Computer Architecture > SOPHIA Milestone > Western Governors University DATABASE 0047 Sophia Database Milestone 1 UNIT 1 — MILESTONE 1. Sc (All)
Western Governors University DATABASE 0047 Sophia Database Milestone 1 UNIT 1 — MILESTONE 1. Score 32/36
Document Content and Description Below
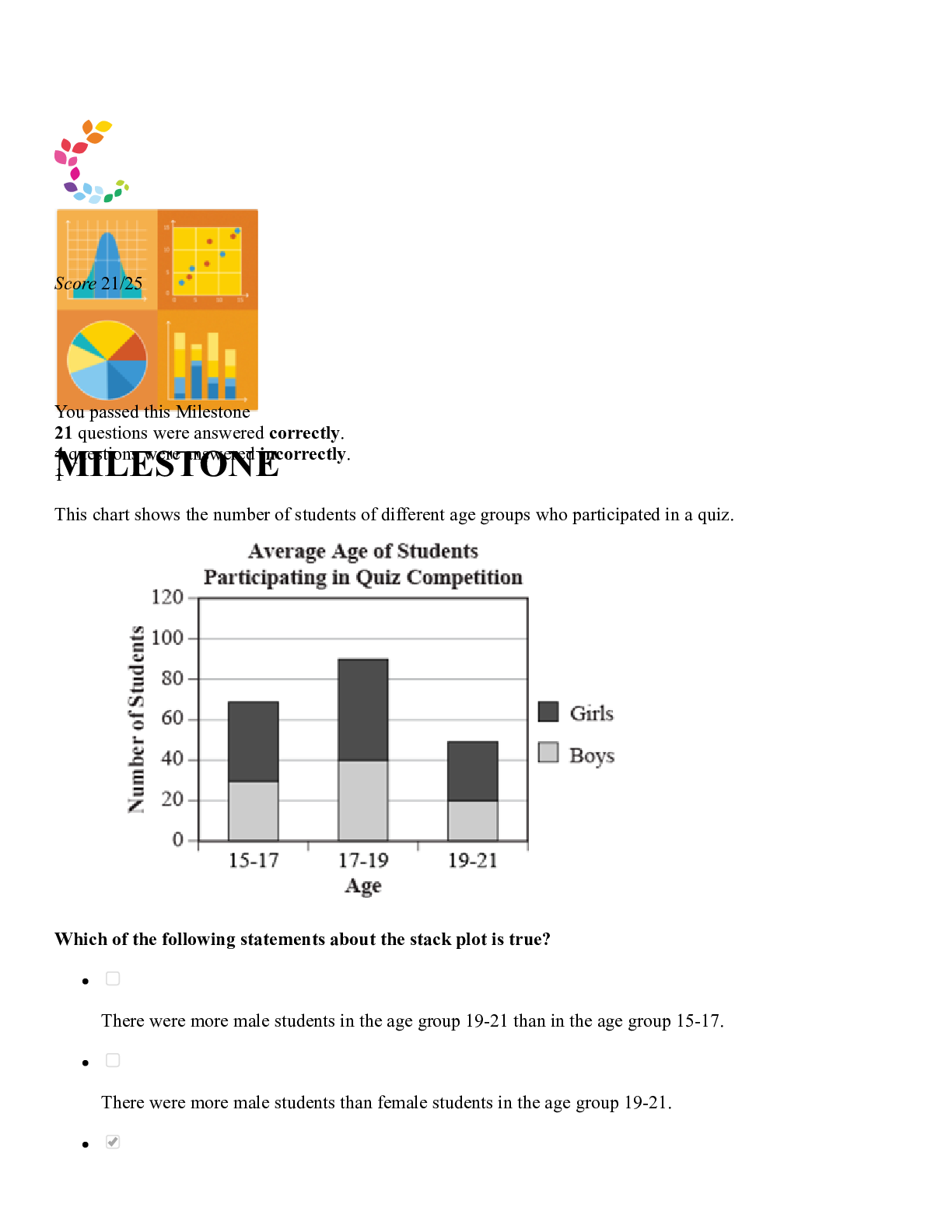
1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 1/26 UNIT 1 — MILESTONE 1 Score 32/36 You passed this Milestone 32 questions were answered correctly. 4 questions were answered incorrectly. 1 In each mile... stone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the SELECT statement, query the customer table to find the number of customers that do not live in the country France. 54 6 5 59 Common mistakes when using the COUNT function include not selecting the right column, forgetting to use () around the column, or forgetting to add in the filter conditions. CONCEPT COUNT to Count Records 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 2/26 2 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ USING the SELECT statement, query the track table ordered by the track_id. Set the LIMIT to 8 and OFFSET to 40. What is the name of the last row returned? Not The Doctor Ironic Right Through You Hand In My Pocket Common mistakes with the LIMIT and OFFSET clauses include mixing up the two, not using the ORDER BY clause to enforce a predictable result set, and not using the rows skipped using OFFSET. CONCEPT LIMIT and OFFSET to Cap Results 3 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ What is the main function of the SELECT clause in SQL? To apply conditions to filter the dataset To retrieve rows from one or more table columns 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 3/26 To identify one or more tables as the source for a query CONCEPT SQL Clauses 4 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the WHERE and HAVING clauses, filter the track table for the tracks having the genre_id being set to 1 or 2 grouped by the album_id having the number of tracks greater than 15. Provide the list of album_id and the sum of unit_price that fit these criteria. Which of the following queries would provide the correct results? SELECT album_id, sum(unit_price) FROM track WHERE genre_id in (1,2) GROUP BY album_id HAVING count(track_id) > 15 SELECT album_id, sum(unit_price) FROM track WHERE count(track_id) > 15 GROUP BY album_id HAVING genre_id in (1,2) SELECT album_id, count(unit_price) FROM track WHERE genre_id in (1,2) GROUP BY album_id HAVING sum(track_id) > 15 SELECT album_id, sum(unit_price) FROM track HAVING count(track_id) > 15 WHERE genre_id in (1,2) GROUP BY album_id 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 4/26 Common mistakes when using both the WHERE and HAVING clause include using the aggregate function in the WHERE clause, listing the clauses in the incorrect order, forgetting to include all of the columns listed in the SELECT clause in the GROUP BY clause, or using the incorrect aggregate functions. CONCEPT Filters to Specify Data 5 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Identify the line of code that would either generate a syntax, logical, or requirements error in the following CREATE TABLE statement. The statement should create a table called 'users' that consists of the user_id as the primary key that is auto-incremented, the username, and password. CREATE TABLE user( user_id serial PRIMARY KEY, username VARCHAR (50) password VARCHAR (50) ); 2 1 4 3 Common mistakes with creating a table include not including all column names, not matching the names exactly, data types not included, not including sizes for strings, commas to separate out each column, not using ( ) around the entire table set, not using serial in the primary key or having serial listed for multiple columns. CONCEPT Primary Key and Auto-increment 6 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 5/26 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Which of the following is a correctly formatted INSERT statement that will successfully add a new record that uses the auto-incremented primary key into the following table? CREATE TABLE video( video_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, video_name VARCHAR NOT NULL ); insert into video (video_id, video_name) values (1, 'home video - first day of school' ) insert into video (video_id, video_name) values (nextval, 'home video - first day of school') insert into video (video_name) values (home video - first day of school) insert into video (video_name) values ('home video - first day of school' ) Common mistakes when inserting a new record into an existing table using an auto-incemented ID include not setting the value for the sequence, not having the same number of values as the number of columns, not including data for rows with a NOT NULL constraint, not adhering to the UNIQUE constraint, not considering foreign keys, not quoting string data and not having the set of values in the same order as the column list. CONCEPT INSERT to Add Data 7 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Identify the correctly constructed ALTER TABLE statement that removes the column phone from the employee table. ALTER TABLE employee DROP COLUMN home_phone; 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 6/26 ALTER TABLE employee DROP COLUMN phone VARCHAR (100); ALTER TABLE employee DROP COLUMN phone; ALTER TABLE employee ADD phone; Common mistakes when adding or dropping a column include incorrectly naming the table or column names, not including the data type and size when adding a column, or forgetting the syntax structure of the ALTER TABLE command. CONCEPT ALTER TABLE to Change Columns: Add/Drop 8 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the SELECT statement, query the track table to find the total cost of the tracks on album_id 5 rounded to the nearest dollar. 14.85 14.9 14 15 Common mistakes when using the ROUND function include not selecting the right column, not including the precision level, forgetting to use () around the column/function, or forgetting to add in the filter conditions. CONCEPT 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 7/26 ROUND to Round Numbers 9 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Which of these SELECT statements would successfully display exactly three columns of data from the employee table? SELECT hiredate, postalcode, employeeid FROM employee; SELECT hire_date; postal_code; employee_id FROM employee; SELECT hire_date, postal_code, employee_id FROM employee; SELECT * FROM employee; Common mistakes when displaying columns of data by SELECT statement include using the * wildcard when the table has more than the desired number of columns, misspelling a clause name, table name, or column name, and forgetting to use commas appropriately. CONCEPT SELECT to Display Data 10 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the BETWEEN operator, filter the invoice table to find the invoices that were invoiced between 2010-01- 01 and 2010-01-15. Identify the 3rd customer ID. 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 8/26 57 45 47 51 Common mistakes include filtering the wrong column of data, using the wrong table, not using the right boundaries in the BETWEEN clause, or not adding the word 'and' between the values. CONCEPT BETWEEN to Filter Data 11 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the AND or OR statement, filter the employee table for employees that has the title that starts with Sales and has the address that has Ave in it. Identify the last name of the 3rd record. Johnson Peacock Margaret Steve 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 9/26 Common mistakes include using the = instead of LIKE when using wild cards, filtering the wrong column of data, using the wrong data table, forgetting to use the single quotes around the data, or forgetting to include the wild cards in all parts of the string rather than just on one end. Other common mistakes when using the AND and OR statements include using the incorrect option. The AND operator should be used when both conditions need to apply whereas the OR operator should be used when only one condition of the two should apply. CONCEPT Multiple Filters 12 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Identify the correctly constructed ALTER TABLE statement to add a UNIQUE constraint to the column student_number with the constraint name student_number_unique on the table student. ALTER TABLE student ADD UNIQUE student_number CONSTRAINT (student_number_unique); ALTER TABLE student ADD CONSTRAINT student_number UNIQUE (student_number); ALTER TABLE student ADD CONSTRAINT student_number_unique UNIQUE (student_number); ALTER TABLE student ADD CONSTRAINT student_number UNIQUE (student_number_unique); Common mistakes with adding the unique constraint to an existing column include not having ( ) around the column names, missing the keyword UNIQUE, incorrectly spelling the column name, or not including the constraint name. CONCEPT UNIQUE to Validate Data 13 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the ORDER BY clause, sort the Customer table by the company name of the customer in ascending order and identify the 10th company name in the list from among the answer options. 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 10/26 Murray Woodstock Discos null Martins Some common mistakes in using ORDER BY are sorting by ASC rather than DESC or vice versa, reporting the wrong column, and using the wrong column for the sort. CONCEPT ORDER BY to Sort Data 14 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the WHERE clause, filter the employee table to include individuals that report to Andrew Adams, who has an employee_id of 1. Identify the title of the 2nd individual listed. IT Manager General Manager Sales Manager Sales Support Agent 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 11/26 Common mistakes when using a WHERE clause include using the wrong inequality operator, filtering on the wrong column of data, using the wrong data table. CONCEPT WHERE to Filter Data 15 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Which of the following is a correctly formatted INSERT statement that will successfully add a record into the genre table? insert into genre (genre_id, name) values (19, 'Funk' ) insert into genre (genre_id, name) values (30, 'Funk' ) insert into genre (genre_id, name) values ('Funk',35) insert into genre (genre_id, name) values (40, Funk) Common mistakes when inserting a new record into an existing table include not having the same number of values as the number of columns, not including data for rows with a NOT NULL constraint, not adhering to the UNIQUE constraint, not considering foreign keys, not quoting string data and not having the set of values in the same order as the column list. CONCEPT INSERT INTO to Add Row 16 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the GROUP BY and HAVING clause, filter the customer table by country. How many countries have more than 3 customers? 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 12/26 18 6 7 5 Common mistakes when using the HAVING clause in the GROUP BY clause in a SELECT statement include not using aggregate functions in the SELECT clause, not including each column in the SELECT clause in the GROUP BY clause, not using the right aggregate function, or including the filter in the WHERE clause instead of the HAVING clause. CONCEPT HAVING to Filter On Aggregates 17 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Which of the following statement(s) would successfully delete the invoice_line_id 5 from the invoice_line table? DELETE FROM invoice WHERE invoice_line_id = 353; DELETE FROM invoice_line WHERE invoice_line_id = 5; DELETE FROM invoice WHERE invoice_line_id = 5; DELETE FROM invoice_line WHERE invoiceline__id = 5; DELETE FROM invoice_line WHERE invoice_line_id = 5; DELETE FROM invoice WHERE invoice_line_id = 5; 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 13/26 Common mistakes when deleting from tables include not removing tables that reference their foreign keys, not deleting from the tables in the right order, not deleting data from all of the tables, not using quotes around string literals, or not using the right syntax. CONCEPT DELETE FROM to Remove Row 18 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the SELECT statement, query the invoice table to find the total cost for all orders placed by the customer_id that's equal to 2. 7 38 2313 2 Common mistakes when using the SUM function include not selecting the right column, forgetting to use () around the column, or forgetting to add in the filter conditions. CONCEPT SUM to Add Values 19 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Given the new table which insert statement would query from the customer table to insert the city, country, and postal_code of all customers in the right columns? 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 14/26 CREATE TABLE locationlist( locationlist_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, city VARCHAR NOT NULL, country VARCHAR NOT NULL, postal_code VARCHAR ); INSERT INTO locationlist SELECT city, country, postal_code FROM customer; INSERT INTO locationlist (locationlist_id, city, country, postal_code) SELECT city, country, postal_code FROM customer; INSERT INTO locationlist (city, country, postal_code) SELECT city, country, postal_code FROM customer; INSERT INTO locationlist (postal_code, country, city) SELECT city, country, postal_code FROM customer; Common mistakes when inserting data queried from another table include not setting the value for the sequence, not having the same number of values as the number of columns, not including data for rows with a NOT NULL constraint, not adhering to the UNIQUE constraint, not considering foreign keys, not quoting string data, and not having the set of values in the same order as the column list. CONCEPT INSERT to Add Queried Data 20 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Which of the following would set the media_type_id to 1 on all tracks where the album_id is set to 3? UPDATE track set media_type_id = 1 where album_id = 3 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 15/26 UPDATE track where album_id = 3 set media_type_id = 1 UPDATE track set media_type_id = 3 where album_id = 1 UPDATE track set media_type_id = 1 where track_id = 3 Common mistakes when using the UPDATE statement that multiple rows in a table include forgetting to use commas between each variable set, including the WHERE clause to identify specific rows, not updating all fields, or using AND in the SET clause. CONCEPT UPDATE to Edit Multiple Rows 21 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Given the employee table and the data that it contains, assuming that you have the rights to modify the table, which of the following ALTER TABLE statements would work without errors? ALTER TABLE employee ALTER postal_code TYPE VARCHAR (100); ALTER TABLE employee ALTER COLUMN email TYPE int; ALTER TABLE employee ALTER COLUMN email TYPE TEXT; ALTER TABLE customer ALTER COLUMN city TYPE int; 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 16/26 Common mistakes when modifying the data type of a column include not casting the variables if needed, not including the table and column names to change, the column being a primary or foreign key, considering the error messages that may exist when converting the data that already exists in the table. CONCEPT ALTER TABLE to Change Columns: Data Type 22 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Select the correctly constructed CHECK constraint to validate the date_of_birth column of type data to ensure that values placed into it is greater than 1850-01-01 CHECK (date_of_birth >= '1850-01-01') CHECK (date_of_birth > '1850-01-01') CHECK (date_of_birth < '1850-01-01') CHECK (date_of_birth > 1850-01-01) Common mistakes with CHECK constraints include having the incorrect range, incorrectly using AND and OR, using the incorrect comparison operator, columns not being named correctly, not considering the right data type, or missing the use of quotes around string data. CONCEPT CHECK to Validate Data 23 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Identify the line of code that would generate an error in the following CREATE TABLE statement. 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 17/26 This statement creates a table called users that consists of the user_id as the primary key, the username, and password. CREATE TABLE user( user_id int PRIMARY KEY, username VARCHAR 50, password VARCHAR (50) ); 2 4 1 3 Common mistakes with creating a table include not including all column names, not matching the names exactly, data types not included, not including sizes for strings, commas to separate out each column, and not using ( ) around the entire table set. CONCEPT CREATE TABLE Syntax 24 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Given the tables provided, which of the following DROP TABLE series of statements would correctly remove the tables without causing an error? DROP TABLE invoice; DROP TABLE invoice_line; DROP TABLE customer; DROP TABLE playlist_track; DROP TABLE invoice_line; 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 18/26 DROP TABLE invoice; DROP TABLE playlist_track DROP TABLE playlist; DROP TABLE genre; DROP TABLE genre; DROP TABLE album; DROP TABLE artist; Common mistakes when dropping a table include not considering the foreign keys linked to the table, not removing the foreign keys on the table or not including the correct table name. CONCEPT DROP TABLE to Remove Tables 25 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the WHERE clause, filter the invoice table to find the invoices that were invoiced on January 15th, 2011. Identify the second customer ID of the invoice. 27 29 35 31 Common mistakes when filtering dates can be mixing up the day, month, and year as different countries may list them in a different order. Always check your data first to ensure the correct order of the day, month, and year. 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 19/26 Other common errors are using the wrong inequality comparison (e.g. > rather than <), filtering on the wrong column of data, and using the wrong data table. Also, make sure that you use the correct format for the date using yyyy-mm-dd. CONCEPT Filter by Date 26 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the IN operator, filter the album table to find the artist ID of 11, 18, 9, or 4. Identify the title of the 1st record. Afrociberdelia Alcohol Fueled Brewtality Live! [Disc 1] Jagged Little Pill BackBeat Soundtrack Common mistakes include filtering the wrong column of data, using the wrong table, not using commas to separate out each criterion, not using single quotes around string data, or spelling the values incorrectly. CONCEPT IN to Filter Data 27 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the SELECT statement, query the invoice table to find the max invoice_date where the billing_country is equal to Canada. 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 20/26 2013-12-22 2009-01-01 2013-12-06 2013-12-21 CONCEPT MAX & MIN to Find Extremes 28 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the LIKE operator in the WHERE clause, filter the customer table to list the individuals that have the country that ends with the lowercase 'a.' Identify the 5th individual's country. Australia Austria USA Canada. CONCEPT LIKE to Search Data 29 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Which of the following is a correctly formatted INSERT statement that will insert three records into the album table? insert into album (artist_id, title, album_id) values (1, 'Genesis', 450), (1, 'Self-Titled', 451), (1, 'Lyrics', 452) insert into album (artist_id, title, album_id) values (1, 'Genesis', 450) (1, 'Self-Titled', 451) (1, 'Lyrics', 452) insert into album (artist_id, title, album_id) values (1, 'Genesis', 450), (1, 'Self-Titled', 451), (1, 'Lyrics', 450) insert into album (album_id, title, artist_id) values (1, 'Genesis', 450), (1, 'Self-Titled', 451), (1, 'Lyrics', 452) CONCEPT INSERT INTO to Add Multiple Rows 30 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 22/26 Which of the following would set the postal_code of the customer with the customer_id = 22 to 33433. UPDATE customer SET postal_code WHERE customer_id = '33433' UPDATE customer WHERE customer_id = 22 SET postal_code = '33433' UPDATE customer SET postal_code = '33433' WHERE customer_id = 22 UPDATE customer IN postal_code = '33433' WHERE customer_id = 22 CONCEPT UPDATE to Edit Row 31 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Identify the SQL command that uses an aggregate function that could be used to find the newest employee in the employee table. SELECT small(hire_date) FROM employee; SELECT max(hire_date) FROM employee; 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome SELECT large(hire_date) FROM employee; SELECT min(hire_date) FROM employee; CONCEPT Aggregate Functions 32 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Which of the following would be a type of constraint? Declaring a data type Naming the table Creating a table Naming the columns CONCEPT Table Constraints 33 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 24/26 https://postgres.sophia.org/ Given the employee table and the data that it contains, assuming that you have the rights to modify the table, which of the following ALTER TABLE statements would create an error. ALTER TABLE employee ALTER COLUMN email TYPE VARCHAR (100); ALTER TABLE employee ALTER COLUMN city TYPE VARCHAR (100); ALTER TABLE employee ALTER COLUMN employee_id TYPE VARCHAR (50); ALTER TABLE employee ALTER COLUMN postal_code TYPE VARCHAR (100); CONCEPT ALTER TABLE to Change Columns: Data Characteristics 34 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the GROUP BY clause and the count aggregate function, filter the track table grouped based on album_id. How many tracks are in album 99? 10 11 12 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 25/26 13 CONCEPT GROUP BY to Combine Data 35 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the LIKE operator in the WHERE clause, use the necessary wildcards to filter the album table to find the albums that have a year start with 19 in the title. Identify the 4th album ID. 146 196 123 104 CONCEPT LIKE Wildcards 36 1/1/22, 3:35 AM Sophia :: Welcome 26/26 In each milestone, you may want or need to use the database and query tool to answer some of the questions. We suggest you open the tool in another browser tab while you are working on this assessment. https://postgres.sophia.org/ Using the SELECT statement, query the invoice table to find the average total cost for all orders placed in the country France. 5.7135278514588859 5.6285714285714286 5.64 5.8021978021978022 CONCEPT AVG to Average Values About Contact Us Privacy Policy Terms of Use [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 26 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 22, 2022
Number of pages
26
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 22, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
204