*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > MEDSURG 2 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE- LATEST UPDATED GUIDE FOR GRADE A (All)
MEDSURG 2 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE- LATEST UPDATED GUIDE FOR GRADE A
Document Content and Description Below
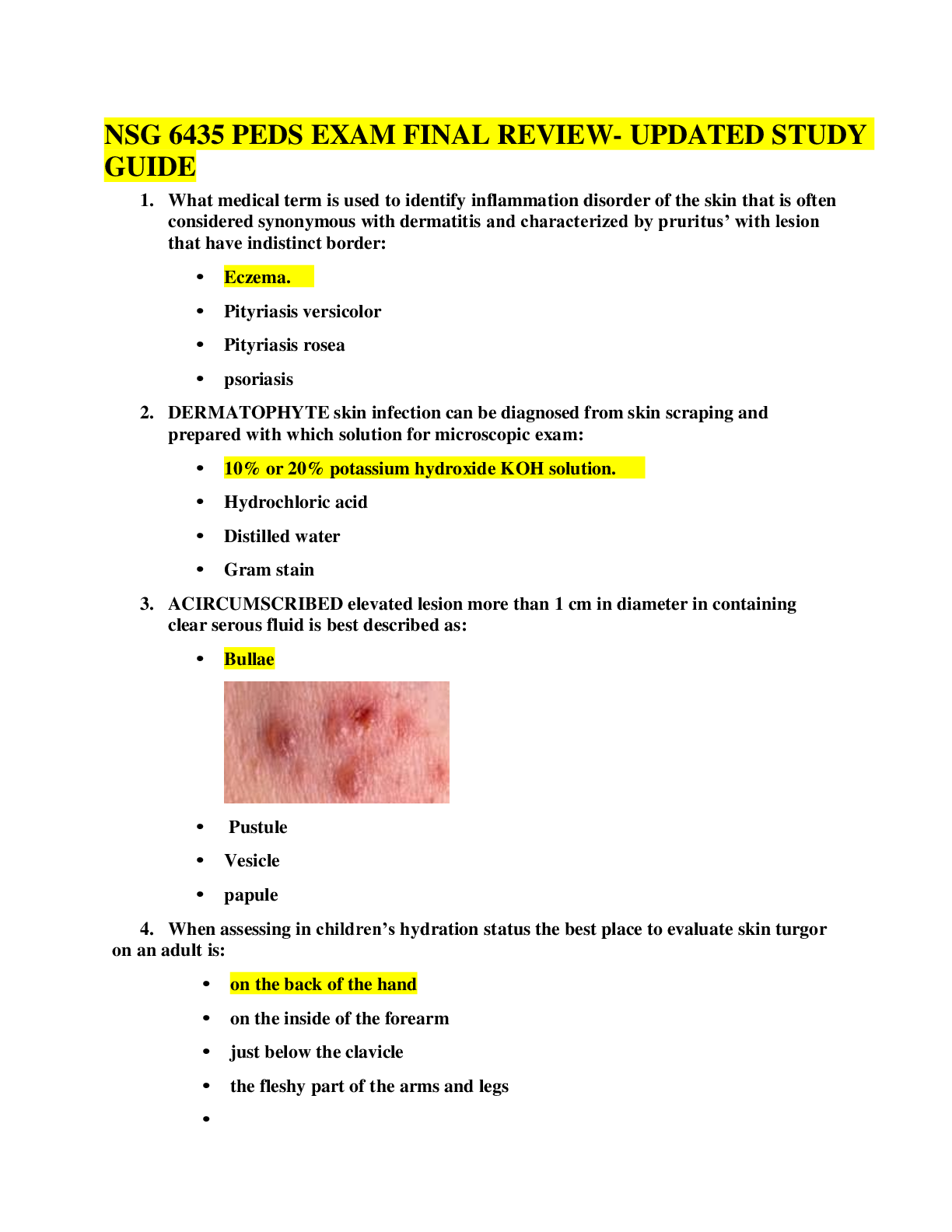
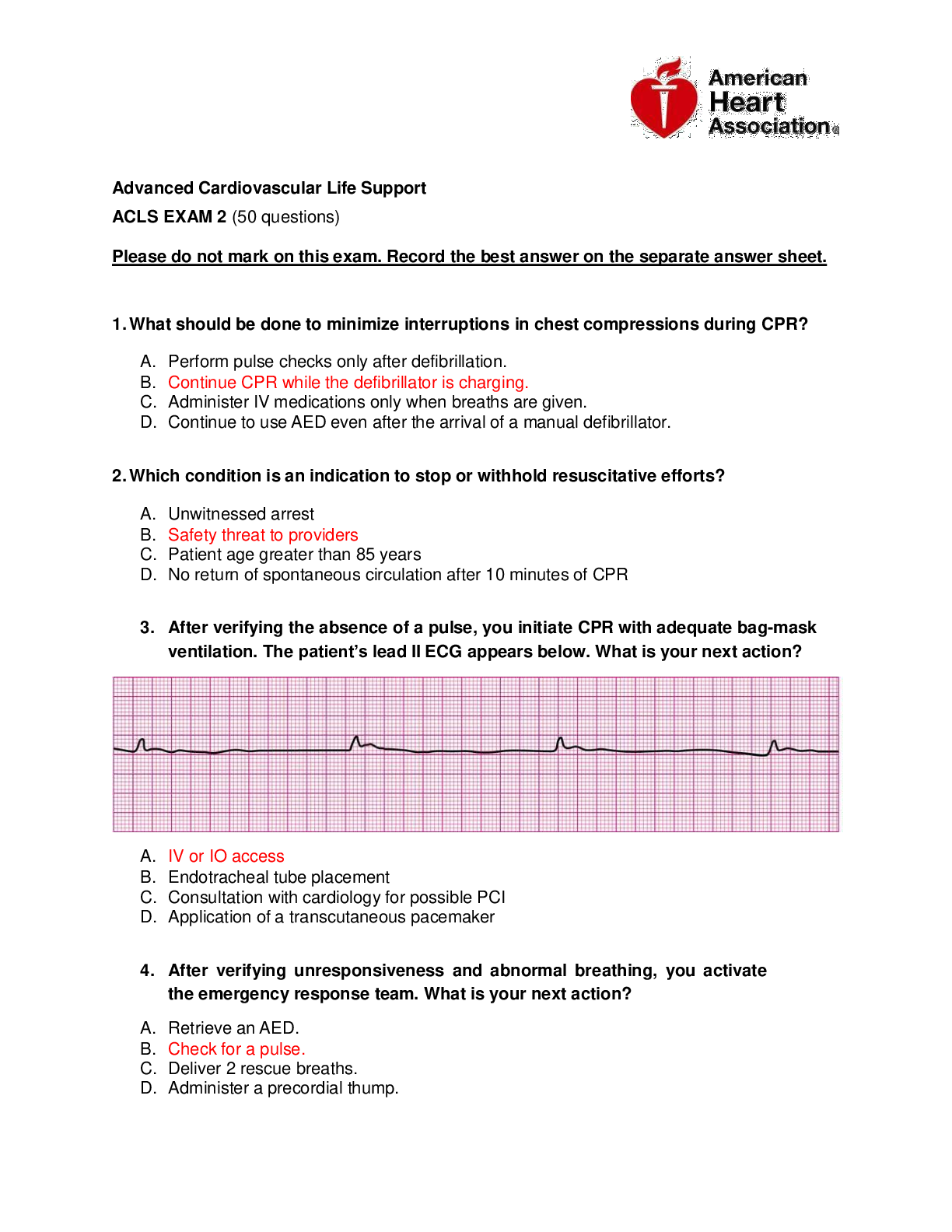
Cardiac Assessment Cardiac Conduction System ➢ Generates and transmits electrical impulses that stimulate contraction of the myocardium ➢ SA node AV node Bundle of his (branches into rig... ht and left) purkinjie fibers ➢ SA node which is the primary pacemaker of the heart o A patient has a HR of 90. Means The SA node is working because normal HR is 60-100 o If the HR falls below the normal value, there is a problem! ➢ AV node which is the secondary pacemaker of the heart o If the SA node malfunctions. The AV node will take over which has a lower rate such as 40-60 bpm Cardiac Action Potential Is the electrical cells generate and transmit impulses across the heart which will stimulate cardiac myocytes to contract. Stimulation of these myocytes occurs due to the exchange of electrically charged particles (ions) across the channels located in the cell membrane ➢ In resting or polarized state o Sodium is the primary extracellular ion o Potassium is the primary intracellular ion Terms of Cardiac Action Potential o Depolarization: electrical activation of cell caused by influx of sodium into cell while potassium exits cell. THIS CREATES A POSITIVELY CHARGED INTRACELLULAR SPACE AND NEGATIVELY CHARGED EXTRACEULAR SPACE o Repolarization: return of cell to resting state caused by re-entry of potassium into cell while sodium exits o Refractory periods – cardiac cells must completely repolarize before they can depolarize AGAIN o 2 phases of refractory period o Effective refractory period: phase in which cells are incapable of depolarizing. It is completely unresponsive to ANY electrical stimulus o Relative refractory period: phase in which cells require stronger-than-normal stimulus to depolarize Cardiac Hemodynamics • HR x SV = Cardiac Output • Cardiac output refers to the total amount of blood ejected by one of the ventricles in liters per minute. • The cardiac output in a resting adult is 4 to 6 L/min but varies greatly depending on metabolic needs • Cardiac output responds to changes in the metabolic demands of the tissues associated with stress, physical exercise, and illness o HR is affected by central nervous system activity and baroreceptor activity. o HR is determined by rate and rhythm – if it is regular or irregular o If HR is affected so is CO o If the heart is not stretching enough – cardiac output is affected o If the heart is not pumping – cardiac output is affected • Stroke volume is determined by preload, afterload, and contractility o Preload: refers to the degree of stretch of the ventricular cardiac muscle fibers at the end of diastole. The end of Diastole is the period when filling volume in the ventricles is the highest and the degree of stretch on the muscle fibers is the greatest (when it is filled with more and more blood = the greater the stretch = the greater the force of contraction) o Diastole is the relaxation/filling phase of the ventricles and once these have filled this is the preload. We can also refer to preload as the EVD (it is at the end of the diastolic phase). Preload is the amount the ventricle stretched! ▪ Think of a balloon (such as the more air you blow in, the greater the stretch) o Afterload: resistance to ejection of blood from the ventricles. This is the pressure required to overcome aortic pressure. The higher the aortic pressure the harder the ventricles have to work – (the LV must overcome the aortic pressure). The pressure in the ventricles work against to open the SL valves to pump blood out of the heart o Contractility: refers to the force generated by the contracting myocardium (the more forceful the more blood that is ejected) • If there is an issue with cardiac output = perfusion issue because there is an issue with oxygenation and flow components • Low HR = CO is affected • Increase in SV and HR = increase in CO Age Related changes in cardiac -Atria, LV, Valves (stiffen and no longer close properly), Conduction system, SNS (decreased response), aorta (stiffen), arteries (stiffen), baroreceptor response (more sensitive) CONTINUED.........................DOWNLOAD FOR BEST GUIDE TO BEST SCORES [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 66 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.50
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 15, 2022
Number of pages
66
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 15, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
46