Pathophysiology > STUDY GUIDE > Chamberlain College of Nursing - NR 507 Mid Term Exam Study Guide. [Complete Guide to score an A] (All)
Chamberlain College of Nursing - NR 507 Mid Term Exam Study Guide. [Complete Guide to score an A]
Document Content and Description Below
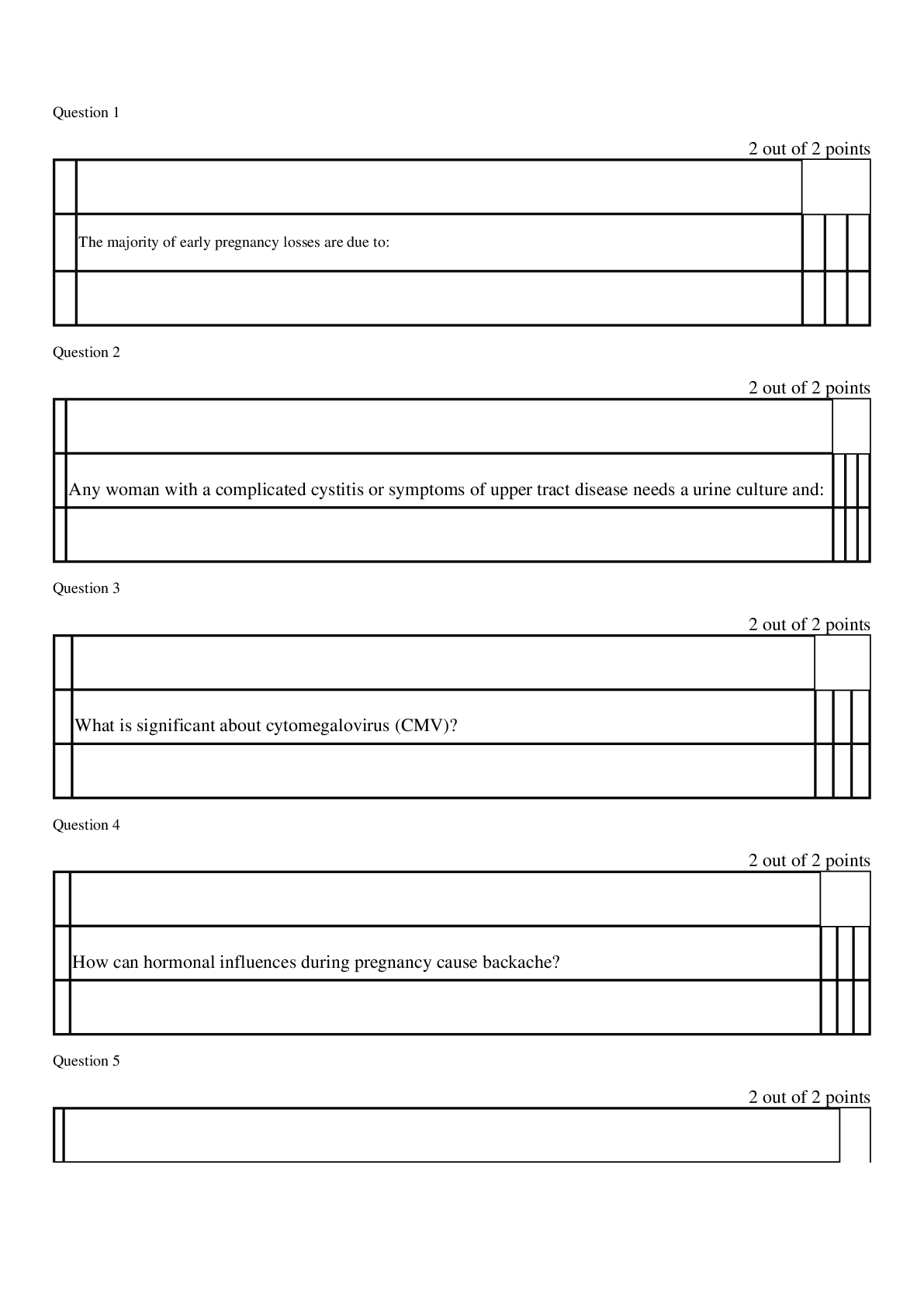
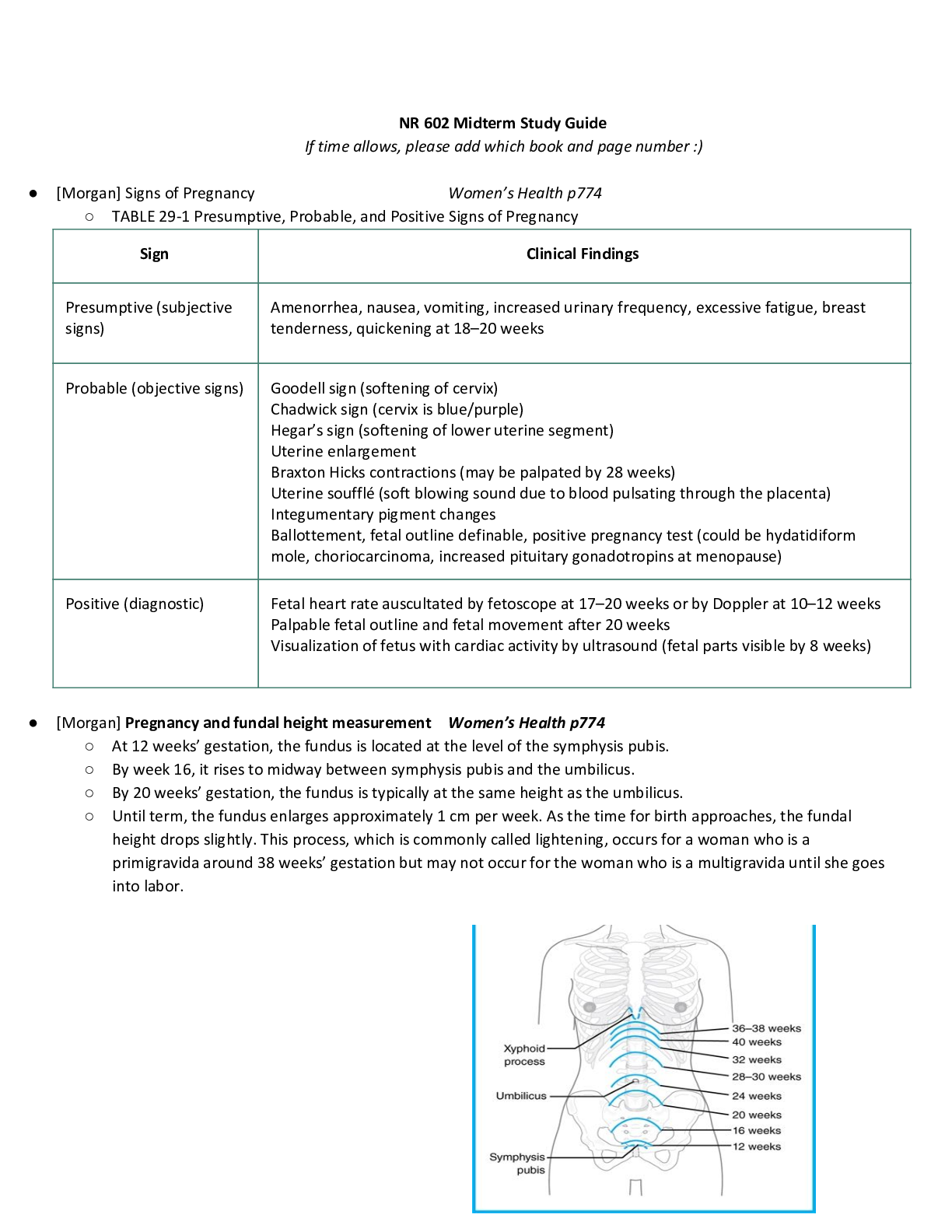
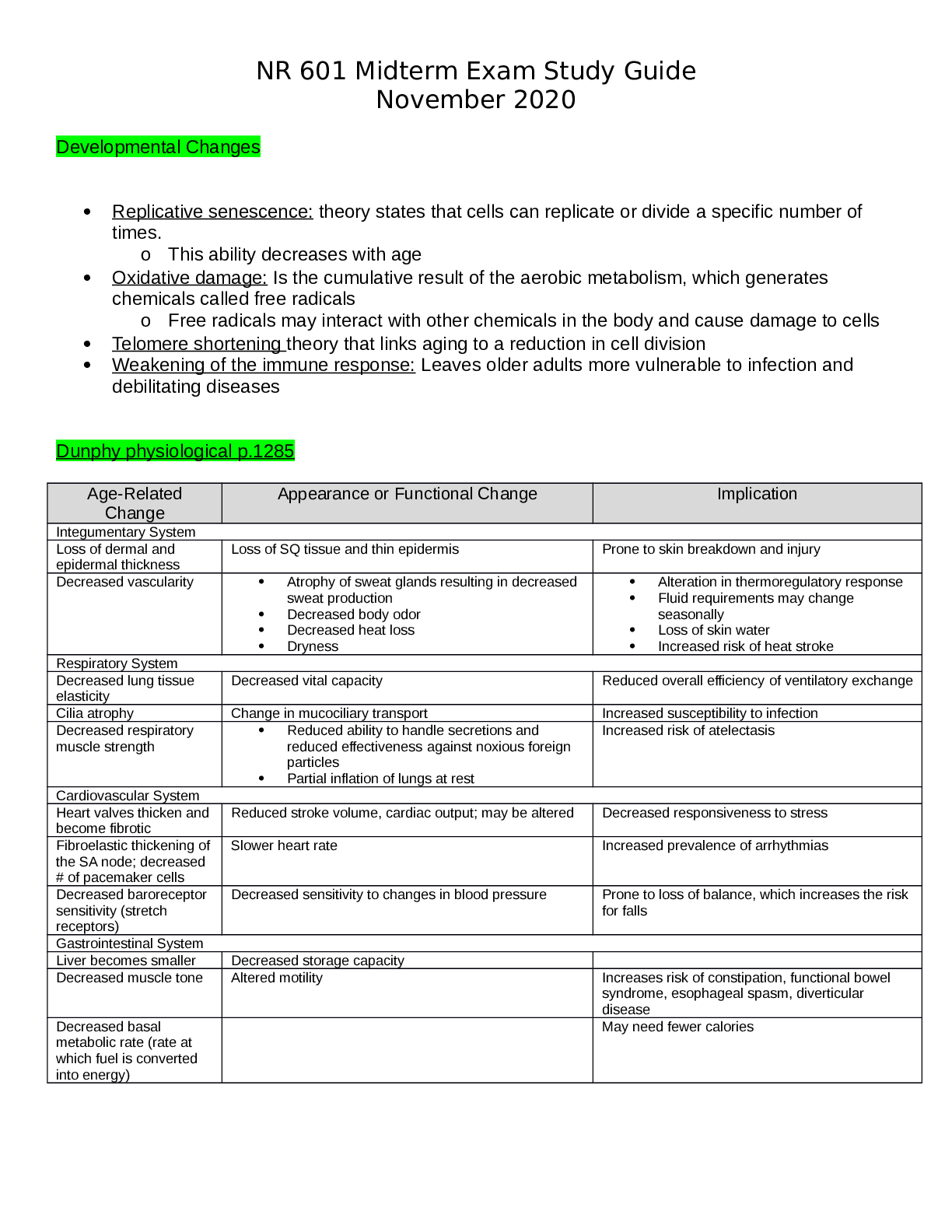
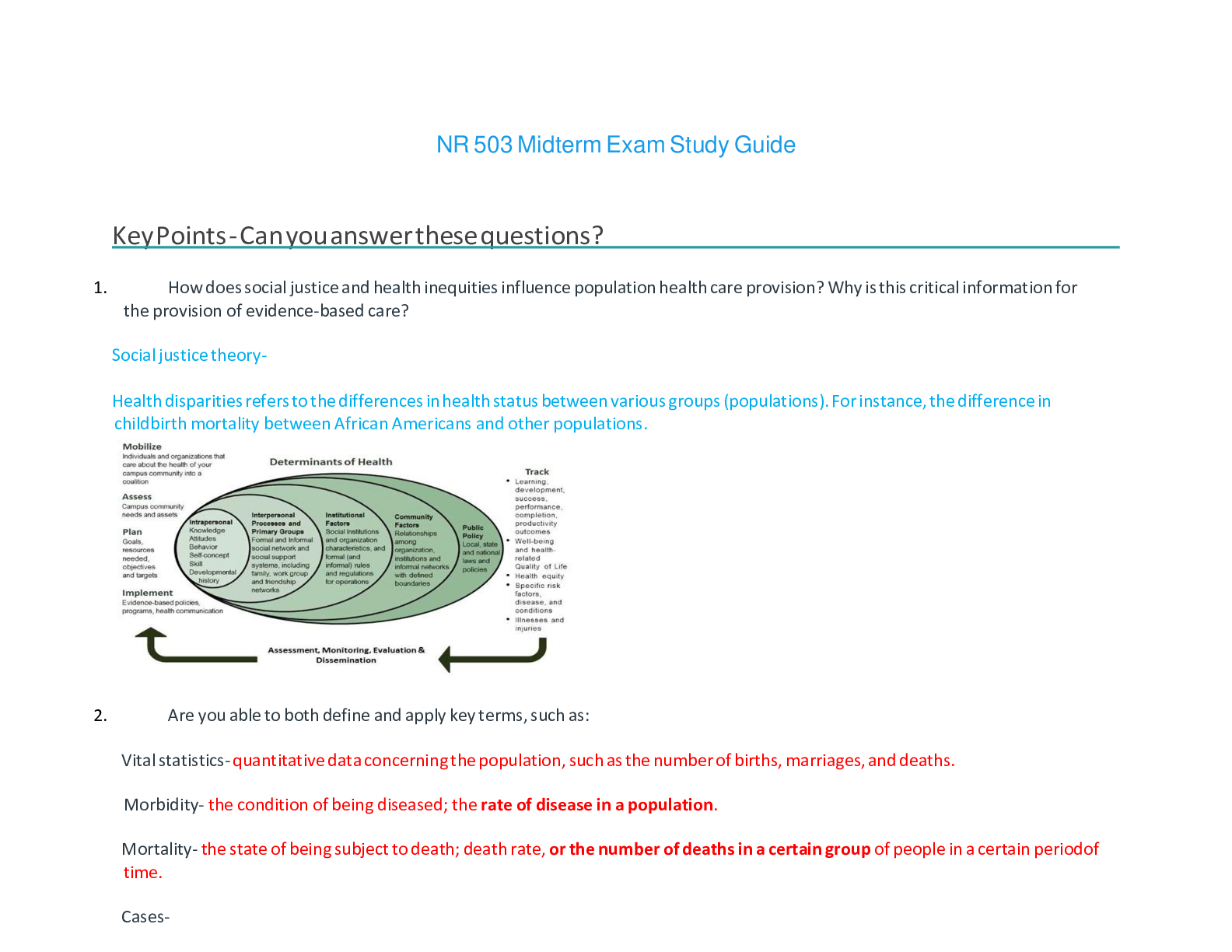
Mid Term Study Guide NR 507 Pulmonary 1. Concepts of anticholinergic drug and asthma: Anticholinergic drugs: block acetylcholine binding (primarily in the lungs) -promotes bronchiole dilation thro... ugh decrease in the parasympathetic response (tiotropium & ipratropium) is fast acting 2. Bronchitis & associated pathogenesis: Begins with an exposure to an irritant (tobacco smoke) – activates bronchiole smooth muscle constriction- mucus secretion- release of inflammatory mediators(histamine, prostaglandins & leukotrienes) normal response to occasional airborne site irritants- over bronchitis is over long term 3 months for over 2 consecutive years- = smooth muscle hypertrophy = increase bronchoconstriction, hypertrophy and hyperplasia of goblet cells= mucus hypersecretion, epithelia cell metaplasia = non-ciliated squamous cells, migration of more WBCs to site = inflammation and fibrosis in bronchial wall, thickening and rigidity of bronchial basement membrane= narrowing of bronchial passageways : Increased mucus production- inflammation process = weight loss, loss of appetite, muscle weakness (interleukin controls appetite) increases protease activity= breakdown of elastin in the connective tissues of the lung= destruction of the wall between the alveoli and lungs = large ineffective air sacs develop-elastic recoil of bronchial wall -destroys bronchi and cant dilate and they stay constricted =air trapping : Chronic bronchitis =Dyspnea- air trapping increased mucus, increase WOB r/t chronic bronchoconstriction Cough- irritated and inflamed bronchial epithelia membrane Hypoxia & Hypercapnia -from impaired gas exchange 3. Chronic bronchitis and related acid/base disturbance: Hypercapnia (CO2 retention) = Respiratory acidosis r/t anatomical changes ventilation is compromised esp. exhalation = alveolar hyperinflation) expanded thorax) hypercapnia CO2 retention = respiratory acidosis\ 4. Perfusion: the actual exchange of O2 and CO2 in the bloodstream occurs via the alveoli and pulmonary capillaries: the passage of fluid to an organ or a tissue usually referring to delivery of blood to an area 5. Blood flow between the heart and lungs in chronic bronchitis: Poor ventilation leads to r to l shunting to occur= deoxygenated blood passes from r ventricle to the lungs to the l ventricle without adequate perfusion (gas exchange) the kidneys respond by secreting erythropoietin increasing RBC production the increase in RBC increase O2 carrying capacity -the increase blood volume increases the workload of the pulmonary and cardiovascular systems increasing blood volume and vasoconstriction = pulmonary HTN= increase workload on the R ventricle =cardiac hypertrophy= R side HF or Cor Pulmonale 6. Asthma signs and symptoms: Coughing esp. at night, chest tightness, shortness of breath, wheezing on exhalation, and rapid breathing: Characteristics: airway inflammation, bronchial hyperactivity, smooth muscle spasms, = excessive mucus production, hypertrophy of bronchial smooth muscle -obstruction and decrease alveolar ventilation 7. Bronchioles in asthma: There are 3 layers of the bronchiole which is a tube-like structure surrounding the lumen or airway passageway: innermost layer is composed of columnar epithelial cells and goblet cellsThe outermost layer is composed of smooth muscle cells responsible for the ability of the airway to constrict and dilate – the middle layer is the laminar propria and it is embedded with connective tissue and immune cells: in asthma these protective features go overactive =inflammation response= damage to host tissue=hypertrophy of the bronchioles smooth muscle and excessive mucus production: bronchioles spasm-mucus production-obstruction 8. Alveolar hyperinflation with asthma: Increase mucus production from the goblet cells in the inflammation process forms plugs of mucus and pus and block alveolar passageways leading to air trapping and hyperinflation = erosion of airway tissue 9. Polycythemia Vera: a rare blood disease in which the body makes too many RBCs making the blood thicker than normal causing blood clots; is often a result of chronic low levels of O2 in the blood, the kidney compensates by increase secretion of erythropoetin, the primary hormone responsible for stimulating RBC production= as a result patients with chronic bronchitis will often exhibit increased HCT levels and can develop a condition called secondary polycythemia vera. 10. Mechanism of action of anticholinergic drugs to treat asthma: Anticholinergic drugs bind to muscarine receptors and block the action of acetylcholine They reduce Broncho motor tone =bronchodilation: block acetylcholine binding, bronchodilation, decrease parasympathetic response [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 10, 2020
Number of pages
12
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 10, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
29