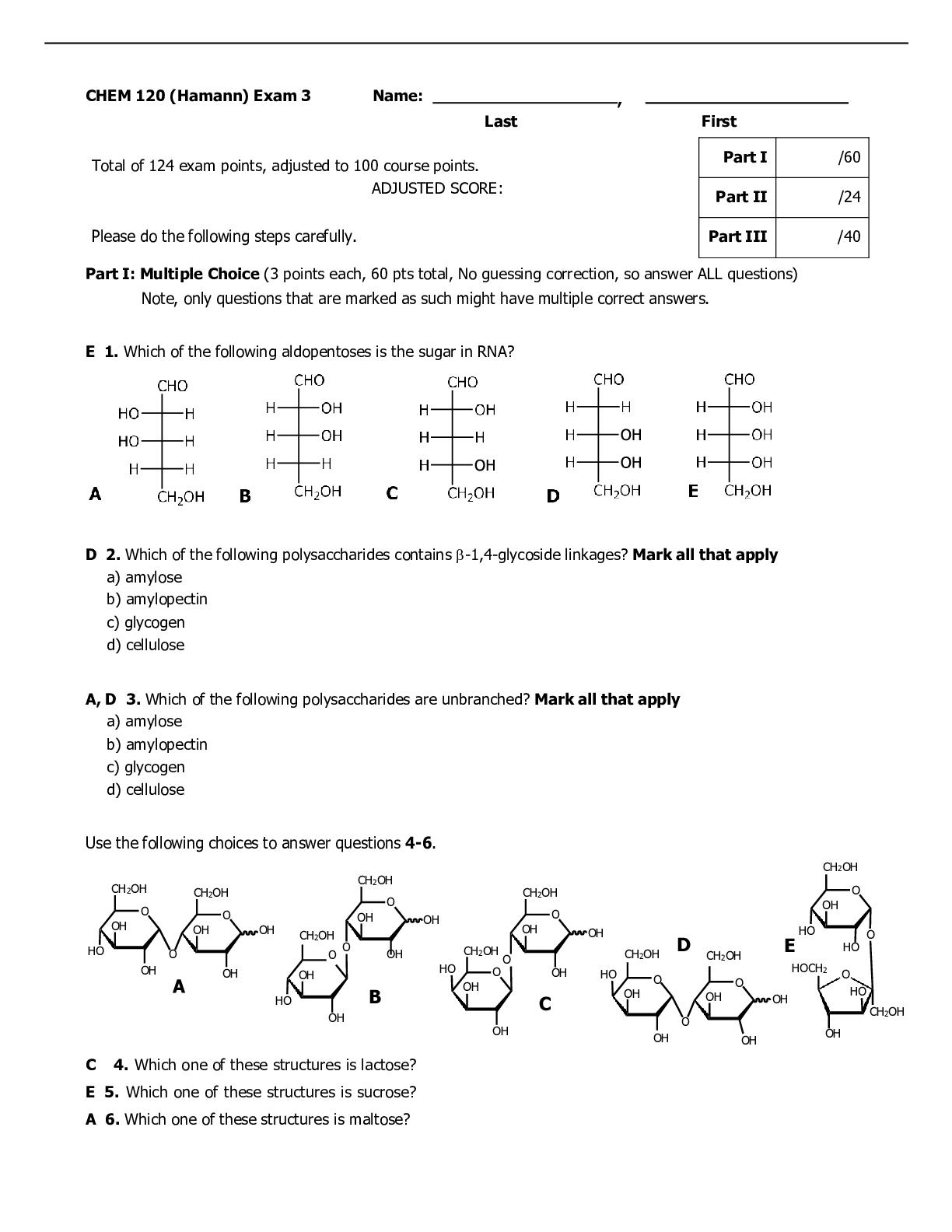*NURSING > EXAM > NSG 6005 Week 5 Midterm Exam 2022- Latest Questions and Answers (Correct Answers Highlighted in Yell (All)
NSG 6005 Week 5 Midterm Exam 2022- Latest Questions and Answers (Correct Answers Highlighted in Yellow)
Document Content and Description Below
1. Charlie is a 65-year-old male who has been diagnosed with hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Doxazosin has been chosen to treat his hypertension because it: 1. Increases peripheral va... soconstriction 2. Decreases detrusor muscle contractility 3. Lowers supine blood pressure more than standing pressure 4. Relaxes smooth muscle in the bladder neck ____ 2. To reduce potential adverse effects, patients taking a peripherally acting alpha1 antagonist should do all of the following EXCEPT: 1. Take the dose at bedtime 2. Sit up slowly and dangle their feet before standing 3. Monitor their blood pressure and skip a dose if the pressure is less than 120/80 4. Weigh daily and report weight gain of greater than 2 pounds in one day ____ 3. John has clonidine, a centrally acting adrenergic blocker, prescribed for his hypertension. He should: 1. Not miss a dose or stop taking the drug because of potential rebound hypertension 2. Increase fiber in the diet to treat any diarrhea that may occur 3. Reduce fluid intake to less than 2 liters per day to prevent fluid retention 4. Avoid sitting for long periods, as this can lead to deep vein thrombosis ____ 4. Clonidine has several off-label uses, including: 1. Alcohol and nicotine withdrawal 2. Post-herpetic neuralgia 3. Both 1 and 2 4. Neither 1 nor 2 ____ 5. Jim is being treated for hypertension. Because he has a history of heart attack, the drug chosen is atenolol. Beta blockers treat hypertension by: 1. Increasing heart rate to improve cardiac output 2. Reducing vascular smooth muscle tone 3. Increasing aldosterone-mediated volume activity 4. Reducing aqueous humor production ____ 6. Which of the following adverse effects are less likely in a beta1-selective blocker? 1. Dysrhythmias 2. Impaired insulin release 3. Reflex orthostatic changes 4. Decreased triglycerides and cholesterol ____ 7. Richard is 70 years old and has a history of cardiac dysrhythmias. He has been prescribed nadolol. You do his annual laboratory work and find a CrCl of 25 ml/min. What action should you take related to his nadolol? 1. Extend the dosage interval. Copyright © 2016 F. A. Davis Company 2. Decrease the dose by 75%. 3. Take no action because this value is expected in the older adult. 4. Schedule a serum creatinine level to validate the CrCl value. ____ 8. Beta blockers are the drugs of choice for exertional angina because they: 1. Improve myocardial oxygen supply by vasodilating the coronary arteries 2. Decrease myocardial oxygen demand by decreasing heart rate and vascular resistance 3. Both 1 and 2 4. Neither 1 nor 2 ____ 9. Adherence to beta blocker therapy may be affected by their: 1. Short half-lives requiring twice daily dosing 2. Tendency to elevate lipid levels 3. Effects on the male genitalia, which may produce impotence 4. None of the above ____ 10. Beta blockers have favorable effects on survival and disease progression in heart failure. Treatment should be initiated when the: 1. Symptoms are severe 2. Patient has not responded to other therapies 3. Patient has concurrent hypertension 4. Left ventricular dysfunction is diagnosed ____ 11. Abrupt withdrawal of beta blockers can be life threatening. Patients at highest risk for serious consequences of rapid withdrawal are those with: 1. Angina 2. Coronary artery disease 3. Both 1 and 2 4. Neither 1 nor 2 ____ 12. To prevent life-threatening events from rapid withdrawal of a beta blocker: 1. The dosage interval should be increased by 1 hour each day. 2. An alpha blocker should be added to the treatment regimen before withdrawal. 3. The dosage should be tapered over a period of weeks. 4. The dosage should be decreased by one-half every 4 days. ____ 13. Beta blockers are prescribed for diabetics with caution because of their ability to produce hypoglycemia and block the common symptoms of it. Which of the following symptoms of hypoglycemia is not blocked by these drugs and so can be used to warn diabetics of possible decreased blood glucose? 1. Dizziness 2. Increased heart rate 3. Nervousness and shakiness 4. Diaphoresis Copyright © 2016 F. A. Davis Company ____ 14. Combined alpha-beta antagonists are used to reduce the progression of heart failure because they: 1. Vasodilate the peripheral vasculature 2. Decrease cardiac output 3. Increase renal vascular resistance 4. Reduce atherosclerosis secondary to elevated serum lipoproteins ____ 15. Carvedilol is heavily metabolized by CYP2D6 and 2C9, resulting in drug interactions with which of the following drug classes? 1. Histamine 2 blockers 2. Quinolones 3. Serotonin re-uptake inhibitors 4. All of the above ____ 16. Alpha-beta blockers are especially effective to treat hypertension for which ethnic group? 1. White 2. Asian 3. African American 4. Native American ____ 17. Bethanechol: 1. Increases detrusor muscle tone to empty the bladder 2. Decreases gastric acid secretion to treat peptic ulcer disease 3. Stimulates voluntary muscle tone to improve strength 4. Reduces bronchial airway constriction to treat asthma ____ 18. Clinical dosing of Bethanechol: 1. Begins at the highest effective dose to obtain a rapid response 2. Starts at 5 mg to 10 mg PO and is repeated every hour until a satisfactory clinical response is achieved 3. Requires dosing only once daily 4. Is the same for both the oral and parenteral route ____ 19. Patients who need to remain alert are taught to avoid which drug due to its antimuscarinic effects? 1. Levothyroxine 2. Prilosec 3. Dulcolax 4. Diphenhydramine ____ 20. Anticholinesterase inhibitors are used to treat: 1. Peptic ulcer disease 2. Myasthenia gravis 3. Both 1 and 2 4. Neither 1 nor 2 ____ 21. Which of the following drugs used to treat Alzheimer’s disease is not an anticholinergic? 1. Donepezil 2. Memantine Copyright © 2016 F. A. Davis Company 3. Rivastigmine 4. Galantamine ____ 22. Taking which drug with food maximizes it bioavailability? 1. Donepezil 2. Galantamine 3. Rivastigmine 4. Memantine ____ 23. Which of the following drugs should be used only when clearly needed in pregnant and breastfeeding women? 1. Memantine 2. Pyridostigmine 3. Galantamine 4. Rivastigmine ____ 24. There is a narrow margin between first appearance of adverse reaction to AChE inhibitors and serious toxic effects. Adverse reactions that require immediate action include: 1. Dizziness and headache 2. Nausea 3. Decreased salivation 4. Fasciculations of voluntary muscles ____ 25. Adherence is improved when a drug can be given once daily. Which of the following drugs can be given once daily? 1. Tacrine 2. Donepezil 3. Memantine 4. Pyridostigmine ____ 26. Nicotine has a variety of effects on nicotinic receptors throughout the body. Which of the following is NOT an effect of nicotine? 1. Vasodilation and decreased heart rate 2. Increased secretion of gastric acid and motility of the GI smooth muscle 3. Release of dopamine at the pleasure center 4. Stimulation of the locus coeruleus ____ 27. Nicotine gum products are: 1. Chewed to release the nicotine and then swallowed for a systemic effect 2. “Parked” in the buccal area of the mouth to produce a constant amount of nicotine release 3. Bound to exchange resins so the nicotine is only released during chewing 4. Approximately the same in nicotine content as smoking two cigarettes ____ 28. Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT): 1. Is widely distributed in the body only when the gum products are used Copyright © 2016 F. A. Davis Company 2. Does not cross the placenta and so is safe for pregnant women 3. Delays healing of esophagitis and peptic ulcers 4. Has no drug interactions when a transdermal patch is used ____ 29. Success rates for smoking cessation using NRT: 1. Are about the same regardless of the method chosen 2. Vary from 40% to 50% at 12 months 3. Both 1 and 2 4. Neither 1 nor 2 ____ 30. Cholinergic blockers are used to: 1. Counteract the extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) effects of phenothiazines 2. Control tremors and relax smooth muscle in Parkinson’s disease 3. Inhibit the muscarinic action of ACh on bladder muscle 4. All of the above ____ 31. Several classes of drugs have interactions with cholinergic blockers. Which of the following is true about these interactions? 1. Drugs with a narrow therapeutic range given orally may not stay in the GI tract long enough to produce an action. 2. Additive antimuscarinic effects may occur with antihistamines. 3. Cholinergic blockers may decrease the sedative effects of hypnotics. 4. Cholinergic blockers are contraindicated with antipsychotics. ____ 32. Scopolamine can be used to prevent the nausea and vomiting associated with motion sickness. The patient is taught to: 1. Apply the transdermal disk at least 4 hours before the antiemetic effect is desired. 2. Swallow the tablet 1 hour before traveling where motion sickness is possible. 3. Place the tablet under the tongue and allow it to dissolve. 4. Change the transdermal disk daily for maximal effect. ____ 33. You are managing the care of a patient recently diagnosed with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). He is taking tamsulosin but reports dizziness when standing abruptly. The best option for this patient is: 1. Continue the tamsulosin because the side effect will resolve with continued treatment. 2. Discontinue the tamsulosin and start doxazosin. 3. Have him double his fluid intake and stand more slowly. 4. Prescribe meclizine as needed for the dizziness. ____ 34. You are treating a patient with a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. The patient’s wife mentions difficulty with transportation to the clinic. Which medication is the best choice? 1. Donepezil 2. Tacrine 3. Doxazosin 4. Verapamil Copyright © 2016 F. A. Davis Company ____ 35. A patient presents with a complaint of dark stools and epigastric pain described as gnawing and burning. Which of the medications is the most likely cause? 1. Acetaminophen 2. Estradiol 3. Donepezil 4. Bethanechol ____ 36. Your patient calls for an appointment before going on vacation. Which medication should you ensure he has an adequate supply of before leaving to avoid life-threatening complications? 1. Carvedilol 2. Donepezil 3. Bethanechol 4. Tacrine ____ 37. Activation of central alpha2 receptors results in inhibition of cardioacceleration and ______________ centers in the brain. 1. Vasodilation 2. Vasoconstriction 3. Cardiovascular 4. Respiratory Copyright © 2016 F. A. Davis Company Chapter 16. Drugs Affecting the Cardiovascular and Renal Systems ____ 1. Ray has been diagnosed with hypertension and an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor is determined to be needed. Prior to prescribing this drug, the NP should assess for: 1. Hypokalemia 2. Impotence 3. Decreased renal function 4. Inability to concentrate ____ 2. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are the drug of choice in treating hypertension in diabetic patients because they: 1. Improve insulin sensitivity 2. Improve renal hemodynamics 3. Reduce the production of angiotensin II 4. All of the above ____ 3. A potentially life-threatening adverse response to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors is angioedema. Which of the following statements is true about this adverse response? 1. Swelling of the tongue or hoarseness are the most common symptoms. 2. It appears to be related to the decrease in aldosterone production. 3. Presence of a dry, hacky cough indicates a high risk for this adverse response. 4. Because it takes time to build up a blood level, it occurs after being on the drug for about 1 week. ____ 4. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are useful in a variety of disorders. Which of the following statements are true about both its usefulness in the disorder and the reason for its use? 1. Stable angina because it decreases the thickening of vascular walls due to decreased modified release. 2. Heart failure because it reduces remodeling of injured myocardial tissues. 3. Both 1 and 2 are true and the reasons are correct. 4. Both 1 and 2 are true but the reasons are wrong. 5. Neither 1 nor 2 are true. ____ 5. Despite good blood pressure control, an NP might change a patient’s drug from an angiotensinconverting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor to an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) because the ARB: 1. Is stronger than the ACE inhibitor 2. Does not produce a dry, hacky cough 3. Has no effect on the renal system 4. Reduces sodium and water retention ____ 6. While taking an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), patients need to avoid certain over-thecounter drugs without first consulting the provider because: 1. Cimetidine is metabolized by the CYP 3A4 isoenzymes 2. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs reduce prostaglandin levels 3. Both 1 and 2 Copyright © 2016 F. A. Davis Company 4. Neither 1 nor 2 ____ 7. Laboratory monitoring for patients on angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers should include: 1. White blood cell counts with the drug dosage increased for elevations above 10,000 feet 2. Liver function tests with the drug dosage stopped for alanine aminotransferase values twice that of normal 3. Serum creatinine levels with the drug dosage reduced for values greater than 2.5 mg/dL 4. Serum glucose levels with the drug dosage increased for levels greater than 120 mg/dL ____ 8. Jacob has hypertension, for which a calcium channel blocker has been prescribed. This drug helps control blood pressure because it: 1. Decreases the amount of calcium inside the cell 2. Reduces stroke volume 3. Increases the activity of the Na+/K+/ATPase pump indirectly 4. Decreases heart rate ____ 9. Which of the following adverse effects may occur due to a dihydropyridine-type calcium channel blocker? 1. Bradycardia 2. Hepatic impairment 3. Increased contractility 4. Edema of the hands and feet ____ 10. Patient teaching related to amlodipine includes: 1. Increase calcium intake to prevent osteoporosis from a calcium blockade. 2. Do not crush the tablet; it must be given in liquid form if the patient has trouble swallowing it. 3. Avoid grapefruit juice as it affects the metabolism of this drug. 4. Rise slowly from a supine position to reduce orthostatic hypotension. ____ 11. Vera, age 70, has isolated systolic hypertension. Calcium channel blocker dosages for her should be: 1. Started at about half the usual dosage 2. Not increased over the usual dosage for an adult 3. Given once daily because of memory issues in the older adult 4. Withheld if she experiences gastroesophageal reflux ____ 12. Larry has heart failure, which is being treated with digoxin because it exhibits: 1. Negative inotropism 2. Positive chronotropism 3. Both 1 and 2 4. Neither 1 nor 2 Copyright © 2016 F. A. Davis Company ____ 13. Furosemide is added to a treatment regimen for heart failure that includes digoxin. Monitoring for this combination includes: 1. Hemoglobin 2. Serum potassium 3. Blood urea nitrogen 4. Serum glucose ____ 14. Which of the following create a higher risk for digoxin toxicity? Both the cause and the reason for it must be correct. 1. Older adults because of reduced renal function 2. Administration of aldosterone antagonist diuretics because of decreased potassium levels 3. Taking an antacid for gastroesophageal reflux disease because it increases the absorption of digoxin 4. Doses between 0.25 and 0.5 mg/day ____ 15. Serum digoxin levels are monitored for potential toxicity. Monitoring should occur: 1. Within 6 hours of the last dose 2. Because a reference point is needed in adjusting a dose 3. After three half-lives from the starting of the drug 4. When a patient has stable renal function ____ 16. Rodrigo has been prescribed procainamide after a myocardial infarction. He is monitored for dyspnea, jugular venous distention, and peripheral edema because they may indicate: 1. Widening of the area of infarction 2. Onset of congestive heart failure 3. An electrolyte imbalance involving potassium 4. Renal dysfunction ____ 17. Which of the following is true about procainamide and its dosing schedule? 1. It produces bradycardia and should be used cautiously in patients with cardiac conditions that a slower heart rate might worsen. 2. Gastrointestinal adverse effects are common so the drug should be taken with food. 3. Adherence can be improved by using a sustained release formulation that can be given once daily. 4. Doses of this drug should be taken evenly spaced around the clock to keep an even blood level. ____ 18. Amiodarone has been prescribed in a patient with a supraventricular dysrhythmia. Patient teaching should include all of the following EXCEPT: 1. Notify your health-care provider immediately if you have visual change. 2. Monitor your own blood pressure and pulse daily. 3. Take a hot shower or bath if you feel dizzy. 4. Use a sunscreen on exposed body surfaces. Copyright © 2016 F. A. Davis Company ____ 19. The NP orders a thyroid panel for a patient on amiodarone. The patient tells the NP that he does not have thyroid disease and wants to know why the test is ordered. Which is a correct response? 1. Amiodarone inhibits an enzyme that is important in making thyroid hormone and can cause hypothyroidism. 2. Amiodarone damages the thyroid gland and can result in inflammation of that gland, causing hyperthyroidism. 3. Amiodarone is a broad spectrum drug with many adverse effects. Many different tests need to be done before it is given. 4. Amiodarone can cause corneal deposits in up to 25% of patients. ____ 20. Isosorbide dinitrate is prescribed for a patient with chronic stable angina. This drug is administered twice daily, but the schedule is 7 a.m. and 2 p.m. because: 1. It is a long-acting drug with potential for toxicity. 2. Nitrate tolerance can develop. 3. Orthostatic hypotension is a common adverse effect. 4. It must be taken with milk or food. ____ 21. Art is a 55-year-old smoker who has been diagnosed with angina and placed on nitrates. He complains of headaches after using his nitrate. An appropriate reply might be: 1. This is a parasympathetic response to the vasodilating effects of the drug. 2. Headaches are common side effects with these drugs. How severe are they? 3. This is associated with your smoking. Let’s work on having you stop smoking. 4. This is not related to your medication. Are you under a lot of stress? ____ 22. In teaching about the use of sublingual nitroglycerine, the patient should be instructed: 1. To swallow the tablet with a full glass of water 2. To place one tablet under the tongue if chest pain occurs and allow it to dissolve 3. To take one tablet every 5 minutes until the chest pain goes away 4. That it should “burn” when placed under the tongue or it is no longer effective ____ 23. Donald has been diagnosed with hyperlipidemia. Based on his lipid profile, atorvastatin is prescribed. Rhabdomyolysis is a rare but serious adverse response to this drug. Donald should be told to: 1. Become a vegetarian because this disorder is associated with eating red meat. 2. Stop taking the drug if abdominal cramps and diarrhea develop. 3. Report muscle weakness or tenderness and dark urine to his provider immediately. 4. Expect “hot flash” sensations during the first 2 weeks of therapy. ____ 24. Which of the following diagnostic studies would NOT indicate a problem related to a reductase inhibitor? 1. Elevated serum transaminase 2. Increased serum creatinine 3. Elevated creatinine kinase 4. Increased white blood cell counts ____ 25. Because of the pattern of cholesterol synthesis, reductase inhibitors are given: Copyright © 2016 F. A. Davis Company 1. In the evening in a single daily dose 2. Twice daily in the morning and the evening 3. With each meal and at bedtime 4. In the morning before eating ____ 26. Janice has elevated LDL, VLDL, and triglyceride levels. Niaspan, an extended-release form of niacin, is chosen to treat her hyperlipidemia. Due to its metabolism and excretion, which of the following laboratory results should be monitored? 1. Serum alanine aminotransferase 2. Serum amylase 3. Serum creatinine 4. Phenylketonuria ____ 27. Niaspan is less likely to cause which side effect that is common to niacin? 1. Gastrointestinal irritation 2. Cutaneous flushing 3. Dehydration 4. Headaches ____ 28. Dulcea has type 2 diabetes and a high triglyceride level. She has gemfibrozil prescribed to treat her hypertriglyceridemia. A history of whic [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 35 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 28, 2022
Number of pages
35
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 28, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
19