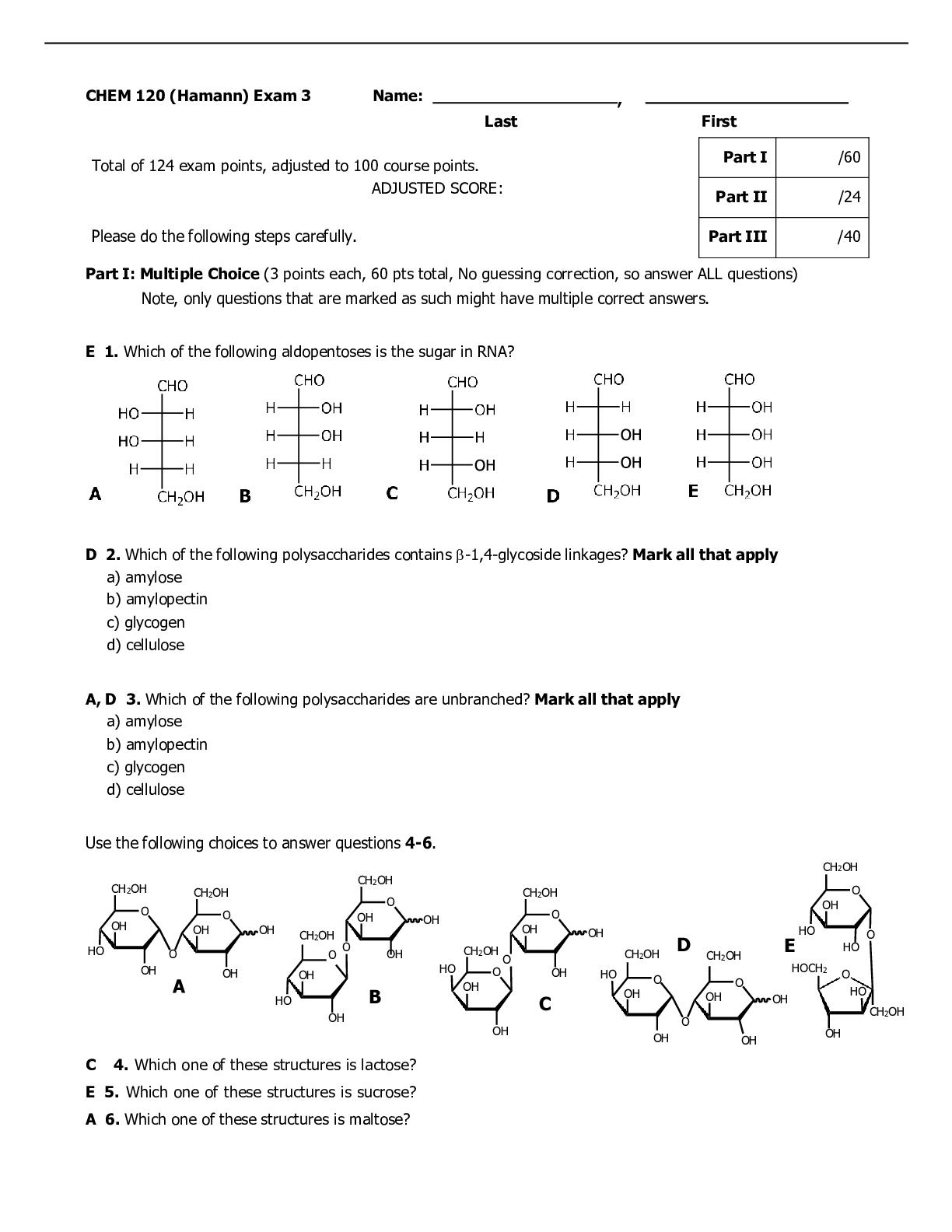*NURSING > EXAM > ATI Practice Assessment Answer Key for Acid Base Mechanical Ventilation Resp Failure. (All)
ATI Practice Assessment Answer Key for Acid Base Mechanical Ventilation Resp Failure.
Document Content and Description Below
Detailed Answer Key Student Success. N4581Resp Practice Questions 1.A nurse is reviewing the arterial blood gas values for a client. The pH is 7.32, PaCO2 48 mm Hg and the HCO3 is 23 mEq/L. The nur... se should recognize that these findings indicate of which of the following acid base balances? A. Respiratory acidosis Rationale:A number of conditions can lead to respiratory acidosis, including COPD and pneumonia. In the presence of respiratory acidosis, the client's blood gas values meet the following criteria: a pH less than 7.35, a PaCO2 greater than greater 45 mg/Hg, and a HCO3 that is normal or slightly elevated (22 to 26 mEq/mL). B. Respiratory alkalosis Rationale: Hyperventilation, from acute pain or anxiety, can causes respiratory alkalosis. In the presence of respiratory alkalosis, the client's blood gas values meet the following criteria: a pH greater than 7.45, a PaCO2 less than 35 mm Hg, and a HCO3 of 22 to 26 mEq/mL. C. Metabolic acidosis Rationale:Ketoacidosis can cause metabolic acidosis. In the presence of metabolic acidosis, the client's blood gas values meet the following criteria: a pH less than 7.35, a PaCO2 that is normal if uncompensated (35 to 45 mm/Hg), and a HCO3 less than 22 mEq/mL. D. Metabolic alkalosis Rationale:Persistent vomiting can cause metabolic alkalosis. In the presence of metabolic acidosis, the client's blood gas values meet the following criteria: a pH greater than 7.45, a PaCO2 that is normal if uncompensated (35 to 45 mm/Hg), and a HCO3 that is greater than 26 mEq/mL. 2.A nurse is providing teaching to a client who is postoperative following coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery and is receiving opioid medications to manage discomfort. Aside from managing pain, which of the following desired effects of medications should the nurse identify as most important for the client’s recovery? A. It decreases the client's level of anxiety. Rationale: The nurse should assess for and manage the client’s anxiety, as this can result in postoperative delirium. Following the administration of an opioid medication, the nurse should assess the client for relief of pain and apprehension. Even though opioid analgesics may decrease the client's level of anxiety (partially from pain reduction alone), there is another effect that is more important. B. It facilitates the client's deep breathing. Rationale: When using the airway, breathing, circulation approach to client care, the nurse should identify facilitation of deep breathing as the most important desired effect of opioids aside from pain relief. Following thoracic type surgeries, the client’s has increased pain with moving, deep breathing and coughing. Opioid medications help minimize the discomfort experienced with deep breathing and coughing which prevents the development of postoperative pneumonia. The nurse should also encourage the client to splint his incision to help minimize pain. C. It enhances the client's ability to sleep. Rationale: The nurse should take measures to facilitate sleep in the postoperative client such as providing Created on:01/15/2021 Page 1 Detailed Answer Key Student Success. N4581Resp Practice Questions quiet time that is undisturbed, dimming lights, and ensuring the client is comfortable and not in pain. Even though opioid analgesics may increase the client’s ability to relax and sleep, another effect is more important. D. It reduces the client's blood pressure. Rationale: The nurse should closely monitor the cardiac status of the client who is postoperative. The client who is experiencing pain releases catecholamines which produce vasoconstriction and increase blood pressure. Even though opioid analgesics may assist in reducing a client’s blood pressure, another effect is more important. 3.A client is admitted to the emergency room with a respiratory rate of 7/min. Arterial blood gases (ABG) reveal the following values. Which of the following is an appropriate analysis of the ABGs? pH 7.22 PaCO2 68 mm Hg Base excess -2 PaO2 78 mm Hg Saturation 80% Bicarbonate 26 mEq/L A. Respiratory acidosis Rationale: Respiratory acidosis occurs when there is retention of CO2 due to an impairment of respiratory function. It can be the result of respiratory depression, seen with anesthesia or opioid administration; inadequate chest expansion, due to a weakness of the respiratory muscles or constriction to the thorax; an obstruction of the airway, seen in aspiration, bronchoconstriction, or laryngeal edema; or from an inability of the lungs to adequately diffuse gases (O2 and CO2), resulting from conditions such as pneumonia, COPD, chest trauma, or pulmonary emboli. Arterial blood gases will reveal a pH that is lower than the normal reference range (7.35 – 7.45) and a CO2 level that is higher than the normal reference range (35 – 45 mm Hg). B. Metabolic acidosis Rationale: Metabolic acidosis occurs when there is an alteration in the level of hydrogen ions or a reduction in the amount of bicarbonate available. It can be the result of diabetic ketoacidosis, starvation, hypoxia, renal or liver failure, dehydration, or diarrhea. Arterial blood gases will reveal a pH that is lower than the normal reference range (7.35 – 7.45) and a bicarbonate (HCO3) level that is lower than the normal reference range (21 – 28 mEq/mL). C. Metabolic alkalosis Rationale: Metabolic alkalosis occurs when there is an alteration in the level of HCO3 along with an increase in the pH of the blood. It can be the result when a client ingests too much antacid from blood transfusions or total parenteral nutrition. It can also occur if the client has prolonged vomiting or NG suction, takes thiazide diuretics, or has a metabolic disorder such as hypercortisolism or hyper aldosteronism. Arterial blood gases will reveal a pH that is higher than the normal reference range (7.35 – 7.45) and an HCO3 level that is higher than the normal reference range (35 – 45 mm Hg). D. Respiratory alkalosis Rationale: Respiratory alkalosis occurs when there is an excessive loss of CO2 through hyperventilation, mechanical ventilation, fever, overdose of salicylates, or lesions to the central nervous system. Arterial blood gases will reveal a pH that is higher than the normal reference range (7.35 – 7.45) and a CO2 level that is lower than the normal reference range (35 – 45 mm Hg). Created on:01/15/2021 Page 2 Detailed Answer Key Student Success. N4581Resp Practice Questions 4.A nurse is reviewing the arterial blood gas (ABG) results of a client who the provider suspects has metabolic acidosis. Which of the following results should the nurse expect to see? A. pH below 7.35 Rationale: With acidosis, the pH is below 7.35. However, the pH alone does not indicate whether the problem is metabolic or respiratory. A pH above 7.45 indicates alkalosis. B. HCO3 above 26 mEq/L Rationale: With metabolic acidosis, the HCO3 is below 21 mEq/L. C. PaO2 below 70 mm Hg Rationale: With metabolic acidosis, the PaO2 is likely to be within the expected reference range of 80 to 100 mm Hg, unless the client has other complications that are causing hypoxia. D. PaCO2 above 45 mm Hg Rationale: With metabolic acidosis, the PaCO2 is within the expected reference range of 35 to 45 mm Hg or below 35 mm Hg with respiratory compensation. An elevated PaCO2 indicates respiratory acidosis. 5.A nurse is caring for a female client in the emergency department who reports shortness of breath and pain in the lung area. She states that she started taking birth control pills 3 weeks ago and that she smokes. Her heart rate is 110/min, respiratory rate 40/min, and blood pressure 140/80 mm Hg. Her arterial blood gases are pH 7.50, PaCO2 29 mm Hg, PaO2 60 mm Hg, HCO3 20 mEq/L, and SaO2 86%. Which of the following is the priority nursing intervention? A. Prepare for mechanical ventilation. Rationale:If the client cannot compensate for this acid-base imbalance and conservative treatment does not help, mechanical ventilation might become necessary; however, it is not the first step in managing this client’s imbalance. B. Administer oxygen via face mask. Rationale: The pH reflects alkalosis, and the low PaCO2 indicates that the lungs are involved, so the client has respiratory alkalosis. The client’s oxygen saturation is low, so one priority is to administer oxygen via mask attempting to achieve an oxygen saturation of at least 95%. The greatest risk to this client is hypoxia, thus the priority is to restore oxygen [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 13 pages
Instant download

Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 20, 2022
Number of pages
13
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 20, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
39