nurse is caring for a client with a head injury. The client's intracranial pressure reading is 8 mm Hg. Which condition should the nurse document? A. ICP is normal B. ICP is elevated C. ICP is borderline D. ICP is too low Ans: A. The normal intracranial pressure is 5 to 15 mm Hg. A pressure of 8 mm Hg is within normal range. 106. The nurse in the neurological unit is monitoring a client for signs of increased intracranial pressure (ICP). The nurse reviews the assessment findings for the client and notes documentation of the presence of Cushing's reflex. The nurse determines that the presence of this reflex is obtained by assessing which item? A. Blood pressure B. Motor response C. Pupillary response D. Level of consciousness Ans: A. Cushing's reflex is a late sign of increased ICP and consists of a widening pulse pressure (systolic pressure rises faster than diastolic pressure) and bradycardia. The remaining options are unrelated to monitoring for Cushing's reflex. 107. The nurse is performing the oculocephalic response (doll's eyes maneuver) on an unconscious client. The nurse turns the client's head and notes movement of the eyes in the same direction as the head. How should the nurse document these findings? A. Normal B. Abnormal C. Insignificant D. Inconclusive Ans: B. In an unconscious client, eye movements are an indication of brainstem activity and are tested by the oculocephalic response. When the doll's eyes maneuver is intact, the eyes move in the opposite direction when the head is turned. Abnormal responses include movement of the eyes in the same direction as the head and maintenance of a midline position of the eyes when the head is turned. An abnormal response indicates a disruption in the processing of information through the brainstem. 108. The nurse is reviewing the medical records of a client admitted to the nursing unit with a diagnosis of a thrombotic brain attack (stroke). The nurse would expect to note that which is documented in the assessment data section of the record? A. Sudden loss of consciousness occurred. B. Signs and symptoms occurred suddenly. C. The client experienced paresthesias a few days before admission to the hospital D. The client complained of a severe headache, which was followed by sudden onset of paralysis. Ans: C. Cerebral thrombosis does not occur suddenly. In the few hours or days preceding a thrombotic brain attack (stroke), the client may experience a transient loss of speech, hemiplegia, or paresthesias on 1 side of the body. Signs and symptoms of thrombotic brain attack (stroke) vary but may include dizziness, cognitive changes, or seizures. Headache is rare, but some clients with stroke (brain attack) experience signs and symptoms similar to those of cerebral embolism or intracranial hemorrhage. 109. The nurse in the health care clinic is providing medication instructions to a client with a seizure disorder who will be taking divalproex sodium. The nurse should instruct the client about the importance of returning 55Adult Health Exam 5 to the clinic for monitoring of which laboratory study? A. Electrolyte panel B. Liver function studies C. Renal function studies D. Blood glucose level determination Ans: B. Divalproex sodium, an anticonvulsant, can cause fatal hepatotoxicity. The nurse should instruct the client about the importance of monitoring the results of liver function studies and ammonia level determinations. The studies in the remaining options are not required with the use of this medication. 110. The nurse assesses a client who is diagnosed with a stroke (brain attack). On assessment, the client is unable to understand the nurse's commands. Which condition should the nurse document? A. Occipital lobe impairment B. Damage to the auditory association areas C. Frontal lobe and optic nerve tracts damage D. Difficulty with concept formation and abstraction areas Ans: B. Auditory association and storage areas are located in the temporal lobe and relate to understanding spoken language. The occipital lobe contains areas related to vision. The frontal lobe controls voluntary muscle activity, including speech, and an impairment can result in expressive aphasia. The parietal lobe contains association areas for concept formation, abstraction, spatial orientation, body and object size and shape, and tactile sensation. 111. The nurse is creating a plan of care for a client with dysphagia following a stroke (brain attack). Which should the nurse include in the plan? Select all that apply. A. Thicken liquids. B. Assist the client with eating C. Assess for the presence of a swallow reflex. D. Place the food on the affected side of the mouth. E. Provide ample time for the client to chew and swallow. Ans: A,B,C,E. Liquids are thickened to prevent aspiration. The nurse should assist the client with eating and place food on the unaffected side of the mouth. The nurse should assess for gag and swallowing reflexes before the client with dysphagia is started on a diet. The client should be allowed ample time to chew and swallow to prevent choking. 112. The nurse in the neurological unit is caring for a client with a supratentorial lesion. The nurse assesses which measurement as the most critical index of central nervous system (CNS) dysfunction? A. Temperature B. Blood pressure C. Ability to speak D. Level of consciousness Ans: D. Level of consciousness is the most critical index of CNS dysfunction. Changes in level of consciousness can indicate clinical improvement or deterioration. Although blood pressure, temperature, and ability to speak may be components of the assessment, the client's level of consciousness is the most critical index of CNS dysfunction. 113. The nurse is caring for a client after a craniotomy and monitors the client for signs of increased intracranial pressure (ICP). Which finding, if noted in the client, would indicate an early sign of increased ICP? A. Confusion B. Bradycardia C. Sluggish pupils D. Widened pulse pressure Ans: A. Early manifestations of increased ICP are subtle and often may be transient, lasting for only a few minutes in some cases. These early clinical manifestations include episodes of confusion, drowsiness, and slight pupillary and breathing changes. Later manifestations include a further decrease in the level of consciousness, a widened pulse pressure, and bradycardia. Cheyne-Stokes respiratory pattern, or a hyperventilation respiratory pattern, and pupillary sluggishness and dilatation appear in the late stages. 114. The nurse is planning discharge teaching for a client started on acetazolamide for a supratentorial lesion. Which information about the primary action of the medication should be included in the client's education? A. It will prevent hypertension. 56Adult Health Exam 5 B. It will prevent hyperthermia. C. It decreases cerebrospinal fluid production. D. It maintains adequate blood pressure for cerebral perfusion. Ans: C. Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and a diuretic. It is used in the client with or at risk for increased intracranial pressure to decrease cerebrospinal fluid production. The remaining options are not actions of this medication. 115. The nurse is preparing for the admission to the unit of a client with a diagnosis of seizures and asks the nursing student to institute full seizure precautions. Which item if noted in the client's room would need to be removed and warrants the need to review seizure precautions with the student? A. Oxygen course B. Suction machine C. Padded tongue blade D. Padding for the side rails Ans: C. Full seizure precautions include bed rest with padded side rails in a raised position, a suction machine at the bedside, having diazepam or lorazepam available, and providing an oxygen source. Objects such as tongue blades are contraindicated and should never be placed in the client's mouth during a seizure. 116. The clinic nurse is reviewing the record of a client scheduled to be seen in the clinic. The nurse notes that the client is taking selegiline hydrochloride. The nurse suspects that the client has which disorder? A. Diabetes mellitus B. Parkinson’s disease C. Alzheimer's disease D. Coronary artery disease Ans: B. Selegiline hydrochloride is an antiparkinsonian medication. The medication increases dopaminergic action, assisting in the reduction of tremor, akinesia, and the rigidity of parkinsonism. This medication is not used to treat diabetes mellitus, Alzheimer's disease, or coronary artery disease. 117. The nurse is creating a plan of care for a client with a diagnosis of stroke (brain attack). On reviewing the client's record, the nurse notes an assessment finding of anosognosia. The nursing care plan should address which manifestation related to this finding? A. Patient will be easily fatigues B. Patient will have difficulty speaking C. Patient will have difficulty swallowing D. Patient will exhibit neglect of the affected side Ans: D. In anosognosia, the client neglects the affected side of the body. The client either may ignore the presence of the affected side (often creating a safety hazard as a result of potential injuries) or may state that the involved arm or leg belongs to someone else. The remaining options are not associated with anosognosia. 118. The nurse is caring for a client who sustained a spinal cord injury. During administration of morning care, the client begins to exhibit signs and symptoms of autonomic dysreflexia. Which initial nursing action should the nurse take? A. Elevate the HOB B. Examine the rectum digitally C. Assess the client’s blood pressure D. Place the cline in the prone position Ans: A. Autonomic dysreflexia is a serious complication that can occur in the spinal cord–injured client. Once the syndrome is identified, the nurse elevates the head of the client's bed and then examines the client for the source of noxious stimuli. The nurse also assesses the client's blood pressure, but the initial action would be to elevate the head of the bed. The client would not be placed in the prone position; lying flat will increase the client's blood pressure. 119. The home care nurse is visiting a client with a diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. The client is taking benztropine mesylate orally daily. The nurse provides information to the spouse regarding the side effects of this medication and should tell the spouse to report which side effect if it occurs? A. Shuffling gait 57Adult Health Exam 5 B. Inability to urinate C. Decreased appetite D. Irregular bowel movements Ans: B. Benztropine mesylate is an anticholinergic, which causes urinary retention as a side effect. The nurse would instruct the client or spouse about the need to monitor for difficulty with urinating, a distended abdomen, infrequent voiding in small amounts, and overflow incontinence. The remaining options are unrelated to the use of this medication. 120. The nurse is documenting nursing observations in the record of a client who experienced a tonic-clonic seizure. Which clinical manifestation did the nurse most likely note in the clonic phase of the seizure? A. Body stiffening B. Spasms of the entire body C. Sudden loss of consciousness D. Brief flexion of the extremities Ans: B. The clonic phase of a seizure is characterized by alternating spasms and momentary muscular relaxation of the entire body, accompanied by strenuous hyperventilation. The face is contorted and the eyes roll. Excessive salivation results in frothing from the mouth. The tongue may be bitten, the client sweats profusely, and the pulse is rapid. The clonic jerking subsides by slowing in frequency and losing strength of contractions over a period of 30 seconds. Body stiffening, sudden loss of consciousness, and brief flexion of the extremities are associated with the tonic phase of a seizure. 121. At 8:00 a.m., A client who has had a stroke (brain attack) was awake and alert with vital signs of temperature 98°F (37.2°C) orally, pulse 80 beats/min, respirations 18 breaths/min, and blood pressure 138/80 mm Hg. At noon, the client is confused and only responsive to tactile stimuli, and vital signs are temperature 99°F (36.7°C) orally, pulse 62 beats/min, respirations 20 breaths/min, and blood pressure 166/72 mm Hg. The nurse should take which action? A. Reorient the client B. Retake the vital signs C. Call the HCP D. Administer an antihypertensive medication as needed Ans: C. The important nursing action is to call the HCP. The deterioration in neurological status, decreasing pulse, and increasing blood pressure with a widening pulse pressure all indicate that the client is experiencing increased intracranial pressure, which requires immediate treatment to prevent further complications and possible death. The nurse should retake the vital signs and reorient the client to surroundings. If the client's blood pressure falls within parameters for PRN antihypertensive medication, the medication also should be administered. However, options 1, 2, and 4 are secondary nursing actions. 122. A client had a transsphenoidal resection of the pituitary gland. The nurse notes drainage on the nasal dressing. Suspecting cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage, the nurse should look for drainage that is of which characteristic? A. Serosanguineous B. Bloody with small clots C. Sanguineous with no clots D. Serosanguineous, surrounded by clear to straw-colored liquid Ans: D. CSF leakage after cranial surgery may be detected by noting drainage that is serosanguineous (from the surgery) and surrounded by an area of clear or straw-colored drainage. The typical appearance of CSF drainage is that of a "halo." The nurse also would further verify actual CSF drainage by testing the drainage for glucose, which would be positive. 123. A client who has a spinal cord injury that resulted in paraplegia experiences a sudden onset of severe headache and nausea. The client is diaphoretic with piloerection and has flushing of the skin. The client's systolic blood pressure (BP) is 210 mm Hg. What should the nurse immediately suspect? A. Return of spinal shock B. Malignant hypertension 58Adult Health Exam 5 C. Impending brain attack (stroke) D. Autonomic dysreflexia Ans: D. Autonomic dysreflexia (hyperreflexia) results from sudden strong discharge of the sympathetic nervous system in response to a noxious stimulus. Signs and symptoms include pounding headache, nausea, nasal stuffiness, flushed skin, piloerection, and diaphoresis. Severe hypertension can occur, with a systolic BP rising potentially as high as 300 mm Hg. It often is triggered by thermal or mechanical events such as a kinking of catheter tubing, constipation, urinary tract infection, or any variety of cutaneous stimuli. The nurse must recognize this situation immediately and take corrective action to remove the stimulus. If untreated, this medical emergency could result in stroke, status epilepticus, or possibly death. 124. The nurse is assessing a client who is experiencing seizure activity. The nurse understands that it is necessary to determine information about which items as part of routine assessment of seizures? Select all that apply. A. Postictal status B. Duration of the seizure C. Changes in pupil size or eye deviation D. Seizure progression and type of movements E. What the client ate in the 2 hours preceding seizure activity Ans: A,B,C,D. Typically seizure assessment includes the time the seizure began, parts of the body affected, type of movements and progression of the seizure, change in pupil size or eye deviation or nystagmus, client condition during the seizure, and postictal status. Determining what the client ate 2 hours prior to the seizure is not a component of seizure assessment. 125. The nurse has a prescription to administer a medication to a client who is experiencing shivering as a result of hyperthermia. Which medication should the nurse anticipate to be prescribed? A. Buspirone B. Fluphenazine C. Chlorpromazine D. Prochlorperazine Ans: C. Chlorpromazine is used to control shivering in hyperthermic states. It is a phenothiazine and has antiemetic and antipsychotic uses, especially when psychosis is accompanied by increased psychomotor activity. Buspirone is an anxiolytic. Prochlorperazine is a phenothiazine that is an antiemetic and antipsychotic. Fluphenazine is a phenothiazine that is used as an antipsychotic 126. The nurse is caring for a client with an intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring device. The nurse should become most concerned if the ICP readings drifted to and stayed in the vicinity of which finding? A. 5mmHg B. 8mmHg C. 14mmHg D. 22mmHg Ans: D. Normal ICP readings range from 5 to 15mmHg pressure. Pressures greater than 20mm Hg are considered to represent increased ICP, which seriously impairs cerebral perfusion. 127. A client with a traumatic brain injury is on mechanical ventilation. The nurse promotes normal intracranial pressure (ICP) by ensuring that the client's arterial blood gas (ABG) results are within which ranges? A. PaO2 60 to 100mmHg (60 to 100mmHg), PaCo2 25 to 30mmHg (25 to 30mmHg) B. PaO2 60 to 100mmHg (60 to 100mmHg), PaCo2 30 to 35mmHg (30 to 35mmHg) C. PaO2 80 to 100mmHg (80 to 100mmHg), PaCo2 25 to 30mmHg (25 to 30mmHg) D. PaO2 80 to 100mmHg (80 to 100mmHg), PaCo2 35 to 38mmHg (35 to 38mmHg) Ans: D. The goal is to maintain the partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide (PaCo2) at 35 to 38 mm Hg (35 to 38 mm Hg). Carbon dioxide is a very potent vasodilator that can contribute to increases in ICP. The PaO2 is not allowed to fall below 80 mm Hg (80 mm Hg), to prevent cerebral vasodilation from hypoxemia, which can also result in an increase 59Adult Health Exam 5 in ICP. Therefore, the remaining options are incorrect. 128. A client was seen and treated in the hospital emergency department for a concussion. The nurse determines that the family needs further teaching if they verbalize to call the health care provider (HCP) for which client sign or symptom? A. Vomiting B. Minor headache C. Difficulty speaking D. Difficulty awakening Ans: B. A concussion after head injury is a temporary loss of consciousness (from a few seconds to a few minutes) without evidence of structural damage. After concussion, the family is taught to monitor the client and call the HCP or return the client to the emergency department for signs and symptoms such as confusion, difficulty awakening or speaking, one-sided weakness, vomiting, and severe headache. Minor headache is expected. 129. The nurse is caring for a client with an intracranial aneurysm who has been alert. Which signs and symptoms are an early indication that the level of consciousness (LOC) is deteriorating? Select all that apply. A. Mild drowsiness B. Drooping eyelids C. Ptosis of left eyelid D. Slight slurring of speech E. Less frequent spontaneous speech Ans: A,D,E. Early changes in LOC relate to orientation, alertness, and verbal responsiveness. Mild drowsiness, slight slurring of speech, and less frequent spontaneous speech are early signs of decreasing LOC. Ptosis (drooping) of the eyelid is caused by pressure on and dysfunction of cranial nerve III. Once ptosis occurs, it is ongoing; it does not relate to LOC. 130. A client has sustained damage to Wernicke's area from a stroke (brain attack). On assessment of the client, which sign or symptom would be noted? A. Difficulty speaking B. Problem with understanding language C. Difficulty controlling voluntary motor activity D. Problem with articulating events from the remote past Ans: B. Wernicke's area consists of a small group of cells in the temporal lobe whose function is the understanding of language. Damage to Broca's area is responsible for aphasia. The motor cortex in the precentral gyrus controls voluntary motor activity. The hippocampus is responsible for the storage of memory. 131. A client has suffered damage to Broca's area of the brain. Which priority assessment should the nurse perform? A. Speech B. Hearing C. Balance D. Level of consciousness Ans: A. Broca's area in the brain is responsible for the motor aspects of speech, through coordination of the muscular activity of the tongue, mouth, and larynx. The term assigned to damage in this area is aphasia. The items listed in the other options are not the responsibility of Broca's area. 132. The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease. The nurse should anticipate that the client has changes in which component of the nervous system? A. Glia B. Peripheral nerves C. Neuronal dendrites D. Monoamine oxidase Ans: C. Alzheimer's disease is characterized by changes in the dendrites of the neurons. The decrease in the number and composition of the dendrites is responsible for the symptoms of the disease. The components in the other options are not related to the pathology of Alzheimer's disease. 60Adult Health Exam 5 133. To promote optimal cerebral tissue perfusion in the postoperative phase following cranial surgery, the nurse should place the client with an incision in the anterior or middle fossa, in which position? A. 15 degrees of Trendelenburg's B. Side-lying with the head of the bed flat C. With the head of the bed elevated at least 30 degrees D. With the head of the bed elevated no more than 10 degrees Ans: C. Correct positioning of the client following cranial surgery is important to avoid increased intracranial pressure and to promote optimal cerebral tissue perfusion. The surgeon's prescription for positioning is always followed. The client with an incision in the anterior or middle fossa should be positioned with the head of bed (HOB) elevated at least 30 degrees. If the incision is in the posterior fossa or burr holes have been made, the client is positioned flat, or with the HOB elevated no more than 10 to 15 degrees. If a craniectomy (bone flap) is performed, the client should not be positioned to the operative side. Trendelenburg's position is contraindicated in the postoperative phase following cranial surgery. 134. A client with myasthenia gravis arrives at the hospital emergency department in suspected crisis. The health care provider plans to administer edrophonium to differentiate between myasthenic and cholinergic crises. The nurse ensures that which medication is available in the event that the client is in cholinergic crisis? A. Atropine sulfate B. Morphine sulfate C. Protamine sulfate D. Pyridostigmine bromide Ans: C. Clients with cholinergic crisis have experienced overdosage of medication. Edrophonium will exacerbate symptoms in cholinergic crisis to the point at which the client may need intubation and mechanical ventilation. Intravenous atropine sulfate is used to reverse the effects of these anticholinesterase medications. Morphine sulfate and pyridostigmine bromide would worsen the symptoms of cholinergic crisis. Protamine sulfate is the antidote for heparin. 135. The nurse is caring for a client who has just been admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of a hemorrhagic stroke. The nurse should place the client in which position? A. Prone B. Supine C. Semi Fowler's with the hip and the neck flexed D. HOB elevated 30 degrees with the head in midline position Ans: D. The health care provider's prescriptions are always followed with regard to positioning the client after stroke. Clients with hemorrhagic stroke usually have the head of the bed elevated to 30 degrees to reduce intracranial pressure that can occur from the hemorrhage. The head should be in a midline, neutral position to facilitate venous drainage from the brain. Extreme hip and neck flexion should be avoided to prevent an increase in intrathoracic pressure and to promote venous drainage from the brain. For clients with ischemic stroke, the head of the bed usually is kept flat to ensure adequate blood flow and thus oxygenation to the brain. Prone, supine, and hip and neck flexion are incorrect positions for clients with hemorrhagic stroke. 136. The nurse is preparing to care for a client who had a supratentorial craniotomy. The nurse should plan to place the client in which position? A. Prone B. Supine C. Side-lying D. Semi Flower’s Ans: D. After supratentorial surgery (surgery above the tentorium of the brain), the head of the client's bed usually is elevated 30 degrees to promote venous outflow through the jugular veins. Prone, supine, and side-lying denote incorrect positions after this surgery, and these positions could result in edema at the surgical site and increased intracranial pressure. The health care provider's prescriptions are always followed with regard to positioning the client. 61Adult Health Exam 5 137. The nurse has just admitted to the nursing unit a client with a basilar skull fracture who is at risk for increased intracranial pressure (ICP). Pending specific health care provider prescriptions, the nurse should plan to place the client in which positions? Select all that apply. A. Head midline B. Neck in neutral position C. Flat, with head turned to the side D. Head of bed elevated 30 to 45 degrees E. Head of bed elevated with the neck extended Ans: A,B,D. The client who is at risk for or who has increased ICP should be positioned so that the head is in a neutral, midline position. The nurse should avoid flexing or extending the client's neck or turning the head from side to side. The head of the bed should be raised to 30 to 45 degrees. Use of proper positions promotes venous drainage from the cranium to keep ICP down. 138. The nurse is caring for a client who is at risk for increased intracranial pressure (ICP) after a stroke. Which activities performed by the nurse will assist with preventing increases in ICP? Select all that apply. A. Clustering nursing activities B. Hyperoxygenating before suctioning C. Maintaining 20 degree flexion of the knees D. Maintaining the head and neck in midline position E. Maintaining the head of the bed (HOB) at 30 degrees elevation Ans: B,D,E. Measures aimed at preventing increased ICP in the poststroke client include hyperoxgenating before suctioning to avoid transient hypoxemia and resultant ICP elevation from dilation of cerebral arteries; maintaining the head in a midline, neutral position to help promote venous drainage from the brain; and keeping the HOB elevated to between 25 and 30 degrees to prevent a decreased blood flow to the brain. Clustering activities can be stressful for the client and increase ICP. Maintaining 20 degree flexion of the knees increases intra-abdominal pressure and consequently ICP. 139. The nurse is caring for the client who suffered a spinal cord injury 48 hours ago. What should the nurse assess for when monitoring for gastrointestinal complications? A. History of diarrhea B. Flattened abdomen C. Hyperactive bowel sounds D. Hematest-positive NGT drainage Ans: D. Development of a stress ulcer also can occur after spinal cord injury and can be detected by Hematestpositive nasogastric tube aspirate or stool. The client is also at risk for paralytic ileus, which is characterized by the absence of bowel sounds and abdominal distention. A history of diarrhea is irrelevant. 140. The client with a head injury opens eyes to sound, has no verbal response, and localizes to painful stimuli when applied to each extremity. How should the nurse document the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score? A. GCS=3 B. GCS=6 C. GCS=9 D. GCS=11 Ans: C. The GCS is a method for assessing neurological status. The highest possible GCS score is 15. A score lower than 8 indicates that coma is present. Motor response points are as follows: Obeys a simple response = 6; Localizes painful stimuli = 5; Normal flexion (withdrawal) = 4; Abnormal flexion (decorticate posturing) = 3; Extensor response (decerebrate posturing) = 2; No motor response to pain = 1. Verbal response points are as follows: Oriented = 5; Confused conversation = 4; Inappropriate words = 3; Responds with incomprehensible sounds = 2; No verbal response = 1. Eye opening points are as follows: Spontaneous = 4; In response to sound = 3; In response to pain = 2; No response, even to painful stimuli = 1. Using the GCS, a score of 3 is given when the client opens the eyes to sound. Localization to pain is scored as 5. When there is no verbal response the score is 1. The total score is then equal to 9. 141. The client with a spinal cord injury at the level of T4 is experiencing a severe throbbing headache with a blood pressure of 180/100 mm Hg. What is the priority nursing intervention? 62Adult Health Exam 5 A. Notify HCP B. Loosen tight clothing on the client. C. Place the client in a sitting position. D. Check the urinary catheter tubing for kinks or obstruction. Ans: C. The client is demonstrating clinical manifestations of autonomic dysreflexia, which is a neurological emergency. The first priority is to place the client in a sitting position to prevent hypertensive stroke. Loosening tight clothing and checking the urinary catheter can then be done, and the HCP can be notified once initial interventions are done. 142. A client is newly admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of stroke (brain attack) manifested by complete hemiplegia. Which item in the medical history of the client should the nurse be most concerned about? A. Glaucoma B. Emphysema C. Hypertension D. Diabetes mellitus Ans: B. The nurse should be most concerned about emphysema. The respiratory system is the priority in the acute phase of a stroke. The client with a stroke is vulnerable to respiratory complications such as atelectasis and pneumonia. Because the client has complete hemiplegia (is unable to move) and has emphysema, these risks are very significant. Although the other conditions of glaucoma, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus are important, they are not as significant as emphysema. 143. The nurse caring for a client following craniotomy who has a supratentorial incision understands that the client should most likely be maintained in which position? A. Prone position B. Supine position C. Semi Fowler’s position D. Dorsal recumbent position Ans: C. In supratentorial surgery (surgery above the brain's tentorium), the client's head is usually elevated 30 degrees to promote venous outflow through the jugular veins. The client's head or the head of the bed is not lowered in the acute phase of care after supratentorial surgery. An exception to this is the client who has undergone evacuation of a chronic subdural hematoma, but a health care provider's (HCP's) prescription is required for positions other than those involving head elevation. In addition, the HCP's prescription regarding positioning is always checked and agency procedures are always followed. 144. The nurse is planning to perform an assessment of the client's level of consciousness using the Glasgow Coma Scale. Which assessments should the nurse include in order to calculate the score? Select all that apply. A. Eye opening B. Reflex response C. Best verbal response D. Best motor response E. Pupil size and reaction Ans: A,C,D. Assessment of pupil size and reaction and reflex response are not part of the Glasgow Coma Scale. The 3 categories included are eye opening, best verbal response, and best motor response. Pupil assessment and reflex response is a necessary part of a total assessment of the neurological status of a client but is not part of this particular scale. 145. A client with a traumatic closed head injury shows signs of secondary brain injury. What are some manifestations of secondary brain injury? Select all that apply. A. Fever B. Seizures C. Hypoxia D. Ischemia E. Hypotension 63Adult Health Exam 5 F. ICP Ans: C,D,E,F. Secondary brain injury can occur several hours to days after the initial brain injury and is a major concern when managing brain trauma. Nursing management of the client with an acute intracranial problem must include management of secondary injury. Manifestations of secondary injury includes hypoxia, ischemia, hypotension, and increased ICP that follows primary injury. It does not include fever or seizures. 146. A patient with a SCI at T5 begins to complain of a severe headache and is diaphoretic and nauseated. Which nursing intervention would not be appropriate? A. Place the patient immediately in a sitting position B. Lower the patient to a flat, side-lying position. C. Assess for bladder distention. D. Assess the rectum for a fecal mass. Ans: The patient is suffering from autonomic dysreflexia the most appropriate intervention is to lower the patient to a flat, side-lying position. 147. When assessing the client with a cord transection above T5 for possible complications, which of the following should the nurse expect as least likely to occur? A. Diarrhea B. Paralytic ileus C. Stress ulcers D. Intra-abdominal bleeding Ans: A, in SCI more likely to have constipation not diarrhea. 148. Which of the following should the nurse use as the best method to assess for the development of lower extremity DVT in a client with a spinal cord injury? A. Homan’s sign B. Pain C. Tenderness D. Leg girth Ans: D. To assess for DVT measure calf/leg circumference and compare with other leg. 149. During the period of spinal shock, the nurse should expect the client’s bladder function to be which of the following? A. Spastic B. Normal C. Atonic D. Uncontrolled Ans: C. Atonic or non functional, need urinary catheter to prevent over distention of bladder. 150. When the client has a cord transection at T4, which of the following is the primary focus of the nursing assessment? A. Renal status B. Vascular status C. GI function D. Biliary function 151. Which of the following will the nurse observe in the client in the ictal phase of a generalized tonic-clonic seizure? A. Jerking in one extremity that spreads gradually to adjacent areas B. Vacant staring and abruptly ceasing all activity C. Facial grimaces, patting motions, and lip smacking D. Loss of consciousness, body stiffening, and violent muscle contractions 152. You see someone having a seizure. What is the order you do the following? A. Maintain a patent airway B. Record the seizure activity observed C. Ease the client to the floor D. Obtain vital signs 64Adult Health Exam 5 153. Which of the following is an initial sign of Parkinson disease? Second? Third? A. Rigidity B. Tremor C. Bradykinesia D. Akinesia 154. Which of the following is the second sign of Parkinson disease? A. Rigidity B. Tremor C. Bradykinesia D. Akinesia 155. Which of the following is an the third sign of Parkinson disease? A. Rigidity B. Tremor C. Bradykinesia D. Akinesia 156. Which of the following is an the fourth sign of Parkinson disease? A. Rigidity B. Tremor C. Bradykinesia D. Akinesia 157. Which nursing approach is most helpful to a patient with PD who is experiencing a freezing gait with difficulty initiating movement? A. Pull the patient forward to initiate movement B. Instruct the patient to use a wheelchair C. Have the patient remain still D. Tell the patient to march in place 158. The nurse develops a teaching plan for a patient newly diagnosed with PD. Which topic is most important to include in the plan? A. Maintaining a balanced nutritional diet B. Enhancing the immune system C. Maintaining a safe environment D. Engaging in diversional activities 159. A patient with PD is prescribed levodopa (L-dopa) therapy. Improvement in which area indicates effective therapy? A. Mood B. Muscle rigidity C. Appetite D. Alertness 160. A 50 yo man develops sudden expressive aphasia and left sided motor weakness. This information tells the RN that the lesion is likely located: A. In the cerebellum B. Right frontal lobe C. Left temporal lobe D. Occipital lobe Ans: B, expressive aphasia is difficulty getting the words out. If s/s present in the left side then the injury is in the opposite side of the brain. 161. A patient with a TBI is positioned with HOB at 45 degrees with the neck in a neutral position. The RN knows that the reason for this position is: A. To prevent aspiration 65Adult Health Exam 5 B. To improve ventilation preventing atelectasis C. To reduce intracranial pressure D. To prevent a DVT 162. A patient is admitted with an ischemic stroke. The RN knows that the best position for this patient is: A. HOB elevated and neck in neutral position B. Supine or Lateral with HOB less than 30 degrees C. High Fowler’s Position D. Trendelenberg Ans: B. Because worried about arterial blood flow Endocrine Disorders 1. A patient diagnosed with a pituitary adenoma has arrived on the neurologic unit. When planning the patients care, the nurse should be aware that the effects of the tumor will primarily depend on what variable? A. Whether the tumor utilizes aerobic or anaerobic respiration B. The specific hormones secreted by the tumor C. The patients pre-existing health status D. Whether the tumor is primary or the result of metastasis Ans: B. Functioning pituitary tumors can produce one or more hormones normally produced by the anterior pituitary and the effects of the tumor depend largely on the identity of these hormones. This variable is more significant than the patients health status or whether the tumor is primary versus secondary. Anaerobic and aerobic respiration is not relevant. 2. The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with hypothyroidism secondary to Hashimoto's thyroiditis. When assessing this patient, what sign or symptom would the nurse expect? A. Fatigue B. Bulging eyes C. Palpitations D. Flushed skin Ans: A. Symptoms of hypothyroidism include extreme fatigue, hair loss, brittle nails, dry skin, voice huskiness or hoarseness, menstrual disturbance, and numbness and tingling of the fingers. Bulging eyes, palpitations, and flushed skin would be signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism. 3. A patient has been admitted to the post-surgical unit following a thyroidectomy. To promote comfort and safety, how should the nurse best position the patient? A. Side-lying (lateral) with one pillow under the head B. Head of the bed elevated 30 degrees and no pillows placed under the head C. Semi-Fowlers with the head supported on two pillows D. Supine, with a small roll supporting the neck Ans: C. When moving and turning the patient, the nurse carefully supports the patients head and avoids tension on the sutures. The most comfortable position is the semi-Fowler's position, with the head elevated and supported by pillows. 4. A patient with thyroid cancer has undergone surgery and a significant amount of parathyroid tissue has been removed. The nurse caring for the patient should prioritize what question when addressing potential complications? A. Do you feel any muscle twitches or spasms? B. Do you feel flushed or sweaty? C. Are you experiencing any dizziness or lightheadedness? D. Are you having any pain that seems to be radiating from your bones? Ans: A. As the blood calcium level falls, hyperirritability of the nerves occurs, with spasms of the hands and feet and muscle twitching. This is characteristic of hypoparathyroidism. Flushing, diaphoresis, dizziness, and pain are atypical signs of the resulting hypocalcemia. 5. The nurse is caring for a patient with a diagnosis of Addison's disease. What sign or symptom is most closely associated with this health problem? A. Truncal obesity 66Adult Health Exam 5 B. Hypertension C. Muscle weakness D. Moon face Ans: C. Patients with Addison's disease demonstrate muscular weakness, anorexia, gastrointestinal symptoms, fatigue, emaciation, dark pigmentation of the skin, and hypotension. Patients with Cushing syndrome demonstrate truncal obesity, moon face, acne, abdominal striae, and hypertension. 6. The nurse is caring for a patient with Addison's disease who is scheduled for discharge. When teaching the patient about hormone replacement therapy, the nurse should address what topic? A. The possibility of precipitous weight gain B. The need for lifelong steroid replacement C. The need to match the daily steroid dose to immediate symptoms D. The importance of monitoring liver function Ans: B. Because of the need for lifelong replacement of adrenal cortex hormones to prevent addisonian crisis, the patient and family members receive explicit education about the rationale for replacement therapy and proper dosage. Doses are not adjusted on a short-term basis. Weight gain and hepatotoxicity are not common adverse effects. 7. The nurse is teaching a patient that the body needs iodine for the thyroid to function. What food would be the best source of iodine for the body? A. Eggs B. Shellfish C. Table salt D. Red meat Ans: C. The major use of iodine in the body is by the thyroid. Iodized table salt is the best source of iodine. 8. A patient is prescribed corticosteroid therapy. What would be the priority information for the nurse to give the patient who is prescribed long-term corticosteroid therapy? A. The patients diet should be low protein with ample fat. B. The patient may experience short-term changes in cognition. C. The patient is at an increased risk for developing infection. D. The patient is at a decreased risk for development of thrombophlebitis and thromboembolism. Ans: C. The patient is at increased risk of infection and masking of signs of infection. The cardiovascular effects of corticosteroid therapy may result in development of thrombophlebitis or thromboembolism. Diet should be high in protein with limited fat. Changes in appearance usually disappear when therapy is no longer necessary. Cognitive changes are not common adverse effects. 9. A nurse caring for a patient with diabetes insipidus is reviewing laboratory results. What is an expected urinalysis finding? A. Glucose in the urine B. Albumin in the urine C. Highly dilute urine D. Leukocytes in the urine Ans: C. Patients with diabetes insipidus produce an enormous daily output of very dilute, water-like urine with a specific gravity of 1.001 to 1.005. The urine contains no abnormal substances such as glucose or albumin. Leukocytes in the urine are not related to the condition of diabetes insipidus, but would indicate a urinary tract infection, if present in the urine. 10. The nurse caring for a patient with Cushing syndrome is describing the dexamethasone suppression test scheduled for tomorrow. What does the nurse explain that this test will involve? A. Administration of dexamethasone orally, followed by a plasma cortisol level every hour for 3 hours 67Adult Health Exam 5 B. Administration of dexamethasone IV, followed by an x-ray of the adrenal glands C. Administration of dexamethasone orally at 11 PM, and a plasma cortisol level at 8 AM the next morning D. Administration of dexamethasone intravenously, followed by a plasma cortisol level 3 hours after the drug is administered Ans: C. Dexamethasone (1 mg) is administered orally at 11 PM, and a plasma cortisol level is obtained at 8 AM the next morning. This test can be performed on an outpatient basis and is the most widely used and sensitive screening test for diagnosis of pituitary and adrenal causes of Cushing syndrome. 11. The home care nurse is conducting patient teaching with a patient on corticosteroid therapy. To achieve consistency with the body's natural secretion of cortisol, when would the home care nurse instruct the patient to take his or her corticosteroids? A. In the evening between 4 PM and 6 PM B. Prior to going to sleep at night C. At noon every day D. In the morning between 7 AM and 8 AM Ans: D. In keeping with the natural secretion of cortisol, the best time of day for the total corticosteroid dose is in the morning from 7 to 8 AM. Large-dose therapy at 8 AM, when the adrenal gland is most active, produces maximal suppression of the gland. Also, a large 8 AM dose is more physiologic because it allows the body to escape effects of the steroids from 4 PM to 6 AM, when serum levels are normally low, thus minimizing cushingoid effects. 12. A patient presents at the walk-in clinic complaining of diarrhea and vomiting. The patient has a documented history of adrenal insufficiency. Considering the patients history and current symptoms, the nurse should anticipate that the patient will be instructed to do which of the following? A. Increase his intake of sodium until the GI symptoms improve. B. Increase his intake of potassium until the GI symptoms improve. C. Increase his intake of glucose until the GI symptoms improve. D. Increase his intake of calcium until the GI symptoms improve. Ans: A. The patient will need to supplement dietary intake with added salt during episodes of GI losses of fluid through vomiting and diarrhea to prevent the onset of addisonian crisis. While the patient may experience the loss of other electrolytes, the major concern is the replacement of lost sodium. 13. While assisting with the surgical removal of an adrenal tumor, the OR nurse is aware that the patients vital signs may change upon manipulation of the tumor. What vital sign changes would the nurse expect to see? A. Hyperthermia and tachypnea B. Hypertension and heart rate changes C. Hypotension and hypothermia D. Hyperthermia and bradycardia Ans: B. Manipulation of the tumor during surgical excision may cause release of stored epinephrine and norepinephrine, with marked increases in BP and changes in heart rate. The use of sodium nitroprusside and alphaadrenergic blocking agents may be required during and after surgery. While other vital sign changes may occur related to surgical complications, the most common changes are related to hypertension and changes in heart rate. 14. A patient has returned to the floor after having a thyroidectomy for thyroid cancer. The nurse knows that sometimes during thyroid surgery the parathyroid glands can be injured or removed. What laboratory finding may be an early indication of parathyroid gland injury or removal? A. Hyponatremia B. Hypophosphatemia C. Hypocalcemia D. Hypokalemia Ans: C. Injury or removal of the parathyroid glands may produce a disturbance in calcium metabolism and result in a decline of calcium levels (hypocalcemia). As the blood calcium levels fall, hyperirritability of the nerves occurs, with spasms of the hands and feet and muscle twitching. This group of symptoms is known as tetany and must be reported to the physician immediately, because laryngospasm may occur and obstruct the airway. Hypophosphatemia, hyponatremia, and hypokalemia are not expected responses to parathyroid injury or removal. In fact, parathyroid removal or injury that results in hypocalcemia may lead to hyperphosphatemia. 68Adult Health Exam 5 15. The nurse is planning the care of a patient with hyperthyroidism. What should the nurse specify in the patients meal plan? A. A clear liquid diet, high in nutrients B. Small, frequent meals, high in protein and calories C. Three large, bland meals a day D. A diet high in fiber and plant-sourced fat Ans: B. A patient with hyperthyroidism has an increased appetite. The patient should be counseled to consume several small, well-balanced meals. High-calories, high-protein foods are encouraged. A clear liquid diet would not satisfy the patients caloric or hunger needs. A diet rich in fiber and fat should be avoided because these foods may lead to GI upset or increase peristalsis. 16. A patient with hypofunction of the adrenal cortex has been admitted to the medical unit. What would the nurse most likely find when assessing this patient? A. Increased body temperature B. Jaundice C. Copious urine output D. Decreased BP Ans: D. Decreased BP may occur with hypofunction of the adrenal cortex. Decreased function of the adrenal cortex does not affect the patients body temperature, urine output, or skin tone. 17. The nurse is assessing a patient diagnosed with Graves disease. What physical characteristics of Graves disease would the nurse expect to find? A. Hair loss B. Moon face C. Bulging eyes D. Fatigue Ans: C. Clinical manifestations of the endocrine disorder Graves disease include exophthalmos (bulging eyes) and fine tremor in the hands. Graves disease is not associated with hair loss, a moon face, or fatigue. 18. A patient with suspected adrenal insufficiency has been ordered an adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulation test. Administration of ACTH caused a marked increase in cortisol levels. How should the nurse interpret this finding? A. The patients pituitary function is compromised. B. The patients adrenal insufficiency is not treatable. C. The patient has insufficient hypothalamic function. D. The patient would benefit from surgery. Ans: A. An adrenal response to the administration of a stimulating hormone suggests inadequate production of the stimulating hormone. In this case, ACTH is produced by the pituitary and, consequently, pituitary hypofunction is suggested. Hypothalamic function is not relevant to the physiology of this problem. Treatment exists, although surgery is not likely indicated. 19. The physician has ordered a fluid deprivation test for a patient suspected of having diabetes insipidus. During the test, the nurse should prioritize what assessments? A. Temperature and oxygen saturation B. Heart rate and BP C. Breath sounds and bowel sounds D. Color, warmth, movement, and sensation of extremities Ans:B. The fluid deprivation test is carried out by withholding fluids for 8 to 12 hours or until 3% to 5% of the body weight is lost. The patients condition needs to be monitored frequently during the test, and the test is terminated if tachycardia, excessive weight loss, or hypotension develops. Consequently, BP and heart rate monitoring are priorities over the other listed assessments. 20. A nurse works in a walk-in clinic. The nurse recognizes that certain patients are at higher risk for different disorders than other patients. What patient is at a greater risk for the development of hypothyroidism? A. A 75-year-old female patient with osteoporosis 69Adult Health Exam 5 B. A 50-year-old male patient who is obese C. A 45-year-old female patient who used oral contraceptives D. A 25-year-old male patient who uses recreational drugs Ans: A. Even though osteoporosis is not a risk factor for hypothyroidism, the condition occurs most frequently in older women. 21. A patient with a recent diagnosis of hypothyroidism is being treated for an unrelated injury. When administering medications to the patient, the nurse should know that the patients diminished thyroid function may have what effect? A. Anaphylaxis B. Nausea and vomiting C. Increased risk of drug interactions D. Prolonged duration of effect Ans: D. In all patients with hypothyroidism, the effects of analgesic agents, sedatives, and anesthetic agents are prolonged. There is no direct increase in the risk of anaphylaxis, nausea, or drug interactions, although these may potentially result from the prolonged half-life of drugs. 22. A patient has been admitted to the critical care unit with a diagnosis of thyroid storm. What interventions should the nurse include in this patients immediate care? Select all that apply. A. Administering diuretics to prevent fluid overload B. Administering beta blockers to reduce heart rate C. Administering insulin to reduce blood glucose levels D. Applying interventions to reduce the patients temperature E. Administering corticosteroids Ans: B, D. Thyroid storm necessitates interventions to reduce heart rate and temperature. Diuretics, insulin, and steroids are not indicated to address the manifestations of this health problem. 23. The nurses assessment of a patient with thyroidectomy suggests tetany and a review of the most recent blood work corroborate this finding. The nurse should prepare to administer what intervention? A. Oral calcium chloride and vitamin D B. IV calcium gluconate C. STAT levothyroxine D. Administration of parathyroid hormone (PTH) Ans: B. When hypocalcemia and tetany occur after a thyroidectomy, the immediate treatment is administration of IV calcium gluconate. This has a much faster therapeutic effect than PO calcium or vitamin D supplements. PTH and levothyroxine are not used to treat this complication. 24. A patient has been taking prednisone for several weeks after experiencing a hypersensitivity reaction. To prevent adrenal insufficiency, the nurse should ensure that the patient knows to do which of the following? A. Take the drug concurrent with levothyroxine (Synthroid). B. Take each dose of prednisone with a dose of calcium chloride. C. Gradually replace the prednisone with an OTC alternative. D. Slowly taper down the dose of prednisone, as ordered. Ans: D. Corticosteroid dosages are reduced gradually (tapered) to allow normal adrenal function to return and to prevent steroid-induced adrenal insufficiency. There are no OTC substitutes for prednisone and neither calcium chloride nor levothyroxine addresses the risk of adrenal insufficiency. 25. A 30 year-old female patient has been diagnosed with Cushing syndrome. What psychosocial nursing diagnosis should the nurse most likely prioritize when planning the patients care? A. Decisional conflict related to treatment options B. Spiritual distress related to changes in cognitive function C. Disturbed body image related to changes in physical appearance 70Adult Health Exam 5 D. Powerlessness related to disease progression Ans: C. Cushing syndrome causes characteristic physical changes that are likely to result in disturbed body image. Decisional conflict and powerless may exist, but disturbed body image is more likely to be present. Cognitive changes take place in patients with Cushing syndrome, but these may or may not cause spiritual distress. 26. A patient with pheochromocytoma has been admitted for an adrenalectomy to be performed the following day. To prevent complications, the nurse should anticipate preoperative administration of which of the following? A. IV antibiotics B. Oral antihypertensives C. Parenteral nutrition D. IV corticosteroids Ans: D. IV administration of corticosteroids (methylprednisolone sodium succinate [Solu-Medrol]) may begin on the evening before surgery and continue during the early postoperative period to prevent adrenal insufficiency. Antibiotics, antihypertensives, and parenteral nutrition do not prevent adrenal insufficiency or other common complications of adrenalectomy. 27. A patient is undergoing testing for suspected adrenocortical insufficiency. The care team should ensure that the patient has been assessed for the most common cause of adrenocortical insufficiency. What is the most common cause of this health problem? A. Therapeutic use of corticosteroids B. Pheochromocytoma C. Inadequate secretion of ACTH D. Adrenal tumor Ans: A. Therapeutic use of corticosteroids is the most common cause of adrenocortical insufficiency. The other options also cause adrenocortical insufficiency, but they are not the most common causes. 28. The nurse providing care for a patient with Cushing syndrome has identified the nursing diagnosis of risk for injury related to weakness. How should the nurse best reduce this risk? A. Establish falls prevention measures. B. Encourage bed rest whenever possible. C. Encourage the use of assistive devices. D. Provide constant supervision. Ans: A. The nurse should take action to prevent the patients risk for falls. Bed rest carries too many harmful effects, however, and assistive devices may or may not be necessary. Constant supervision is not normally required or practicable. 29. A patient with Cushing syndrome has been hospitalized after a fall. The dietician consulted works with the patient to improve the patients nutritional intake. What foods should a patient with Cushing syndrome eat to optimize health? Select all that apply. A. Foods high in vitamin D B. Foods high in calories C. Foods high in protein D. Foods high in calcium E. Foods high in sodium Ans: A, C, D. Foods high in vitamin D, protein, and calcium are recommended to minimize muscle wasting and osteoporosis. Referral to a dietitian may assist the patient in selecting appropriate foods that are also low in sodium and calories. 30. A patient on corticosteroid therapy needs to be taught that a course of corticosteroids of 2 weeks duration can suppress the adrenal cortex for how long? A. Up to 4 weeks B. Up to 3 months 71Adult Health Exam 5 C. Up to 9 months D. Up to 1 year Ans: D. Suppression of the adrenal cortex may persist up to 1 year after a course of corticosteroids of only 2 weeks duration. 31. A patient with Cushing syndrome as a result of a pituitary tumor has been admitted for a transsphenoidal hypophysectomy. What would be most important for the nurse to monitor before, during, and after surgery? A. Blood glucose B. Assessment of urine for blood C. Weight D. Oral temperature Ans: A. Before, during, and after this surgery, blood glucose monitoring and assessment of stools for blood are carried out. The patients blood sugar is more likely to be volatile than body weight or temperature. Hematuria is not a common complication. 32. What should the nurse teach a patient on corticosteroid therapy in order to reduce the patients risk of adrenal insufficiency? A. Take the medication late in the day to mimic the body's natural rhythms. B. Always have enough medication on hand to avoid running out. C. Skip up to 2 doses in cases of illness involving nausea. D. Take up to 1 extra dose per day during times of stress. Ans: B. The patient and family should be informed that acute adrenal insufficiency and underlying symptoms will recur if corticosteroid therapy is stopped abruptly without medical supervision. The patient should be instructed to have an adequate supply of the corticosteroid medication always available to avoid running out. Doses should not be skipped or added without explicit instructions to do so. Corticosteroids should normally be taken in the morning to mimic natural rhythms. 33. The nurse is caring for a patient at risk for an addisonian crisis. For what associated signs and symptoms should the nurse monitor the patient? Select all that apply. A. Epistaxis B. Pallor C. Rapid respiratory rate D. Bounding pulse E. Hypotension Ans: B, C, E. The patient at risk is monitored for signs and symptoms indicative of addisonian crisis, which can include shock; hypotension; rapid, weak pulse; rapid respiratory rate; pallor; and extreme weakness. Epistaxis and a bounding pulse are not symptoms or signs of an addisonian crisis. 34. A patient has been assessed for aldosteronism and has recently begun treatment. What are priority areas for assessment that the nurse should frequently address? Select all that apply. A. Pupillary response B. Creatinine and BUN levels C. Potassium level D. Peripheral pulses E. BP Ans: C, E. Patients with aldosteronism exhibit a profound decline in the serum levels of potassium, and hypertension is the most prominent and almost universal sign of aldosteronism. Pupillary response, peripheral pulses, and renal function are not directly affected. 35. A patient who has been taking corticosteroids for several months has been experiencing muscle wasting. The patient has asked the nurse for suggestions to address this adverse effect. What should the nurse recommend? A. Activity limitation to conserve energy B. Consumption of a high-protein diet 72Adult Health Exam 5 C. Use of OTC vitamin D and calcium supplements D. Passive range-of-motion exercises Ans: B. Muscle wasting can be partly addressed through increased protein intake. Passive ROM exercises maintain flexibility, but do not build muscle mass. Vitamin D and calcium supplements do not decrease muscle wasting. Activity limitation would exacerbate the problem. 36. The nurse is providing care for an older adult patient whose current medication regimen includes levothyroxine (Synthroid). As a result, the nurse should be aware of the heightened risk of adverse effects when administering an IV dose of what medication? A. A fluoroquinolone antibiotic B. A loop diuretic C. A proton pump inhibitor (PPI) D. A benzodiazepine Ans: D. Oral thyroid hormones interact with many other medications.Even in small IV doses, hypnotic and sedative agents may induce profound somnolence, lasting far longer than anticipated and leading to narcosis (stupor like condition). Furthermore, they are likely to cause respiratory depression, which can easily be fatal because of decreased respiratory reserve and alveolar hypoventilation. Antibiotics, PPIs and diuretics do not cause the same risk. 37. The nurse is caring for a client after hypophysectomy and notes clear nasal drainage from the client's nostril. The nurse should take which initial action? A. Lower the head of the bed. B. Test the drainage for glucose. C. Obtain a culture of the drainage. D. Continue to observe the drainage. Ans: B. After hypophysectomy, the client should be monitored for rhinorrhea, which could indicate a cerebrospinal fluid leak. If this occurs, the drainage should be collected and tested for the presence of cerebrospinal fluid. Cerebrospinal fluid contains glucose, and if positive, this would indicate that the drainage is cerebrospinal fluid. The head of the bed should remain elevated to prevent increased intracranial pressure. Clear nasal drainage would not indicate the need for a culture. Continuing to observe the drainage without taking action could result in a serious complication. 38. A client is admitted to an emergency department, and a diagnosis of myxedema coma is made. Which action should the nurse prepare to carry out initially? A. Warm the client. B. Maintain a patent airway. C. Administer thyroid hormone. D. Administer fluid replacement. Ans: B. Myxedema coma is a rare but serious disorder that results from persistently low thyroid production. Coma can be precipitated by acute illness, rapid withdrawal of thyroid medication, anesthesia and surgery, hypothermia, and the use of sedatives and opioid analgesics. In myxedema coma, the initial nursing action is to maintain a patent airway. Oxygen should be administered, followed by fluid replacement, keeping the client warm, monitoring vital signs, and administering thyroid hormones by the intravenous route. 39. The nurse is completing an assessment on a client who is being admitted for a diagnostic workup for primary hyperparathyroidism. Which client complaint would be characteristic of this disorder? Select all that apply. A. Polyuria B. Headache C. Bone pain D. Nervousness E. Weight gain Ans: A, C. The role of parathyroid hormone (PTH) in the body is to maintain serum calcium homeostasis. In hyperparathyroidism, PTH levels are high, which causes bone resorption (calcium is pulled from the bones). Hypercalcemia occurs with hyperparathyroidism. Elevated serum calcium levels produce osmotic diuresis and thus polyuria. This diuresis leads to dehydration (weight loss rather than weight gain). Loss of calcium from the bones 73Adult Health Exam 5 causes bone pain. Options 2, 4, and 5 are not associated with hyperparathyroidism. Some gastrointestinal symptoms include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and constipation. 40. The nurse is teaching a client with hyperparathyroidism how to manage the condition at home. Which response by the client indicates the need for additional teaching? A. "I should limit my fluids to 1 liter per day." B. “I should use my treadmill or go for walks daily." C. "I should follow a moderate-calcium, high-fiber diet." D. “My alendronate helps to keep calcium from coming out of my bones." Ans: A. In hyperparathyroidism, clients experience excess parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion. A role of PTH in the body is to maintain serum calcium homeostasis. When PTH levels are high, there is excess bone resorption (calcium is pulled from the bones). In clients with elevated serum calcium levels, there is a risk of nephrolithiasis. One to 2 liters of fluids daily should be encouraged to protect the kidneys and decrease the risk of nephrolithiasis. Moderate physical activity, particularly weight-bearing activity, minimizes bone resorption and helps to protect against pathological fracture. Walking, as an exercise, should be encouraged in the client with hyperparathyroidism. Clients should follow a moderate-calcium, high-fiber diet. Even though serum calcium is already high, clients should follow a moderate-calcium diet because a low-calcium diet will surge PTH. Calcium causes constipation, so a diet high in fiber is recommended. Alendronate is a bisphosphate that inhibits bone resorption. In bone resorption, bone is broken down and calcium is deposited into the serum. 41. A client with a diagnosis of Addisonian crisis is being admitted to the intensive care unit. Which findings will the interprofessional health care team focus on? Select all that apply. A. Hypotension B. Leukocytosis C. Hyperkalemia D. Hypercalcemia E. Hypernatremia Ans: A, C. In Addison's disease, also known as adrenal insufficiency, destruction of the adrenal gland leads to decreased production of adrenocortical hormones, including the glucocorticoid cortisol and the mineralocorticoid aldosterone. Addisonian crisis, also known as acute adrenal insufficiency, occurs when there is extreme physical or emotional stress and lack of sufficient adrenocortical hormones to manage the stressor. Addisonian crisis is a lifethreatening emergency. One of the roles of endogenous cortisol is to enhance vascular tone and vascular response to the catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine. Hypotension occurs when vascular tone is decreased and blood vessels cannot respond to epinephrine and norepinephrine. The role of aldosterone in the body is to support the blood pressure by holding salt and water and excreting potassium. When there is insufficient aldosterone, salt and water are lost and potassium builds up; this leads to hypotension from decreased vascular volume, hyponatremia, and hyperkalemia. The remaining options are not associated with Addisonian crisis. 42. The nurse is performing an assessment on a client with pheochromocytoma. Which assessment data would indicate a potential complication associated with this disorder? A. A urinary output of 50 mL/hour B. A coagulation time of 5 minutes C. A heart rate that is 90 beats/minute and irregular D. A blood urea nitrogen level of 20 mg/dL (7.1 mmol/L) Ans: C. Pheochromocytoma is a catecholamine-producing tumor usually found in the adrenal medulla, but extraadrenal locations include the chest, bladder, abdomen, and brain; it is typically a benign tumor but can be malignant. Excessive amounts of epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted. The complications associated with pheochromocytoma include hypertensive retinopathy and nephropathy, myocarditis, increased platelet aggregation, and stroke. Death can occur from shock, stroke, kidney failure, dysrhythmias, or dissecting aortic aneurysm. An irregular heart rate indicates the presence of a dysrhythmia. A coagulation time of 5 minutes is normal. A urinary output of 50 mL/hour is an adequate output. A blood urea nitrogen level of 20 mg/dL (7.1 mmol/L) is a normal finding. 43. The nurse is preparing a client with a new diagnosis of hypothyroidism for discharge. The nurse determines that the client understands discharge instructions if the client states that which signs and symptoms are 74Adult Health Exam 5 associated with this diagnosis? Select all that apply. A. Tremors B. Weight loss C. Feeling cold D. Loss of body hair E. Persistent therapy F. Puffiness of face Ans: C,D,E,F. Feeling cold, hair loss, lethargy, and facial puffiness are signs of hypothyroidism. Tremors and weight loss are signs of hyperthyroidism. 44. A client has just been admitted to the nursing unit following thyroidectomy. Which assessment is the priority for this client? A. Hypoglycemia B. Level of hoarseness C. Respiratory distress D. Edema at surgical site Ans: C. Thyroidectomy is the removal of the thyroid gland, which is located in the anterior neck. It is very important to monitor airway status, as any swelling to the surgical site could cause respiratory distress. Although all of the options are important for the nurse to monitor, the priority nursing action is to monitor the airway. 45. A client has been diagnosed with hyperthyroidism. The nurse monitors for which signs and symptoms indicating a complication of this disorder? Select all that apply. A. Fever B. Nausea C. Lethargy D. Tremors E. Confusion F. Bradycardia Ans: A, B, D,E. Thyroid storm is an acute and life-threatening complication that occurs in a client with uncontrollable hyperthyroidism. Signs and symptoms of thyroid storm include elevated temperature (fever), nausea, and tremors. In addition, as the condition progresses, the client becomes confused. The client is restless and anxious and experiences tachycardia. 46. The nurse is caring for a client scheduled for a transsphenoidal hypophysectomy. The preoperative teaching instructions should include which statement? A. "Your hair will need to be shaved." B. "You will receive spinal anesthesia." C. "You will need to ambulate after surgery." D. "Brushing your teeth needs to be avoided for at least 2 weeks after surgery.” Ans: D. A transsphenoidal hypophysectomy is a surgical approach that uses the nasal sinuses and nose for access to the pituitary gland. Based on the location of the surgical procedure, spinal anesthesia would not be used. In addition, the hair would not be shaved. Although ambulating is important, specific to this procedure is avoiding brushing the teeth to prevent disruption of the surgical site. 47. The nurse should include which interventions in the plan of care for a client with hypothyroidism? Select all that apply. A. Provide a cool environment for the client. B. Instruct the client to consume a high-fat diet. C. Instruct the client about thyroid replacement therapy. D. Encourage the client to consume fluids and high-fiber foods in the diet. E. Inform the client that iodine preparations will be prescribed to treat the disorder. F. Instruct the client to contact the health care provider (HCP) if episodes of chest pain occur. Ans: C, D, F. The clinical manifestations of hypothyroidism are the result of decreased metabolism from low levels of thyroid hormone. Interventions are aimed at replacement of the hormone and providing measures to support the signs and symptoms related to decreased metabolism. The client often has cold intolerance and requires a warm environment. The nurse encourages the client to consume a well-balanced diet that is low in fat for weight reduction 75Adult Health Exam 5 and high in fluids and high-fiber foods to prevent constipation. Iodine preparations may be used to treat hyperthyroidism. Iodine preparations decrease blood flow through the thyroid gland and reduce the production and release of thyroid hormone; they are not used to treat hypothyroidism. The client is instructed to notify the HCP if chest pain occurs because it could be an indication of overreplacement of thyroid hormone. 48. The nurse is caring for a client after thyroidectomy. The nurse notes that calcium gluconate is prescribed for the client. The nurse determines that this medication has been prescribed for which purpose? A. To treat thyroid storm B. To prevent cardiac irritability C. To treat hypocalcemic tetany D. To stimulate release of parathyroid hormone Ans: C. Hypocalcemia, resulting in tetany, can develop after thyroidectomy if the parathyroid glands are accidentally removed during surgery. Manifestations develop 1 to 7 days after surgery. If the client develops numbness and tingling around the mouth, fingertips, or toes; muscle spasms; or twitching, the health care provider is notified immediately. Calcium gluconate should be readily available in the nursing unit. 49. The nurse should include which interventions in the plan of care for a client with hyperthyroidism? Select all that apply. A. Provide a warm environment for the client B. Instruct the client to consume a low-fat diet. C. A thyroid-releasing inhibitor will be prescribed. D. Encourage the client to consume a well-balanced diet. E. Instruct the client that thyroid replacement therapy will be needed. F. Instruct the client that episodes of chest pain are expected to occur. Ans: C, D. The clinical manifestations of hyperthyroidism are the result of increased metabolism caused by high levels of thyroid hormone. Interventions are aimed at reduction of the hormones and measures to support the signs and symptoms related to an increased metabolism. The client often has heat intolerance and requires a cool environment. The nurse encourages the client to consume a well-balanced diet because clients with this condition experience increased appetite. Iodine preparations are used to treat hyperthyroidism. Iodine preparations decrease blood flow through the thyroid gland and reduce the production and release of thyroid hormone. Thyroid replacement is needed for hypothyroidism. The client would notify the health care provider if chest pain occurs because it could be an indication of an excessive medication dose. 50. The nurse is reviewing the laboratory test results for a client with a diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome. Which laboratory finding would the nurse expect to note in this client? A. A platelet count of 200,000 mm3 (200 × 109/L) B. A blood glucose level of 110 mg/dL (6.28 mmol/L) C. A potassium (K+) level of 3.0 mEq/L (3.0 mmol/L) D. A white blood cell (WBC) count of 6000 mm3 (6 × 109/L) Ans: C. The client with Cushing's syndrome experiences hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, an elevated WBC count, and elevated plasma cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone levels. These abnormalities are caused by the effects of excess glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids in the body. The laboratory values listed in the remaining options would not be noted in the client with Cushing's syndrome. 51. The nurse caring for a client with a diagnosis of hypoparathyroidism reviews the laboratory results of blood tests for this client and notes that the calcium level is extremely low. The nurse should expect to note which finding on assessment of the client? A. Unresponsive pupils B. Positive Trousseau's sign C. Negative Chvostek's sign D. Hypoactive bowel sounds Ans: B. Hypoparathyroidism is related to a lack of parathyroid hormone secretion or a decreased effectiveness of parathyroid hormone on target tissues. The end result of this disorder is hypocalcemia. When serum calcium levels are critically low, the client may exhibit Chvostek's and Trousseau's signs, which indicate potential tetany. The remaining options are not related to the presence of hypocalcemia. 76Adult Health Exam 5 52. The nurse is caring for a client with a diagnosis of Addison's disease and is monitoring the client for signs of addisonian crisis. The nurse should assess the client for which manifestation that would be associated with this crisis? A. Agitation B. Diaphoresis C. Restlessness D. Severe abdominal pain Ans: D. Addisonian crisis is a serious life-threatening response to acute adrenal insufficiency that most commonly is precipitated by a major stressor. The client in addisonian crisis may demonstrate any of the signs and symptoms of Addison's disease, but the primary problems are sudden profound weakness; severe abdominal, back, and leg pain; hyperpyrexia followed by hypothermia; peripheral vascular collapse; coma; and renal failure. The remaining options do not identify clinical manifestations associated with addisonian crisis. 53. The nurse is developing a plan of care for a client who is scheduled for a thyroidectomy. The nurse focuses on psychosocial needs, knowing that which is likely to occur in the client? A. Infertility B. Gynecomastia C. Sexual dysfunction D. Body image changes Ans: D. Because of the location of the incision in the neck area, many clients are afraid of thyroid surgery for fear of having a visible large scar postoperatively. Having all or part of the thyroid gland removed will not cause the client to experience gynecomastia. Sexual dysfunction and infertility could occur if the entire thyroid is removed and the client is not placed on thyroid replacement medications. 54. The nurse is reviewing the record of a client admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. The nurse reads the assessment findings and expects to note documentation of which major symptom associated with this condition? A. Glycosuria B. Diaphoresis C. Weight loss D. Hypertension Ans: D. Hypertension is the major symptom associated with pheochromocytoma. Glycosuria, weight loss, and diaphoresis also are clinical manifestations of pheochromocytoma; however, they are not major symptoms. 55. The nurse is performing an assessment on a client with a diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome. Which should the nurse expect to note on assessment of the client? A. Skin atrophy B. The presence of sunken eyes C. Drooping on 1 side of the face D. A rounded "moonlike" appearance to the face Ans: D. With excessive secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and chronic corticosteroid use, the person with Cushing's syndrome develops a rounded moonlike face; prominent jowls; red cheeks; and hirsutism on the upper lip, lower cheek, and chin. The remaining options are not associated with the assessment findings in Cushing's syndrome. 56. The nurse is performing an assessment on a client with a diagnosis of myxedema (hypothyroidism). Which assessment finding should the nurse expect to note in this client? A. Dry skin B. Thin, silky hair C. Bulging eyeballs D. Fine muscle tremors Ans: A. Myxedema is a deficiency of thyroid hormone. The client will present with a puffy, edematous face, especially around the eyes (periorbital edema), along with coarse facial features; dry skin; and dry, coarse hair and eyebrows. The remaining options are noted in the client with hyperthyroidism. 57. The nurse is performing an assessment on a client with a diagnosis of hyperthyroidism. Which assessment finding should the nurse expect to note in this client? A. Dry skin 77Adult Health Exam 5 B. Bulging eyeballs C. Periorbital edema D. Coarse facial features Ans: B. Hyperthyroidism is clinically manifested by goiter (increase in the size of the thyroid gland) and exophthalmos (bulging eyeballs). Other clinical manifestations include nervousness, fatigue, weight loss, muscle cramps, and heat intolerance. Additional signs found in this disorder include tachycardia; shortness of breath; excessive sweating; fine muscle tremors; thin, silky hair and thin skin; infrequent blinking; and a staring appearance. 58. The nurse is developing a plan of care for a client with Cushing's syndrome. The nurse documents a client problem of excess fluid volume. Which nursing actions should be included in the care plan for this client? Select all that apply. A. Monitor daily weight. B. Monitor intake and output. C. Assess extremities for edema. D. Maintain a high-sodium diet. E. Maintain a low-potassium diet. Ans: A, B, C. The client with Cushing's syndrome and a problem of excess fluid volume should be on daily weights and intake and output and have extremities assessed for edema. He or she should be maintained on a high-potassium, low-sodium diet. Decreased sodium intake decreases renal retention of sodium and water. 59. The nurse is caring for a client who has had an adrenalectomy and is monitoring the client for signs of adrenal insufficiency. Which signs and symptoms indicate adrenal insufficiency in this client? A. Hypotension and fever B. Mental status changes and hypertension C. Subnormal temperature and hypotension D. Complaints of weakness and hypertension Ans: A. The nurse should be alert to signs and symptoms of adrenal insufficiency after adrenalectomy. These signs and symptoms include weakness, hypotension, fever, and mental status changes. The remaining options are incorrect. 60. The nurse is providing home care instructions to the client with a diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome and prepares a list of instructions for the client. Which instructions should be included on the list? Select all that apply. A. The signs and symptoms of hypoadrenalism B. The signs and symptoms of hyperadrenalism C. Instructions to take the medications exactly as prescribed D. The importance of maintaining regular outpatient follow-up care E. A reminder to read the labels on over-the-counter medications before purchase Ans: A,B,C,D. The client with Cushing's syndrome should be instructed to take the medications exactly as prescribed. The nurse should emphasize the importance of continuing medications, consulting with the health care provider (HCP) before purchasing any over-the-counter medications, and maintaining regular outpatient follow-up care. The nurse also should instruct the client in the signs and symptoms of both hypoadrenalism and hyperadrenalism. 61. The nurse is developing a plan of care for a client with Addison's disease. The nurse has identified a problem of risk for deficient fluid volume and identifies nursing interventions that will prevent this occurrence. Which nursing interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care? Select all that apply. A. Monitor for changes in mentation. B. Encourage an intake of low-protein foods. C. Encourage an intake of low-sodium foods. D. Encourage fluid intake of at least 3000 mL per day. E. Monitor vital signs, skin turgor, and intake and output Ans: A, C, E. The client at risk for deficient fluid volume should be encouraged to eat regular meals and snacks and to increase intake of sodium, protein, and complex carbohydrates and fluids. Oral replacement of sodium losses is necessary, and maintenance of adequate blood glucose levels is required. Mentation, vital signs, skin turgor and intake and output should be monitored for signs of fluid volume deficit. 78Adult Health Exam 5 62. The nurse has developed a postoperative plan of care for a client who had a thyroidectomy and documents that the client is at risk for developing an ineffective breathing pattern. Which nursing intervention should the nurse include in the plan of care? A. Maintain a supine position. B. Monitor neck circumference every 4 hours. C. Maintain a pressure dressing on the operative site. D. Encourage deep-breathing exercises and vigorous coughing exercises. Ans: B. After thyroidectomy, neck circumference is monitored every 4 hours to assess for the occurrence of postoperative edema. The client should be placed in an upright position to facilitate air exchange. A pressure dressing is not placed on the operative site because it may restrict breathing. The nurse should monitor the dressing closely and should loosen the dressing if necessary. The nurse should assist the client with deep-breathing exercises, but coughing is minimized to prevent tissue damage and stress to the incision. 63. The nurse is monitoring a client for signs of hypocalcemia after thyroidectomy. Which sign or symptom, if noted in the client, would most likely indicate the presence of hypocalcemia? A. Bradycardia B. Flaccid paralysis C. Tingling around the mouth D. Absence of Chvostek’s sign Ans: C. After thyroidectomy the nurse assesses the client for signs of hypocalcemia and tetany. Early signs include tingling around the mouth and in the fingertips, muscle twitching or spasms, palpitations or arrhythmias, and Chvostek's and Trousseau's signs. Bradycardia, flaccid paralysis, and absence of Chvostek's sign are not signs of hypocalcemia. 64. The nurse is monitoring a client with Graves' disease for signs of thyrotoxic crisis (thyroid storm). Which signs or symptoms, if noted in the client, will alert the nurse to the presence of this crisis? A. Fever and tachycardia B. Pallor and tachycardia C. Agitation and bradycardia D. Restlessness and bradycardia Ans: A. Thyrotoxic crisis (thyroid storm) is an acute, potentially life-threatening state of extreme thyroid activity that represents a breakdown in the body's tolerance to a chronic excess of thyroid hormones. The clinical manifestations include fever with temperatures greater than 100°F, severe tachycardia, flushing and sweating, and marked agitation and restlessness. Delirium and coma can occur. 65. The nursing instructor asks a nursing student to identify the risk factors associated with the development of thyrotoxicosis. The student demonstrates understanding of the risk factors by identifying an increased risk for thyrotoxicosis in which client? A. A client with hypothyroidism B. A client with Graves' disease who is having surgery C. A client with diabetes mellitus scheduled for a diagnostic test D. A client with diabetes mellitus scheduled for debridement of a foot ulcer Ans: B. Thyrotoxicosis usually is seen in clients with Graves' disease in whom the symptoms are precipitated by a major stressor. This complication typically occurs during periods of severe physiological or psychological stress such as trauma, sepsis, delivery, or major surgery. It also must be recognized as a potential complication after thyroidectomy. The client conditions in the remaining options are not associated with thyrotoxicosis. 66. The home care nurse visits a client with a diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism who is taking furosemide and provides dietary instructions to the client. Which statement by the client indicates a need for additional instruction? A. "I need to eat foods high in potassium." B. "I need to drink at least 2 to 3 L of fluid daily." 79Adult Health Exam 5 C. "I need to eat small, frequent meals and snacks if nauseated." D. "I need to increase my intake of dietary items that are high in calcium." Ans: D. The aim of treatment in the client with hyperparathyroidism is to increase the renal excretion of calcium and decrease gastrointestinal absorption and bone resorption of calcium. Dietary restriction of calcium may be used as a component of therapy. The client should eat foods high in potassium, especially if the client is taking furosemide. Drinking 2 to 3 L of fluid daily and eating small, frequent meals and snacks if nauseated are appropriate instructions for the client. 67. A nurse is reviewing the assessment findings and laboratory data for a client with the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH). The nurse understands that which symptoms are associated characteristics of this disorder? Select all that apply. A. Hypernatremia B. Signs of water deficit C. High urine osmolality D. Low urine osmolality E. Hypotonicity of body fluids F. Continued release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Ans: C,D,E,F. SIADH is characterized by inappropriate continued release of ADH. This results in water intoxication, manifested as fluid volume expansion, hypotonicity of body fluids, and hyponatremia as a result of the high urine osmolality and low serum osmolality. 68. A nurse is reviewing the assessment findings for a client who was admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of diabetes insipidus. The nurse understands that which manifestations are associated with this disorder? Select all that apply. A. Polyuria B. Polydipsia C. Concentrated urine D. Complaints of excessive thirst E. Specific gravity lower than 1.005 Ans: A, B, D, E. A triad of clinical symptoms–polyuria, polydipsia, and excessive thirst–often occurs suddenly in the client with diabetes insipidus. The urine is dilute, with a specific gravity lower than 1.005, and the urine osmolality is low (50 to 200 mOsm/L). 69. A client has been hospitalized for impaired function of the posterior pituitary gland. The nurse plans to monitor for signs and symptoms of which hormone imbalance? A. Growth hormone (GH) B. Luteinizing hormone (LH) C. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) D. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) Ans: C. ADH is secreted by the posterior pituitary gland. The other hormone stored in the posterior pituitary gland is oxytocin. Both ADH and oxytocin are synthesized by the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary gland. These hormones are released as needed into the bloodstream. The anterior pituitary gland produces GH, LH, and FSH. 70. The nurse is admitting a client diagnosed with pheochromocytoma. The client is complaining of a pounding headache and palpitations and the blood pressure is 170/90 mm Hg. The nurse is aware that which substance is responsible for these clinical manifestations? A. Cortisol B. Androgens C. Aldosterone D. Epinephrine Ans: D. Pheochromocytoma is a catecholamine-producing tumor and causes secretion of excessive amounts of epinephrine and norepinephrine, which are produced by the adrenal medulla. Hypertension is the principal manifestation, and the client has episodes of high blood pressure accompanied by pounding headaches. The excessive release of catecholamines also results in excessive conversion of glycogen into glucose in the liver. Consequently, hyperglycemia and glucosuria occur during attacks. In addition, the other substances listed (cortisol, 80Adult Health Exam 5 androgens, and aldosterone) are produced by the adrenal cortex. 71. A client has a tumor that is interfering with the function of the hypothalamus. The nurse should monitor for signs and symptoms related to which imbalance? A. Melatonin excess or deficit B. Glucocorticoid excess or deficit C. Mineralocorticoid excess or deficit D. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) excess or deficit Ans: The hypothalamus exerts an influence on both the anterior and the posterior pituitary gland. Abnormalities can result in excess or deficit of substances normally mediated by the pituitary. ADH could be affected by disease of the hypothalamus because the hypothalamus produces ADH and stores it in the posterior pituitary gland. The pineal gland is responsible for melatonin production. The adrenal cortex is responsible for the production of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. 72. A client with an endocrine disorder has experienced recent weight loss and exhibits tachycardia. Based on the clinical manifestations, the nurse should suspect dysfunction of which endocrine gland? A. Thyroid B. Pituitary C. Parathyroid D. Adrenal cortex Ans: A. The thyroid gland is responsible for a number of metabolic functions in the body. Among these are metabolism of nutrients such as fats and carbohydrates. Increased metabolic function places a demand on the cardiovascular system for a higher cardiac output. A client with increased activity of the thyroid gland will experience weight loss from the higher metabolic rate and will have an increased pulse rate. The anterior pituitary gland produces growth hormone, luteinizing hormone, and follicle-stimulating hormone. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin are secreted by the posterior pituitary gland. Both ADH and oxytocin are synthesized by the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary gland. These hormones are released as needed into the bloodstream. Parathyroid hormone is responsible for maintaining serum calcium and phosphorus levels within normal range. The adrenal cortex is responsible for the production of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. 73. A client has abnormal amounts of circulating thyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). While obtaining the health history, the nurse asks the client about dietary intake. Lack of which dietary element is most likely the cause? A. Iodine B. Calcium C. Phosphorous D. Magnesium Ans: A. Adequate dietary iodine is needed to produce T3 and T4. The other requirements for adequate T3 and T4 production are an intact thyroid gland and a functional hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid feedback system. The remaining options are not responsible for the abnormal amounts of circulating T3 and T4. 74. A client with medullary carcinoma of the thyroid has an excess function of the C cells of the thyroid gland. When reviewing the most recent laboratory results, the nurse should expect which electrolyte abnormality? A. Sodium B. Calcium C. Potassium D. Magnesium Ans: B. The C cells of the thyroid gland are helpful in maintaining normal plasma calcium levels. They do not affect the levels of sodium, potassium, or magnesium 75. A client has overactivity of the thyroid gland. The nurse should expect which finding? A. Weight gain B. Nutritional deficiencies C. Low blood glucose levels D. Increased body fat stores Ans: B. Although the client may experience an increased appetite with overactivity of the thyroid gland, food intake does not meet energy demands, and nutritional deficiencies can develop. Weight loss occurs as a result of the increased metabolic activity. Glucose tolerance is decreased, and the client experiences hyperglycemia. Overactivity 81Adult Health Exam 5 of the thyroid gland also causes increased metabolism, including fat metabolism. This leads to decreased levels of fat in the bloodstream, including cholesterol, and decreased body fat stores. 76. A client is diagnosed with Cushing's syndrome. When reviewing the recent laboratory results, the nurse should expect an excess of which substance? A. Calcium B. Cortisol C. Epinephrine D. Norepinephrine Ans: B. Cushing's syndrome is characterized by an excess of cortisol, a glucocorticoid. Glucocorticoids are produced by the adrenal cortex. Calcium would be decreased in this disorder. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are produced by the adrenal medulla. 77. The nurse is caring for a client with a new diagnosis of hypothyroidism. Which clinical manifestations might the nurse expect to note on examination of this client? Select all that apply. A. Irritability B. Periorbital edema C. Coarse, brittle hair D. Slow or slurred speech E. Abdominal distention F. Soft, silky, thinning hair Ans: B,C,D,E. The manifestations of hypothyroidism are the result of decreased metabolism from low levels of thyroid hormones. The client may exhibit skin manifestations, such as coarse, brittle hair; thick, brittle nails; coarse, scaly skin; delayed wound healing; periorbital edema; and face puffiness. Neuromuscular manifestations include lethargy, slow or slurred speech, and impaired memory. Gastrointestinal manifestations include complaints of constipation, weight gain, and abdominal distention. Irritability and soft, silky, thinning hair on the scalp are manifestations of hyperthyroidism. 78. A nurse is reviewing the health care provider's prescriptions for a client diagnosed with hypothyroidism. Which medication prescription should the nurse question and verify? A. Acetaminophen B. Docusate sodium C. Morphine sulfate D. Levothyroxine sodium Ans: C. Medications are administered very cautiously to the client with hypothyroidism because of altered metabolism and excretion and depressed metabolic rate and respiratory status. Morphine sulfate would further depress bodily functions. Hormone replacement with levothyroxine sodium, a thyroid hormone, is a component of therapy. Stool softeners, such as docusate sodium, are prescribed to prevent constipation. 79. A preoperative client is scheduled for adrenalectomy to remove a pheochromocytoma. The nurse would most closely monitor which item in the preoperative period? A. Vital signs B. Fluid balance C. Anxiety level D. Creatinine levels Ans: A. Hypertension is the hallmark symptom of pheochromocytoma. Severe hypertension can precipitate a stroke (brain attack) or sudden blindness. Although all of the items are appropriate nursing assessments for the client with pheochromocytoma, the priority is to monitor the vital signs, especially the blood pressure. 80. A client is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of Addison's disease. The nurse would assess for which problem as a manifestation of this disorder? A. Edema B. Obesity C. Hirsutism D. Hypotension Ans: D. Common manifestations of Addison's disease include postural hypotension from fluid loss, syncope, muscle weakness, anorexia, nausea and vomiting, abdominal cramps, weight loss, depression, and irritability. The remaining 82Adult Health Exam 5 options do not occur with this disease. 81. A client with suspected primary hyperparathyroidism is undergoing diagnostic testing. The nurse would assess for which as a manifestation of this disorder? A. Polyuria B. Diarrhea C. Polyphagia D. Weight gain Ans: A. Hypercalcemia classically occurs with hyperparathyroidism. Elevated serum calcium levels produce osmotic diuresis, making polyuria the correct option. The other manifestations listed are not associated with this disorder. 82. A nurse is assessing the status of a client who returned to the surgical nursing unit after a parathyroidectomy procedure. The nurse would place highest priority on which assessment finding? A. Laryngeal stridor B. Difficulty voiding C. Mild incisional pain D. Absence of bowel sounds Ans: A. During the early postoperative period, the nurse carefully observes the client for signs of bleeding, which may cause swelling and compression of adjacent tissues. Laryngeal stridor results from compression of the trachea and is a harsh, high-pitched sound heard on inspiration and expiration. Laryngeal stridor is an acute emergency, necessitating immediate attention to avoid complete obstruction of the airway. The other options describe usual postoperative problems that are not life threatening. 83. A client is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. The nurse would check which item to detect the primary manifestation of this disorder? A. Weight B. Urine ketones C. Blood pressure D. Skin temperature Ans: C. Hypertension is the major symptom associated with pheochromocytoma and is assessed by taking the client's blood pressure. Glycosuria, weight loss, and diaphoresis are other clinical manifestations of pheochromocytoma; however, hypertension is the major symptom. 84. A nurse is caring for a client with thyrotoxicosis who is at risk for the development of thyroid storm. To detect this complication, the nurse should assess for which sign or symptom? A. Bradycardia B. Constipation C. Hypertension D. Low grade temperature Ans: C. Thyroid storm is an acute, life-threatening condition that occurs in a client with uncontrollable hyperthyroidism. Clinical manifestations of thyroid storm include systolic hypertension, tachycardia, diarrhea, and a fever as high as 106°F. Other manifestations include abdominal pain, dehydration, extreme vasodilation, stupor rapidly progressing to coma, atrial fibrillation, and cardiovascular collapse. Bradycardia, constipation and low-grade temperature are not a part of the clinical picture in thyroid storm. 85. During routine nursing assessment after hypophysectomy, a client complains of thirst and frequent urination. Knowing the expected complications of this surgery, what should the nurse assess next? A. Serum glucose B. Blood pressure C. Respiratory rate D. Urine specific gravity Ans: D. After hypophysectomy, temporary diabetes insipidus can result from antidiuretic hormone deficiency. This deficiency is related to surgical manipulation. The nurse should assess urine specific gravity and notify the health care provider if the result is less than 1.005. Although the remaining options may be components of the assessment, the nurse would next assess urine specific gravity. 86. A client has been diagnosed with Cushing's syndrome. The nurse should assess the client for which expected 83Adult Health Exam 5 manifestations of this disorder? A. Dizziness B. Weight loss C. Hypoglycemia D. Truncal obesity Ans: D. The client with Cushing's syndrome may exhibit a number of different manifestations. These may include moon face, truncal obesity, and a "buffalo hump" fat pad. Other signs include hyperglycemia, hypernatremia, hypocalcemia, peripheral edema, hypertension, increased appetite, and weight gain. Dizziness is not part of the clinical picture for this disorder. 87. A client has returned to the nursing unit after a thyroidectomy. The nurse notes that the client is complaining of tingling sensations around the mouth, fingers, and toes. On the basis of these findings, the nurse should next assess the results of which serum laboratory study? A. Sodium B. Calcium C. Potassium D. Magnesium Ans: B. After surgery on the thyroid gland, the client may experience a temporary calcium imbalance. This is due to transient malfunction of the parathyroid glands. The nurse also would assess for Chvostek's and Trousseau's signs. The correct treatment is administration of calcium gluconate or calcium lactate. The remaining options are unrelated to the client's complaints. 88. A client visits the health care provider's office for a routine physical examination and reports a new onset of intolerance to cold. Since hypothyroidism is suspected, which additional information would be noted during the client's assessment? A. Weight loss and tachycardia B. Complaints of weakness and lethargy C. Diaphoresis and increased hair growth D. Increased heart rate and respiratory rate Ans: B. Weakness and lethargy are the most common complaints associated with hypothyroidism. Other common symptoms include intolerance to cold, weight gain, bradycardia, decreased respiratory rate, dry skin, and hair loss. 89.A 33-year-old female client is admitted to the hospital with a tentative diagnosis of Graves' disease. Which symptom related to the menstrual cycle would the client be most likely to report during the initial assessment? A. Amenorrhea B. Menorrhagia C. Metrorrhagia D. Dysmenorrhea Ans: A. Amenorrhea or a decreased menstrual flow occurs in the client with Graves' disease. Menorrhagia, metrorrhagia, and dysmenorrhea are also disorders related to the female reproductive system; however, they are not typical manifestations of Graves' disease. 90. The nurse is instructing a client with Cushing's syndrome on follow-up care. Which of these client statements would indicate a need for further instruction? A. "I should avoid contact sports." B. "I should check my ankles for swelling." C. "I need to avoid foods high in potassium." D. "I need to check my blood glucose regularly." Ans: C. Hypokalemia is a common characteristic of Cushing's syndrome, and the client is instructed to consume foods high in potassium. Clients with this condition experience activity intolerance, osteoporosis, and frequent bruising. Fluid volume excess results from water and sodium retention. Hyperglycemia is caused by an increased cortisol secretion. 91. The nurse is caring for a postoperative client who has had an adrenalectomy. What should the nurse check for during the client's focused assessment? A. Peripheral edema 84Adult Health Exam 5 B. Bilateral exophthalmos C. Signs of hypovolemia D. Signs of hypocalcemia Ans: C. Aldosterone, secreted by the adrenal cortex, plays a major role in fluid volume balance by retaining sodium and water. Thus, a deficiency can cause hypovolemia. A deficiency of adrenocortical hormones (such as after adrenalectomy) does not cause the clinical manifestations noted in the remaining options. 92. The nurse is caring for a client with Addison's disease. The client asks the nurse about the risks associated with this disease, specifically about addisonian crisis. Regarding prevention of this complication, how should the nurse inform the client? A. "You can take either hydrocortisone or fludrocortisone for replacement. B. "You need to take your fludrocortisone 3 times a day to prevent a crisis." C. “You need to increase salt in your diet, particularly during stressful situations." D. "You need to decrease your dosages of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids during stressful situations." Ans: C. Addison's disease is a result of adrenocortical insufficiency, and management is focused on treating the underlying cause. Hormone therapy is used for replacement. Hydrocortisone has both glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid properties and needs to be taken 3 times daily, with two thirds of the daily dose taken on awakening. Fludrocortisone is taken once daily in the morning. Salt additives are necessary, particularly during times of stress, to compensate for excess heat or humidity as a result of the condition. There needs to be an increased dose of cortisol given for stressful situations such as surgery or hospitalization. Therefore, option 3 is the correct answer. 93. The nurse is assessing a client who has a diagnosis of goiter. Which should the nurse expect to note during the assessment of the client? A. An enlarged thyroid gland B. The presence of heart damage C. Client complaints of chronic fatigue D. Client complaints of slow wound healing Ans: A. An enlarged thyroid gland develops in the client with goiter because of an excessive amount of thyroxine in the thyroid gland. Heart damage occurs with selenium deficiency. In addition, heart damage would not likely be noted during the nursing assessment. Further diagnostic tests in addition to the assessment would be necessary to determine heart damage. Chronic fatigue occurs with iron deficiency. Slow wound healing occurs with zinc deficiency. 94. A health care provider has prescribed propylthiouracil for a client with hyperthyroidism. The nurse recalls that first-line treatment calls for methimazole for medication therapy. The nurse should question the client about her past medical history, specifically regarding which condition? A. Pregnancy B. Renal failure C. Prolonged QT interval D. Adverse reactions to thyroxine Ans: A. Methimazole and propylthiouracil are both used to treat hyperthyroidism. Methimazole is considered firstline treatment; however, this medication cannot be used for clients who are in their first trimester of pregnancy, have had a previous adverse reaction to methimazole, or need rapid reduction of symptoms. Renal failure, prolonged QT interval, and adverse reaction to levothyroxine are not related to contraindications for methimazole. 95. During physical examination of a client, which finding is characteristic of hypothyroidism? A. Periorbital edema B. Flushed, warm skin C. Hyperactive bowel sounds D. Heart rate of 120 bpm Ans: A. Because cellular edema occurs in hypothyroidism, the client's appearance is changed. Nonpitting edema occurs, especially around the eyes and in the feet and hands. Knowing this should direct you to option 1. Flushed, warm skin; hyperactive bowel sounds; and tachycardia (heart rate >100 beats/min) are clinical manifestations of 85Adult Health Exam 5 hyperthyroidism, which occurs as a result of excess thyroid hormone secretion, resulting in a hypermetabolic state. 96. A client's laboratory results indicate the serum calcium is 12 mg/dL (3 mmol/L) and the serum phosphorous is 2.1 mg/dL (0.697 mmol/L). Based on these findings, the nurse suspects imbalance of which hormone? A. Thyroid hormone B. Parathyroid hormone C. Follicle stimulating hormone D. Adrenocorticotropic hormone Ans: B. Parathyroid hormone is responsible for maintaining serum calcium and phosphorous levels within normal range. Knowledge of normal ranges for serum calcium (9 to 10.5 mg/dL [2.25 to 2.75 mmol/L]) and serum phosphorous (3.0 to 4.5 mg/dL [0.97 to 1.45 mmol/L]) is needed to determine that the client's calcium is elevated and phosphorus is decreased, consistent with hyperparathyroidism. Thyroid hormone is responsible for maintaining a normal metabolic rate in the body. Follicle-stimulating hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone are produced by the anterior pituitary gland. They are responsible for growth and maturation of the ovarian follicle and stimulation of the adrenal glands, respectively. 97. A nurse is caring for a client with a dysfunctional thyroid gland and is concerned that the client will exhibit a sign of thyroid storm. Which is an early indicator of this complication? A. Bradycardia B. Constipation C. Hyperreflexia D. Low grade temp Ans: C. Clinical manifestations of thyroid storm include a fever as high as 106°F, hyperreflexia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, dehydration rapidly progressing to coma, severe tachycardia, extreme vasodilation, hypotension, atrial fibrillation, and cardiovascular collapse. 98. The nurse is caring for a client with a diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome. Which expected signs and symptoms should the nurse monitor for? Select all that apply. A. Anorexia B. Dizziness C. Weight loss D. Moon face E. Hypertension F. Truncal obesity Ans: D, E, E. A client with Cushing's syndrome may exhibit a number of different manifestations. These could include moon face, truncal obesity, and a buffalo hump fat pad. Other signs include hypokalemia, peripheral edema, hypertension, increased appetite, and weight gain. Dizziness is not part of the clinical picture for this disorder. 99. A client has begun medication therapy with propylthiouracil. The nurse should assess the client for which condition as an adverse effect of this medication? A. Joint pain B. Renal toxicity C. Hyperglycemia D. Hypothyroidism Ans: D. Propylthiouracil is prescribed for the treatment of hyperthyroidism. Excessive dosing with this agent may convert a hyperthyroid state to a hypothyroid state. If this occurs, the dosage should be reduced. Temporary administration of thyroid hormone may be required to treat the hypothyroid state. Propylthiouracil is not used for relief of joint pain. It does not cause renal toxicity or hyperglycemia. 86 [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 86 pages
Instant download
 Study Guide.png)
Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 22, 2021
Number of pages
86
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 22, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
38









.png)

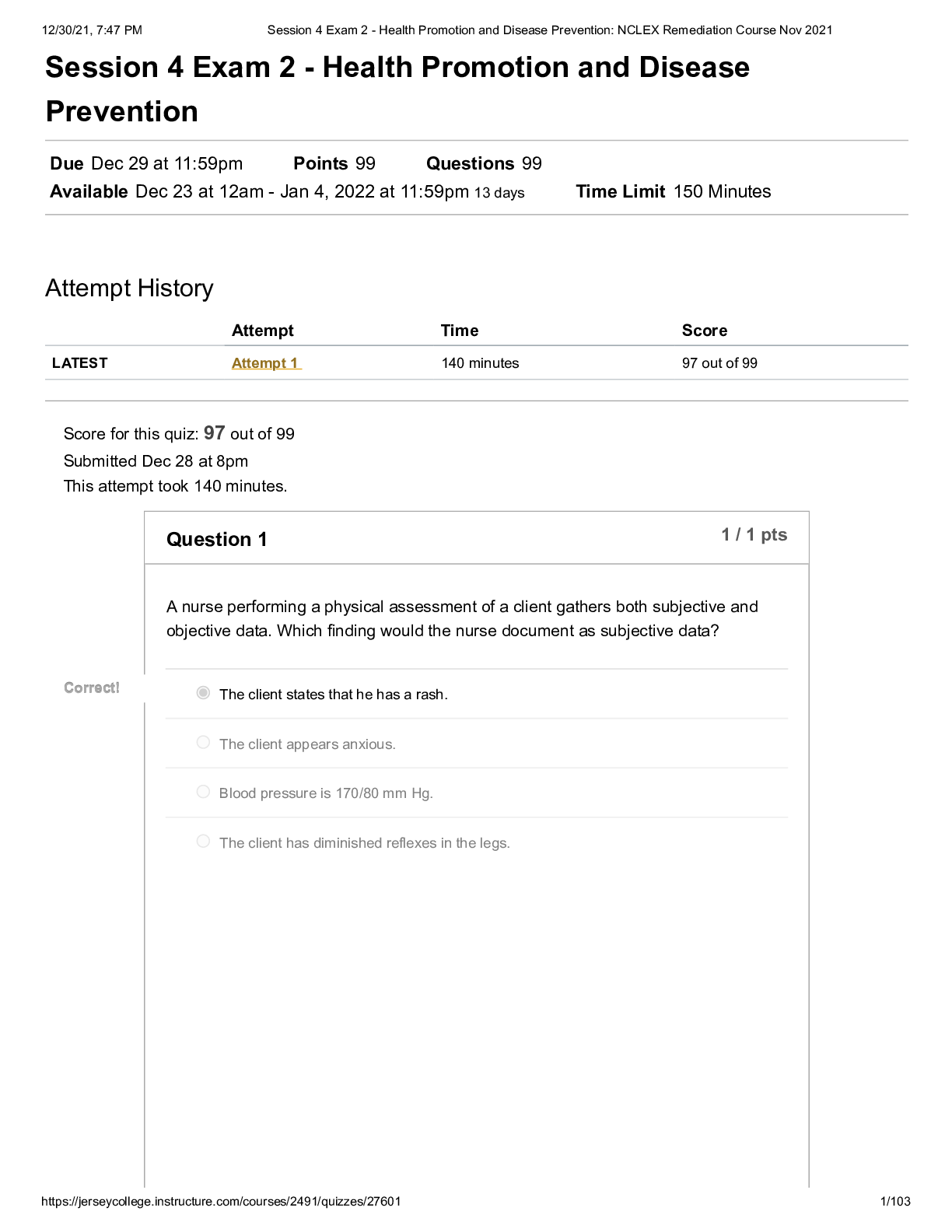
 ORGMED ORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL PHARMACY.png)












.png)











