*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NUR 631 Midterm Study Guide. A+ RATED (All)
NUR 631 Midterm Study Guide. A+ RATED
Document Content and Description Below
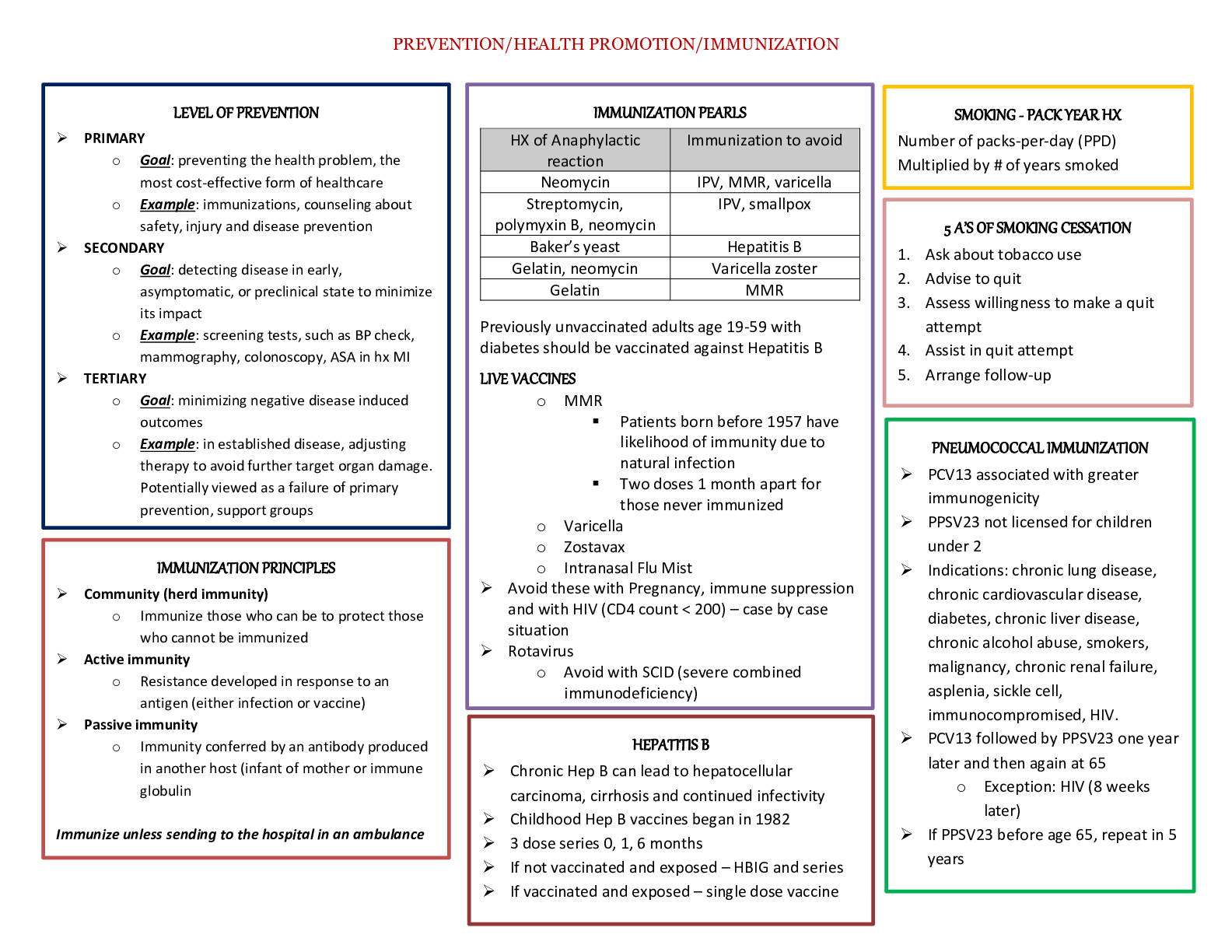
NUR 631 Study Guide for Midterm This study guide provides a content outline that can be used to prepare for the topic quiz. This outline may not be inclusive of all quiz content. Cellular biology ... and Alterations • Compensatory hyperplasia after partial resections (mod 1) (51-53) o Ex: liver, hepatocyte growth o Adaptive mechanism that enables certain organs to regenerate o Even with removal of 70% of the liver, it will regenerate within about 2 weeks o Compensatory hyperplasia occurs in epidermal, intestinal epithelia, hepatocytes, bone marrow and fibroblasts. Some type off hyperplasia is noted in bone, cartilage and smooth muscles – Example- callus, wound healing as part of inflammation process • Tumor progress from benign to malignant (364-366) o Benign tumors are usually encapsulated and well differentiated. They retain some normal tissue structure and do not invade the capsules surrounding them or spread to regional lymph nodes or distant locations. Generally named according to the tissues from which they arise, and include the suffix –oma. o Some benign tumors can progress to cancer and are then referred to as malignant. They have more rapid growth rates and specific microscopic alterations, including loss of differentiation and absence of normal tissue organization. One hallmark is anaplasia – loss of cellular differentiation, irregularities of the size and shape of the nucleus, and the loss of normal tissue structure. May present with different degrees of encapsulation; some lack a capsule, and even if one is apparent, it’s integrity has been compromised so that tumor cells can grow to invade nearby blood vessels, lymph and surrounding structures. Most deadly characteristic is their ability to spread far beyond the tissue of origin – metastasis BENIGN TUMORS MALIGNANT TUMORS Grow slowly Have a well-defined capsule Are not invasive Are well differentiated; look like the tissue from which they arose Have a low miotic index; dividing cells are rare Do not metastasize Grow rapidly Are not encapsulated Invade local structures and tissues Are poorly differentiated; may not be able to determine the tissue of orgin High miotic index; many dividing cells Can spread distantly; often through blood vessels and lymphatics [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 30, 2021
Number of pages
17
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 30, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
41