Biology > EXAM REVIEW > BIO 123 Weekly Quizess,Week 1 2. Biology, the Study of Life Quiz, . Week 1 2. Basic Chemistry of Cel (All)
BIO 123 Weekly Quizess,Week 1 2. Biology, the Study of Life Quiz, . Week 1 2. Basic Chemistry of Cells Quiz, Week 2 2. Organic Molecules and Cells Quiz , Week 2 2. Structure and Function of Cells Quiz, and Week 2 2. Exam 1. Answers and Reviews.
Document Content and Description Below
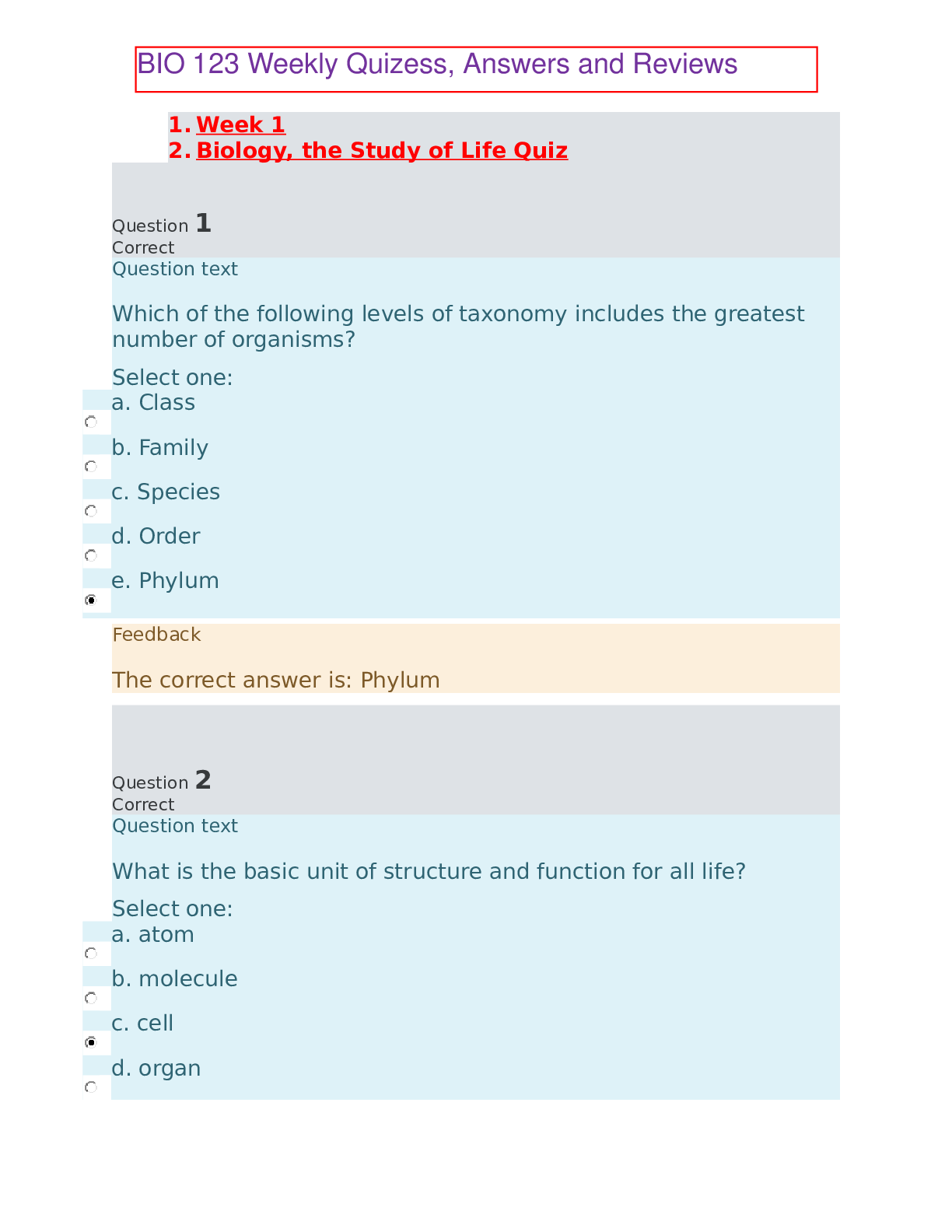
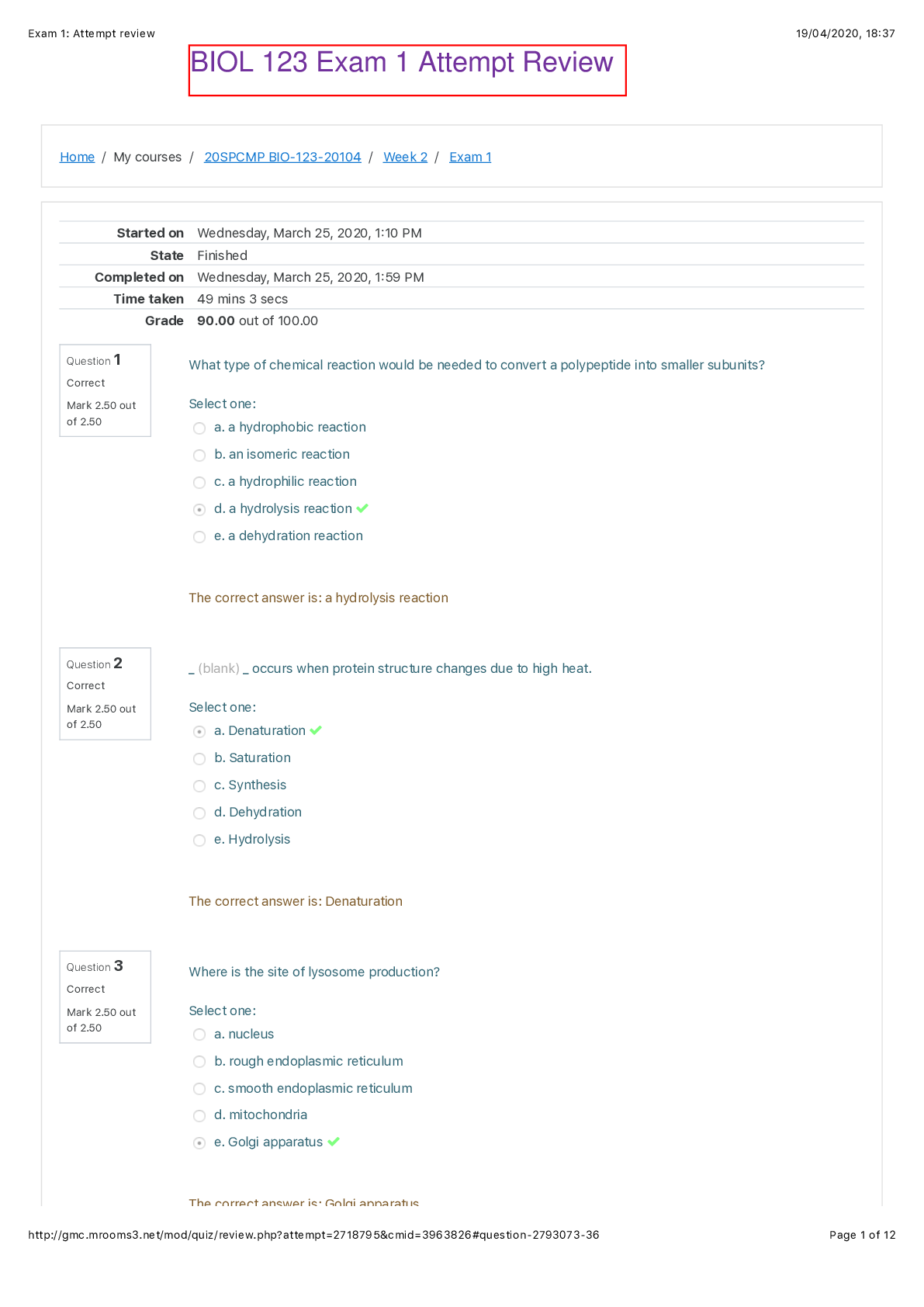
1. Week 1 2. Biology, the Study of Life Quiz Question 1 Question text Which of the following levels of taxonomy includes the greatest number of organisms? a. Class b. Family c. Species d.... Order e. Phylum Phylum Question 2 Question text What is the basic unit of structure and function for all life? a. atom b. molecule c. cell d. organ e. organism cell Question 3 Question text Members of the same species located within a particular area are called _ (blank) _. a. a community b. an ecosystem c. a population d. an organism e. a biosphere a population Question 4 Question text Where do all organisms ultimately get their energy from? a. the sun b. inorganic matter c. organic matter d. water e. nutrient cycling the sun Question 5 In Question text Which of the following shows three taxonomic levels from most to least inclusive? a. species, genus, family b. domain, kingdom, phylum c. family, species, genus d. phylum, domain, kingdom e. family, class, species domain, kingdom, phylum Question 6 Question text You discover a new group of organisms with the following characteristics: no nuclei to hold its DNA, mitochondria, rigid, bacterial flagella. What level of classification would this new organism be placed under? a. Domain b. Kingdom c. Phylum d. Genus e. Species Domain Question 7 Question text What is the main driving force behind evolution? a. natural selection b. metabolism c. homeostasis d. photosynthesis e. organization natural selection Question 8 Question text The _ (blank) _ theory provides insight into why various species differ from one another, predisposition to diseases, and the production of drugs for diseases. a. Cell b. Gene c. Evolution d. Homeostasis e. Ecosystem Gene Question 9 Question text What process explains the unity and diversity of living organisms on our planet? a. taxonomy b. metabolism c. evolution d. homeostasis e. reproduction evolution Question 10 Question text Which of the following is not considered a basic theory of biology? a. Atomic b. Cell c. Homeostasis d. Ecosystem e. Gene Atomic Question 11 Question text What is the term for a possible explanation for a natural event? a. an observation b. a conclusion c. a hypothesis d. a test e. data a hypothesis Question 12 Question text To what kingdom do humans belong? a. Animals b. Plants c. Protists d. Fungi e. Archaea Animals Question 13 Question text What kingdom is characterized by eukaryotic, multicellular organisms that ingest their food? a. Fungi b. Plants c. Protists d. Animals e. Archaea Animals Question 14 Question text You are observing a cell through a microscope and can see that it contains no nucleus. Based exclusively on this information, to which domain(s) might this organism belong? a. Bacteria only b. Archaea only c. Eukarya only d. Bacteria or Archaea but not Eukarya e. Bacteria, Archaea, or Eukarya Bacteria or Archaea but not Eukarya Question 15 Question text What is true of humans? a. they are classified as protists b. they are descended from apes c. they belong to the domain Archaea d. they share a common ancestor with apes e. they are prokaryotes they share a common ancestor with apes 1. Week 1 2. Basic Chemistry of Cells Quiz Question 1 Question text What is the result of unequal sharing of electrons between two atoms? a. a nonpolar molecule, such as methane b. an ionic compound, such as salt c. an electronegative molecule, such as calcium ion d. a hydrophobic molecule, such as fat e. a polar molecule, such as water a polar molecule, such as water Question 2 Question text What diagnostic procedure could be done in order to determine if a patient has a thyroid tumor? a. Patient drinks low levels of radioactive Iodine-131, then has an X-ray b. Patient drinks high levels of radioactive Iodine-131, then has a PET scan c. Injection of low levels of radioactive glucose, then patient has a PET scan d. Injection of low levels of radioactive Thallium-201, then patient has a PET scan e. Injection of high levels of radioactive glucose, then patient has an X-ray Patient drinks low levels of radioactive Iodine-131, then has an X-ray Question 3 Question text Which of the following would occur that could cause an atom to become a different element? a. increase the number of neutrons b. increase the number of electrons c. increase the number of protons d. decrease the number of neutrons e. decrease the number of electrons increase the number of protons Question 4 Question text Water molecules disassociate _ (blank) _ in salt crystals when they are dissolved in water. a. nonpolar covalent bonds b. hydrogen bonds c. polar covalent bonds d. ionic bonds e. hydrophobic interactions ionic bonds Question 5 Question text Which of the following has a positive charge? a. proton b. electron c. atomic mass d. neutron e. isotope proton Question 6 Question text What type of bond occurs between positively and negatively charged atoms? a. covalent bond b. adhesive interaction c. hydrogen bond d. ionic bond e. hydrophobic interaction ionic bond Question 7 Question text Which factor determines whether an atom will be chemically reactive? a. the number of electrons in the outer shell b. the ratio of protons to electrons c. the number of electrons in the inner shell d. the ratio of protons to neutrons e. the number of electron shells an atom has the number of electrons in the outer shell Question 8 Question text What are the six elements that make up living organisms? a. carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur b. copper, iron, magnesium, sodium, water, zinc c. carbon dioxide, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphate, sulfate d. calcium, hydrogen, iron, potassium, sulfur, water e. aluminum, magnesium, nitrogen, silicon, sodium, sulfur carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur Question 9 Question text What type of bond occurs when electrons are equally shared between two atoms? a. polar b. hydrogen c. ionic d. nonpolar e. adhesive nonpolar Question 10 Question text Ions located in bones and teeth that are also important in muscle contractions and nerve conduction are _ (blank) _. a. sodium b. chloride c. bicarbonate d. potassium e. calcium calcium Question 11 Question text What is the type of solution if the hydroxide ion concentration exceeds the hydrogen ion concentration? a. a buffer b. an acid c. a neutral solution d. a base e. a solute a base Question 12 Question text What is the total number of electrons in a neutral atom of phosphorus with an atomic number of 15 and a mass number of 31? a. 16 b. 15 c. 31 d. 8 e. 46 15 Question 13 Question text Which of the following is the largest number describing an atom? a. Electron number b. Neutron number c. Atomic number d. Proton number e. Mass number Mass number Question 14 Question text How does one determine the mass number of an element? a. the number of neutrons plus the number of electrons b. the number of electrons only c. the number of protons plus the number of neutrons d. the number of protons plus the number of electrons e. the number of protons only the number of protons plus the number of neutrons Question 15 Not answered Question text If a sulfur atom has 6 electrons in the outermost shell, how will it likely react? a. gain two electrons from another atom b. lose 6 neutrons to another atom c. nothing, as this is a very stable atom d. lose two electrons to another atom e. stay as a single atom in nature gain two electrons from another atom 1. Week 2 2. Organic Molecules and Cells Quiz Question 1 Question text Why are fats and oils referred to as triglycerides? a. They have three glycerol molecules b. They have three fatty acid molecules c. They have three amino acids d. They have three phospholipids e. They have three steroid groups They have three fatty acid molecules Question 2 Question text What type of sugar is transported in plants and used as table sugar? a. sucrose b. glucose c. lactose d. galactose e. fructose sucrose Question 3 Question text A molecule from a new organism contains adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. What molecules is being looked at? a. DNA b. RNA c. lipid d. protein e. carbohydrate DNA Question 4 In Question text What molecule can ionize and release hydrogen ions to make the solution more acidic? a. carbonyl b. phosphate c. sulfhydryl d. carboxyl e. hydroxyl carboxyl Question 5 In Question text What level of protein structure is found in most enzymes and hemoglobin? a. dipeptide b. primary c. tertiary d. quaternary e. secondary quaternary Question 6 In Question text What type of protein structure describes a linear sequence of amino acids? a. quaternary b. primary c. pleated sheet d. alpha helix e. tertiary primary Question 7 Question text What is the DNA base pair matching? a. T-T, C-C b. C-C, G-G c. A-A, T-T d. A-U, C-G e. A-T, C-G A-T, C-G Question 8 In Question text When added to a carbon chain which functional group will convert it into an alcohol molecule? a. sulfhydryl b. hydroxyl c. phosphate d. carboxyl e. carbonyl hydroxyl Question 9 In Question text Which of the following is not a association of a lipid molecule and its specific function? a. beeswax: main structural component of the bee honeycomb b. phospholipid: main component of fats and oils c. wax: waterproof covering of plant leaves d. testosterone: steroid involved in muscle development in males e. cholesterol: stabilize cell membrane of animal cells phospholipid: main component of fats and oils Question 10 Question text All of the following are likely to be a function of proteins in living organisms except _ (blank) _. a. defense b. support c. metabolism d. transport e. long term energy storage long term energy storage Question 11 Question text Which of the following molecules could be used for an immediate source of energy? a. nucleic acids b. carbohydrates c. water d. protein e. lipids carbohydrates Question 12 In Question text What type of chemical reaction would be needed to convert a polypeptide into smaller subunits? a. a hydrophobic reaction b. an isomeric reaction c. a hydrophilic reaction d. a hydrolysis reaction e. a dehydration reaction a hydrolysis reaction Question 13 Question text Why is sickle cell disease more common in Americans with African ancestors than Americans with European ancestors? a. Sickle-shaped blood cells caused malarial parasites to die, and thus gave protection against malarial infections prevalent in Africa b. Sickle-shaped blood cells were good hosts for tuberculosis, and thus spread tuberculosis widely throughout Africa c. Sickle-shaped blood cells caused cholera bacteria to die, and thus gave protection against large-scale cholera epidemics throughout Europe d. Sickle-shaped blood cells caused tuberculosis bacteria to die, and thus gave protection against large-scale Tb epidemics throughout crowded areas in Africa e. Sickle-shaped blood cells were good hosts for cholera bacteria, and thus caused many people to die from cholera and diarrhea Sickle-shaped blood cells caused malarial parasites to die, and thus gave protection against malarial infections prevalent in Africa Question 14 Question text Why does the molecule shown make plaques along the walls of blood vessels? a. it is hydrophillic and can trap dust b. it is hydrophobic and would not dissolve in blood fluid c. it is hydrophobic and can repel insects d. it is hydrophillic and likes to stick to blood fluid e. it is hydrophobic and serves as a waterproof barrier it is hydrophobic and would not dissolve in blood fluid Question 15 Question text What is the term for a large organic molecule with many subunits? a. hydromer b. monomer c. polymer d. isomer e. hydrophilic polymer 1. Week 2 2. Structure and Function of Cells Quiz Question 1 Question text Using the animal cell diagram, identify the cell structure marked "e." a. lysosome b. mitochondrion c. nucleus d. centrioles e. nucleolus centrioles Question 2 In Question text How is it possible to contrast chloroplasts and mitochondria? a. whether the organelle contains its own DNA b. whether the organelle converts solar energy into cellular energy c. whether the organelle is found in plant cells d. whether the organelle has multiple membranes e. whether the organelle has a large internal surface area whether the organelle converts solar energy into cellular energy Question 3 Question text What would occur if a eukaryotic cell lacked the Golgi apparatus? a. it could not digest macromolecules b. it could not package proteins c. it could not maintain its shape d. it would not have genetic information e. it could not make energy it could not package proteins Question 4 Question text Which of the following cells would have a nucleus, a cell wall, and a large central vacuole? a. archaean cell b. animal cell c. bacterial cell d. plant cell e. prokaryotic cell plant cell Question 5 In Question text Where are lipids synthesized outside of the endomembrane system? a. smooth endoplasmic reticulum b. rough endoplasmic reticulum c. Golgi apparatus d. nucleus e. mitochondria mitochondria Question 6 Question text Arrange the order of cytoskeletal fibers from smallest to largest. a. actin filaments, microtubules, intermediate filaments b. actin filaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules c. microtubules, actin filaments, intermediate filaments d. intermediate filaments, actin filaments, microtubules e. microtubules, intermediate filaments, actin filaments actin filaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules Question 7 Question text What is the basic unit of structure and function for all life? a. molecule b. cell c. organism d. atom e. organ cell Question 8 Question text Which cell organelle is responsible for processing, packaging, and the secretion of proteins? a. Golgi apparatus b. nucleus c. lysosomes d. smooth endoplasmic reticulum e. rough endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Question 9 Question text Using the plant cell diagram, identify the cell structure marked "a." a. cytoplasm b. nucleus c. mitochondria d. central vacuole e. Chloroplast central vacuole Question 10 Question text Where are the majority of ribosomes found inside the cell? a. cytoskeleton b. nuclear envelope c. smooth endoplasmic reticulum d. rough endoplasmic reticulum e. mitochondria rough endoplasmic reticulum Question 11 Question text Using the animal cell diagram, identify the cell structure marked "c." a. smooth endoplasmic reticulum b. rough endoplasmic reticulum c. Golgi apparatus d. nucleus e. mitochondria Golgi apparatus Question 12 In Question text Select the pair of cytoskeletal structure and its physical makeup. a. centriole: short barrels of intermediate filaments b. actin filaments: twisted strands of keratin proteins c. microtubules: cylinders made of keratin proteins d. flagellum: microtubule doublets and actin side arms e. intermediate filaments: ropes made of proteins intermediate filaments: ropes made of proteins Question 13 Question text Which structure can occupy up to 90% of the volume in a plant cell? a. central vacuole b. endoplasmic reticulum c. nucleus d. chloroplasts e. cytoplasm central vacuole Question 14 Question text What structure is not typically found in a prokaryotic cell? a. capsule b. nucleus c. ribosome d. plasma membrane e. cell wall nucleus Question 15 Question text What type of cell would have lysosomes and a nucleus, but no chloroplasts? a. bacterial cell b. archaean cell c. animal cell d. plant cell e. prokaryotic cell animal cell 1. Week 2 2. Exam 1 Question 1 In Question text What kind of bond occurs between nucleotides in a DNA molecule, such as the polar "G" nucleotide on one strand with the polar "C" nucleotide on the other strand? a. hydrophobic interactions b. hydrogen bonds c. adhesive interactions d. covalent bonds e. ionic bonds hydrogen bonds Question 2 Question text Which of the following is not considered a basic theory of biology? a. Atomic b. Cell c. Homeostasis d. Ecosystem e. Gene Atomic Question 3 Question text What would be the result of a cell that did not have RNA molecules? a. The DNA would take over its job b. The cell would not have genes c. There would be no effect on the cell d. The cell could not make energy e. The cell would not be able to make proteins The cell would not be able to make proteins Question 4 Question text Which of the following is not a association of a lipid molecule and its specific function? a. beeswax: main structural component of the bee honeycomb b. phospholipid: main component of fats and oils c. wax: waterproof covering of plant leaves d. testosterone: steroid involved in muscle development in males e. cholesterol: stabilize cell membrane of animal cells phospholipid: main component of fats and oils Question 5 Question text Where is the site for breakdown of engulfed bacteria, debris and macromolecules in an animal cell? a. peroxisomes b. rough endoplasmic reticulum c. lysosomes d. mitochondria e. smooth endoplasmic reticulum lysosomes Question 6 In Question text What level of protein structure is found in most enzymes and hemoglobin? a. dipeptide b. primary c. tertiary d. quaternary e. secondary quaternary Question 7 Question text Which of the following molecules is more complex than a monosaccharide? a. sucrose b. galactose c. deoxyribose d. glucose e. ribose sucrose Question 8 Question text Which of the following is true about eukaryotic cells when compared to prokaryotic cells? a. eukaryotic cells are smaller b. eukaryotic cells have a capsule c. eukaryotic cells have no cell membrane d. eukaryotic cells have no nucleus e. eukaryotic cells have a nucleus eukaryotic cells have a nucleus Question 9 Question text What is true of carbon because it has four electrons in its outer shell? a. gain four electrons to complete its outer shell b. lose four electrons to become stable c. gain or lose two electrons to become stable d. share four electrons to complete its outer shell e. share two electrons to complete its outer shell share four electrons to complete its outer shell Question 10 In Question text What is the type of solution if the hydroxide ion concentration exceeds the hydrogen ion concentration? a. a buffer b. an acid c. a neutral solution d. a base e. a solute a base Question 11 Question text Which of the following cells would have a nucleus, a cell wall, and a large central vacuole? a. archaean cell b. animal cell c. bacterial cell d. plant cell e. prokaryotic cell plant cell Question 12 Question text If water is mixed with salt in a beaker, what does the salt represent? a. the solvent b. the solute c. the solution d. the buffer e. the ion the solute Question 13 Question text The tendency of water molecules to cling to other water molecules is _ (blank) _. a. adhesion b. electronegativity c. polar d. cohesion e. nonpolar cohesion Question 14 Question text Which of the following is true of ATP? a. It is used for long term energy storage b. It has a base of adenine, the sugar ribose, and three phosphate groups c. It contains adenine, ribose, and two phosphate groups d. It has a base of adenine, the sugar deoxyribose, and three phosphate groups e. It is very stable) It has a base of adenine, the sugar ribose, and three phosphate groups Question 15 Question text What type of organism uses chitin for structure and support? a. bacterium b. cactus c. human d. tree e. crab crab Question 16 In Question text Why is hydrochloric acid classified as an acid? a. it absorbs excess hydroxide ions from the solution b. it dissociates to release hydroxide ions c. it dissociates to release hydrogen ions and absorbs excess hydroxide ions from the solution d. it absorbs excess hydrogen ions from the solution e. it dissociates to release hydrogen ions it dissociates to release hydrogen ions and absorbs excess hydroxide ions from the solution Question 17 Question text Which of the following is about saturated fatty acids? a. They are made of glycerol b. They have no double bonds between carbon atoms c. They are made of nucleotides d. They are composed of glucose subunit e. They are composed of amino acid subunits) They have no double bonds between carbon atoms Question 18 Question text Why does the molecule shown make plaques along the walls of blood vessels? a. it is hydrophillic and can trap dust b. it is hydrophobic and would not dissolve in blood fluid c. it is hydrophobic and can repel insects d. it is hydrophillic and likes to stick to blood fluid e. it is hydrophobic and serves as a waterproof barrier it is hydrophobic and would not dissolve in blood fluid Question 19 Question text What is the term for the building blocks of proteins? a. monosaccharides b. amino acids c. phospholipids d. peptides e. nucleotides amino acids Question 20 Question text What is the function of transport vesicles inside a cell? a. move proteins between the SER and the RER b. move proteins between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus c. move proteins between the endoplasmic reticulum and the cell membrane d. move proteins between the nucleus and the endoplasmic reticulum e. move proteins between the nucleus and the Golgi apparatus move proteins between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus Question 21 Question text Using the animal cell diagram, identify the cell structure marked "a." a. nucleus b. rough endoplasmic reticulum c. mitochondria d. Golgi apparatus e. smooth endoplasmic reticulum rough endoplasmic reticulum Question 22 Question text Where are saturated fats primarily found? a. fungi b. crustaceans c. bacterial cell walls d. plant oils e. mammals mammals Question 23 Question text What type of reaction removes a hydroxyl group and a hydrogen atom from two molecules to join them together? a. a dehydration reaction b. a hydrophilic reaction c. a monomer reaction d. a polymer reaction e. a hydrolysis reaction a dehydration reaction Question 24 Question text The cytoskeleton performs all of these functions except _ (blank) _. a. help white blood cells break down bacteria that have been engulfed b. strengthen a layer of skin cells c. help connective cells crawl along a surface d. help organelles move inside a cell e. maintain the shape of intestinal cells help white blood cells break down bacteria that have been engulfed Question 25 Question text What molecule can ionize and release hydrogen ions to make the solution more acidic? a. carbonyl b. phosphate c. sulfhydryl d. carboxyl e. hydroxyl carboxyl Question 26 Question text What is the basic unit of structure and function for all life? a. molecule b. cell c. organism d. atom e. organ cell Question 27 Question text What kind of interaction occurs between atoms of sodium and chlorine? a. The sodium atom gives up one proton b. The sodium atom gives up one neutron c. The chlorine atom gives up one neutron d. The chlorine atom gives up one electron e. The sodium atom gives up one electron The sodium atom gives up one electron Question 28 Question text What type of chemical reaction would be needed to convert a polypeptide into smaller subunits? a. a hydrophobic reaction b. an isomeric reaction c. a hydrophilic reaction d. a hydrolysis reaction e. a dehydration reaction a hydrolysis reaction Question 29 Question text If a sulfur atom has 6 electrons in the outermost shell, how will it likely react? a. gain two electrons from another atom b. lose 6 neutrons to another atom c. nothing, as this is a very stable atom d. lose two electrons to another atom e. stay as a single atom in nature gain two electrons from another atom Question 30 Question text _ (blank) _ occurs when protein structure changes due to high heat. a. Denaturation b. Saturation c. Synthesis d. Dehydration e. Hydrolysis Denaturation Question 31 Question text What is the benefit of low levels of radioactive isotopes in a medicinal setting? a. as tracers in imaging organs using Xrays and PET Scans b. to reduce obesity and diabetes in teenagers c. to create drugs that work faster than normal d. to destroy aging and unwanted cells e. to prevent ultraviolet damage from the sun as tracers in imaging organs using Xrays and PET Scans Question 32 Question text The type of bond between one hydrogen atom and one oxygen atom in a water molecule is _ (blank) _. a. a polar covalent bond b. an ionic bond c. hydrogen bond d. a nonpolar covalent bond e. a hydrophobic interaction a polar covalent bond Question 33 Question text What is the term for a specific combination of bonded atoms which always react in the same way? a. a hydrophilic group b. a hydrophobic group c. an organic group d. a functional group e. a covalent group a functional group Question 34 In Question text _ (blank) _ is an atom with an unequal number of protons and electrons. a. An isotope b. An ion c. A compound d. An octet e. A valance An ion Question 35 Question text Which organelle acts as the powerhouse of the cell? a. mitochondria b. nucleus c. rough endoplasmic reticulum d. chloroplast e. lysosome mitochondria Question 36 Question text An example of _ (blank) _ is flat leaves in plants that are able to provide more surface area for light exposure. a. an adaptation b. homeostasis c. a mutation d. a gene e. a cell an adaptation Question 37 Question text What is the basic unit of structure and function for all life? a. atom b. molecule c. cell d. organ e. organism cell Question 38 Question text When you mix sugar into Kool-Aid, the sugar dissolves in the liquid. This shows that sugar molecules are _ (blank) _. a. hydrophilic b. cohesive c. covalent d. neither hydrophobic nor hydrophilic e. hydrophobic hydrophilic Question 39 Question text Which of these functional groups would be related to nucleotides and phospholipids? a. hydroxyl b. phosphate c. sulfhydryl d. carbonyl e. carboxyl phosphate Question 40 Question text Each of the following is a use of water by living organisms except _ (blank) _. a. external transportation for chemicals b. help exchange heat c. aids in homeostasis d. provides nutrients for metabolism e. provides a medium for movement provides nutrients for metabolism [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 60 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 15, 2021
Number of pages
60
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 15, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
160



.png)





.png)













