Physics > Report > Experiment #6 Lab Report ALL SOLUTION 100% CORRECT SPRING FALL-2022 LATEST GUARANTEED GRADE A+ (All)
Experiment #6 Lab Report ALL SOLUTION 100% CORRECT SPRING FALL-2022 LATEST GUARANTEED GRADE A+
Document Content and Description Below
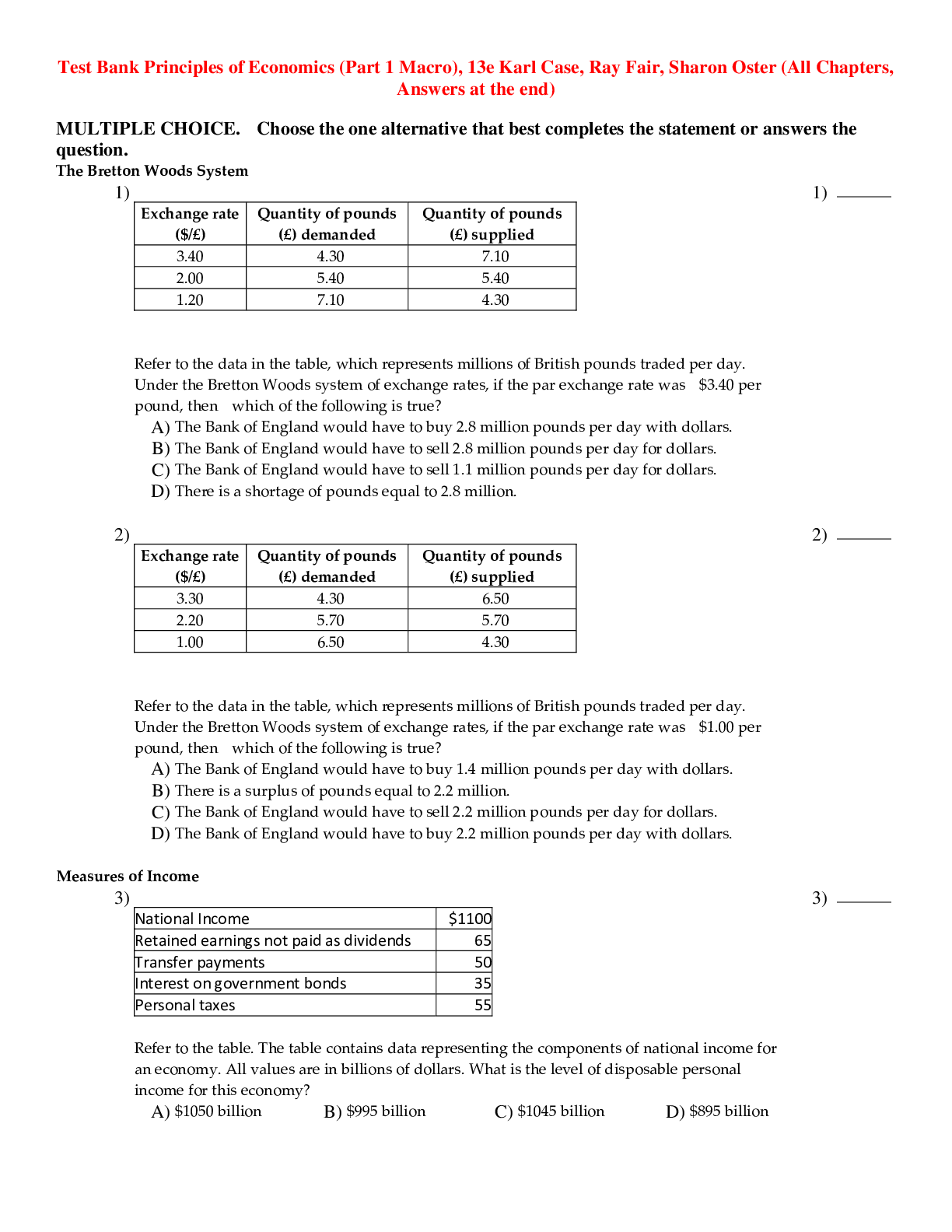
Purpose: To study elastic and inelastic collisions between two balls and to verify energy conservation law when a ball’s potential energy is converted to its kinetic energy. Theory: In this exp... eriment, two identical steel balls are suspended by massless, non-stretchable strings. The separation of the two strings when the balls are in their vertical equilibrium positions is d, where the balls just barely touch each other. The level B, of the balls in their equilibrium position is set as zero height, where the balls have no potential energy. In the collisions, ball #1 will be pulled back to a height A, where it has potential energy equal to mgh and once released from rest this potential energy will be converted into kinetic energy and the ball will achieve a maximum velocity, kinetic energy ((1/2)mv2) and linear momentum right before its collision with ball #2. The first measurement in this experiment is an elastic collision, where total energy and momentum are conserved before and after collision. In this collision, ball #1 stops when it collides with ball #2, and ball #2 gains the velocity, momentum and kinetic energy from ball #1. To obtain the velocities of the balls after collision use the equations v1=d/t1 and v ’=d/t2. The second measurement in this experiment is an inelastic collision, where the two balls stick together upon collision and the momentum of the system is conserved, but the kinetic energy of the system is not. The loss of kinetic energy is shown in the equation: Kafter= ½Kbefore. The conservation of momentum is shown in the equation: 2mv=mv1(initial). In this measurement, v and v1 are determined by v1=d1/t1 and v=d2/t2. Experimental Method and Apparatus: This experiment uses a pair of metal balls, a pair of Velcro pads, two photogates, a vernier caliper, a 15cm ruler, a triple beam balance, the 850 Universal Interface, a computer and the AstroBlaster. Method: 1. Connect photogate one to port one of the interface and connect photogate two to port two of the interface. 2. Measure and record the mass and diameter of the steel ball. Measure and record h1 and h2 using the ruler. 3. To set up the software, click hardware setup in the tools palette, then click port one on the digital inputs and select photogate, then do the same for port two. 4. Set up the timer by clicking timer setup, selecting preconfigured timer, click next and select photogate ch1, photogate ch2, and Collision (Single Flag). Then check timer in gate 1 and timer in gate 2. Then select photogate S 0.1m and collision (single flag) and click finish. 5. In control palette, select keep mode and set sampling rate to 10 Hz. 6. To set up the table, double click the table icon and in the first column click select measurement and choose time in gate 1 (s) and in the second column click select measurement and choose time in gate 2 (s). [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 3 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 08, 2022
Number of pages
3
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 08, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
76




.png)