Biology > STUDY GUIDE > BIOL 130 CHAPTER 7-11 STUDY Questions and Answers | 100% CORRECT. (All)
BIOL 130 CHAPTER 7-11 STUDY Questions and Answers | 100% CORRECT.
Document Content and Description Below
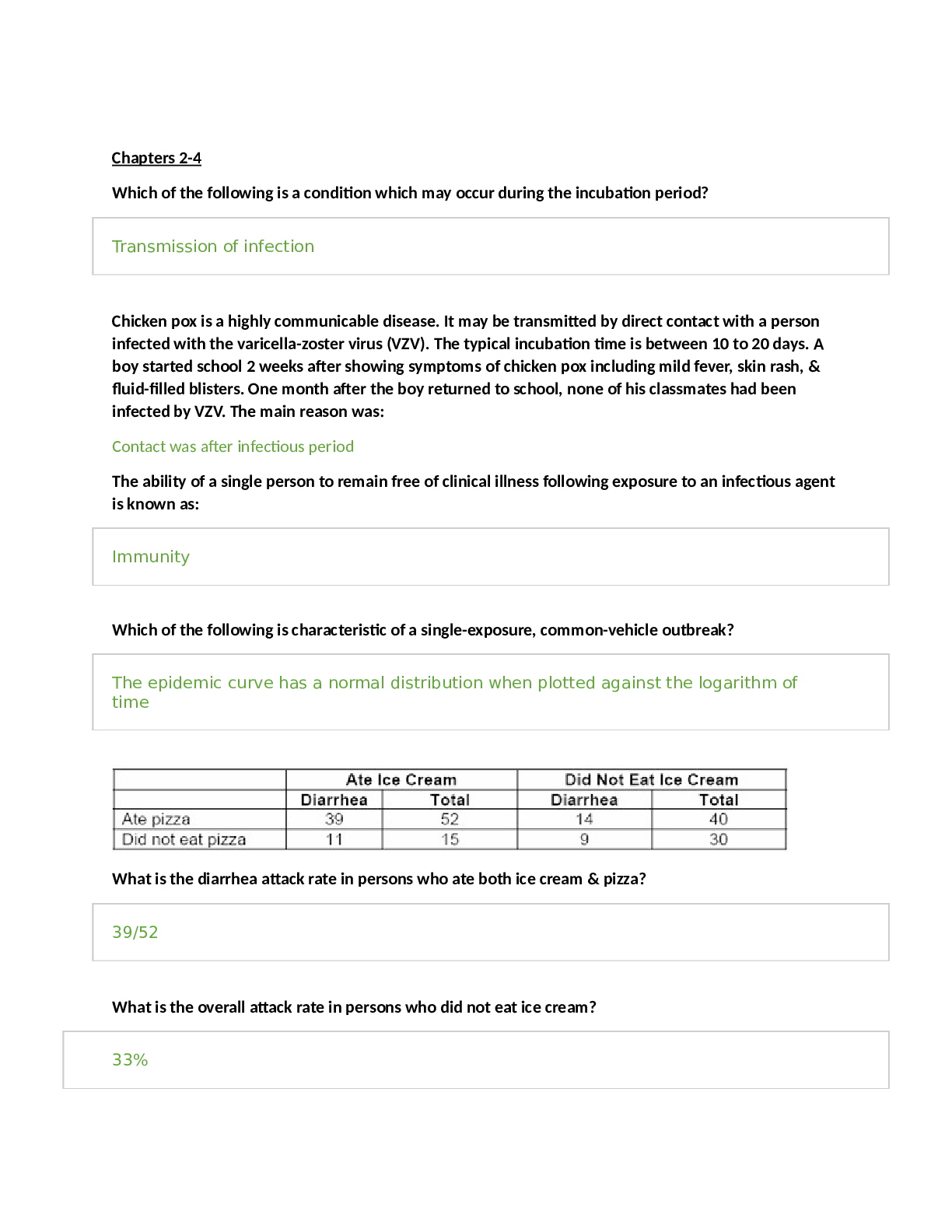
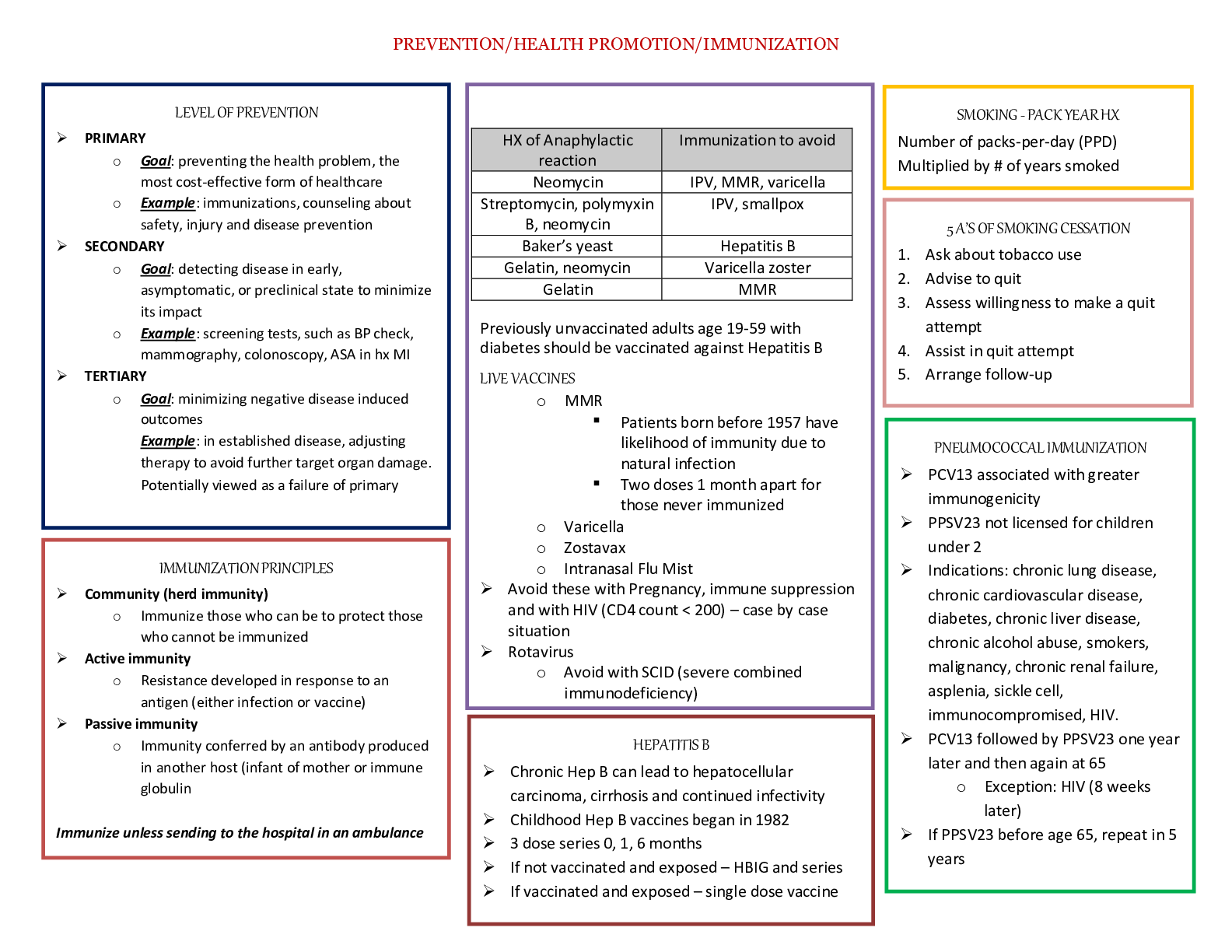
CHAPTER 7 STUDY QUESTIONS Question 1 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points NADH and FADH2 are products of A.oxidation/reduction reactions B.chemiosmosis C.substrate level phosphorylation D.glycolysis Feedback: ... Correct Question 2 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points What is not a good biological oxidizing agent? A. Fe3+ B. O2 C.NAD+ D.FAD Feedback: Correct Question 3 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points What vitamin derivative accepts hydrogen for complex I during ETC? A.thiamine B.riboflavin C.niacin D.pantothenic acid Feedback: Correct Question 4 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points What area is not involved with pumping protons to the intermembrane space? A.complex I B.complex II C.complex III D.complex IV Feedback: Correct Question 5 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points carbon dioxide molecules are given off during three turns of the Krebs cycle? A.1 B.2 C.3 D.4 E.6 Feedback: Correct Question 6 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points Molecules generated from butter will enter aerobic cellular respiration at A.pyruvate oxidation B.oxidative phosphorylation C.Krebs cycle D.glycolysis Feedback: Correct Question 7 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points When has glucose been broken down from its original 6 carbon molecule to 6 molecules of carbon dioxide? A.oxidation of pyruvate B.glycolysis C.when isocitrate is oxidized to αKetoglutarate D.when αKetoglutarate is oxidized to Succinyl CoA E.condensation of acetyleCoA with oxaloacetate Feedback: Learning Objective: Explain how a circular pathway, such as the citric acid cycle, fundamentally differs from a linear pathway, such as glycolysis Question 8 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points Removal of NH3 is best described as . A.beta oxidation B.deamination C.lipolysis D.glycolysis Feedback: Learning Objective: Discuss the ways in which carbohydrate metabolic pathways, glycolysis, and the citric acid cycle interrelate with protein and lipid metabolic pathways Question 9 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points Assuming 2 ATPs are produced per FADH2, how many ATPs will be produced in oxidative phosphorylation per glucose molecule? A.0 B.2 C.4 D.6 Feedback: Learning Objective: Explain how a proton (H+) gradient is established and maintained by the electron transport chain Question 10 of 10 0.0/ 1.0 Points In gluconeogenesis, organisms use ATP to make glucose, then in cellular respiration they break down the glucose again to get energy. Why not just store the ATP? (Select all that apply.) A. ATP does not have highenergy bonds. B. ATP is not energy dense enough. C. ATP only has energy after it is activated by glucose. D. ATP only has energy when it is attached to glucose. E. ATP is not stable enough. F. ATP without a cofactor forms crystalline structures. G. Using glucose directly to power enzymes is more efficient. Feedback: Learning Objective: Analyze the reactions of cellular respiration in terms of net energy input and output using critical thinking skills. CHAPTER 8 STUDY QUESTIONS Lightdependent reactions build NADPH and oxygen by . A.oxidation B.reduction C.oxidation and reduction Feedback: Learning Objective: Identify the substrates and products of photosynthesis Question 2 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points Organic molecules are made in the . A.light dependent reactions B.Calvin cycle C.Krebs cycle D.glycolysis Feedback: Correct Question 3 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points What statement shows the relationship among chloroplasts and mitochondria? A.both use oxygen as the final electron acceptor B.both generate ATP by proton gradient C.both reduce NADP+ D. both release carbon dioxide Feedback: Correct Question 4 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points What is the flow of energy in order from source to end? A.human→sun→grass→cow B.cow→human→grass→sun C.sun→grass→cow→human D.plant→sun→human→cow Feedback: Learning Objective: Explain the relevance of photosynthesis to other living things Question 5 of 10 0.25/ 1.0 Points What properties are expressed by wavelengths? Select all that apply. A. Visible light’s wavelengths are between 400740nm B. Chlorophyll b absorbs a lot of energy from 460nm wavelengths C. Red absorbs little energy D. Green is useful in absorbing light during photosynthesis E. Chlorophyll a reflects red light well F. Visible light’s wavelengths are between 400740nm Feedback: Incorrect: Learning Objective Text: Describe short and long wavelengths of light Question 6 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points Protons from electron transport will amass in the A.stroma B.intermembrane space C.matrix D.thylakoid lumen Feedback: Learning Objective: Describe how and where photosynthesis takes place within a plant Question 7 of 10 0.0/ 1.0 Points The light independent reactions are important because they A.make ATP and NADPH B.convert CO2 into glucose C.split H2O to harvest electrons D.release O2 Feedback: Learning Objective: Describe the Calvin cycle Question 8 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points If rubisco does not function properly, what process would be affected? A.ability to absorb photons B.ability to fix carbon C.ability to reduce NADP+ D.ability to split water Feedback: Correct Question 9 of 10 0.0/ 1.0 Points membranes can be found in a chloroplasts. A.1 B.2 C.3 D.4 Feedback: Learning Objective: Describe the main structures involved in photosynthesis Question 10 of 10 0.0/ 1.0 Points P700 first transfers an electron through chlorophyll and a bound A.quinone B.ferredoxin C.2Fe2S D.plastocyanin Feedback: Incorrect: Learning Objective Text: Describe how and where photosynthesis takes place within a plant CHAPTER 9 STUDY QUESTIONS Question 1 of 10 0.33/ 1.0 Points Cell surface receptors have three domains with different roles. Match each role to the domain that is responsible. A. Cytosolic domain B. Hydrophobic domain C. Extracellular domain select A B C 1. Binds the signaling molecule select A B C 2. Sends conformational change through the plasma membrane select A B C 3. Interacts with downstream signaling cascade Feedback: Incorrect Learning Objective Text: Analyze intercellular and intracellular communication Question 2 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points Protein phosphorylating enzymes help regulated gene expression by A.protein activation B.DNA synthesis C.moving mRNA into the cytoplasm D.translation Feedback: Correct! Question 3 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points A common theme in many pathways is a cascade of similar enzymes acting on each other in sequence. For instance, MAP kinase kinase kinase adds a phosphate to MAP kinase kinase, which adds phosphate to MAP kinase, which adds phosphate to another substrate. What is the benefit of using a cascade of enzymes? A.Extra genes provide backup in case the original became mutated. B.A cascade amplifies output from the original signal. C.There is no benefit – “selfish genes” are often maintained in evolution for reasons unrelated to the function of their encoded proteins. D.A cascade is used for timing since it delays the response. Feedback: Learning Objective: Analyze intercellular and intracellular communication Question 4 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points What describes transcription factors? A.control of gene expression B.regulation of DNA duplication C.ATP into cAMP D.synthesis of glycogen Feedback: Learning Objective: Explain how the binding of a ligand initiates signal transduction throughout a cell Question 5 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points Vibrio fischeri are bioluminescent when the population reaches a certain size. This is an example of A.population density B.quorum sensing C.exponential growth D.principle of growth E.binary fission Feedback: Learning Objective: Relate the role of quorum sensing to the ability of some bacteria to form biofilms Question 6 of 10 0.0/ 1.0 Points is the substrate for adenylyl cylcase. A.cAMP B.ADP C.GTP D.ATP E.GDP Feedback: Incorrect: Learning Objective Text: Evaluate the role of second messengers in signal transmission Question 7 of 10 0.0/ 1.0 Points If calcium levels are low, cAMP activity increases which leads to synthesis and release of parathyroid hormone. cAMP acts as a(n) A.enzyme B.phosphorylating agent C.ligand D.second messenger Feedback: Learning Objective: Evaluate the role of second messengers in signal transmission Question 8 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points Since plants have rigid cell walls formed from cellulose, transfer of information and materials between cells is prohibited. True False Feedback: Correct! Plant cells can communicate two ways: extracellular signals can pass through pores in cell walls, or intracellular signals can use plasmadesmata to travel directly from cell to cell. Question 9 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points Teeth can have a biofilm formed on the surface. Cell signaling will A.cause increase saliva production B.cause apoptosis C.cause uncontrolled cell division D.increase cell quantity Feedback: Correct! Question 10 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points Diacylglycerol and inositol triphosphate are released from phosphatidylinositol biphosphate by . A.adenylyl cyclase B.phospholipase C C.protein kinase C D.Gprotein E.Akinase Feedback: Learning Objective: Evaluate the role of second messengers in signal transmission CHAPTER 10 STUDY QUESTIONS Question 1 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points In which type of human cell(s) would 46 chromosomes be located? Select all that apply. A. diploid B. egg C. somatic D. gamete E. sperm F. haploid Feedback: Correct Question 2 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points Place the order of events in chromosome packaging from beginning to end. A.DNA double helix, chromatin, nucleosomes, sister chromatids B.sister chromatids, DNA double helix, chromatin, nucleosome C.DNA double helix, nucleosome, sister chromatids, chromatin D.Chromatin, nucleosomes, DNA double helix, sister chromatids Feedback: Correct Question 3 of 10 0.0/ 1.0 Points In nature, there is an exception to every rule. Of the species below, which one has a very unusual genome that violates the “rule”? A. Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacterium responsible for Lyme disease, has a linear genome and up to 21 plasmids. B. E. coli, a common bacterium in the human intestine, has DNA nucleotides A, T, C, and G, with only one OH group on the sugar moiety. C. Humans have a genome formed from 23 pairs of linear chromosomes, each of which is so long that it must be wrapped up and condensed into a special structure to fit in the nucleus. D.Arabidopsis pollen is haploid, carrying only one copy each of five linear chromosomes. Feedback: Learning Objective: Analyze the cell cycle, mitosis and cell division Question 4 of 10 0.0/ 1.0 Points Which molecule initiates the halt of the cycle when damaged DNA is detected in G1? A.Rb B.p53 C.Cdk/cyclin complex D.p21 E.E2F Feedback: Learning Objective: Describe the molecules that control the cell cycle through positive and negative regulation Question 5 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points When the p53 gene is damaged, which event may happen? A. Cells can divide uncontrollobly B. Cells will fix the DNA pass the G1 checkpoint C. Cells will pass the G2 checkpoint D. Cells will always undergo apoptosis Feedback: Correct Question 6 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points Damaged DNA can potentially be repaired during which checkpoint. Select all that apply. A. G1 B. S C. G2 D. G0 E. M Feedback: Correct Question 7 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points If there are 8 centromeres in metaphase, how many centromeres will be present in anaphase? A.4 B.8 C.16 D.32 Feedback: Learning Objective: Discuss the behavior of chromosomes during karyokinesis Question 8 of 10 0.0/ 1.0 Points A cell’s entire amount of hereditary information is the A.nucleoid B.nucleus C.genome D.DNA Feedback: Learning Objective: Describe the structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes Question 9 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points If a researcher looks at a cell and notices a straight line of sister chromatids, which phase are they viewing? A.interphase B.prophase C.prometaphase D.metaphase E.anaphase F.telophase Feedback: Correct Question 10 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points A large cell will be initiated to divide because A.a decrease in surface-to-volume ratio B.an increase in surface-to-volume ratio C. crowding from smaller cells D. large cells do not experience quiescent stage E. large cells use more nutrients than small cells Feedback: Learning Objective: Describe the internal and external mechanisms that control the cell cycle. CHAPTER 11 STUDY QUESTIONS An organism has 36 chromosomes. At the end of meiosis I, each gamete contains A.18 chromosomes, 18 chromatids B.18 chromosomes, 36 chromatids C.36 chromosomes, 72 chromtids D.26 chromosomes, 36 chromatids Feedback: Incorrect Learning Objective Text: Describe the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis Question 2 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points A large family has a history of multiple aneuploid diseases such as Down Syndrome, trisomy18 and Klinefelter Syndrome (XXY). The propensity to defects seems to be inherited, but the gene responsible is unknown. What types of candidate genes would be most likely to lead to aneuploidy if they were mutated? A.Genes that are part of the G1 checkpoint of mitosis. B.Genes that encode proteins involved in chiasma formation. C.Histone genes. D.Genes that control DNA synthesis. Feedback: Learning Objective: Analyze meiosis Question 3 of 10 0.0/ 1.0 Points A nuclear envelope does not usually form around each set of chromosomes in the haploid daughter cells in . A.interphase B.prophase I C.metaphase I D.anaphase I E.telophase I F.prophase II G.metaphase II H.anaphase II I.telophase II J.cytokinesis Feedback: Incorrect Learning Objective Text: Describe cellular events during meiosis Question 4 of 10 0.33/ 1.0 Points What is an advantage of asexual reproduction? Select all that apply. A. it occurs quickly B. populates areas rapidly C. all organizms are clones D. high genetic diversity E. only need one parent Feedback: Incorrect Learning Objective Text: Identify variation among offspring as a potential evolutionary advantage to of sexual re Question 5 of 10 0.0/ 1.0 Points Which structure is separated by microtubules resulting in sister chromatids? A.A B.B C.C D.D Feedback: Learning Objective: Describe cellular events during meiosis. Question 6 of 10 0.75/ 1.0 Points Which event is similar between prophase I and prophase? Select all that apply. A. The nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate B. Spindle fibers appear C. Each chromosome is composed of two chromatids D. Chromosomes condense E. Each chromosome has potentially experienced crossover F. Tetrads are present Feedback: Incorrect Learning Objective Text: Explain how meiosis and mitosis differ Question 7 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points Which is important in stabilization of homolog pairing and formation of crossover in meiotic prophase? A.A B.B C.C D.D E.E Feedback: Learning Objective: Describe cellular events during meiosis. Question 8 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points Which describes the relationship between gametes and spores? A.gametes can fuse to become a zygote, but spores can develop into organisms without forming a zygote B.gametes, not spores, can only contribute to genetic diversity in populations C.gametes are always haploid and spores are always diploid D.gametes come directly from sporophytes to develop into gametophytes Feedback: Learning Objective: Describe the three different lifecycle types among sexual multicellular organism Question 9 of 10 1.0/ 1.0 Points How does metaphase in meiosis I and meiosis II differ? A.Sister chromatids are on the metaphase plate in meiosis I and tetrads are on the metaphase plate in meiosis II. B.Homologous chromosomes line up in meiosis I and duplicated chromosomes line up in meiosis II. C.All chromatids are the exact same in meiosis I and differ in meiosis II due to independent assortment D.The ploidy level remains the same in meiosis I but will be reduced in meiosis II. Feedback: Learning Objective: Describe cellular events during meiosis Question 10 of 10 0.0/ 1.0 Points Meiosis and sexual reproduction increase diversity because A.it allows for populations to adapt to environmental changes B.they are archaic processes C. they only need one parent D. they produce offspring extremely quickly E. they will almost always have different offspring arise Feedback: Incorrect Learning Objective Text: Identify variation among offspring as a potential evolutionary advantage to of sexual re [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 05, 2022
Number of pages
15
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 05, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
25






















.png)







