*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > Nursing - NR 508/NR508 Midterm Study Guide, Chamberlain. (All)
Nursing - NR 508/NR508 Midterm Study Guide, Chamberlain.
Document Content and Description Below
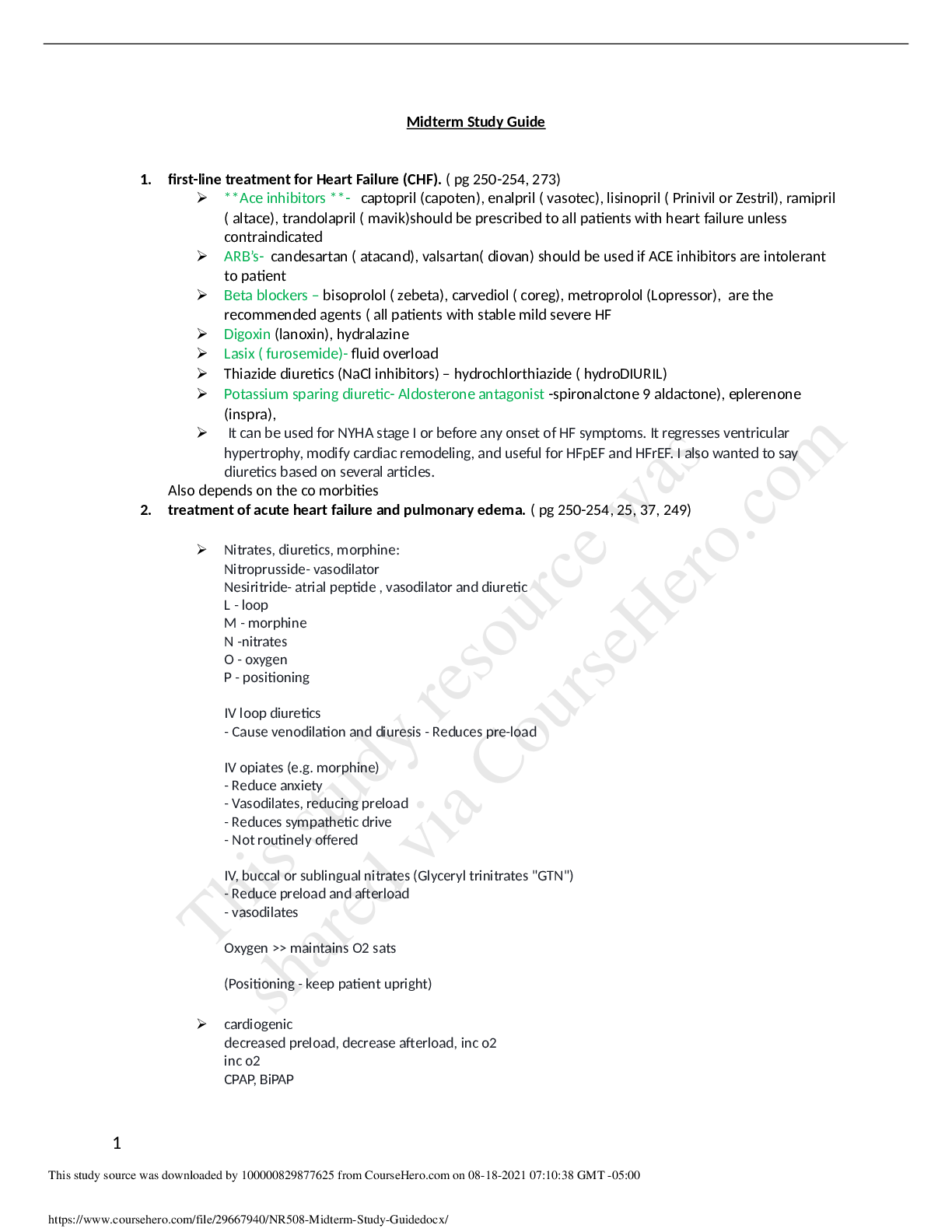
Midterm Study Guide 1. first-line treatment for Heart Failure (CHF). ( pg 250-254, 273) **Ace inhibitors **- captopril (capoten), enalpril ( vasotec), lisinopril ( Prinivil or Zestril), ramipril... ( altace), trandolapril ( mavik)should be prescribed to all patients with heart failure unless contraindicated ARB’s- candesartan ( atacand), valsartan( diovan) should be used if ACE inhibitors are intolerant to patient Beta blockers – bisoprolol ( zebeta), carvediol ( coreg), metroprolol (Lopressor), are the recommended agents ( all patients with stable mild severe HF Digoxin (lanoxin), hydralazine Lasix ( furosemide)- fluid overload Thiazide diuretics (NaCl inhibitors) – hydrochlorthiazide ( hydroDIURIL) Potassium sparing diuretic- Aldosterone antagonist -spironalctone 9 aldactone), eplerenone (inspra), It can be used for NYHA stage I or before any onset of HF symptoms. It regresses ventricular hypertrophy, modify cardiac remodeling, and useful for HFpEF and HFrEF. I also wanted to say diuretics based on several articles. Also depends on the co morbities 2. treatment of acute heart failure and pulmonary edema. ( pg 250-254, 25, 37, 249) Nitrates, diuretics, morphine: Nitroprusside- vasodilator Nesiritride- atrial peptide , vasodilator and diuretic L - loop M - morphine N -nitrates O - oxygen P - positioning IV loop diuretics - Cause venodilation and diuresis - Reduces pre-load IV opiates (e.g. morphine) - Reduce anxiety - Vasodilates, reducing preload - Reduces sympathetic drive - Not routinely offered IV, buccal or sublingual nitrates (Glyceryl trinitrates "GTN") - Reduce preload and afterload - vasodilates Oxygen >> maintains O2 sats (Positioning - keep patient upright) cardiogenic decreased preload, decrease afterload, inc o2 inc o2 CPAP, BiPAP dec preload nitroglycerin, loop diuretics (furosemide, bumetanide) 2 dec afterload nitroprusside, ACEi/ARB noncardiogenic treat underlying cause, mechanical ventilation 3. side effects of ACE inhibitors and mechanism of action of ACE inhibitors. (pg. 279, 274-275) side effects- cough (change to an ARB) Angioedema, rash, diaphoresis, angioedema, cough, abdominal pain, leukopenia, myalgia, headache, renal insufficiency. INCREASES creatinine, hyperkalemia, hypotension. Teratogen (fetal renal malformations) MOA- inhibits angiotensin converting enzyme, interfering with conversion of angiotension I to angiotensin II. ACE inhibitors inhibit the breakdown of bradykinin a potent and naturally occurring vasodilator by blocking the enzyme kininase II. This is thought to be the cause of the cough commonly experienced by patients who take this class of drugs. Uses: HTN, Chronic HF, Prevention of renal failure in diabetes 4. which antihypertensive medication classes are contraindicated in patients with asthma. (pg. 261) Beta blockers- such as metoprolol (Toprol), carvedilol ( coreg), nadolol (corgard), penbutolol ( levatol), pindolol ( visken), atenolol ( tenormin), Propranolol (Non-selective beta blocker) 5. mechanism of action of Digoxin. ( pg 248-255, 274t) increases intracellular concentration of calcium which increases force of myocardial contraction decreases activation of sympathetic nervous system improved quality of life but no decrease in mortality directly inhibits the Na+/K+ ATPase location in the plasma membrane, which leads to indirect inhibition of Na+Ca2+, increase in cardiac contractility 6. uses and the mechanism of action of Penicillin. (pg. 672-673, 674) PCN’s inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis Penicillins, which are bactericidal against susceptible organisms, disrupt synthesis of the bacterial cell wall and compete for and bind to specific enzyme proteins that catalyze transpeptidation and cross-linking. The enzymes to which they bind are called penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). They consist of transpeptidases, transglycosylases, and D-alanine carboxykinase and are implicated in the final phases of building and reshaping of the bacterial cell wall while it is growing and dividing. This action interferes with the biosynthesis of mucopeptides and prevents linkage of structural components of the cell wall. After the penicillin molecules bind and inhibit the transpeptidase enzymes, susceptible bacteria are no longer able to lay protein cross-links across the peptidoglycan backbone of the cell wall. In addition to being structurally weak, this formation is thought to catalyze the activation of autolytic enzymes in the cell wall that cause progressive bacterial lysis [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 27, 2020
Number of pages
9
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 27, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
42

























.png)


 Rasmussen College.png)



