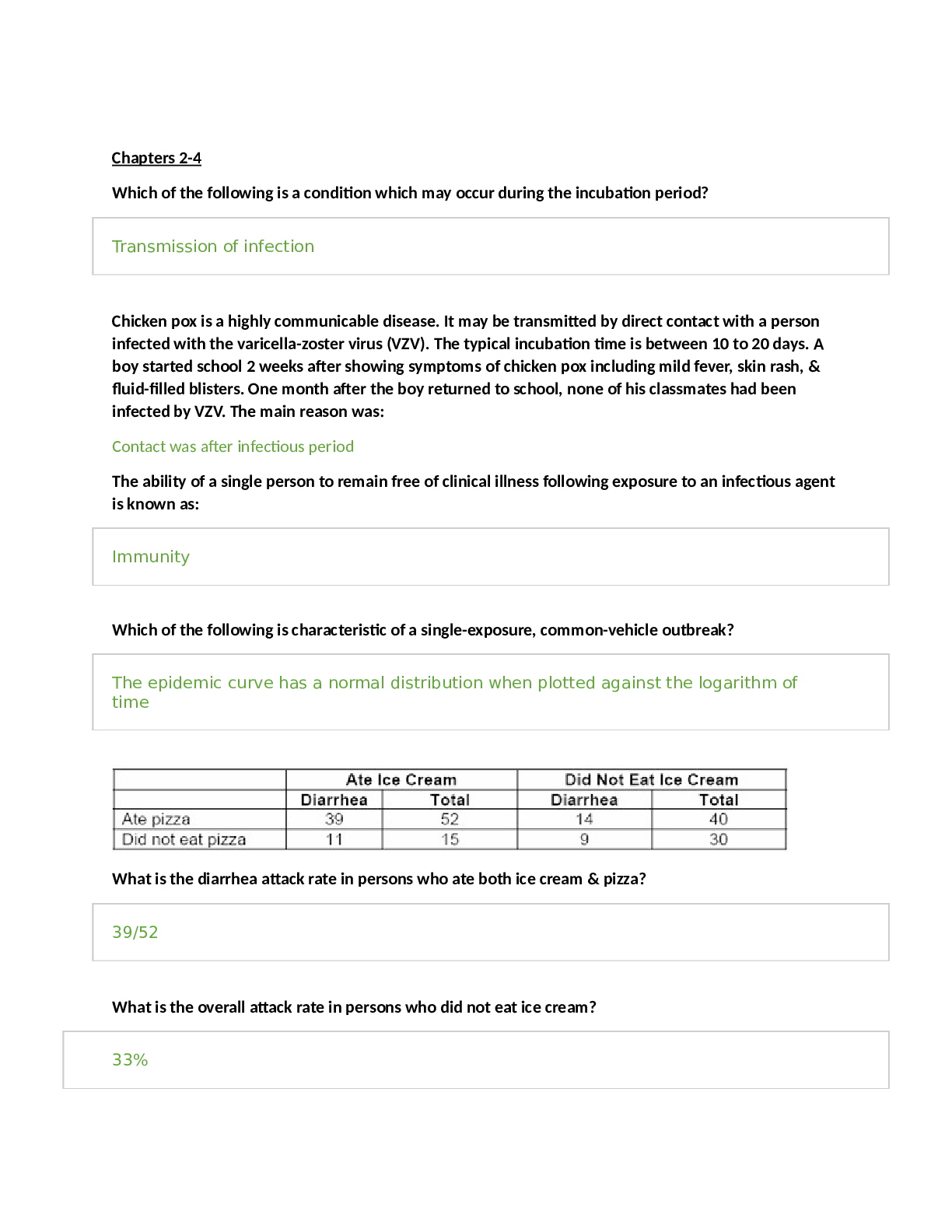
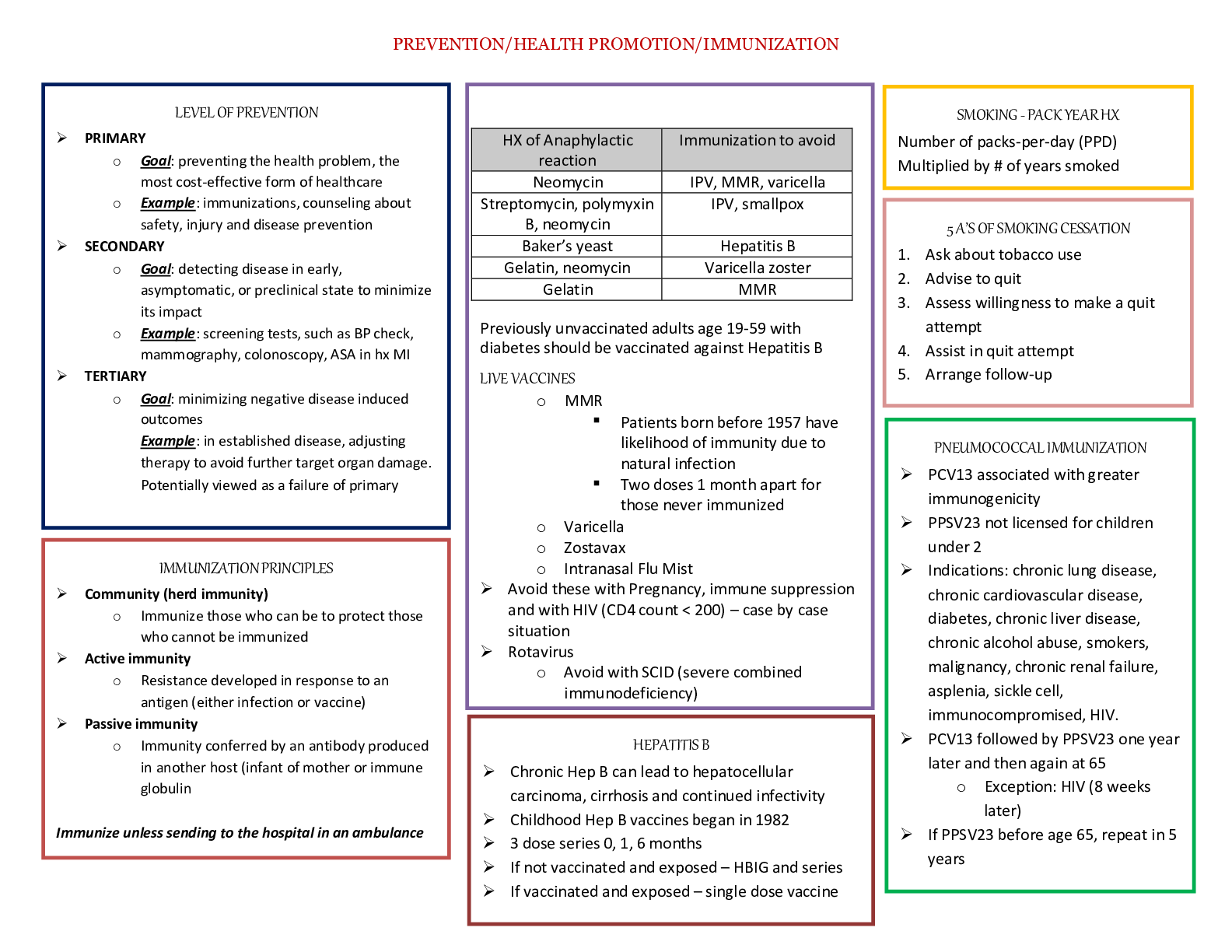
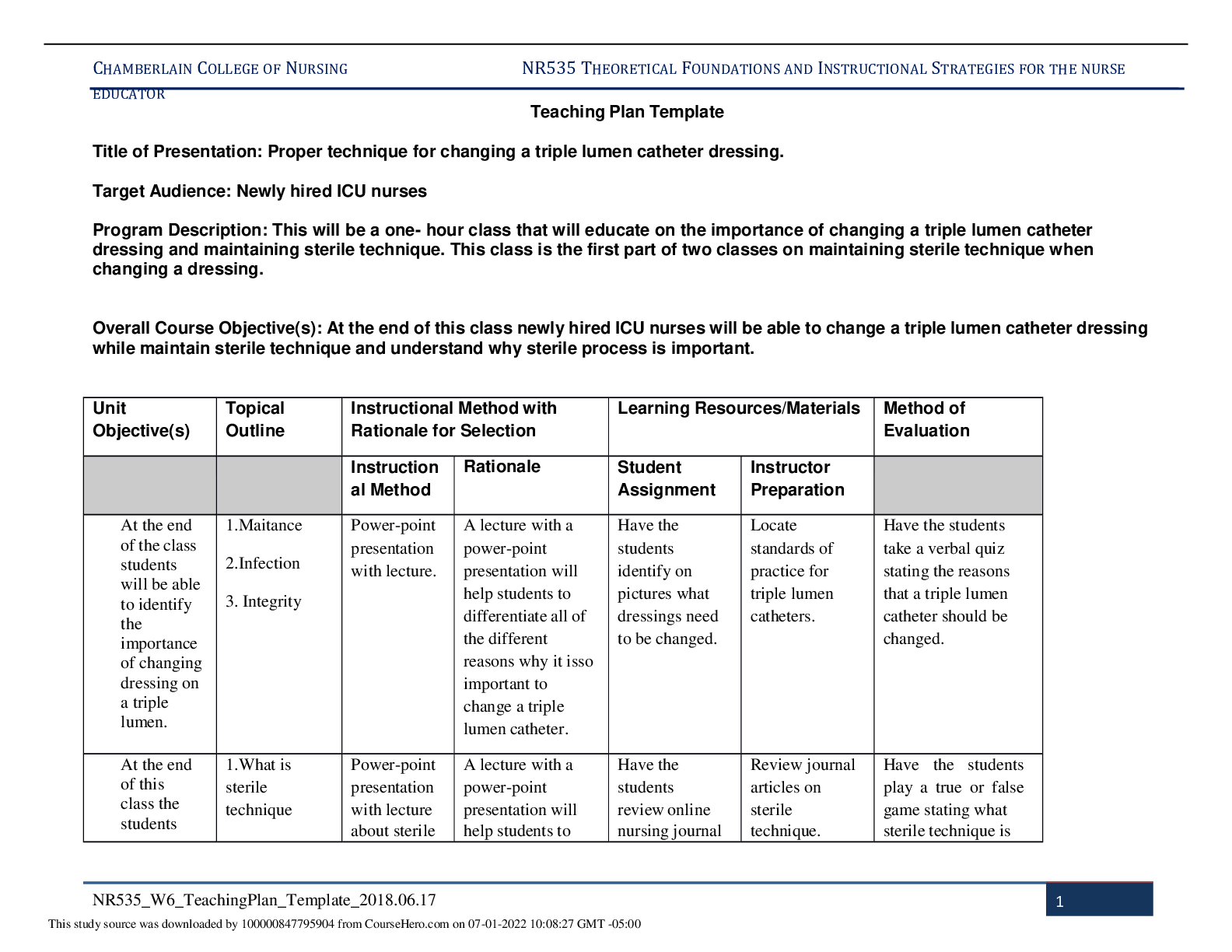
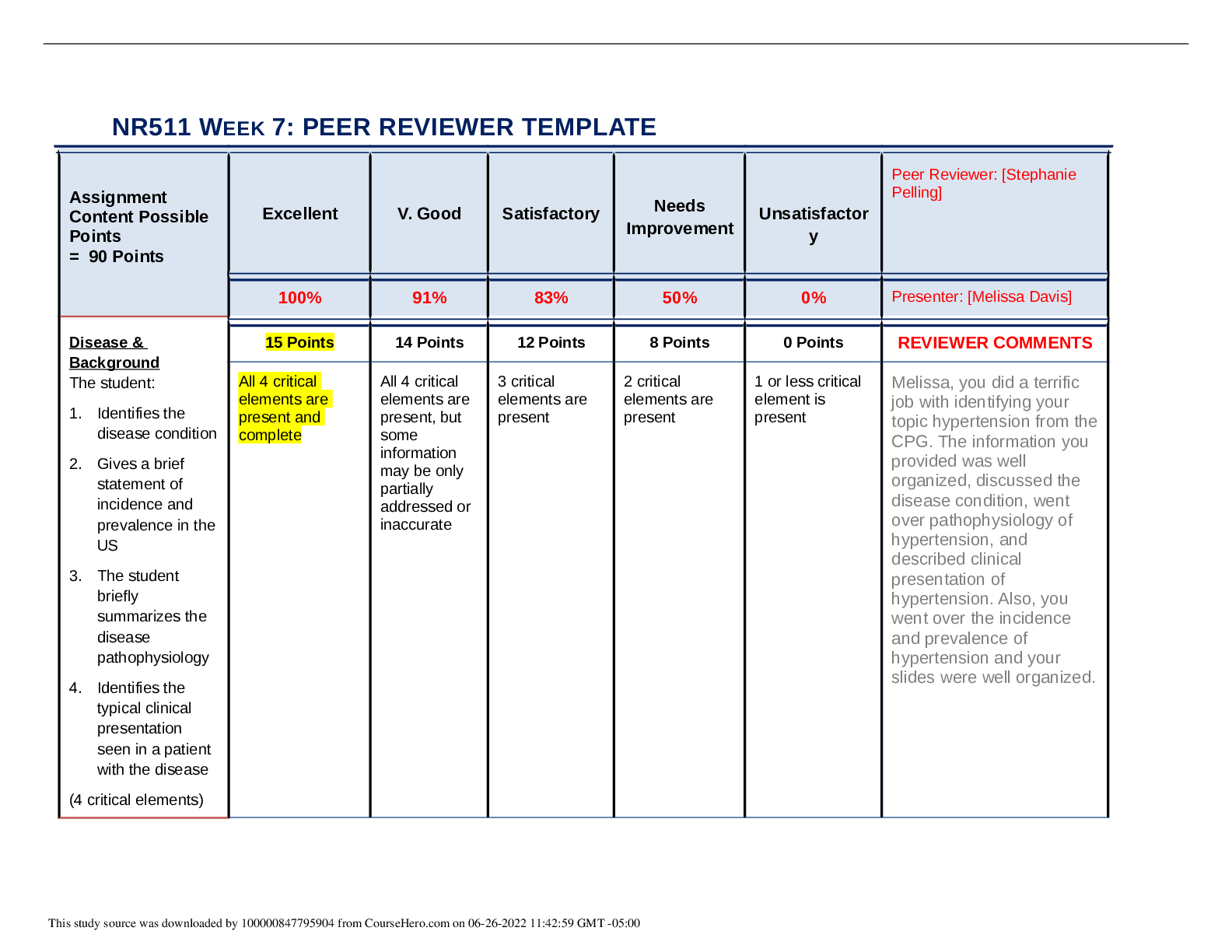
Business > STUDY GUIDE > BUS 120 Final Study Guide 4 (GRADED A) Questions and Answers | Straighterline (All)
BUS 120 Final Study Guide 4 (GRADED A) Questions and Answers | Straighterline
Document Content and Description Below
• Question 1 are planned activities conducted specifically for the benefit of an audience. Selected Answer: Ceremonie s 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Ceremonies are m... ore formal artifacts than rituals. Ceremonies are planned activities conducted specifically for the benefit of an audience. This would include publicly rewarding (or punishing) employees or celebrating the launch of a new product or newly won contract. • Question 2 Scenario B 2 out of 2 points BarkBark Inc. and Happy Toys Ltd. are considering a merger and are unsure whether their two organizations will have a difficult time with clashing cultures. They perform a detailed diagnosis, collecting and analyzing the gathered data about the two merging companies. They identify several overlapping values, which they feel that they can effectively meld into a cohesive new culture. What type of cultural merge would be best for BarkBark? Selected Answer: integration Response Feedback: Integration is used to combine two or more cultures into a new composite culture that preserves the best features of the previous cultures. Integration is slow and potentially risky because there are many forces preserving the existing cultures. Still, this strategy should be considered when the companies have relatively weak cultures or when their cultures include several overlapping values. • Question 3 2 out of 2 points During which of the following stages of socialization do people first learn about the organization and job? Selected Answer: preemployment Response Feedback: Socialization is a continuous process, beginning long before the first day of employment and continuing throughout one's career within the company. • Question 4 Which one of the following is true about strong cultures? 0 out of 2 points Selected Answer: They seek job applicants whose values are different to expand the cultural beliefs. Response Feedback: An organization's culture is embedded in the minds of its employees. Organizational stories are rarely written down; rituals and ceremonies do not usually exist in procedure manuals; organizational metaphors are not found in corporate directories. Thus, a strong culture depends on a stable workforce. Workforce stability is also important because it takes time for employees to fully understand the organization's culture and how to enact it in their daily work lives. The organization's culture can literally disintegrate during periods of high turnover and precipitous downsizing because the corporate memory leaves with these employees. • Question 5 2 out of 2 points If artifacts of organizational culture are the physical structure, language, rituals, and stories, then what are shared values and assumptions? Selected Answer: organizational culture Response Feedback: Organizational culture consists of shared values and assumptions. • Question 6 2 out of 2 points In the context of organizational socialization, the adjustment process is better for Selected Answer: newcomers with diverse work experience. Response Feedback: Research reports that the adjustment process is fairly rapid for many people, usually occurring within a few months. However, newcomers with diverse work experience seem to adjust better than those with limited previous experience, possibly because they have a larger toolkit of knowledge and skills to make the adjustment possible. • Question 7 Which of the following is true about socialization agents? 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Socialization agents help integrate new employees into the team. Response Feedback: Coworkers are important socialization agents because they are easily accessible, can answer questions when problems arise, and serve as role models for appropriate behavior. New employees tend to receive this information and support when coworkers integrate them into the work team. • Question 8 Ceremonies are 0 out of 2 points Selected Answer: physical structures that convey the dominant values of an organization's culture. Response Feedback: Ceremonies are more formal artifacts than rituals. Ceremonies are planned activities conducted specifically for the benefit of an audience. • Question 9 2 out of 2 points occurs when employees at the acquired company willingly embrace the cultural values of the acquiring organization. Selected Answer: Assimilation Response Feedback: Assimilation occurs when employees at the acquired company willingly embrace the cultural values of the acquiring organization. Typically, this strategy works best when the acquired company has a weak, dysfunctional culture and the acquiring company's culture is strong and aligned with the external environment. • Question 10 2 out of 2 points A deculturation strategy of merging two corporate cultures should be applied when Selected Answer: Response Feedback: employees in the acquired firm want to hold on to their firm's culture even though it does not fit the external environment. Employees usually resist organizational change, particularly when they are asked to throw away personal and cultural values. Under these conditions, some acquiring companies apply a deculturation strategy by imposing their culture and business practices on the acquired organization. • Question 11 0 out of 2 points Which of the following is true about using the strategy of integration for merging different corporate cultures? Selected Answer: It is the fastest strategy for merging different corporate cultures. Response Feedback: Integration combines two or more cultures into a new composite culture that preserves the best features of the previous cultures. Integration should be considered when the companies have relatively weak cultures or when their cultures include several overlapping values. Integration also works best when people realize that their existing cultures are ineffective and therefore are motivated to adopt a new set of dominant values. • Question 12 2 out of 2 points Which of the following tends to happen when an organization's culture is misaligned with its external environment? Selected Answer: Response Feedback: The organization has more difficulty anticipating and responding to stakeholder needs. One of the contingencies between cultural strength and organizational effectiveness is whether the organization's culture contents—its dominant values and assumptions—is aligned with the external environment. When an organization's culture is misaligned with its external environment, the organization has more difficulty anticipating and responding to stakeholder needs. • Question 13 The principle states that organizations are open books, so we have choices in how they may be perceived, framed, and described. Selected Answer: poetic 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: The poetic principle states that organizations are open books, so we have choices in how they may be perceived, framed, and described. • Question 14 2 out of 2 points The unfreezing process requires that participants disconfirm their existing beliefs, sometimes including their own competence at certain tasks or interpersonal relations, thus creating an ethical dilemma of Selected Answer: undermining an individual's self-esteem. Response Feedback: Some organizational change practices also face ethical issues. One concern is that some organizational change interventions undermine the individual's self-esteem. The unfreezing process requires that participants disconfirm their existing beliefs, sometimes including their own competence at certain tasks or interpersonal relations. • Question 15 In organizational change, future search conferences are used mainly to 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Response Feedback: involve as many employees and other stakeholders as possible in the change process. Future search refers to systemwide group sessions, usually lasting a few days, in which participants identify trends and identify ways to adapt to the changes. Future search tries to involve as many employees and other stakeholders as possible in the change process. • Question 16 0 out of 2 points Which of the following is true about organizational change? Selected Answer: Viral change should be avoided in organizations. Response Feedback: A guiding coalition is a formally structured group, but change also occurs more informally through social networks. To some extent, coalition members support the change process by feeding in to these networks. • Question 17 Scenario C 0 out of 2 points BusCorp wants to introduce a new procedure to improve how customer requests are handled. This change will require employees to break old routines and adopt new role patterns. They decide to adopt two new programs. One asks the employees to learn how to work as teams as the company changes. The other involves forming task forces within the company to help determine new customer service practices. BusCorp's second half of their strategy is the formation of task forces to minimize resistance, or a(n) strategy. Selected Answer: negotiation Response Feedback: Employees who participate in decisions about a change tend to feel more personal responsibility for its successful implementation, rather than being disinterested agents of someone else's decisions. • Question 18 Employees typically oppose organizational change because they lack Selected Answer: motivation. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Change management experts have developed a long list of reasons why people resist change. Some people inherently oppose change because of their personality and values. Aside from these dispositional factors, employees typically oppose organizational change because they lack sufficient motivation, ability, role clarity, or situational support to change their attitudes, decisions, and behavior. In other words, an employee's readiness for change depends on all four elements of the MARS model. These MARS elements are the foundations of the six most commonly cited reasons why people resist change: 1. negative valence of change, 2. fear of the unknown, 3. not-invented-here syndrome, 4. breaking routines, 5. incongruent team dynamics, and 6. incongruent organizational systems and structures. • Question 19 0 out of 2 points Which of the following types of resistance to change is a strategy to "prove" that the decision is wrong? Selected Answer: negative valence of change Response Feedback: Due to the "not-invented-here" syndrome, staff members sometimes deliberately inflate problems with changes that they did not initiate, just to "prove" that the decision is wrong. • Question 20 2 out of 2 points The positive principle, the constructionist principle, and the simultaneity principle are principles of Selected Answer: appreciative inquiry. Response Feedback: The positive principle, the constructionist principle, and the simultaneity principle are principles of appreciative inquiry. • Question 21 2 out of 2 points One problem the learning strategy has in minimizing resistance to change is that it Selected Answer: is a time-consuming process. Response Feedback: Learning is an important process in most change initiatives because employees require new knowledge and skills to fit the organization's evolving requirements. However, the learning process is time- consuming. • Question 22 2 out of 2 points Which of the following change management strategies should be given a priority when employees need to break old routines and adopt new role patterns? Selected Answer: learnin g Response Feedback: Learning is an important process in most change initiatives because employees require new knowledge and skills to fit the organization's evolving requirements. Training is time-consuming, but it helps people break routines by learning new role patterns. • Question 23 2 out of 2 points Increasing the restraining forces and reducing or removing the driving forces would Selected Answer: make the change process more difficult to implement. Response Feedback: Unfreezing occurs when the driving forces are stronger than the restraining forces. This happens by making the driving forces stronger, weakening or removing the restraining forces, or combining both. Increasing the restraining forces and reducing or removing the driving forces would make the change process difficult. • Question 24 Scenario A 2 out of 2 points XYZ Office Supplies is about to introduce a new customer service program that will affect all of its 355 sales and service employees. Job duties will be changed and the employee reward system will be altered to fit this new customer focus. Moreover, the company wants to improve the efficiency of work processes, thereby removing some of the comfortable (and often leisurely) routines that employees have followed over the years. Top management is concerned about what types of forces resisting change the company will potentially experience during this change process. XYZ attempts to assist the change process by putting employees in direct contact with customers. Here, the company is trying to Selected Answer: create an urgency for change. Response Feedback: Some companies fuel the urgency to change by putting employees in direct contact with customers. Here, XYZ is attempting to do that. • Question 25 2 out of 2 points By creating , employee involvement reduces the fear of the unknown and the not-invented-here syndrome. Selected Answer: a sense of ownership Response Feedback: Employees who participate in decisions about a change tend to feel more personal responsibility for its successful implementation. This sense of ownership also minimizes the not-invented-here syndrome and fear of the unknown. TEST 7 BUSI 240 FINAL • Question 1 2 out of 2 points Charisma refers to Selected Answer: the personal traits that provide referent power over others. Response Feedback: Charisma is a personal trait or relational quality that provides referent power over followers. • Question 2 2 out of 2 points Managerial leaders Selected Answer: support and guide the performance and well-being of individual employees. Response Feedback: Managerial leaders support and guide the performance and well-being of individual employees and the work unit to support current objectives and practices. • Question 3 2 out of 2 points Scenario D MoneySafe, a financial services organization, trains employees to new skills and uses coworkers to train new employees, while providing social support in the form of daycare facilities. MoneySafe management believes that using this system will help replace or reduce the need to micromanage by assigning and clarifying work responsibilities, setting goals and deadlines for employees, and establishing well-defined work procedures. Which of the following leadership styles is of least importance under the circumstances at MoneySafe? Selected Answer: task-oriented Response Feedback: Task-oriented leadership might be less important when performance-based reward systems keep employees directed toward organizational goals. • Question 4 0 out of 2 points People with an external locus of control tend to be more satisfied with leadership styles. Selected Answer: achievement-oriented and directive Response Feedback: People with an external locus of control believe their performance is due more to luck and fate, so they tend to be more satisfied with directive and supportive leadership. • Question 5 2 out of 2 points Leaders build commitment through Selected Answer: rewards. Response Feedback: Transforming a vision into reality requires employee commitment, and transformational leaders build this commitment in several ways. Their words, symbols, and stories build a contagious enthusiasm that energizes people to adopt the vision as their own. Leaders demonstrate a can-do attitude by enacting and behaving consistently with their vision. This persistence and consistency reflect an image of honesty, trust, and integrity. By encouraging experimentation, leaders involve employees in the change process so it is a collective activity. Leaders also build commitment through rewards, recognition, and celebrations as they pass milestones along the road to the desired vision. • Question 6 2 out of 2 points When people have leadership prototypes, they Selected Answer: believe that leaders are effective only if they behave consistently with their own preconceptions of how an effective leader should act. Response Feedback: If a leader looks like and acts consistently with people's prototype, they are more likely to believe that the leader is effective. This prototype comparison process occurs because people have an inherent need to quickly evaluate individuals as leaders, yet leadership effectiveness is often ambiguous and might not be apparent for a long time. • Question 7 2 out of 2 points How do women differ from men in their use of leadership styles? Selected Answer: Women tend to use more of the participative leadership style than do men. Response Feedback: Women adopt a participative leadership style more readily than their male counterparts do. One possible reason is that, compared to boys, girls are often raised to be more egalitarian and less status-oriented, which is consistent with being participative. • Question 8 2 out of 2 points Which of the following refers to "walking the talk"? Selected Answer: The leader steps out and behaves in ways that symbolize the vision. Response Feedback: Transformational leaders not only talk about a vision; they enact it. They "walk the talk" by stepping outside the executive suite and doing things that symbolize the vision. • Question 9 2 out of 2 points Transformational leaders Selected Answer: energize and direct employees to a new vision and corresponding behaviors. Response Feedback: Transformational leaders are change agents who energize and direct employees to a new vision and corresponding behaviors. • Question 10 2 out of 2 points Scenario D MoneySafe, a financial services organization, trains employees to new skills and uses coworkers to train new employees, while providing social support in the form of daycare facilities. MoneySafe management believes that using this system will help replace or reduce the need to micromanage by assigning and clarifying work responsibilities, setting goals and deadlines for employees, and establishing well-defined work procedures. Instead of focusing on rewards, MoneySafe could encourage employees to reach their peak performance by emphasizing behaviors. Selected Answer: achievement-oriented Response Feedback: Achievement-oriented leadership style emphasizes behaviors that encourage employees to reach their peak performance. The leader sets challenging goals, expects employees to perform at their highest level, continuously seeks improvement in employee performance, and shows a high degree of confidence that employees will assume responsibility and accomplish challenging goals. Achievement-oriented leadership applies goal-setting theory as well as positive expectations in self-fulfilling prophecy. • Question 11 2 out of 2 points Fiedler's contingency model of leadership states that the best leadership style depends on Selected Answer: the level of situational control. Response Feedback: Fiedler's model suggests that the best leadership style depends on the level of situational control, that is, the degree of power and influence the leader possesses in a particular situation. • Question 12 2 out of 2 points Effective leaders have a strong need for socialized power, meaning that they want power as a means to accomplish organizational objectives and similar good deeds. These leaders have Selected Answer: leadership motivation. Response Feedback: Effective leaders are motivated to lead others. They have a strong need for socialized power, meaning that they want power as a means to accomplish organizational objectives and similar good deeds. This is referred to as leadership motivation. • Question 13 0 out of 2 points Scenario B Food4U, a wholesale grocery business, operates in one city and provides one service— stocking retailers with fresh produce. The company wants to ensure that employees develop expertise in their skill specialization and that these specializations are used efficiently. A potential problem with Food4U's form of structure is Selected Answer: increased costs. Response Feedback: Compared with other structures, the functional structure usually produces higher dysfunctional conflict and poorer coordination in serving clients or developing products. • Question 14 0 out of 2 points Which of the following is an issue with flatter hierarchies? Selected Answer: This type of hierarchy has a lower quality and less timely information available. Response Feedback: Unfortunately, building a taller hierarchy (more layers of management) creates problems. One concern is that executives in tall structures tend to receive lower quality and less timely information. People tend to filter, distort, and simplify information before it is passed to higher levels in the hierarchy because they are motivated to frame the information in a positive light or to summarize it more efficiently. In contrast, in flat hierarchies, information is manipulated less and is usually transmitted much more quickly than in tall hierarchies. • Question 15 2 out of 2 points Which organizational structure has liaison roles? Selected Answer: informal communication Response Feedback: Larger organizations also encourage coordination through informal communication by assigning liaison roles to employees, who are expected to communicate and share information with coworkers in other work units. • Question 16 2 out of 2 points Scenario C ABC Production, a consumer products firm with a functional structure, is expanding from a single product line into several diverse product groups, with most sales within one country. What form of departmentalization should ABC Production eventually adopt to manage the new conditions most effectively? Selected Answer: divisional product structure Response Feedback: The firm should eventually adopt divisional product structure to manage the new conditions most effectively. The divisional structure groups employees around geographic areas, outputs (products or services), or clients. The product/service divisional structure organizes employees around distinct outputs. • Question 17 0 out of 2 points The more complex the environment, the more the organization should become. Selected Answer: centralized Response Feedback: The more complex the environment, the more decentralized the organization should become. Decentralization is a logical choice for complex environments because decisions are pushed down to people and subunits who possess the information needed to make informed choices. • Question 18 2 out of 2 points Standardizing work through job descriptions and procedures Selected Answer: is a form of coordination. Response Feedback: Standardizing work through job descriptions and procedures is a form of coordination. This coordinating mechanism is feasible when the work is routine (such as mass production) or simple (such as making cupcakes), but it is less effective in nonroutine and complex work such as product design. • Question 19 2 out of 2 points refers to the subdivision of work into separate jobs assigned to different people. Selected Answer: Division of labor Response Feedback: Division of labor refers to the subdivision of work into separate jobs assigned to different people. Subdivided work leads to job specialization, because each job now includes a narrow subset of the tasks necessary to complete the product or service. • Question 20 2 out of 2 points Organic structures are better suited to , so the organization can adapt more quickly to changes. Selected Answer: dynamic environments Response Feedback: Dynamic environments have a high rate of change, leading to novel situations and a lack of identifiable patterns. Organic structures in which employees are experienced and coordinate well in teams are better suited to dynamic environments, so the organization can adapt more quickly to changes. • Question 21 0 out of 2 points Dionne was just hired to be the manager at the local retail store. One of her first decisions is to create temporary teams. She is using which coordinating mechanism? Selected Answer: standardized processes Response Feedback: Another way that larger organizations encourage coordination through informal communication is by organizing employees from several departments into temporary teams. Temporary cross-functional teams give employees more authority and opportunity to coordinate through informal communication. • Question 22 2 out of 2 points makes worldwide communication much easier, but it will never replace the degree of control organizations have when manufacturing, marketing, and other functions are in- house. Selected Answer: Technology Response Feedback: Information technology makes worldwide communication much easier, but it will never replace the degree of control organizations have when manufacturing, marketing, and other functions are in-house. The core firm can use arm's-length incentives and contract provisions to maintain the subcontractor's quality, but these actions are relatively crude compared with maintaining the quality of work performed by in-house employees. • Question 23 0 out of 2 points A steel manufacturing firm with about 1,000 employees operates in an environment that is simple and integrated (it makes a small number of steel products for a few key customers) but also dynamic and hostile (rapidly changing technology and customer needs with many competitors). Based on the environment in which this company operates, it would be more successful with a(n) structure. Selected Answer: mechanistic Response Feedback: An organic structure would be more successful in a simple, integrated, dynamic, and hostile environment, as in this scenario. Hostile environments are typically dynamic ones because they reduce the predictability of access to resources and demand for outputs. Organic structures tend to be best in hostile environments. • Question 24 0 out of 2 points Where the technology has low variability and high analyzability, a(n) structure is preferred. Selected Answer: simple Response Feedback: A mechanistic structure is preferred where the technology has low variability and high analyzability, such as an assembly line. Assembly work is routine, highly predictable, and with well-established procedures—an ideal situation for a mechanistic structure to operate efficiently. • Question 25 2 out of 2 points A wider span of control is possible if Selected employees manage themselves rather than being coordinated through close Answer: supervision. Response Feedback: A wider span of control is possible where employees manage themselves rather than being coordinated through close supervision. The best-performing manufacturing operations today rely on self-directed teams, so direct supervision (formal hierarchy) is supplemented with other coordinating mechanisms. Saturday, March 30, 2019 12:52:43 PM EDT • Question 1 2 out of 2 points According to studies of task- and people-oriented leadership effectiveness, the best leaders Selected Answer: use both task-oriented and people-oriented behaviors. Response Feedback: Recent evidence suggests that effective leaders rely on both styles, but in different ways. • Question 2 2 out of 2 points Effective leaders have a strong need for socialized power, meaning that they want power as a means to accomplish organizational objectives and similar good deeds. These leaders have Selected Answer: leadership motivation. Response Feedback: Effective leaders are motivated to lead others. They have a strong need for socialized power, meaning that they want power as a means to accomplish organizational objectives and similar good deeds. This is referred to as leadership motivation. • Question 3 It is easier to explain organizational successes and failures in terms of the than by analyzing a complex array of other forces. Selected Answer: leader's ability 0 out of 2 points Response Feedback: There are two basic reasons why people overestimate the leader's influence on organizational outcomes. First, leadership is a useful way for us to simplify life events. It is easier to explain organizational successes and failures in terms of the leader's ability than by analyzing a complex array of other forces. Second, there is a strong tendency in the United States and other Western cultures to believe that life events are generated more by people than by uncontrollable natural forces. This illusion of control is satisfied by believing that events result from the rational actions of leaders. In other words, employees feel better believing that leaders make a difference, so they actively look for evidence that this is so. • Question 4 leadership is the view that leaders serve their followers. Selected Answer: Servant 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Servant leadership is an extension or variation of people-oriented leadership because it defines leadership as serving others. In particular, servant leaders assist others in their need fulfillment, personal development, and growth. Servant leaders ask "How can I help you?" rather than expecting employees to serve them. Servant leaders have been described as selfless, egalitarian, humble, nurturing, empathetic, and ethical coaches. The main objective of servant leadership is to help followers and other stakeholders fulfill their needs and potential, particularly "to become healthier, wiser, freer, more autonomous, more likely themselves to become servants." • Question 5 The personal attribute perspective of leadership indicates leadership Selected Answer: contingency. 0 out of 2 points Response Feedback: The personal attribute perspective of leadership does not necessarily imply that leadership is a talent acquired at birth rather than developed throughout life. On the contrary, personal attributes indicate only leadership potential, not leadership performance. • Question 6 Managerial leaders 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Response Feedback: support and guide the performance and well-being of individual employees. Managerial leaders support and guide the performance and well- being of individual employees and the work unit to support current objectives and practices. • Question 7 2 out of 2 points According to the situational leadership theory developed by Hersey and Blanchard, effective leaders should vary their style with the Selected Answer: ability and motivation of followers. Response Feedback: Hersey and Blanchard's situational leadership model suggests that effective leaders vary their style with the ability and motivation (or commitment) of followers. • Question 8 2 out of 2 points According to the perspective of leadership, leadership is associated with the personal characteristics of the person. Selected Answer: attribute Response Feedback: According to the attribute perspective of leadership, leadership is associated with the personal characteristics of the person. • Question 9 2 out of 2 points One way that followers inflate their perceptions that leaders make a difference is through Selected Answer: attribution error. Response Feedback: One way that followers inflate their perceptions that leaders make a difference is through fundamental attribution error. Research has found that (at least in Western cultures) leaders are given credit or blame for the company's success or failure because employees do not readily see the external forces that also influence these events. Leaders reinforce this belief by taking credit for organizational successes. • Question 10 In order for shared leadership to work, the leader needs to be willing to Selected Answer: delegate work. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Shared leadership flourishes in organizations where the formal leaders are willing to delegate power and encourage employees to take initiative and risks without fear of failure (i.e., a learning orientation culture). Shared leadership also calls for a collaborative rather than internally competitive culture because employees take on shared leadership roles when coworkers support them for their initiative. Furthermore, shared leadership lacks formal authority, so it operates best when employees learn to influence others through their enthusiasm, logical analysis, and involvement of coworkers in their idea or vision. • Question 11 Which of the following leadership approaches directly support the idea that the "romance of leadership" is important in leadership? Selected Answer: implicit leadership perspective 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: According to the implicit leadership perspective, along with relying on implicit prototypes of effective leaders, followers tend to distort their perceptions of the influence that leaders have on the environment. This "romance of leadership" effect exists because, in most cultures, people want to believe leaders make a difference. • Question 12 2 out of 2 points A problem associated with path-goal theory is that Selected Answer: some elements of the theory have not yet been investigated. Response Feedback: Path-goal theory has received more research support than other contingency leadership models, but the evidence is far from complete. Some contingencies and leadership styles in the path-goal leadership model haven't been investigated at all. • Question 13 As organizations grow older, they tend to Selected Answer: become more formalized. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Older companies tend to become more formalized because work activities become routinized, making them easier to document into standardized practices. Larger companies also tend to have more formalization because direct supervision and informal communication among employees do not operate as easily when large numbers of people are involved. • Question 14 2 out of 2 points Organic structures are better suited to , so the organization can adapt more quickly to changes. Selected Answer: dynamic environments Response Feedback: Dynamic environments have a high rate of change, leading to novel situations and a lack of identifiable patterns. Organic structures in which employees are experienced and coordinate well in teams are better suited to dynamic environments, so the organization can adapt more quickly to changes. • Question 15 2 out of 2 points When functional structures are compared with divisionalized structures, functional structures are known to Selected Answer: create better economies of scale. Response Feedback: The functional structure creates specialized pools of talent that typically serve everyone in the organization. This provides more economies of scale than are possible if functional specialists are spread over different parts of the organization. • Question 16 2 out of 2 points Communication flows in all directions with little concern for the formal hierarchy in a structure, but this structure is costly to maintain due to the need for ongoing interpersonal skill training. Selected Answer: team-based Response Feedback: Communication flows in all directions with little concern for the formal hierarchy in a team-based structure. A cross-functional team structure improves communication and cooperation across traditional boundaries. Team-based structures have low formalization because teams are given relatively few rules about how to organize their work. • Question 17 0 out of 2 points Where the technology has low variability and high analyzability, a(n) structure is preferred. Selected Answer: organic Response Feedback: A mechanistic structure is preferred where the technology has low variability and high analyzability, such as an assembly line. Assembly work is routine, highly predictable, and with well-established procedures—an ideal situation for a mechanistic structure to operate efficiently. • Question 18 Scenario B 2 out of 2 points Food4U, a wholesale grocery business, operates in one city and provides one service—stocking retailers with fresh produce. The company wants to ensure that employees develop expertise in their skill specialization and that these specializations are used efficiently. A potential problem with Food4U's form of structure is Selected Answer: higher dysfunctional conflict. Response Feedback: Compared with other structures, the functional structure usually produces higher dysfunctional conflict and poorer coordination in serving clients or developing products. • Question 19 Creative Advertising Corp. wants its 100 employees to work together around specific clients yet maintain an equal emphasis on alignment with their skill 2 out of 2 points specializations (advertising, graphics, copywriting, and public relations). Which of the following organizational structures would work best for Creative Advertising Corp.? Selected Answer: matrix structure that overlays project teams with a functional structure Response Feedback: Under the given circumstances, a matrix structure that overlays project teams with a functional structure would work best for Creative Advertising Corp. This matrix structure focuses employees on the final product yet keeps them organized around their expertise to encourage knowledge sharing. • Question 20 An organic structure has Selected Answer: little formalization. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Organic structures operate with a wide span of control, decentralized decision making, and little formalization. Tasks are fluid, adjusting to new situations and organizational needs. • Question 21 Many of the best-performing production plants are able to widen their span of control to more than 70 employees per supervisor by Selected Answer: relying on self-directed work teams and other coordinating mechanisms. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: The best-performing manufacturing operations today rely on self- directed teams, so direct supervision (formal hierarchy) is supplemented with other coordinating mechanisms. Self-directed teams coordinate mainly through informal communication and specialized knowledge, so formal hierarchy plays a minor role. • Question 22 2 out of 2 points The local county government is flattening its hierarchy to address a budget crisis. As a result, they must Selected Answer: widen the span of control. Response Feedback: A company with a wider span of control necessarily as more employees per supervisor, more supervisors for each middle manager, and so on. This large number of direct reports compared to a company with a narrower span of control is possible only by removing layers of management. Taller structures have higher overhead costs. With more managers per employee, tall hierarchies necessarily have more people administering the company, thereby reducing the percentage of staff who are actually making the product or providing the service. • Question 23 2 out of 2 points A potential disadvantage of structures is that they expose the core firm to market forces. Selected Answer: network Response Feedback: A potential disadvantage of network structures is that they expose the core firm to market forces. Other companies may bid up the price for subcontractors, whereas the short-term cost would be lower if the company hired its own employees to perform the same function. • Question 24 Formalization in organizational structures tends to Selected Answer: reduce organizational flexibility. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Formalization may increase efficiency and compliance, but it can also create problems. Rules and procedures reduce organizational flexibility, so employees follow prescribed behaviors even when the situation clearly calls for a customized response. • Question 25 Scenario C 0 out of 2 points ABC Production, a consumer products firm with a functional structure, is expanding from a single product line into several diverse product groups, with most sales within one country. A potential benefit with ABC's form of structure is Selected Answer: being flexible and responsive in a turbulent environment. Response Feedback: The divisional organizational structure is a building-block structure; it accommodates growth relatively easily. As the company develops new products, services, or clients, it can sprout new divisions. The divisional structure is also outcome-focused. It directs employee attention to customers and products, rather than to their own specialized knowledge. User Lauren McWilliams Course 201840 Fall 2018 BUSI 240-B19 LUO Test Quiz 7 Started 10/11/18 1:46 PM Submitted 10/11/18 2:36 PM Due Date 10/15/18 11:59 PM Status Completed Attempt Score 36 out of 50 points Time Elapsed 50 minutes out of 50 minutes Instructions Time limit: 50 minutes 25 multiple-choice questions Open-book/open-notes Do not hit the BACK button as this will lock you out of the quiz. The timer will continue if you leave this quiz without submitting it. Results Displayed Submitted Answers, Feedback • Question 1 Which of the following refers to "walking the talk"? 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Response Feedback: The leader steps out and behaves in ways that symbolize the vision. Transformational leaders not only talk about a vision; they enact it. They "walk the talk" by stepping outside the executive suite and doing things that symbolize the vision. • Question 2 Fiedler's contingency model of leadership has made an important and lasting contribution to the study of leadership because it 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Response Feedback: suggests that organizations need to engineer the situation to fit the leader's preferred style. Fiedler's contingency model argues that if leadership style is influenced by a leader's personality, organizations should engineer the situation to fit the leader's dominant style, rather than expecting leaders to change their styles to fit situations. • Question 3 Scenario B 0 out of 2 points Johni is the CEO of a struggling company. She has listened to her employees complaints and concerns about where the corporation is going and has developed a new vision that she feels will help develop a common bond throughout the organization. Johni then hosted a company-wide picnic where she delivered an inspiring speech about the new plans for the business, including her plans for more open communication between management and employees. After her speech, management and employees all participated in trust building exercises, and each employee had a one-on-one conversation with Johni. What is the next step Johni should take if she wants to continue on toward her vision? Selected Answer: Model the vision. Response Feedback: Transforming a vision into reality requires employee commitment, and transformational leaders build this commitment in several ways. Their words, symbols, and stories build a contagious enthusiasm that energizes people to adopt the vision as their own. Leaders demonstrate a "can do" attitude by enacting their vision and staying on course. Their persistence and consistency reflect an image of honesty, trust, and integrity. Finally, leaders build commitment by involving employees in the process of shaping the organization's vision. • Question 4 Transformational leaders 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Response Feedback: energize and direct employees to a new vision and corresponding behaviors. Transformational leaders are change agents who energize and direct employees to a new vision and corresponding behaviors. • Question 5 2 out of 2 points According to 54 leadership experts of 38 countries, there are two key components to leadership. The first is the ability to persuade and influence others; the second is that leaders are Selected Answer: Response Feedback: enablers. Several years ago, 54 leadership experts from 38 countries reached a consensus that leadership is about influencing, motivating, and enabling others to contribute toward the effectiveness and success of the organizations of which they are members. This definition has two key components. First, leaders motivate others through persuasion and other influence tactics. They use their communication skills, rewards, and other resources to energize the collective toward the achievement of challenging objectives. Second, leaders are enablers. They allocate resources, alter work relationships, minimize external disruptions, and establish other work environment changes that make it easier for employees to achieve organizational objectives. • Question 6 0 out of 2 points Which of the following explicitly argues that people have a preferred leadership style based on their personality, so organizations should move leaders into situations that fit their preferred style? Selected Answer: transformational leadership Response Feedback: According to Fiedler's contingency model, leader effectiveness depends on whether the person's natural leadership style is appropriately matched to the situation. It explicitly argues that people have a preferred leadership style based on their personality. • Question 7 2 out of 2 points leadership refers to how well leaders are aware of, feel comfortable with, and act consistently with their self-concepts. Selected Answer: Authentic Response Feedback: Several competencies associated with effective leaders relate to an important characteristic, called authentic leadership. Authentic leadership refers to how well leaders are aware of, feel comfortable with, and act consistently with their self-concepts. • Question 8 2 out of 2 points Effective leaders have strong moral principles, which are demonstrated through truthfulness and consistency of words with deeds demonstrating the attribute of Selected Answer: integrity. Response Feedback: Integrity involves having strong moral principles, which supports the tendency to be truthful and to be consistent in words and deeds. Leaders have a high moral capacity to judge dilemmas using sound values and to act accordingly. Notice that integrity is ultimately based on the leader's values, which provide an anchor for consistency. Several large-scale studies have reported that integrity and honesty are the most important characteristics of effective leaders. • Question 9 Why does the leadership prototype comparison process occur? 0 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Response Feedback: Socialization within the family and society shape the leader's expectations and acceptance of others as followers. Why does this prototype comparison process occur? People want to trust their leader before they are willing to serve as followers, yet the leader's actual effectiveness usually isn't known for several months or possibly years. The prototype comparison process is a quick (although faulty) way of estimating the leader's effectiveness. • Question 10 0 out of 2 points Which of the following leadership styles in path-goal theory is the same as task-oriented leadership? Selected Answer: achievement-oriented Response Feedback: Directive leadership is the same as task-oriented leadership and shows the importance of clear role perceptions in employee performance. • Question 11 How do women differ from men in their use of leadership styles? 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Response Feedback: Women tend to use more of the participative leadership style than do men. Women adopt a participative leadership style more readily than their male counterparts do. One possible reason is that, compared to boys, girls are often raised to be more egalitarian and less status-oriented, which is consistent with being participative. • Question 12 0 out of 2 points Which of the following leadership styles in path-goal theory is the same as people- oriented leadership? Selected Answer: directive Response Feedback: In the supportive style, the leader's behaviors provide psychological support for subordinates. Supportive leadership is the same as people- oriented leadership and reflects the benefits of social support to help employees cope with stressful situations. • Question 13 2 out of 2 points is the degree to which organizations standardize behavior through rules, procedures, formal training, and related mechanisms. Selected Answer: Response Feedback: Formalization Formalization is the degree to which organizations standardize behavior through rules, procedures, formal training, and related mechanisms. In other words, companies become more formalized as they increasingly rely on various forms of standardization to coordinate work. • Question 14 Which of the following is an issue with flatter hierarchies? Selected Answer: A flatter hierarchy's information is manipulated less often. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Unfortunately, building a taller hierarchy (more layers of management) creates problems. One concern is that executives in tall structures tend to receive lower quality and less timely information. People tend to filter, distort, and simplify information before it is passed to higher levels in the hierarchy because they are motivated to frame the information in a positive light or to summarize it more efficiently. In contrast, in flat hierarchies, information is manipulated less and is usually transmitted much more quickly than in tall hierarchies. • Question 15 Scenario B 0 out of 2 points Food4U, a wholesale grocery business, operates in one city and provides one service— stocking retailers with fresh produce. The company wants to ensure that employees develop expertise in their skill specialization and that these specializations are used efficiently. A potential problem with Food4U's form of structure is Selected Answer: inefficient resource utilization. Response Feedback: Compared with other structures, the functional structure usually produces higher dysfunctional conflict and poorer coordination in serving clients or developing products. • Question 16 Coordination of work activities is Selected Answer: required whenever there is division of labor. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: When people divide work among themselves, they require coordinating mechanisms to ensure that everyone works in concert. Coordination is so closely connected to division of labor that the optimal level of specialization is limited by the feasibility of coordinating the work. • Question 17 2 out of 2 points One of the main forces pushing toward a structure is the recognition that an organization has only a few core competencies. Selected Answer: network Response Feedback: One of the main forces pushing toward a network structure is the recognition that an organization has only a few core competencies. A core competency is a knowledge base that resides throughout the organization and provides a strategic advantage. As companies discover their core competency, they outsource noncritical tasks to other organizations that have a core competency at performing those tasks. • Question 18 Scenario C 2 out of 2 points ABC Production, a consumer products firm with a functional structure, is expanding from a single product line into several diverse product groups, with most sales within one country. What form of departmentalization should ABC Production eventually adopt to manage the new conditions most effectively? Selected Answer: divisional product structure Response Feedback: The firm should eventually adopt divisional product structure to manage the new conditions most effectively. The divisional structure groups employees around geographic areas, outputs (products or services), or clients. The product/service divisional structure organizes employees around distinct outputs. • Question 19 2 out of 2 points Structures determine executive power and what should receive priority; the matrix structure works best when the business environment is deserve equal attention and integration. Selected Answer: Response Feedback: complex and two different dimensions Structures determine executive power and what should receive priority; the matrix structure works best when the business environment is complex and two different dimensions deserve equal attention and integration. • Question 20 2 out of 2 points Communication flows in all directions with little concern for the formal hierarchy in a structure, but this structure is costly to maintain due to the need for ongoing interpersonal skill training. Selected Answer: team-based Response Feedback: Communication flows in all directions with little concern for the formal hierarchy in a team-based structure. A cross-functional team structure improves communication and cooperation across traditional boundaries. Team-based structures have low formalization because teams are given relatively few rules about how to organize their work. • Question 21 Scenario C 0 out of 2 points ABC Production, a consumer products firm with a functional structure, is expanding from a single product line into several diverse product groups, with most sales within one country. A potential benefit with ABC's form of structure is Selected Answer: being flexible and responsive in a turbulent environment. Response Feedback: The divisional organizational structure is a building-block structure; it accommodates growth relatively easily. As the company develops new products, services, or clients, it can sprout new divisions. The divisional structure is also outcome-focused. It directs employee attention to customers and products, rather than to their own specialized knowledge. • Question 22 2 out of 2 points A potential disadvantage of structures is that they expose the core firm to market forces. Selected Answer: network Response Feedback: A potential disadvantage of network structures is that they expose the core firm to market forces. Other companies may bid up the price for subcontractors, whereas the short-term cost would be lower if the company hired its own employees to perform the same function. • Question 23 2 out of 2 points A wholesale florist operates in one state and provides one service—floral design for delivery. The company's aim is to create specialized pools of talent. Which of the following forms of departmentalization would be most appropriate here? Selected Answer: Response Feedback: functional structure The functional structure creates specialized pools of talent that typically serve everyone in the organization. Pooling talent into one group improves economies of scale compared to dispersing functional specialists over different parts of the organization. The functional structure also increases employee identity with the specialization or profession. Direct supervision is easier in a functional structure because managers oversee people with common issues and expertise. • Question 24 Executives who have worked in a global matrix say they have Selected Answer: more freedom. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Executives who have worked in a global matrix say they have more freedom, likely because their two bosses are more advisory and less command and control focused. • Question 25 2 out of 2 points Which of the following is one of the common pure types of departmentalization? Selected Answer: Response Feedback: matrix There are almost as many organizational charts as there are businesses, but the six most common pure types of departmentalization are simple, functional, divisional, team-based, matrix, and network. Thursday, October 11, 2018 2:36:20 PM EDT • Question 1 Which of the following is a limitation of the personal attribute perspective of leadership? Selected Answer: It views leadership as something within a person. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: The personal attribute perspective views leadership as something within a person, yet experts emphasize that leadership is relational. This is a drawback of the competency perspective of leadership. • Question 2 2 out of 2 points According to the perspective of leadership, leadership is associated with the personal characteristics of the person. Selected Answer: attribute Response Feedback: According to the attribute perspective of leadership, leadership is associated with the personal characteristics of the person. • Question 3 0 out of 2 points Which of the following characteristics addresses leaders' high need for achievement? Selected Answer: self-confidence Response Feedback: Drive refers to the leader's inner motivation to pursue goals. It is related to a leader's high conscientiousness and positive self-concept. It is also associated with high need for achievement. • Question 4 The attribute perspective of leadership identifies drive, integrity, and emotional intelligence as the Selected Answer: attributes of effective leaders. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Drive, integrity, and emotional intelligence are identified by the attribute perspective of leadership as the competencies of effective leaders. • Question 5 The personal attribute perspective of leadership indicates leadership Selected Answer: contingency. 0 out of 2 points Response Feedback: The personal attribute perspective of leadership does not necessarily imply that leadership is a talent acquired at birth rather than developed throughout life. On the contrary, personal attributes indicate only leadership potential, not leadership performance. • Question 6 2 out of 2 points Some research suggests that effective leaders help team members learn to lead themselves through Selected Answer: leadership substitutes. Response Feedback: Some research suggests that effective leaders help team members learn to lead themselves through leadership substitutes; in other words, coworkers substitute for leadership in high-involvement team structures. Coworkers instruct new employees, thereby providing directive leadership. They also provide social support, which reduces stress among fellow employees. Teams with norms that support organizational goals may substitute for achievement-oriented leadership, because employees encourage (or pressure) coworkers to stretch their performance levels. • Question 7 Managerial leaders 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Response Feedback: support and guide the performance and well-being of individual employees. Managerial leaders support and guide the performance and well-being of individual employees and the work unit to support current objectives and practices. • Question 8 2 out of 2 points According to Exhibit 12.4, which one of the following is not a leadership attribute? Selected Answer: authenticity Response Feedback: According to Exhibit 12.4, extroverted personality, self-concept, drive, integrity, leadership motivation, knowledge of the business, cognitive and practical intelligence, and emotional intelligence are the attributes of effective leaders. • Question 9 The concept of leadership prototypes is an important component of Selected Answer: implicit leadership theory. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: One aspect of implicit leadership theory states that everyone has leadership prototypes—preconceived beliefs about the features and behaviors of effective leaders. • Question 10 Scenario B 2 out of 2 points Johni is the CEO of a struggling company. She has listened to her employees complaints and concerns about where the corporation is going and has developed a new vision that she feels will help develop a common bond throughout the organization. Johni then hosted a company-wide picnic where she delivered an inspiring speech about the new plans for the business, including her plans for more open communication between management and employees. After her speech, management and employees all participated in trust building exercises, and each employee had a one-on-one conversation with Johni. Which of the following is a pitfall that Johni needs to avoid, since she is full of charisma? Selected Answer: Response Feedback: Leaders who possess the gift of charisma may become intoxicated by this power, which leads to a greater focus on self-interest than on the common good. Being charismatic is not inherently good or bad, but several research studies have concluded that charismatic leadership can produce negative consequences. One concern is that charismatic leadership tends to produce dependent followers. Transformational leadership has the opposite effect—it builds follower empowerment, which tends to reduce dependence on the leader. Another concern is that leaders who possess the gift of charisma may become intoxicated by this power, which leads to a greater focus on self-interest than on the common good. • Question 11 Scenario D 0 out of 2 points MoneySafe, a financial services organization, trains employees to new skills and uses coworkers to train new employees, while providing social support in the form of daycare facilities. MoneySafe management believes that using this system will help replace or reduce the need to micromanage by assigning and clarifying work responsibilities, setting goals and deadlines for employees, and establishing well- defined work procedures. Instead of focusing on rewards, MoneySafe could encourage employees to reach their peak performance by emphasizing behaviors. Selected Answer: task-oriented Response Feedback: Achievement-oriented leadership style emphasizes behaviors that encourage employees to reach their peak performance. The leader sets challenging goals, expects employees to perform at their highest level, continuously seeks improvement in employee performance, and shows a high degree of confidence that employees will assume responsibility and accomplish challenging goals. Achievement-oriented leadership applies goal-setting theory as well as positive expectations in self- fulfilling prophecy. • Question 12 Which of the following leadership approaches directly support the idea that the "romance of leadership" is important in leadership? Selected Answer: implicit leadership perspective 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: According to the implicit leadership perspective, along with relying on implicit prototypes of effective leaders, followers tend to distort their perceptions of the influence that leaders have on the environment. This "romance of leadership" effect exists because, in most cultures, people want to believe leaders make a difference. • Question 13 Coordination of work activities is Selected Answer: required whenever there is division of labor. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: When people divide work among themselves, they require coordinating mechanisms to ensure that everyone works in concert. Coordination is so closely connected to division of labor that the optimal level of specialization is limited by the feasibility of coordinating the work. • Question 14 2 out of 2 points A(n) structure should be introduced where employees perform tasks with high variability and low analyzability. Selected Answer: organic Response Feedback: An organic, rather than a mechanistic, structure should be introduced where employees perform tasks with high variability and low analyzability, such as in a research setting. The reason is that employees face unique situations with little opportunity for repetition. • Question 15 Which one of the following is a limitation of the divisional structure? Selected Answer: The divisional structure tends to duplicate resources. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: The divisional structure tends to duplicate resources, such as production equipment and engineering or information technology expertise. Also, unless the division is quite large, resources are not used as efficiently as they are in functional structures, where resources are pooled across the entire organization. The divisional structure also creates silos of knowledge. Expertise is spread across several autonomous business units, which reduces the ability and perhaps motivation of the people in one division to share their knowledge with counterparts in other divisions. In contrast, a functional structure groups experts together, thereby supporting knowledge sharing. Finally, the preferred divisional structure depends on the company's primary source of environmental diversity or uncertainty. • Question 16 2 out of 2 points means that formal decision-making authority is held by a small group of people. Selected Answer: Centralization Response Feedback: Centralization means that formal decision-making authority is held by a small group of people, typically those at the top of the organizational hierarchy. Most organizations begin with centralized structures, because the founder makes most of the decisions and tries to direct the business toward his or her vision. • Question 17 Organizational size, technology, and environment are Selected Answer: the three dimensions of span of control. 0 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Most organizational behavior theories and concepts have contingencies; ideas that work well in one situation might not work as well in another situation. This contingency approach is certainly relevant when choosing the most appropriate organizational structure. The four contingencies of organizational design are external environment, size, technology, and strategy. • Question 18 Scenario B 2 out of 2 points Food4U, a wholesale grocery business, operates in one city and provides one service—stocking retailers with fresh produce. The company wants to ensure that employees develop expertise in their skill specialization and that these specializations are used efficiently. What form of departmentalization would be most appropriate here? Selected Answer: functional structure Response Feedback: A functional structure would be appropriate under the given circumstances. A functional structure organizes employees around specific knowledge or other resources. The functional structure creates specialized pools of talent that typically serve everyone in the organization. • Question 19 Coordination though formal hierarchy relies on Selected Answer: informal communication. 0 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Hierarchy assigns legitimate power to individuals, who then use this power to direct work processes and allocate resources. In other words, work is coordinated through direct supervision—the chain of command. A century ago, management scholars applauded the formal hierarchy as the best coordinating mechanism for large organizations. They argued that organizations are most effective when managers exercise their authority and employees receive orders from only one supervisor. The chain of command—in which formal communication and information flow across work units only through supervisors and managers—was viewed as the backbone of organizational strength. • Question 20 2 out of 2 points Which of the following is one of the common pure types of departmentalization? Selected Answer: matrix Response Feedback: There are almost as many organizational charts as there are businesses, but the six most common pure types of departmentalization are simple, functional, divisional, team-based, matrix, and network. • Question 21 Dividing work into more specialized jobs 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: gives an opportunity to the job incumbents to master their tasks quickly. Response Feedback: Dividing work into more specialized jobs gives an opportunity to the job incumbents to master their tasks quickly. Less time is wasted changing from one task to another. Training costs are reduced because employees require fewer physical and mental skills to accomplish the assigned work. • Question 22 2 out of 2 points refers to the subdivision of work into separate jobs assigned to different people. Selected Answer: Division of labor Response Feedback: Division of labor refers to the subdivision of work into separate jobs assigned to different people. Subdivided work leads to job specialization, because each job now includes a narrow subset of the tasks necessary to complete the product or service. • Question 23 Scenario A 2 out of 2 points Tammy recently earned her degree in nursing and has begun a career path in the surgical ward at a local hospital. Her training program consists of a year-long internship, working with senior nurses. While in school, Tammy worked in a medical lab performing routine blood tests. The lab technician job required her to take a two- week course and refer to a procedures manual for her work on a daily basis. On the hospital floor, the senior nurse has set targets for each nurse with regard to how many patients are to be seen and how many charts are to be coded. This is an example of Selected Answer: standardized outputs. Response Feedback: Standardized output involves ensuring that individuals and work units have clearly defined goals and output measures (e.g., customer satisfaction, production efficiency). For instance, to coordinate the work of salespeople, companies assign sales targets rather than specific behaviors. • Question 24 A wider span of control is possible if 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Response Feedback: employees manage themselves rather than being coordinated through close supervision. A wider span of control is possible where employees manage themselves rather than being coordinated through close supervision. The best-performing manufacturing operations today rely on self- directed teams, so direct supervision (formal hierarchy) is supplemented with other coordinating mechanisms. • Question 25 2 out of 2 points is the degree to which organizations standardize behavior through rules, procedures, formal training, and related mechanisms. Selected Answer: Formalization Response Feedback: Formalization is the degree to which organizations standardize behavior through rules, procedures, formal training, and related mechanisms. In other words, companies become more formalized as they increasingly rely on various forms of standardization to coordinate work. Leaders have a superior ability to analyze a variety of complex alternatives and opportunities due to their Selected Answer: practical intelligence. Response Feedback: Leaders have above-average cognitive ability to process enormous amounts of information. Leaders aren't necessarily geniuses; rather, they have a superior ability to analyze a variety of complex alternatives and opportunities. Furthermore, leaders have practical intelligence. This means that they can think through the relevance and application of ideas in real-world settings. Practical intelligence is particularly evident where problems are poorly defined, information is missing, and more than one solution may be plausible. • Question 2 Fiedler's contingency model of leadership has made an important and lasting contribution to the study of leadership because it 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Response Feedback: suggests that organizations need to engineer the situation to fit the leader's preferred style. Fiedler's contingency model argues that if leadership style is influenced by a leader's personality, organizations should engineer the situation to fit the leader's dominant style, rather than expecting leaders to change their styles to fit situations. • Question 3 2 out of 2 points Effective transformational leaders generate meaning and motivation in followers by relying on Selected Answer: metaphors. Response Feedback: Effective transformational leaders generate meaning and motivation in followers by relying on symbols, metaphors, stories, and other vehicles that transcend plain language. These tools borrow images from other experiences, thereby creating richer meaning of the not-yet-experienced vision. Borrowing from existing experiences also generates desired emotions, which motivates people to pursue the vision. For instance, when McDonald's faced the daunting challenge of opening the company's first restaurants in Russia (back when it was the USSR), CEO George Cohen frequently reminded his team members that they were establishing "hamburger diplomacy." • Question 4 Scenario B 2 out of 2 points Johni is the CEO of a struggling company. She has listened to her employees complaints and concerns about where the corporation is going and has developed a new vision that she feels will help develop a common bond throughout the organization. Johni then hosted a company-wide picnic where she delivered an inspiring speech about the new plans for the business, including her plans for more open communication between management and employees. After her speech, management and employees all participated in trust building exercises, and each employee had a one-on-one conversation with Johni. What is the next step Johni should take if she wants to continue on toward her vision? Selected Answer: Build commitment toward the vision. Response Feedback: Transforming a vision into reality requires employee commitment, and transformational leaders build this commitment in several ways. Their words, symbols, and stories build a contagious enthusiasm that energizes people to adopt the vision as their own. Leaders demonstrate a "can do" attitude by enacting their vision and staying on course. Their persistence and consistency reflect an image of honesty, trust, and integrity. Finally, leaders build commitment by involving employees in the process of shaping the organization's vision. • Question 5 0 out of 2 points Which of the following leadership styles in path-goal theory is the same as people- oriented leadership? Selected Answer: directive Response Feedback: In the supportive style, the leader's behaviors provide psychological support for subordinates. Supportive leadership is the same as people- oriented leadership and reflects the benefits of social support to help employees cope with stressful situations. • Question 6 Scenario C 2 out of 2 points Gina and Chen are both managers at CPA4U, a large accounting firm. Each has a very different management style. Gina is very outgoing and constantly checking on her subordinates to see if there is any way she can help them to complete their projects. She also brings in fresh flowers for the lunchroom weekly and always remembers everyone's birthday. Chen is much more introverted and communicates with his subordinates mainly through email, and he has his subordinates submit daily reports on their progress toward the weekly goals he has assigned them. Which type of leader is Gina? Selected Answer: servant leader Response Feedback: Servant leadership is an extension or variation of the people-oriented leadership style because it defines leadership as serving others toward their need fulfillment and personal development and growth. Servant leaders ask, "How can I help you?" rather than expect employees to serve them. People who epitomize servant leadership have been described as selfless, egalitarian, humble, nurturing, empathetic, and ethical coaches. • Question 7 0 out of 2 points It is easier to explain organizational successes and failures in terms of the than by analyzing a complex array of other forces. Selected Answer: leader's ability Response Feedback: There are two basic reasons why people overestimate the leader's influence on organizational outcomes. First, leadership is a useful way for us to simplify life events. It is easier to explain organizational successes and failures in terms of the leader's ability than by analyzing a complex array of other forces. Second, there is a strong tendency in the United States and other Western cultures to believe that life events are generated more by people than by uncontrollable natural forces. This illusion of control is satisfied by believing that events result from the rational actions of leaders. In other words, employees feel better believing that leaders make a difference, so they actively look for evidence that this is so. • Question 8 Which of the following statements is most consistent with the view of shared leadership? 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Response Feedback: Leadership of an organization is broadly distributed rather than assigned to one person. Shared leadership is the view that leadership is broadly distributed rather than assigned to one person, such that people within the team and organization lead each other. • Question 9 2 out of 2 points exists when employees champion the introduction of new technologies and products. Selected Answer: Shared leadership Response Feedback: Shared leadership exists when employees champion the introduction of new technologies and products. It also exists when employees engage in organizational citizenship behaviors to assist the performance and well-being of coworkers and the overall team. • Question 10 An effective vision is Selected Answer: unifying. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Another feature of an effective vision is that it is unifying. It is a superordinate objective that bonds employees together and aligns their personal values with the organization's values. In fact, a successful vision is really a shared vision because employees collectively define themselves by this aspirational image of the future as part of their identification with the organization. • Question 11 2 out of 2 points theory identifies conditions that either limit the leader's ability to influence subordinates or make a particular leadership style unnecessary. Selected Answer: Leadership substitutes Response Feedback: A theory called leadership substitutes identifies conditions that either limit the leader's ability to influence subordinates or make a particular leadership style unnecessary. • Question 12 Which of the following is a leadership style identified in path-goal theory? Selected Answer: achievement-oriented leadership 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: The path-goal theory of leadership specifically highlights four leadership styles. They are directive, supportive, participative, and achievement-oriented. • Question 13 2 out of 2 points Which of the following is one of the common pure types of departmentalization? Selected Answer: matrix Response Feedback: There are almost as many organizational charts as there are businesses, but the six most common pure types of departmentalization are simple, functional, divisional, team-based, matrix, and network. • Question 14 2 out of 2 points Which form of departmentalization tends to have a very flat hierarchy, to have little formalization, and to organize employees around work processes? Selected Answer: team-based structure Response Feedback: A team-based organizational structure is usually organic. There is a wide span of control because teams operate with minimal supervision. Many team-based structures have low formalization because teams are given relatively few rules about how to organize their work. • Question 15 One problem with a functional structure is that 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: it produces higher dysfunctional conflict and poorer coordination. Response Feedback: Compared with other structures, the functional structure usually produces higher dysfunctional conflict and poorer coordination in serving clients or developing products. These problems occur because employees need to work with coworkers in other departments to complete organizational tasks, yet they have different subgoals and mental models of ideal work. • Question 16 2 out of 2 points Many of the best-performing production plants are able to widen their span of control to more than 70 employees per supervisor by Selected Answer: relying on self-directed work teams and other coordinating mechanisms. Response Feedback: The best-performing manufacturing operations today rely on self- directed teams, so direct supervision (formal hierarchy) is supplemented with other coordinating mechanisms. Self-directed teams coordinate mainly through informal communication and specialized knowledge, so formal hierarchy plays a minor role. • Question 17 A divisionalized structure is recommended mainly for environments. Selected Answer: diverse 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Organizations located in diverse environments have a greater variety of products or services, clients, and regions. The more diversified the environment, the more the firm needs to use a divisional structure aligned with that diversity. • Question 18 2 out of 2 points A consumer products firm with a functional structure is expanding from a single product line into several diverse product groups, with most sales within one country. Which of the following should it eventually adopt to manage the new conditions most effectively? Selected Answer: product divisional structure Response Feedback: The firm should eventually adopt a divisional product structure to manage the new conditions most effectively. The divisional structure groups employees around geographic areas, outputs (products or services), or clients. The product/service divisional structure organizes employees around distinct outputs. • Question 19 2 out of 2 points A steel manufacturing firm with about 1,000 employees operates in an environment that is simple and integrated (it makes a small number of steel products for a few key customers) but also dynamic and hostile (rapidly changing technology and customer needs with many competitors). Based on the environment in which this company operates, it would be more successful with a(n) structure. Selected Answer: organic Response Feedback: An organic structure would be more successful in a simple, integrated, dynamic, and hostile environment, as in this scenario. Hostile environments are typically dynamic ones because they reduce the predictability of access to resources and demand for outputs. Organic structures tend to be best in hostile environments. • Question 20 2 out of 2 points Which of the following forms of departmentalization organizes employees around specific skills or other resources? Selected Answer: functional structure Response Feedback: A functional structure organizes employees around specific knowledge or other resources. Employees with marketing expertise are grouped into a marketing unit, those with production skills are located in manufacturing, engineers are found in product development, and so on. • Question 21 2 out of 2 points The structure usually makes very good use of resources and expertise, making it ideal for project-based organizations with fluctuating workloads. Selected Answer: matrix Response Feedback: The project-functional matrix structure usually makes very good use of resources and expertise, making it ideal for project-based organizations with fluctuating workloads. When properly managed, it improves communication efficiency, project flexibility, and innovation, compared to purely functional or divisional designs. It focuses employees on serving clients or creating products, yet keeps people organized around their specialization. The result is that knowledge sharing improves, and human resources are used more efficiently. Matrix structures for global organizations (e.g., product-geographic structures) are also a logical choice when two different dimensions (regions and products) are equally important. • Question 22 Dividing work into more specialized jobs 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: gives an opportunity to the job incumbents to master their tasks quickly. Response Feedback: Dividing work into more specialized jobs gives an opportunity to the job incumbents to master their tasks quickly. Less time is wasted changing from one task to another. Training costs are reduced because employees require fewer physical and mental skills to accomplish the assigned work. • Question 23 In organizational structures, integrator roles serve mainly as Selected Answer: an informal communication coordinating mechanism. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: In organizational structures, integrator roles serve mainly as an informal communication coordinating mechanism. Where coordination is required among several work units, companies create integrator roles. These people are responsible for coordinating a work process by encouraging employees in each work unit to share information and informally coordinate work activities. • Question 24 0 out of 2 points The simple structure usually depends on to coordinate work activities, so it is very difficult to operate as the company grows and becomes more complex. Selected Answer: standardization through formal instructions Response Feedback: Most companies begin with a simple structure. They employ only a few people and typically offer only one distinct product or service. The simple structure usually depends on the owner's direct supervision to coordinate work activities, so it is difficult to operate as the company grows and becomes more complex. • Question 25 Two technological contingencies that influence the best type of organizational structure are Selected Answer: organic and mechanistic. 0 out of 2 points Response Feedback: One technological contingency is variability—the number of exceptions to standard procedure that tend to occur. In work processes with low variability, jobs are routine and follow standard operating procedures. Another contingency is analyzability—the predictability or difficulty of the required work. Sunday, March 1, 2020 5:12:03 PM EST • Question 1 Which of the following is true about organizational culture? 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Response Feedback: The strength of an organization's culture refers to how widely and deeply employees hold the company's dominant values and assumptions. The strength of an organization's culture refers to how widely and deeply employees hold the company's dominant values and assumptions. In a strong organizational culture, most employees across all subunits understand and embrace the dominant values. • Question 2 Ceremonies are Selected Answer: more formal artifacts than rituals. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Ceremonies are more formal artifacts than rituals. Ceremonies are planned activities conducted specifically for the benefit of an audience. • Question 3 Which of the following are the observable indicators of organizational culture? Selected Answer: artifacts 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Artifacts are the observable symbols and signs of an organization's culture, such as the way visitors are greeted, the organization's physical layout, and how employees are rewarded. Artifacts are important because they reinforce an organization's culture. • Question 4 0 out of 2 points Corporate leaders hope will eventually become the organization's culture and guide the organization's decisions and actions. Selected Answer: enacted values Response Feedback: The espoused values are values that corporate leaders hope will eventually become the organization's culture, or at least the values they want others to believe guide the organization's decisions and actions. Espoused values are usually socially desirable, so they present a positive public image. • Question 5 Organizational culture is a(n) Selected Answer: social control mechanism. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Organizational culture is a deeply embedded form of social control that influences employee decisions and behavior. Culture is pervasive and operates nonconsciously. Think of it as an automatic pilot, nonconsciously directing employees so their behavior is consistent with organizational expectations. For this reason, some writers describe organizational culture as a compass that points everyone in the same direction. • Question 6 2 out of 2 points Organizational socialization is best described as a process of , where newcomers try to make sense of and adapt to the company's environment. Selected Answer: learning and adjustment Response Feedback: Organizational socialization is a process of both learning and adjustment. It is a learning process because newcomers try to make sense of the company's physical workplace, social dynamics, and strategic and cultural environment. It is also a process of adjustment, because individuals need to adapt to their new work environment. • Question 7 Scenario B 0 out of 2 points BarkBark Inc. and Happy Toys Ltd. are considering a merger and are unsure whether their two organizations will have a difficult time with clashing cultures. They perform a detailed diagnosis, collecting and analyzing the gathered data about the two merging companies. They identify several overlapping values, which they feel that they can effectively meld into a cohesive new culture. What type of cultural merge would be worst in this situation? Selected Answer: integration Response Feedback: Some acquiring companies apply a deculturation strategy by imposing their culture and business practices on the acquired organization. The acquiring firm strips away artifacts and reward systems that support the old culture. People who cannot adopt the acquiring company's culture often lose their jobs. Deculturation may be necessary when the acquired firm's culture doesn't work, even when employees in the acquired company aren't convinced of this. However, this strategy is difficult to apply effectively because the acquired firm's employees resist the cultural intrusions from the buying firm, thereby delaying or undermining the merger process. • Question 8 A deculturation strategy of merging two corporate cultures should be applied when 0 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Response Feedback: employees at the acquired company willingly embrace the cultural values of the acquiring organization. Employees usually resist organizational change, particularly when they are asked to throw away personal and cultural values. Under these conditions, some acquiring companies apply a deculturation strategy by imposing their culture and business practices on the acquired organization. • Question 9 2 out of 2 points One of the functions of is that it is a spawning ground for emerging values that keep the firm aligned with the needs of customers, suppliers, society, and other stakeholders. Selected Answer: a subculture Response Feedback: One of the functions of subcultures is that they are the spawning grounds for emerging values that keep the firm aligned with the needs of customers, suppliers, society, and other stakeholders. Companies eventually need to replace their dominant values with ones that are more appropriate for the changing environment. • Question 10 During which of the following stages of socialization do people first learn about the organization and job? Selected Answer: preemployment 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Socialization is a continuous process, beginning long before the first day of employment and continuing throughout one's career within the company. • Question 11 What is the significance of artifacts in organizational culture? 2 out of 2 points Selected Answer: Response Feedback: Artifacts represent the directly observable symbols and signs of an organization's culture. Artifacts are the observable symbols and signs of an organization's culture, such as the way visitors are greeted, the organization's physical layout, and how employees are rewarded. Artifacts provide valuable evidence about a company's culture. • Question 12 Which of the following is an artifact? Selected Answer: language 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: There are four broad categories of artifacts: organizational stories and legends, rituals and ceremonies, language, and physical structures and symbols. The language of the workplace speaks volumes about the company's culture. How employees talk to each other, describe customers, express anger, and greet stakeholders are all verbal symbols of cultural values. • Question 13 The four stages of appreciative inquiry, in order, are Selected Answer: discovery, dreaming, designing, and delivering. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: The four stages of appreciative inquiry, in order, are discovery, dreaming, designing, and delivering. • Question 14 2 out of 2 points marketing occurs when information seeded to a few people is transmitted to others through their friendship connections. Selected Answer: Viral Response Feedback: The viral change process adopts principles found in word-of-mouth and viral marketing. Viral and word-of-mouth marketing occur when information seeded to a few people is transmitted to others through their friendship connections. Within organizations, social networks represent the channels through which news and opinions about change initiatives are transmitted. Participants in that network have relatively high trust, so their information and views are more persuasive than when communication occurs through more formal channels of communication. • Question 15 2 out of 2 points Senior executives at a large retail organization want employees to become more customer- friendly. Employees think they are serving customers well enough, and the company is the dominant player in the market. What should the executives do to create an urgency to change in this situation? Selected Answer: Response Feedback: Inform employees about the driving forces in the external environment indicating that the company's dominant position will be threatened unless they become more customer-friendly. The change process begins by ensuring that employees develop urgency for change. This typically occurs by informing employees about competitors, changing consumer trends, impending government regulations, and other driving forces in the external environment. • Question 16 2 out of 2 points Firing people is the least desirable way to change organizations. However, dismissals and other forms of are sometimes necessary when speed is essential and other tactics are ineffective. Selected Answer: coercion Response Feedback: Replacing or threatening to replace staff who will not support the change is an extreme step, but it is fairly common in major organizational transformations. Firing people is the least desirable way to change organizations. However, dismissals and other forms of coercion are sometimes necessary when speed is essential and other tactics are ineffective. • Question 17 Increasing the restraining forces and reducing or removing the driving forces would Selected Answer: make the change process more difficult to implement. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Unfreezing occurs when the driving forces are stronger than the restraining forces. This happens by making the driving forces stronger, weakening or removing the restraining forces, or combining both. Increasing the restraining forces and reducing or removing the driving forces would make the change process difficult. • Question 18 2 out of 2 points People typically resist initiatives that force them to and require them to learn new role patterns. Selected Answer: break routines Response Feedback: People are creatures of habit. They typically resist initiatives that force them to break those automated routines and require them to learn new role patterns. Unless the new patterns of behavior are strongly supported and reinforced, employees tend to revert to their past routines and habits. • Question 19 2 out of 2 points One problem that communication, learning, and employee involvement have in minimizing resistance to change is that they Selected Answer: are time-consuming. Response Feedback: Communication, learning, and employee involvement are all time- consuming. • Question 20 Cross-cultural changes occur in all of the following ways except Selected Answer: a linear fashion. 0 out of 2 points Response Feedback: One possible cross-cultural limitation is that Western organizational change models, such as Lewin's force field analysis, often assume that change has a beginning and an ending in a logical linear sequence (i.e., a straight line from point A to point B). Yet change is viewed more as a cyclical phenomenon in some cultures, such as the earth's revolution around the sun or a pendulum swinging back and forth. Other cultures have more of an interconnected view of change, whereby one change leads to another (often unplanned) change, which leads to another change, and so on, until the change objective is ultimately achieved in a more circuitous way. • Question 21 Employee involvement is almost an essential part of the change process unless the Selected Answer: change must occur quickly in the organization. 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Unless the change must occur quickly or employee interests are highly incompatible with the organization's needs, employee involvement is almost an essential part of the change process. • Question 22 2 out of 2 points is a human-centered, solution-focused creative process that applies both intuition and analytical thinking to clarify problems and generate innovative solutions. Selected Answer: Design thinking Response Feedback: Design thinking is a human-centered, solution-focused creative process that applies both intuition and analytical thinking to clarify problems and generate innovative solutions. This approach is neither easy nor comfortable for most businesspeople. • Question 23 0 out of 2 points Which organizational change approach is best known for its affirmation rather than problem- solving approach to change? Selected Answer: action research Response Feedback: Appreciative inquiry is deeply grounded in the philosophy of positive organizational behavior, which suggests that focusing on the positive rather than the negative aspects of life will improve organizational success and individual well-being. • Question 24 occurs when employees resist change because they believe the new work environment will have high probability of negative outcomes. Selected Answer: Negative valence of change 2 out of 2 points Response Feedback: Employees tend to resist change when they believe the new work environment will have more negative than positive outcomes, particularly when the negative outcomes have a high probability of occurring and the positive outcomes have a low probability of occurring. In other words, they apply (although imperfectly) the rational choice decision-making model to estimate whether the change will make them better or worse off. This cost–benefit analysis mainly considers personal outcomes. However, resistance also increases when employees believe the change will do more harm than good to the team, organization, or society. • Question 25 Scenario C 2 out of 2 points BusCorp wants to introduce a new procedure to improve how customer requests are handled. This change will require employees to break old routines and adopt new role patterns. They decide to adopt two new programs. One asks the employees to learn how to work as teams as the company changes. The other involves forming task forces within the company to help determine new customer service practices. In Scenario C, BusCorp is using to minimize resistance to change. Selected Answer: learning Response Feedback: Learning is an important process in most change initiatives because employees require new knowledge and skills to fit the organization's evolving requirements. Training is time-consuming, but it helps people break routines by learning new role patterns. • Question 1 2 out of 2 points What has the most powerful effect on strengthening or reshaping an organization's culture? Selected Answer: rewards Response Feedback: Reward systems and informal recognition practices are artifacts, but they deserve separate discussion because of their powerful effect on strengthening or reshaping an organization's culture. • Question 2 2 out of 2 points One advantage of countercultures is that they Selected Answer: Response Feedback: maintain surveillance over and critically review the company's dominant culture. Countercultures maintain the organization's standards of performance and ethical behavior. Employees who hold countercultural values are an important source of surveillance and critical review of the dominant order. • Question 3 2 out of 2 points Which strategy for merging two distinct cultures is most effective when the two companies have relatively weak cultures with overlapping values? Selected Answer: integration Response Feedback: Integration should be considered when the companies have relatively weak cultures or when their cultures include several overlapping values. Integration also works best when people realize that their existing cultures are ineffective and therefore are motivated to adopt a new set of dominant values. • Question 4 2 out of 2 points Which of the following are the observable indicators of organizational culture? Selected Answer: artifacts Response Feedback: Artifacts are the observable symbols and signs of an organization's culture, such as the way visitors are greeted, the organization's physical layout, and how employees are rewarded. Artifacts are important because they reinforce an organization's culture. • Question 5 2 out of 2 points Organizations with an adaptive corporate culture Selected Answer: have employees who see things from an open systems perspective. Response Feedback: Organizations with an adaptive culture assume that their future depends on monitoring the external environment and serving stakeholders with the resources available. Thus, employees in adaptive cultures see things from an open systems perspective. They take responsibility for the organization's performance and alignment with the external environment. • Question 6 2 out of 2 points Scenario C Reagan is a new HR manager for a large company. She is concerned about the number of employees leaving the company and the lack of job applicants. She begins with a review of the company's policies and then a look at the culture. She talks with long-time employees to learn the stories and the rituals. After listening and researching, Reagan now knows why people are leaving. She has found that is the cause. Selected Answer: attrition Response Feedback: In attrition, people are motivated to seek environments that are sufficiently congruent with their personal values and to leave environments that are a poor fit. This occurs because person–organization values congruence supports their social identity and minimizes internal role conflict. Even if employees aren't forced out, many quit when values incongruence is sufficiently high. • Question 7 2 out of 2 points Wells Fargo is now under investigation for its cultural practices. Rewards were given based on meeting account quotas. This practice caused employees to behave Selected Answer: unethically. Response Feedback: An organization's culture influences the ethical conduct of its employees. This makes sense because good behavior is driven by ethical values, and ethical values become embedded in an organization's dominant culture. The opposite is equally true. There are numerous instances where an organization's culture has caused unethical conduct. • Question 8 2 out of 2 points Reality shock is Selected Answer: a perceived discrepancy between employee expectations and reality. Response Feedback: Reality shock is the stress that results when employees perceive discrepancies between their preemployment expectations and on-the-job reality. • Question 9 2 out of 2 points Which one of the following is true about strong cultures? Selected Answer: They have a stable workforce. Response Feedback: An organization's culture is embedded in the minds of its employees. Organizational stories are rarely written down; rituals and ceremonies do not usually exist in procedure manuals; organizational metaphors are not found in corporate directories. Thus, a strong culture depends on a stable workforce. Workforce stability is also important because it takes time for employees to fully understand the organization's culture and how to enact it in their daily work lives. The organization's culture can literally disintegrate during periods of high turnover and precipitous downsizing because the corporate memory leaves with these employees. • Question 10 2 out of 2 points In which strategy does the acquiring company impose its culture and business practices on the acquired organization? Selected Answer: deculturation Response Feedback: Employees usually resist organizational change, particularly when they are asked to throw away personal and cultural values. Under these conditions, some acquiring companies apply a deculturation strategy by imposing their culture and business practices on the acquired organization. • Question 11 2 out of 2 points Many employees experience a reality shock on their first day at work because Selected Answer: Response Feedback: newcomers test how well their preemployment expectations fit reality, and many companies fail this test. The first day on the job typically marks the beginning of the encounter stage of organizational socialization. This is the stage in which newcomers test how well their preemployment expectations fit reality. Many companies fail the test, resulting in reality shock—the stress that results when employees perceive discrepancies between their preemployment expectations and on-the- job reality. • Question 12 2 out of 2 points When merging cultures, it is best to Selected Answer: take time to be sure it is a cultural fit. Response Feedback: The cultural fit is just as important or maybe more important than the financial side because if the culture doesn't fit, the financial side will never work. • Question 13 2 out of 2 points Scenario B The chief executive of Telecommco, a large telecommunications company, wanted to restructure the organization so product leaders would have more power than the executives in charge of each region. The regional executives tried to prevent this restructuring because it would weaken their power and possibly reduce their salaries in the long term. The product leaders also put up some resistance because they felt that things worked the way they were. The resistance from the product leaders is an example of resistance due to Selected Answer: breaking routines. Response Feedback: Breaking routines occurs when people resist initiatives that force them out of their comfort zones and require them to invest time and energy in learning new role patterns. Indeed, most employees in one survey admitted they don't follow through with organizational changes because they "like to keep things the way they are" or the changes seem to be too complicated or time wasting. • Question 14 2 out of 2 points Which of these forces is commonly called resistance to change? Selected Answer: restraining forces Response Feedback: The restraining forces in Lewin's model help to maintain the status quo. These restraining forces are commonly called "resistance to change" because they appear to block the change process. • Question 15 2 out of 2 points Which model of organizational change explicitly refers to unfreezing the current situation and refreezing the desired state? Selected Answer: force field analysis Response Feedback: Lewin's force field analysis model emphasizes that effective change occurs by unfreezing the current situation, moving to a desired condition, and then refreezing the system so it remains in the desired state. • Question 16 2 out of 2 points Which organizational change is mostly compliance with, rather than commitment to, the change effort? Selected Answer: negotiation Response Feedback: As long as people resist change, organizational change strategies will require a variety of influence tactics. Negotiation is a form of influence that involves the promise of benefits or resources in exchange for the target person's compliance with the influencer's request. This strategy potentially gains support from those who would otherwise lose out from the change. However, this support is mostly compliance with, rather than commitment to, the change effort, so negotiation might not be effective in the long term. • Question 17 2 out of 2 points Scenario B The chief executive of Telecommco, a large telecommunications company, wanted to restructure the organization so product leaders would have more power than the executives in charge of each region. The regional executives tried to prevent this restructuring because it would weaken their power and possibly reduce their salaries in the long term. The product leaders also put up some resistance because they felt that things worked the way they were. This action by the regional executives is mainly an example of resistance due to Selected Answer: negative valence of change. Response Feedback: People tend to oppose changes that they believe will put them in a worse situation, because they represent outcomes with a negative valence of change (such as a long-term salary reduction) as given in the scenario. • Question 18 2 out of 2 points leaders are agents of change because they develop an appealing vision of the desired future state, communicate that vision in ways that are meaningful to others, make decisions and act in ways that are consistent with that vision, and build commitment to that vision. Selected Answer: Transformational Response Feedback: Transformational leaders are agents of change because they develop an appealing vision of the desired future state, communicate that vision in ways that are meaningful to others, make decisions and act in ways that are consistent with that vision, and build commitment to that vision. • Question 19 0 out of 2 points By creating , employee involvement reduces the fear of the unknown and the not- invented-here syndrome. Selected Answer: a goal Response Feedback: Employees who participate in decisions about a change tend to feel more personal responsibility for its successful implementation. This sense of ownership also minimizes the not-invented-here syndrome and fear of the unknown. • Question 20 2 out of 2 points Action research usually assumes that the change agent originates outside the system, so the process begins by Selected Answer: forming the client-consultant relationship. Response Feedback: Action research usually assumes that the change agent originates outside the system (such as a consultant), so the process begins by forming the client- consultant relationship. Consultants need to determine the client's readiness for change, including whether people are motivated to participate in the process, are open to meaningful change, and possess the abilities to complete the process. • Question 21 0 out of 2 points Scenario D Trendy Fashions, a large retail chain, is experiencing conflict and organizational politics among its managers. The company's customer service ratings are suffering, and managers are pointing to other departments as the cause of the problem. The conflicts and politics are further contributing to the customer service problems. The CEO of this chain has just heard about the appreciative inquiry process and thinks this might be a good technique to use to improve this situation. He needs more information on this process. The CEO will need to know that the first step in his appreciative inquiry change effort will begin with: Selected Answer: determining whether there exists a problem that needs to be fixed. Response Feedback: Appreciative inquiry begins with discovery, identifying the positive elements of the observed events or organization. • Question 22 2 out of 2 points The principle takes the position that conversations don't describe reality; they shape that reality. Selected Answer: constructionist Response Feedback: The constructionist principle takes the position that conversations don't describe reality; they shape that reality. • Question 23 2 out of 2 points Employees in successful companies embrace as an integral part of organizational life. Selected Answer: change Response Feedback: Successful organizations monitor their environments and take appropriate steps to maintain a compatible fit with new external conditions. Rather than resisting change, employees in successful companies embrace change as an integral part of organizational life. • Question 24 2 out of 2 points Scenario D Trendy Fashions, a large retail chain, is experiencing conflict and organizational politics among its managers. The company's customer service ratings are suffering, and managers are pointing to other departments as the cause of the problem. The conflicts and politics are further contributing to the customer service problems. The CEO of this chain has just heard about the appreciative inquiry process and thinks this might be a good technique to use to improve this situation. He needs more information on this process. The CEO of Trendy Fashions should know that the four stages of appreciative inquiry, in order, are Selected Answer: discovery, dreaming, designing, and delivering. Response Feedback: The four stages of appreciative inquiry, in order, are discovery, dreaming, designing, and delivering. • Question 25 2 out of 2 points Increasing the driving forces and reducing the restraining forces tends to Selected Answer: unfreeze the status quo. Response Feedback: Unfreezing may occur by increasing the driving forces, reducing the restraining forces, or having a combination of both. • Question 1 2 out of 2 points Which of these statements about shared assumptions is true? Selected Answer: Response Feedback: They are so deeply embedded they probably cannot be discovered by surveying employees. Shared assumptions are nonconscious, taken-for-granted perceptions or ideal prototypes of behavior that are considered the correct way to think and act toward problems and opportunities. Shared assumptions are so deeply ingrained that you probably wouldn't discover them by surveying employees. The Target motto, "Expect more, pay less," is an example of Selected Answer: organizational language. Response Feedback: The language of the workplace speaks volumes about the company's culture. How employees talk to each other, describe customers, express anger, and greet stakeholders are all verbal symbols of shared values and assumptions. Which one of the following is true about strong cultures? Selected Answer: They have a stable workforce. Response Feedback: An organization's culture is embedded in the minds of its employees. Organizational stories are rarely written down; rituals and ceremonies do not usually exist in procedure manuals; organizational metaphors are not found in corporate directories. Thus, a strong culture depends on a stable workforce. Workforce stability is also important because it takes time for employees to fully understand the organization's culture and how to enact it in their daily work lives. The organization's culture can literally disintegrate during periods of high turnover and precipitous downsizing because the corporate memory leaves with these employees. are unconscious, taken-for-granted perceptions or ideal prototypes of behavior that are considered the correct way to think and act toward problems and opportunities. Selected Answer: Shared assumptions Response Feedback: Organizational culture consists of shared assumptions—a deeper element that some experts believe is the essence of corporate culture. Shared assumptions are unconscious, taken-for-granted perceptions or ideal prototypes of behavior that are considered the correct way to think and act toward problems and opportunities. Which of the following are the observable indicators of organizational culture? Selected Answer: artifacts Response Feedback: Artifacts are the observable symbols and signs of an organization's culture, such as the way visitors are greeted, the organization's physical layout, and how employees are rewarded. Artifacts are important because they reinforce an organization's culture. What are spawning grounds for emerging values that keep the firm aligned with the evolving needs and expectations of customers, suppliers, communities, and other stakeholders? Selected Answer: subcultures Response Feedback: The second function of subcultures is to act as spawning grounds for emerging values that keep the firm aligned with the evolving needs and expectations of customers, suppliers, communities, and other stakeholders. Companies eventually need to replace their dominant values with ones that are more appropriate for the changing environment. Those emerging cultural values and assumptions usually exist in subcultures long before they are ideal for the organization. If subcultures are suppressed, the organization may take longer to discover, develop, and adopt the emerging desired culture. Which of the following is true about socialization agents? Selected Answer: Socialization agents help integrate new employees into the team. Response Feedback: Coworkers are important socialization agents because they are easily accessible, can answer questions when problems arise, and serve as role models for appropriate behavior. New employees tend to receive this information and support when coworkers integrate them into the work team. When merging cultures, it is best to Selected Answer: take time to be sure it is a cultural fit. Response Feedback: The cultural fit is just as important or maybe more important than the financial side because if the culture doesn't fit, the financial side will never work. 2 out of 2 points Which of the following is true about the work space in a controlling and competitive culture? Selected Answer: symmetrical layout Response Feedback: Collaborative and creative cultures value more teamwork and flexibility, so space design is informal and enables spontaneous group discussion. Controlling and competitive cultures tend to have more structural office arrangements and provide more space for individual work than teamwork. For example: • More individual space • More formal than informal space • High/medium enclosure • More fixed environment • More structured, symmetrical layout Companies are initiating a to help reduce turnover and increase job performance. Selected Answer: realistic job preview Response Feedback: A realistic job preview (RJP) offers a balance of positive and negative information about the job and work context. This balanced description of the company and work helps job applicants decide for themselves whether their skills, needs, and values are compatible with the job and organization. RJPs scare away some applicants, but they also tend to reduce turnover and increase job performance. This occurs because RJPs help applicants develop more accurate preemployment expectations, which, in turn, minimize reality shock. RJPs represent a type of vaccination by preparing employees for the more challenging and troublesome aspects of work life. There is also some evidence that RJPs increase affective organizational commitment. One explanation is that companies providing candid information are easier to trust. Another explanation is that RJPs show respect for the psychological contract and concern for employee welfare. Resolving conflicts between work and nonwork activities mainly occurs during the stage of socialization. Selected Answer: role management Response Feedback: Role management involves resolving the conflicts between work and nonwork activities, including resolving discrepancies between one's existing values and those emphasized by the organizational culture. James has just joined CoraTech Systems, where he has been assigned to Paul and Natalie for sources of information about the company. Paul and Natalie introduce James to others at Coratech, give him an office tour, and assure him that they will meet him regularly for the first few weeks, to help him in the transition to the new company. In this scenario, Paul and Natalie are part of the CoraTech's Selected Answer: buddy system. Response Feedback: Several organizations rely on a "buddy system," whereby newcomers are assigned to coworkers for sources of information and social support. Buddies introduce new hires to other employees, give them campus tours, and generally familiarize them with the physical layout of the workplace. They have lunch with employees on their first day and meet weekly with them for their first two months. Who developed the force field analysis model? Selected Answer: Kurt Lewin Response Feedback: Social psychologist Kurt Lewin developed the force field analysis model to describe this process using the metaphor of a force field. Although it was developed more than 50 years ago, recent reviews affirm that Lewin's force field analysis model remains one of the most widely respected ways of viewing the change process. One problem the learning strategy has in minimizing resistance to change is that it Selected Answer: Response Feedback: attempts to change the drives instead of reducing the restraining forces. Learning is an important process in most change initiatives because employees require new knowledge and skills to fit the organization's evolving requirements. However, the learning process is time- consuming. Which of the following organizational change activities adopts a "whole systems" perspective of the change process? Selected Answer: large group interventions Response Feedback: Scenario A Large group interventions adopt a "whole systems" perspective of the change process. This means that they view organizations as open systems. XYZ Office Supplies is about to introduce a new customer service program that will affect all of its 355 sales and service employees. Job duties will be changed and the employee reward system will be altered to fit this new customer focus. Moreover, the company wants to improve the efficiency of work processes, thereby removing some of the comfortable (and often leisurely) routines that employees have followed over the years. Top management is concerned about what types of forces resisting change the company will potentially experience during this change process. XYZ attempts to assist the change process by putting employees in direct contact with customers. Here, the company is trying to Selected Answer: use the stress management technique. Response Feedback: Some companies fuel the urgency to change by putting employees in direct contact with customers. Here, XYZ is attempting to do that. marketing occurs when information seeded to a few people is transmitted to others through their friendship connections. Selected Answer: Viral Response Feedback: The viral change process adopts principles found in word-of-mouth and viral marketing. Viral and word-of-mouth marketing occur when information seeded to a few people is transmitted to others through their friendship connections. Within organizations, social networks represent the channels through which news and opinions about change initiatives are transmitted. Participants in that network have relatively high trust, so their information and views are more persuasive than when communication occurs through more formal channels of communication. Cross-cultural changes occur in all of the following ways except Selected Answer: a cyclical fashion. Response Feedback: One possible cross-cultural limitation is that Western organizational change models, such as Lewin's force field analysis, often assume that change has a beginning and an ending in a logical linear sequence (i.e., a straight line from point A to point B). Yet change is viewed more as a cyclical phenomenon in some cultures, such as the earth's revolution around the sun or a pendulum swinging back and forth. Other cultures have more of an interconnected view of change, whereby one change leads to another (often unplanned) change, which leads to another change, and so on, until the change objective is ultimately achieved in a more circuitous way. Which of the following is true about strategic visions? Selected Answer: They could minimize the fear of the unknown. Response Feedback: Scenario A A key element of leading change is a strategic vision. A leader's vision provides a sense of direction and establishes the critical success factors against which the real changes are evaluated. Furthermore, a vision provides an emotional foundation for the change because it links the individual's values and self-concept to the desired change. A strategic vision also minimizes employee fear of the unknown and provides a better understanding of what behaviors employees must learn for the desired future. XYZ Office Supplies is about to introduce a new customer service program that will affect all of its 355 sales and service employees. Job duties will be changed and the employee reward system will be altered to fit this new customer focus. Moreover, the company wants to improve the efficiency of work processes, thereby removing some of the comfortable (and often leisurely) routines that employees have followed over the years. Top management is concerned about what types of forces resisting change the company will potentially experience during this change process. Which of the following types of resistance to change might be used by employees at XYZ as a deliberate strategy to "prove" that the decision is wrong or that the change agent is incompetent? Selected Answer: incongruent organizational systems Response Feedback: Due to this "not-invented-here" syndrome, staff members sometimes deliberately inflate problems with changes that they did not initiate, just to "prove" that the decision is wrong. Action research usually assumes that the change agent originates outside the system, so the process begins by Selected Answer: forming the client-consultant relationship. Response Feedback: Action research usually assumes that the change agent originates outside the system (such as a consultant), so the process begins by forming the client-consultant relationship. Consultants need to determine the client's readiness for change, including whether people are motivated to participate in the process, are open to meaningful change, and possess the abilities to complete the process. is a form of conflict, but change agents unfortunately sometimes interpret that disagreement as relationship conflict. Selected Answer: Resistance Response Feedback: Resistance is a form of conflict, but change agents unfortunately sometimes interpret that disagreement as relationship conflict. They describe the people opposing change as unreasonable, dysfunctional, and irrational reactionaries to a desirable initiative. This perspective shapes the change agent's response to resistance. Perversely, the change agent's conflict-oriented response to resistance tends to escalate the conflict, which often generates even stronger resistance to the change initiative. Unfreezing refers to Selected Answer: Response Feedback: producing disequilibrium between the driving and restraining forces of change. Unfreezing involves producing disequilibrium between the driving and restraining forces. Which organizational change is mostly compliance with, rather than commitment to, the change effort? Selected Answer: coercion Response Feedback: As long as people resist change, organizational change strategies will require a variety of influence tactics. Negotiation is a form of influence that involves the promise of benefits or resources in exchange for the target person's compliance with the influencer's request. This strategy potentially gains support from those who would otherwise lose out from the change. However, this support is mostly compliance with, rather than commitment to, the change effort, so negotiation might not be effective in the long term. According to the action research model, which of the following occurs during the "diagnose need for change" step? Selected Answer: analysis of data Response Feedback: Organizational diagnosis identifies the appropriate direction for the change effort by gathering and analyzing data about an ongoing system, such as through interviews and surveys of employees and other stakeholders. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 78 pages
Instant download
 Questions and Answers Straighterline.png)
Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 20, 2023
Number of pages
78
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 20, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
74