*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NSG 307 Exam 1 Study Guide >NSG 307 Care of the Childbearing Client | Already Graded A (All)
NSG 307 Exam 1 Study Guide >NSG 307 Care of the Childbearing Client | Already Graded A
Document Content and Description Below
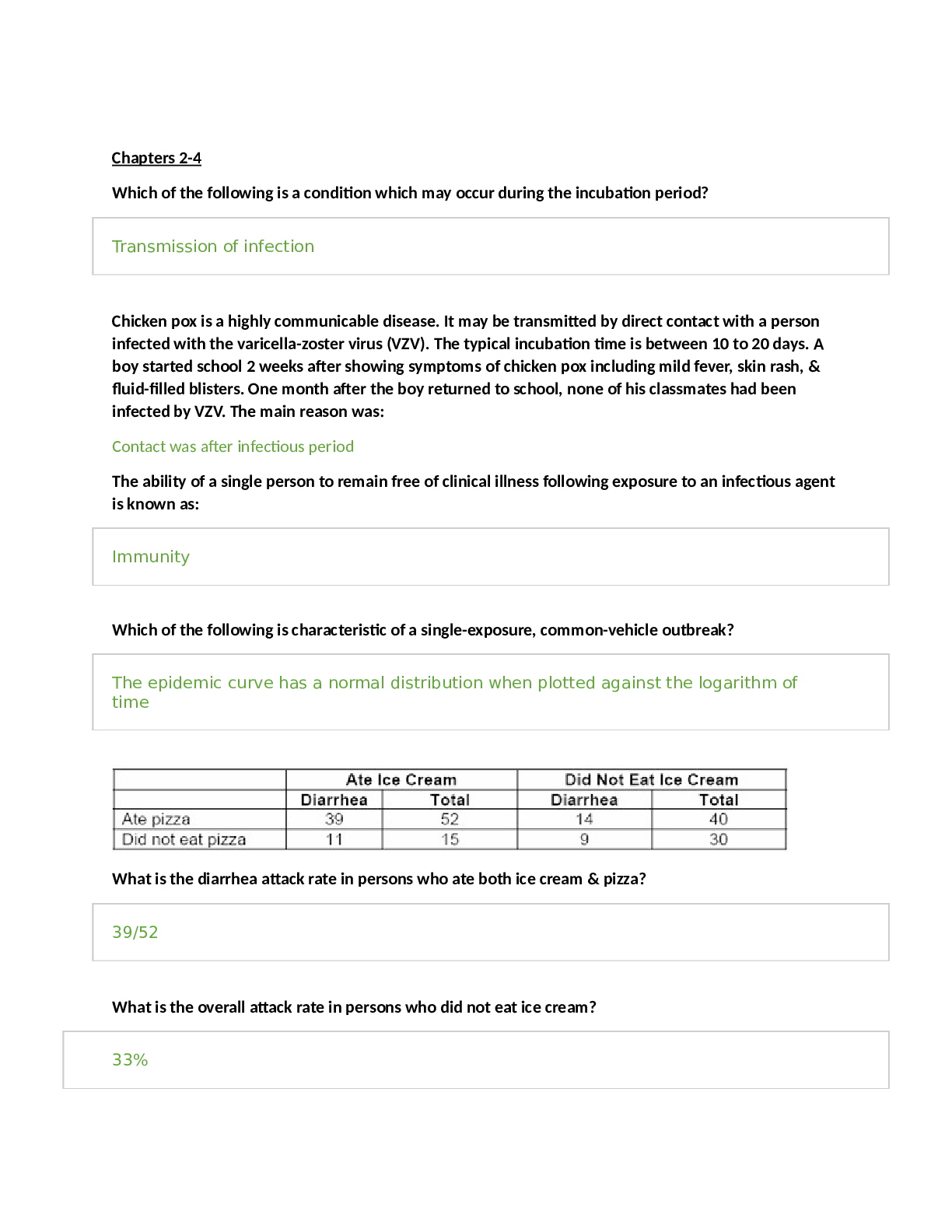
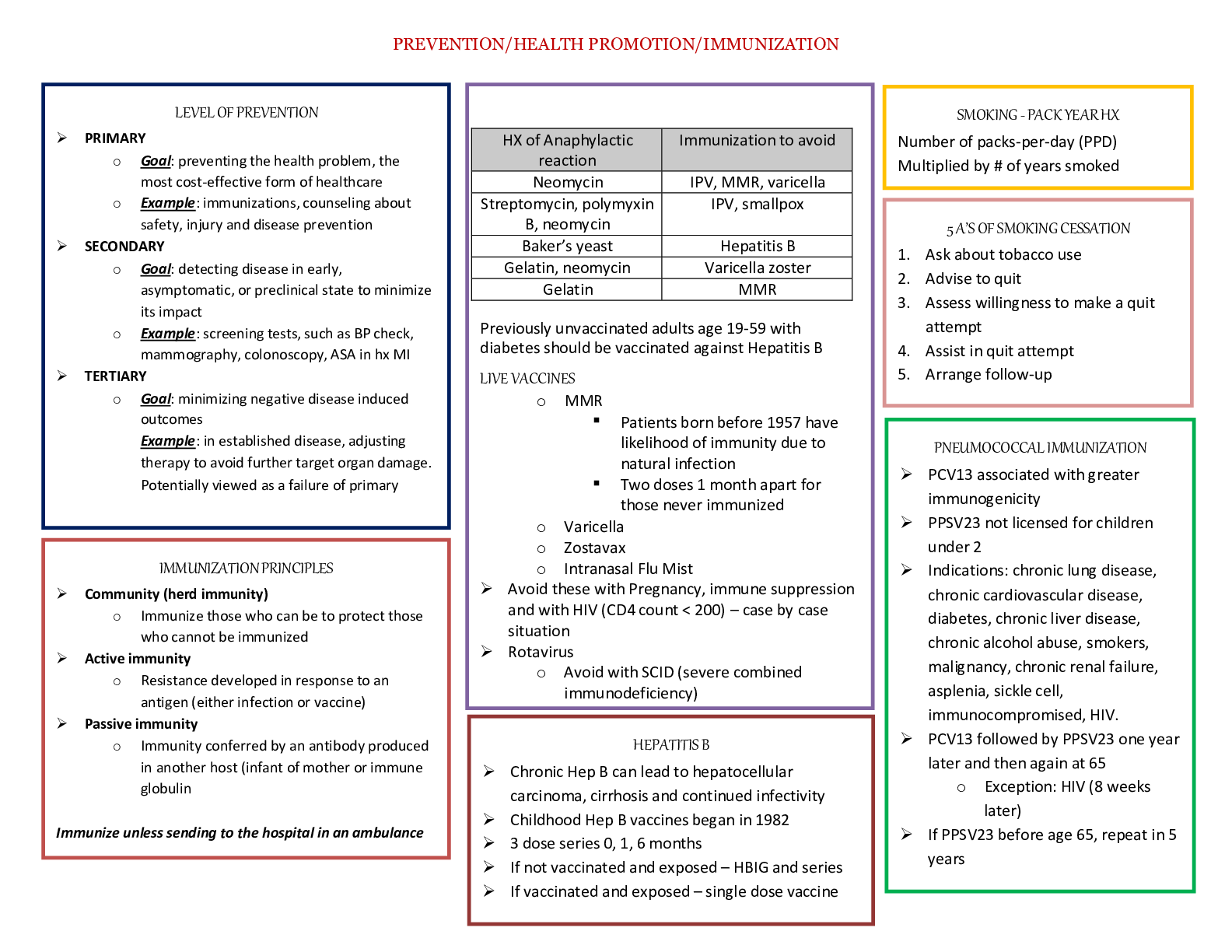
NSG 307 Care of the Childbearing Client Exam 1 Study Guide Please use the PowerPoints to guide your textbook reading/study. This is not an all-inclusive Study Guide. You will need to do your book r... eadings as well as review your PowerPoints. Community Health Concepts: Reproductive Health • Infant and maternal mortality rates as an indicator of health • Purpose of preconception counseling • Issues of pregnancy and infancy o Infant mortality o Preterm and low birth weight o Preconception health o Prenatal care o Prenatal substance abuse o Breast feeding • Reproductive health and nutrition • Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Prevention measures o Primary: education, prevention; educating on prenatal vitamins, care, and diet o Secondary: screening; screening for glucose tolerance o Tertiary: preventing worsening of disease Ch 3 Female Reproductive System • External and internal structures o External ▪ Vulva, mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, prepuce, clitoris, urethra, Skeen and Bartholin glands, perineum o Internal ▪ Vagina, uterine ligaments, uterus, fundus, uterine wall (endometrium, myometrium, perimetrium), cervix, squamocolumnar junction, uterine (fallopian tubes), ovaries • Menstrual Cycle (Hypothalamic-pituitary cycle, Ovarian cycle, & Endometrial cycle) o Hypothalamic-pituitary cycle ▪ Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH): is triggered by low levels of estrogen and progesterone ▪ Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH): anterior pituitary stimulated by GnRH, stimulates development of ovarian Graafian follicle’s and their production of estrogen ▪ Luteinizing hormone (LH): anterior pituitary stimulated by GnRH, a marked surge and smaller peak of estrogen causes release of ovum o Ovarian cycle ▪ Graafian follicles (follicular phase) ovulation: oocyte matures ▪ Corpus luteum (luteal phase): (ranges 13-15 days) begins immediately after ovulation and ends up with the start of menstruation; peak functional activity 8 days after ovulation ▪ Estrogen and progesterone: increase allows fertilized ovum to be implanted ▪ What happens during ovulation o Endometrial cycle ▪ Menstrual phase: Shedding of the functional two thirds of the endometrium is initiated by vasocontraction ▪ Proliferative phase: rapid growth lasting from the fifth day to the time of ovulation • Completely restored in 4 days or slightly before bleeding ceases ▪ Secretory phase: day of ovulation to about 3 days before then next menstrual period • Large amounts of progesterone ▪ Ischemic phase: occurs 7-10 days after ovulation • Signs and Symptoms of ovulation o Spike in temperature o Changes in cervix and cervical mucus thin and clear o Localized abdominal pain (mittelschmerz) o Some spotting may occur Ch 6 Genetics • Prenatal tests, carrier screening tests, and predictive testing o Prenatal test ▪ Maternal serum screening • Blood test ▪ Fetal ultrasound or sonogram • Use to see fetus inside utero ▪ Invasive procedures • Chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis o 2 different times you do amniocentesis. Know when and what you’re looking for. What do their results mean? o invasive definitive tests on fetal cells can be obtained through amniocentesis (during second trimester) and chorionic villus sampling (during 1st trimester) are offered by providers to test for fetal chromosomal abnormalities. o Looking for chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus o Carrier screening test ▪ Test parents to see if they carry the gene o Predictive testing ▪ Presymptomatic: has the gene and shows symptoms ▪ Predispositional: has the gene but does not show symptoms • Number of chromosomes and karyotyping o 46 chromosomes o Karyotype: pictorial analysis of the number, form, and size of the individual’s chromosomes • Autosomal dominant disorders and estimation of risk of occurrence o 50 % chance of passing the gene o Huntington disease, achondroplasia, neurofibromatosis, polycystic kidney disease • Autosomal recessive disorders and estimation of risk of occurrence o 25% chance of passing the gene o Cystic fibrosis, PKU, Tay-Sachs disease, sickle cell anemia, inborn errors of metabolism Ch 6 Conception and Fetal Development • Process of Conception (Fertilization) and implantation o Ovulation the ovum is released (estrogen levels increase to enhance cilia propel ovum down the fallopian tube) o Once the ovum gets to ampulla, fertilization occurs 3-4 days and the fertilized ovum comes to the uterus o 6-10 days after conception implantation occurs • Pregnancy duration including pre-embryonic, embryonic and fetal periods o Pre-embryonic: fertilization to 2 weeks o Embryonic: 2 weeks to 8 weeks o fetal • Functions of amniotic fluid o Maintain constant body temp o Serves as a source of oral fluid and repository for waste o Assist in maintenance of fluid and electrolyte homeostasis o Cushions fetus from trauma o Allows freedom of movement for musculoskeletal development o Barrier to infection and allows fetal lung development o Fluid keeps embryo from tangling with the membranes facilitating symmetric growth • Placental endocrine functions (know role during pregnancy) o hCG first hormone secreted and then gradually decline as placenta takes over o progesterone ▪ produced after corpus luteum stops functioning ▪ maintains endometrium ▪ decreases uterine contractility ▪ stimulates maternal metabolism o estrogen ▪ responsible for enlargement of uterine, breasts and breast glandular tissue ▪ role in increasing contractility ▪ stimulates uterine contractility o hCS ▪ hPL ▪ stimulates maternal metabolism ▪ increases resistance to insulin • Fetal maturation week by week o Know why amniotic fluid is important and what its made out of (in notebook) ▪ Formed by transudate of fetal plasma and later fetal urine (11wks) o 4 weeks ▪ Heart formed and beating, eyes and ear begin to form o 8 weeks ▪ Human form ▪ Every organ system and external structures present ▪ CNS remains vulnerable to teratogens ▪ Growth and refinement o 12 weeks ▪ Head dominate ▪ Fetal heart rate heard by electronic devices (ex: doppler) ▪ Gender apparent o 16 weeks ▪ Quickening in multigravida https://www.coursehero.com/file/o4935622008w/NeSGe-k3s07-Exam-1-Study-Guide-1tgdocx/ ▪ Quickening in primigravida ▪ Fine hairs over body, vernix caseosa appears ▪ Heart beat audible with fetoscope o 24 weeks ▪ Alveoli present ▪ Skin red covered with vernix caseosa (to protect baby from amniotic fluid) ▪ Responds to sound o 28 weeks ▪ Improved survival rates, some surfactant ▪ Eyes open and close, nails appear ▪ Weak suck reflux ▪ Human development (ears and eyes and such) o 32 weeks ▪ Skin pigmentation ▪ Nails ▪ Some subcutaneous fat ▪ Lungs matures o 36 weeks ▪ Weight gain, fills uterus ▪ Sufficient surfactant ▪ Lanugo disappearing, vernix in creases only ▪ Receives antibodies from mother • Fetal circulation o Two arteries that carry deoxygenated blood o One vein that carries oxygenated blood o Ductus venosus connects umbilical vein to inferior vena cava, the some blood bypasses the liver o Foramen ovale shunts blood from right to left atrium bypassing the lungs o Ductus arteriosus connects pulmonary artery to descending aorta bypassing lungs o Hypogastric arteries become umbilical arteries Ch 7 Anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy • Determine Gravity and Parity using the 5 digit system o G: number of pregnancies o T: babies carried to term >37 weeks (twins count as one (one pregnancy and one birth experience)!!) o P: babies carried less than <36.6 weeks o A: number of babies lost from abortion (spontaneous or elective) o L: number of children living • Presumptive, Probable, and Positive signs of pregnancy o Presumptive: subjective ▪ Amenorrhea, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, breast changes o Probable: objective ▪ Chadwick, Hagar, Goodell’s Sign, ballottement, pregnancy tests o Positive: actual signs of the baby ▪ Hearing fetal heart tones, visualizing the fetus, palpating fetal movements by examiner • Uterine structure and fundal height during pregnancy https://www.coursehero.com/file/o4935612208-/1N4SGw-3e07e-kExsa:mp-1a-lSptuadtye-Gduiadbe-o1tvgdeoctxh/ e symphysis pubis o 20 weeks: umbilicus o 37 weeks: xyphoid process o 38-40 weeks: fundal height decreases • Uteroplacental blood flow and Vena Cava Syndrome o Woman lays on her back and the weight of the baby decreases blood flow of the mother—postural hypotension • Normal physiologic changes during pregnancy including the Endocrine system o Prolactin causes colostrum (can happen before delivery but great for baby because of antibodies) o What does it do to cardiac output and blood volume, heart rate, and blood pressure at diff. trimesters (case study) o Postural hypotension (when a pregnant lady lays on her back and blood pressure drops. Baby laying on uterine artery and cuts off circulation. Affects mom and baby) o Advice for heartburn o Acid-base differences (respiratory alkalosis) o Insulin needs during pregnancy in diff trimesters. When we check for that. o Priority care: ABCs and then safety Ch 8 Nursing Care of the Family during Pregnancy • Determining EDB (Nagele’s rule) o Subtract 3 months and add 7 days • Normal psychological adaptations to pregnancy o Case study; what would we say to a patient who isn’t coping well • Common Lab tests throughout pregnancy o Strep B (when do we test for it? Antibiotic prophylactically) ▪ Anything unknown is “positive”. We treat them like they’re positive • Initial PN care and follow-up clinic visits throughout pregnancy • S&S of common discomforts versus danger signs or potential complications o • Patient educational needs o How to position, side lying is best Ch 9 Maternal and Fetal Nutrition • Recommended weight gain o 2-4 lbs. the first trimester o 1lb/week for remainder of pregnancy o Approx. 30 lbs o If you’re overweight they don’t want you to gain as much o Pregnancy only requires and extra 300 calories per day • Importance of Folate/Folic acid o Prevent neural tube defects • Nutrients needed during pregnancy o Answered in question below • Food choices which supply essential nutrients during pregnancy o Protein ▪ Increase slightly during pregnancy (meat, egg, cheese, yogurt, nuts, grains) o Omega-3 fatty acids ▪ Prevents preterm births (8-12 oz of seafood) o Fluids ▪ Increase 8-10 glasses of water o Minerals ▪ Iron (liver, meats, whole grain, enriched breads and cereal, veggies, fruit, dark leafy greens, legumes ▪ Calcium (salmon, sardines, Beans and legumes, greens, cornbread, muffins, French toast, waffles, figs, orange juice, milk, cheese, dairy products) ▪ Magnesium (nuts, legumes, cocoa, meats, whole grains o Fat soluble vitamins ▪ A: yellow and dark green veggies and fruits (broccoli, carrots, cantaloupe, and apricots) ▪ D: milk, salmon, tuna, butter, liver, fortified milk and cereal ▪ E: veggy oil, whole grains, liver, nuts and seeds, cheese, fish, dark leafy veggies o Water Soluble Vitamins ▪ Folate/ folic acid 400 mcg/day or more • Neural tube defects (supplement, fortified cereal, dark green leafy veggies, oranges, broccoli, artichokes, liver ▪ Vitamin C • Enhances iron uptake (citrus foods or juices) • Indicators of nutritional risk during pregnancy o Adolescence ▪ Should be encouraged to gain weight at the higher range of their BMI ▪ Should be taught about proper nutrition, meal planning, and selection of food and prep o Chronic illness ▪ Can be caused by malnutrition ▪ Puts infant at risk ▪ Puts mother at risk of preeclampsia o Having close pregnancies ▪ May not lose weight in between pregnancies ▪ Depleted storage of essential vitamins and minerals o History of smoking, alcohol or drug use ▪ Contraindicated throughout the pregnancy because of fetal growth complications o Poverty ▪ Lack of knowledge about nutrition o Pica and food cravings ▪ May be caused by missing nutrients in the diet ▪ Adds empty calories to the daily diet and may take away from essential nutrients o Lactation ▪ Similar to prenatal needs ▪ Increase 400-500 kcals ▪ Average weight loss 0.5-1 kg a month/up to 2 kg a month for overweight women • Nutrition-related discomforts o Nausea and Vomiting ▪ Antiemetic medication, vitamin B6, ginger, P6 acupressure used to reduce severity of nausea ▪ Eat small amounts frequently ▪ Avoid skipping meals ▪ Decrease intake of fried and other fatty foods ▪ Breathe in fresh air to help relieve nausea ▪ Eat foods at cool temp and foods that give off little aroma ▪ Try salty and tart foods ▪ Try herbal teas ▪ Avoid brushing teeth immediately after eating ▪ Avoid sudden movements. Get out of bed slowly ▪ Avoid consuming excessive amount of fluids early in the day ▪ Eat dry, starchy foods such as dry toast, melba toast, or crackers on awakening in the morning o Constipation ▪ Increase intake of fiber 25-30 g and 8-10 cups of water o Pyrosis ▪ Can be minimized by eating small, frequent meals rather than two or three larger meals daily ▪ Avoid spicy foods, laying down immediately after eating, and wearing tight clothing across the abdomen Going to be given plate options and will have to know which is best for your patient based off what is wrong with them [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 7 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 20, 2021
Number of pages
7
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 20, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
54