*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > OB NURS 306 - Test Bank Chapters 1 to 19 ( Awesome stuff) A+ Guide, West Coast University, Los Angel (All)
OB NURS 306 - Test Bank Chapters 1 to 19 ( Awesome stuff) A+ Guide, West Coast University, Los Angeles.
Document Content and Description Below
NURS 306 OB-Study Guide by chapters Ch1-to-Ch19 Chapter 1: Trends and Issues Multiple Choice 1. Since 1995 there has been a significant decrease in the rate of infant death related to which of ... the following: a. Disorders associated with short gestation and low birth weight b. Accidents c. Sudden infant death d. Newborns affected by complications of placenta, cord, and membranes Feedback a. The rates of prematurity and low birth weight are increasing. b. The rates of accidents have increased. c. Correct. The rate of infant death related to SIDS has decreased from 87.1 to 47.2. The decrease in rate is partially attributed to placing infants on their backs when sleeping. d. The rates of newborns affected by complications of placenta, cord, and membranes have increased. 2. Tobacco use during pregnancy is associated with adverse effects on the unborn infant such as intrauterine growth restriction, preterm births, and respiratory problems. By race, which has the highest percentages of smokers? a. American Indian and Alaskan Natives b. Asian or Pacific Islanders c. Non-Hispanic blacks d. Non-Hispanic whites Feedback a. 36% of American Indian and Native American women are cigarette smokers. b. 4.3% of Asian or Pacific Islander women are cigarette smokers. c. 17.1% of non-Hispanic black women are cigarette smokers. d. 19.6% of non-Hispanic white women are cigarette smokers. 3. Which of the following women is at the highest risk for health disparity? a. A white, middle-class, 16-year-old woman b. An African American, middle-class, 25-year-old woman c. An African American, upper-middle-class, 19-year-old woman d. An Asian, low-income, 30-year-old woman Feedback a. Although age is a risk factor, income contributes to disparity. b. Although African American women are at increased risk, income accounts for the largest disparity. c. Although age and race contribute to increased risk, income accounts for the largest disparity. d. Although age and race contribute to increased risk, income accounts for the largest disparity. 4. A neonate born at 36 weeks gestation is classified as which of the following? a. Very premature b. Moderately premature c. Late premature d. Term Feedback a. Very premature is less than 32 weeks’ gestation. b. Moderately premature is 32 to 33 completed weeks’ gestation. c. Correct. Late premature is 34 to 36 completed weeks’ gestation. d. Term is 37 to 42 weeks’ gestation. 5. The perinatal nurse explains to the student nurse that a goal of the Healthy People 2020 report is to: a. Increase proportion of infants who are breastfed to 93.1%. b. Increase proportion of infants who are breastfed to 90.7%. c. Increase proportion of infants who are breastfed to 85.6%. d. Increase proportion of infants who are breastfed to 83.9%. A goal of Healthy People 2020 is to increase the proportion of infants who are breastfed from 74% to 81.9%. 6. The perinatal nurse explains to the student nurse that __________ is the leading cause of infant death in the United States. a. Sudden Infant Death Syndrome b. Respiratory distress of newborns c. Disorders related to short gestation and low birth weight d. Congenital malformations and chromosomal abnormalities Multiple Response 7. Which of the following statements are true related to teen pregnancies? (Select all that apply.) a. Teen mothers are at higher risk for HIV. b. Teen mothers are at higher risk for hypertensive problems. c. The birth rate for teenaged women has increased in the past 15 years. d. Infants born to teen mothers are at higher risk for health problems. Chapter 2: Ethics and Standards of Practice Issues Multiple Choice 1. An ethical dilemma unique to perinatal nursing is the:a. Innate conflict between maternal and fetal rights b. Intensive use of technologyc. Shortage of health-care resourcesd. Risk of violation of the principle of veracity Feedback a. A unique aspect of maternity nursing is that the nurse advocates for two individuals: the woman and the fetus. b. The use of technology is not unique to perinatal nursing. c. Currently, in the United States, decisions in perinatal nursing are not based on resources available. d. In perinatal nursing, the obligation to tell the truth is generally adhered to. 2. The American Nurses Association Code of Ethics for Nurses directs nurses to provide patient care that is:a. Curativeb. Utilitarianc. Negotiabled. Respectful Feedback a. Adaptation rather than cure is the goal of nursing. b. Nursing does not define the value of a person by his or her utility. c. The Code of Ethics outlines the nursing profession’s nonnegotiable ethical standard. d. Respect for the inherent dignity, worth, and uniqueness of every individual is part of the Code of Ethics. 3. Evidence-based practice is the integration of the best: a. Randomized clinical trials, clinical expertise, and patients’ requestsb. Research evidence, clinical expertise, and patients’ valuesc. Quantitative research, clinical expertise, and patients’ preferencesd. Research findings, clinical experience, and patients’ preferences Feedback a. Evidence-based practice is the use of evidence that may include research beyond randomized clinical trials. b. These elements are the accepted definition of evidence-based practice. c. Qualitative research, as well as quantitative research, contributes to evidence-based practice. d. Clinical expertise, as well as clinical experience, defines evidence-based practice. Multiple Response 4. Infants whose mothers were obese during pregnancy are at higher risk for which of the following? (Select all that apply.) a. Childhood diabetes b. Heart defects c. Hypospadias d. Respiratory distress Chapter 3: Genetics, Conception, Fetal Development, and Reproductive Technology Multiple Choice 1. The color of a person’s hair is an example of which of the following? a. Genome b. Sex-link inheritance. C. Genotype d. Phenotype Feedback a. Genome is an organism’s complete set of DNA. b. Sex-link inheritance refers to genes or traits that are located only on the X chromosome. c. Genotype refers to a person’s genetic makeup. d. Correct. Phenotype refers to how genes are outwardly expressed, such as eye color, hair color, and height. 2. Which of the following statements by a pregnant woman indicates she needs additional teaching on ways to reduce risks to her unborn child from the potential effects of exposure to toxoplasmosis? a. “I will avoid rare lamb.” b. “I will wear a mask when cleaning my cat’s litter box.” c. “I understand that exposure to toxoplasmosis can cause blindness in the baby.” d. “I will avoid rare beef.” Feedback a. Exposure occurs when the protozoan parasite found in cat feces and uncooked or rare beef and lamb is ingested. b. Correct. Pregnant women and women who are attempting pregnancy should avoid contact with cat feces. Exposure occurs when the protozoan parasite found in cat feces and uncooked or rare beef and lamb is ingested. Wearing a mask will not decrease the risk through ingestion of the parasite. c. Exposure to toxoplasmosis can cause fetal death, mental retardation, and blindness. d. Exposure occurs when the protozoan parasite found in cat feces and uncooked or rare beef and lamb is ingested. 3. The fetal circulatory structure that connects the pulmonary artery with the descending aorta is known as which of the following? a. Ductus venosus b. Foramen ovale c. Ductus arteriosus d. Internal iliac artery Feedback a. The ductus venosus connects the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava. b. The foramen ovale is the opening between the right and left atria. c. Correct. d. The internal iliac artery connects the external iliac artery to the umbilical artery. 4. A woman at 40 weeks’ gestation has a diagnosis of oligohydramnios. Which of the following statements related to oligohydramnios is correct? a. It indicates that there is a 25% increase in amniotic fluid. b. It indicates that there is a 25% reduction of amniotic fluid. c. It indicates that there is a 50% increase in amniotic fluid. d. It indicates that there is a 50% reduction of amniotic fluid. Feedback a. Oligohydramnios is a decrease, not an increase in amniotic fluid. b. Oligohydramnios is a 50% reduction in amniotic fluid. c. Oligohydramnios is a decrease, not an increase in amniotic fluid. d. Correct. Oligohydramnios refers to a decreased amount of amniotic fluid of less than 500 mL at term or 50% reduction of normal amounts. 5. A diagnostic test commonly used to assess problems of the fallopian tubes is: a. Endometrial biopsy b. Ovarian reserve testing c. Hysterosalpingogram d. Screening for sexually transmitted infections Feedback a. Endometrial biopsy provides information on the response of the uterus to hormonal signals. b. Ovarian reserve testing is used to assess ovulatory functioning. c. Correct. Hysterosalpingogram provides information on the endocervical canal, uterine cavity, and fallopian tubes. d. STIs can cause adhesions within the fallopian tubes, but screening cannot confirm that adhesions are present. KEY: Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning | Cognitive Level: Knowledge | Content Area: Maternity | Client Need: Safe and Effective Care Environment | Difficulty Level: Moderate 6. The nurse is interviewing a gravid woman during the first prenatal visit. The woman confides to the nurse that she lives with a number of pets. The nurse should advise the woman to be especially careful to refrain from coming in contact with the stool of which of the pets? a. Cat b. Dog c. Hamster d. Bird Feedback a. The patient should refrain from coming in direct contact with cat feces. Cats often harbor toxoplasmosis, a teratogenic illness. b. No pathology has been associated with the feces of pet dogs. c. No pathology has been associated with the feces of pet hamsters. d. No pathology has been associated with the feces of pet birds. 7. A client is to take Clomiphene Citrate for infertility. Which of the following is the expected action of this medication? a. Decrease the symptoms of endometriosis b. Increase serum progesterone levels c. Stimulate release of FSH and LH d. Reduce the acidity of vaginal secretions Feedback a. Clomiphene Citrate will not reduce a client’s symptoms of endometriosis. b. Clomiphene Citrate will not increase a client’s progesterone levels. c. Clomiphene Citrate stimulates release of FSH and LH. d. Clomiphene Citrate will not reduce the acidity of vaginal secretions. 8. The nurse takes the history of a client, G2 P1, at her first prenatal visit. The client is referred to a genetic counselor, due to her previous child having a diagnosis of __________. a. Unilateral amblyopia b. Subdural hematoma c. Sickle cell anemia d. Glomerular nephritis Feedback a. Amblyopia rarely results from a genetic predisposition. b. A subdural hematoma does not result from a genetic defect. c. Sickle cell anemia is an autosomal recessive illness. This client needs to be seen by a genetic counselor. d. Glomerular nephritis does not result from a genetic defect. 9. A nurse is teaching a woman about her menstrual cycle. The nurse states that __________ is the most important change that happens during the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle. a. Maturation of the graafian follicle b. Multiplication of the fimbriae c. Secretion of human chorionic gonadotropin d. Proliferation of the endometrium Feedback a. The maturation of the graafian follicle occurs during the follicular phase. b. There is no such thing as the multiplication of the fimbriae. c. Human chorionic gonadotropin is secreted by the fertilized ovum during the early weeks of a pregnancy. d. The proliferation of the endometrium occurs during the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle. 10. An ultrasound of a fetus’ heart shows that “normal fetal circulation is occurring.” Which of the following statements is consistent with the finding? a. A right to left shunt is seen between the atria. b. Blood is returning to the placenta via the umbilical vein. c. Blood is returning to the right atrium from the pulmonary system. d. A right to left shunt is seen between the umbilical arteries. Feedback a. This is correct. The foramen ovale is a duct between the atria. In fetal circulation, there is a right to left shunt through the duct. b. Blood returns to the placenta via the umbilical arteries. c. Most of the blood bypasses the pulmonary system. The blood that does enter the pulmonary system returns to the left atrium. d. There is no duct between the umbilical arteries. 11. The clinic nurse knows that the part of the endometrial cycle occurring from ovulation to just prior to menses is known as the: a. Menstrual phase b. Proliferative phase c. Secretory phase d. Ischemic phase Feedback a. The menstrual phase is the time of vaginal bleeding, approximately days 1 to 6. b. The proliferative phase ends the menses through ovulation, approximately days 7 to 14. c. The secretory phases occurs from the time of ovulation to the period just prior to menses, or approximately days 15 to 26. d. The ischemic phase occurs from the end of the secretory phase to the onset of menstruation, approximately days 27 to 28. 12. A clinic nurse explains to the pregnant woman that the amount of amniotic fluid present at 24 weeks’ gestation is approximately: a. 500 mL b. 750 mL c. 800 mL d. 1000 mL . 13. Information provided by the nurse that addresses the function of the amniotic fluid is that the amniotic fluid helps the fetus to maintain a normal body temperature and also: a. Facilitates asymmetrical growth of the fetal limbs b. Cushions the fetus from mechanical injury c. Promotes development of muscle tone d. Promotes adherence of fetal lung tissue Feedback a. Amniotic fluid allows for symmetrical fetal growth. b. Amniotic fluid cushions the fetus from mechanical injury. c. Amniotic fluid does not promote muscle tone. d. Amniotic fluid prevents adherence of the amnion to the fetus. 14. During preconception counseling, the clinic nurse explains that the time period when the fetus is most vulnerable to the effects of teratogens occurs from: a. 2 to 8 weeks b. 4 to12 weeks c. 5 to 10 weeks d. 6 to 15 weeks 15. A major fetal development characteristic at 16 weeks’ gestation is: a. The average fetal weight is 450 grams b. Lanugo covers entire body c. Brown fat begins to develop d. Teeth begin to form Feedback a. The average fetal weight at 16 weeks is 200 grams. b. Lanugo is present on the head. c. Brown fat begins to develop at 20 weeks. d. This is the correct answer. 16. Karen, a 26-year-old woman, has come for preconception counseling and asks about caring for her cat as she has heard that she “should not touch the cat during pregnancy.” The clinic nurse’s best response is: a. It is best if someone other than you change the cat’s litter pan during pregnancy so that you have no risk of toxoplasmosis during pregnancy. b. It is important to have someone else change the litter pan during pregnancy and also avoid consuming raw vegetables. c. Have you had any “flu-like” symptoms since you got your cat? If so, you may have already had toxoplasmosis and there is nothing to worry about. d. Toxoplasmosis is a concern during pregnancy, so it is important to have someone else change the cat’s litter pan and also to avoid consuming uncooked meat. Feedback a. The nurse should also explain that the patient should not eat uncooked meat as it is a potential source for toxoplasmosis. b. Raw vegetables are not a source for toxoplasmosis. c. This is not an accurate way to diagnose if the woman has had toxoplasmosis. d. Women need to be aware that Toxoplasma gondii, a single-celled parasite, is responsible for the infection toxoplasmosis. The majority of individuals who become infected with toxoplasmosis are asymptomatic, although when present, symptoms are described as “flu like” and include glandular pain and enlargement and myalgia. Severe toxoplasmosis infection may cause damage to the fetal brain, eyes, or other organs. Toxoplasmosis is usually acquired by consuming raw or poorly cooked meat that has been contaminated with T. gondii. Toxoplasmosis may also be acquired through close contact with feces from an infected animal (usually cats) or soil that has been contaminated with T. gondii. 17. A couple who has sought infertility counseling has been told that the man’s sperm count is very low. The nurse advises the couple that spermatogenesis is impaired when which of the following occur? a. The testes are overheated. b. The vas deferens is ligated. c. The prostate gland is enlarged. d. The flagella are segmented. Feedback a. Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes. High temperatures harm the development of the sperm. b. When the vas deferens is ligated, a man has had a vasectomy and is sterile. The sterility is not due to impaired spermatogenesis, but rather to the inability of the sperm to migrate to the woman’s reproductive track. c. The enlarged prostrate has no effect on spermatogenesis. d. The flagella are the “tails” of the sperm. They are normally divided into the middle segment and an end segment. 18. A nurse working with an infertile couple has made the following nursing diagnosis: Sexual dysfunction related to decreased libido. Which of the following assessments is the likely reason for this diagnosis? a. The couple has established a set schedule for their sexual encounters. b. The couple has been married for more than 8 years. c. The couple lives with one set of parents. d. The couple has close friends who gave birth within the last year. Feedback a. Couples who “schedule” intercourse often complain that their sexual relationship is unsatisfying. b. Years of marriage are not directly related to a couple’s sexual relationship. c. The fact that the couple lives with one set of parents is unlikely related to their sexual relationship. d. Although it can be very difficult to be around couples who have become pregnant or have healthy babies, this factor is not usually related to a couple’s sexual relationship. True/False 19. The perinatal nurse explains to the student nurse that in the fetal circulation, the lowest level of oxygen concentration is found in the umbilical arteries. ANS: True The highest oxygen concentration (PO2 = 30–35 mm Hg) is found in the blood returning from the placenta via the umbilical vein; the lowest oxygen concentration occurs in blood shunted to the placenta where reoxygenation takes place. The blood with the highest oxygen content is delivered to the fetal heart, head, neck, and upper limbs, and the blood with the lowest oxygen content is shunted toward the placenta. Fill-in-the-Blank 20. After birth, the perinatal nurse explains to the new mother that __________ is the hormone responsible for stimulating milk production. ANS: prolactin Following birth and delivery of the placenta, there is an abrupt decrease in estrogen. This event triggers an increased secretion of prolactin (the hormone that stimulates milk production) by the anterior pituitary gland. The posterior pituitary and hypothalamus play a role in the production and secretion of oxytocin, a hormone that causes release of milk from the alveoli. 21. During prenatal class, the childbirth educator describes the two membranes that envelop the fetus. The __________ contains the amniotic fluid, and the __________ is the thick, outer membrane. 22. The perinatal nurse is teaching nursing students about fetal circulation and explains that fetal blood flows through the superior vena cava into the right __________ via the __________. 23. The perinatal nurse explains to the student nurse that the growing embryo is called a __________ beginning at 8 weeks of gestational age. 24. The perinatal nurse defines a __________ as any substance that adversely affects the growth and development of the embryo/fetus. 25. __________ __________ __________ is when sperm and oocytes are mixed outside the woman’s body and then placed into the fallopian tube via laparoscopy. Multiple Response 26. A woman seeks care at an infertility clinic. Which of the following tests may this woman undergo to determine what, if any, infertility problem she may have? (Select all that apply.) a. Chorionic villus sampling b. Endometrial biopsy c. Hysterosalpingogram d. Serum FSH analysis ANS. b, c, d Feedback a. Chorionic villus sampling is done to assess for genetic disorders of the fetus. b. Endometrial biopsy is performed about 1 week following ovulation to detect the endometrium’s response to progesterone. c. Hysterosalpingogram is used to determine if fallopian tubes are patent. d. Serum FSH levels are used to assess ovarian function. 27. A couple who has been attempting to become pregnant for 5 years is seeking assistance from an infertility clinic. The nurse assesses the clients’ emotional responses to their infertility. Which of the following responses would the nurse expect to find? (Select all that apply.) a. Anger at others who have babies. b. Feelings of failure because they cannot make a baby. c. Sexual excitement because they want to conceive a baby. d. Guilt on the part of one partner because he or she is unable to give the other a baby. , b, d Feedback a. Infertile couples often feel anger toward couples who have babies. b. Infertile couples often express feelings of personal failure. c. Infertile couples undergoing infertility testing and treatment often express an aversion to sex. d. Guilt is often expressed by the couple. 28. Which of the following places a couple at higher risk for conceiving a child with a genetic abnormality? (Select all that apply.) a. Maternal age over 35 years b. Partner who has a genetic disorder c. Maternal type 1 diabetes d. Paternal heart disease 29. The ovarian cycle includes which of the following phases? (Select all that apply.) a. Follicular phase b. Secretory phase c. Ovulatory phase d. Luteal phase e. Menstrual phase 30. A couple is undergoing an infertility workup. The semen analysis indicates a decreased number of sperm and immature sperm. Which of the following factors can have a potential effect on sperm maturity? (Select all that apply.) a. The man rides a bike to and from work each day. b. The man takes a calcium channel blocker for the treatment of hypertension. c. The man drinks 6 cups of coffee a day. d. The man was treated for prostatitis 12 months ago and has been symptom free since treatment. 31. The clinic nurse recognizes that pregnant women who are in particular need of support are those who (select all that apply): a. Are experiencing a second pregnancy b. Are awaiting genetic testing results c. Are experiencing a first pregnancy d. Are trying to conceal this pregnancy as long as possible Chapter 4: Physiological Aspects of Antepartum Care Multiple Choice 1. Folic acid supplementation during pregnancy is to:a. Improve the bone density of pregnant women b. Decrease the incidence of neural tube defects in the fetus c. Decrease the incidence of Down syndrome in the fetusd. Improve calcium uptake in pregnant women Feedback a. Folic acid is not related to bone density. b. Correct. The use of folic acid has decreased the incidence of neural tube defects by 50%. c. The use of folic acid is not associated with a reduction in Down syndrome. d. Folic acid is not related to calcium uptake in women. 2. The positive signs of pregnancy are: a. All physiological and anatomical changes of pregnancy b. All subjective signs of pregnancy c. All those physiological changes perceived by the woman herself d. The objective signs of pregnancy that can only be attributed to the fetus Feedback a. Physiological and anatomical changes of pregnancy are presumptive signs of pregnancy. b. All subjective signs of pregnancy are the probable signs of pregnancy. c. All those physiological changes perceived by the woman herself are presumptive signs of pregnancy. d. Correct. Positive signs of pregnancy are the objective signs of pregnancy that can only be attributed to the fetus, such as fetal heart tones. 3. During a routine prenatal visit in the third trimester, a woman reports she is dizzy and lightheaded when she is lying on her back. The most appropriate nursing action would be to: a. Order an EKG. b. Report this abnormal finding immediately to her care provider. c. Teach the woman to avoid lying on her back and to rise slowly because of supine hypotension. d. Order a nonstress test to assess fetal well-being. Feedback a. This is a normal occurrence in pregnancy and does not indicate pathology. The probable cause of the problem is supine hypotension. b. This is a normal finding that does not warrant immediate notification to her care provider. c. Correct. Teaching the woman to avoid lying on her back because of occlusion of the vena cava with the gravid uterus causes supine hypotension syndrome. d. Antenatal testing is not indicated with supine hypotension. 4. Blood volume expansion during pregnancy leads to: a. Iron-deficiency anemia b. Maternal iron stores being insufficient to meet the demands for iron in fetal development c. Plasma fibrin increase of 40% and fibrinogen increase of 50%d. Physiological anemia of pregnancy Feedback a. Iron-deficiency anemia is treated with iron supplementation. Iron-deficiency anemia is defined as hemoglobin of less than 11 g/dL and hematocrit less than 33%. b. Maternal iron stores that are insufficient to meet the demands for iron in fetal development result in iron-deficiency anemia. c. Hypercoagulation that occurs during pregnancy is to decrease the risk of postpartum hemorrhage. These changes taking place are not related to blood volume expansion. d. Correct. Physiological anemia of pregnancy, also referred to as pseudo-anemia of pregnancy, is due to hemodilution. The increase in plasma volume is relatively larger than the increase in RBCs that results in decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit values. 5. Intimate partner violence (IPV) against women consists of actual or threatened physical or sexual violence and psychological and emotional abuse. Screening for IPV during pregnancy is recommended for: a. Pregnant women with a history of domestic violence b. All pregnant women c. All low-income pregnant women d. Pregnant adolescents Feedback a. Intimate partner violence is underreported by women, necessitating universal screening. b. Correct. AWHONN advocates for universal screening for domestic violence for all pregnant women. Homicide is the most likely cause of death for pregnant or recently pregnant women, and a significant portion of those homicides are committed by their intimate partners. One in six pregnant women reported physical or sexual abuse during pregnancy, seriously impacting maternal and fetal health and infant birth weight. c. IPV crosses all ethnic, racial, religious, and socioeconomic levels. d. IPV crosses all ethnic, racial, religious, and socioeconomic levels. 6. A woman presents to the prenatal clinic at 30 weeks’ gestation reporting dysuria, frequency, and urgency with urination. Appropriate nursing actions include: a. Obtain clean-catch urine to assess for a possible urinary tract infection. b. Reassure the woman that the signs are normal urinary changes in the third trimester. c. Teach the woman to decrease fluid intake to manage these symptoms. d. Perform a Leopold’s maneuver to assess fetal position and station. Feedback a. Correct. Dysuria, frequency, and urgency with urination are signs and symptoms of a urinary tract infection, necessitating further assessment and testing. b. These are abnormal urinary symptoms in the third trimester. c. Pregnant women need to increase their fluid intake during pregnancy, and dysuria and urgency are abnormal. d. Assessment of fetal position and station is not an appropriate response to reported signs and symptoms of a urinary tract infection. 7. At the end of her 32-week prenatal visit, a woman reports discomfort with intercourse and tells you shyly that she wants to maintain a sexual relationship with her partner. The best response is to: a. Reassure woman/couple of normalcy of response b. Suggest alternative positions for sexual intercourse and alternative sexual activity to sexual intercourse c. Recommend cessation of intercourse until after delivery due to advanced gestation d. Suggest woman discuss this with her care provider at her next appointment Feedback a. Although this is a normal response, providing reassurance is not enough. Further intervention is indicated. b. Although shy to discuss this, she wants to maintain a sexual relationship with her partner. Suggesting alternative positions for sexual intercourse and alternative sexual activity to sexual intercourse provides the woman with information to maintain sexual relations. c. She wants to maintain a sexual relationship with her partner, and there are no contraindications to intercourse during a healthy pregnancy. d. The patient is seeking out information and to defer her to her care provider at her next appointment is inappropriate. Additionally, she may not be comfortable discussing this with anyone else. 8. The clinic nurse talks to a 30-year-old woman at 34 weeks’ gestation who complains of having difficulty sleeping. Jayne has noticed that getting back to sleep after she has been up at night is difficult. The nurse’s best response is: a. “This is abnormal; it is important that you describe this problem to the doctor.” b. “This is normal, and many women have this same problem during pregnancy; try napping for several hours each morning and afternoon.” c. “This is abnormal; tell the doctor about this problem because diagnostic testing may be necessary.” d. “This is normal in pregnancy, particularly during the third trimester when you also feel fetal movement at night; try napping once a day.” Feedback a. This sleep pattern is a normal finding. b. Sleeping for several hours in the morning and afternoon would contribute to further sleep disturbances at night. c. This sleep pattern is a normal finding. d. Pregnancy sleep patterns are characterized by reduced sleep efficiency, fewer hours of night sleep, frequent awakenings, and difficulty going to sleep. Nurses can advise patients that afternoon napping may help alleviate the fatigue associated with the sleep alterations. 9. A 26-year-old woman at 29 weeks’ gestation experienced epigastric pain following the consumption of a large meal of fried fish and onion rings. The pain resolved a few hours later. The most likely diagnosis for this symptom is: a. Cholelithiasis b. Influenza c. Urinary tract infection d. Indigestion Feedback a. The progesterone-induced prolonged emptying time of bile from the gallbladder, combined with elevated blood cholesterol levels, may predispose the pregnant woman to gallstone formation (cholelithiasis). Pain in the epigastric region following ingestion of a high-fat meal constitutes the major symptom of these conditions. The pain is self-limiting and usually resolves within 2 hours. b. The symptoms described are not associated with influenza. c. The symptoms described are not associated with urinary tract infection. d. Prolonged emptying time of bile from the gallbladder, combined with elevated blood cholesterol levels, make cholelithiasis a more probable diagnosis than indigestion. 10. The clinic nurse reviews the complete blood count results for a 30-year-old woman who is now 33 weeks’ gestation. Tamara’s hemoglobin value is 11.2 g/dL, and her hematocrit is 38%. The clinic nurse interprets these findings as: a. Normal adult values b. Normal pregnancy values for the third trimester c. Increased adult values d. Increased values for 33 weeks’ gestation Feedback a. The values are low normal for adults but represent normal findings for pregnant women. b. During pregnancy the woman’s hematocrit values may appear low due to the increase in total plasma volume (on average, 50%). Because the plasma volume is greater than the increase in erythrocytes (30%), the hematocrit decreases by about 7%. This alteration is termed “physiologic anemia of pregnancy,” or “pseudo-anemia.” The hemodilution effect is most apparent at 32 to 34 weeks. The mean acceptable hemoglobin level in pregnancy is 11 to 12 g/dL of blood. c. The values are not increased; they are low normal for adults but represent normal findings for pregnant women. d. The values are not increased; they are low normal for adults but represent normal findings for pregnant women. 11. The clinic nurse is aware that the pregnant woman’s blood volume increases by: a. 20% to 25% b. 30% to 35% c. 40% to 45% d. 50% to 55% Feedback a. An increase in maternal blood volume begins during the first trimester and peaks at term. The increase approaches 40% to 45%, not 20% to 25%. b. An increase in maternal blood volume begins during the first trimester and peaks at term. The increase approaches 40% to 45, not 30% to 35%. c. An increase in maternal blood volume begins during the first trimester and peaks at term. The increase approaches 40% to 45% and is primarily due to an increase in plasma and erythrocyte volume. Additional erythrocytes, needed because of the extra oxygen requirements of the maternal and placental tissue, ensure an adequate supply of oxygen to the fetus. The elevation in erythrocyte volume remains constant during pregnancy. d. An increase in maternal blood volume begins during the first trimester and peaks at term. The increase approaches 40% to 45%, not as high as 50% to 55%. 12. The clinic nurse uses Leopold maneuvers to determine the fetal lie, presentation, and position. The nurse’s hands are placed on the maternal abdomen to gently palpate the fundal region of the uterus. This action is best described as the: a. First maneuver b. Second maneuver c. Third maneuver d. Fourth maneuver Feedback a. Leopold maneuvers are a four-part clinical assessment method used to determine the lie, presentation, and position of the fetus. The first maneuver determines which fetal body part (e.g., head or buttocks) occupies the uterine fundus. The examiner faces the patient’s head and places the hands on the abdomen, using the palmar surface of the hands to gently palpate the fundal region of the uterus. The buttocks feel soft, broad, and poorly defined and move with the trunk. The fetal head feels firm and round and moves independently of the trunk. b. Leopold maneuvers are a four-part clinical assessment method used to determine the lie, presentation, and position of the fetus. The first maneuver is described in this scenario. c. Leopold maneuvers are a four-part clinical assessment method used to determine the lie, presentation, and position of the fetus. The first maneuver is described in this scenario. d. Leopold maneuvers are a four-part clinical assessment method used to determine the lie, presentation, and position of the fetus. The first maneuver is described in this scenario. 13. The clinic nurse talks with Kathy about her possible pregnancy. Kathy has experienced amenorrhea for 2 months, nausea during the day with vomiting every other morning, and breast tenderness. These symptoms are best described as: a. Positive signs of pregnancy b. Presumptive signs of pregnancy c. Probable signs of pregnancy d. Possible signs of pregnancy Feedback a. Positive signs include fetal heartbeat, visualization of the fetus, and fetal movements palpated by the examiner. b. Presumptive signs of pregnancy include amenorrhea, nausea and vomiting, frequent urination, breast tenderness, perception of fetal movement, skin changes, and fatigue. Probable signs of pregnancy include abdominal enlargement, Piskacek sign, Hegar sign, Goodell sign, Braxton Hicks sign, positive pregnancy test, and ballottement. Positive signs include fetal heartbeat, visualization of the fetus, and fetal movements palpated by the examiner. c. Probable signs of pregnancy include abdominal enlargement, Piskacek sign, Hegar sign, Goodell sign, Braxton Hicks sign, positive pregnancy test, and ballottement. d. Possible signs of pregnancy may vary widely. 14. Lina is an 18-year-old woman at 20 weeks’ gestation. This is her first pregnancy. Lina is complaining of fatigue and listlessness. Her vital signs are within a normal range: BP = 118/60, pulse = 70, and respiratory rate 16 breaths per minute. Lina’s fundal height is at the umbilicus, and she states that she is beginning to feel fetal movements. Her weight gain is 25 pounds over the prepregnant weight (110 lb), and her height is 5 feet 4 inches. The perinatal nurse’s best approach to care at this visit is to: a. Ask Lina to keep a 3-day food diary to bring in to her next visit in 1 week. b. Explain to Lina that weight gain is not a concern in pregnancy, and she should not worry. c. Teach Lina about the expected normal weight gain during pregnancy (approximately 20 pounds by 20 weeks’ gestation). d. Explain to Lina the possible concerns related to excessive weight gain in pregnancy, including the risk of gestational diabetes. Feedback a. Nutrition and weight management play an essential role in the development of a healthy pregnancy. Not only does the patient need to have an understanding of the essential nutritional elements, she must also be able to assess and modify her diet for the developing fetus and her own nutritional maintenance. To facilitate this process, it is the nurse’s responsibility to provide education and counseling concerning dietary intake, weight management, and potentially harmful nutritional practices. To facilitate this process, it is the nurse’s responsibility to gather more information on the woman’s dietary practices through a food diary. b. Nutrition and weight management play an essential role in the development of a healthy pregnancy. To facilitate this process, it is the nurse’s responsibility to provide education and counseling concerning dietary intake, weight management, and potentially harmful nutritional practices. c. Nutrition and weight management play an essential role in the development of a healthy pregnancy. Not only does the patient need to have an understanding of the essential nutritional elements, she must also be able to assess and modify her diet for the developing fetus and her own nutritional maintenance. To facilitate this process, it is the nurse’s responsibility to provide education and counseling concerning dietary intake, weight management, and potentially harmful nutritional practices, not just inform the patient of expected normal weight gain. d. Nutrition and weight management play an essential role in the development of a healthy pregnancy. Not only does the patient need to have an understanding of the essential nutritional elements, she must also be able to assess and modify her diet for the developing fetus and her own nutritional maintenance. To facilitate this process, it is the nurse’s responsibility to provide education and counseling concerning dietary intake, weight management, and potentially harmful nutritional practices. 15. A woman presents to a prenatal clinic appointment at 10 weeks’ gestation, in the first trimester of pregnancy. Which of the following symptoms would be considered a normal finding at this point in pregnancy? a. Occipital headache b. Urinary frequency c. Diarrhea d. Leg cramps Feedback a. Headaches may be benign or, especially if noted after 20 weeks’ gestation, may be a symptom of pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH). b. Urinary frequency is a common complaint of women during their first trimester. c. Diarrhea is rarely seen in pregnancy. Constipation is a common complaint. d. Leg cramps are commonly seen during the second and third trimesters. 16. The nurse is providing prenatal teaching to a group of diverse pregnant women. One woman, who indicates she smokes two to three cigarettes a day, asks about its impact on her pregnancy. The nurse explains that the most significant risk to the fetus is: a. Respiratory distress at birth b. Severe neonatal anemia c. Low neonatal birth weight d. Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia Feedback a. Respiratory distress is not the most significant risk to the fetus unless the fetus is also premature. b. Severe neonatal anemia is not associated with pregnancies complicated by cigarette smoking. c. Low neonatal birth weight is the most common complication seen in pregnancies complicated by cigarette smoking. d. Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia is not associated with pregnancies complicated by cigarette smoking. 17. While performing Leopold’s maneuvers on a woman in early labor, the nurse palpates a flat area in the fundal region, a hard-round mass on the left side, a soft round mass on the right side, and small parts just above the symphysis. The nurse concludes which of the following? a. The fetal position is right occiput posterior. b. The fetal attitude is flexed. c. The fetal presentation is scapular. d. The fetal lie is vertical. Feedback a. This is a shoulder presentation. b. It is not possible to determine whether the attitude is flexed or not when doing Leopold’s maneuvers. c. This is a shoulder presentation. d. The lie is transverse or horizontal. 18. A nurse is reviewing diet with a pregnant woman in her second trimester. Which of the following foods should the nurse advise the patient to avoid consuming during her pregnancy? a. Brie cheese b. Bartlett pears c. Sweet potatoes d. Grilled lamb Feedback a. Soft cheese may harbor Listeria. The patient should avoid consuming uncooked soft cheese. b. A pear is an excellent food for a pregnant woman to consume. c. Sweet potatoes are an excellent food for a pregnant woman to consume. d. Grilled lamb is an excellent food for a pregnant woman to consume, although it should be well cooked. 19. The nurse is working in a prenatal clinic caring for a patient at 14 weeks’ gestation, G2 P1001. Which of the following findings should the nurse highlight for the nurse midwife? a. Body mass index of 23 b. Blood pressure of 100/60 c. Hematocrit of 29% d. Pulse rate of 76 bpm Feedback a. A body mass index of 23 is normal. b. A blood pressure of 100/60 is normal. c. A hematocrit of 29% indicates that the patient is anemic. The nurse should highlight the finding for the nurse-midwife. d. A pulse rate of 76 bpm is a normal rate. 20. A gravida, G4 P1203, fetal heart rate 150s, is 14 weeks pregnant, fundal height 1 cm above the symphysis. She denies experiencing quickening. Which of the following nursing conclusions made by the nurse is correct? a. The woman is experiencing a normal pregnancy. b. The woman may be having difficulty accepting this pregnancy. c. The woman must see a nutritionist as soon as possible. d. The woman will likely miscarry the conceptus. Feedback a. The patient is experiencing a normal pregnancy. b. Quickening is not felt until 16 to 20 weeks’ gestation. c. There is no apparent need for a nutritionist to see this patient. d. There is no indication in the scenario that this patient is at high risk for a miscarriage. 21. A patient at 37 weeks’ gestation is being seen in the prenatal clinic. Where would the nurse expect the fundal height to be palpated? a. At the xiphoid process b. At a point between the umbilicus and the xiphoid c. At the umbilicus d. At a level directly above the symphysis pubis Feedback a. At 36 weeks’ gestation, the fundus should be felt at the xiphoid process. b. At 36 weeks’ gestation, the fundus should be felt at the xiphoid process. c. At 20 weeks’ gestation, the fundus should be felt at the umbilicus. d. At 12 weeks’ gestation, the fundus should be felt directly above the symphysis pubis. 22. A nurse is performing an assessment on a pregnant woman during a prenatal visit. Which of the following findings would lead the nurse to report to the obstetrician that the patient may be experiencing intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)? a. Leopold’s maneuvers: Hard round object in the fundus, flat object on left of uterus, small parts on right of uterus, soft round object above the symphysis b. Weight gain: 6-pound increase over 4-week period c. Fundal height measurement: 22 cm at 26 weeks’ gestation d. Alpha-fetoprotein assessment: level is one-half normal, accompanied by complaints of severe nausea and vomiting Feedback a. This baby is in the breech position. This is not a sign of IUGR. b. This weight gain is slightly above normal. This is not a sign of IUGR. c. The fundal height at 26 weeks should be approximately 26 cm. The fundal height, therefore, is below expected. This patient may be experiencing intrauterine growth restriction. d. A low AFP level is seen in patients whose babies have spina bifida and other central nervous system defects. 23. A pregnant woman informs the nurse that her last normal menstrual period was on July 6, 2007. Using Naegele’s rule, which of the following would the nurse determine to be the patient’s estimated date of delivery (EDC)? a. January 9, 2008 b. April 13, 2008 c. April 20, 2008 d. September 6, 2008 Feedback a. The EDC is calculated as April 13, 2008. b. The EDC is calculated as April 13, 2008. Naegele’s rule: subtract 3 months and add 7 days to the first day of the last normal menstrual period. c. The EDC is calculated as April 13, 2008. d. The EDC is calculated as April 13, 2008. 24. Which of the following findings, seen in pregnant women in the third trimester, would the nurse consider to be within normal limits? a. Diplopia b. Epistaxis c. Bradycardia d. Oliguria Feedback a. Diplopia is sometimes seen in patients with pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH). b. Epistaxis is commonly seen in pregnant patients. The bleeding is related to the increased vascularity of the mucous membranes. Unless the blood loss is significant, it is a normal finding. c. Bradycardia is often seen immediately after delivery but not during the third trimester. d. Oliguria is seen in patients with PIH. 25. A primigravida patient is 39 weeks pregnant. Which of the following symptoms would the nurse expect the patient to exhibit? a. Nausea b. Dysuria c. Urinary frequency d. Intermittent diarrhea Feedback a. Nausea is usually not seen in the third trimester. b. Dysuria is not a normal finding at any time during a pregnancy. The possibility of a urinary traction infection (UTI) should be considered. c. Urinary frequency recurs at the end of the third trimester. As the uterus enlarges, it again compresses the bladder causing urinary frequency. d. Diarrhea is not a normal finding at any time during a pregnancy. 26. The nurse has taken a health history on four multigravida patients at their first prenatal visits. It is high priority that the patient whose first child was diagnosed with which of the following diseases receives nutrition counseling? a. Development dysplasia of the hip b. Achondroplastic dwarfism c. Spina bifida d. Muscular dystrophy Feedback a. The etiology of developmental dysplasia of the hip is unrelated to the mother’s nutritional status. b. Achondroplasia is an inherited defect. Its etiology is unrelated to the mother’s nutritional status. c. The incidence of spina bifida is much higher in women with poor folic acid intakes. It is a priority that this patient receives nutrition counseling. d. Most forms of muscular dystrophy are inherited. Their etiologies are unrelated to the mother’s nutritional status. 27. A nurse working in a prenatal clinic is caring for a woman who asks advice on foods that are high in vitamin C because “I hate oranges.” The nurse states that 1 cup of which of the following raw foods will meet the patient’s daily vitamin C needs? a. Strawberries b. Asparagus c. Iceberg lettuce d. Cucumber Feedback a. Strawberries are an excellent source of vitamin C. b. Although asparagus has some vitamin C, it is not an excellent source. c. Iceberg lettuce is a poor source of vitamin C. d. Cucumber is a poor source of vitamin C. 28. The nurse notes each of the following findings in a woman at 10 weeks’ gestation. Which of the findings would enable the nurse to tell the woman that she is probably pregnant? a. Fetal heart rate via Doppler b. Positive pregnancy test c. Positive ultrasound assessment d. Absence of menstrual period Feedback a. A fetal heart rate is a positive sign of pregnancy. b. A positive pregnancy test is a probable sign of pregnancy. It is not a positive sign because the hormone tested for—human chorionic gonadatropin (hCG)—may be being produced by, for example, a hydatidiform mole. c. A positive ultrasound is a positive sign of pregnancy. d. Amenorrhea is a presumptive sign of pregnancy. 29. A nurse who is discussing serving sizes of foods with a new prenatal patient would state that which of the following is equal to 1 (one) serving from the dairy food group? a.1 cup low-fat milk b. ½ cup vanilla yogurt c. ½ cup cottage cheese d.1-ounce cream cheese Feedback a. 1 cup of any milk (e.g., whole milk, skim milk, buttermilk, chocolate milk) is equal to 1 serving size from the dairy group. b. 1 cup of yogurt is equal to 1 serving size from the dairy group. c. 1 ½ cup of cottage cheese is equal to 1 serving size from the dairy group. d. Cream cheese is not included in the dairy group. It is a fat product. 30. The nurse who is assessing a G2 P1 palpates the fundal height at the location noted on the picture below. The nurse concludes that the fetus is equal to which of the following gestational ages? a. 12 weeks b. 20 weeks c. 28 weeks d. 36 weeks Feedback a. At 12 weeks’ gestation, the fundus should be felt at the level of the symphysis pubis. b. The fundus at the level of the umbilicus indicates 20 weeks’ gestation. In this question, the fact that this patient is a multigravida is not relevant. Uterine growth should be consistent for both primigravidas and multigravidas. c. At 28 weeks’ gestation, the fundus should be felt 8 cm above the level of the umbilicus. d. At 36 weeks’ gestation, the fundus should be felt at the xiphoid process. 31. A patient at 28 weeks’ gestation was last seen in the prenatal clinic at 24 weeks’ gestation. Which of the following changes should the nurse bring to the attention of the Certified Nurse Midwife? a. Weight change from 128 pounds to 132 pounds b. Pulse change from 88 bpm to 92 bpm c. Blood pressure change from 110/70 to 140/90 d. Respiratory change from 16 rpm to 20 rpm Feedback a. A weight change of approximately 4 pounds in 4 weeks is normal in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. b. This pulse rate change is within normal limits. c. A blood pressure elevation to 140/90 is a sign of mild preeclampsia. d. This respiratory rate change is within normal limits. 32. The clinic nurse includes screening for domestic violence in the first prenatal visit for all patients. An appropriate question would be: a. This is something that we ask everyone. Do you feel safe in your current living environment and relationships? b. This is something we ask everyone. Do you have any abuse in your life right now? c. Is your partner threatening or harming you in any way right now? d. I need to ask you, do you feel safe from abuse right now? Feedback a. Intimate partner violence is a difficult subject to discuss, and the nurse may fear insulting or psychologically hurting the patient more. A nonthreatening approach is to ask patients directly whether they feel safe going home and whether they have been hurt physically, emotionally, or sexually by a past or present partner. b. Intimate partner violence is a difficult subject to discuss, and the nurse may fear insulting or psychologically hurting the patient more. A nonthreatening approach is to ask patients directly whether they feel safe going home rather than asking if they have any abuse, as women may define abuse differently than care providers. c. Intimate partner violence is a difficult subject to discuss, and the nurse may fear insulting or psychologically hurting the patient more. A nonthreatening approach is to ask patients directly whether they feel safe going home and whether they have been hurt physically, emotionally, or sexually by a past or present partner. d. Intimate partner violence is a difficult subject to discuss, and the nurse may fear insulting or psychologically hurting the patient more. A nonthreatening approach is to ask patients directly whether they feel safe going home rather than asking if they have any abuse, as women may define abuse differently than care providers. Multiple Response 33. An 18-year-old woman at 23 weeks’ gestation tells the nurse that she has fainted two times. The nurse teaches about the warning signs that often precede syncope so that she can sit or lie down to prevent personal injury. Warning signs include (select all that apply): a. Sweating b. Nausea c. Chills d. Yawning Sweating is a warning sign that often precedes syncope. Syncope (a trandient loss of consciousness and postural tone with spontaneous recovery) during pregnancy is frequently attributed to orthostatic hypotension or inferior vena cava compression by the gravid uterus. Nausea and yawning are warning signs that often precede syncope. Lightheadedness, sweating, nausea, yawning, and feelings of warmth are warning signs that often precede syncope. Chills are not a warning sign that often precede syncope. 34. The perinatal nurse teaches the student nurse about the physiological changes in pregnancy that most often contribute to the increased incidence of urinary tract infections. These changes include (select all that apply): a. Relaxation of the smooth muscle of the urinary sphincter b. Relaxation of the smooth muscle of the bladder c. Inadequate emptying of the bladder d. Increased incidence of bacteriuria 35. The clinic nurse discusses normal bladder function in pregnancy with a 22-year-old pregnant woman who is now in her 29th gestational week. The nurse explains that at this time in pregnancy, it is normal to experience (select all that apply): a. Urinary frequency b. Urinary urgency c. Nocturia d. Incontinence 36. A 32-year-old woman now at 32 weeks’ gestation is complaining of right-sided sharp abdominal pain. The patient is examined by the clinic nurse and given information about abdominal discomfort in pregnancy. She is also instructed to seek immediate attention if she (select all that apply): a. Has heartburn b. Has chills or a fever c. Feels decreased fetal movements d. Has increased abdominal pain Heartburn is a common discomfort throughout pregnancy. Because the appendix is pushed upward and posterior by the gravid uterus, the typical location of pain is not a reliable indicator for a ruptured appendix during pregnancy. The pain should gradually subside, but if it persists or is accompanied by fever, a change in bowel habits, or decreased fetal movement, the patient should promptly contact her medical provider. 37. The clinic nurse talks with Suzy, a pregnant woman at 9 weeks’ gestation who has just learned of her pregnancy. Suzy’s nausea and vomiting are most likely caused by (select all that apply): a. Increased levels of estrogen b. Increased levels of progesterone c. An altered carbohydrate metabolism d. Increased levels of human chorionic gonadotropin 38. The clinic nurse encourages all pregnant women to increase their water intake to at least 8 to 10 glasses per day in order to (select all that apply): a. Decrease the risk of constipation b. Decrease the risk of bile stasis c. Decrease their feelings of fatigue d. Decrease the risk of urinary tract infections 39. The perinatal nurse examines the thyroid gland as part of the physical examination of Savannah, a pregnant woman who is now at 16 weeks’ gestation. The perinatal nurse informs Savannah that during pregnancy (select all that apply): a. Increased size of the thyroid gland is normal b. Increased function of the thyroid gland is normal c. Decreased function of the thyroid gland is normal d. The thyroid gland will return to its normal size and function during the postpartal period 40. The clinic nurse describes the respiratory system changes common to pregnancy to the new nurse. These changes include (select all that apply): a. An increased tidal volume b. A decreased airway resistance c. An increased chest circumference d. An increased airway resistance 41. The clinic nurse teaches the new nurse about pregnancy-induced blood clotting changes. The nurse explains that a pregnant woman is at risk for venous thrombosis due to (select all that apply): a. Increased fibrinogen volume b. Increased blood factor V c. Increased blood factor X d. Venous stasis 42. The clinic nurse describes possible interventions for the pregnant woman who is experiencing pain and numbness in her wrists. The nurse suggests (select all that apply): a. Elevating the arms and wrists at night b. Reassessment during the postpartum period c. The use of “cock splints” to prevent wrist flexion d. Massaging the hands and wrists with alcohol 43. The clinic nurse advocates for smoking cessation during pregnancy. Potential harmful effects of prenatal tobacco use include (select all that apply): a. Preterm birth b. Gestational hypertension c. Gestational diabetes d. Low birth weight 44. Asking the pregnant woman about her use of recreational drugs is an essential component of the prenatal history. Harmful fetal effects that may occur from recreational drugs include (select all that apply): a. Miscarriage/spontaneous abortion b. Low birth weight c. Macrosomia d. Post-term labor/birth 45. The clinic nurse schedules Tracy for her first prenatal appointment with the certified nurse-midwife (CNM) in the clinic. Tracy has appropriate questions for her potential health-care provider that include (select all that apply): a. Complementary and alternative methods used during labor and birth b. An opportunity to meet other providers in the practice c. Beliefs and practices concerning an episiotomy and an epidural anesthetic d. Whether the nurse-midwife will be continually available for support during labor 46. The clinic nurse explains to Margaret, a newly diagnosed pregnant woman at 10 weeks’ gestation, that her rubella titer indicates that she is not immune. Margaret should be advised to (select all that apply): a. Avoid contact with all children b. Be retested in 3 months c. Receive the rubella vaccine postpartum d. Report signs or symptoms of fever, runny nose, and generalized red rash to the health-care provider 47. An overweight or obese pre-pregnancy weight increases the risk for which poor maternal outcomes? (Select all that apply.) a. Preeclampsia b. Hemorrhage c. Difficult delivery d. Vaginal infections 48. Presumptive signs of pregnancy include (select all that apply): a. Nausea b. Fatigue c. Ballottement d. Amenorrhea . 49. Physiologic changes that occur in the renal system during pregnancy predispose the pregnant woman to urinary tract infections (UTIs). Symptoms of a UTI include (select all that apply): a. Dysuria b. Hematuria c. Urgency d. Delayed urination 50. Urinary tract infection (UTI) prevention measures during pregnancy include counseling the pregnant woman to (select all that apply): a. Delay urination until bladder is full b. Limit hydration c. Wipe from front to back d. Urinate after intercourse 51. Interventions for low back pain during pregnancy should include (select all that apply): a. Utilizing proper body mechanics b. Applying ice or heat to affected area c. Avoiding pelvic rock and pelvic tilt d. Using additional pillows for support during sleep 52. Jorgina is a 24-year-old pregnant woman at 26 weeks’ gestation. This is Jorgina’s third pregnancy, and her obstetrical history includes one full-term birth, one preterm birth, and two living children. Today Jorgina arrives at the clinic with complaints of fatigue, insomnia, and backache. She reports that she is a nurse on an oncology unit and is worried about continuing with working her 12-hour shifts. The perinatal nurse identifies concerns in Jorgina’s history and work environment including (select all that apply): a. Risk of preterm birth b. Presence of chemotherapeutic agents c. Requirement for heavy lifting d. History of diabetes 53. The clinic nurse is assessing the complete blood count results for Kim-Ly, a 23-year-old pregnant woman. Kim-Ly’s hemoglobin is 9.8 g/dL. This laboratory finding places Kim-Ly’s pregnancy at risk for (select all that apply): a. Preterm birth b. Placental abruption c. Intrauterine growth restriction d. Thrombocytopenia 54. Teera is a 22-year-old woman who is experiencing her third pregnancy. Her obstetrical history includes one first-trimester elective abortion and one first-trimester spontaneous abortion. Teera is a semi-vegetarian who drinks milk and eats yogurt and fish as part of her daily intake. The perinatal nurse discusses Teera’s diet with her as she may be deficient in (select all that apply): a. Iron b. Magnesium c. Zinc d. Vitamin B12 55. During the initial antenatal visit, the clinic nurse asks questions about the woman’s nutritional intake. Specific questions should include information pertaining to (select all that apply): a. Preferred foods b. The presence of cravings c. Use of herbal supplements d. Aversions to certain foods and odors 56. The perinatal nurse talks to the prenatal class attendees about guidelines for exercise in pregnancy. Recommended guidelines include (select all that apply): a. Stopping if the woman is tired b. Bouncing and slowly arching the back c. Increasing fluid intake throughout the physical activity d. Maintaining the ability to walk and talk during exercise Short Answer 57. Lesions at the gum line that bleed easily 58. Anterior convexity of the lumbar spine Refer To: Glossary 59. Increased saliva production Refer To: Glossary 60. Reflux of the stomach contents into the esophagus Refer To: Glossary 61. Severe itching due to stasis of bile in the liver Refer To: Glossary 62. Nosebleeds Refer To: Glossary True/False 63. The clinic nurse speaks with the student nurse prior to the physical examination of a pregnant woman who is 32 weeks’ gestation. The clinic nurse explains that the heart sounds heard in pregnancy are usually S1 and S3 with a possible murmur related to increased cardiac output. 64. Cecilia, a pregnant woman at 30 weeks’ gestation, has her vital signs assessed during a routine prenatal visit. Cecilia’s blood pressure has remained at 110/70 for the last few visits, and her pulse rate has increased from 70 to 80 beats per minute. These findings would be considered normal at this time in pregnancy. 65. The clinic nurse knows that every time a woman of childbearing age comes in to the office for a health maintenance visit, she should be counseled about the benefits of daily folic acid supplementation. 66. The perinatal nurse recommends strengthening exercises during pregnancy, as this can improve posture and increase energy levels. 67. The perinatal nurse explains to the new nurse that ptyalize is a condition more acute than the normal nausea and vomiting of pregnancy and is often associated with dehydration, hypokalemia, and weight loss. Fill-in-the-Blank 68. The clinic nurse explains to the new nurse that during pregnancy, the maternal metabolism is altered to support the pregnancy by the hormones __________ and __________, which are produced by the anterior __________ gland. 69. During the prenatal class, the perinatal nurse describes factors that may initiate the process of labor. One of these factors is the production of __________, which are found in the uterine __________ and are released from the __________ at term as it softens and dilates. 70. The perinatal nurse describes common complaints of pregnancy to the prenatal class attendees. Nasal __________, medically termed “__________ of pregnancy,” is caused by increased levels of estrogen and progesterone. Nasal stuffiness and congestion (rhinitis of pregnancy) are common complaints during pregnancy. The nurse should educate the patient about these normal changes and offer reassurance. Increasing oral fluid intake helps to keep the mucus thin and easier to mobilize. 71. The clinic nurse promotes a diet rich in vitamin __________ during the third trimester to prevent the possibility of __________ rupture of the membranes. 72. The clinic nurse monitors the blood pressure and assesses a woman’s urine at each prenatal visit to assess for signs or symptoms of __________. A previous history or the presence of a __________ are also risk factors. 73. The clinic nurse is aware of the importance of chlamydia screening during pregnancy. Chlamydia transmission to the infant at __________ may result in __________. 74. The prenatal nurse describes the need for __________ and __________ screening at the first antenatal visit. If the pregnant woman is not immune, she will be counseled to avoid contact with young children who have a rash and could be infectious. 75. The prenatal nurse cautions a pregnant woman about Caesar salad consumption during pregnancy or any source of __________ or __________ milk. 76. The clinic nurse describes to the student nurse that __________ is excessive saliva production in pregnancy. This condition is most likely caused by increased __________ levels. 77. The clinic nurse talks with the newly diagnosed pregnant woman about the nausea that the woman is experiencing in this pregnancy. The clinic nurse suggests eating __________ meals more often, remaining __________ after eating, and the using __________ techniques. 78. The clinic nurse understands that the physiological changes of pregnancy include vascular relaxation from the effects of __________ and impaired venous circulation from pressure exerted by the enlarged uterus, predisposing the pregnant woman to __________. 79. The perinatal nurse knows that __________, which is the eating of nonnutritive substances, is a common __________. ANS: pica; eating disorder Pica, the consumption of nonnutritive substances or food, is a common eating disorder that can affect pregnancy. Substances that are most often ingested include clay, dirt, cornstarch, and ice. Matching The clinic nurse understands the meaning of the following terms related to pregnancy care. Match these terms with the definitions listed below: Advocacy Lordosis Amenorrhea Ballottement Striae gravidarum Preterm birth 80. Passive movement of the unengaged fetus allottement Refer To: Glossary 81. Verbalizing someone else’s wishes if he or she is unable to do so dvocacy Refer To: Chapter 2 82. Absence of menses menorrhea Refer To: Glossary 83. Curvature of the spine ANS: Lordosis Refer To: Glossary 84. Stretch marks ANS: Striae gravidarum Refer To: Glossary Chapter 5: Psycho-Social-Cultural Aspects of the Antepartum Period Multiple Choice 1. Sally is in her third trimester and has begun to sing and talk to the fetus. Sally is probably exhibiting signs of: a. Mental illness b. Delusions c. Attachment d. Crisis Feedback a. This is normal maternal–fetal adaptation. b. Delusions are not real, and the fetus is real. c. Correct, because talking to the fetus is a sign of positive maternal adaptation. All other answers indicate pathology. d. Interacting with the fetus in utero represents normal development of attachment to the fetus. 2. What is the most common expected emotional reaction of a woman to the news that she is pregnant? a. Jealousy b. Acceptance c. Ambivalence d. Depression Feedback a. Others in the family may be jealous of the fetus, but that is not a common maternal response. b. Acceptance of the pregnancy typically occurs later in the pregnancy. c. Ambivalence is a normal expected reaction to the news of pregnancy, whether or not the pregnancy is planned or wanted. d. This would represent an abnormal emotional response to pregnancy. 3. Which of the following information regarding sexual activity would the nurse give a pregnant woman who is 35 weeks’ gestation? a. Sexual activity should be avoided from now until 6 weeks postpartum. b. Sexual desire may be affected by nausea and fatigue. c. Sexual desire may be increased due to increased pelvic congestion. d. Sexual activity may require different positions to accommodate the woman’s comfort. Feedback a. There are no contraindications to sexual activity during this time for a normally progressing pregnancy. b. Nausea and fatigue affect sexual desire during the first trimester, not the third. c. Increased sexual desire r/t increased pelvic congestion is a characteristic of the second trimester, not the third. d. Correct. An enlarging abdomen creates feelings of awkwardness and bulkiness and may require couples to modify intercourse positions for the pregnant woman’s comfort. 4. Which statement best exemplifies adaptation to pregnancy in relation to the adolescent? a. Adolescents adapt to motherhood in a similar way to other childbearing women. b. Social support has very little effect on adolescent adaptation to pregnancy. c. The pregnant adolescent faces the challenge of multiple developmental tasks. d. Pregnant adolescents of all ages can be capable and active participants in health-care decisions. Feedback a. Adolescents must cope with the conflicting developmental tasks of pregnancy and adolescence at the same time. b. Social support has been associated with a more positive adaptation to mothering for adolescents. c. Correct. Pregnant adolescents face conflicting and multiple developmental tasks of pregnancy and adolescence at the same time. d. By late adolescence (ages 17 to 20) this can occur, but early adolescents are oriented toward the present and are self-centered, and often pregnancy at this age is a result of abuse or coercion. 5. Jane’s husband Brian has begun to put on weight. What is this a possible sign of? a. Culturalism syndrome b. Couvade syndrome c. Moratorium phased. Attachment Feedback a. This is not related to culture. b. Correct. Couvade syndrome has symptoms that mimic changes of pregnancy. c. Moratorium phase represents one of the phases of the father’s responses to pregnancy. d. Attachment is reflected in behaviors. 6. Cathy is pregnant for the second time. Her son, Steven, has just turned 2 years old. She asks you what she should do to help him get ready for the expected birth. What is the nurse’s most appropriate response? a. Steven will probably not understand any explanations about the arrival of the new baby, so Cathy should do nothing. b. If Steven’s sleeping arrangements need to be changed, it should be done well in advance of the birth. c. Steven should come to the next prenatal visit and listen to the fetal heartbeat to encourage sibling attachment. d. Steven should be encouraged to plan an elaborate welcome for the newborn. Feedback a. This applies to very young children under the age of 2. b. Children still sleeping in a crib should be moved to a bed at least 2 months before the baby is due, as this age group is particularly sensitive to disruptions of the physical environment. c. This is not appropriate for a 2-year-old but may be appropriate for older age groups. d. This is not appropriate for a 2-year-old but may be appropriate for older age groups. 7. The nurse is interviewing a pregnant client who states she plans to drink chamomile tea to ensure an effective labor. The nurse knows that this is an example of: a. Cultural prescription b. Cultural taboo c. Cultural restriction d. Cultural demonstration Feedback a. Correct. Cultural prescription is an expected behavior of the pregnant woman during the childbearing period. b. Taboos are cultural restrictions believed to have serious supernatural consequences. Drinking chamomile tea would not be in this category. c. Restrictions are activities during the childbearing period which are limited for the pregnant woman. Drinking chamomile tea would not be in this category. d. Demonstration is not a term that is used in relation to cultural behaviors. 8. Which of the following would be a priority for the nurse when caring for a pregnant woman who has recently emigrated from another country? a. Help her develop a realistic, detailed birth plan. b. Identify her support system. c. Teach her about expected emotional changes of pregnancy. d. Refer her to a doula for labor support. Feedback a. A detailed birth plan may not be culturally appropriate and is not first priority. b. Correct, because lack of social support has been correlated with an increased risk of pregnancy complications and difficult adaptation to pregnancy. Pregnant women who are recent immigrants face many challenges in obtaining needed social support, and the nurse should first identify her support system to plan further interventions and referrals. c. There may be cultural variations in emotional changes of pregnancy. d. The nurse should first identify her support system before planning further interventions and referrals. 9. A pregnant client at 20 weeks’ gestation comes to the clinic for her prenatal visit. Which of the following client statements would indicate a need for further assessment? a. “I hate it when the baby moves.” b. “I’ve started calling my mom every day.” c. “My partner and I can’t stop talking about the baby.” d. “I still don’t know much time I’m going to take off work after the baby comes.” Feedback a. Experiencing quickening as unpleasant may be a sign of maladaptation to pregnancy and needs further assessment by the nurse. b. This is an expected finding in maternal adaptation and development of the maternal role. c. This is an expected finding in maternal adaptation and development of the maternal role. d. At 20 weeks’ gestation, the client still has plenty of time to process this decision. 10. A pregnant client asks the nurse why she should attend childbirth classes. The nurse’s response would be based on which of the following information? a. Attending childbirth class is a good way to make new friends. b. Childbirth classes will help new families develop skills to meet the challenges of childbirth and parenting. c. Attending childbirth classes will help a pregnant woman have a shorter labor. d. Childbirth classes will help a pregnant woman decrease her chance of having a cesarean delivery. Feedback a. There may be a beneficial effect of childbirth classes, but this is not the primary goal of childbirth education. b. Correct. These are the stated goals of childbirth education (ICEA, Lamaze). c. Evidence remains inconclusive regarding linking attendance at childbirth classes with a decreased incidence of cesarean section and shorter labors. d. Evidence remains inconclusive regarding linking attendance at childbirth classes with a decreased incidence of cesarean section and shorter labors. 11. A woman presents for prenatal care at 6 weeks’ gestation by LMP. Which of the following findings would the nurse expect to see? a. Multiple pillow orthopnea b. Maternal ambivalence c. Fundus at the umbilicus d. Pedal and ankle edema Feedback a. Orthopnea is a common complaint of women during the third trimester. b. Ambivalence is a common feeling of women during the first trimester. c. The fundus should be at the umbilicus at 20 weeks’ gestation. d. Dependent edema is a common complaint of women during the third trimester. 12. A first-time father is experiencing couvade syndrome. He is likely to exhibit which of the following symptoms or behaviors? a. Urinary frequency b. Hypotension c. Bradycardia d. Prostatic hypertrophy Feedback a. Urinary frequency is a common symptom of couvade. b. The father’s blood pressure is not usually affected. c. The father’s heart rate is not usually affected. d. Prostatic changes are not related to couvade. 13. When providing a psychosocial assessment on a pregnant woman at 21 weeks’ gestation, the nurse would expect to observe which of the following signs? a. Ambivalence b. Depression c. Anxiety d. Happiness Feedback a. Ambivalence is often seen during the first trimester. b. The nurse would not expect to see depression at any time during the pregnancy. c. The patient may express some anxiety near the time of delivery. d. The nurse would expect the patient to exhibit signs of happiness at this time. 14. An example of a cultural prescriptive belief during pregnancy is: a. Remain active during pregnancy b. Coldness in any form should be avoided c. Do not have your picture taken d. Avoid sexual intercourse during the third trimester The belief that the patient should remain active during pregnancy is the only example of a cultural prescriptive belief. All of the other answers are examples of cultural restrictive beliefs. 15. Taboos are cultural restrictions that: a. Have serious supernatural consequences b. Have serious clinical consequences c. Have superstitious consequences d. Are functional and neutral practices Taboos are believed to have serious supernatural consequences. Taboos are not known to have clinical or superstitious consequences and are not functional or neutral practices. 16. Jenny, a 21-year-old single woman, comes for her first prenatal appointment at 31 weeks’ gestation with her first pregnancy. The clinic nurse’s most appropriate statement is: a. “Jenny, it is late in your pregnancy to be having your first appointment, but it is nice to meet you and I will try to help you get caught up in your care.” b. “Jenny, have you had care in another clinic? I can’t believe this is your first appointment!” c. “Jenny, by the date of your last menstrual period, you are 31 weeks and now that you are finally here, we need you to come monthly for the next two visits and then weekly.” d. “Jenny, by your information, you are 31 weeks’ gestation in this pregnancy. Do you have questions for me before I begin your prenatal history and information sharing?” Feedback a. The initial interview time with the patient should be used to build a positive, nonthreatening relationship and to gain her confidence by respecting her choices and advocating for continued prenatal care that is woman centered. b. The initial interview time with the patient should be used to build a positive, nonthreatening relationship and to gain her confidence by respecting her choices and advocating for continued prenatal care and not making assumptions about prior care. The prenatal nurse’s objective is to provide a user-friendly service that is efficient, effective, caring, and patient centered. c. The initial interview time with the patient should be used to build a positive, nonthreatening, and nonjudgmental relationship and to gain her confidence by respecting her choices and advocating for continued prenatal care. d. The initial interview time with the patient should be used to build a positive, nonthreatening relationship and to gain her confidence by respecting her choices and advocating for continued prenatal care. The prenatal nurse’s objective is to provide a user-friendly service that is efficient, effective, caring, and patient centered. 17. The clinic nurse visits with Wayne, a 32-year-old man whose partner is pregnant for the first time and is at 12 weeks. Wayne describes nausea and vomiting, fatigue, and weight gain. His symptoms are best described as: a. Influenza b. Couvade syndrome c. Acid reflux d. Cholelithiasis Feedback a. This cluster of symptoms is indicative of couvade syndrome, the experience of maternal signs and symptoms of pregnancy. b. In preparation for parenthood, the male partner moves through a series of developmental tasks. During the first trimester, the father begins to deal with the reality of the pregnancy and may worry about financial strain and his ability to be a good father. Feelings of confusion and guilt often surface with the recognition that he is not as excited about the pregnancy as his partner, and couvade syndrome, the experience of maternal signs and symptoms, may develop. c. This cluster of symptoms is indicative of couvade syndrome, the experience of maternal signs and symptoms of pregnancy. d. This cluster of symptoms is indicative of couvade syndrome, the experience of maternal signs and symptoms of pregnancy. Multiple Response 18. The clinic nurse encourages paternal attachment during pregnancy by including the father in (select all that apply): a. Prenatal visits b. Ultrasound appointments c. Prenatal class information d. History taking and obtaining prenatal screening information , c, d Pregnancy is psychologically stressful for men; some enjoy the role of nurturer, but others feel alienated and begin to stray from the relationship. The nurse can be instrumental in promoting early paternal attachment. Involvement of the father during examinations and tests and prenatal classes, along with thorough explanations of the need for them, can minimize the father’s feelings of being left out. A history and prenatal screening should be conducted at the first prenatal visit with the woman alone to ensure confidentiality and an open discussion of any problems or concerns she may have. The history should include information about the current pregnancy; the obstetric and gynecologic history; and a cultural assessment, and a medical, nutritional, social, and family (including the father’s) medical history. 19. The perinatal nurse screens all pregnant women early in pregnancy for maternal attachment risk factors, which include (select all that apply): a. Adolescence b. Low educational level c. History of depression d. A strong support system for the pregnancy , b, c Maternal attachment to the fetus is an important area to assess and can be useful in identifying families at risk for maladaptive behaviors. The nurse should assess for indicators such as unintended pregnancy, domestic violence, difficulties in the partner relationship, sexually transmitted infections, limited financial resources, substance use, adolescence, poor social support systems, low educational level, the presence of mental conditions, or adolescence that might interfere with the patient’s ability to bond with and care for the infant. A strong support system can facilitate the patient’s ability to bond with and care for the infant. 20. Strategies for culturally responsive care include (select all that apply): a. Practicing ethnocentrism b. Applying stereotyping c. Examining one’s own biases d. Learning another language , d The only actions among the choices that are culturally responsive are examining one’s own biases and learning another language. Ethnocentrism and stereotyping are not culturally responsive actions. Fill-in-the-Blank 21. The clinic nurse talks with Becky, a 16-year-old woman who is now 28 weeks’ gestation. Today’s visit is only the second prenatal appointment that Becky has kept. The nurse wonders if Becky’s failure to come for routine prenatal checks is, in part, related to an adolescent’s orientation to the __________, rather than to the __________. ANS: present; future The adolescent may not seek prenatal care unless pressured by authority figures or peers to do so. By nature, adolescents are not future oriented. Hence, the pregnant adolescent may not be able to readily accept the reality of the unborn child. 22. According to Rubin, the mother-to-be needs to accept the pregnancy and incorporate it into her own reality and __________. This process is known as “__________.” ANS: self-concept; binding in The mother-to-be needs to accept the pregnancy and incorporate it into her own reality and self-concept. This process is known as “binding in.” Acceptance of the child is critical to a successful adjustment to the pregnancy. Acceptance must come from the expectant woman as well as from others. 23. The clinic nurse asks pregnant women about their acceptance and planning for this pregnancy as a component of domestic violence screening. The nurse is aware that a(n) __________ pregnancy __________ the risk for domestic violence. ANS: unplanned; increases Intimate partner violence (IPV) may occur for the first time during pregnancy, or the nurse may identify evidence during the physical examination that is suspicious of ongoing physical abuse. Acceptance of pregnancy may be delayed if it was unplanned or unwanted. As a women’s advocate, nurses have a duty to be observant, to actively listen, and to use communication skills to gain clarification and understanding. Chapter 6: Antepartal Tests Multiple Choice 1. Your pregnant patient is in her first trimester and is scheduled for an abdominal ultrasound. When explaining the rationale for early pregnancy ultrasound, the best response is: a. “The test will help to determine the baby’s position.” b. “The test will help to determine how many weeks you are pregnant.” c. “The test will help to determine if your baby is growing appropriately.” d. “The test will help to determine if you have a boy or girl.” Feedback a. Fetal position during pregnancy changes, and position in the first trimester is not indicative of position later in pregnancy. b. Fetal growth and size are fairly consistent during the first trimester and are a reliable indicator of the weeks of gestation. c. Fetal growth is best assessed later in pregnancy. d. The primary rationale for ultrasounds is not to determine gender. 2. Your pregnant patient is having maternal alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) screening. She does not understand how a test on her blood can indicate a birth defect in the fetus. The best reply by the nurse is: a. “We have done this test for a long time.” b. “If babies have a neural tube defect, alpha-fetoprotein leaks out of the fetus and is absorbed into your blood, causing your level to rise. This serum blood test detects that rise.” c. “Neural tube defects are a genetic anomaly, and we examine the amount of alpha-fetoprotein in your DNA.” d. “If babies have a neural tube defect, this results in a decrease in your level of alpha-fetoprotein.” Feedback a. This response does not explain AFP screening. b. When a neural tube defect is present, AFP is absorbed in the maternal circulation, resulting in a rise in the maternal AFP level. c. AFP testing is not related to DNA. d. Fetal neural tube defects result in an increase in maternal AFP. 3. The primary complications of amniocentesis are: a. Damage to fetal organs b. Puncture of umbilical cord c. Maternal pain d. Infection Feedback a. Amniocentesis is done under ultrasound guidance, and damage to fetal organs is very rare. b. Amniocentesis is done under ultrasound guidance, and damage to the umbilical cord is very rare. c. Amniocentesis is done under local anesthesia, and maternal pain is generally minimal. d. Amniocentesis involves insertion of a needle into the amniotic sac, and infection is the primary complication. 4. Your patient is 34 weeks pregnant and during a regular prenatal visit tells you she does not understand how to do “kick counts.” The best response by the nurse would be to explain: a. “Here is an information sheet on how to do kick counts.” b. “It is not important to do kick counts because you have a low-risk pregnancy.” c. “Fetal kick counts are not a reliable indicator of fetal well-being in the third trimester.” d. “Fetal movements are an indicator of fetal well-being. You should count twice a day, and you should feel 10 fetal movements in 2 hours.” Feedback a. Providing written information may not be enough, and the patient may need a verbal explanation. b. Kick counts are indicated for all pregnancies. c. Kick counts are a reliable indicator of fetal well-being after 32 to 34 weeks’ gestation. d. This response provides the patient with information on how to do kick counts and the rationale for doing kick counts and criteria for normal fetal movement. 5. Your patient is a 37-year-old pregnant woman who is 5 weeks pregnant and is considering genetic testing. During your discussion, the woman asks the nurse what the advantages of chorionic villus sampling (CVS) are over amniocentesis. The best response is: a. “You will need anesthesia for amniocentesis, but not for CVS.” b. “CVS is a faster procedure.” c. “CVS provides more detailed information than amniocentesis.” d. “CVS can be done earlier in your pregnancy, and the results are available more quickly.” Feedback a. Anesthesia is not done for either procedure. b. The length of time for either procedure is similar. c. Both amniocentesis and CVS provide the same information. d. CVS can be done earlier in gestation. 6. The clinic nurse meets with Rebecca, a 30-year-old woman who is experiencing her first pregnancy. Rebecca’s quadruple marker screen result is positive at 17 weeks’ gestation. The nurse explains that Rebecca needs a referral to: a. A genetics counselor/specialist b. An obstetrician c. A gynecologist d. A social worker Feedback a. All women should be offered screening with maternal serum markers. The Triple Marker screen and the Quadruple Marker screen test for the presence of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), estradiol, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), and other markers. These tests screen for potential neural tube defects, Down syndrome, and Trisomy 18. If the screen is positive, the woman should be referred to a genetics specialist for counseling, and further testing, such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis, should be performed. b. If genetic screening is positive, the woman should be referred to a genetics specialist for counseling, and further testing, such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis, should be performed. c. If genetic screening is positive, the woman should be referred to a genetics specialist for counseling, and further testing, such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis, should be performed. d. If genetic screening is positive, the woman should be referred to a genetics specialist for counseling, and further testing, such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis, should be performed. 7. A 37-year-old woman who is 17 weeks pregnant has had an amniocentesis. Before discharge, the nurse teaches the woman to call her doctor if she experiences which of the following side effects? a. Pain at the puncture site b. Macular rash on the abdomen c. Decrease in urinary output d. Cramping of the uterus Feedback a. It is normal for the patient to experience pain at the puncture site. b. A rash is not an expected complication. c. Oliguria is not an expected complication. d. The woman should report any uterine cramping. Although rare, amniocentesis could stimulate preterm labor. 8. A laboratory report indicates the L/S ratio (lecithin/sphingomyelin) results from an amniocentesis of a gravid patient with preeclampsia are 2:1. The nurse interprets the result as which of the following? a. The baby’s lung fields are mature. b. The mother is high risk for hemorrhage. c. The baby’s kidneys are functioning poorly. d. The mother is high risk for eclampsia. Feedback a. An L/S ratio of 2:1 usually indicates that the fetal lungs are mature. b. L/S ratios are unrelated to maternal blood loss. c. L/S ratios are unrelated to fetal renal function. d. L/S ratios are unrelated to maternal risk for becoming eclamptic. Chapter 7: High-Risk Antepartum Nursing Care Multiple Choice 1. A client on 2 gm/hr. of magnesium sulfate has decreased deep tendon reflexes. Identify the priority nursing assessment to ensure client safety. a. Assess uterine contractions continuously. b. Assess fetal heart rate continuously. c. Assess urinary output. d. Assess respiratory rate. Feedback a. Monitoring contractions does not indicate magnesium toxicity. b. Magnesium sulfate will decrease fetal variability and not provide an accurate assessment of magnesium toxicity. c. Urinary output does not correlate to decreased deep tendon reflexes. d. Correct. Respiratory effort and deep tendon reflexes (DTRs) are involuntary, and a decrease in DTRs could indicate the risk of magnesium sulfate toxicity and the risk for decreased respiratory effort. 2. A pregnant client with a history of multiple sexual partners is at highest risk for which of the following complications: a. Premature rupture of membranes b. Gestational diabetes c. Ectopic pregnancy d. Pregnancy-induced hypertension Feedback a. Multiple partners do not increase a woman’s risk of premature rupture of membranes. b. Genetics and client diet and weight are contributing factors to gestational diabetes. c. Correct. A history of multiple sexual partners places the client at a higher risk of having contracted a sexually transmitted disease that could have ascended the uterus to the fallopian tubes and caused fallopian tube blockage, placing the client at high risk for an ectopic pregnancy. d. Multiple sexual partners are not a risk factor for pregnancy-induced hypertension. 3. Identify the hallmark of placenta previa that differentiates it from abruptio placenta. a. Sudden onset of painless vaginal bleeding b. Board-like abdomen with severe pain c. Sudden onset of bright red vaginal bleeding d. Severe vaginal pain with bright red bleeding Feedback a. Correct. When the placenta attaches to the lower uterine segment near or over the cervical os, bleeding may occur without the onset of contractions or pain. b. The hallmark for abruptio placenta is pain and a board-like abdomen. c. Bright red bleeding could be related to abruptio placenta, placenta previa, or other complications of pregnancy. d. Pain is not a hallmark of placenta previa. 4. Which of the following assessments would indicate instability in the client hospitalized for placenta previa? a. BP <90/60 mm/Hg, Pulse <60 BPM or >120 BPM b. FHR moderate variability without accelerations c. Dark brown vaginal discharge when voiding d. Oral temperature of 99.9F Feedback a. A decrease in BP accompanied by bradycardia or tachycardia is an indication of hypovolemic shock. b. FHR with moderate variability can be absent of accelerations during fetal sleep cycles or after maternal sedation. c. Bright red vaginal bleeding is an indication of current bleeding. d. Oral temperature may fluctuate based on the client’s hydration status. It should be reassessed. Cause for concern is a temperature of 100.4F or more. 5. During pregnancy, poorly controlled asthma can place the fetus at risk for: a. Hyperglycemia b. IUGR c. Hypoglycemia d. Macrosomia Feedback a. Maternal asthma does not place the fetus at risk for hyperglycemia. b. Compromised pulmonary function can lead to decompensation and hypoxia that decrease oxygen flow to the fetus and can cause intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). c. Asthma does not directly affect glycemic control. d. A fetus experiencing hypoxia would be small for gestational age, not large for gestational age. 6. Which of the following nursing diagnoses is of highest priority for a client with an ectopic pregnancy who has developed disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)? a. Risk for deficient fluid volume b. Risk for family process interrupted c. Risk for disturbed identity d. High risk for injury Feedback a. Correct. The client is at high risk for hypovolemia which is life threatening and takes precedence over any psychosocial or less pressing diagnoses. b. This is a psychosocial diagnosis and is not life threatening. c. This is a psychosocial diagnosis and is not life threatening. d. The client is at risk for injury; however, the diagnosis of deficient fluid volume is more descriptive and has clearly defined goals and interventions. 7. Which of the following laboratory values is most concerning in a client with pregnancy-induced hypertension? a. Total urine protein of 200 mg/dL b. Total platelet count of 40,000 mm c. Uric acid level of 8 mg/dL d. Blood urea nitrogen 24 mg/dL Feedback a. The client’s urine protein is elevated. A urine protein of ≥300 mg/dL in a 24-hour collection is considered concerning. b. Correct. A platelet count of 50,000 is a critical value and should be reported to the health-care provider immediately. This client is at increased risk of hemorrhage. c. The uric acid level is only slightly elevated. d. The BUN is only slightly elevated. KEY: Integrated Process: Clinical Problem Solving | Cognitive Level: Comprehension | Content Area: Maternity | Client Need: Physiological Adaptation | Difficulty Level: Difficult 8. Which of the following medications administered to the pregnant client with GDM and experiencing preterm labor requires close monitoring of the client’s blood glucose levels? a. Nifedipine b. Betamethasone c. Magnesium sulfated. Indomethacin Feedback a. Nifedipine does not affect maternal blood glucose levels. b. Beta-sympathomimetics may stimulate hyperglycemia which will require an increased need for insulin. c. Magnesium sulfate does not affect blood glucose levels. d. Indomethacin does not affect blood glucose levels. 9. While educating the client with class II cardiac disease, at 28 weeks’ gestation, the nurse instructs the client to notify the physician if she experiences which of the following conditions? a. Emotional stress at work b. Increased dyspnea while resting c. Mild pedal and ankle edema d. Weight gain of 1 pound in 1 week Feedback a. Emotional stress increases cardiac workload; however, without symptoms of cardiac decompensation, this is not immediately concerning. b. Increasing dyspnea, at rest, can be a sign of cardiac decompensation leading to increased congestive heart failure. c. Mild edema during the third trimester is normal. However, increasing edema and pitting edema should be reported as they can be a sign of increasing CHF. d. A weight gain of 1 pound per week is expected during the third trimester. 10. The nurse working in a prenatal clinic is providing care to three primigravida patients. Which of the patient findings would the nurse highlight for the physician? a. 15 weeks, denies feeling fetal movement b. 20 weeks, fundal height at the umbilicus c. 25 weeks, complains of excess salivation d. 30 weeks, states that her vision is blurry Feedback a. This finding is normal. Quickening is usually felt between 16 and 20 weeks’ gestation. b. This finding is normal. The fundal height at 20 weeks’ gestation is usually at the level of the umbilicus. c. Excess salivation is a normal, albeit annoying, finding. d. Blurred vision is a sign of pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH). This finding should be reported to the woman’s health-care practitioner. 11. The perinatal nurse is assessing a woman in triage who is 34 + 3 weeks’ gestation in her first pregnancy. She is worried about having her baby “too soon,” and she is experiencing uterine contractions every 10 to 15 minutes. The fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. A vaginal examination performed by the health-care provider reveals that the cervix is closed, long, and posterior. The most likely diagnosis would be: a. Preterm labor b. Term labor c. Back labor d. Braxton-Hicks contractions Feedback a. Preterm labor (PTL) is defined as regular uterine contractions and cervical dilation before the end of the 36th week of gestation. Many patients present with preterm contractions, but only those who demonstrate changes in the cervix are diagnosed with preterm labor. b. Term labor occurs after 37 weeks’ gestation. c. There is no indication in this scenario that this is back labor. d. Braxton-Hicks contractions are regular contractions occurring after the third month of pregnancy. They may be mistaken for regular labor, but unlike true labor, the contractions do not grow consistently longer, stronger, and closer together, and the cervix is not dilated. Some patients present with preterm contractions, but only those who demonstrate changes in the cervix are diagnosed with preterm labor. 12. The perinatal nurse knows that the term to describe a woman at 26 weeks’ gestation with a history of elevated blood pressure who presents with a urine showing 2+ protein (by dipstick) is: a. Preeclampsia b. Chronic hypertension c. Gestational hypertension d. Chronic hypertension with superimposed preeclampsia Feedback a. Preeclampsia is a multisystem, vasopressive disease process that targets the cardiovascular, hematologic, hepatic, and renal and central nervous systems. b. Chronic hypertension is hypertension that is present and observable prior to pregnancy or hypertension that is diagnosed before the 20th week of gestation. c. Gestational hypertension is a nonspecific term used to describe the woman who has a blood pressure elevation detected for the first time during pregnancy, without proteinuria. d. The following criteria are necessary to establish a diagnosis of superimposed preeclampsia: hypertension and no proteinuria early in pregnancy (prior to 20 weeks’ gestation) and new-onset proteinuria, a sudden increase in protein—urinary excretion of 0.3 g protein or more in a 24-hour specimen, or two dipstick test results of 2+ (100 mg/dL), with the values recorded at least 4 hours apart, with no evidence of urinary tract infection; a sudden increase in blood pressure in a woman whose blood pressure has been well controlled; thrombocytopenia (platelet count lower than 100,000/mmC); and an increase in the liver enzymes alanine transaminase (ALT) or aspartate transaminase (AST) to abnormal levels. 13. A patient is receiving magnesium sulfate for severe preeclampsia. The nurse must notify the attending physician immediately of which of the following findings? a. Patellar and biceps reflexes of +4 b. Urinary output of 50 mL/hr c. Respiratory rate of 10 rpm d. Serum magnesium level of 5 mg/dL Feedback a. The magnesium sulfate has been ordered because the patient has severe pregnancy-induced hypertension. Patellar and biceps reflexes of +4 are symptoms of the disease. b. The urinary output must be above 25 mL/hr. c. The drop in respiratory rate may indicate that the patient is suffering from magnesium toxicity. The nurse should report the finding to the physician. d. The therapeutic range of magnesium is 4 to 7 mg/dL. 14. A woman in labor and delivery is being given subcutaneous terbutaline for preterm labor. Which of the following common medication effects would the nurse expect to see in the mother? a. Serum potassium level increases b. Diarrhea c. Urticaria d. Complaints of nervousness Feedback a. The nurse would not expect to see a rise in the mother’s serum potassium levels. b. The beta agonists are not associated with diarrhea. c. The beta agonists are not associated with urticaria. d. Complaints of nervousness are commonly made by women receiving subcutaneous beta agonists. 15. Which of the following signs or symptoms would the nurse expect to see in a woman with concealed abruptio placentae? a. Increasing abdominal girth measurements b. Profuse vaginal bleeding c. Bradycardia with an aortic thrill d. Hypothermia with chills Feedback a. The nurse would expect to see increasing abdominal girth measurements. b. Profuse vaginal bleeding is rarely seen in placental abruption and is never seen when the abruption is concealed. c. With excessive blood loss, the nurse would expect to see tachycardia. d. The nurse would expect to see a stable temperature. 16. A woman who has had no prenatal care was assessed and found to have hydramnios on admission to the labor unit and has since delivered a baby weighing 4500 grams. Which of the following complications of pregnancy likely contributed to these findings? a. Pyelonephritis b. Pregnancy-induced hypertension c. Gestational diabetes d. Abruptio placentae Feedback a. Pyelonephritis does not lead to the development of hydramnios or macrosomia. b. Pregnancy-induced hypertension does not lead to the development of hydramnios or macrosomia. c. Untreated gestational diabetics often have hydramnios and often deliver macrosomic babies. d. Abruptio placentae does not lead to the development of hydramnios or macrosomia. 17. For the patient with which of the following medical problems should the nurse question a physician’s order for beta agonist tocolytics? a. Type 1 diabetes mellitus b. Cerebral palsy c. Myelomeningocele d. Positive group B streptococci culture Feedback a. Beta agonists often elevate serum glucose levels. The nurse should question the order. b. Beta agonists are not contraindicated for patients with cerebral palsy. c. Beta agonists are not contraindicated for patients with myelomeningocele. d. Beta agonists are not contraindicated for patients with group B streptococci. 18. The nurse is caring for two laboring women. Which of the patients should be monitored most carefully for signs of placental abruption? a. The patient with placenta previa b. The patient whose vagina is colonized with group B streptococci c. The patient who is hepatitis B surface antigen positive d. The patient with eclampsia Feedback a. Patients with placenta previa are not especially high risk for placental abruption. b. Patients colonized with group B streptococci are not especially high risk for placental abruption. c. Patients who are hepatitis B surface antigen positive are not especially high risk for placental abruption. d. Patients with eclampsia are high risk for placental abruption. 19. The nurse is caring for a woman at 28 weeks’ gestation with a history of preterm delivery. Which of the following laboratory data should the nurse carefully assess in relation to this diagnosis? a. Human relaxing levels b. Amniotic fluid levels c. Alpha-fetoprotein levels d. Fetal fibronectin levels Feedback a. Relaxing levels are rarely assessed. In addition, they are unrelated to the incidence of preterm labor. b. Amniotic fluid levels are not directly related to the incidence of preterm labor. c. Alpha-fetoprotein levels are not related to the incidence of preterm labor. d. A rise in the fetal fibronectin levels in cervical secretions has been associated with preterm labor. 20. Which of the following statements is most appropriate for the nurse to say to a patient with a complete placenta previa? a. “During the second stage of labor you will need to bear down.” b. “You should ambulate in the halls at least twice each day.” c. “The doctor will likely induce your labor with oxytocin.” d. “Please promptly report if you experience any bleeding or feel any back discomfort.” Feedback a. This response is inappropriate. This patient will be delivered by cesarean section. b. This response is inappropriate. Patients with placenta previa are usually on bed rest. c. This response is inappropriate. This patient will be delivered by cesarean section. d. Labor often begins with back pain. Labor is contraindicated for a patient with complete placenta previa. 21. A woman at 32 weeks’ gestation is diagnosed with severe preeclampsia with HELLP syndrome. The nurse will identify which of the following as a positive patient care outcome? a. Rise in serum creatinine b. Drop in serum protein c. Resolution of thrombocytopenia d. Resolution of polycythemia Feedback a. A rise in serum creatinine indicates that the kidneys are not effectively excreting creatinine. It is a negative outcome. b. A drop in serum protein indicates that the kidneys are allowing protein to be excreted. This is a negative outcome. c. Resolution of thrombocytopenia is a positive sign. It indicates that the platelet count is returning to normal. d. Polycythemia is not related to HELLP syndrome. Rather one sees a drop in red cell and platelet counts with HELLP. A positive sign, therefore, would be a rise in the RBC count. 22. A 16-year-old patient is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of severe preeclampsia. The nurse must closely monitor the woman for which of the following? a. High leukocyte count b. Explosive diarrhea c. Fractured pelvis d. Low platelet count Feedback a. High leukocyte count is not associated with severe pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) or HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome. b. Explosive diarrhea is not associated with severe PIH or HELLP syndrome. c. A fractured pelvis is not associated with severe PIH or HELLP syndrome. d. Low platelet count is one of the signs associated with HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome. 23. A woman at 10 weeks’ gestation is diagnosed with gestational trophoblastic disease (hydatiform mole). Which of the following findings would the nurse expect to see? a. Platelet count of 550,000/ mm3 b. Dark brown vaginal bleeding c. White blood cell count 17,000/ mm3 d. Macular papular rash Feedback a. The nurse would not expect to see an elevated platelet count. b. The nurse would expect to see dark brown vaginal discharge c. The nurse would not expect to see an elevated white blood cell count. d. The nurse would not expect to see a rash. 24. After an education class, the nurse overhears an adolescent woman discussing safe sex practices. Which of the following comments by the young woman indicates that additional teaching about sexually transmitted infection (STI) control issues is needed? a. “I could get an STI even if I just have oral sex.” b. “Girls over 16 are less likely to get STDs than younger girls.” c. “The best way to prevent an STI is to use a diaphragm.” d. “Girls get human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) easier than boys do.” Feedback a. This statement is true. Organisms that cause sexually transmitted infections can invade the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. b. This statement is true. Young women are especially high risk for becoming infected with sexually transmitted diseases. c. This statement is untrue. The young woman needs further teaching. Condoms protect against STDs and pregnancy. In addition, condoms can be kept in readiness for whenever sex may occur spontaneously. Using condoms does not require the teen to plan to have sex. A diaphragm is not an effective infection-control method. Plus, it would require the teen to plan for intercourse. d. This statement is true. Young women are higher risk for becoming infected with HIV than are young men. 25. A woman who is admitted to labor and delivery at 30 weeks’ gestation, is 1 cm dilated, and is contracting q 5 minutes. She is receiving magnesium sulfate IV piggyback. Which of the following maternal vital signs is most important for the nurse to assess each hour? a. Temperature b. Pulse c. Respiratory rate d. Blood pressure Feedback a. The temperature should be monitored, but it is not the most important vital sign. b. The pulse rate should be monitored, but it is not the most important vital sign. c. The respiratory rate is the most important vital sign. Respiratory depression is a sign of magnesium toxicity. d. The blood pressure should be monitored, but it is not the most important vital sign. 26. You are caring for a patient who was admitted to labor and delivery at 32 weeks’ gestation and diagnosed with preterm labor. She is currently on magnesium sulfate, 2 gm per hour. Upon your initial assessment you note that she has a respiratory rate of 8 with absent deep tendon reflexes. What will be your first nursing intervention? a. Elevate head of the bed b. Notify the MD c. Discontinue magnesium sulfate d. Draw a serum magnesium level Initial nursing intervention needs to be discontinuing magnesium sulfate because the patient is exhibiting signs of magnesium toxicity with absent deep tendon reflexes and decreased respiratory rate. 27. A 34-weeks’ gestation multigravida, G3 P1 is admitted to the labor suite. She is contracting every 7 minutes and 40 seconds. The woman has several medical problems. Which of the following of her comorbidities is most consistent with the clinical picture? a. Kyphosis b. Urinary tract infection c. Congestive heart failure d. Cerebral palsy Feedback a. Kyphosis is unrelated to preterm labor. b. Urinary tract infections often precipitate preterm labor. c. It is unlikely that the congestive heart failure precipitated the preterm labor. d. Cerebral palsy is unrelated to preterm labor. 28. A primiparous woman has been admitted at 35 weeks’ gestation and diagnosed with HELLP syndrome. Which of the following laboratory changes is consistent with this diagnosis? a. Hematocrit dropped to 28%. b. Platelets increased to 300,000 cells/mm3. c. Red blood cells increased to 5.1 million cells/mm3. d. Sodium dropped to 132 mEq/dL. Feedback a. The nurse would expect to see a drop in the hematocrit: The H in HELLP stands for hemolysis. b. The nurse would expect to see low platelets. c. The nurse would expect to see hemolysis. d. The sodium is usually unaffected in HELLP syndrome. 29. A labor nurse is caring for a patient, 39 weeks’ gestation, who has been diagnosed with placenta previa. Which of the following physician orders should the nurse question? a. Type and cross-match her blood. b. Insert an internal fetal monitor electrode. c. Administer an oral stool softener. d. Assess her complete blood count. Feedback a. It would be appropriate to type and cross-match the patient for a blood transfusion. b. This action is inappropriate. When a patient has a placenta previa, nothing should be inserted into the vagina. c. To prevent constipation, it is appropriate for a patient to take a stool softener. d. It is appropriate to monitor the patient for signs of anemia. 30. A type 1 diabetic patient has repeatedly experienced elevated serum glucose levels throughout her pregnancy. Which of the following complications of pregnancy would the nurse expect to see? a. Postpartum hemorrhage b. Neonatal hyperglycemia c. Postpartum oliguria d. Neonatal macrosomia Feedback a. The patient is not especially high risk for a postpartum hemorrhage. b. The nurse would expect to see neonatal hypoglycemia, not hyperglycemia. c. The nurse would expect to see postpartum polyuria. d. The nurse would expect to see neonatal macrosomia. 31. According to agency policy, the perinatal nurse provides the following intrapartal nursing care for the patient with preeclampsia: a. Take the patient’s blood pressure every 6 hours b. Encourage the patient to rest on her back c. Notify the physician of a urine output greater than 30 mL/hr d. Administer magnesium sulfate according to agency policy Feedback a. The nurse is the manager of care for the woman with preeclampsia during the intrapartal period. Careful assessments are critical. The blood pressure is taken every 1 hour or more frequently according to physician orders or institutional protocol. b. The nurse is the manager of care for the woman with preeclampsia during the intrapartal period. Careful assessments are critical. The patient should be encouraged to assume a side-lying position to enhance uterine perfusion. c. The nurse is the manager of care for the woman with preeclampsia during the intrapartal period. Careful assessments are critical. A urine output less than 30 mL/hr is indicative of oliguria and the physician must be notified. d. The nurse is the manager of care for the woman with preeclampsia during the intrapartal period. Careful assessments are critical. The nurse administers medications as ordered and should adhere to hospital protocol for a magnesium sulfate infusion. 32. The perinatal nurse is providing care to Marilyn, a 25-year-old G1 TPAL 0000 woman hospitalized with severe hypertension at 33 weeks’ gestation. The nurse is preparing to administer the second dose of beta-methasone prescribed by the physician. Marilyn asks: “What is this injection for again?” The nurse’s best response is: a. “This is to help your baby’s lungs to mature.” b. “This is to prepare your body to begin the labor process.” c. “This is to help stabilize your blood pressure.” d. “This is to help your baby grow and develop in preparation for birth.” Feedback a. Antenatal glucocorticoids such as beta-methasone may be given (12 mg IM 24 hours apart) to promote fetal lung maturity if the gestational age is less than 34 weeks and childbirth can be delayed for 48 hours. b. Antenatal glucocorticoids such as beta-methasone may be given (12 mg IM 24 hours apart) to promote fetal lung maturity if the gestational age is less than 34 weeks and childbirth can be delayed for 48 hours. c. Antenatal glucocorticoids such as beta-methasone may be given (12 mg IM 24 hours apart) to promote fetal lung maturity if the gestational age is less than 34 weeks and childbirth can be delayed for 48 hours. d. Antenatal glucocorticoids such as beta-methasone may be given (12 mg IM 24 hours apart) to promote fetal lung maturity if the gestational age is less than 34 weeks and childbirth can be delayed for 48 hours. 33. A woman who is 36 weeks pregnant presents to the labor and delivery unit with a history of congestive heart disease. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the primary health-care practitioner? a. Presence of chloasma b. Presence of severe heartburn c. 10-pound weight gain in a month d. Patellar reflexes +1 Feedback a. Chloasma is a normal pregnancy finding. b. Heartburn is an expected finding during the third trimester. c. The weight gain may be due to fluid retention. Fluid retention may occur in patients with pregnancy-induced hypertension and in patients with congestive heart failure. The physician should be notified. d. Although slightly hyporeflexic, patellar reflexes of +1 are within normal limits. 34. The single most important risk factor for preterm birth includes: a. Uterine and cervical anomalies b. Infection c. Increased BMI d. Prior preterm birth The single most important factor is prior preterm birth with a reoccurrence rate of up to 40%. 35. Your antepartal patient is 38 weeks’ gestation, has a history of thrombosis, and has been on strict bed rest for the last 12 hours. She is now experiencing shortness of breath. What about the patient may be a contributing factor for her shortness of breath? a. Physiologic changes in pregnancy result in vasodilation, which increases the tendency to form blood clots. b. Physiologic changes in pregnancy result in vasoconstriction, which increases the tendency to form blood clots. c. Physiologic changes in pregnancy result in anemia, which increases the tendency to form blood clots. d. Physiologic changes in pregnancy result in decreased perfusion to the lungs, which increases the tendency to form blood clots. The patient’s shortness of breath, bed rest, and history of thrombosis indicate possible pulmonary embolism. Her pregnant state also increases the potential for thrombosis resulting from increased levels of coagulation factors and decreased fibrinolysis, venous dilation, and obstruction of the venous system by the gravid uterus. Thromboembolitic diseases occurring most frequently in pregnancy include deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. 36. Metabolic changes during pregnancy __________ glucose tolerance. a. lower b. increase c. maintain d. alter Metabolic changes during pregnancy lower glucose tolerance. True/False 37. Immediately postpartum, the insulin needs in diabetic women increase dramatically. ANS: FalseThere is a significant decrease in the need for insulin immediately after delivery related to the loss of antagonistic placental hormones and suppression of the anterior pituitary growth hormone. 38. The perinatal nurse observes the placental inspection by the health-care provider after birth. This examination may help to determine whether an abruption has occurred prior to or during labor. ANS: True Fifty percent of abruptions occur before labor and after the 30th week, 15% occur during labor, and 30% are identified only upon inspection of the placenta after delivery. 39. It is critical for the perinatal nurse to learn, as part of the facility’s policies and procedures, to immediately perform a vaginal examination on a woman who presents with vaginal bleeding after 24 weeks’ gestation. ANS: False Placenta previa should be suspected in all patients who present with bleeding after 24 completed weeks of gestation. Because of the risk of placental perforation, vaginal examinations are not performed. 40. The perinatal nurse knows that the survival rate for infants born at or greater than 28 to 29 gestational weeks is greater than 90%. ANS: True With appropriate medical care, neonatal survival dramatically improves as the gestational age increases, with over 50% of neonates surviving at 25 weeks’ gestation, and over 90% surviving at 28 to 29 weeks of gestation. 41. A patient with hypertension who is receiving intravenous magnesium sulfate therapy has requested an epidural anesthetic. The perinatal nurse should first review the patient’s complete blood count results for evidence of a decreased platelet count. ANS: True Baseline information, including complete blood count (CBC), clotting studies, serum electrolytes, and renal function tests, is used to alert the care providers to changes in the patient’s condition as additional laboratory tests are obtained. 42. The perinatal nurse knows that the laboring diabetic patient’s blood glucose level should always be less than 120 mg/dL. ANS: True Blood glucose levels are assessed every hour, and fluid/insulin adjustments are made as needed to maintain maternal blood glucose levels between 80 and 120 mg/dL. Multiple Response 43. The perinatal nurse describes risk factors for placenta previa to the student nurse. Placenta previa risk factors include (select all that apply): a. Cocaine use b. Tobacco use c. Previous caesarean birth d. Previous use of medroxyprogesterone (Depo-Provera) , b, c Feedback a. Placenta previa may be associated with risk factors including smoking, cocaine use, a prior history of placenta previa, closely spaced pregnancies, African or Asian ethnicity, and maternal age greater than 35 years. b. Placenta previa may be associated with risk factors including smoking, cocaine use, a prior history of placenta previa, closely spaced pregnancies, African or Asian ethnicity, and maternal age greater than 35 years. c. Placenta previa may be associated with conditions that cause scarring of the uterus such as a prior cesarean section, multiparity, or increased maternal age. d. Previous use of medroxyprogesterone (Depo-Provera) is not a risk factor for placenta previa. 44. Kerry, a 30-year-old G3 TPAL 0110 woman presents to the labor unit triage with complaints of lower abdominal cramping and urinary frequency at 30 weeks’ gestation. An appropriate nursing action would be to (select all that apply): a. Assess the fetal heart rate b. Obtain urine for culture and sensitivity c. Assess Kerry’s blood pressure and pulse d. Palpate Kerry’s abdomen for contractions , b, d Feedback a. Women experiencing preterm labor may complain of backache, pelvic aching, menstrual-like cramps, increased vaginal discharge, pelvic pressure, urinary frequency, and intestinal cramping with or without diarrhea. The patient’s abdomen should be palpated to assess for contractions, and the fetus’s heart rate should be monitored. b. Women experiencing preterm labor may complain of backache, pelvic aching, menstrual-like cramps, increased vaginal discharge, pelvic pressure, urinary frequency, and intestinal cramping with or without diarrhea. A urinalysis and urine culture and sensitivity (C & S) should be obtained on all patients who present with signs of preterm labor, and the nurse must remember that signs of UTI often mimic normal pregnancy complaints (i.e., urgency, frequency). The patient’s abdomen should be palpated to assess for contractions, and the fetus’s heart rate should be monitored. c. Assessment of blood pressure and pulse is not an important nursing action in this scenario. d. Women experiencing preterm labor may complain of backache, pelvic aching, menstrual-like cramps, increased vaginal discharge, pelvic pressure, urinary frequency, and intestinal cramping with or without diarrhea. The patient’s abdomen should be palpated to assess for contractions and the fetus’s heart rate should be monitored. 45. The perinatal nurse knows that tocolytic agents are most often used to (select all that apply): a. Prevent maternal infection b. Prolong pregnancy to 40 weeks’ gestation c. Prolong pregnancy to facilitate administration of antenatal corticosteroids d. Allow for transport of the woman to a tertiary care facility , d Feedback a. Tocolytics are not used to treat maternal infection. b. Tocolytics are generally only effective in delaying delivery for several days. c. Presently, it is believed that the best reason to use tocolytic drugs is to allow an opportunity to begin the administration of antenatal corticosteroids to accelerate fetal lung maturity. d. Delaying the birth provides time for maternal transport to a facility equipped with a neonatal intensive care unit. 46. The perinatal nurse provides a hospital tour for couples and families preparing for labor and birth in the future. Teaching is an important component of the tour. Information provided about preterm labor and birth prevention includes (select all that apply): a. Encouraging regular, ongoing prenatal care b. Reporting symptoms of urinary frequency and burning to the health-care provider c. Coming to the labor triage unit if back pain or cramping persist or become regular d. Lying on the right side, withholding fluids, and counting fetal movements if contractions occur every 5 minutes , b, c Feedback a. The nurse should encourage all pregnant women to obtain prenatal care and screen for vaginal and urogenital infections and treat appropriately, and remind pregnant women to call their provider repeatedly if symptoms of preterm labor occur. b. Educating all women of childbearing age about preterm labor is a crucial component of prevention. The nurse should encourage all pregnant women to obtain prenatal care and screen for vaginal and urogenital infections and treat appropriately, and remind pregnant women to call their provider repeatedly if symptoms of preterm labor occur. c. Educating all women of childbearing age about preterm labor is a crucial component of prevention. The nurse should encourage all pregnant women to obtain prenatal care and screen for vaginal and urogenital infections and treat appropriately and remind pregnant women to call their provider if symptoms of preterm labor occur. d. Lying on the right side; drinking fluids, not withholding fluids; and counting fetal movements if contractions occur every 5 minutes are recommended if a woman thinks she is contracting. 47. The perinatal nurse describes for the new nurse the various risks associated with prolonged premature preterm rupture of membranes. These risks include (select all that apply): a. Chorioamnionitis b. Abruptio placentae c. Operative birth d. Cord prolapse , b, d Even though maintaining the pregnancy to gain further fetal maturity can be beneficial, prolonged PPROM has been correlated with an increased risk of chorioamnionitis, placental abruption, and cord prolapse. 48. Betamethasone is a steroid that is given to a pregnant woman with signs of preterm labor. The purpose of giving steroids is to (select all that apply): a. Stimulate the production of surfactant in the preterm infant b. Be given between 24 and 34 weeks’ gestation c. Increase the severity of respiratory distress d. Accelerate fetal lung maturity , b, d Betamethasone is a steroid that is given to pregnant women with signs of preterm labor between 24 and 34 weeks’ gestation. It stimulates the production of surfactant in the preterm infant and accelerates fetal lung maturity. 49. Marked hemodynamic changes in pregnancy can impact the pregnant woman with cardiac disease. Signs and symptoms of deteriorating cardiac status include (select all that apply): a. Orthopnea b. Nocturnal dyspnea c. Palpitations d. Irritation , b, c Signs and symptoms of deteriorating cardiac status with cardiac disease include orthopnea, nocturnal dyspnea, and palpitations, but do not include irritation. Short Answer 50. A condition where the placenta attaches to the lower uterine segment of the uterus ANS: Placenta previa 51. A pregnancy that ends before 20 weeks’ gestation ANS: Miscarriage 52. Birth prior to 37 completed weeks of pregnancy ANS: Preterm birth 53. Specks or spots in the vision where the patient cannot see; “blind spots” ANS: Scotoma 54. A disease characterized by an abnormal placental development that results in the production of fluid-filled grapelike clusters and a vast proliferation of trophoblastic tissue ANS: Hydatidiform mole/Gestational trophoblastic disease 55. No expulsion of the products of conception, but bleeding and dilation of the cervix such that a pregnancy is unlikely ANS: Inevitable abortion 56. Placement of suture to mechanically close a weak cervix ervical cerclage Fill-in-the-Blank 57. The perinatal nurse knows that an early pregnancy loss occurs before __________ weeks, and a late pregnancy loss is one that occurs between 12 and __________ weeks. ANS: 12; 20 Not all conceptions result in a live-born infant. Of all clinically recognized pregnancies, 10% to 20% are lost, and approximately 22% of pregnancies detected on the basis of hCG assays are lost before the appearance of any clinical signs or symptoms. By definition, an early pregnancy loss occurs before 12 weeks of gestation; a late pregnancy loss is one that occurs between 12 and 20 weeks. 58. Mary, a G3 TPAL 0020 woman at 20 weeks’ gestation, has had a transvaginal ultrasound. Mary has been informed that she has cervical incompetence. The perinatal nurse explains that this diagnosis means that her cervix has __________ without __________ contractions. ilated; regular Patients with cervical incompetence usually present with painless dilation and effacement of the cervix, often during the second trimester of pregnancy. The patient frequently gives a history of repeated second trimester losses with no apparent etiology. Incompetent cervix is estimated to cause approximately 15% of all second trimester losses. 59. The perinatal nurse knows that nausea and vomiting are common in pregnancy and usually resolve by __________ weeks’ gestation. The severe form of this condition is __________. ANS: 16; hyperemesis gravidarum Feedback 1: Nausea and vomiting are a common condition of pregnancy which affect 70% to 85% of pregnant women and usually resolve by the 16th week of gestation. Feedback 2: Hyperemesis gravidarum represents the extreme end of the nausea/vomiting spectrum in terms of severity. Criteria for the diagnosis of hyperemesis gravidarum include persistent vomiting unrelated to other causes, a measure of acute starvation (usually large ketonuria), and some discrete weight loss, most often 5% of the prepregnancy weight. 60. The perinatal nurse explains to the student nurse who is assessing the abdomen of a 32-week pregnant woman with placenta previa that it would not be unusual to find the fetus in a __________ or __________ position. reech; transverse Placenta previa is an implantation of the placenta in the lower uterine segment, near or over the internal cervical os. This condition accounts for 20% of all antepartal hemorrhages. Leopold maneuvers often reveal the fetus to be in a breech or oblique position or transverse lie because of the abnormal location of the placenta. 61. The perinatal nurse knows that a __________ hemorrhage is limited to the uterus, and a __________ hemorrhage moves blood toward and through the cervix. oncealed; revealed Feedback 1: A concealed hemorrhage occurs in 20% of cases and describes an abruption in which the bleeding is confined within the uterine cavity. The most common abruption is associated with a revealed or external hemorrhage, where the blood dissects downward toward the cervix. Feedback 2: The most common abruption is associated with a revealed or external hemorrhage, where the blood dissects downward toward the cervix. 62. The perinatal nurse encourages Colleen, who has just been discharged from the hospital for intravenous therapy for severe nausea and vomiting, to ensure that she __________ often, eats frequent, __________ meals and avoids __________ odors. ANS: rests; small; cooking The nurse should counsel the woman with nausea and vomiting to avoid foods and sensory stimuli that provoke symptoms (i.e., some women become nauseous when they smell certain foods being prepared) and also to eat small, frequent meals of dry, bland foods and include high-protein snacks in their diet. Chapter 8: Intrapartum Assessment and Interventions Multiple Choice 1. In caring for a primiparous woman in labor, one of the factors to evaluate is uterine activity. This is referred to as the __________ of labor.a. Passengerb. Passagec. Powersd. Psyche Feedback a. The passenger refers to the fetus. b. The passage refers to the pelvis and birth canal. c. Powers refer to the contractions. d. Psyche refers to the response of a woman to labor. 2. The provision of support during labor has demonstrated that women experience a decrease in anxiety and a feeling of being in more control. In clinical situations, this has resulted in: a. A decrease in interventions b. Increased epidural rates c. Earlier admission to the hospital d. Improved gestational age Feedback a. Studies have shown that with a support person, be it a family member, friend, or professional such as a Doula or nurse, the patient experiences a decrease in anxiety and has a feeling of being in more control. This, in turn, results in a decrease in interventions, a significantly lower level of pain, and an enhanced overall maternal satisfaction. b. There is decreased use of pain medication with continuous labor support. c. There is no evidence that continuous labor support results in earlier admission to the hospital. d. There is no evidence that continuous labor support results in improved gestational age for the fetus. KEY: Integrated Process: Clinical Problem Solving | Cognitive Level: Comprehension | Content Area: Maternity | Client Need: PSI, Psychosocial Integrity | Difficulty Level: Moderate 3. When caring for a primiparous woman being evaluated for admission for labor, a key distinction between true versus false labor is:a. True labor contractions result in rupture of membranes, and with false labor, the membranes remain intact.b. True labor contractions result in increasing anxiety and discomfort, and false labor does not.c. True labor contractions are accompanied by loss of the mucus plug and bloody show, and with false labor there is no vaginal discharge. d. True labor contractions bring about changes in cervical effacement and dilation, and with false labor there are irregular contractions with little or no cervical changes. Feedback a. Rupture of membranes can occur prior to labor or during labor. b. A woman’s response to labor may not be reflective of her status in labor but is influenced by expectations and emotional status. c. Loss of the mucus plug can occur prior to the onset of labor. d. True labor contractions bring about changes in cervical effacement and dilation, and with false labor there are irregular contractions with little or no cervical changes. 4. The mechanism of labor known as cardinal movements of labor are the positional changes that the fetus goes through to best navigate the birth process. These cardinal movements are: a. Engagement, Descent, Flexion, Extension, Internal rotation, External rotation, Expulsion b. Engagement, Descent, Flexion, Internal rotation, Extension, External rotation, Expulsion c. Engagement, Flexion, Internal rotation, Extension, External rotation, Descent, Expulsion d. Engagement, Flexion, Internal rotation, Extension, External rotation, Flexion, Expulsion Feedback a. The order of the cardinal movements is incorrect. b. Engagement occurs when the greatest diameter of the fetal head passes through the pelvic inlet. Engagement can occur late in pregnancy or early in labor. Descent is the movement of the fetus through the birth canal during the first and second stages of labor. Flexion is when the chin of the fetus moves toward the fetal chest. Flexion occurs when the descending head meets resistance from maternal tissues. This movement results in the smallest fetal diameter to the maternal pelvic dimensions. It typically occurs early in labor. Internal rotation is the movement, the rotation of the fetal head, that aligns the long axis of the fetal head with the long axis of the maternal pelvis. It occurs mainly during the second stage of labor. Extension is the movement facilitated by resistance of the pelvic floor, causing the presenting part to pivot beneath the pubic symphysis and the head to be delivered. This occurs during the second stage of labor. External rotation is when the sagittal suture moves to a transverse diameter and the shoulders align in the anteroposterior diameter. The sagittal suture maintains alignment with the fetal trunk as the trunk navigates through the pelvis. Expulsion is the movement that occurs when the shoulders and remainder of the body are delivered. c. The order of the cardinal movements is incorrect. d. The order of the cardinal movements is incorrect. 5. A woman is considered in active labor when: a. Cervical dilation progresses from 4 to 7 cm with effacement of 40% to 80%, contractions become more intense, occurring every 2 to 5 minutes with duration of 45 to 60 seconds. b. Cervical dilation progresses to 3 cm with effacement of 30, contractions become more intense, occurring every 2 to 5 minutes with duration of 45 to 60 seconds. c. Cervical dilation progresses to 8 cm with effacement of 80%, contractions become more intense, occurring every 2 to 5 minutes with duration of 45 to 60 seconds. d. Cervical dilation progresses to 10 cm with effacement of 90%, contractions become more intense, occurring every 2 to 5 minutes with duration of 45 to 60 seconds. Feedback a. Characteristics of this phase are the cervix dilates, on an average, 1.2 cm/hr for primiparous women and 1.5 cm/hr for multiparous women. Cervical dilation progresses from 4 to 7 cm with effacement of 40% to 80%. Fetal descent continues, and contractions become more intense, occurring every 2 to 5 minutes with duration of 45 to 60 seconds, and discomfort increases. b. Cervical dilation progresses to 3 cm with effacement of 30, indicating the early or latent phase of labor. c. Cervical dilation progresses to 8 cm with effacement of 80%, indicating the transition phase of labor. d. Cervical dilation of 10 cm with effacement is the end of the first stage of labor. 6. You are caring for a woman in labor who is 6 cm dilated with a reassuring FHT pattern and regular strong UCs. The fetal heart rate (FHR) should be: a. Monitored continuously b. Monitored every 15 minutes c. Monitored every 30 minutes d. Monitored every 60 minutes Feedback a. Assessment of fetal heart rate (FHR) during the active phase of labor with a reassuring FHR is not indicated continuously. b. Assessment of fetal heart rate (FHR) during the active phase of labor with a reassuring FHR is not indicated every 15 minutes. c. Assessment of fetal heart rate (FHR) during the active phase of labor with a reassuring FHR is indicated every 30 minutes. d. Assessment of fetal heart rate (FHR) during the active phase of labor with a reassuring FHR is indicated every 30 minutes, not every 60 minutes. 7. A woman you are caring for in labor requests an epidural for pain relief in labor. Included in your preparation for epidural placement is a baseline set of vital signs. The most common vital sign to change after epidural placement: a. Blood pressure, hypotension b. Blood pressure, hypertension c. Pulse, tachycardia d. Pulse, bradycardia Feedback a. Blood pressure, hypotension, as up to 40% of women may experience hypotension. Hypotension is defined as systolic BP <100 mm Hg or 20% decrease in BP from preanesthesia levels. Intravenous bolus is typically given to decrease the incidence of hypotension. b. Blood pressure, hypertension is incorrect because hypotension is the common complication after epidural placement. c. Pulse, tachycardia is incorrect because hypotension is the common complication after epidural placement. d. Pulse, bradycardia is incorrect because hypotension is the common complication after epidural placement. 8. The labor patient you are caring for is ambulating in the hall. Her vaginal exam 1 hour ago indicated she was 4/70/–1 station. She tells you she has fluid running down her leg. Your priority nursing intervention is to: a. Assess the color, odor, and amount of fluid. b. Assist your patient to the bathroom. c. Assess the fetal heart rate. d. Call the care provider. Feedback a. Although assessing the color, odor, and amount of fluid is appropriate, the priority nursing action is to assess the FHR because of the risk of umbilical cord prolapse with rupture of membranes. b. The fluid is probably related to rupture of membranes rather than the patient needing to go to the bathroom to urinate. c. Assessing the fetal heart rate is the first priority because of the risk of umbilical cord prolapse with rupture of membranes. d. Although you may call the care provider, the priority nursing action is to assess the FHR because of the risk of umbilical cord prolapse with rupture of membranes. 9. You are in the process of admitting a multiparous woman to labor and delivery from the triage area. One hour ago, her vaginal exam was 4/70/0. While completing your review of her prenatal record and completing the admission questionnaire, she tells you she has an urge to have a bowel movement and feels like pushing. Your priority nursing intervention is to: a. Reassure the patient and rapidly complete the admission. b. Assist your patient to the bathroom to have a bowel movement. c. Assess the fetal heart rate and uterine contractions. d. Perform a vaginal exam. Feedback a. Completing the admission paperwork is not a priority when birth may be imminent. b. The urge to have a bowel movement is probably related to fetal descent and complete dilation rather than the patient needing to have a bowel movement. c. Doing a vaginal exam is the first priority as birth may be imminent. d. Perform a vaginal exam to assess the progress of labor. The urge to have a bowel movement and feeling like pushing indicate that birth may be imminent. 10. The Apgar score consists of a rapid assessment of five physiological signs that indicate the physiological status of the newborn and includes: a. Apical pulse strength, respiratory rate, muscle flexion, reflex irritability, and color b. Heart rate, clarity of lungs, muscle tone, reflexes, and color c. Apical pulse strength, respiratory rate, muscle tone, reflex irritability, and color of extremities d. Heart rate, respiratory rate, muscle tone, reflex irritability, and color Feedback a. Heart rate, not apical pulse strength, is the criterion for Apgar scoring; muscle tone, not flexion, is assessed. b. Clarity of lungs and reflexes are not assessed as part of Apgar scoring. Neonatal lungs can be congested normally at birth, and reflexes are not assessed. Rather, reflex irritability is assessed, based on response to tactile stimulation. c. Heart rate, not apical pulse strength, is assessed along with respiratory rate, muscle tone, reflex irritability, and color of extremities. d. The Apgar score includes assessment of heart rate based on auscultation, respiratory rate based on observed movement of chest, muscle tone based on degree of flexion and movement of extremities, reflex irritability based on response to tactile stimulation, and color based on observation. 11. The perinatal nurse is assessing a woman in triage who is 34 + 3 weeks’ gestation in her first pregnancy. She is worried about having her baby “too soon,” and she is experiencing uterine contractions every 10 to 15 minutes. The fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. A vaginal examination performed by the health-care provider reveals that the cervix is closed, long, and posterior. The most likely diagnosis would be: a. Preterm labor b. Term labor c. Back labor d. Braxton-Hicks contractions Feedback a. Preterm labor (PTL) is defined as regular uterine contractions and cervical dilation before the end of the 36th week of gestation. Many patients present with preterm contractions, but only those who demonstrate changes in the cervix are diagnosed with preterm labor. b. Term labor occurs after 37 weeks’ gestation. c. There is no indication in this scenario that this is back labor. d. Braxton-Hicks contractions are regular contractions occurring after the third month of pregnancy. They may be mistaken for regular labor, but unlike true labor, the contractions do not grow consistently longer, stronger, and closer together, and the cervix is not dilated. Some patients present with preterm contractions, but only those who demonstrate changes in the cervix are diagnosed with preterm labor. 12. The perinatal nurse knows that the term to describe a woman at 26 weeks’ gestation with a history of elevated blood pressure who presents with a urine showing 2+ protein (by dipstick) is: a. Preeclampsia b. Chronic hypertension c. Gestational hypertension d. Chronic hypertension with superimposed preeclampsia Feedback a. Preeclampsia is a multisystem, vasopressive disease process that targets the cardiovascular, hematologic, hepatic, and renal and central nervous systems. b. Chronic hypertension is hypertension that is present and observable prior to pregnancy or hypertension that is diagnosed before the 20th week of gestation. c. Gestational hypertension is a nonspecific term used to describe the woman who has a blood pressure elevation detected for the first time during pregnancy, without proteinuria. d. The following criteria are necessary to establish a diagnosis of superimposed preeclampsia: hypertension and no proteinuria early in pregnancy (prior to 20 weeks’ gestation) and new-onset proteinuria, a sudden increase in protein—urinary excretion of 0.3 g protein or more in a 24-hour specimen, or two dipstick test results of 2+ (100 mg/dL), with the values recorded at least 4 hours apart, with no evidence of urinary tract infection; a sudden increase in blood pressure in a woman whose blood pressure has been well controlled; thrombocytopenia (platelet count lower than 100,000/mmC); and an increase in the liver enzymes alanine transaminase (ALT) or aspartate transaminase (AST) to abnormal levels. 13. A patient is receiving magnesium sulfate for severe preeclampsia. The nurse must notify the attending physician immediately of which of the following findings? a. Patellar and biceps reflexes of +4 b. Urinary output of 50 mL/hr c. Respiratory rate of 10 rpm d. Serum magnesium level of 5 mg/dL Feedback a. Magnesium sulfate has been ordered because the patient has severe pregnancy-induced hypertension. Patellar and biceps reflexes of +4 are symptoms of the disease. b. The urinary output must be above 25 mL/hr. c. The drop in respiratory rate may indicate that the patient is suffering from magnesium toxicity. The nurse should report the finding to the physician. d. The therapeutic range of magnesium is 4 to 7 mg/dL. 14. A woman in labor and delivery is being given subcutaneous terbutaline for preterm labor. Which of the following common medication effects would the nurse expect to see in the mother? a. Serum potassium level increases b. Diarrhea c. Urticaria d. Complaints of nervousness Feedback a. The nurse would not expect to see a rise in the mother’s serum potassium levels. b. The beta agonists are not associated with diarrhea. c. The beta agonists are not associated with urticaria. d. Complaints of nervousness are commonly made by women receiving subcutaneous beta agonists. 15. Which of the following signs or symptoms would the nurse expect to see in a woman with concealed abruptio placentae? a. Increasing abdominal girth measurements b. Profuse vaginal bleeding c. Bradycardia with an aortic thrill d. Hypothermia with chills Feedback a. The nurse would expect to see increasing abdominal girth measurements. b. Profuse vaginal bleeding is rarely seen in placental abruption and is never seen when the abruption is concealed. c. With excessive blood loss, the nurse would expect to see tachycardia. d. The nurse would expect to see a stable temperature. 16. A woman who has had no prenatal care was assessed and found to have hydramnios on admission to the labor unit and has since delivered a baby weighing 4500 grams. Which of the following complications of pregnancy likely contributed to these findings? a. Pyelonephritis b. Pregnancy-induced hypertension c. Gestational diabetes d. Abruptio placentae Feedback a. Pyelonephritis does not lead to the development of hydramnios or macrosomia. b. Pregnancy-induced hypertension does not lead to the development of hydramnios or macrosomia. c. Untreated gestational diabetics often have hydramnios and often deliver macrosomic babies. d. Abruptio placentae does not lead to the development of hydramnios or macrosomia. 17. For the patient with which of the following medical problems should the nurse question a physician’s order for beta agonist tocolytics? a. Type 1 diabetes mellitus b. Cerebral palsy c. Myelomeningocele d. Positive group B streptococci culture Feedback a. Beta agonists often elevate serum glucose levels. The nurse should question the order. b. Beta agonists are not contraindicated for patients with cerebral palsy. c. Beta agonists are not contraindicated for patients with myelomeningocele. d. Beta agonists are not contraindicated for patients with group B streptococci. 18. The nurse is caring for two laboring women. Which of the patients should be monitored most carefully for signs of placental abruption? a. The patient with placenta previa b. The patient whose vagina is colonized with group B streptococci c. The patient who is hepatitis B surface antigen positive d. The patient with eclampsia Feedback a. Patients with placenta previa are not especially high risk for placental abruption. b. Patients colonized with group B streptococci are not especially high risk for placental abruption. c. Patients who are hepatitis B surface antigen positive are not especially high risk for placental abruption. d. Patients with eclampsia are high risk for placental abruption. 19. The nurse is caring for a woman at 28 weeks’ gestation with a history of preterm delivery. Which of the following laboratory data should the nurse carefully assess in relation to this diagnosis? a. Human relaxing levels b. Amniotic fluid levels c. Alpha-fetoprotein levels d. Fetal fibronectin levels Feedback a. Relaxing levels are rarely assessed. In addition, they are unrelated to the incidence of preterm labor. b. Amniotic fluid levels are not directly related to the incidence of preterm labor. c. Alpha-fetoprotein levels are not related to the incidence of preterm labor. d. A rise in the fetal fibronectin levels in cervical secretions has been associated with preterm labor. 20. Which of the following statements is most appropriate for the nurse to say to a patient with a complete placenta previa? a. “During the second stage of labor you will need to bear down.” b. “You should ambulate in the halls at least twice each day.” c. “The doctor will likely induce your labor with oxytocin.” d. “Please promptly report if you experience any bleeding or feel any back discomfort.” Feedback a. This response is inappropriate. This patient will be delivered by cesarean section. b. This response is inappropriate. Patients with placenta previa are usually on bed rest. c. This response is inappropriate. This patient will be delivered by cesarean section. d. Labor often begins with back pain. Labor is contraindicated for a patient with complete placenta previa. 21. A woman at 32 weeks’ gestation is diagnosed with severe preeclampsia with HELLP syndrome. The nurse will identify which of the following as a positive patient care outcome? a. Rise in serum creatinine b. Drop in serum protein c. Resolution of thrombocytopenia d. Resolution of polycythemia Feedback a. A rise in serum creatinine indicates that the kidneys are not effectively excreting creatinine. It is a negative outcome. b. A drop in serum protein indicates that the kidneys are allowing protein to be excreted. This is a negative outcome. c. Resolution of thrombocytopenia is a positive sign. It indicates that the platelet count is returning to normal. d. Polycythemia is not related to HELLP syndrome. Rather one sees a drop in red cell and platelet counts with HELLP. A positive sign, therefore, would be a rise in the RBC count. 22. A 16-year-old patient is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of severe preeclampsia. The nurse must closely monitor the woman for which of the following? a. High leukocyte count b. Explosive diarrhea c. Fractured pelvis d. Low platelet count Feedback a. High leukocyte count is not associated with severe pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) or HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome. b. Explosive diarrhea is not associated with severe PIH or HELLP syndrome. c. A fractured pelvis is not associated with severe PIH or HELLP syndrome. d. Low platelet count is one of the signs associated with HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome. 23. A woman at 10 weeks’ gestation is diagnosed with gestational trophoblastic disease (hydatidiform mole). Which of the following findings would the nurse expect to see? a. Platelet count of 550,000/mm3 b. Dark brown vaginal bleeding c. White blood cell count 17,000/mm3 d. Macular papular rash Feedback a. The nurse would not expect to see an elevated platelet count. b. The nurse would expect to see dark brown vaginal discharge. c. The nurse would not expect to see an elevated white blood cell count. d. The nurse would not expect to see a rash. 24. After an education class, the nurse overhears an adolescent woman discussing safe sex practices. Which of the following comments by the young woman indicates that additional teaching about sexually transmitted infection (STI) control issues is needed? a. “I could get an STI even if I just have oral sex.” b. “Girls over 16 are less likely to get STDs than younger girls.” c. “The best way to prevent an STI is to use a diaphragm.” d. “Girls get human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) easier than boys do.” Feedback a. This statement is true. Organisms that cause sexually transmitted infections can invade the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. b. This statement is true. Young women are especially high risk for becoming infected with sexually transmitted diseases. c. This statement is untrue. The young woman needs further teaching. Condoms protect against STDs and pregnancy. In addition, condoms can be kept in readiness for whenever sex may occur spontaneously. Using condoms does not require the teen to plan to have sex. A diaphragm is not an effective infection-control method. Plus, it would require the teen to plan for intercourse. d. This statement is true. Young women are higher risk for becoming infected with HIV than are young men. 25. A woman who is admitted to labor and delivery at 30 weeks’ gestation, is 1 cm dilated, and is contracting q 5 minutes. She is receiving magnesium sulfate IV piggyback. Which of the following maternal vital signs is most important for the nurse to assess each hour? a. Temperature b. Pulse c. Respiratory rate d. Blood pressure Feedback a. The temperature should be monitored, but it is not the most important vital sign. b. The pulse rate should be monitored, but it is not the most important vital sign. c. The respiratory rate is the most important vital sign. Respiratory depression is a sign of magnesium toxicity. d. The blood pressure should be monitored, but it is not the most important vital sign. 26. A primiparous woman has been admitted at 35 weeks’ gestation and diagnosed with HELLP syndrome. Which of the following laboratory changes is consistent with this diagnosis? a. Hematocrit dropped to 28%. b. Platelets increased to 300,000 cells/mm3. c. Red blood cells increased to 5.1 million cells/mm3. d. Sodium dropped to 132 mEq/dL. Feedback a. The nurse would expect to see a drop in the hematocrit: The H in HELLP stands for hemolysis. b. The nurse would expect to see low platelets. c. The nurse would expect to see hemolysis. d. The sodium is usually unaffected in HELLP syndrome. 27. A labor nurse is caring for a patient, 39 weeks’ gestation, who has been diagnosed with placenta previa. Which of the following physician orders should the nurse question? a. Type and cross-match her blood. b. Insert an internal fetal monitor electrode. c. Administer an oral stool softener. d. Assess her complete blood count. Feedback a. It would be appropriate to type and cross-match the patient for a blood transfusion. b. This action is inappropriate. When a patient has a placenta previa, nothing should be inserted into the vagina. c. To prevent constipation, it is appropriate for a patient to take a stool softener. d. It is appropriate to monitor the patient for signs of anemia. 28. A type 1 diabetic patient has repeatedly experienced elevated serum glucose levels throughout her pregnancy. Which of the following complications of pregnancy would the nurse expect to see? a. Postpartum hemorrhage b. Neonatal hyperglycemia c. Postpartum oliguria d. Neonatal macrosomia Feedback a. The patient is not especially high risk for a postpartum hemorrhage. b. The nurse would expect to see neonatal hypoglycemia, not hyperglycemia. c. The nurse would expect to see postpartum polyuria. d. The nurse would expect to see neonatal macrosomia. 29. According to agency policy, the perinatal nurse provides the following intrapartal nursing care for the patient with preeclampsia: a. Take the patient’s blood pressure every 6 hours b. Encourage the patient to rest on her back c. Notify the physician of urine output greater than 30 mL/hr d. Administer magnesium sulfate according to agency policy Feedback a. The nurse is the manager of care for the woman with preeclampsia during the intrapartal period. Careful assessments are critical. The blood pressure is taken every 1 hour or more frequently according to physician orders or institutional protocol. b. The nurse is the manager of care for the woman with preeclampsia during the intrapartal period. Careful assessments are critical. The patient should be encouraged to assume a side-lying position to enhance uterine perfusion. c. The nurse is the manager of care for the woman with preeclampsia during the intrapartal period. Careful assessments are critical. A urine output less than 30 mL/hr is indicative of oliguria, and the physician must be notified. d. The nurse is the manager of care for the woman with preeclampsia during the intrapartal period. Careful assessments are critical. The nurse administers medications as ordered and should adhere to hospital protocol for a magnesium sulfate infusion. 30. A woman who is 36 weeks pregnant presents to the labor and delivery unit with a history of congestive heart disease. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the primary health-care practitioner? a. Presence of chloasma b. Presence of severe heartburn c. 10-pound weight gain in a month d. Patellar reflexes +1 Feedback a. Chloasma is a normal pregnancy finding. b. Heartburn is an expected finding during the third trimester. c. The weight gain may be due to fluid retention. Fluid retention may occur in patients with pregnancy-induced hypertension and in patients with congestive heart failure. The physician should be notified. d. Although slightly hyporeflexic, patellar reflexes of +1 are within normal limits. 31. Ms. M is 38 weeks’ gestation and is a G1 P0. At 10 pm Ms. M has just been informed by the nurse that she is 3 to 4 cm dilated, cervix is 100% effaced, and contractions are every 4 to 5 minutes. When the nurse tells her the findings from the SVE, Ms. M states that she had been contracting since early that morning and she becomes extremely frustrated stating “I should have had this baby by now.” What is the best response by the nurse? a. Remind her that length of labor for the first child can be 18 to 24 hours b. Promote relaxation techniques c. Discuss various analgesic options d. Tell Ms. M that the provider will be contacted immediately about the slow progress of labor Women in the latent phase of labor may be frustrated with lack of progress or slow progress of labor and desire companionship and encouragement. The other responses are inappropriate. The nurse should first encourage breathing and relaxation methods as well as provide reassurance, and then contact the provider. 32. Ms. P has delivered her first baby 30 minutes ago and the placenta delivered 15 minutes ago. She is attempting to breastfeed her newborn daughter for the first time. Which action by the nurse would NOT be appropriate? a. The nurse is checking the BP every 15 minutes b. The nurse is massaging the fundus vigorously c. The nurse is auscultating the infant’s heart and lungs while on the mother’s chest d. The nurse is leaving the patient unattended for 30 minutes to bond with her newborn 33. It would be most important for a nurse caring for a mother and the infant in the fourth stage of labor to do which of the following? a. Assess and massage the fundus every 15 minutes or more often if needed b. Massage the uterus continuously c. Administer oxytocin per protocol d. Assess the patient for a distended bladder The fourth stage of labor immediately follows the delivery of the placenta. The nurse should be assessing the fundus every 15 minutes for position, tone, and location. The provider may order oxytocin at this stage, and the nurse should assist the woman to the bathroom if she has a distended bladder which could interfere with the contraction of the uterus. 34. Mrs. H is telling you she feels the urge to push. This is most likely caused by what? a. Low fetal station triggering the Ferguson reflex b. A fetal position of occiput posterior (OP) c. The second stage of labor d. Transition phase 35. A low-risk patient calls the labor unit and says “I need to come in to be checked right now, there were pink streaks on the toilet paper when I went to the bathroom. I think I’m bleeding.” What response should the nurse say first? a. “How much blood is there?” b. “You sound concerned, what other labor symptoms do you have? c. “Don’t worry that sounds like a mucus plug.” d. “Does it burn when you urinate?” The nurse is using reflection to acknowledge the woman’s concerns and asks for further assessment. The woman’s fear must first be acknowledged, and then other questions or comments can be made. Multiple Response 36. The perinatal nurse describes risk factors for placenta previa to the student nurse. Placenta previa risk factors include (select all that apply): a. Cocaine use b. Tobacco use c. Previous caesarean birth d. Previous use of medroxyprogesterone (Depo-Provera) , b, c Feedback a. Placenta previa may be associated with risk factors including smoking, cocaine use, a prior history of placenta previa, closely spaced pregnancies, African or Asian ethnicity, and maternal age greater than 35 years. b. Placenta previa may be associated with risk factors including smoking, cocaine use, a prior history of placenta previa, closely spaced pregnancies, African or Asian ethnicity, and maternal age greater than 35 years. c. Placenta previa may be associated with conditions that cause scarring of the uterus such as a prior cesarean section, multiparity, or increased maternal age. d. Previous use of medroxyprogesterone (Depo-Provera) is not a risk factor for placenta previa. 37. Kerry, a 30-year-old G3 TPAL 0110 woman presents to the labor unit triage with complaints of lower abdominal cramping and urinary frequency at 30 weeks’ gestation. An appropriate nursing action would be to (select all that apply): a. Assess the fetal heart rate b. Obtain urine for culture and sensitivity c. Assess Kerry’s blood pressure and pulse d. Palpate Kerry’s abdomen for contractions Feedback a. Women experiencing preterm labor may complain of backache, pelvic aching, menstrual-like cramps, increased vaginal discharge, pelvic pressure, urinary frequency, and intestinal cramping with or without diarrhea. The patient’s abdomen should be palpated to assess for contractions, and the fetus’s heart rate should be monitored. b. Women experiencing preterm labor may complain of backache, pelvic aching, menstrual-like cramps, increased vaginal discharge, pelvic pressure, urinary frequency, and intestinal cramping with or without diarrhea. A urinalysis and urine culture and sensitivity (C & S) should be obtained on all patients who present with signs of preterm labor, and the nurse must remember that signs of UTI often mimic normal pregnancy complaints (i.e., urgency, frequency). The patient’s abdomen should be palpated to assess for contractions, and the fetus’s heart rate should be monitored. c. Assessment of blood pressure and pulse is not an important nursing action in this scenario. d. Women experiencing preterm labor may complain of backache, pelvic aching, menstrual-like cramps, increased vaginal discharge, pelvic pressure, urinary frequency, and intestinal cramping with or without diarrhea. The patient’s abdomen should be palpated to assess for contractions, and the fetus’s heart rate should be monitored. 38. The perinatal nurse knows that tocolytic agents are most often used to (select all that apply): a. Prevent maternal infection b. Prolong pregnancy to 40 weeks’ gestation c. Prolong pregnancy to facilitate administration of antenatal corticosteroids d. Allow for transport of the woman to a tertiary care facility , d Feedback a. Tocolytics are not used to treat maternal infection. b. Tocolytics are generally only effective in delaying delivery for several days. c. Presently, it is believed that the best reason to use tocolytic drugs is to allow an opportunity to begin the administration of antenatal corticosteroids to accelerate fetal lung maturity. d. Delaying the birth provides time for maternal transport to a facility equipped with a neonatal intensive care unit. 39. The perinatal nurse provides a hospital tour for couples and families preparing for labor and birth in the future. Teaching is an important component of the tour. Information provided about preterm labor and birth prevention includes (select all that apply): a. Encouraging regular, ongoing prenatal care b. Reporting symptoms of urinary frequency and burning to the health-care provider c. Coming to the labor triage unit if back pain or cramping persist or become regular d. Lying on the right side, withholding fluids, and counting fetal movements if contractions occur every 5 minutes , b, c Feedback a. The nurse should encourage all pregnant women to obtain prenatal care and screen for vaginal and urogenital infections and treat appropriately, and remind pregnant women to call their provider repeatedly if symptoms of preterm labor occur. b. Educating all women of childbearing age about preterm labor is a crucial component of prevention. The nurse should encourage all pregnant women to obtain prenatal care and screen for vaginal and urogenital infections and treat appropriately, and remind pregnant women to call their provider repeatedly if symptoms of preterm labor occur. c. Educating all women of childbearing age about preterm labor is a crucial component of prevention. The nurse should encourage all pregnant women to obtain prenatal care and screen for vaginal and urogenital infections and treat appropriately and remind pregnant women to call their provider if symptoms of preterm labor occur. d. Lying on the right side; drinking fluids, not withholding fluids; and counting fetal movements if contractions occur every 5 minutes are recommended if a woman thinks she is contracting. 40. The perinatal nurse describes for the new nurse the various risks associated with prolonged premature preterm rupture of membranes. These risks include (select all that apply): a. Chorioamnionitis b. Abruptio placentae c. Operative birth d. Cord prolapse Short Answer 41. A condition where the placenta attaches to the lower uterine segment of the uterus 42. A pregnancy that ends before 20 weeks’ gestation 43. Specks or spots in the vision where the patient cannot see; “blind spots” 44. A disease characterized by an abnormal placental development that results in the production of fluid-filled grapelike clusters and a vast proliferation of trophoblastic tissue 45. No expulsion of the products of conception, but bleeding and dilation of the cervix such that a pregnancy is unlikely 46. Placement of suture to mechanically close a weak cervix True/False 47. The perinatal nurse observes the placental inspection by the health-care provider after birth. This examination may help to determine whether an abruption has occurred prior to or during labor. 48. It is critical for the perinatal nurse to learn, as part of the facility’s policies and procedures, to immediately perform a vaginal examination on a woman who presents with vaginal bleeding after 24 weeks’ gestation. 49. The perinatal nurse knows that the survival rate for infants born at or greater than 28 to 29 gestational weeks is greater than 90%. Fill-in-the-Blank 50. The perinatal nurse knows that an early pregnancy loss occurs before __________ weeks, and a late pregnancy loss is one that occurs between 12 and __________ weeks. 51. Mary, a G3 TPAL 0020 woman at 20 weeks’ gestation, has had a transvaginal ultrasound. Mary has been informed that she has cervical incompetence. The perinatal nurse explains that this diagnosis means that her cervix has __________ without __________ contractions. 52. The perinatal nurse knows that nausea and vomiting are common in pregnancy and usually resolve by __________ weeks’ gestation. The severe form of this condition is __________. 53. The perinatal nurse explains to the student nurse who is assessing the abdomen of a 32-week pregnant woman with placenta previa that it would not be unusual to find the fetus in a __________ or __________ position. 54. The perinatal nurse knows that a __________ hemorrhage is limited to the uterus, and a __________ hemorrhage moves blood toward and through the cervix. 55. The perinatal nurse encourages Colleen, who has just been discharged from the hospital for intravenous therapy for severe nausea and vomiting, to ensure that she __________ often, eats frequent, __________ meals, and avoids __________ odors. Matching Match the term with the definition 56. Third stage of labor 57. Transition phase 58. False labor 59. Latent phase a. Early and slow labor. Can last up to 9 hours. Many women choose to stay home. b. Irregular contractions, with no increase in frequency, intensity, and duration, cause little or no cervical change c. Cervical dilation from 8 to 10 cm, contractions every 1 to 2 minutes. Woman may be panicky and irritable. d. Occurs immediately after the delivery of the fetus. Involves the separation and delivery of the placenta. Can last up to 20 minutes. Chapter 9: Fetal Heart Rate Assessment Multiple Choice 1. The nurse uses the external electronic fetal heart monitor to evaluate fetal status. The fetal heart tracing shows accelerations. Accelerations in the fetal heart are: a. Associated with fetal well-being and oxygenation b. An indication of potential fetal intolerance to labor c. Never associated with the uterine contraction pattern d. A reason to notify the care provider Feedback a. Accelerations are a sign of fetal well-being. b. Accelerations are a sign of fetal well-being and are reassuring. c. Accelerations may or may not be associated with uterine contractions. d. Accelerations are reassuring, and there is no need to notify the care provider. 2. The nurse knows that a FHR monitor printout indicates a Category III abnormal fetal heart rate pattern when: a. Baseline variability is minimal or absent with decelerations. b. FHR mirrors the uterine contractions. c. Occasional periodic accelerations occur. d. Baseline variability is 6 to 25 bpm with decelerations Feedback a. Minimal or absent baseline variability may be an indication of fetal hypoxia. b. This answer describes early decelerations that are not an indication of fetal intolerance of labor. c. Periodic accelerations are a sign of fetal well-being. d. A baseline variability of 6 to 25 bpm is normal. 3. As the nurse explains the purpose of the tocotransducer (Toco), which she places on the abdomen, she states that this monitoring device provides an accurate evaluation of which of the following? a. Uterine hypertonus b. Frequency of contractions c. Intensity of contractions d. Progress of labor Feedback a. Uterine tone is palpated or measured with an intrauterine pressure catheter (IUPC). b. A tocotransducer measures frequency and duration of uterine contractions. c. Contraction strength is palpated or measured with an intrauterine pressure catheter (IUPC). d. Progress of labor is evaluated with a sterile vaginal examination (SVE). 4. Early decelerations are probably caused by: a. Decreased maternal–fetal exchange b. Umbilical cord occlusion c. Momentary increase in intracranial pressure due to head compression d. Compression of umbilical cord Feedback a. Decreased maternal–fetal exchange results in late decelerations. b. Umbilical cord occlusion results in variable deceleration or bradycardia. c. Early decelerations are related to increased intracranial pressure due to head compression. d. Compression of the umbilical cord results in variable decelerations. 5. Which statement correctly describes the nurse’s responsibility related to electronic fetal monitoring? a. Teach the woman and her family about the monitoring equipment and discuss any questions they have. b. Report abnormal findings to the care provider before initiating corrective actions. c. Inform the support person that the nurse will be responsible for all comfort measures when the electronic equipment is in place. d. Document the frequency, duration, and intensity of contractions measured by the external device. Feedback a. Teaching is an essential part of the nurse’s role. b. Corrective measures for a non-reassuring fetal heart rate are done before notifying a provider. c. The support person can help to provide comfort measures for women in labor. d. Only an IUPC will measure the intensity of uterine contractions. 6. The nurse is caring for a woman, G2 P1001, 40 weeks’ gestation, in labor. A 12 P.M. assessment revealed: cervix 4 cm, 80% effaced, –3 station, and fetal heart 124 with moderate variability. 5 p.m. assessment: cervix 6 cm, 90% effaced, –3 station, and fetal heart 120 with minimal variability. 10 a.m. assessment: cervix 8 cm, 100% effaced, –3 station, and fetal heart 124 with absent variability. Based on the assessments, which of the following should the nurse conclude? a. Descent is progressing well. b. Woman is carrying a small-for-gestational age fetus. c. Baby is potentially acidotic. d. Woman should begin to push with the next contraction. Feedback a. The baby has not descended since admission. The station is still –3. b. The baby may be macrosomic. Because the baby is not descending, the baby may be too large to traverse through the pelvis. c. The variability is decreasing. This is an indication that the fetus is in distress. d. The woman is only 8 cm dilated. She should not begin to push until she has reached 10 cm dilation. Plus, the fetal station is still –3. 7. After assessing the FHR tracing shown below, which of the following interventions should the nurse perform? a. Turn the woman on her side. b. Administer oxygen by nasal cannula. c. Encourage the patient to push with each contraction. d. Provide the patient with caring labor support. Feedback a. The woman’s position should be changed. The side-lying position is the best. b. If a laboring patient needs oxygen, it should be administered via face mask. c. There is no indication in the scenario that the patient is fully dilated. d. The nurse should not wait to intervene. He or she should intervene as quickly as possible in order to reverse the problem. 8. A nurse is preparing to monitor a patient who is to receive an amnioinfusion. Which of the following actions should the nurse make at this time? a. Attach the patient to an electronic blood pressure cuff. b. Assist in insertion of an internal uterine pressure catheter. c. Attach the patient to an oxygen saturation monitor. d. Perform an amniotic fluid Nitrazine test. Feedback a. The patient’s blood pressure will need to be monitored, but a manual cuff is sufficient. b. There is a possibility of uterine rupture during an amnioinfusion. An internal pressure transducer, therefore, must be inserted to monitor the patient’s intrauterine pressures. c. The woman’s oxygen saturation levels need not be monitored during the amnioinfusion. d. Because the woman’s membranes are already ruptured, there is no need for a Nitrazine test to be performed. 9. The perinatal nurse providing care to a laboring woman recognizes a category II, fetal heart rate tracing. The most appropriate initial action is to: a. Assist the laboring woman to a left lateral position b. Decrease the intravenous solution c. Request that the physician/certified nurse-midwife come to the hospital STAT d. Document the fetal heart rate and variability Feedback a. Because Category II fetal heart rate patterns could deteriorate, they constitute a risk indicator for fetal hypoxia, the nurse should change the woman’s position to her side to increase oxygen flow to the baby. b. Because Category II fetal heart rate patterns could deteriorate, they constitute a risk indicator for fetal hypoxia, the nurse should increase, not decrease, the IV infusion to increase perfusion through the placenta. c. The scenario described does not require STAT intervention but continued assessment after intrauterine resuscitation interventions. d. Documentation of the FHR is important but not the most important action in this scenario. Fill-in-the-Blank 10. The perinatal nurse assists the nursing student who is preparing the patient with oligohydramnios for a fluid infusion into the uterine cavity. This procedure is described as a(n) __________. mnioinfusion Pregnancy outcome in patients experiencing variable fetal heart rate decelerations caused by cord compression is improved through the use of amnioinfusion, which is the instillation of normal saline or lactated Ringer’s solution into the uterine cavity. Chapter 10: High-Risk Labor and Birth Multiple Choice 1. During labor induction with oxytocin, the fetal heart rate baseline is in the 140s with moderate variability. Contraction frequency is assessed to be every 2 minutes with duration of 60 seconds, of moderate strength to palpation. Based on this assessment, the nurse should take which action? a. Increase oxytocin infusion rate per physician’s protocol. b. Stop oxytocin infusion immediately. c. Maintain present oxytocin infusion rate and continue to assess. d. Decrease oxytocin infusion rate by 2 mU/min and report to physician. Feedback a. Increasing the oxytocin infusion could result in uterine hyperstimulation. b. The uterine contraction pattern is normal, and oxytocin infusion should be maintained, not stopped. c. Correct. Maintain present oxytocin infusion rate and continue to assess is the correct response, as this question describes a normal uterine contraction pattern. d. The uterine contraction pattern is normal, and oxytocin infusion should be maintained, not stopped or decreased. 2. If the umbilical cord prolapses during labor, the nurse should immediately: a. Type and cross-match blood for an emergency transfusion. b. Await MD order for preparation for an emergency cesarean section. c. Attempt to reposition the cord above the presenting part. d. Apply manual pressure to the presenting part to relieve pressure on the cord. Feedback a. Type and cross-match is one of the interventions with cord prolapse but not a priority. b. Awaiting MD intervention is not appropriate as umbilical cord prolapse is an obstetrical emergency requiring immediate intervention. c. Once the cord has prolapsed, it cannot be repositioned. d. Apply manual pressure to the presenting part to relieve pressure on the cord represents the first nursing intervention to attempt to improve circulation to the fetus. 3. Augmentation of labor: a. Is part of the active management of labor instituted when the labor process is unsatisfactory and uterine contractions are inadequate b. Relies on more invasive methods when oxytocin and amniotomy have failed c. Is elective induction of labor d. Is an operative vaginal delivery that uses vacuum cups Feedback a. Augmentation stimulates uterine contractions after labor has started but not progressed appropriately. b. Augmentation uses amniotomy and oxytocin. c. Augmentation stimulates labor. d. Vacuum delivery is not part of augmentation of labor. 4. Your patient is a 28-year-old gravida 2 para 1 in active labor. She has been in labor for 12 hours. Upon further assessment, the nurse determines that she is experiencing a hypotonic labor pattern. Possible maternal and fetal implications from hypotonic labor patterns are: a. Intrauterine infection and maternal exhaustion with fetal distress usually occurring early in labor. b. Intrauterine infection and maternal exhaustion with fetal distress usually occurring late in labor. c. Intrauterine infection and postpartum hemorrhage with fetal distress early in labor. d. Intrauterine infection and ruptured uterus and fetal death. Feedback a. The risk of hypotonic labor occurs later in labor. b. Hypotonic labor patterns increase risk for infection and maternal exhaustion, with fetal distress occurring late in labor as hypotonic patterns prolong labor. c. There is not an increased risk of postpartum hemorrhage or fetal distress in early labor. d. Hypotonic patterns do not result in rupture of the uterus. 5. A primigravida woman at 42 weeks’ gestation received Prepidil (dinoprostone) for induction 12 hours ago. The Bishop score is now 3. Which of the following actions by the nurse is appropriate? a. Perform Nitrazine analysis of the amniotic fluid. b. Report the lack of progress to the obstetrician. c. Place the woman on her left side. d. Ask the doctor for an order for oxytocin. Feedback a. There is nothing in the scenario that implies that the membranes may have ruptured. b. Little progress has taken place. The Bishop score of a primigravida will need to be 9 or higher before oxytocin will be effective. c. There is nothing in the scenario that implies that the patient needs to be placed on her side. d. The Bishop score of a primigravida will need to be 9 or higher before oxytocin will be effective. 6. The nurse is assisting a physician in the delivery of a baby via vacuum extraction. Which of the following nursing diagnoses for the gravida is appropriate at this time? a. Risk for injury b. Colonic constipation c. Risk for impaired parenting d. Ineffective individual coping Feedback a. There is a risk for injury. For example, the patient could suffer a cervical, vaginal, or perineal laceration. b. A diagnosis of colonic constipation is unrelated to the fact that the baby was delivered by forceps. c. There is nothing in the scenario that implies that the patient is at risk for impaired parenting. d. There is nothing in the scenario that implies that the patient is at risk for ineffective individual coping. 7. Four women are close to delivery on the labor and delivery unit. The nurse knows to be vigilant to the signs of neonatal respiratory distress in which delivery? a. 42-week-gestation pregnancy complicated by intrauterine growth restriction b. 41-week-gestation pregnancy with biophysical profile score of 10 that morning c. 40-week-gestation pregnancy with estimated fetal weight of 3200 grams d. 39-week-gestation pregnancy complicated by maternal cholecystitis Feedback a. A post-term baby with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) is high risk for meconium aspiration syndrome, cold stress syndrome, hypoglycemia, and acidosis. In each case, the baby may exhibit signs of respiratory distress. b. A biophysical profile (BPP) of 10 is a normal finding. c. The normal birth weight is between 2500 and 4000 grams. d. Maternal gallbladder disease does not place the baby in danger of developing respiratory distress. 8. You are caring for a primiparous woman admitted to labor and delivery for induction of labor at 42 weeks’ gestation. She asks you to explain the factors that contribute to prolonged labor. The best response would be to state the following: a. Primiparous women are not at risk for dystocia because they usually have small babies. b. Dystocia is related to uterine contractions, the pelvis, the fetus, the position of the mother, and psychosocial response. c. Labor is primarily associated with pelvic abnormalities. d. Dystocia is typically diagnosed prior to labor based on pelvimetry. Feedback a. Dystocia is not exclusively related to fetal size and being primiparous. b. This is the only correct definition of prolonged labor and dystocia. The success of any labor depends on the complex interrelationship of several factors: fetal size, presentation, position, size and shape of the pelvis, and quality of uterine contractions. c. Pelvic abnormality is the least important contributor to dystocia. d. Dystocia is diagnosed during, not prior to, labor. 9. A patient, G1 P0, is admitted to the labor and delivery unit for induction of labor. The following assessments were made on admission: Bishop score of 4, fetal heart rate 140s with good variability and no decelerations, TPR 98.6ºF, 88, 20, BP 120/80, negative obstetrical history. A prostaglandin suppository was inserted at that time. Which of the following findings, 6 hours after insertion, would warrant the removal of the Cervidil (dinoprostone)? a. Bishop score of 5 b. Fetal heart of 152 bpm c. Respiratory rate of 24 rpm d. Contraction frequency of every 2 minutes Feedback a. A Bishop score of 9 or higher indicates that the primigravida woman’s cervix is ripe. b. A fetal heart rate of 152 is within normal limits for this fetus. c. A respiratory rate of 24 is within normal limits. d. Cervidil should be removed for tachysystole. 10. A pregnant woman who has a history of cesarean births is requesting to have a vaginal birth after cesarean (VBAC). In which of the following situations should the nurse advise the patient that her request may be declined? a. Transverse fetal lie b. Flexed fetal attitude c. Previous low flap uterine incision d. Positive vaginal candidiasis Feedback a. A baby in the transverse lie is lying sideways in the uterus. This lie is incompatible physiologically with a vaginal delivery. b. A baby in the flexed fetal attitude is in a physiologic position for a vaginal delivery. c. A previous low flap uterine incision is not incompatible physiologically with a vaginal delivery. d. A positive vaginal Candidiasis culture is not an indication for cesarean birth. 11. The physician has ordered intravenous oxytocin for induction for four gravidas. In which of the following situations should the nurse refuse to comply with the order? a. Primigravida with complete placenta previa b. Multigravida with extrinsic asthma c. Primigravida who is 38 years old d. Multigravida who is colonized with group B streptococci Feedback a. The nurse should refuse to comply with this order because labor is contraindicated for a patient with complete placenta previa. This patient will have to be delivered via cesarean section. b. Induction is not contraindicated for patients with asthma. c. Induction is not contraindicated for patients who are 38 years old. d. Induction is not contraindicated for patients with group B streptococci. 12. The perinatal nurse notes a rapid decrease in the fetal heart rate that does not recover immediately following an amniotomy. The most likely cause of this obstetrical emergency is: a. Prolapsed umbilical cord b. Vasa previa c. Oligohydramnios d. Placental abruption Feedback a. The nurse needs to assess the fetal heart rate immediately before and after the artificial rupture of membranes. Changes such as transient fetal tachycardia may occur and are common. However, other FHR patterns such as bradycardia and variable decelerations may be indicative of cord compression or prolapse. b. Vasa previa is abnormal insertion of the cord into the placenta c. Oligohydramnios is a decreased amount of amniotic fluid. d. Placenta abruption is separation of the placenta from the uterine wall. In this scenario, prolapsed cord is the most likely cause of the abrupt deceleration in the FHR. 13. During the postpartum assessment, the perinatal nurse notes that a patient who has just experienced a forceps-assisted birth now has a large quantity of bright red bleeding. Her uterine fundus is firm. The nurse’s most appropriate action is to notify the physician/certified nurse midwife and describe a: a. Need for vaginal assessment and repair b. Requirement for an oxytocin infusion c. Need for further information for the woman/family about forceps d. Requirement for bladder assessment and catheterization Feedback a. In the presence of a firm fundus and bright red bleeding, after a forceps-assisted birth there is a need for vaginal assessment and there may be a need for repair. b. The fundus is firm, and oxytocin is not indicated. c. There is no indication in this scenario that the family needs more information. d. There is no indication in this scenario that the bladder is contributing to the bleeding. 14. The perinatal nurse is providing care to Carol, a 28-year-old multiparous woman in labor. Upon arrival to the birthing suite, Carol was 7 cm dilated and experiencing contractions every 1 to 2 minutes which she describes as “strong.” Carol states she labored for 1 hour at home. As the nurse assists Carol from the assessment area to her labor and birth room, Carol states that she is feeling some rectal pressure. Carol is most likely experiencing: a. Hypertonic contractions b. Hypotonic contractions c. Precipitous labor d. Uterine hyperstimulation Feedback a. Hypertonic contractions result in little cervical change. b. Hypotonic contractions result in little cervical change. c. Contrary to both hypertonic and hypotonic labor, precipitate labor contractions produce very rapid, intense contractions. A precipitous labor lasts less than 3 hours from the beginning of contractions to birth. Patients often progress through the first stage of labor with little or no pain and may present to the birth setting already advanced into the second stage of labor. d. Patients with precipitous labor often progress through the first stage of labor with little or no pain and may present to the birth setting already advanced into the second stage of labor. Precipitous labor contractions produce very rapid, intense contractions. Multiple Response 15. Hyperstimulation is defined as: a. Contractions lasting more than 2 minutes b. Five or more contractions in 10 minutes c. Contractions occurring within 1 minute of each other d. Uterine resting tone below 20 mm/Hg 16. Documentation related to vacuum delivery includes which of the following: a. Fetal heart rate b. Timing and number of applications c. Position and station of fetal head d. Maternal position 17. Contraindications for induction of labor include: a. Abnormal fetal position b. Postdated pregnancy c. Pregnancy-induced hypertension d. Placental abnormalities 18. Documentation related to vacuum delivery includes which of the following: a. Fetal heart rate b. Timing and number of applications c. Position and station of fetal head d. Maternal position True/False 19. The perinatal nurse includes the following when explaining the physiology of artificial rupture of membranes to the student nurse: rupture of membranes causes a release of arachidonic acid, which converts to prostaglandins, substances known to stimulate oxytocin in the pregnant uterus. 20. The perinatal nurse describes asynclitism to students as a presentation that occurs when the fetal head is turned toward the maternal sacrum or symphysis at an oblique angle. 21. The perinatal nurse explains to the student nurse that the most frequent fetal risk associated with the use of forceps is cord compression. Fill-in-the-Blank 22. The perinatal nurse prepares for two potential complications that may accompany a precipitous labor and birth: postpartum __________ and a need for neonatal __________. 23. The perinatal nurse understands that the most appropriate nursing action following an amniotomy is an assessment of the __________ as well as the __________¬¬ and __________ of the amniotic fluid. 24. The perinatal nurse caring for a laboring woman who is receiving an oxytocin infusion documents the following information: rate of __________, frequency and strength of __________, fetal __________, and cervical __________ and __________. 25. The perinatal nurse recognizes that the laboring multiparous patient who is attempting a vaginal birth following a previous cesarean birth (VBAC) needs frequent assessments to ensure that there is __________ during her labor. 26. During labor, oxytocin is always administered __________. 27. __________ is contraindicated with shoulder dystocia. . Chapter 11: Intrapartum and Postpartum Care of Cesarean Birth Families Multiple Response 1. Which of the following is a medical indication for a cesarean birth? (Select all that apply.) a. Maternal blood pressure of 130/90b. Cervical dilation of 1.5 cm per hour during the active phase of labor c. Late deceleration of the fetal heart rate with minimal variability d. Complete placenta previa e. Arrest of fetal descent 2. A nurse is caring for a woman who is 4 hours post-cesarean birth for arrest of labor. The labor and operative records indicate that she had premature rupture of membranes followed by 36 hours of labor. Her IV fluid intake for the past 24 hours is 2500 mL. The estimated blood loss is 1500 mL. Based on this data, the woman is at risk for which of the following? (Select all that apply.) a. Fluid volume deficit b. Infection c. Impaired mother–infant attachment d. Falls . 3. The perinatal nurse teaches the student nurse that deep breathing exercises following a cesarean birth are critical to the prevention of (select all that apply): a. Pneumonia b. Atelectasis c. Abdominal distension d. Increased tidal volume Incisional pain and abdominal distension often cause patients to adopt shallow breathing patterns Multiple Choice 4. A nurse is admitting a woman for a scheduled cesarean section. Which of the following assessment data should be immediately reported to the physician? a. White cell count of 11,000b. Hemoglobin of 11 g/dL c. Hematocrit of 33%d. Platelet count of 97,000 Feedback a. This laboratory value is within normal limits for a pregnant woman. b. This laboratory value is within normal limits for a pregnant woman. c. This laboratory value is within normal limits for a pregnant woman. d. Normal range of platelets is 150,000 to 400,000. A low platelet count places the woman at risk for increased bleeding. 5. A nurse is preparing a woman in early labor for an urgent cesarean birth related to breech presentation. Select the best nursing action for reducing the couple’s anxiety levels. a. Explain the reason for the need for a cesarean section. b. Inform parents that their baby is in distress. c. Ask the couple to share their concerns. d. Reassure the couple that both the woman and baby are in no danger. Feedback a. Explaining the reason she is having a cesarean birth is helpful but may not address their concerns. b. It is important to acknowledge that the baby is stable, but this response does not allow the couple to share their concerns that may be causing an increase in anxiety. c. By asking the couple to share their concerns, the nurse can address these concerns. d. Reassuring the couple that the woman and baby are in no danger is correct, but it is not the best answer because it does not allow the couple to verbalize their concerns. 6. A nurse is caring for a woman 10 hours post-cesarean birth. She received a dose of intrathecal morphine at the time of the birth. Which of the following assessment data would require immediate intervention? a. Itching of the palms and feet b. Nausea c. Urinary output of 300 mL in the past 4 hours d. Respiratory rate of 10 breaths/minute Feedback a. This is a side effect of intrathecal morphine which is not life threatening. b. This is a side effect of intrathecal morphine which is not life threatening. c. A urinary output of 300 mL in 4 hours is within normal limits. d. Correct. An adverse effect of intrathecal morphine that requires immediate intervention is respiratory distress. 7. A client delivered a 2800-gram neonate 4 hours ago by cesarean section with epidural anesthesia. Which of the following interventions should the nurse perform on the mother at this time? a. Maintain the client flat in bed. b. Assess the client’s patellar reflexes. c. Monitor hourly urinary outputs. d. Assess the client’s respiratory rate. Feedback a. The client should be assisted to a position of comfort. b. There is no indication in the scenario that the client must have her reflexes assessed. c. The client’s hydration should be monitored postsurgery, but hourly assessments are unnecessary. d. The client has undergone major abdominal surgery. Her respiratory function should be assessed regularly. 8. A post-cesarean birth woman has been diagnosed with paralytic ileus. Which of the following symptoms would the nurse expect to see? a. Abdominal distension b. Polyuria c. Diastasis recti d. Dependent edema Feedback a. The nurse would expect to see a distended abdomen in a client with a paralytic ileus. b. Polyuria is unrelated to a paralytic ileus. c. Diastasis recti is unrelated to a paralytic ileus. d. Dependent edema is unrelated to a paralytic ileus. 9. The perinatal nurse is preparing a woman for a scheduled cesarean birth. The woman will be receiving spinal anesthesia for the birth. In order to prevent maternal hypotension, the nurse: a. Assists the woman to lie down in a supine position. b. Administers a rapid intravenous infusion of 500 mL of normal saline. c. Assesses blood pressure and pulse every 5 minutes, three times, before the spinal insertion. d. Encourages frequent cleansing breaths after the patient has been placed in the correct position for the anesthesia administration. Complications that may occur with spinal anesthesia block include maternal hypotension, decreased placental perfusion, and an ineffective breathing pattern. Prior to administration, the patient’s fluid balance is assessed, and IV fluids are administered to reduce the potential for sympathetic blockade (decreased cardiac output that results from vasodilation with pooling of blood in the lower extremities). Following administration of the anesthetic, the patient’s blood pressure, pulse, and respirations and fetal heart rate must be taken and documented every 5 to 10 minutes. 10. The perinatal nurse understands that the purpose of combining an opioid with a local anesthetic agent in an epidural is primarily to: a. Increase the total anesthetic volume b. Preserve a greater amount of maternal motor function c. Increase the intensity of the motor and sensory block d. Decrease the number of side effects Combining an opioid with a local anesthetic agent reduces the total amount of anesthetic required and helps to preserve a greater amount of maternal motor function. 11. Tanya, a 30-year-old woman, is being prepared for an elective cesarean birth. The perinatal nurse assists the anesthesiologist with the spinal block and then positions Tanya in a supine position. Tanya’s blood pressure drops to 90/52, and there is a decrease in the fetal heart rate to 110 bpm. The perinatal nurse’s best response is to: a. Place a wedge under Tanya’s left hip. b. Discontinue Tanya’s intravenous administration. c. Have naloxone (Narcan) ready for administration. d. Have epinephrine ready for administration. In the event of severe maternal hypotension, the nurse should place the patient in a lateral position or use a wedge under the hip to displace the uterus, elevate the legs, maintain or increase the IV infusion rate, and administer oxygen by face mask at 10 to 12 L/min, or according to institution protocol. 12. The perinatal nurse listens as Chantal describes her labor and emergency cesarean birth. Providing an opportunity to review this experience may assist Chantal in: a. Her role development in the “letting go” stage b. Decreasing her ambivalence about her labor and birth c. Understanding her guilt involved in her labor and birth d. Developing more positive feelings about her labor and birth After a cesarean birth, especially when unplanned, nurses must be aware of the myriad of potential psychological issues that may arise. Research suggests that women may perceive cesarean birth to be a less positive experience than a vaginal birth. Unplanned or emergent cesarean deliveries and the experience of cesarean birth may be associated with more negative perceptions of the birthing experience. Allowing Chantal to talk about the experience can help her develop a more positive attitude about her own experience. 13. The best time to give prophylactic antibiotics to the women undergoing cesarean section is: a. One hour before the surgery b. Two hours before the surgery c. Not indicated unless she has an active infection d. At the time the cord is clamped Administration of narrow-spectrum prophylactic antibiotics should occur within 60 minutes prior to the skin incision. 14. During a cesarean section, which action by the nurse is done to prevent compression of the descending aorta and vena cava? a. Right lateral tilt b. Left lateral tilt c. Elevate head of gurney at 30 degrees d. Administration of IV fluid preload of 500 to 1000 mL Positioning of the patient with a left tilt maintains a left uterine displacement to decrease the risk of aortocaval compression related to compression on the aorta and inferior vena cava due to weight of the gravid uterus. Fill-in-the-Blank 15. A post-cesarean section client has been ordered to receive 500 mL of 5% dextrose in water every 4 hours. The drop factor of the macrodrip tubing is 10 gtt/mL. To what drip rate should the nurse regulate the IV? __________¬¬ gtt/min 16. The perinatal nurse knows that the presence of abdominal distension and gas in the post-cesarean birth mother is due to __________. 17. The Joint Commission Standard states that the __________, __________, and __________ are accurately identified and clearly communicated during the final verification process before the start of any surgical or invasive procedure. True/False 18. During an emergency cesarean birth the “time-out” procedure may be omitted based on the obstetrical emergency. ANS: False Joint commission guidelines for patient safety necessitate there always be a time-out to prevent wrong patient, wrong site, wrong procedure, and medical errors. Chapter 12: Postpartum Physiological Assessments and Nursing Care Multiple Choice 1. A 25-year-old woman gave birth to her second child 6 hours ago. She informs the nurse that she is bleeding more than with her previous birth experience. The initial nursing action is to: a. Explain that this is normal for second-time moms. b. Assess the location and firmness of the fundus. c. Change her pad and return in 1 hour and reassess. d. Give her 10 units of oxytocin as per standing order. Feedback a. The nurse should not inform the patient that this is normal until she has assessed for the degree and potential cause of bleeding. b. It is important to first assess for uterine atony or displaced uterus from full bladder. c. If the uterus is firm and midline, then the nurse should change the pad and return within 30 minutes to assess the amount of lochia. d. The nurse would give oxytocin if the uterus is boggy and does not respond to uterine massage. 2. Which of these medications is commonly used to control postpartum bleeding related to uterine atony? a. Magnesium sulfate b. Phytonadione c. Oxytocin d. Warfarin Feedback a. Magnesium sulfate is commonly used for PIH and preterm labor. It is a smooth muscle relaxant and can cause the uterus to relax. b. Phytonadione (vitamin K) is important for clotting but will not cause the uterus to contract. c. Oxytocin is commonly used to control postpartum bleeding related to uterine atony. d. Warfarin is an anticoagulant and will increase the risk of hemorrhage. 3. During a postpartum assessment, the nurse notes that the uterus is midline and boggy. The immediate nursing action is: a. To notify the patient’s midwife or physician b. Massage the fundus until firm and reevaluate within 30 minutes c. Give Syntocinon as per orders d. Assist the patient to the bathroom and ask her to void Feedback a. If the uterus does not respond to massage, then the nurse would give Syntocinon and notify the primary health provider. b. The first nursing action for a boggy uterus is to massage the fundus. c. If the uterus does not respond to massage, then the nurse would give Syntocinon and notify the primary health provider. d. You would assist the woman to the bathroom if the uterus is boggy and displaced to the side. 4. On day four following the birth of an average size baby, the nurse would expect the fundus to be at: a. 1 cm below umbilicus b. 2 cm below umbilicus c. 3 cm below umbilicus d. 4 cm below umbilicus Feedback a. Expected location for day 1 b. Expected location for day 2 c. Expected location for day 3 d. Correct. The uterus on the average descends 1 centimeter per day. 5. A nurse is preparing to administer RhoGam to a client who delivered a fetal demise. Which of the following must the nurse check before giving the injection? a. Verify that the direct Coombs test results are positive. b. Check that the fetus was at least 28 weeks’ gestation. c. Make sure that the client is at least 3 days postdelivery. d. Confirm that the client is Rh negative. Feedback a. The direct Coombs test is irrelevant, and because the baby has died, the Coombs will likely not be performed. b. RhoGam should be given no matter how old the fetus was. c. RhoGam must be administered before 72 hours postpartum. d. RhoGam is contraindicated for clients who are Rh+ (positive). The nurse must confirm that any client receiving RhoGam is Rh negative. 6. A nurse is performing a postpartum assessment 30 minutes after a vaginal delivery. Which of the following actions indicates that the nurse is performing the assessment correctly? a. The nurse measures the fundal height in relation to the symphysis pubis. b. The nurse monitors the client’s central venous pressure. c. The nurse assesses the client’s perineum for edema and ecchymoses. d. The nurse performs a sterile vaginal speculum exam. Feedback a. The fundal height should be measured in relation to the umbilicus. b. The central venous pressure is not monitored during postpartum assessments. c. The nurse should assess the perineum for signs of edema and ecchymoses. d. If a speculum exam were needed, a physician or midwife would perform the procedure. Speculum exams are rarely needed postpartum. 7. A woman is 2 days postpartum from a normal vaginal delivery over an intact perineum of a 3000-gram baby. Where would the nurse expect to palpate the client’s fundus? a. At the umbilicus b. 2 cm below the umbilicus c. 2 cm above the symphysis d. At the symphysis Feedback a. Expected location for 6 to 12 hours postpartum. b. The firm fundus should be 2 cm below the umbilicus. c. This is an abnormal finding and may be related to subinvolution of the uterus. d. Expected location for 6 days postpartum. 8. Which of the following clients is most likely to complain of afterbirth pains during her postpartum period? a. G1 P0, diagnosed with preeclampsia b. G2 P0, group B streptococci in the vagina c. G3 P2, gave birth to a 4100-gram baby d. G4 P1, diagnosed with preterm labor Feedback a. This client is a primipara. The nurse would not expect her to complain excessively of afterbirth pains. b. This client is a primipara. The nurse would not expect her to complain excessively of afterbirth pains. c. This client is a multipara and she delivered a macrosomic baby. She is likely to complain of severe afterbirth pains. d. Although this client is a gravida 4, she is a para 1. The nurse would not expect her to complain excessively of afterbirth pains. 9. The nurse is providing discharge counseling to a woman who is breastfeeding her baby. The nurse advises the woman that if she experiences unilateral breast inflammation, she should do which of the following? a. Apply warm soaks to the reddened area. b. Consume an herbal galactagogue. c. Bottle feed the baby during the next day. d. Take expressed breast milk to the laboratory for analysis. Feedback a. The client may be developing mastitis. She should apply warm soaks to the area. b. There is no need for a galactagogue. c. It is essential that the client continue to breastfeed. If she were to stop feeding, she could develop a breast abscess. d. Unless ordered by the physician, the milk need not be cultured. 10. The nurse is working with a 36-year-old, married client, G6 P6, who smokes. The woman states, “I don’t expect to have any more kids, but I hate the thought of being sterile.” Which of the following contraceptive methods would be best for the nurse to recommend to this client? a. Intrauterine device b. Contraceptive patch c. Bilateral tubal ligation d. Birth control pills Feedback a. An intrauterine device (IUD) is an excellent contraceptive method for women who have had at least one delivery, are in a monogamous relationship, and wish to have long-term contraception. b. The contraceptive patch is not recommended for women over 35 or for women who smoke. c. A bilateral tubal ligation is a sterilization procedure. d. Birth control pills are not recommended for women over 35 or for women who smoke. 11. The perinatal nurse demonstrates for the student nurse the correct technique of postpartum uterine palpation. Support for the lower uterine segment is critical, as without it, there is an increased risk of: a. Uterine edema b. Uterine inversion c. Incorrect measurement d. Intensifying the patient’s level of pain Feedback a. Placing the hand over the base of the uterus does not cause uterine edema. b. The uterine fundus is palpated by placing one hand on the base of the uterus immediately above the symphysis pubis and the other hand at the level of the umbilicus. The nurse presses inward and downward with the hand positioned on the umbilicus until the fundus is located. It should feel like a firm, globular mass located at or slightly above the umbilicus during the first hour after birth. The uterus should never be palpated without supporting the lower uterine segment. Failure to do so may result in uterine inversion and hemorrhage. c. Measurement is the same with or without the hand supporting the lower uterine segment. d. Not supporting the lower uterine segment has no effect on the level of pain felt by the patient. 12. Maddy, a G3 P1 woman, gave birth 12 hours ago to a 9 lb. 13 oz. daughter. She experiences severe cramps with breastfeeding. The perinatal nurse best describes this condition as: a. Afterpains b. Uterine hypertonia c. Bladder hypertonia d. Rectus abdominis diastasis ANS : a Afterpains (afterbirth pains) are intermittent uterine contractions that occur during the process of involution. Afterpains are more pronounced in patients with decreased uterine tone due to overdistension, which is associated with multiparity and macrosomia. Patients often describe the sensation as a discomfort similar to menstrual cramps. 13. A 35-year-old G1 P0 postpartum woman is Rh0(D)-negative and needs Rh0(D) immune globulin to be administered. The most appropriate dose that the perinatal nurse would expect to be ordered would be: a. 120 ug b. 250 ug c. 300 ug d. 350 ug Non-sensitized women who are Rh0(D)-negative and have given birth to an Rh(D)-positive infant should receive 300 ug of Rh0(D) immune globulin (RhoGAM) within 72 hours after giving birth. RhoGAM should be given whether or not the mother received RhoGAM during the antepartum period. In some situations, depending on the extent of hemorrhage and exchange of maternal–fetal blood, a larger dose of RhoGAM may be indicated. 14. Heather, a postpartum woman who experienced a spontaneous vaginal birth 12 hours ago, describes a headache that is worsening. Heather was given two regular strength acetaminophen (Tylenol) tablets approximately 30 minutes ago but has had no relief from the pain. Several friends and family members are presently visiting Heather. The nurse notes that Heather’s pain relief during labor consisted of a single dose of an IM narcotic. The most appropriate nursing action at this time is to: a. Notify Heather’s health-care provider about Heather’s headache. b. Dim the lights in Heather’s room so that she is able to get some rest. c. Ask Heather’s visitors to leave now to decrease Heather’s environmental stimuli. d. Ask Heather where she is experiencing this headache and to identify the pain score that best describes the intensity of the pain. The nurse should perform routine, comprehensive pain assessments to include onset, location, intensity, quality, characteristics, and aggravating and alleviating factors of the discomfort in order to provide interventions in a timely manner and enhance effectiveness of medications. The nurse should also ask the patient to rate her pain on a standard 0 to 10 pain scale before and after interventions and to identify her own acceptable comfort level on the scale. 15. The perinatal nurse teaches the postpartum woman about the normal process of diuresis that she can expect to occur approximately 6 to 8 hours after birth. A decrease in which of the following hormones is primarily responsible for the diuresis? a. Prolactin b. Progesterone c. Oxytocin d. Estrogen ANS : d Maternal diuresis occurs almost immediately after birth and urinary output reaches up to 3000 mL each day by the second to fifth postpartum days. After childbirth, a decrease in the level of estrogen naturally occurs and contributes to the diuresis. 16. During change of shift report, the nurse hears the following information on a newly delivered client: 27 years old, married, G4 P3, 8 hours post spontaneous vaginal delivery over 3º laceration, vitals—110/70, 98.6ºF, 82, 18, fundus firm at umbilicus, moderate lochia, ambulated to bathroom to void three times for a total of 900 mL, breastfeeding every 2 hours. Which of the following nursing diagnoses should the nurse include in this client’s nursing care plan? a. Fluid volume deficit b. Impaired skin integrity c. Impaired urinary elimination d. Ineffective breastfeeding Feedback a. There is nothing in the scenario that indicates that this client has had a significant blood loss. b. The client has a 3º laceration. A nursing diagnosis of impaired skin integrity is appropriate. c. The client is voiding well. There is no indication of impaired urinary elimination. d. The client is feeding q 2 h. There is no indication of impaired breastfeeding. True/False 17. The perinatal nurse teaches the postpartum woman that the most critical time to achieve effectiveness from the application of ice packs to the perineum is during the first 24 hours following birth. ANS: True To reduce perineal swelling and pain that result from bruising, ice packs may be applied every 2 to 4 hours. Patients obtain the most relief when ice packs are applied within the first 24 hours after childbirth. Fill-in-the-Blank 18. When reviewing potential causes for postpartum hemorrhage with the student nurse, the nurse is sure to include the finding of a(n) __________ bladder. . 19. The postpartum period is the first __________ weeks following childbirth. 20. The serosa stage of lochia usually occurs between day __________ and ______¬¬____ and the lochia is a _______¬¬¬___ or __________ color, and the amount is normally __________. 21. Mastitis is an inflammation of the __________. 22. Primary breast engorgement is an increase in the __________ and __________ systems that precedes the initiation of milk production. Primary breast engorgement is an increase in the vascular and lymphatic systems that precedes the initiation of milk production. Subsequent breast engorgement is related to distention of milk glands. Multiple Response 23. Which of the following nursing actions are important in the care of a postpartum woman who is at risk for orthostatic hypotension? (Select all that apply.) a. Have patient remain in bed for the first 4 hours post birth. b. Instruct patient to slowly rise to a standing position. c. Open an ammonia ampule and have the patient smell the ammonia prior to getting out of bed. d. Explain to the patient the cause and incidence of orthostatic hypotension. 24. A woman who gave birth 2 hours ago has a temperature of 37.9°C. Select all of the immediate nursing actions. a. Have patient drink two glasses of fluid over the next hour. b. Explain to the patient that she needs to rest and assist her into a comfortable position. c. Medicate the patient with 500 mg of acetaminophen as per orders. d. Call the patient’s physician or midwife to report the elevated temperature. Chapter 13: Transition to Parenthood Multiple Response 1. The nurse is caring for a recently immigrated Chinese woman in the postpartum unit. Based on cultural beliefs and practices of the woman, the nurse would anticipate which of the following? (Select all that apply.) a. The woman prefers cold water for drinking. b. The woman prefers not to shower. c. The woman prefers to have her female relatives care for her baby. d. The woman prefers to have her family bring her food to eat. 2. The nurse is caring for a postpartum woman who gave birth to a healthy, full-term baby girl. She has a 2-year-old son. She voices concern about her older child’s adjustment to the new baby. Nursing actions that will facilitate the older son’s adjustment to having a new baby in the house would include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) a. Explain to the mother that she can have her son lie in bed with her when he is visiting her in the hospital. b. Teach her son how to change the baby’s diapers. c. Assist her son in holding his new baby sister. d. Recommend that she spend time reading to her older son while he sits in her lap. 3. Which of the following nursing actions are directed at assisting men in their transition to fatherhood? (Select all that apply.) a. Encourage the woman to take on the major responsibility for infant care. b. Talk to the man, away from his partner, about his expectations of the fathering role. c. Praise the father for his interactions with his infant. d. Provide information on infant care and behavior to both parents. 4. Which of the following nursing actions are directed at promoting bonding? (Select all that apply.) a. Providing opportunity for parents to hold their newborn as soon as possible following the birth. b. Providing opportunities for the couple to talk about their birth experience and about becoming parents. c. Promoting rest and comfort by keeping the newborn in the nursery at night. d. Providing positive comments to parents regarding their interactions with their newborn. 5. Which of the following factors place a new mother at risk for parenting? (Select all that apply.) a. She is 17 years old. b. Family income is below the average income. c. Her parents live in the same city and are perceived as helpful. d. She dropped out of school at age 13. 6. Which of the following nursing actions can assist a man in his transition to fatherhood? (Select all that apply.) a. Ask the man to share his ideas of what it means to be a father. b. Demonstrate infant care such as diapering and feeding. c. Engage couple in a discussion regarding each other’s expectations of the fathering role. d. Provide the man with information on infant care. Multiple Choice 7. A 16-year-old woman delivers a healthy, full-term male infant. The nurse notes the following behaviors 2 hours after the birth: Woman holds baby away from her body; woman refers to baby as “he”; woman verbalizes she wanted a baby girl; woman requests that baby be placed in the bassinet, so she can eat her lunch. The most appropriate nursing diagnosis for this woman is: a. At risk for impaired parenting related to disappointment with baby as evidenced by verbalizing she wanted a girl b. At risk for impaired parenting related to nonnurturing behaviors as evidenced by holding baby away from body c. At risk for impaired mother–infant attachment as evidenced by woman requesting baby being placed in bassinet d. At risk for impaired mother–infant attachment related to disappointment as evidenced by calling baby “he” Feedback a. The potential is for impaired parenting related to disappointment in the gender of the baby. b. Holding baby away from her body during the first few hours is part of the maternal touch process. c. Focusing on eating during the first few hours is a behavior of taking-in and is anticipated during this phase. d. Some parents have not selected a name for their baby and will refer to their baby as “he” or “she.” There is concern if the woman calls her baby “it.” 8. The nurse notes that a new father gazes at his baby for prolonged periods of time and comments that his baby is beautiful and he is very happy having a baby. These behaviors are commonly associated with: a. Bonding b. Engrossment c. Couvade syndrome d. Attachment Feedback a. Bonding is defined as the emotional feelings that begin during pregnancy or shortly after birth between the parent and the newborn. Bonding is unidirectional from parent to newborn. b. Correct. Characteristics of engrossment are visual awareness of baby, tactile awareness of baby, perception that baby is perfect, strong attraction to baby, feeling of strong elation, and increased self-esteem. c. Couvade syndrome relates to a set of pregnancy symptoms the father experiences during pregnancy of the woman. d. Attachment is a connection that forms from parent to infant and infant to parent. Attachment has a lifelong impact on the developing individual. 9. A woman on the day of discharge from the postpartum unit requests clean towels so she can take a shower, asks a number of questions regarding breastfeeding, and shares that she is nervous about taking her baby home and not being able to remember everything she has been taught. These are behaviors associated with: a. Bonding b. Taking in c. Taking hold d. Attachment Feedback a. Bonding is defined as the emotional feelings that begin during pregnancy or shortly after birth between the parent and the newborn. Bonding is unidirectional from parent to newborn. b. In the taking-in phase, women are dependent and need assistance with self-care and care of the infant. c. Correct. These are common behaviors of women in the taking-hold phase. Women during this phase have moved to being more independent and able to initiate self-care. They are highly interested in learning about the care of their baby but can easily become frustrated and discouraged when they do not immediately master a new skill. d. Attachment is a connection that forms from parent to infant and infant to parent. Attachment has a lifelong impact on the developing individual. 10. The nurse is developing a plan of care for a client who is in the “taking-in” phase after delivering a healthy baby boy. Which of the following should the nurse include in the plan? a. Provide the client with a nutritious meal. b. Teach baby care skills like diapering. c. Discuss the pros and cons of circumcision. d. Counsel her regarding future sexual encounters. Feedback a. Mothers are very hungry immediately after delivery. The nurse should provide the client with food. b. Baby care skills should be taught during the “taking-hold” phase. c. Baby care needs should be discussed during the “taking-hold” phase. d. A discussion of sexual issues should be deferred until the “taking-hold” phase or the “letting go” phase. 11. The perinatal nurse observes the new mother watching her baby daughter closely, touching her face, and asking many questions about infant feeding. This stage of mothering is best described as: a. Taking in b. Taking hold c. Taking charge d. Taking time 12. The postpartum nurse caring for a 20-year-old G1 P0 woman who 3 hours ago delivered a healthy full-term infant, observes the woman who is lightly touching her baby girl with her fingertips but who seems to be uncomfortable holding her baby close to her body. Which of the following is an accurate interpretation of these observed behaviors? a. The woman is in the initial stage of maternal touch. b. The woman is in the taking-in phase. c. The woman is having difficulty in bonding with her baby. d. The woman needs to be medicated for pain. These are classical signs of the initial stage of Rubin’s maternal touch. True/False 13. Eye movements are an example of newborn/infant style of communication. 14. Bonding is bidirectional from parent to infant and infant to parent. 15. The postpartum nurse is caring for a couple who experienced an unplanned emergency cesarean birth. The nurse observes the following behaviors: Parents are gently touching their newborn. Mother is softly singing to her baby. Father is gazing into his baby’s eyes. Based on this data, the correct nursing diagnosis is altered parent–infant bonding related to emergency cesarean birth. Cesarean birth can place the parents at risk for bonding, but based on the observed interaction with their newborn, the parents display positive signs of bonding. Chapter 14: High-Risk Postpartum Nursing Care Multiple Choice 1. A postpartum woman has been diagnosed with postpartum psychosis. Which of the following actions should the nurse perform? a. Supervise all infant care. b. Maintain client on strict bed rest. c. Restrict visitation to her partner. d. Carefully monitor toileting. Feedback a. It is essential that a client diagnosed with postpartum (PP) psychosis not be left alone with her infant. b. There is no need for a client with PP psychosis to be on strict bed rest. c. Visitation is not usually restricted to the woman’s partner. d. There is no need to monitor the client’s toileting. 2. Which of the following sites is priority for the nurse to assess when caring for a breastfeeding client, G8 P5, who is 1-hour postdelivery? a. Nipples b. Fundus c. Lungs d. Rectum Feedback a. Her nipples should be assessed, but this is not the priority assessment. b. This client is a grand multipara. She is high risk for uterine atony and postpartum hemorrhage. The nurse should monitor her fundus very carefully. c. Her lungs should be assessed bilaterally, but this is not the priority assessment. d. Her rectum should be assessed for hemorrhoids, but this is not the priority assessment. 3. A client is 1 hour postpartum from a vacuum delivery over a midline episiotomy of a 4500-gram neonate. Which of the following nursing diagnoses is appropriate for this mother? a. Risk for altered parenting b. Risk for imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements c. Risk for ineffective individual coping d. Risk for fluid volume deficit Feedback a. Although the baby is macrosomic, there is no evidence that this mother is high risk for altered parenting. b. This woman’s baby is macrosomic—there is no indication that this woman is consuming a diet that is less than body requirements. c. There is no evidence that this mother is high risk for altered coping. d. This client is high risk for fluid volume deficit. Women who deliver macrosomic babies are high risk for uterine atony, which can lead to heavy flow of lochia. 4. The perinatal nurse accurately defines postpartum hemorrhage by including a decrease in hematocrit levels from pre- to post birth by: a. 5% b. 8% c. 10% d. 15% 5. The perinatal nurse teaches the postpartum woman about warning signs regarding development of postpartum infection. Signs and symptoms that merit assessment by the health-care provider include the development of a fever and: a. Breast engorgement b. Uterine tenderness c. Diarrhea d. Emotional lability 6. The perinatal nurse recognizes that a risk factor for postpartum depression is: a. Inadequate social support b. Age >35 years c. Gestational hypertension d. Regular schedule of prenatal care 7. Karen, a G2, P1, experienced a precipitous birth 90 minutes ago. Her infant is 4200 grams and a repair of a second-degree laceration was needed following the birth. As part of the nursing assessment, the nurse discovers that Karen’s uterus is boggy. Furthermore, it is noted that Karen’s vaginal bleeding has increased. The nurse’s most appropriate first action is to: a. Assess vital signs including blood pressure and pulse. b. Massage the uterine fundus with continual lower segment support. c. Measure and document each perineal pad changed in order to assess blood loss. d. Ensure appropriate lighting for a perineal repair if it is needed. 8. The nurse is massaging a boggy uterus. The uterus does not respond to the massage. Which medication would the nurse expect would be given first: a. Methergine b. Ergotrate c. Carboprost d. Oxytocin or pitocin 9. Approximately 8 hours ago, Juanita, a 32-year-old G1 P0, gave birth after 2 ½ hours of pushing. She required an episiotomy and an assisted birth (forceps) due to the weight and size of her baby (9 lb. 9 oz.). The perinatal nurse is performing an assessment of Juanita’s perineal area. A slight bulge is palpated and the presence of ecchymoses to the right of the episiotomy is noted. The area feels “full” and is approximately 4 cm in diameter. Juanita describes this area as “very tender.” The most likely cause of these signs and symptoms is: a. Hematoma formation b. Sepsis in the episiotomy site c. Inadequate repair of the episiotomy d. Postpartum hemorrhage 10. The perinatal nurse notifies the physician of the findings related to Juanita’s assessment. The first step in care will most likely be to: a. Prepare Juanita for surgery b. Administer intravenous fluids c. Apply ice to the perineum d. Insert a urinary catheter If the hematoma is less than 3 to 5 centimeters in diameter, the physician usually orders palliative treatments such as ice to the area for the first 12 hours along with pain medication. After 12 hours, sitz baths are prescribed to replace the application of ice. However, a hematoma larger than 5 centimeters may require incision and drainage with the possible placement of a drain. 11. The clinic nurse sees Xiao and her infant in the clinic for their 2-week follow-up visit. Xiao appears to be tired, her clothes and hair appear unwashed, and she does not make eye contact with her infant. She is carrying her son in the infant carrier and when asked to put him on the examining table, she holds him away from her body. The clinic nurse’s most appropriate question to ask would be: a. “What has happened to you?” b. “Do you have help at home?” c. “Is there anything wrong with your son?” d. “Would you tell me about the first few days at home?” The well-baby checkup that generally takes place 1 to 2 weeks following the hospital discharge may offer the first opportunity to assess the mother–baby dyad. In this setting, the nurse needs to be alert for subtle cues from the new mother, such as making negative comments about the baby or herself, ignoring the baby’s or other children’s needs, as well as the mother’s physical appearance. In a private area, the nurse should take time to explore the new mother’s feelings. A nonthreatening way to open the dialogue might be to say: “Tell me how the first few days at home have gone.” This statement provides the new mother with an opportunity to share both positive and negative impressions. 12. A postpartum nurse has received an exchange report on the four-following mother–baby couplets. Based on the provided information, which couplet should the nurse first assess? a. A 25-year-old G2P1 woman who is 36 hours post birth and is having difficulty breastfeeding her baby girl. Her fundus is firm at the umbilicus, and lochia is moderate to scant. b. A 16-year-old G1P0 who will be discharged in the afternoon. It was reported that she refers to her baby boy as “it” and that she requested to have her baby stay in the nursery, so she could sleep. c. A 32-year-old G5P4 woman who delivered a 4500-gram baby boy 2 hours ago after a 20-hour labor that was augmented. It was reported that her fundus is 2 cm above umbilicus with moderate lochia. d. A 28-year-old G2P1 woman who delivered a 3800-gram baby girl by elective cesarean birth. She had spinal anesthesia and was given intrathecal preservative-free morphine for postoperative pain management. Her vital signs are B/P 115/75, P 80, R 18 T 98. Feedback a. The priority need for this woman is breastfeeding assistance which does not require immediate attention. b. The data indicate that the woman is experiencing a delay in bonding and that social services should become involved. This needs to be done prior to discharge but does not require immediate attention. c. This woman is at risk for hemorrhage (large baby, prolonged labor, augmented labor, high parity, and immediate postpartum). This woman needs to be assessed first to determine whether the fundus is firm and if lochia is within normal limits. d. Based on data provided, this woman is stable, but should be assessed second. 13. Which of the following is an indication for the administration of methylergonovine? a. Boggy uterus that does not respond to massage and oxytocin therapy b. Woman with a large hematoma c. Woman with a deep vein thrombosis d. Woman with severe postpartum depression Feedback a. Methylergonovine (methergine) is ordered for PPH due to uterine atony or subinvolution. It is used when massage and oxytocin therapy have failed to contract the uterus. b. Hematoma occurs when blood collects within the connective tissues of the vagina or perineal areas related to a vessel that ruptured and continues to bleed. Methylergonovine stimulates contraction of the smooth muscle of the uterus and would not have an effect on the vaginal or perineal areas. c. Heparin is usually prescribed for treatment of thrombosis. d. Methylergonovine is prescribed for treatment of uterine atony. 14. A 37-year-old gravid 8 para 7 woman was admitted to the postpartum unit at 2 hours post birth. On admission to the unit, her fundus was U/U, midline, and firm, and her lochia was moderate rubra. An hour later, her fundus is midline and boggy, and the lochia is heavy with small clots. Based on this assessment data, the first nursing action is: a. Massage the fundus of the uterus. b. Assist the woman to the bathroom and reassess the fundus. c. Notify the physician or midwife. d. Start IV oxytocin therapy as per standing orders. Feedback a. Correct. Based on the assessment data that the uterus is midline and boggy, the woman is experiencing uterine atony. b. Assisting the woman to the bathroom would be a nursing action if the uterus was not midline. c. Oxytocin would be given and the primary health provider would be notified if the uterus did not respond to uterine massage. d. Oxytocin would be given and the primary health provider would be notified if the uterus did not respond to uterine massage. 15. A woman who is 12 weeks postpartum presents with the following behavior: she reports severe mood swings and hearing voices, believes her infant is going to die, she has to be reminded to shower and put on clean clothes, and she feels she is unable to care for her baby. These behaviors are associated with which of the following? a. Postpartum blues b. Postpartum depression c. Postpartum psychosis d. Maladaptive mother–infant attachment Feedback a. Postpartum blues usually occurs within the first few weeks of the postpartum period. Women experiencing postpartum blues will have mild mood swings, and they can take care of themselves as well as their baby. b. Women with PPD are predominately depressed and do not have mood swings. c. Postpartum psychosis is associated with a break from reality reflected in the woman hearing voices. d. The symptoms reported are reflective of a psychiatric disorder beyond maladaptive attachment. KEY: Integrated Process: Clinical Problem Solving | Cognitive Level: Analysis | Content Area: Maternity | Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity | Difficulty Level: Moderate True/False 16. A hematoma is the collection of blood beneath the intact skin layer following an injury to a blood vessel. 17. Abruptio placenta is a risk factor for amniotic fluid embolism. 18. Metritis is an infection that usually starts at the placental site. Fill-in-the-Blank 19. The development of a large hematoma can place the postpartum woman at risk for __________. 20. The perinatal nurse explains to a new mother that the first sign of a postpartum infection will most likely be an increased __________. 21. The perinatal nurse provides information about postpartum depression to all family members because of the potential danger not only to the mother but also to the __________. 22. A postpartum woman who describes symptoms of hallucinations and suicidal thoughts is most likely experiencing postpartum __________. 23. Postpartum woman are at an increased risk of thrombus formation immediately following birth due to an increased __________ level. 24. A nurse assesses a G2 P1 woman who gave birth to a 4500-gram baby boy 2 hours ago. The nurse notes that the woman’s labor was only 2 hours and that the infant was delivered by the labor nurse. The nurse’s assessment findings are: Fundus firm and midline at umbilicus Lochia heavy—saturates pad within 15 minutes and bleeding is a steady stream without clots Perineum intact, slight bruising Ice pack on perineum Vital signs are B/P 105/65, P 98, R 20, T 38° Based on this information, the nurse is concerned that the woman has a __________ of the __________ or __________. Multiple Response 25. Which of the following are primary risk factors for subinvolution of the uterus? (Select all that apply.) a. Fibroids b. Retained placental tissue c. Metritis d. Urinary tract infection 26. A woman is 3 hours post-early-postpartum hemorrhage of 800 mL at delivery. Select the nursing actions for care of this patient. (Select all that apply.) a. Limit fluid intake to prevent nausea and vomiting. b. Assess fundus every 4 hours during the first 8 hours. c. Explain the importance of preventing an overdistended bladder. d. Provide assistance with ambulation. 27. Which of the following actions can decrease the risk for a postpartum infection? (Select all that apply.) a. Diet high in protein and vitamin C b. Increased fluid intake c. Ambulating within a few hours after delivery d. Washing nipples with soap prior to each breastfeeding session 28. Nursing actions focused at reducing a postpartum woman’s risk for cystitis include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) a. Voiding within a few hours post-birth b. Oral intake of a minimum of 1000 mL per day c. Changing peri-pads every 3 to 4 hours or more frequently as indicated d. Reminding the woman to void every 3 to 4 hours while awake 29. A G2 P1 woman who experienced a prolonged labor and prolonged rupture of membranes is at risk for metritis. Which of the following nursing actions are directed at decreasing this risk? (Select all that apply.) a. Instruct woman to increase her fluid intake b. Instruct woman to change her peri-pads after each voiding c. Instruct woman to ambulate in the halls four times a day d. Instruct woman to apply ice packs to the perineum , b, c Feedback a. Maintaining adequate hydration can decrease a person’s risk for infection. b. Lochia is a media for bacterial growth, so it is important to frequently change the peri-pads. c. Ambulation can decrease the risk of infection by promoting uterine drainage. d. Ice pack therapy is directed at decreasing edema of the perineum and promoting comfort. It has no effect on metriosis. Chapter 15: Physiological and Behavioral Responses of the Neonate Multiple Choice 1. A woman gave birth to a 3200 g baby girl with an estimated gestational age of 40 weeks. The baby is 1 hour of age. In preparation of giving the baby an injection of vitamin K, the nurse will: a. Explain to the parents the action of the medication and answer their questions. b. Remove the neonate from the room, so the parents will not be distressed by seeing the injection. c. Completely undress the neonate to identify the injection site. d. Replace needle with a 21-gauge 5/8 needle. Feedback a. It is important to always explain to parents what and why a procedure is being done on the newborn. b. It is best to give parents an option to be with their newborn when giving injections. c. It is best to keep the newborn covered as much as possible to reduce heat loss. d. A 25-gauge 5/8 needle is used for giving injections to full-term neonates. 2. To accurately measure the neonate’s head, the nurse places the measuring tape around the head: a. Just above the ears and eyebrows b. Middle of the ear and over the eyes c. Middle of the ear and over the bridge of the nose d. Just below the ears and over the upper lip Feedback a. This is the standard measurement for the diameter of the head. b. This is not the standard measurement for the diameter of the head. c. This is not the standard measurement for the diameter of the head. d. This is not the standard measurement for the diameter of the head. 3. Which of the following neonates is at highest risk for cold stress? a. A 36 gestational week LGA neonate b. A 32 gestational week AGA neonate c. A 33 gestational week SGA neonate d. A 38 gestational week AGA neonate Feedback a. This neonate should have adequate stores of brown fat. b. This neonate is at risk for cold stress due to gestational age that results in less brown fat. c. This neonate is at risk for cold stress due to gestational age that results in less brown fat. This neonate is at higher risk because this neonate is SGA and has a higher probability of less brown fat than the 32-week AGA. d. This neonate should have adequate stores of brown fat. 4. When assessing the apical pulse of the neonate, the stethoscope should be placed at the: a. First or second intercostal space b. Second or third intercostal space c. Third or fourth intercostal space d. Fourth or fifth intercostal space Feedback a. This is not the point of maximal impulse (PMI). b. This is not the point of maximal impulse (PMI). c. This is the point of maximal impulse (PMI). d. This is not the point of maximal impulse (PMI). 5. Which of the following breath sounds are normal to hear in the neonate during the first few hours post birth? a. Scattered crackles b. Wheezes c. Stridor d. Grunting Feedback a. It is normal to hear scattered crackles during the first few hours. This is due to retained amniotic fluid that will be absorbed through the lymphatic system. b. This may indicate difficulty in breathing. c. This may indicate respiratory obstruction. d. This may indicate respiratory distress. 6. The nurse assesses that a full-term neonate’s temperature is 36.2°C. The first nursing action is to: a. Turn up the heat in the room. b. Place the neonate on the mother’s chest with a warm blanket over the mother and baby. c. Take the neonate to the nursery and place in a radiant warmer. d. Notify the neonate’s primary provider. Feedback a. Increasing the heat in the room will take a long period of time before it has an effect on the neonate. b. Skin-to-skin contact along with use of a warm blanket is the best intervention with mild temperature decrease in the neonate. c. If the temperature remains low, then the neonate needs to be placed under a radiant warmer. d. The primary health provider is notified if the temperature remains low after interventions. 7. A nurse is assessing for the tonic neck reflex. This is elicited by: a. Making a load sound near the neonate. b. Placing the neonate in a sitting position. c. Turning the neonate’s head to the side so that the chin is over the shoulder while the neonate is in a supine position. d. Holding the neonate in a semi-sitting position and letting the head slightly drop back. Feedback a. This will elicit a startle reflex. b. This is not used for eliciting a reflex. c. This is correct. d. This tests for head lag. 8. An infant admitted to the newborn nursery has a blood glucose level of 55 mg/dL. Which of the following actions should the nurse perform at this time? a. Provide the baby with routine feedings. b. Assess the baby’s blood pressure. c. Place the baby under the infant warmer. d. Monitor the baby’s urinary output. Feedback a. This blood glucose level is normal. The nurse should provide routine nursing care. b. There is no apparent need to assess this baby’s blood pressure. c. There is no apparent need to place the baby under the infant warmer. d. There is no apparent need to monitor the baby’s output. 9. Four babies have just been admitted into the neonatal nursery. Which of the babies should the nurse assess first? a. The baby with respirations 52, oxygen saturation 98% b. The baby with Apgar 9/9, weight 2960 grams c. The baby with temperature 96.3°F, length 17 inches d. The baby with glucose 60 mg/dL, heart rate 132 Feedback a. The baby’s findings are within normal limits. Another baby should be seen first. b. The baby’s findings are within normal limits. Another baby should be seen first. c. This baby should be assessed first. The baby’s temperature is low; therefore, the baby could develop cold stress syndrome. In addition, the baby is short and, therefore, could be preterm. d. The baby’s findings are within normal limits. Another baby should be seen first. 10. The nurse is about to elicit the rooting reflex on a newborn baby. Which of the following responses should the nurse expect to see? a. When the cheek of the baby is touched, the newborn turns toward the side that is touched. b. When the lateral aspect of the sole of the baby’s foot is stroked, the toes extend and fan outward. c. When the baby is suddenly lowered or startled, the neonate’s arms straighten outward and the knees flex. d. When the newborn is supine, and the head is turned to one side, the arm on that same side extends. Feedback a. This is a description of the rooting reflex. b. This is a description of the Babinski reflex. c. This is a description of the Moro reflex. d. This is a description of the tonic neck reflex. 11. A mother refused to allow her son to receive the vitamin K injection at birth. Which of the following signs or symptoms might the nurse observe in the baby as a result? a. Skin color is dusky. b. Vital signs are labile. c. Glucose levels are subnormal. d. Circumcision site oozes blood. Feedback a. Dusky coloring is due to poor oxygenation. b. Labile vital signs can be caused by a number of things, including cold stress syndrome, sepsis, and poor oxygenation. c. Subnormal glucose levels can be caused by a number of things, including prenatal diabetes mellitus, cold stress syndrome, and sepsis. d. The circumcision may ooze blood due to the lack of vitamin K, which is required for the hepatic synthesis of blood coagulation factors II, VII, and X. 12. A nurse is assisting a physician during a baby’s circumcision. Which of the following demonstrates that the nurse is acting as the baby’s patient care advocate? a. The nurse requests that oral sucrose be ordered as a pain relief measure. b. The nurse restrains the baby on the circumcision board. c. The nurse wears a surgical mask during the procedure. d. The nurse provides the physician with an iodine solution for cleansing the skin. Feedback a. This response is correct. Because the baby is unable to ask for pain medication for the procedure, the nurse is advocating for the child. b. The restraint is used to keep the baby from moving during the procedure, a safety precaution. c. The nurse is using aseptic technique during the procedure when he or she wears a mask. d. The nurse is using aseptic technique during the procedure when he or she gives the physician iodine solution for the procedure. 13. A neonate is admitted to the nursery. The nurse makes the following assessments: weight 2845 grams, overriding sagittal suture, closed posterior fontanel, and point of maximum intensity at the xiphoid process. Which of the assessments should be reported to the health-care practitioner? a. Birth weight b. Sagittal suture line c. Closed posterior fontanel d. Point of maximum intensity Feedback a. The birth weight is normally between 2500 and 4000 grams. b. With molding, there may be an overlapping sagittal suture at birth. c. With molding, the posterior fontanel may be closed at birth. d. The point of maximum intensity should be felt lateral to the left nipple at about the third or fourth intracostal space. 14. The nurse is about to elicit the Moro reflex. Which of the following responses should the nurse expect to see? a. When the cheek of the baby is touched, the newborn turns toward the side that is touched. b. When the lateral aspect of the sole of the baby’s foot is stroked, the toes extend and fan outward. c. When the baby is suddenly lowered or startled, the neonate’s arms straighten outward and the knees flex. d. When the newborn is supine, and the head is turned to one side, the arm on that same side extends. Feedback a. This is a description of the rooting reflex. b. This is a description of the Babinski reflex. c. This is a description of the Moro reflex. d. This is a description of the tonic neck reflex. 15. A nurse is doing a newborn assessment on a new admission to the nursery. Which of the following actions should the nurse make when evaluating the baby for developmental dysplasia of the hip? a. Grasp the inner aspects of the baby’s calves with thumbs and forefingers. b. Gently abduct the baby’s thighs. c. Palpate the baby’s patellae to assess for subluxation of the bones. d. Dorsiflex the baby’s feet. Feedback a. The nurse would grasp the baby’s thighs with thumbs and forefingers. b. The nurse would gently abduct the baby’s legs. c. The nurse would palpate the trochanter to assess for changes. d. The nurse would not dorsiflex the feet to assess for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). 16. A certified nursing assistant (CNA) is working with a registered nurse (RN) in the neonatal nursery. Which of the following actions would be appropriate for the nurse to delegate to the CNA? a. Admit a newly delivered baby to the nursery. b. Bathe and weigh a 3-hour-old baby. c. Provide discharge teaching to the mother of a 4-day-old baby. d. Interpret a bilirubin level reported by the laboratory. Feedback a. The RN should admit a new baby to the nursery. b. The CNA could bathe and weigh a 3-hour-old baby. c. The RN should provide clients with needed teaching. d. The RN should interpret a bilirubin level. 17. A pregnant patient at 35 weeks’ gestation gives birth to a healthy baby boy. What factors regarding the development of the normal respiratory system should the nurse consider when performing an assessment of the neonate? a. As the fetus approaches term, there is an increase in the secretion of intrapulmonary fluid. b. Lung expansion after birth suppresses the release of surfactant. c. Surfactant causes an increased surface tension within the alveoli, which allows for alveolar re-expansion following each exhalation. d. Under normal circumstances, by the 34th to 36th weeks of gestation, surfactant is produced in sufficient amounts to maintain alveolar stability. Feedback a. As the fetus approaches term, there is a decrease in the secretion of intrapulmonary fluid, which assists in reducing the pulmonary resistance to blood flow and facilitates the initiation of air breathing. b. Lung expansion after birth stimulates the release of surfactant, a slippery, detergent-like lipoprotein. c. Surfactant causes a decreased surface tension within the alveoli, which allows for alveolar re-expansion following each exhalation. d. Under normal circumstances, by the 34th to 36th weeks of gestation, surfactant is produced in sufficient amounts to maintain alveolar stability. 18. The perinatal nurse explains to a student nurse the cardiopulmonary adaptations that occur in the neonate. Which one of the following statements accurately describes the sequence of these changes? a. As air enters the lungs, the PO2 rises in the alveoli, which causes pulmonary artery relaxation and results in an increase in pulmonary vascular resistance. b. As the pulmonary vascular resistance increases, pulmonary blood flow increases, reaching 100% by the first 24 hours of life. c. Decreased pulmonary blood volume contributes to the conversion from fetal to newborn circulation. d. Once the pulmonary circulation has been functionally established, blood is distributed throughout the lungs. Feedback a. As air enters the lungs, the PO2 rises in the alveoli. This normal physiologic response causes pulmonary artery relaxation and results in a decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance. b. As the pulmonary vascular resistance decreases, pulmonary blood flow increases, reaching 100% by the first 24 hours of life. c. The increased pulmonary blood volume contributes to the conversion from fetal to newborn circulation. d. Once the pulmonary circulation has been functionally established, blood is distributed throughout the lungs. 19. A perinatal nurse assesses the skin condition of a newborn, which is characterized by a yellow coloration of the skin, sclera, and oral mucous membranes. What condition is most likely the cause of this symptom? a. Hypoglycemia b. Physiologic anemia of infancy c. Low glomerular filtration rate d. Jaundice Feedback a. Signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia include jitteriness, diaphoresis, poor muscle tone, poor sucking reflex, temperature instability, respiratory distress, tachycardia, dyspnea, apnea, high-pitched cry, irritability, lethargy, and seizures or coma. b. A low red blood cell (RBC) count signals physiologic anemia of infancy. c. The neonate’s elevated hematocrit (related to the high concentration of RBCs) and low blood pressure may lead to a decreased glomerular filtration rate. d. Jaundice is a condition characterized by a yellow (icteric) coloration of the skin, sclera, and oral mucous membranes and results from the accumulation of bile pigments associated with an excessive amount of bilirubin in the blood. 20. The nurse is assessing the neonate’s skin and notes the presence of small, irregular, red patches on the cheeks that will develop into single, yellow pimples on the chest or abdomen. The name for this common neonatal skin condition is: a. Milia b. Neonatal acne c. Erythema toxicum d. Pustular melanosis Feedback a. Milia presents as small, white papules or sebaceous cysts on the infant’s face that resemble pimples. b. Acne, a skin condition common in adolescents, may also be present in newborns and is related to excessive amounts of maternal hormones. Over time, neonatal acne disappears spontaneously from the infant’s cheeks and chest. c. Erythema toxicum is a newborn rash that consists of small, irregular, flat, red patches on the checks that develop into singular, small, yellow pimples appearing on the chest, abdomen, and extremities. d. Pustular melanosis is a condition in which small pustules are formed prior to birth. As the pustule disintegrates, a small residue or “scale” in the shape of the pustule is formed, and this lesion later develops into a small (1 to 2 millimeter) macule, or flat spot. Macules, which are brown in color, appear similar to freckles and are frequently located on the chest and extremities. Pustular melanosis occurs more commonly on African American infants than on Caucasian infants. 21. The nurse completes an initial newborn examination on a baby boy at 90 minutes of age. The baby was born at 40 weeks’ gestation with no birth trauma. The nurse’s findings include the following parameters: heart rate, 136 beats per minute; respiratory rate, 64 breaths per minute; temperature, 98.2°F (36.8°C); length, 49.5 cm; and weight, 3500 g. The nurse documents the presence of a heart murmur, absence of bowel sounds, symmetry of ears and eyes, no grunting or nasal flaring, and full range of movement of all extremities. Which assessment would warrant further investigation and require immediate consultation with the baby’s health-care provider? a. Respiratory rate b. Presence of a heart murmur c. Absent bowel sounds d. Weight Feedback a. The respiratory rate and weight are normal findings. It is not uncommon to hear murmurs in infants less than 24 hours old. b. It is not uncommon to hear murmurs in infants less than 24 hours old. c. Bowel obstruction in the neonate is often first identified by an absence of bowel sounds in a small, distinct section of the intestines; therefore, this finding should be reported. d. The weight is within normal limits. 22. The nursery nurse notes the presence of diffuse edema on a baby girl’s head. Review of the birth record indicates that her mother experienced a prolonged labor and difficult childbirth. By the second day of life, the edema has disappeared. The nurse documents the following condition in the infant’s chart. a. Caput succedaneum b. Cephalhematoma c. Subperiosteal hemorrhage d. Epstein pearls Feedback a. Caput succedaneum is diffuse edema that crosses the cranial suture lines and disappears without treatment during the first few days of life. b. Cephalhematoma, a more serious condition, results from a subperiosteal hemorrhage that does not cross the suture lines. It appears as a localized swelling on one side of the infant’s head and persists for weeks while the tissue fluid is slowly broken down and absorbed. c. Cephalhematoma, a more serious condition, results from a subperiosteal hemorrhage that does not cross the suture lines. It appears as a localized swelling on one side of the infant’s head and persists for weeks while the tissue fluid is slowly broken down and absorbed. d. Epstein pearls are whitish, hardened nodules on the gums or roof of the mouth. 23. The perinatal nurse contacts the pediatrician about a heart murmur that was auscultated during a routine newborn assessment. This finding would be abnormal at: a. 8 to 12 hours b. 12 to 24 hours c. 24 to 48 hours d. 48 to 72 hours 24. Heat loss through radiation can be reduced by: a. Closing door to room b. Warming equipment used on the neonate c. Drying the neonate d. Placing crib near a warm wall Feedback a. This is an example of preventing heat loss due to convection. b. This is an example of reducing heat loss due to conduction. c. This is an example of reducing heat loss due to evaporation. d. Placing the crib near a warm wall is an example of heat loss due to radiation. Multiple Response 25. A healthy, full-term baby is scheduled for a circumcision. Nursing actions prior to the procedure include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) a. Obtain written consent from the mother. b. Administer acetaminophen PO 1 hour before procedure per MD order. c. Feed the neonate glucose water 30 minutes before the procedure. d. Obtain the neonate’s protime. , b, c Feedback a. Circumcision is a surgical procedure and requires written consent signed by the parent. b. Administration of acetaminophen is a method of pain management for the newborn. c. Glucose water is a method of pain management for the newborn. d. It is not a standard protocol to obtain a protime prior to circumcision. 26. A first-time mother informs her nurse that another staff member came in and wanted to take her baby to the nursery. The mother refused to let the woman take her baby because the staff member did not have a picture ID. The nurse should do which of the following? (Select all that apply.) a. Praise the mother for not allowing a person without proper ID to take her baby. b. Check with the nursery to see if a staff member was recently in the patient’s room. c. Notify security of an unauthorized person in the unit. d. Alert staff of the incident. , b, c, d Feedback a. Parents are instructed not to allow anyone who does not have proper identification to take their newborn from their room. b. Check and see if there is a staff member who is not wearing picture ID. c. This incident needs to be reported to security. Usually the unit is locked, and there are security checks for unauthorized persons on the unit. d. All staff on the different shifts need to be alerted so they can watch for unauthorized persons on the unit. 27. The clinical nurse recalls that the newborn has four mechanisms by which heat is lost following birth: evaporation, conduction, convection, and radiation. Which of the following are examples of heat lost via convection? (Select all that apply.) a. An infant loses heat when not dried adequately after birth b. An infant is placed on a cold scale c. An infant is placed under a ceiling fan d. An infant is placed near an open window , d Feedback a. Evaporation is the loss of heat that occurs when water is converted into a vapor, such as inadequately dried skin. b. Conduction is the loss of heat to a cooler surface by direct skin contact, such as occurs when the infant is placed on a cold surface. c. Convective heat loss occurs when the neonate is exposed to drafts and cool circulating air, such as when being placed near an open window or fan. d. Convective heat loss occurs when the neonate is exposed to drafts and cool circulating air, such as when being placed near an open window or fan. 28. A perinatal nurse assesses a term newborn for respiratory functioning. The nurse knows that which of the following conditions is normal for newborns? (Select all that apply.) a. A respiratory rate of 60 to 80 breaths per minute b. A breathing pattern that is often shallow, diaphragmatic, and irregular c. Periodic episodes of apnea d. The neonate’s lung sounds may sound moist during early auscultation , d Feedback a. The normal respiratory rate for a healthy term newborn is 40 to 60 breaths per minute. b. The breathing pattern is often shallow, diaphragmatic, and irregular. c. Apnea is cessation of breathing that lasts more than 20 seconds; it is abnormal in the term neonate. d. Most fetal fluid is reabsorbed within the first few hours, but in some infants this process may take up to 24 hours and the lungs may sound moist for the first 24 hours. 29. The perinatal nurse observed the pediatrician completing the Ballard Gestational Age by Maturity Rating tool. The maturity components used with this assessment tool are (select all that apply): a. Physical b. Behavioral c. Reflexive d. Neuromuscular True/False 30. The nurse assessing a newborn for heat loss is aware that non-shivering thermogenesis utilizes the newborn’s stores of brown adipose tissue (BAT) to provide heat in the cold-stressed newborn. Fill-in-the-Blank 31. A newborn was born weighing 2576 grams. On day 2 of life, the baby weighed 2345 grams. What percentage of weight loss did the baby experience? (Calculate to the nearest hundredth.) 32. The perinatal nurse explains to the student nurse that successful cardiopulmonary adaptation in the neonate involves five major changes: an increased aortic pressure and decreased venous pressure; an increased systemic pressure and decreased pulmonary pressure; and closure of the __________, the __________, and the __________. 33. Upon assessment of the temperature of a newborn, the nurse recalls that the __________ is the range of temperature in which the newborn’s body temperature can be maintained with minimal metabolic demands and oxygen consumption. 34. When assessing a newborn for coagulation factors, the perinatal nurse recalls that coagulation factors to enable the newborn to effectively clot blood after childbirth are activated by __________. 35. The nurse explains to a pregnant patient that the mother’s prior exposure to illness and immunizations prompts the development of antibodies in the newborn in a process termed __________ immunity. 36. The nurse is aware that the __________ state, which generally occurs during the first 30 minutes to 1 hour after birth, characterizes the first period of reactivity and provides an excellent time for parents to bond with their infant. 37. The gray, blue, or purple areas on the buttocks of a neonate are referred to as __________. 38. __________ is a vasomotor response to decreased body temperature after birth. . 39. As the perinatal nurse performs an assessment of the infant’s head, ears, eyes, nose, and throat, the ears are noted to be low set. This clinical finding would require follow-up due to the potential for __________. 40. Assessment of the infant’s anterior fontanel is an important part of the physical examination. The nurse knows that dehydration can cause a __________ in the fontanel and __________ might increase the pressure in the fontanel. Chapter 16: Discharge Planning and Teaching Multiple Choice 1. A nurse is making a home visit on the seventh postpartum day to assess a 23-year-old primipara woman and her full-term, healthy baby. Breastfeeding is the method of infant nutrition. The woman tells the nurse that she does not think her milk is good because it looks very watery when she expresses a little before each feeding. The nurse’s best response is: a. “This is normal. You only have to be concerned when your baby does not gain weight.” b. “What types of foods are you eating? A lack of protein in the diet can cause watery looking breast milk.” c. “How much fluid are you drinking while you are nursing your baby? Too much fluid during the feeding session can dilute the breast milk.” d. “This is normal and is referred to as foremilk which is higher in water content. Later in the feeding the fat content increases and the milk becomes richer in appearance.” Feedback a. Correct information but does not provide information for the woman to understand the different types of milk. b. Incorrect information. c. Incorrect information. d. Correct. This provides an explanation for the consistency of the milk and reassures the woman that the appearance of the milk is normal. 2. A postpartum woman, who gave birth 12 hours ago, is breastfeeding her baby. She tells her nurse that she is concerned that her baby is not getting enough food since her milk has not come in. The best response for this patient is: a. “I understand your concern, but your baby will be okay until your milk comes in.” b. “Your baby seems content, so you should not worry about him getting enough to eat.” c. “Milk normally comes in around the third day. Prior to that, he is getting colostrum which is high in protein and immunoglobulins which are important for your baby’s health.” d. “You can bottle feed until your milk comes in.” Feedback a. Incorrect because it does not inform the woman of what to expect with the stages of milk. b. This conveys a message that the woman’s concern is not important. c. This response provides information on the stages of milk production to help the woman understand her newborn’s nutritional needs. d. Incorrect response. It is important to avoid bottles until breastfeeding has been well established. 3. Which of the following positions for breastfeeding is preferred for a 2-day post-cesarean-birth woman? a. Lying down on side b. Sitting c. Cradle d. Cross-cradle Feedback a. Having the woman lying on her side to breastfeed prevents pressure on her abdomen and the pain that can result from the pressure. b. In this position, the baby is on the woman’s abdomen, and this can be painful for the woman. c. In this position, the baby is on the woman’s abdomen, and this can be painful for the woman. d. In this position, the baby is on the woman’s abdomen, and this can be painful for the woman. 4. Painful nipples are a major reason why women stop breastfeeding. A primary intervention to decrease nipple irritation is: a. Teaching proper techniques for latching-on and releasing of suction b. Applying hot compresses to breast prior to feeding c. Instructing woman to express colostrum or milk at the end of the feeding session and rub it on her nipples d. Air drying nipples for 10 minutes at the end of the feeding session Feedback a. Correct. All of the answers are correct, but problems with latching-on are a primary cause of nipple irritation. b. All of the answers are correct, but problems with latching-on are a primary cause of nipple irritation. c. All of the answers are correct, but problems with latching-on are a primary cause of nipple irritation. d. All of the answers are correct, but problems with latching-on are a primary cause of nipple irritation. 5. The nurse is developing a discharge teaching plan for a 21-year-old first-time mom. This was an unplanned pregnancy. She had a prolonged labor and an early postpartum hemorrhage. The woman plans to breastfeed her baby. She plans to return to work when her baby is 3 months old. Based on this information, the three primary learning needs of this woman are: a. Breastfeeding, bathing of the newborn, and infant safety b. Breastfeeding, storage of milk, and nutrition c. Breastfeeding, contraception, infant safety d. Breastfeeding, storage of milk, and rest Feedback a. These are important learning needs but do not reflect an understanding of learning needs based on early postpartum hemorrhage and returning to work in 3 months. b. Because this is the woman’s first time breastfeeding and she plans to return to work, it is important that she feels comfortable with her understanding of breastfeeding and knows how to store her milk when she returns to work. Because she had a postpartum hemorrhage, she needs to learn what foods are high in iron. c. These are important learning needs but do not reflect an understanding of learning needs based on early postpartum hemorrhage and returning to work in 3 months. d. These are important learning needs but do not reflect an understanding of learning needs based on early postpartum hemorrhage. 6. Instructions to a mother of an uncircumcised male infant should include which of the following? a. Instruct her to use a cotton swab to clean under the foreskin. b. Instruct her to clean the penis by retracting the foreskin. c. Instruct her to clean the penis with alcohol. d. Instruct her not to retract the foreskin. Feedback a. Use of cotton swabs or retracting the foreskin can damage the inner layer of the foreskin and cause adhesions. b. Retracting the foreskin can damage the inner layer of the foreskin and cause adhesions. c. Use of alcohol is irritating and painful. d. Parents should not retract the foreskin. The foreskin will fully retract on its own around 5 years of age. 7. A mother of a 10-day-old infant calls the clinic and reports that her baby is having loose, green stools. The mother is breastfeeding her infant. Which of the following is the best nursing action? a. Instruct the woman to bring her infant to the clinic. b. Instruct the woman to decrease the amount of feeding for 24 hours and to call if the stools continue to be loose. c. Explain that this is a normal stool pattern. d. Instruct the woman to eat a bland diet for the next 24 hours and call back if the stools continue to be loose and green. Feedback a. The loose, green stools indicate that the baby is having diarrhea. The infant needs to be evaluated by the primary health provider, because prolonged diarrhea can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. b. The baby is having diarrhea. Decreasing the amount of feeding can further dehydrate the baby. c. This is not a normal stool pattern; the baby is having diarrhea. d. This neonate needs to be evaluated first, before determining a treatment plan. 8. The perinatal nurse is teaching her new mother about breastfeeding and explains that the most appropriate time to breastfeed is: a. 3 to 4 hours after the last feeding b. When her infant is in a quiet alert state c. When her infant is in an active alert state d. When her infant exhibits hunger-related crying The optimal time to breastfeed is when the baby is in a quiet alert state. Crying is usually a late sign of hunger and achieving satisfactory latch-on at this time is difficult. Latch-on is proper attachment of the infant to the breast for feeding. The neonate is most alert during the first 1 to 2 hours after an unmedicated birth, and this is the ideal time to put the infant to the breast. 9. Felicity Chan, a new mother, is accompanied by her mother during her hospital stay on the postpartum unit. Felicity’s mother makes specific, various requests of the nurses including bringing warm tea, a cot to sleep on, and that the baby not be bathed at this time. Felicity’s mother is also concerned about the amount of work that Felicity may be doing in the provision of infant care. Felicity asks for help with breastfeeding. After Felicity has finished breastfeeding, her mother asks for a bottle, so they can warm it and “feed” the baby. How would the perinatal nurse best respond to Felicity’s mother in a culturally sensitive way? a. Ask Felicity’s mother to leave for 30 minutes to allow for some private time with Felicity to explore her learning needs privately. b. Ask both Felicity and her mother about the preferred infant feeding method and assess what they already know. c. Convey to Felicity and her mother an understanding of the concepts of “hot” and “cold” within their belief system. d. Ask Felicity what she knows about breastfeeding and provide information to both women to support Felicity’s decision. In certain multicultural populations such as India, Thailand, and China, the woman’s postpartum confinement lasts for 40 days. During this time, prolonged rest with restricted activity is believed to be essential. The postpartum period is an important time for ensuring future good health, and great emphasis is placed on allowing the mother’s body to regain balance after the birth of a child. To provide sensitive, appropriate care, nurses need to adopt a flexible approach when caring for women who embrace non-Western health beliefs and practices. The nurse should advocate for the patient by inquiring about her feeding preferences and by providing information to the mother and her family to support her in her decision. 10. A neonatal nurse caring for newborns knows that the best time for a mother to first attempt breastfeeding is during which one of the following stages of activity? a. First period of reactivity b. First period of inactivity and sleep c. Second period of reactivity d. Second period of inactivity and sleep The best stage for initiating breastfeeding is the first period of active, alert wakefulness that the infant displays immediately after birth, which may last from 30 minutes to 2 hours. 11. A nurse is providing discharge teaching to the parents of a 2-day-old neonate. Which of the following information should be included in the discharge teaching on umbilical cord care? a. Cleanse the cord twice a day with hydrogen peroxide. b. Remove the cord with sterile tweezers if the cord does not fall off by 10 days of age. c. Call the doctor if greenish discharge appears. d. Cover the cord with sterile dressing until it falls off. Feedback a. There is a controversy in the literature regarding what should be used to clean the cord, but hydrogen peroxide is not one of the recommended agents. b. The cord should be allowed to fall off on its own. c. The green drainage may be a sign of infection. d. There is no need to cover the cord. 12. The nurse is teaching the parents of a 1-day-old baby how to give their baby a bath. Which of the following actions should be included? a. Clean the eye from the outer canthus to the inner canthus. b. Keep the door of the room open to allow for ventilation. c. Gather all supplies before beginning the bath. d. Check the temperature of the water with your fingertip. Feedback a. To decrease the risk of infection, the eyes should be cleaned from the inner to the outer canthus. b. Keeping doors open can cause a drop in baby’s temperature by convection. c. If items must be obtained while the bath is being given, the baby may become hypothermic from evaporation resulting from exposure to the air when wet. d. The safest way to check the temperature is with a thermometer or, if none, with the elbow or forearm. 13. The nurse is teaching the parents of a female baby how to change a baby’s diapers. Which of the following should be included in the teaching? a. Always wipe the perineum from front to back. b. Remove any vernix caseosa from the labia folds. c. Put powder on the buttocks every time the baby stools. d. Weigh every diaper in order to assess for hydration. Feedback a. To decrease risk of infection from bacteria from the rectum, the perineum of female babies should always be cleansed from front to back. b. Vernix is a natural lanolin that will be absorbed over time. Actively removing the vernix can irritate the baby’s skin. c. Powder is not recommended for use on babies. When mixed with urine, powders can produce an irritating paste. d. The number of wet diapers per day should be counted to assess hydration, but weighing diapers of full-term, healthy neonates is not necessary. 14. The nurse is advising parents of a full-term neonate being discharged from the hospital regarding car seat safety. Which of the following should be included in the teaching plan? a. Put the car seat facing forward only after the baby reaches 20 pounds. b. The infant car seat should be placed facing the rear seat in the front seat of the car. c. A fist should fit between the straps of the seat and the baby’s body. d. Seat belt adjusters should always be used to support infant car seats. Feedback a. It is unsafe for infants to be facing forward until they have reached 20 pounds, even if they are over 1 year of age. b. The baby should be facing the rear of the back seat and not the front seat. c. The straps of the car seat should fit snugly, allowing only two fingers to be inserted between them and the baby. d. Seat belt adjusters that are being sold as adding to a car seat have not been shown to be safe. 15. The nurse is teaching the parents of a healthy newborn about infant safety. Which of the following should be included in the teaching plan? a. Water temperature for the infant’s bath should be 39°C. b. Crib slates should be a maximum of 3 inches apart. c. Cover electrical outlets once the infant is crawling. d. Remove strings from infant sleepwear. Feedback a. Water temperature should be 38°C. b. Crib slates should be no wider than 2 3/8 inches. c. Electrical covers should be covered before the infant begins to crawl, because infants can roll around to move and reach outlets before they crawl. d. Strings should be removed from bedding, sleepwear, pacifiers, and other objects that come in contact with the infant to decrease the risk of strangulation. 16. Which of the following statements indicates that a new mother needs additional teaching? a. “I need to supervise my cat when she is in the same room as my baby.” b. “I will place my baby on her back when she is sleeping.” c. “I will not leave my baby on an elevated flat surface after she is able to turn over on her own.” d. “I have asked my husband to install safety latches on the lower cabinets.” Feedback a. Pets should always be supervised when in the same room as the infant, because they can intentionally and unintentionally harm the infant. b. True statement. c. Newborns/infants should never be left on an elevated flat surface because they may roll or wiggle and fall off. d. True statement. Multiple Response 17. The let-down reflex occurs in response to the release of oxytocin. Which of the following can stimulate the release of oxytocin? (Select all that apply.) a. Prolactin release b. Infant suckling c. Infant crying d. Sexual activity Feedback a. Prolactin stimulates milk production but does not have a direct effect on the release of oxytocin. b. Infant suckling can cause the release of oxytocin. c. Hearing an infant cry can cause the release of oxytocin. d. An orgasm triggers the release of oxytocin. 18. Which of the following are disadvantages of bottle feeding? (Select all that apply.) a. Hampers mother–infant attachment b. Increases cost c. Increases risk of infection d. Increases risk of childhood obesity Feedback a. Bottle feeding does not interfere with mother–infant attachment. b. The cost of formula is greater than the cost of eating a well-balanced diet. c. Bottle-fed babies are at higher risk for infection because formulas lack the antibiotics that are found in colostrum and human milk. d. There is a relationship between childhood obesity and bottle feeding. 19. The clinic nurse teaches expectant mothers about the differences between breast milk and commercially prepared infant formulas. When compared to commercially prepared formulas, breast milk has (select all that apply): a. More carbohydrates b. Less protein c. Fewer nutrients d. Less cholesterol Human breast milk contains more carbohydrates, less protein, and more cholesterol than cow’s milk or infant formulas. Commercially prepared infant formulas use vegetable oils which are void of cholesterol. 20. The perinatal nurse is teaching the new mother who has chosen to formula feed her infant. Appropriate instructions to be given to this mother include (select all that apply): a. Mix the formula with hot water only. b. Periodically check the nipple for slow flow. c. Prepare only enough formula to last for 24 hours. d. Discard any unused formula that remains in a bottle following use. Parents should be advised to read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions explicitly when preparing the formula, because some require no water and some need to be diluted with water. Cold water should be used to mix the powder, only the amount to be used for each feeding should be prepared, and any unused formula should be discarded. The nipples should be checked periodically during feedings for correct flow and should be replaced regularly. 21. The perinatal nurse describes infant feeding cues to a new mother. These feeding cues include (select all that apply): a. Vocalizations b. Mouth movements c. Moving the hand to the mouth d. Yawning The infant demonstrates readiness for feeding when he or she begins to stir, bobs the head against the mattress or mother’s neck or shoulder, makes hand-to-mouth or hand-to-hand movements, exhibits sucking or licking, exhibits rooting, and demonstrates increased activity with the arms and legs flexed and the hands in a fist. 22. Typical signs of abusive head trauma (Shaken Baby Syndrome) include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) a. Broken clavicle b. Poor feeding c. Vomiting d. Breathing problems Symptoms of abusive head trauma are extreme irritability, breathing problems, convulsions, vomiting, and pale or bluish skin. 23. General skin care for full-term infants includes which of the following? (Select all that apply.) a. Avoid daily bathing with soap. b. Use a cleanser with an alkaline pH. c. Avoid fragrant soaps. d. Apply petrolatum-based ointments sparingly to dry skin, but avoid head and face. It is not necessary to bathe an infant daily. Daily bathing with soap can cause dry skin in the infant. The cleanser should be of neutral pH and free of additives such as fragrances that could be irritants. 24. A nurse is going to teach her postpartum patient about newborn bathing, diapering, and swaddling. Which of the following indicates that the nurse incorporated teaching/learning principles in her teaching plans? (Select all that apply.) a. Asked family members to leave b. Turned off TV c. Closed the door of the room d. Administered analgesics a few hours before teaching session Feedback a. It is often helpful to have family members present, with the woman’s permission, so they can also learn about caring for the newborn. b. Turning off the TV decreases the amount of distractions and allows the woman to focus on learning about infant care. c. Closing the door decreases the amount of distractions and allows the woman to focus on learning about infant care. d. Administering analgesia prior to the teaching session will enhance the woman’s comfort and facilitate her ability to focus on the teaching session. True/False 25. The clinic nurse recognizes that the longer an infant is formula fed, the greater is the immunity and resistance the infant will develop against bacterial and viral infections. 26. It is a common custom for traditional Chinese women to bottle feed their infants until their milk comes in. Fill-in-the-Blank 27. The clinic nurse discusses gradual warming of expressed breast milk or formula and cautions against use of the __________ for heating breast milk or formula. ANS: microwave oven With regard to infant feeding and safety, parents should be taught to warm bottles slowly, never to use a microwave oven to heat breast milk or formula, and never to prop a bottle in the infant’s mouth, as this practice creates a choking hazard. 28. The perinatal nurse encourages all mothers to place their infants under 12 months of age in the supine position for sleeping, because a leading cause of death for this age group is __________. Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) is a leading cause of death among infants between the ages of 1 and 12 months. Having infants sleep on their backs has decreased the risk of SIDS. 29. The perinatal nurse understands that the hormonal processes involved in breastfeeding include decreased serum __________ and __________ levels immediately following birth which lead to an increased serum __________ level that causes milk production by the fourth to fifth postpartum days. Chapter 17: High-Risk Neonatal Nursing Care Multiple Choice 1. A neonate is born at 33 weeks’ gestation with a birth weight of 2400 gram. This neonate would be classified as: a. Low birth weight b. Very low birth weight c. Extremely low birth weight d. Very premature Feedback a. Neonates with a birth weight of less than 2500 grams but greater than 1500 grams are classified as low birth weight. b. Neonates with birth weight less than 1500 grams but greater than 1000 grams are classified as very low birth weight. c. Neonates with birth weight less than 1000 grams are classified as extremely low birth weight. d. Neonates born less than 32 weeks’ gestation are classified as very premature. 2. A nurse assesses that a 3-day-old neonate who was born at 34 weeks’ gestation has abdominal distention and vomiting. These assessment findings are most likely related to:a. Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)b. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD)c. Periventricular Hemorrhage (PVH)d. Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) Feedback a. Assessment findings for RDS include tachypnea, intercostal retractions, respiratory grunting, and nasal flaring. b. Assessment findings for BPD include chest retractions; audible wheezing, rales, and rhonchi; hypoxia; and bronchospasm. c. Assessment findings for PVH include bradycardia, hypotonia, full and/or tense anterior fontanel, and hyperglycemia. d. Assessment findings related to NEC include abdominal distention, bloody stools, abdominal distention, vomiting, and increased gastric residual. These signs and symptoms are related to the premature neonate’s inability to fully digest stomach contents and limitation in absorptive function. 3. A full-term neonate who is 30 hours old has a bilirubin level of 10 mg/dL. The neonate has a yellowish tint to the skin of the face. The mother is breastfeeding her newborn. The nurse caring for this neonate would anticipate which of the following interventions? a. Phototherapy b. Feeding neonate every 2 to 3 hours c. Switch from breastfeeding to bottle feeding d. Assess red blood cell count Feedback a. Phototherapy is considered when the levels are 12 mg/dL or higher when the neonate is 25 to 48 hours old. Neonates re-absorb increased amounts of unconjugated bilirubin in the intestines due to lack of intestinal bacteria and decreased gastrointestinal motility. b. Adequate hydration promotes excretion of bilirubin in the urine. c. Colostrum acts as a laxative and assists in the passage of meconium. d. Assessing RBC is not a treatment for hyperbilirubinemia. 4. A NICU nurse is caring for a full-term neonate being treated for group B streptococcus. The mother of the neonate is crying and shares that she cannot understand how her baby became infected. The best response by the nurse is: a. “Newborns are more susceptible to infections due to an immature immune system. Would you like additional information on the newborn immune system?” b. “The infection was transmitted to your baby during the birthing process. Do you have a history of sexual transmitted infections?” c. “Approximately 10% to 30% of women are asymptomatic carries of group B streptococcus which is found in the vaginal area. What other questions do you have regarding your baby’s health?” d. “I see that this is very upsetting for you. I will come back later and answer your questions.” Feedback a. Correct information but does not fully address the woman’s concern. b. Correct, but GBS is not a sexually transmitted disease. c. Correct. This response answers her questions and allows her to ask additional questions about her baby’s health. d. Acknowledges that she is upset but does not provide immediate information. 5. A nursery nurse observes that a full-term AGA neonate has nasal congestion, hypertonia, and tremors and is extremely irritable. Based on these observations, the nurse suspects which of the following? a. Hypoglycemia b. Hypercalcemia c. Cold stress d. Neonatal withdrawal Feedback a. Signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia are jitteriness, hypotonia, irritability, apnea, lethargy, and temperature instability, but not nasal congestion. b. Signs and symptoms of hypercalcemia are vomiting, constipation, and cardiac arrhythmias. c. Signs and symptoms of cold stress are decreased temperature, cool skin, lethargy, pallor, tachypnea, hypotonia, jitteriness, weak cry, and grunting. d. These are common signs and symptoms of neonatal withdrawal. 6. The following four babies are in the neonatal nursery. Which of the babies should be seen by the neonatologist as soon as possible? a. 1-day-old, HR 170 bpm, crying b. 2-day-old, T 98.9°F, slightly jaundice c. 3-day-old, breastfeeding q 2 h, rooting d. 4-day-old, RR 70 rpm, dusky coloring Feedback a. A slight tachycardia—170 bpm—is normal when a baby is crying. b. Slight jaundice on day 2 is within normal limits. c. It is normal for a breastfed baby to feed every 2 hours. d. A dusky skin color is abnormal in any neonate, whether or not the respiration rate is normal, although this baby is also slightly tachypneic. 7. A multipara, 26 weeks’ gestation and accompanied by her husband, has just delivered a fetal demise. Which of the following nursing actions is appropriate at this time? a. Encourage the parents to pray for the baby’s soul. b. Advise the parents that it is better for the baby to have died than to have had to live with a defect. c. Encourage the parents to hold the baby. d. Advise the parents to refrain from discussing the baby’s death with their other children. Feedback a. It is inappropriate for the nurse to advise prayer. The parents must decide for themselves how they wish to express their spirituality. b. This is an inappropriate suggestion. c. This is an appropriate suggestion. Encouraging parents to spend time with their baby and hold their baby is an action that supports the parents during the grieving process. d. This is an inappropriate suggestion. It is very important for the parents to clearly communicate the baby’s death with their other children. 8. The nurse is assessing a baby girl on admission to the newborn nursery. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the neonatologist? a. Intermittent strabismus b. Startling c. Grunting d. Vaginal bleeding Feedback a. Pseudo strabismus is a normal finding. b. Startling is a normal finding. c. Grunting is a sign of respiratory distress. The neonatologist should be notified. d. Vaginal bleeding is a normal finding. 9. It is noted that the amniotic fluid of a 42-week gestation baby, born 30 seconds ago, is thick and green. Which of the following actions by the nurse is critical at this time? a. Perform a gavage feeding immediately. b. Assess the brachial pulse. c. Assist a physician with intubation. d. Stimulate the baby to cry. Feedback a. This action is not appropriate. The baby needs tracheal suctioning. b. The baby needs to have tracheal suctioning. The most important action to promote health for the baby is for the health-care team to establish an airway that is free of meconium. c. This action is appropriate. The baby needs to be intubated in order for deep suctioning to be performed by the physician. A nurse would not intubate and suction but rather would assist with the procedures. d. It is strictly contraindicated to stimulate the baby to cry until the trachea has been suctioned. The baby would aspirate the meconium-stained fluid, which could result in meconium-aspiration syndrome. 10. A 42-week gestation neonate is admitted to the NICU (neonatal intensive care unit). This neonate is at risk for which complication? a. Meconium aspiration syndrome b. Failure to thrive c. Necrotizing enterocolitis d. Intraventricular hemorrhage Feedback a. Although there is nothing in the scenario that states that the amniotic fluid is green tinged, post-term babies are high risk for meconium aspiration syndrome. b. Post-term babies often gain weight very quickly. c. Preterm, not post-term, babies are high risk for necrotizing enterocolitis. d. Preterm, not post-term, babies are high risk for intraventricular hemorrhages. 11. A 1-day-old neonate in the well-baby nursery is suspected of suffering from drug withdrawal because he is markedly hyperreflexia and is exhibiting which of the following additional sign or symptom? a. Prolonged periods of sleep b. Hypovolemic anemia c. Repeated bouts of diarrhea d. Pronounced pustular rash Feedback a. Babies who are withdrawing from drugs have disorganized behavioral states and sleep very poorly. b. There is nothing in the scenario that indicates that this child is hypovolemic or anemic. c. Babies who are experiencing withdrawal often experience bouts of diarrhea. d. A pustular rash is characteristic of an infectious problem, not of neonatal abstinence syndrome. 12. A baby boy was just born to a mother who had positive vaginal cultures for group B streptococci. The mother was admitted to the labor room 30 minutes before the birth. For which of the following should the nursery nurse closely observe this baby? a. Grunting b. Acrocyanosis c. Pseudo strabismus d. Hydrocele Feedback a. This infant is high risk for respiratory distress. The nurse should observe this baby carefully for grunting. b. Acrocyanosis is a normal finding. c. Pseudo strabismus is a normal finding. d. Hydrocele should be reported to the neonatologist. It is not, however, an emergent problem, and it is not related to group B streptococci colonization in the mother. 13. The laboratory reported that the L/S ratio (lecithin/sphingomyelin) results from an amniocentesis of a gravid client with preeclampsia are 2:1. The nurse interprets the result as which of the following? a. The baby’s lung fields are mature. b. The mother is high risk for hemorrhage. c. The baby’s kidneys are functioning poorly. d. The mother is high risk for eclampsia. Feedback a. An L/S ratio of 2:1 usually indicates that the fetal lungs are mature. b. L/S ratios are unrelated to maternal blood loss. c. L/S ratios are unrelated to fetal renal function. d. L/S ratios are unrelated to maternal risk for becoming eclamptic. 14. Which of the following neonatal signs or symptoms would the nurse expect to see in a neonate with an elevated bilirubin level? a. Low glucose b. Poor feeding c. Hyperactivity d. Hyperthermia Feedback a. Hypoglycemia is not a sign that is related to an elevated bilirubin level. b. The baby is likely to feed poorly. An elevated bilirubin level adversely affects the central nervous system. Babies are often sleepy and feed poorly when the bilirubin level is elevated. c. Hyperactivity is the opposite of the behavior one would expect the baby to exhibit. d. Hyperthermia is not directly related to an elevated bilirubin level. 15. The perinatal nurse is assisting the student nurse with completion of documentation. The laboring woman has just given birth to a 2700-gram infant at 36 weeks’ gestation. The most appropriate term for this is: a. Preterm birth b. Term birth c. Small for gestational age infant d. Large for gestational age infant Feedback a. A preterm infant is an infant with gestational age of fewer than 36 completed weeks. b. Term births are infants born between 37 and 40 weeks. c. SAG infants at 36 weeks weigh less than 2000 grams. d. LAG infants at 36 weeks weigh over 3400 grams. 16. The NICU nurse recognizes that respiratory distress syndrome results from a developmental lack of: a. Lecithin b. Calcium c. Surfactant d. Magnesium Feedback a. The ratio of lecithin to sphingomyelin in the amniotic fluid is used to assess maturity of fetal lungs. b. Calcium is needed to prevent under mineralization of bones. c. Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) is a developmental respiratory disorder that affects preterm newborns due to lack of lung surfactant. The pathology of RDS is that there is diffuse atelectasis with congestion and edema in the lung spaces. On deflation, the alveoli collapse, and there is decreased lung compliance. d. Magnesium is needed to prevent under mineralization of bones. 17. The NICU nurse is providing care to a 35-week-old infant who has been in the neonatal intensive care unit for the past 3 weeks. His mother wants to breastfeed her son naturally but is currently pumping her breasts to obtain milk. His mother is concerned that she is only producing about 1 ounce of milk every 3 hours. The nurse’s best response to the patient’s mother would be: a. “Pumping is hard work and you are doing very well. It is good to get about 1 ounce of milk every 3 hours.” b. “Natural breastfeeding will be a challenging goal for your baby. Beginning today, you will need to begin to pump your breasts more often.” c. “Your baby will not be ready to go home for at least another week. You can begin to pump more often in the next few days in preparation for taking your child home.” d. “You have been working hard to give your son your breast milk. We can map out a schedule to help you begin today to pump more often to prepare to take your baby home.” Feedback a. This is correct information but does not assist the women in producing more milk. b. This does not provide her with a plan to increase her milk. c. This does not provide her with a plan. d. The mother should be praised for her efforts to breastfeed and encouraged to continue to pump her milk. A determined schedule for pumping the milk will help the mother keep her milk flow steady and provide enough nutrients for the infant after discharge. Multiple Response 18. A nurse is caring for a 2-day-old neonate who was born at 31 weeks’ gestation. The neonate has a diagnosis of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). Which of the following medical treatments would the nurse anticipate for this neonate? (Select all that apply.) a. Exogenous surfactant b. Corticosteroids c. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) d. Bronchodilators Feedback a. This is a common medical treatment for RDS. b. Corticosteroids are given to women in preterm labor to decrease the risk of RDS. c. CPAP is used to assist neonates with RDS. d. Bronchodilators are given to neonates with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). 19. Which of the following factors increases the risk of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) in very premature neonates? (Select all that apply.) a. Early oral feedings with formula b. Prolonged use of mechanical ventilation c. Hyperbilirubinemia d. Nasogastric feedings Feedback a. Preterm neonates have a decreased ability to digest and absorb formula. Undigested formula can cause a blockage in the intestines leading to necrosis of the bowel. b. Preterm neonates are predisposed to NEC due to alteration in blood flow to the intestines, impaired gastrointestinal host defense, and alteration in inflammatory response. c. Preterm neonates are predisposed to NEC due to alteration in blood flow to the intestines, impaired gastrointestinal host defense, and alteration in inflammatory response. d. Bacterial colonization in the intestines can occur from contaminated feeding tubes causing an inflammatory response in the bowel. 20. Nursing actions that decrease the risk of skin breakdown include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) a. Using gelled mattresses b. Using emollients in groin and thigh areas c. Using transparent dressings d. Drying thoroughly Feedback a. Use of gelled mattresses decreases the risk of pressure sores. b. Use of emollients reduces the risk of irritation from urine. c. Use of transparent dressings reduces the risk of friction injuries. d. Drying thoroughly is important in maintaining body heat. 21. Nursing actions that minimize oxygen demands in the neonate include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) a. Providing frequent rest breaks when feeding b. Placing neonate on back for sleeping c. Maintaining a neutral thermal environment (NTE) d. Clustering nursing care , d Feedback a. A prolonged feeding session increases energy consumption that increases oxygen consumption. b. Placing the neonate on the back for sleeping has no effect on oxygen consumption. c. A decrease in environmental temperature leads to a decrease in the neonate’s body temperature which leads to an increase in respiratory and heart rate that leads to an increase in oxygen consumption. d. Clustering of nursing care decreases stress which decreases oxygen requirements. 22. A nurse is caring for a 10-day-old neonate who was born at 33 weeks’ gestation. Which of the following actions assist the nurse in assessing for signs of feeding tolerance? (Select all that apply.) a. Check for presence of bowel sounds b. Assess temperature c. Check gastric residual by aspirating stomach contents d. Assess stools Feedback a. Feedings should be held and physician notified if bowel sounds are absent. b. The neonate’s temperature has no direct effect on feeding tolerance. c. Aspirated stomach contents are assessed for amount, color, and consistency. This assists in the evaluation of the degree of digestion and absorption. d. Stools are assessed for consistency, amount, and frequency. This assists in the evaluation of the degree of digestion and absorption. 23. Which of the following are common assessment findings of postmature neonates? (Select all that apply.) a. Dry and peeling skin b. Abundant vernix caseosa c. Hypoglycemia d. Thin, wasted appearance Feedback a. Vernix caseosa covers the fetus’s body around 17 to 20 weeks’ gestation; as pregnancy advances, the amount of vernix decreases. Vernix prevents water loss from the skin to the amniotic fluid; as the amount of vernix decreases, an increasing amount of water is lost from the skin. This contributes to the dry and peeling skin seen in postmature neonates. b. Vernix caseosa covers the fetus’s body around 17 to 20 weeks’ gestation; as pregnancy advances, the amount of vernix decreases. c. Placental insufficiency related to the aging of the placenta may result in post maturity syndrome, in which the fetus begins to use its subcutaneous fat stores and glycemic stores. This results in the thin and wasted appearance of the neonate and risk for hypoglycemia during the first few hours post-birth. d. Placental insufficiency related to the aging of the placenta may result in post maturity syndrome, in which the fetus begins to use its subcutaneous fat stores and glycemic stores. This results in the thin and wasted appearance of the neonate and risk for hypoglycemia during the first few hours post-birth. 24. A nurse is caring for a 40 weeks’ gestation neonate. The neonate is 12 hours post-birth and has been admitted to the NICU for meconium aspiration. The nurse recalls that the following are potential complications related to meconium aspiration (select all that apply): a. Obstructed airway b. Hyperinflation of the alveoli c. Hypo inflation of the alveoli d. Decreased surfactant proteins Feedback a. The presence of meconium in the neonate’s lungs can cause a partial obstruction of the lower airway that leads to a trapping of air and a hyperinflation of the alveoli. b. The presence of meconium in the neonate’s lungs can cause a partial obstruction of the lower airway that leads to a trapping of air and a hyperinflation of the alveoli. c. The presence of meconium in the neonate’s lungs can cause a partial obstruction of the lower airway that leads to a trapping of air and a hyperinflation of the alveoli. d. The presence of meconium in the lungs can also cause a chemical pneumonitis and inhibit surfactant production. 25. A nurse is completing the initial assessment on a neonate of a mother with type I diabetes. Important assessment areas for this neonate include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) a. Assessment of cardiovascular system b. Assessment of respiratory system c. Assessment of musculoskeletal system d. Assessment of neurological system , Feedback a. Neonates of mothers with type I diabetes are at higher risk for cardiac anomalies. b. Neonates of mothers with type I diabetes are at higher risk for RDS due to a delay in surfactant production related to high maternal glucose levels. c. Neonates of mothers with type I diabetes are usually large and are at risk for a fractured clavicle. d. Neonates of mothers with type I diabetes are at higher risk for neurological damage and seizures due to neonatal hyperinsulinism. 26. A baby was born 4 days ago at 34 weeks’ gestation. She is receiving phototherapy as ordered by the physician for physiological jaundice. She has symptoms of temperature instability, dry skin, poor feeding, lethargy, and irritability. The nurse’s priority nursing action(s) is (are) to (select all that apply): a. Verify laboratory results to check for hypo magnesia. b. Verify laboratory results to check for hypoglycemia. c. Monitor the baby’s temperature to check for hypothermia. d. Calculate 24-hour intake and output to check for dehydration. There are two priority nursing interventions for hyperbilirubinemia. Hydration status is important if the newborn shows signs of dehydration such as dry skin and mucus membranes, poor intake, concentrated urine or limited urine output, and irritability. The newborn should also be kept warm while receiving phototherapy. When an infant is under phototherapy, the temperature needs to be monitored closely because the lights give off extra heat, but if the newborn is in an open crib and undressed, hypothermia may occur. Hypo magnesia and hypoglycemia are not related to phototherapy. 27. The perinatal nurse caring for Emily, a 24-year-old mother of an infant born at 26 weeks’ gestation, is providing discharge teaching. Emily is going to travel to the specialty center approximately 200 miles away where her daughter is receiving care. The nurse tells Emily that it is normal for Emily to feel (select all that apply): a. In control b. Anxious c. Guilty d. Overwhelmed , c, d Feedback a. Parents usually feel out of control. b. Correct answer. c. Correct answer. d. Correct answer. 28. A baby has just been admitted into the neonatal intensive care unit with a diagnosis of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). Which of the following maternal problems could have resulted in this complication? (Select all that apply.) a. Cholecystitis b. Hypertension c. Cigarette smoker d. Candidiasis e. Cerebral palsy Babies born to women with cholecystitis are not especially high risk for IUGR. Babies born to women with PIH or who smoke are high risk for IUGR. Babies born to women with candidiasis or cerebral palsy are not especially high risk for IUGR. Fill-in-the-Blank 29. The perinatal nurse assessing a newborn for jaundice recalls that __________ is a process that converts the yellow lipid-soluble (nonexcretable) bilirubin pigment (present in bile) into a water-soluble (excretable) pigment. Conjugation of bilirubin constitutes a major function of the newborn’s liver. Conjugation is a process that converts the yellow lipid-soluble (nonexcretable) bilirubin pigment (present in bile) into a water-soluble (excretable) pigment. 30. Providing information to parents about jaundice constitutes an important component of the nurse’s discharge teaching. Ensuring that parents know when and who to call if their infant develops signs of jaundice will help decrease the risk of __________, or permanent brain damage. All newborns are screened before discharge for physiological jaundice. The central nervous system can be damaged from unconjugated bilirubin. If bilirubin crosses the blood–brain barrier, it can damage the cerebrum, causing a condition called kernicterus. Kernicterus occurs from brain cell necrosis and can permanently damage a newborn, depending on the amount of time the neurons are exposed to bilirubin, the susceptibility of the nervous system, and the function of the surviving neurons. 31. The NICU nurse recognizes that the infant who requires ventilation for meconium aspiration syndrome is most often __________. Meconium aspiration pneumonia occurs in 10% to 26% of all deliveries, and the incidence increases directly with gestational age. (Before 37 weeks’ gestation there is a 2% incidence, and at 42 weeks’ gestation there is a 44% incidence.) 32. The NICU nurse’s patient assignment includes an infant who is 25 weeks’ gestation. The nurse knows that according to the gestational age, this infant would be described as __________. The definition of very premature is a neonate born at less than 32 weeks’ gestation. The definition of premature is a neonate born between 32 and 34 weeks’ gestation. The definition of late premature is a neonate born between 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation. 33. Part of the assessment of a preterm infant includes obtaining an abdominal girth measurement. The NICU nurse performs this assessment because the patient is at risk for __________. When caring for a child with necrotizing enterocolitis, the nurse must measure and record frequent abdominal circumferences, auscultate bowel sounds before every feeding, and observe the abdomen for distention (observable loops or shiny skin indicating distention). Chapter 18: Well Women’s Health Multiple Response 1. Physical activity can lower a woman’s risk for (select all that apply): a. Endometriosis b. Depression c. Colon cancer d. Arthritis According to the US Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Women’s Health, physical activity can lower a woman’s risk for heart disease, type 2 diabetes, colon cancer, breast cancer, falls, and depression. 2. During a routine physical of a 31-year-old non-Hispanic black woman, it was noted that the woman’s BMI is 32, her only exercise is taking care of her two children, her last Pap test was 2 years ago, and her last clinical breast exam was 2 years ago. Based on this information the woman (select all that apply): a. Needs to be scheduled for a Pap test b. Needs to be scheduled for a clinical breast exam c. Is at risk for type 2 diabetes d. Is at risk for depression Recommended screenings for women ages 19 to 39 are clinical breast exams and Pap test every 3 years. Obesity (a BMI of 30 or greater) places the woman at risk for type 2 diabetes; decreased physical activity places the woman at risk of depression. 3. Excessive drinking places the woman at risk for (select all that apply): a. Suicide b. Stroke c. Breast cancer d. Menstrual disorders Excessive drinking places a woman at risk for alcoholism, elevated blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, stroke, breast cancer, suicide and accidents. 4. The woman’s health clinic nurse is providing information to a 21-year-old woman who is being scheduled for a pelvic exam and Pap test. This information should include (select all that apply): a. The Pap test is a diagnostic test for cervical cancer. b. The woman should not use tampons or vaginal medication or engage in sexual intercourse within 48 hours of the exam. c. The best time to have a Pap test is 5 days after the menstrual period has ended. d. The woman should have a yearly Pap test. The Pap test is a screening versus a diagnostic test. Women should not douche; use tampons; use vaginal creams, spermicide foams, creams, or jellies; use vaginal lubricants or moisturizers; use vaginal medications; or have sexual intercourse for 48 hours prior to the exam. The best time to obtain a Pap test is 5 days after the period ends. Women ages 19 to 39 should have a Pap test every 3 years. 5. A 60-year-old woman is scheduled for a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scan (DXA). The woman’s health clinic nurse should provide the following information: a. DXA is a diagnostic test for osteoporosis. b. DXA measures the bone density of the hip, spine, and forearm. c. The T score is a comparison of the woman’s bone density with that of other women her age. d. Osteoporosis can cause a stooped posture. Answers a, b, and d are true statements. A T-score is a comparison of the woman’s bone density with that of a woman 30 year of age and the same race. 6. Lesbians are at higher risk for breast, cervical, endometrial, and ovarian cancer than heterosexual women due to (select all that apply): a. A higher percentage of lesbians are smokers b. Lesbians are less likely to have a Pap test c. A higher percentage of lesbians are obese d. Lesbians are less likely to exercise Lesbians have higher rates of smoking, alcohol use, and obesity. They are also less likely to follow the recommended frequency of health screening tests. These behaviors place a woman at higher risk for breast and gynecological cancers. True/False 7. Lesbian women are at a higher risk for heart disease than heterosexual women. The rates of smoking and obesity in lesbians are higher than those of heterosexual women which places them at higher risk for heart disease. 8. Which of the following women is at highest risk for osteoporosis? a. A 70-year-old non-Hispanic white woman who has smoked for 50 years b. A 70-year-old non-Hispanic black woman who is a heavy drinker c. A 60-year-old Asian woman who takes steroids to treat SLE d. A 70-year-old Hispanic woman who has had weight loss surgery Each of the women has a risk factor for osteoporosis, but answer (a) has the additional risk factor of being a non-Hispanic white woman. Multiple Choice 9. A 65-year-old woman is complaining of jaw pain, nausea, shortness of breath without chest pain, and sweating. These are warning signs of: a. Heart attack b. Stroke c. Diabetes d. Dental disease Warning signs of heart attack in women are uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center of the chest; pain or discomfort in one or both arms; shortness of breath with or without chest discomfort; nausea; lightheadedness; sweating. 10. Which of the following foods is highest in calcium? a. An 8 oz. glass of milk b. A 1.5 oz. piece of cheddar cheese c. An 8 oz. container of plain, low-fat yogurt d. A 3 oz. piece of salmon Milk has 293 mg of calcium; cheddar cheese has 307 mg; yogurt has 415; salmon has 181 mg. Chapter 19: Alterations in Women’s Health Multiple Response 1. Postoperative nursing care for a woman who had a total hysterectomy includes (select all that apply): a. Administering hormone replacement therapy as per MD orders b. Informing the woman that she will experience small amounts of vaginal bleeding for several days c. Instructing the woman to use tampons d. Instructing the woman to increase her ambulation to facilitate return of normal intestinal peristalsis , d Feedback a. Hormone therapy is ordered for women who had a hysterectomy with salpingo-oophorectomy. b. Women will experience a few days of vaginal bleeding. c. Women should not put anything into the vagina until the area has healed. d. Ambulation decreases the risk for deep vein thrombosis and also facilitates intestinal peristalsis. 2. Menorrhagia may result from (select all that apply): a. Anovulatory cycle b. Metritis c. Anorexia d. Emotional distress Metritis can be a cause of menorrhagia. 3. Secondary amenorrhea results from (select all that apply): a. Polycystic ovary syndrome b. Diabetes c. Metritis d. Pregnancy Nutritional disturbances such as anoxia and emotional distress can cause secondary amenorrhea. 4. During a health visit, a 23-year-old patient shares with her health-care provider that she has been experiencing a yellowish mucus vaginal discharge, pain during sexual intercourse, and burning on urination. A culture of the cervical epithelial cells is obtained. Based on the patient information, the culture is obtained to assist in the diagnosis of which of the following? (Select all that apply.) a. Chlamydia b. Gonorrhea c. Genital herpes d. Syphilis These are symptoms that can be related to either chlamydia or gonorrhea. Syphilis is diagnosed via blood test. Genital herpes has symptoms similar to the flu, and the person usually has an itching or burning sensation in the genital or anal area. 5. A woman who is receiving radiation therapy for treatment of stage I cervical cancer is experiencing diarrhea. She contacts the oncology advice nurse. The advice nurse recommends that the woman (select all that apply): a. Eat five or six small meals a day instead of three large meals b. Eat cooked vegetables instead of raw vegetables c. Use baby wipes instead of toilet paper d. Reduce fluid intake to four glasses of water Radiation damages the cells of the intestines. Interventions are aimed at decreasing stress on the intestines such as eating small, frequent meals and foods low in fiber. Baby wipes help reduce irritation to the anal area. A person should increase fluid intake to compensate for fluid loss caused by the diarrhea. Multiple Choice 6. A primary topic for health promotion for a 25-year-old woman with a history of polycystic ovary syndrome is (select the most important topic): a. The adverse effects of cigarette smoking b. The adverse effects of excessive alcohol consumption c. Nutrition d. Self-esteem issues Women with PCOS are at higher risk for being obese. Obesity increases the woman’s risk for type 2 diabetes. Obesity and type 2 diabetes increase the woman’s risk for cardiovascular disease, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome. It is also important to talk about self-esteem issues related to hirsutism and the effects of smoking and drinking, but the long-term effects of obesity are a greater risk to a woman with PCOS. 7. Which of the following is correct regarding endometriosis? a. The physical symptoms of endometriosis can affect the woman’s mental health. b. The abnormal tissue bleeds into surrounding tissue during the secretory stage of the menstrual cycle. c. Endometriosis causes sterility. d. Metronidazole is used to treat endometriosis. Feedback a. The physical symptoms can have an effect on the woman’s mental health. The woman may experience anger and grief related to loss of fertility. The pain of endometriosis can interfere with social activities, and dyspareunia can have an effect on intimate relationships. b. In endometriosis, there is an abnormal tissue response to the changes of hormone levels of the menstrual cycle and the tissue breaks down and bleeds into surrounding areas during the menstrual phase. c. Endometriosis has an effect on fertility but does not cause sterility. d. Metronidazole is used to treat trichomoniasis. 8. The daughter of an 85-year-old woman informs the doctor that her mother has suddenly become disoriented/confused and that she is dizzy and having difficulty with her balance. She is agitated and has fallen twice in the last 24 hours. The patient’s blood pressure and VS are within normal limits. Her medications include Synthroid, Lisinopril, and Crestor. Based on this data, the woman is most likely experiencing: a. Stroke b. Beginning stages of dementia c. Urinary tract infection d. Adverse reaction to her medications These are classic signs/symptoms of a UTI in older women. 9. A total hysterectomy is the removal of: a. The uterus b. The uterus and cervix c. The uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, and ovaries d. The uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, ovaries, upper portion of the vagina, and lymph nodes Feedback a. This is a supracervical hysterectomy. b. This constitutes a total hysterectomy. c. This would be a salpingo-oophorectomy. d. This is a radical hysterectomy. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 199 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$20.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 07, 2020
Number of pages
199
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 07, 2020
Downloads
1
Views
134






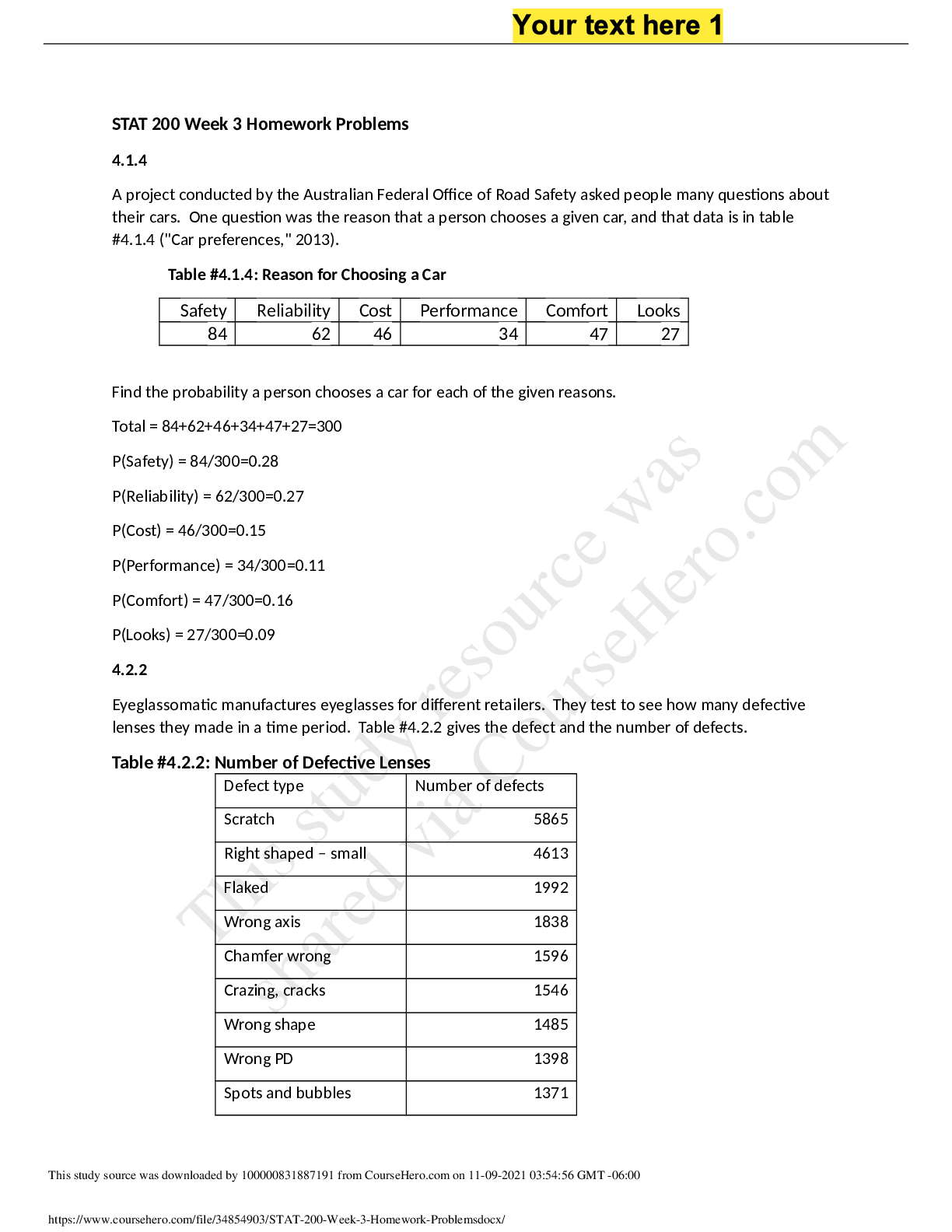




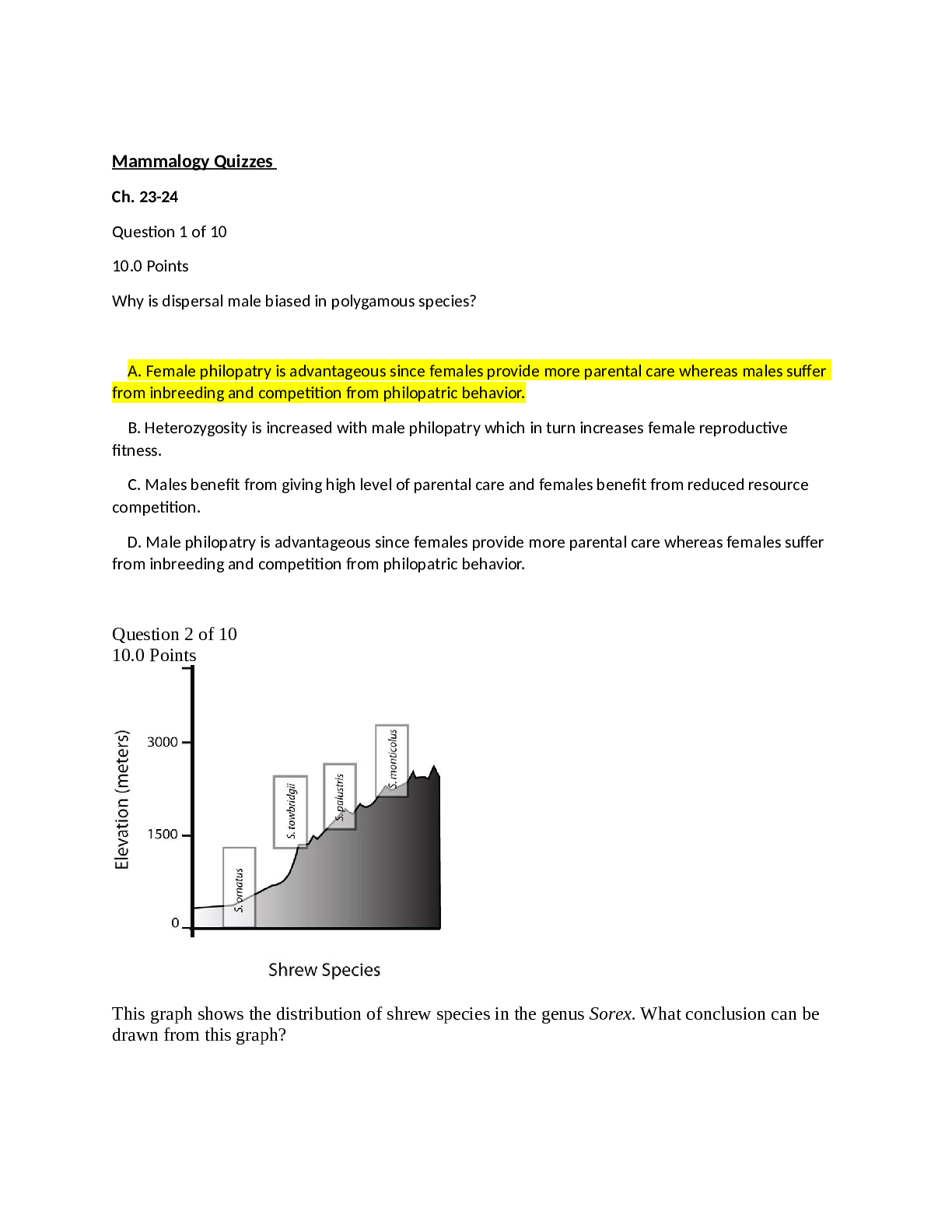
.png)




