*NURSING > EXAM > ATI maternity / Maternal Newborn Questions And Answers (Complete Guide 100%) (All)
ATI maternity / Maternal Newborn Questions And Answers (Complete Guide 100%)
Document Content and Description Below
ATI. MATERNAL-NEWBORN 1. Two days after delivery, a postpartum client prepares for discharge. What should the nurse teach her about lochia flow? Incorrect: Lochia does change color but goes from... lochia rubra (bright red) on days 1-3, to lochia serosa (pinkish brown) on days 4-9, to lochia alba (creamy white) days 10-21. Incorrect: Numerous clots are abnormal and should be reported to the physician. Incorrect: Saturation of the perineal pad is considered abnormal and may indicate postpartum hemorrhage. Correct: Lochia normally lasts for about 21 days, and changes from a bright red, to pinkish brown, to creamy white. The color of the lochia changes from a bright red to white after four days Numerous large clots are normal for the next three to four days Saturation of the perineal pad with blood is expected when getting up from the bed Lochia should last for about 3 weeks, changing color every few days 2. A nurse monitors fetal well-being by means of an external monitor. At the peak of the contractions, the fetal heart rate has repeatedly dropped 30 beats/min below the baseline. Late decelerations are suspected and the nurse notifies the physician. Which is the rationale for this action? Incorrect: A nuchal cord (cord around the neck) is associated with variable decelerations, not late decelerations. Incorrect: Variable decelerations (not late decelerations) are associated with cord compression. Incorrect: Late decelerations are a result of hypoxia. They are not reflective of the strength of maternal contractions. Correct: Late decelerations are associated with uteroplacental insufficiency and are a sign of fetal hypoxia. Repeated late decelerations indicate fetal distress. The umbilical cord is wrapped tightly around the fetus' neck The fetal cord is being compressed due to rapid descent of the fetal head Maternal contractions are not adequate enough to deliver the fetus The fetus is not receiving adequate oxygen and is in distress 3. Which preoperative nursing interventions should be included for a client who is scheduled to have an emergency cesarean birth? Incorrect: Monitoring O2 saturations and administering pain medications are postoperative interventions. Incorrect: Taking vital signs every 15 minutes is a postoperative intervention. Instructing the client regarding breathing exercises is not appropriate in a crisis situation when the client's anxiety is high, because information would probably not be retained. In an emergency, there is time only for essential interventions. Correct: Because this is an emergency, surgery must be performed quickly. Anxiety of the client and the family will be high. Inserting an indwelling catheter helps to keep the bladder empty and free from injury when the incision is made. Incorrect: The nurse should have assessed breath sounds upon admission. Breath sounds are important if the client is to receive general anesthesia, but the anesthesiologist will be listening to breath sounds in surgery in that case. Monitor oxygen saturation and administer pain medication. Assess vital signs every 15 minutes and instruct the client about postoperative care. Alleviate anxiety and insert an indwelling catheter. Perform a sterile vaginal examination and assess breath sounds. 4. Which nursing instruction should be given to the breastfeeding mother regarding care of the breasts after discharge? Incorrect: Engorgement occurs on about the third or fourth postpartum day and is a result of the breast milk formation. The primary way to relieve engorgement is by pumping or longer nursing. Giving a bottle of formula will compound the problem because the baby will not be hungry and will not empty the breasts well. Incorrect: Applying lotion to the nipples is not effective for keeping them soft. Excessive amounts of lotion may harbor microorganisms. Correct: In order to stimulate adequate milk production, the breasts should be pumped if the infant is not sucking or eating well, or if the breasts are not fully emptied. Incorrect: Using soap on the breasts dries the nipples and can cause cracking. The baby should be given a bottle of formula if engorgement occurs. The nipples should be covered with lotion when the baby is not nursing. The breasts should be pumped if the baby is not sucking adequately. The breasts should be washed with soap and water once per day. 5. A client in preterm labor is admitted to the hospital. Which classification of drugs should the nurse anticipate administering? Correct: Tocolytics are used to stop labor. One of the most commonly used tocolytic drugs is ritodrine (Yutopar). Incorrect: Anticonvulsants are used for clients with pregnancy-induced hypertension who are likely to seize. Incorrect: The glucocorticoids (e.g., betamethasone and dexamethasone) are used for accelerating fetal lung maturation and production of surfactant. They are commonly used if the membranes are ruptured or labor cannot be stopped. Incorrect: Anti-infective are used if there is infection. Preterm labor may or may not involve ruptured membranes with its accompanying risk of infection. Tocolytics Anticonvulsants Glucocorticoids Anti-infective 6. Which of the following are probable signs, strongly indicating pregnancy? Incorrect: The presence of fetal heart sounds is a positive sign of pregnancy; quickening is a presumptive Sign of pregnancy. Incorrect: These are presumptive signs. They may indicate pregnancy or they may be caused by other conditions, such as disease processes. Correct: These are probable signs that strongly indicate pregnancy. Hegar’s sign is a softening of the lower uterine segment, and Chadwick's sign is the bluish or purplish color of the cervix as a result of the increased blood supply and increased estrogen. Ballottement occurs when the cervix is tapped by an examiner's finger and the fetus floats upward in the amniotic fluid and then falls downward. Incorrect: These are presumptive signs that might indicate pregnancy, but they might be caused by other conditions, such as disease processes. Presence of fetal heart sounds and quickening Missed menstrual periods, nausea, and vomiting Hegar's sign, Chadwick's sign, and ballottement Increased urination and tenderness of the breasts 7. Two hours after delivery the nurse assesses the client and documents that the fundus is soft, boggy, above the level of the umbilicus, and displaced to the right side. The nurse encourages the client to void. Which is the rationale for this nursing action? Correct: Bladder distention can lead to postpartum hemorrhage. A full bladder displaces the uterus causing it not to contract properly. Emptying the bladder allows the uterus to contract more firmly. Incorrect: A distended bladder rises out of the abdomen, causing the uterus to be displaced and increasing the risk of hemorrhage. It does not affect the perineum. Incorrect: Bladder distention can lead to urinary stasis and infection. This, however, does not relate to the soft, boggy uterus or the potential for hemorrhage. Incorrect: Massaging is uncomfortable regardless of whether the bladder is full or not. A full bladder displaces the uterus causing it not to contract properly, which may lead to postpartum hemorrhage. A full bladder prevents normal contractions of the uterus. An overdistended bladder may press against the episiotomy causing dehiscence. Distention of the bladder can cause urinary stasis and infection. It makes the client more comfortable when the fundus is massaged. 8. Which site is preferred for giving an IM injection to a newborn? Incorrect: Ventrogluteal muscles are located in the hip area. It is not the preferred site for injections in the newborn because of lack of muscle mass. Correct: The middle third of the vastus lateralis is the preferred site for injections. Incorrect: Ventrogluteal muscles are located in the hip area. It is not the preferred site for injections in the newborn because of lack of muscle mass. Incorrect: Newborns do not receive injections in the dorsogluteal site (gluteus maximus) due to decreased muscle mass. Ventrogluteal Vastus lateralis Rectus femoris Dorsogluteal 9. During the first twelve hours following a normal vaginal delivery, the client voids 2,000 mL of urine. How should the nurse interpret this finding? Incorrect: Urinary tract infections are common during pregnancy and in the postpartum period. Urinary frequency is a common finding. However, voiding large amounts of urine is not a sign of a UTI. Incorrect: High output renal failure occurs with injury/trauma to the kidneys. There has been no damage to the kidneys. Incorrect: Most women do receive some IV fluids during labor and delivery, however the IV rates are carefully calculated according to weight. Correct: During pregnancy, the circulating blood volume increases by about 50%. In order to get rid of the excess fluid volume after delivery, the woman experiences an increased amount of urine output during the first few hours. Urinary tract infection High output renal failure Excessive use of IV fluids during delivery Normal diuresis after delivery 10. If a pregnant client diagnosed with gestational diabetes cannot maintain control of her blood sugar by diet alone, which medication will she receive? Incorrect: Glucophage is an oral hypoglycemic. Oral hypoglycemic cross the placenta and can cause damage to the fetus. They are not used in gestational diabetes for that reason. Incorrect: Glucagon is a hormone used to raise blood sugar and manage severe hypoglycemia. Clients with gestational diabetes have hyperglycemia. Correct: Insulin is the drug of choice for gestational diabetes. Insulin lowers the client's blood sugar without harming the fetus. Incorrect: DiaBeta is an oral hypoglycemic drug. Oral hypoglycemic agents cross the placenta and can cause damage to the fetus. They are not used for gestational diabetes for that reason. Metformin (Glucophage) Glucagon Insulin Glyburide (DiaBeta) 11. Which assessment finding indicates that placental separation has occurred during the third stage of labor? Incorrect: There is usually an increase in bleeding (a sudden gush of blood) when the placenta separates. Incorrect: Contractions continue in an attempt to expel the placenta. The contractions may not be as intense, but they do not stop. Also, fundal massage helps contract the uterus preventing postpartum bleeding. Incorrect: Shaking and chills occur about 10-15 minutes after the delivery of the baby, but are not related to the placental detachment. They are a result of the release of pressure on pelvic nerves and the release of epinephrine during labor. Correct: As the placenta detaches, the cord that has been clamped becomes longer as it slides out of the vagina. Decreased vaginal bleeding Contractions stop Maternal shaking and chills Lengthening of the umbilical cord 12. The nurse midwife is concerned about a pregnant client who is suspected of having a TORCH infection. Which is the main reason TORCH infections are grouped together? They are: Incorrect: Most TORCH infections can cause mild flu-like symptoms for the mother. Death may or may not occur in the fetus. Incorrect: TORCH is an abbreviation for Toxoplasmosis, Other (syphilis, HIV and Hepatitis B), Rubella, Cytomegalovirus, and Herpes simplex—not all of these are sexually transmitted. Correct: All TORCH infections have the capability of infecting the fetus or causing serious effects to the newborn. Incorrect: A vector is a carrier of the disease such as a mosquito. Not all of the TORCH infections are carried by vector. benign to the woman but cause death to the fetus. sexually transmitted. capable of infecting the fetus. transmitted to the pregnant woman by a vector. 13. During the postpartum period, a hospitalized client complains of discomfort related to her episiotomy. The nurse assigns the diagnosis of “pain related to perineal sutures.” Which nursing intervention is most appropriate during the first 24 hours following an episiotomy? Incorrect: Petroleum jelly will harbor bacteria, which may hinder healing. Incorrect: The client should practice Kegel exercises to increase bladder tone, but these exercises would add to the client's discomfort during the first 24hours.Incorrect: Taking a warm sitz bath is recommended after the first 24 hours. Correct: Ice packs will decrease edema and discomfort, and prevent formation of a hematoma. Instruct the client to use petroleum jelly on the episiotomy after voiding. Encourage the client to practice Kegel exercises. Advise the client to take a warm sitz bath every four hours. Apply ice packs to the perineum. 14. A client asks the nurse about the benefits of breastfeeding. Which response by the nurse provides the most accurate information? Incorrect: Breastfeeding does not help speed up weight loss. The lactating mother requires more calories, but usually has an increased appetite to accommodate that need. Incorrect: Protein amounts are greater in formula and cow's milk. Correct: Breast milk is easier to digest because of the type of fat and protein in the milk. Incorrect: Breastfeeding does not prevent to woman from getting pregnant because it does not prevent ovulation. Most women ovulate within the first 6 weeks after delivery. Breastfeeding helps women lose weight faster. Breast milk contains a greater amount of protein. Breast milk is easier to digest than formula. Breastfeeding is a good method of contraception. 15. Which physiological change takes place during the puerperium? Incorrect: The puerperium is the first 6 weeks after delivery. The client will experience lochia for the first few weeks, and hormone levels will stabilize. Menstruation cannot occur until ovulation occurs. Incorrect: This occurs in stage three of labor. Correct: The uterine changes are called involution. The uterus should return to its pre- pregnancy state within 6 weeks after delivery. Incorrect: This describes the labor process, not the puerperium. The endometrium begins to undergo alterations necessary for menstruation. The placenta begins to separate from the uterine wall. The uterus returns to a pre-pregnant size and location. The uterus contracts at regular intervals with dilation of the cervix occurring. 16. A client delivered two days ago and is suspected of having postpartum "blues." Which symptoms confirm the diagnosis? Correct: These are signs of the postpartum blues, which typically diminishes within three- four days after delivery. Postpartum blues, a transient period of tearfulness, is a result of hormonal shifts. Other symptoms of the blues include: sadness, anxiety about the health of the baby, insomnia, anorexia, anger, feelings of anticlimax. Incorrect: Postpartum blues, a transient period of tearfulness, is a result of hormonal shifts. Depression and suicidal thoughts are signs of postpartum depression, not the blues and should be followed up with psychiatric treatment. Incorrect: Excess anxiety and the inability to care for the family are signs of postpartum depression, not the blues. Postpartum blues, a transient period of tearfulness, is a result of hormonal shifts. Incorrect: Nausea and vomiting are psychosomatic symptoms of postpartum depression and require psychiatric treatment. Postpartum blues, a transient period of tearfulness, is a result of hormonal shifts. Uncontrollable crying and insecurity Depression and suicidal thoughts Sense of the inability to care for the family and extreme anxiety Nausea and vomiting 17. Shortly after delivery, the nursery nurse gives the newborn an injection of phytonadione (Vitamin K). The infant's grandmother wants to know why the baby got “a shot in his leg.” Which response by the nurse is most appropriate? Incorrect: Calcium is needed for bone and muscle growth, not Vitamin K. Incorrect: Vitamin K is used to promote clotting, and does not affect digestion. Incorrect: The B vitamins are responsible for carbohydrate metabolism and the energy derived from glucose, not Vitamin K. Correct: Vitamin K is given to prevent bleeding until the intestinal bacteria can start to produce it. The intestines of a newborn are sterile until it starts to feed. Vitamin K helps with the clotting factors necessary to control bleeding. "Vitamin K promotes bone and muscle growth." "Vitamin K helps the baby digest milk." "Vitamin K helps stabilize the baby's blood sugar." "Vitamin K is used to prevent bleeding." 18. At 10 weeks gestation, a primigravida asks the nurse what is occurring developmentally with her baby. Which response by the nurse is correct? Incorrect: Wrinkles do not form until late in the pregnancy. Fat stores usually do not form until the third trimester. Incorrect: The eyelids are fused until about 26 weeks. Correct: The kidneys are making urine, which is excreted by the fetus into the amniotic fluid. Incorrect: The heart is already formed and beating at 8 weeks. "The skin is wrinkled and fat is being formed." "The eyelids are open and he can see." "The kidneys are making urine." "The heart is being developed." 19. A nurse in the clinic instructs a primigravida about the danger signs of pregnancy. The client demonstrates understanding of the instructions, stating she will notify the physician if which sign occurs? Incorrect: White vaginal discharge is a normal occurrence during pregnancy due to increased amounts of estrogen and increased blood supply to the cervix and vagina. It is not a “danger sign. “ Incorrect: Backache is common in pregnancy due to the alteration of the woman's center of gravity; it is not a “danger sign.” Backaches become worse as the uterus enlarges. Incorrect: Frequent, urgent urination is a common discomfort; it is not a danger sign. The pressure of the enlarging uterus causes frequency and urgency. Correct: Abdominal pain is a danger sign and can be indicative of an abruptio placenta. It is important for a physician to evaluate this symptom. It is one of several danger signs, including: headache, rupture of membranes, vaginal bleeding, edema, epigastric pain, elevated temperature, painful urination, prolonged vomiting, blurred vision, change in or absence of fetal movement. White vaginal discharge Dull backache Frequent, urgent urination Abdominal pain 20. An hour after delivery, the nurse instills erythromycin (Ilotycin) ointment into the eyes of a newborn. The main objective of the treatment is to prevent infection caused by which organism? Incorrect: Erythromycin (Ilotycin) is an antibiotic ointment used to prevent blindness related to gonorrhea. Antibiotics are effective against bacteria. Rubella is a virus. Correct: Ilotycin, an antibiotic, is used for the prophylaxis treatment of gonorrhea and chlamydia. If left untreated, it could result in blindness. Incorrect: Ilotycin, an antibiotic, is not effective in combating syphilis infections. Incorrect: HIV is a virus. Antibiotics are effective against bacteria. Ilotycinis an antibiotic ointment and therefore not effective against HIV. Rubella Gonorrhea Syphilis Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) 21. A woman in active labor receives a narcotic analgesic for pain control. If the narcotic is given a half an hour before delivery, which effect will the medication have on the infant? It will cause the infant's: Incorrect: Narcotic analgesics cause respiratory depression and do not affect the infant's blood sugar. Correct: Narcotic analgesics can cause respiratory depression for the infant and also for the mother. This is evidenced by low Apgar scores (apnea and bradycardia) in the infant. If respiratory depression occurs, a narcotic antagonist (Narcan) is usually given. Incorrect: Narcotic analgesics, if given too close to delivery, can cause bradycardia, not tachycardia. Incorrect: Narcotics, such as Demerol, cause CNS depression, not hyperactivity. blood sugar to fall. respiratory rate to decrease. heart rate to increase. movements to be hyperactive. 22. For a client in the second trimester of pregnancy, which assessment data support a diagnosis of pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH)? Incorrect: A decrease in hemoglobin is indicative of anemia, while uterine tenderness may indicate abruptio placenta. Incorrect: Polyuria and weight loss are signs of gestational diabetes. Correct: PIH is characterized by two components: elevated blood pressure and proteinuria. Vasospasm in the arterioles leads to increased blood pressure and a decrease in blood flow to the uterus and placenta. This results in a questionable outcome for the fetus due to placental insufficiency. Renal blood flow is affected, ultimately resulting in proteinuria. Incorrect: Elevated blood glucose is a sign of gestational diabetes. Hematuria may indicate a U.T.I. Hemoglobin 10.2 mg/dL and uterine tenderness Polyuria and weight loss of 3 pounds in the last month Blood pressure 168/110 and 3+ proteinuria Hematuria and blood glucose of 160 mg/dL 23. A 35-week gestation infant was delivered by forceps. Which assessment findings should alert the nurse to a possible complication of the forceps delivery? Correct: A weak, ineffective suck could be a result of facial paralysis which is a major complication of forceps deliveries. Scalp edema is another complication and should subside within 2-3 days. Other complications of forceps deliveries include: cephalohematomas, intracranial hemorrhage (especially in premature infants) and excessive bruising, which increases the risk for hyperbilirubinemia. Incorrect: Molding of the head is a common occurrence with vaginal deliveries. Jitteriness is a sign of low blood sugar, not forceps delivery. Incorrect: A shrill, high-pitched cry and tachypnea are signs of drug withdrawal, not a complication of forceps delivery. Incorrect: Hypothermia is not a complication of forceps deliveries. The hemoglobin level is quite low (should be about 15-16 g/dL), but unless there is excessive bleeding, the hemoglobin level should be unaffected by the forceps delivery. Weak, ineffective suck, and scalp edema Molding of the head and jitteriness Shrill, high pitched cry, and tachypnea Hypothermia and hemoglobin of 12.5 g/dL 24. In which position should the nurse place the laboring client in order to increase the intensity of the contractions and improve oxygenation to the fetus? Incorrect: This position is contraindicated because the fetus creates pressure on the mother's vena cava. Incorrect: Squatting widens the pelvic inlet, but does not improve contractions or fetal oxygenation. Correct: This prevents vena cava compression and, therefore, improves fetal oxygenation; at the same time, it provides a restful position between contractions. Incorrect: High Fowler's (sitting upright) will assist with the intensity of the contractions because of gravity, but it will not help with fetal oxygenation. Supine with legs elevated Squatting Left side-lying High Fowler's 25. A woman enters the birthing center in active labor. She tells the nurse that her membranes ruptured 26 hours ago. The nurse immediately takes the client's vital signs. Which is the rationale for the nurse's actions? Incorrect: Pulse rates increase due to pain, not because of rupture of membranes. Incorrect: The woman is not reporting pain and ruptured membranes do not cause pain. Lack of fluid (ruptured membranes) has no influence on respiratory rates. Incorrect: Blood pressure is not affected by prolonged rupture of membranes. Correct: The membranes are a protective barrier for the fetus. If the membranes are ruptured for a prolonged period of time, microorganisms from the vagina can ascend into the uterus. The longer the membranes have been ruptured, the greater the risk for infection. Pulse rates rise the longer the membranes are ruptured Respiratory rates decrease due to lack of fluid in the uterus Prolonged rupture of membranes can lead to transient hypertension Infection is a complication of prolonged rupture of membranes 26. A new client's pregnancy is confirmed at 10 weeks gestation. Her history reveals that her first two pregnancies ended in spontaneous abortion at 12 and 20 weeks. She has a4-year-old and a set of 1-year-old twins. How should the nurse record the client's current gravida and para status? Incorrect: Gravida includes the number of times the woman has been pregnant. She has been pregnant 5 times. A parity of 3 would be obtained by incorrectly counting the 20-week spontaneous abortion as a viable infant. Incorrect: The woman has been pregnant 5 times, including the present pregnancy. The abortions count as pregnancies, but not in the parity. Correct: Gravida is the number of times a woman has been pregnant, including the present pregnancy. Para is the number of pregnancies carried past 20 weeks' gestation, regardless of the number of fetuses delivered. The woman has been pregnant five times, including this pregnancy, and has had two pregnancies that have exceeded 20 weeks. Even though she delivered two children as a result of one of those pregnancies, the para for her twin pregnancy remains at 1. The pregnancy after which she delivered her four-year-old child makes her a para 2. Incorrect: A para of 4 would be obtained by incorrectly counting the 2 spontaneous abortions as viable at delivery. Gravida 2, para 3 Gravida 4, para 2 Gravida 5, para 2 Gravida 5, para 4 27. A 16-year-old client reports to the school nurse because of nausea and vomiting. After exploring the signs and symptoms with the client, the nurse asks the girl whether she could be pregnant. The girl confirms that she is pregnant, but states that she does not know how it happened. Which nursing diagnosis is most important? Incorrect: Although this addresses the client's nausea and vomiting, it is not the most important diagnosis at this time. There are no data to indicate that the client actually has a nutritional deficit. Because nausea and vomiting place her at risk for nutritional deficit, a diagnosis of “risk for altered nutrition. . .” would be appropriate. The knowledge diagnosis is an actual problem and should be addressed at this contact with the client; the nutrition problem will be ongoing during the pregnancy. Incorrect: This diagnosis does not address the reason for the lack of client knowledge—she may be at risk for poor parenting, but this is not the priority because there will be time to address that issue as the pregnancy progresses. Incorrect: There is no clear evidence of the denial of pregnancy nor of the lack of coping skills. Correct: This client clearly has a knowledge deficit about the causes of pregnancy and the physiological changes associated with it. It is important for teaching to begin immediately because her understandings essential to her compliance with suggestions for a healthy pregnancy. Altered nutrition: less than body requirements related to nausea and vomiting Risk for altered family processes related to the client's age Ineffective individual coping related to denial of pregnancy Knowledge deficit related to the client's developmental stage and age 28. A client is admitted to the hospital for induction of labor. Which are the main indications for labor induction? Incorrect: These are contraindications for labor induction. Correct: Induction of labor is the stimulation of contractions (usually by the use of Pitocin) before they begin on their own. Maternal indications for induction of labor include: pregnancy induced hypertension, chorioamnionitis, gestational diabetes, chronic hypertension and premature rupture of membranes. Fetal indications include intrauterine growth retardation, post-term dates and fetal demise. Incorrect: These are contraindications for labor induction. Incorrect: These are contraindications for labor induction. They are indications for a C-section. Placenta previa and twins Pregnancy-induced hypertension and postterm fetus Breech position and prematurity Cephalopelvic disproportion and fetal distress 29. A client in active labor receives a regional anesthetic. Which is the main purpose of regional anesthetics? Incorrect: This choice describes general anesthesia. Correct: Regional anesthetics provide numbness and loss of pain sensation to an area. The most common regional blocks are: local, pudendal, epidural, and spinal. Incorrect: Pain sensations travel to the central nervous system not away from it. Incorrect: This choice describes the action for narcotic medications, not regional anesthetics. To relieve pain by decreasing the client's level of consciousness To provide general loss of sensation by blocking sensory nerves to an area To provide pain relief by blocking descending impulses from the central nervous system To relieve pain by decreasing the perception of pain leading to the pain centers in the brain 30. The nursery nurse reviews a newborn's birth history and notes that the Apgar scores were 5 at one minute after birth, and 7 at five minutes after birth. How should the nurse interpret these scores? The infant: Incorrect: Usually babies that only need suctioning of the mouth and nose have Apgars that are 8 or 9. Incorrect: If intubation is required, it means that the baby's heart and respiratory rates are not stable, and Apgars would be lower than 5. Incorrect: Apgar scores are used to quickly assess the well-being of the baby. Apgar scores range from 0-10. A score of 0 indicates that the baby is dead. An Apgar score of 5 indicates that the baby needs assistance. Correct: Apgar scores of 5 and 7 indicate that the heart rate was below 100, the respiratory effort was irregular, there was little muscle tone, the baby was pink with blue extremities, and there was a grimace. These scores indicate that the baby needed stimulation in order to breathe, and oxygen to increase its oxygen saturation. needed brief oral and nasal suctioning. required endotracheal intubation and bagging with a hand-held resuscitator. was stillborn and required CPR. required physical stimulation and supplemental oxygen. 31. With routine prenatal screening, a woman in the second trimester of pregnancy is confirmed to have gestational diabetes. How may the nurse explain the role of diet and insulin in the management of blood sugar during pregnancy? Correct: Insulin is given to gestational diabetic clients because their insulin requirements cannot keep up with the metabolic needs of the fetus in the last trimester. Insulin decreases the blood sugar. Incorrect: Oral hypoglycemic agents are not given to clients with gestational diabetes because they cross the placenta and are harmful to the fetus. Incorrect: The client will need frequent follow-up after delivery and into the postpartum period, but she should not need insulin after delivery because in gestational diabetes, blood glucose usually returns to normal after delivery. Incorrect: Clients with gestational diabetes need to eat three balanced meals and three snacks daily. The glucose load is best when maintained at a steady level throughout the day to avoid periodic overproduction of insulin. The last snack of the day should contain protein to stabilize the energy production during the night. "Insulin lowers an elevated blood sugar during pregnancy to meet the increased metabolic needs of the baby." "You will need to take an oral hypoglycemic, which is a pill to lower your blood sugar." "There is a good possibility you will be taking insulin for the rest of your life." "You should eat three large meals per day to maintain steady glucose load." 32. A breastfeeding mother complains of cramping. Which is the main cause of the client's afterpains? Incorrect: Infection of the suture line can cause pain and discomfort, but is not the cause of afterpains. Afterpains are postpartum uterine contractions. Incorrect: Constipation and bloating do occur in the postpartum period as peristalsis resumes, but constipation does not cause afterpains, which are uterine contractions. Correct: Afterpains are caused by uterine contractions that occur for the first 2-3 days postpartum. Breast-feeding mothers have more afterpains due to the release of oxytocin stimulated by the nursing baby. Oxytocin strengthens uterine contractions and compresses blood vessels, preventing blood loss. Incorrect: Trauma is not the cause of afterpains. Afterpains are postpartum uterine contractions. Infection of the suture line Constipation and bloating Contractions of the uterus Trauma during delivery 33. A client who is 37 weeks gestation comes to the office for a routine visit. This is the client's first baby and she asks the nurse how she will know when labor begins. Which signs indicate that true labor has begun? Incorrect: These signs describe Braxton-Hicks contractions, which occur throughout pregnancy and increase in intensity and frequency as labor grows closer. Incorrect: True labor pains start in the lower back and sweep to the front in waves. Incorrect: These signs occur with lightening, usually 10-14 days before labor begins. Correct: These are true signs of labor, along with the rupturing of the membranes and cervical dilatation. Contractions that are irregular and decrease in intensity when walking Abdominal pain that starts at the fundus and progresses to the lower back Increased pressure on the bladder and urinary frequency Expulsion of pink-tinged mucous and contractions that start in the lower back 34. A multiparous woman with a history of all vaginal births is admitted to the hospital in labor. After several hours, the client's labor has not progressed and she is getting tired and restless. The decision is made to proceed with cesarean delivery. The nurse recognizes the client's knowledge deficit regarding the surgical delivery and care afterbirth. Which is the appropriate expected outcome for correction of the client's knowledge deficit? The client will: Incorrect: This expected outcome does not address the client's knowledge deficit. Instead, this is an expected outcome for the nursing diagnosis of ineffective individual coping. Incorrect: This choice does not address the client's knowledge deficit, but instead addresses a problem with interrupted bonding. Correct: Goals/outcomes should reflect resolution of the stated nursing diagnosis—in this case, knowledge deficit. Verbalization of reasons for the surgery would indicate resolution of the knowledge deficit. If interventions for knowledge deficit are effective, other problems (e.g., anxiety, ineffective coping) may be prevented. Incorrect: This choice addresses the anxiety that will occur because of the unknown, but does not address the stated problem, knowledge deficit. demonstrate appropriate coping mechanisms needed to get through the surgery. accept that the type of delivery will not affect the bonding with the baby. verbalize understanding about the reason for the unplanned surgery. demonstrate decreased anxiety and fear of the unknown. 35. The physician performs an amniotomy for a woman in labor. Which nursing action should follow the procedure? Incorrect: Maternal oxygenation is not affected by an amniotomy. Incorrect: Maternal pulse and blood pressure are not affected by an amniotomy. Incorrect: Assessing the perineum should be done after an episiotomy, not after amniotomy. Correct: An amniotomy, or artificial rupture of membranes (AROM), is used to speed up labor. The nurse must document the color, amount, character and odor of the fluid, and assess for fetal well being. Check the client's capillary refill and oxygenation. Monitor the maternal pulse and blood pressure. Inspect the perineum for lacerations, bleeding, and hematoma. Assess the fluid for color, odor, and amount. 36. For a pregnant adolescent who is anemic, which foods should the nurse include In the client's dietary plan to increase iron levels? Incorrect: Milk does not contain iron and it interferes with iron absorption. Correct: Orange juice enhances the absorption of iron. Apricots are a good source of iron. Incorrect: Chicken does contain iron, but cottage cheese, a dairy product, does not. Incorrect: Pickles contain large amounts of salt, not iron. Peanut butter sandwiches do not contain much iron. Milk and fish Orange juice and apricots Chicken and cottage cheese Pickles and peanut butter sandwiches 37. Which condition must occur in order for identical (monozygotic) twins to develop? Incorrect: Usually only one ovum is released per month; one sperm cannot fertilize two ova. Incorrect: This is the case in fraternal (dizygotic) twins. There are two placentas, two chorions, and two amnions. The twins may be the same or different sex. Correct: One sperm fertilizes one ovum, and then the zygote divides into two individuals with one placenta, one chorion, two amnion and two umbilical cords. These twins are always the same sex. Incorrect: The enzyme on the head of the sperm dissolves the coating of the ovum so eventually only one sperm penetrates one egg. One sperm fertilizes two ova Two sperm fertilize two ova One sperm fertilizes one ovum Two sperm fertilize one ovum 38. Which fetal structure is responsible for carrying oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus? Incorrect: The ductus arteriosus is a shunt that connects the lungs to the aorta, allowing the blood to bypass the lungs. Incorrect: Except in the case of fetal circulation, arteries do carry oxygenated blood; but during pregnancy, the two umbilical arteries carry unoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta, where preoxygenation occurs. Incorrect: The portal vein carries blood from the intestine to the liver. Correct: The umbilical vein carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus. The direction of blood flow is toward the fetal heart. Ductus arteriosus Umbilical artery Portal vein Umbilical vein 39. A client at 33 weeks gestation is admitted for suspected abruptio placenta. Which factor in the client's history supports this diagnosis? The client states that she: Incorrect: Drinking alcohol is not usually associated with abruptio placenta. Incorrect: Clients with abruptio placenta do not have contractions that can be relieved by walking. Usually the pain is quite intense. Incorrect: Intercourse should not cause an abruptio placenta, although it is contraindicated in clients with placenta previa. Correct: The use of crack cocaine is associated with the separation of the placenta and the bleeding/ hemorrhage that results. Cocaine use is not usually an isolated incident, so the nurse should ask the client about the frequency/amount of the drug usage. drinks two glasses of wine before dinner every night. has intermittent contractions that are relieved by walking. had intercourse with her partner last night. used crack an hour before the symptoms began. 40. Which explanation is most appropriate when describing physiological jaundice to the parents of a newborn? Incorrect: Pathological jaundice, not physiological jaundice, occurs within the first 24 hours and is a result of an ABO incompatibility or Rh incompatibility. Correct: Physiological jaundice is the result of the breakdown of excessive amounts of red blood cells that are not needed after birth. Physiological jaundice is also related to the inability of the immature liver to rid the body of bilirubin, which occurs as the red blood cells are broken down. The bilirubin accumulates in the blood causing it to be yellow. Incorrect: Jaundice related to breast milk occurs after the first 7 days, not within the first three. It is not the cause of physiological jaundice. Incorrect: Hepatitis B may have been acquired during delivery and may cause jaundice, but it is not the cause of physiological jaundice, which this case represents. "The baby has a minor incompatibility of the blood." “The baby is breaking down the extra red blood cells that were present at birth.” “The baby is getting too much breast milk, but this is not dangerous.” “The baby may have gotten exposed to hepatitis B during the delivery.” 41. A woman at 42 weeks gestation enters the hospital for induction of labor. Since the infant is postterm, which complications should the nurse anticipate when planning for the delivery? Incorrect: Cephalopelvic disproportion is seen in large-for-gestational age infants, not postterm infants. Hypothermia occurs in premature and small-for-gestational age infants. Correct: Asphyxia is a result of chronic hypoxia in utero because of the progressive degeneration of the placenta. Meconium stained amniotic fluid is a result of the relaxation of the anal sphincter and the passage of meconium into the fluid related to hypoxia. If the meconium stained fluid is aspirated into the infant's lungs at delivery, pneumonia (and possibly death) will result. If there is meconium stained fluid, the infant's mouth and throat are suctioned as soon as the head is delivered. Incorrect: Intraventricular hemorrhage occurs as a major complication in premature infants, not postterm infants. Dry, cracked skin is a normal finding of postterm infants and is not considered a complication. Incorrect: Hyperbilirubinemia is not a complication of postterm infants at birth. Hypocalcemia is a complication in small-for gestational age infants Cephalopelvic disproportion and hypothermia Asphyxia and meconium aspiration Intraventricular hemorrhage and dry, cracked skin Hyperbilirubinemia and hypocalcemia 42. Which method of temperature regulation would safely and effectively prevent cold stress in a newly delivered infant? Incorrect: The baby should be wrapped snuggly with a warm blanket in order to preserve heat loss. Incorrect: It helps to cover the feet, of course. However, because the scalp is so vascular (and the blood is close to the surface) and because the head makes up a large portion of the baby's surface area, most heat loss occurs via the head initially. Peripheral circulation is sluggish at first, so not much blood would be cooled by circulating through cold feet. Correct: Newly delivered infants lose a great deal of heat as the amniotic fluid evaporates from the surface of the skin. To prevent rapid heat loss, the baby's face and head should be dried and a hat placed on the baby's head. Incorrect: Infants should NEVER be placed on a heating pad because of risk for burns. Wrap the baby loosely with a blanket. Be sure the baby's feet are covered. Cover the baby's head with a hat. Position the baby on a heating pad. 43. The nurse performs Leopold's maneuvers for a client admitted in labor. Which is the main goal of Leopold's maneuvers? Incorrect: Sterile vaginal exams are used to assess the dilation of the cervix. Incorrect: Leopold's maneuvers are not used to assess contraction frequency or intensity. However, some nurses do place their hands on the abdomen to palpate the intensity and frequency of the contractions. Incorrect: Leopold's maneuvers are not used to assess membrane rupture. Sterile vaginal exams may assess this if membranes are intact. Correct: Leopold's maneuvers are a method of determining fetal position by abdominal palpation. It assesses the position, presentation and engagement of the fetus. It also assists in the location of fetal heart sounds. To determine whether the client's cervix has dilated To assess the frequency and intensity of the contractions To assess whether membranes have been ruptured To determine the presentation and position of the fetus 44. Immediately after birth, the nurse places the newborn under a radiant warmer. Which is the primary rationale for the nurse's action? Correct: Temperature regulation is the priority for the newborn. Infants who are cold stressed are at risk for respiratory complications or death. Incorrect: Placing the infant in the warmer does assist the nurse with easier access, but temperature regulation is the main priority. Incorrect: Most infants are not connected to the cardiac monitor unless the Apgar scores are low. Incorrect: The warmer does provide easy access for the family, but this is not the main reason for its use. To facilitate an efficient means of thermoregulation To facilitate initial assessment by the nurse To permit the use of the cardiac monitor To permit close observation by the family members 45. A client, gravida 1, para 0, in active labor, is becoming increasingly anxious. Which statement by the nurse will block therapeutic communication with the client? Incorrect: Since this is the client's first baby, there will be concerns/anxiety because of the unknown expectations. This response is appropriate, and will help decrease anxiety by allowing identification and ventilation of fears. Incorrect: This response will encourage the client to talk and will foster good communication. Correct: This is an example of meaningless reassurance and will block therapeutic communication because the needs of the client are not being met. Incorrect: This response will facilitate communication, not block it. "What concerns are you having now?" "Tell me how you are feeling." "Everything is going just fine." "You seem a little nervous." 46. A nurse prepares to teach a class regarding postpartum care and includes infections in the teaching plan. Which is the main cause of mastitis in the postpartum client? Correct: Poor breast-feeding technique and improper positioning of the baby are the main reasons for mastitis. Improper release of the baby's suction can lead to sore, cracked nipples, creating a portal of entry for pathogens. Incorrect: Poor hand washing is not the main reason that a woman gets mastitis but can be a contributing cause. For example, if the woman touches her perineal pad and then the breast, the bacteria on the hands can cause an infection. Incorrect: Systemic infections such as flu or cold are not the cause of mastitis, which is a localized infection. Incorrect: Prolonged nursing by itself does not cause mastitis. Often babies engage in nonnutritive sucking. Poor breast feeding technique Inadequate hand washing Systemic maternal infection Prolonged nursing 47. A postterm infant is delivered by cesarean section because of fetal distress and meconium- stained amniotic fluid. The nursery nurse frequently monitors the baby's respiratory rate, observing for tachypnea. Which is the reason for the nurse's actions? The infant may: Incorrect: Respiratory depression does not result in tachypnea but in apnea. Correct: This infant is a risk for meconium aspiration pneumonia related to post maturity, meconium staining, fetal distress and being delivered by c-section. Incorrect: Infants with respiratory distress (tachypneic) are usually cold stressed and hypothermic, not hyperthermic. Incorrect: A pneumothorax usually is seen in premature infants who lack surfactant. experience respiratory depression from the medications used during delivery. develop meconium aspiration pneumonia. have an elevated temperature. have a pneumothorax related to delivery. 48. The nurse notices a variable deceleration on a fetal monitor strip. Which nursing action is appropriate? Incorrect: Hyperventilation is not the cause of the variable decelerations. Incorrect: Hypertonic uterine contractions refer to a labor with very painful but not necessarily effective contractions. The uterus does not relax between contractions. This leads to fetal distress and results in late decelerations, not variable decelerations. Correct: Variable decelerations are a result of cord compression. Turning the client onto her left side may improve fetal oxygenation by relieving pressure on the cord. Incorrect: Variable decelerations are a result of fetal cord compression. Decreasing the fluids will not relieve cord compression. Instruct the mother to breathe slowly because this is a sign of hyperventilation. Decrease the amount of Pitocin because this is a sign of hypertonic uterine contractions. Turn the woman onto her left side to relieve pressure on the umbilical cord. Reduce the oral and IV fluids to decrease circulatory overload. 49. The nursery nurse delays the first bottle feeding of a newborn. Which is the most common reason for the nurse's actions? The infant has: Incorrect: One method of increasing an infant's low blood sugar is by feeding him. Correct: Bottle feeding of an infant who is tachypneic (resp. rate > 60) is contraindicated due to risk of aspiration. Incorrect: Acrocyanosis (blue hands and feet) is a normal finding for the first 24 hours. Incorrect: It is not unusual for the nurse to hear a heart murmur shortly after birth. a blood glucose of 45 gm/dL. a respiratory rate above 60. blue hands and feet. a heart murmur. 50. During active labor, after a sudden slowing of the fetal heart rate, the nurse assesses the woman's perineum and observes a prolapsed cord. Which nursing action is most appropriate? Correct: With a sterile gloved hand, the nurse should push the presenting part away from the cord, thus preventing cord compression. The cord supplies the fetus with oxygen and nutrients. The fetus is already showing signs of distress because of the slowing of the heart rate. In addition, the nurse should prepare for immediate delivery. Incorrect: Since the head is not engaged (which is why the cord prolapsed), it will be very difficult to insert a scalp electrode. Incorrect: Trendelenburg position places the client with her head lower than her feet. Reverse Trendelenburg places the client with the head higher than the feet. Due to gravity, this will place additional pressure on the cord. Incorrect: Covering the cord with a dry gauze will not help the situation. The gauze will get wet in a matter of seconds. There is a risk that the gauze will be lost internally. Hold the presenting part away from the cord. Insert a scalp electrode for an internal fetal monitor. Place the client in reverse Trendelenburg position. Cover the cord with a dry, sterile gauze. 51. A client is in the latent stage of labor. Which nursing intervention is most appropriate? Correct: Latent stage is an early stage of labor, which begins with the onset of contractions and ends when the cervix is dilated to 4 cm. Walking adds gravity to the force of the contractions, promotes fetal descent, and relieves backache. Once the membranes rupture, bed rest may be indicated, for example if the fetal head is not engaged. Incorrect: Pushing is not indicated until full cervical dilation. Incorrect: This type of breathing pattern is used late in labor when pushing begins. Incorrect: Once labor begins fluids and ice chips are preferred. Nausea and vomiting are common as labor progresses. During labor, peristalsis stops. Therefore, having food in the stomach is not advisable. Encourage the client to walk in the hall until membranes rupture. Instruct the client to place her head on her chest and push with the contraction. Teach the client to use the “pant-blow” method of breathing. Advise the client to eat a light meal consisting of carbohydrates. 52. Which conditions create a risk for uterine atony in the immediate postpartum period? Incorrect: Breastfeeding causes uterine contractions due to the release of oxytocin. Uterine atony is not related to the delivery of a child with chromosomal defect. Incorrect: Uterine atony is not a result of postterm pregnancy or amniotomy. Incorrect: Gestational diabetes in and of itself does not cause uterine atony. However, clients with gestational diabetes do have babies that are large for gestational age (> 4000 grams). Pregnancy-induced hypertension is associated with vasospasm, which does not result in uterine atony. Correct: Uterine atony is the inability of the uterus to contract, which leads to hemorrhage. Clients who have had more than one delivery have decreased muscle tone in the uterus. Clients with twins or triplets are at risk for overdistention of the uterus, which may lead to uterine atony and hemorrhage. Breast feeding and delivery of an infant with chromosome defects Postterm birth and an amniotomy during labor Gestational diabetes and pregnancy-induced hypertension Multiparity and multiple gestation 53. A client at ten weeks gestation tells the nurse that she has been having “morning sickness.” The nurse advises the client to eat foods that are easy to digest and low in fat. Which is the rationale for the nurse's instruction? Incorrect: Low fat diets do not stimulate peristalsis. On the contrary, high fat foods can lead to bloating, increased peristalsis and diarrhea. Correct: Foods containing a high fat content stay in the digestive system longer. Decreasing the amount of fat causes faster gastric emptying, which leaves less in the stomach to be vomited. Incorrect: Fluid and electrolyte imbalance is not a cause of nausea and vomiting related to pregnancy. Incorrect: Relaxation of the cardiac sphincter, causing heartburn, is a result of increased progesterone. It causes heartburn, not nausea and vomiting. A low-fat diet increases peristalsis, which reduces the food volume in the stomach A low-fat diet is digested faster and leaves less in the stomach that can be vomited Easily digested foods provide a better balance of fluids and electrolytes, resulting in less nausea and vomiting Easily digested foods are less likely to cause relaxation of the cardiac sphincter, which causes regurgitation and vomiting 54. Which information is most important for the nurse to gather when a client is admitted to the unit in labor? Incorrect: This is useful information, but the priority information is that regarding medical conditions which may create serious risks to the fetus and mother. Correct: Asking the client about any medical problems should be the priority because it provides a quick assessment for risks to the fetus and mother. Incorrect: Fluids are given in the latent phases of labor, but gathering this information at the initial admission interview is not as important as obtaining information about medical conditions which may create serious risks to the fetus and mother. Incorrect: This is not important unless the client has PIH or a cardiac condition. Even then, the initial assessment would be to find out if the client actually has PIH or cardiac condition (e.g., by checking the history), not to diagnose it. Name of the support person Medical problems or complications Fluid preferences Amount of weight gained during the pregnancy 55. The nurse conducting a physical assessment notes that a 1-day-old newborn with dark skin has a bluish-gray discoloration over the lower back, the buttocks, and the scrotum. How should this assessment finding be documented? Incorrect: Bruising usually does not involve the scrotum, and is not usually gray. Correct: Mongolian spots are the result of increased pigmentation over parts of the baby. They are most commonly found in infants of Asian, Indian, African-American or Mediterranean descent. They are harmless and fade during the first two years of life. Incorrect: Nevus flammeus is a dark red lesion called a port wine stain. It does not blanch when touched, and does not fade with age. This type of hemangioma usually is seen on the face or thigh rather than the back. Incorrect: Acrocyanosis, a normal finding, is a bluish discoloration of the hands and feet (not the back or buttocks), and is related to sluggishness of the peripheral circulation. Extensive bruising Mongolian spots Nevus flammeus Acrocyanosis 56. A small-for-gestational-age infant is irritable and jittery, and has hyperreflexia and clonus. He is jaundiced, has temperature instability, and spitty after feedings. The nurse suspects the infant is displaying signs of passive addiction during pregnancy. When planning for the infant's care at home, which nursing assessment is most important for the infant experiencing neonatal abstinence syndrome? Correct: In cases of maternal drug addiction, it is very important that the home situation be assessed because infant abuse and neglect are common in homes where there is drug/alcohol abuse. Incorrect: While this may be important information to know, it does not address the infant or its care. Incorrect: Assessing whether or not the mother has money enough to afford treatment for her addiction is not as important as the infant's safety. Incorrect: Drug withdrawal is not measured in degree of severity. The baby is withdrawing, and that is all that is important. The mother's ability to provide a safe environment The extent of addiction of the mother The mother's ability to obtain treatment The severity of the infant' s withdrawal 57. A woman in active labor is admitted to the labor and delivery unit, accompanied by her partner. As labor progresses, the nurse notes he is not interacting with the woman and sits in the corner, looking out the window. How may the nurse understand the man's actions? Incorrect: Other factors such as culture, personality, and language should be considered before assessing the inability to cope due to overwhelming concern for the woman. At this point there are no data to indicate overwhelming concern. Correct: These factors must first be considered along with ability to speak the language. Keeping in mind that there are individual and cultural differences in expressing concern will enable the nurse to make unbiased assessments. Incorrect: Embarrassment may be a reason for the man's actions, but is not the first consideration. It is important to first consider that there individual and cultural differences in expressing concern. This will enable the nurse to make unbiased assessments. Incorrect: If a man's religious beliefs prohibited him from viewing a birth, he is not likely to be in the room during the active phase of labor. He is likely to be very concerned about the woman's health to the point that his ability to cope with the situation is compromised. His actions reflect personality or cultural differences, which do not necessarily indicate a lack of concern. Due to his embarrassment and discomfort regarding the woman's expressions of pain, he withdraws from the situation. His religious beliefs regarding participation in the birth experience affect his interactivity and communication in this situation. 58. A client is admitted to the hospital with severe pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH). The physician orders magnesium sulfate. Which nursing intervention is important when administering this drug? Correct: Because hypertension is a sign of PIH, the client's BP must be monitored. The client's respiratory rate should be monitored because one sign of magnesium sulfate toxicity is a respiratory rate under 12/min. Incorrect: Assessing blood glucose levels does not pertain to PIH but to gestational diabetes. Incorrect: A side effect of magnesium sulfate is a decrease in blood pressure, which might cause orthostatic hypotension; however, the client with severe PIH will be on strict bed rest and not allowed to walk. Incorrect: Magnesium sulfate may be used for preterm labor to slow contractions, but this does not pertain to PIH. Assess blood pressure and respiratory rate every fifteen minutes. Monitor blood glucose levels every eight hours. Evaluate for orthostatic hypotension when getting the client up to walk. Observe for premature labor every shift. 59. A 27-week gestation infant is taken to a newborn intensive care unit 150 miles away. Initially, which emotion should the nurse expect the mother to display after the transfer? Incorrect: Usually denial is seen when the mother fails to recognize the severity of the situation. Denial would probably have occurred before the transfer, when the mother first learned about the baby's critical status. Incorrect: The mother may display frustration but it is aimed at not being able to follow the baby to the intensive care unit, and lack of knowledge about the child's condition. Correct: The mother feels a great deal of guilt for not having a perfect baby and perhaps for causing the baby pain and discomfort. The mother may also feel that she could have done something to prevent the early delivery. This is the primary emotion to expect. Incorrect: Anger is not usually seen initially. It occurs later in the grieving process. Denial Frustration Guilt Anger 60. A 38 week gestation newborn weighs 4020 grams, is sluggish, and has limp muscle tone. The baby experienced a broken clavicle during delivery. Based on this information, which can the nurse conclude about the baby? Incorrect: Normally infants who are withdrawing from drugs are hyperactive and jittery, not lethargic and limp. Correct: These symptoms indicate a large-for-gestational-age (LGA) infant. LGA infants typically have diabetic mothers and have respiratory problems and difficulty with stabilization of blood sugar. Incorrect: The baby's signs and symptoms are reflective of large-for-gestational age, not a heart defect. Incorrect: Respiratory depression may cause the infant to be limp, but this does not account for the baby's elevated weight. Neonatal abstinence symptoms Large for gestational age Congenital cardiac defect Respiratory depression 61. Which assessment finding suggests thrombophlebitis in a postpartum client? Incorrect: These signs and symptoms are indications of pulmonary embolism. Incorrect: These are signs and symptoms of a pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary emboli may occur as a result of clot formation in the calf. Correct: These signs and symptoms are common for clients with thrombophlebitis. Thrombophlebitis occurs because of changes in the blood volume and coagulation factors that result after delivery. Although eliciting a Homan's sign could dislodge a thrombus, it is considered a positive sign. Incorrect: These signs and symptoms do not relate to thrombophlebitis. Dyspnea, tachypnea, and apprehension Chills, hypotension, and abdominal tenderness Positive Homan's sign, calf warmth, and pain Dizziness, loss of consciousness, and chest pain 62. A client comes to the clinic to confirm that she is pregnant. Her last menstrual period was January 31st. According to Naegele's rule, when should the client expect to deliver? Incorrect: Seven days have not been added. Incorrect: Only two months have been subtracted. Correct: When using Nagele's rule to estimate delivery dates, the nurse takes the client's last menstrual period (LMP), adds 7days, and then subtracts 3 months. Adding 7 days to the LMP of January 31st makes it February 7th. Subtracting 3 months then makes the due date November 7th.Incorrect: Seven days have been subtracted instead of added to the LMP. November 31 December 7 November 7 December 24 63. Which procedure should be avoided for the client known to have a placenta previa? Incorrect: Non-stress tests are necessary to monitor the well-being of the fetus. Non-stress tests are usually performed if the client returns home after a bleeding episode. Incorrect: Performing a catheterization has nothing to do with placenta previa. Correct: In placenta previa, the placenta covers all or part of the cervical opening. Therefore, vaginal exams are contraindicated because of risk of bleeding or infection. Hemorrhage is the main complication of placenta previa. Incorrect: Abdominal ultrasounds are non-invasive and are commonly performed upon admission to the hospital to locate the position of the placenta. A non-stress test A urinary catheterization A sterile vaginal exam An abdominal ultrasound 64. A woman in the first trimester comes to the clinic with vaginal bleeding. The physician determines that the fetus has died and that the placenta, fetus, and tissues still remain in the uterus. How should the findings be documented? Incorrect: A complete abortion occurs when all products of conception are expelled. Incorrect: Stillborn is a lay term that means the baby has died. This does not address the products of conception such as the placenta or tissues. Correct: Prolonged retention of the products of conception (placenta/tissues) after the fetus has died is known as a missed abortion. Infection and coagulation defects are common complications. Incorrect: An incomplete abortion occurs when some, but not all, of the products of conception have been expelled. Complete abortion Stillborn abortion Missed abortion Incomplete abortion 65. A woman in the transition stage of labor is using paced breathing to relieve pain. She complains of blurred vision, numbness, and tingling of her hands and mouth. Which condition is indicated by these signs and symptoms? Incorrect: Anoxia/hypoxia results in restlessness, nasal flaring, and cyanosis of the lips and nailbeds. The signs and symptoms listed in the question are not related to anoxia. Correct: These signs and symptoms are a result of hyperventilation. The nurse should have the client breathe slower and into a paper bag to counteract the signs and symptoms. Incorrect: Anxiety usually causes rapid heart rate and muscle tenseness, not the symptoms listed in the question. Incorrect: While hypertension often affects vision, it is not the reason for this cluster of signs and symptoms. Anoxia Hyperventilation Anxiety Hypertension 66. Which data support a diagnosis of abruptio placenta in a pregnant woman? Correct: These are classic signs of an abruptio placenta. Other signs and symptoms include: dark, red vaginal bleeding, fetal distress, signs of hypovolemic shock. Incorrect: These are signs of placenta previa, not abruptio placenta. Incorrect: These have nothing to do with abruptio placenta. Incorrect: Bright red blood loss is a sign of placenta previa. Hypertension may occur in abruptio placenta, however. Uterine rigidity and abdominal pain Painless bleeding with soft abdomen Premature rupture of membranes and uterine contractions Bright red blood loss and elevated blood pressure 67. A women in her first trimester contracts rubella. How is the fetus likely to be affected? Incorrect: Rubella is usually associated with hearing, vision and cardiac defects. Correct: The rubella virus usually causes mild illness in the mother, but has devastating effects on the fetus, including cataracts, heart defects (patent ductus arteriosus and pulmonary stenosis are the most common), deafness, mental and motor retardation, growth retardation and clotting disorders. Incorrect: Spinal cord defects are a result of the inability of the vertebrae to fuse—it is a congenital problem and not related to rubella. Incorrect: Polydactyly, the presence of extra digits (fingers or toes), and club feet are not usually seen in fetuses with rubella. Reproductive and urinary defects Heart defects and cataracts Spinal cord and skeletal defects Polydactyly and club feet 68. An hour after delivery, a 4000 gram infant exhibits pallor, jitteriness, a blood sugar level of 40 gm/dL, irritability and periodic apnea. Which maternal condition could be the cause of the newborn's symptoms? Incorrect: Jitteriness and irritability may indicate a drug withdrawal problem, but the large birth weight and the low glucose levels indicate an infant of a diabetic mother. Incorrect: Jitteriness, irritability, and pallor are classic signs of hypoglycemia in the infant with a history of gestational diabetes. Infants born to mothers with pregnancy induced hypertension may be small for gestational age due to uteroplacental insufficiency. Incorrect: TORCH infections do affect the baby, but the symptoms described do not indicate a TORCH infection. Correct: These signs and symptoms are classic of an infant of a diabetic mother. Drug addiction Pregnancy-induced hypertension TORCH infection Gestational diabetes 69. A client delivered vaginally six hours ago. Which assessment finding can be interpreted as normal? Correct: A slight elevation in temperature during the first 24 hours post-delivery may be a result of dehydration. Temperature elevations after 24 hours are considered abnormal. Incorrect: A reading of 140/90 may indicate hypertension, which is a serious complication. Incorrect: A respiratory rate of 10 is not normal and could be a result of medications/narcotics given during labor. Incorrect: After delivery, the pulse rate is usually slightly lower than normal (usually 60-70 bpm) because of the fluid shifts and diuresis. Temperature 100.0 degrees F Blood pressure 140/90 Respirations 10 Pulse 90 70. A new mother receives instructions about care of her newborn son's circumcision. Which statement made by the mother indicates that further teaching is needed? Incorrect: The doctor should be notified if there is prolonged, excessive bleeding or signs of infection. Correct: This statement indicates that the client does not understand about the care of the circumcision. The yellowish mucous is normal and is from accumulated yellow serum. It helps in normal healing and should not be washed away. Incorrect: Vaseline gauze or betadine ointment should be applied with each diaper change to prevent the penis from sticking to the diaper. Incorrect: Sponge baths should be given to circumcised babies for the first 7 to 10 days. If a plastibell is used, tub baths may be given when the bell falls off (usually 7 –10 days). "I will call the doctor if my baby's penis starts to bleed." "I should wash off any yellowish mucous on my baby's penis." "I will put vaseline on his penis every time I change his diaper." "I should give my baby a sponge bath for the first week." 71. A 17-year-old client delivered her first baby 8 hours ago. Which of the following is an indication that appropriate bonding is occurring? The client: Correct: Making eye contact is a sign of positive attachment. Other signs include: speaking or singing to the infant, talking about the physical characteristics of the baby, (big feet, little nose etc.), calling the baby by name, stroking or massaging the baby to quiet it. Incorrect: Asking why the baby cries is not a sign of attachment and it may be a sign of rejection or neglect. Incorrect: This may indicate the lack of caretaker responsibility. Participation in infant care increases bonding. Incorrect: Asking if the baby is cute is not an indication that an attachment is occurring. The nurse's response must be carefully thought out to avoid blocking expressions of concern by the client. makes eye contact with the baby. wonders why the baby cries so much. asks the nurse to help change the baby' s diaper. asks the nurse if the baby is cute. 72. A new mother is crying in her room. She tells the nurse that her new baby boy has enlarged breasts and she thinks that there is something wrong. How should the nurse respond? Incorrect: This statement would increase the client's worry and anxiety by confirming her fears that something is wrong. The baby's symptom is completely normal. Correct: Enlarged breasts are common as a result of hormonal withdrawal. Breast enlargement usually subsides within the first few weeks after delivery. This response provides the mother with information, which should decrease her anxiety. Incorrect: This may be an appropriate response, but should not be the nurse's first response because it suggests the possibility that something is wrong with the baby. The baby's symptom is completely normal. Incorrect: This statement is an example of meaningless reassurance. "You should ask your doctor about that." "Enlarged breasts are common for both boys and girls. It will go away." "Let me look at the baby for you." "Everything is going to be just fine. Your baby is healthy." 73. During the active phase of labor, the membranes rupture and the nurse notes green amniotic fluid. Which nursing action should be initiated immediately? Incorrect: Green amniotic fluid is an indication of meconium staining, which may indicate fetal distress. The physician should be notified but not before assessing the status of the fetus. Incorrect: This is a comfort measure. It can wait until after the nurse assesses for fetal distress. Incorrect: Testing the fluid usually differentiates amniotic fluid from urine. Correct: Any time the membranes rupture, the nurse should immediately assess fetal heart rate, especially when the fluid is meconium stained, as this may indicate fetal distress. Call the physician. Replace the soiled underpad. Test the fluid with pH (Nitrazine) paper. Assess fetal heart rate. 74. At 28 weeks gestation, a woman enters the hospital in preterm labor and receives atocolytic medication to stop labor. Which assessment findings should be reported immediately to the physician? Incorrect: Fetal heart rate of 160 is considered normal. Incorrect: These represent Braxton Hick contractions, not true labor. Contractions should be monitored closely for intensity, frequency and duration. Incorrect: The vital signs are within normal limits. Correct: Ferning is an indication of amniotic fluid, which indicates that the membranes are ruptured. This should be reported immediately because delivery may be imminent. With ruptured membranes, the client should be monitored for infection. Fetal heart rate averaging 160 beats/min Irregular contractions every 15-20 minutes that last 30 seconds before stopping Maternal temperature 98.8 degrees F, pulse 84, respiratory rate 22, BP 130/70 Ferning pattern of vaginal discharge under a microscope 75. A labor and delivery nurse suspects that a client is in the transition stage of labor. Which information supports this conclusion? The client is: Incorrect: These are typical signs of the latent or early phase of labor. Correct: These are typical signs of the transition phase of labor. In addition to irritability and the inability to focus, the client may exhibit anger, loss of control, anxiety, mood swings, rectal pressure, and increasing amounts of pain. Incorrect: These occur in the second stage of labor, just prior to birth. Incorrect: These are signs that the client is in the latent or early phase of labor. walking around the unit and talking with her partner. irritable and needs frequent repetition of directions. expelling feces and the fetal head is crowning. reading a magazine and talking on the phone. ATI. CHILD CARE 2.0 1 The parents of a 5-month-old infant state that their infant seems to eat very little. Most of the food comes out of the infant's mouth and onto his clothes. Which of the following explanations should the nurse give to the parents? Trying to introduce food after the intake of a bottle formula is usually not recommended because the infant is satiated and has no inclination to try something new. Solid foods should be offered at 4 to 6 months. The gastrointestinal tract has matured enough to handle more nutrients and is less sensitive to potentially allergenic foods. This deprives the infant of the pleasure of learning new tastes and developing a discriminating palate. It may cause problems with poor chewing because of lack of experience. Due to the extrusion (protrusion) reflex, the infant’s tongue pushes the food out of the mouth. It is most helpful to suggest using a long-handled spoon and placing the food in the back of the infant's mouth to avoid the reflex. "Give the baby a bottle of formula before solid food to assure adequate caloric intake." "Stop the solid foods and try again when the baby is 12 months old." "Put the cereal in a bottle and feed the baby through a nipple with a large hole." "Place the food in the back of the baby's mouth using a long-handled spoon." 2 A nurse smells an odor identified as marijuana coming from a room. Which of the following client findings would confirm inhalation of the substance? All are findings of a client who has smoked/inhaled cannabis/marijuana. These clients are typically euphoric or somewhat mildly intoxicated. They have poor coordination with bloodshot (red) eyes and may laugh inappropriately. These findings are more commonly due to of the effects of depressants. These findings are more commonly due to the effects of opiates. These findings are more commonly due to the effects of cocaine. Poor coordination, red eyes, and euphoria Slurred speech, confusion, and combativeness Loss of consciousness, respiratory depression, and coma Hypertension, tachycardia, and hyperflexia 3 A nurse is checking children at an orthopedic outpatient setting. Which of the following should the nurse expect to see as manifestations of scoliosis? Lumbar curvature is a manifestation of lordosis. These are manifestations of scoliosis. Often parents observe that a child's skirt doesn't hang straight or the pant legs are uneven. Tenderness is a general symptom that may indicate something is wrong in an underlying organ. A nurse could not see changes such as swelling of the spine. These symptoms could be associated with other orthopedic problems but are not characteristic of scoliosis. Pain and an exaggerated lumbar curvature Uneven shoulder heights and poorly fitting slacks Tenderness and swelling of the spine Limited range of motion of the back and a limp 4 A nurse is providing client/patient education to the mother of an 8-year-old child diagnosed with B-hemolytic streptococci infection (strep throat). The nurse emphasizes the importance of promptly starting and completing the entire course of antibiotics. The mother asks why this is important. The nurse states that the antibiotic will Pain may interfere with oral intake, but this is not the priority concern with prompt diagnosis and care of strep throat. Cool fluids or ice chips may be comforting. Relief to the neck may be provided by the application of cold or warm compresses to the area. Warm saline gargles may also relieve throat discomfort. Sinusitis and abscess formation on the pharyngeal and peri tonsillar areas are complications that can develop with a strep throat infection, but these complications are not of the greatest concern with this infection. Anterior cervical lymphadenopathy is a symptom of a streptococcal infection resulting in pharyngitis and tender lymph nodes. This usually subsides in 3 to 5 days if uncomplicated. Antibiotics should be initiated as soon as possible and taken as prescribed to quickly and completely eliminate the streptococcal organism, which can lead to acute rheumatic fever, glomerulonephritis, and acute renal failure. alleviate painful swallowing to avoid complications of dehydration and malnutrition. prevent sinusitis or abscess formation on the pharyngeal or peri tonsillar areas. reduce the risk of anterior cervical lymphadenopathy. eliminate organisms that might initiate acute renal failure or rheumatic fever. 5 A nurse is reinforcing teaching about accidental poisoning to a parent during a routine well- child visit. The nurse asks the parent, "What would be your first response if your child accidentally took an overdose of acetaminophen (Tylenol)?" Which of the following statements by the parent would indicate a correct understanding? Syrup of ipecac is no longer recommended as a routine home treatment of poisoning. Giving syrup of ipecac might possibly be appropriate, but certain substances that are corrosive would make using this measure contraindicated because it would increase the damage to the mucosa lining. Placing the child into a side-lying position is an appropriate measure to prevent aspiration. Calling the Poison Control Center is the best initial response to an accidental poisoning because each case needs to be dealt with by getting prompt medical attention to initiate the appropriate emergency treatment actions. Giving the child one sip of water, not a full glass, is appropriate to dilute the ingested poison. However, this is not the first action that should be taken. "I will give my child a dose of ipecac." "I will place my child on her back." "I will call the Poison Control Center." "I will get my child to drink a full glass of water." 6 A nurse is caring for a 23-month-old child with iron-deficiency anemia. The parents indicate they have been taught about the diagnosis, but are concerned that they are not doing all that they need to do. Which of the following should the nurse include when reinforcing teaching? Cow's milk contains substances that bind with iron and interfere with its absorption. Iron should not be given with milk or milk products. There are no food limitations or suggestions when children are taking oral iron preparations. Foods with vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, enhance the absorption of iron. Oral iron supplements do not cause GI bleeding or ulcers. Liquid iron may stain the teeth, so the nurse should instruct the parents to give it through a straw placed in the back of the child's mouth to avoid staining the teeth. Give the oral iron supplementation with a glass of cow's milk to prevent stomach problems. Provide diet instructions including limiting citrus fruits in favor of more vegetables. Provide information about complications of iron including gastrointestinal bleeding and ulcers. Give liquid iron through a straw placed in the back of the mouth. 7 A nurse is reviewing discharge teaching with the parents of a child who has pediculosis. Which of the following should the nurse include in the teaching? Children should not share combs, hair ornaments, hats, caps, scarves, coats, and other items used on or near the hair. Pets are not carriers of lice. Clothes should be dried in a hot dryer for at least 20 min to kill the lice. Lice need a blood source to survive. Placing the nonwashable items in a sealed plastic bag for 14 days will kill the lice. "Children can share scarves and coats, but not hats or combs." "Household pets can carry and transmit lice to people." "After washing clothing, hang clothes outside to dry." "Seal nonwashable items in plastic bags for 14 days." 8 A nurse is caring for a toddler who is in an oxygen tent. Which of the following actions should the nurse take in order to promote comfort while maintaining the child's safety? Not all toys are safe to put inside an oxygen tent. Vinyl or plastic toys that do not absorb moisture are suitable to put inside the tent. Stuffed animals absorb moisture and are difficult to dry. High levels of oxygen are a source of sparks, so mechanical or electrical toys are a potential fire hazard. The moisture inside an oxygen tent will make the child cold and the child’s clothes moist. Therefore, the nurse should try to keep the child warm and dry by changing bedding and clothes, which will enhance the child's comfort without compromising safety. Oxygen is heavier than air; therefore, oxygen loss will be greater at the bottom of the tent. The tent should be tucked snugly without open edges to prevent oxygen loss. Some tents are opened at the top. Oxygen is a heavy gas and most of it will stay at the bottom of the tent. This measure does not promote the child's comfort while in the oxygen tent. Give the child a stuffed animal and car with rubber wheels to play with. Change the bedding and the child's clothing frequently or as often as needed. Tuck the bottom of the tent under the mattress on three sides, leaving one side open so the child can look out. Cover the opening on the roof of the tent with a blanket to prevent the child from becoming chilled. 9 A nurse is reinforcing teaching with the parent of a child with a urinary tract infection. Which of the following statements made by the parent indicates understanding of how to prevent future infections? Children should be encouraged to void frequently, especially before long trips or other circumstances in which toilet facilities may not be available for an extended period of time. Urine that is held can harbor bacteria that can result in a urinary tract infection. Cotton underwear allows for more air flow to the perineal area and reduces the risk of urinary tract infections. Wiping from back to front increases the risk of feces entering the urethra and causing a urinary tract infection. Bubble baths and perfumed perineal products can irritate the urethra and lead to a urinary tract infection. These should be avoided, especially for girls. "I will bring my child to the bathroom before we leave for extended trips." "I need to switch my child from cotton underwear to nylon underwear." "I should teach my child to wipe from back to front after urinating." "I will have my child soak in a bubble bath once or twice a week." 10 A nurse is reviewing discharge instructions with the parent of an infant who has acute laryngotracheobronchitis (croup). Which of the following statements made by the parent indicates a need for further teaching? This is a correct intervention. Corticosteroids have an anti-inflammatory effect that decreases subglottic edema. This will make breathing easier. This is a correct intervention. Clearing the nasal passages decreases the amount of secretions in the upper and lower airways. Dry air will exacerbate the child's croup. Cool temperature therapies are advocated for this condition. Cool mist constricts edematous blood vessels. A cool air vaporizer can be used at home to maintain high humidity and provide relief. Warm mist from warm running water such as a hot shower in a closed bathroom may be beneficial. It is essential that children with laryngotracheobronchitis (croup) be allowed and encouraged to drink any fluids they like to increase fluid intake. "I will give my child the corticosteroids prescribed by the doctor." "I will clear the child's nasal passages with a bulb syringe to aid in breathing." "I will place a dehumidifier in my child's room." "I will encourage my child to take plenty of fluids over the next several days." 11 A 15-year-old client visits the clinic to get medical clearance to play a sport. The nurse reviews measures to prevent athlete's foot with the client. Which of the following statements by the client indicates that the instructions were understood? Many people believe tinea pedis is transmitted via showering in the same location as someone who is infected. However, transmission of tinea pedis to other individuals is rare. Ointments have not proven to be successful in treating tinea pedis. Application of antifungal powder containing tolnaftate or tolnaftate liquid is a treatment measure. Medication is not usually recommended as a preventative measure. The client should avoid heat and perspiration by wearing light socks. Wearing well-ventilated shoes and clean, lightweight socks is encouraged in order to prevent heat and perspiration conditions. Occlusive shoes should be avoided. "I will avoid showering at the gym." "I can apply an antifungal cream daily." "I should wear dark-colored socks." "I should wear well-ventilated shoes." 12 A nurse is collecting data on a 3-year-old child with eczema in an outpatient center. The parent asks whether any changes can be made at home to prevent the recurrence of eczema. Which of the following is an appropriate response by the nurse? Clients with eczema should avoid any material that produces heat, as this can cause perspiration and itching. Bubble baths and harsh soaps cause drying of the skin and can further irritate the eczema. A room humidifier or vaporizer may be helpful for keeping moisture in the air and keeping the skin from drying. Woolen clothing or blankets cause itching and should not be used. "Cover the crib mattress with a plastic cover." "Give the child a bubble bath for 20 min each day." "Place a humidifier in the child's room." "Dress the child in warm wool clothing in cold weather." 13 A nurse is caring for a 7-year-old child who is admitted with an asthma exacerbation. This is the third admission since diagnosis 6 months ago. Which of the following topics should be reinforced with the parents and child in order to prevent future readmissions? Monitoring the child's oxygen saturation and respiratory rate provides information about how well the child is oxygenating, but does not prevent future attacks. Allergen control is aimed at the prevention of exposure to airborne allergens and irritants that can trigger an asthma attack. Preventing exposure to allergens does reduce the risk for future attacks. Peak flow readings allow parents to make educated decisions regarding asthma management. However, these measurements will not prevent future asthma attacks or hospitalization. Upright positioning is important to help with lung expansion during an asthma attack, but it is not a preventative measure. Monitoring oxygen saturation and respiratory rate daily Identification and avoidance of factors that trigger symptoms Monitoring peak flow measurements regularly Positioning the client upright in a position of comfort 14 Which of the following physical manifestations of a client with anorexia nervosa best indicates compliance with the treatment plan of care? Effectiveness of nursing interventions includes weight gain or no further weight loss. Measuring weight is routinely completed to determine the effectiveness of the plan of care. This is the best indicator of compliance with the treatment plan. Return of soft bowel movements indicates that the client is not using laxatives or enemas to speed up the intestinal passage of food. This is a good indication but is not the best indicator of compliance. This is a good indication of weight gain and normalizing of body function, but it is not the best indication of treatment plan success. Improvement of the oral mucosa indicates that nutritional deficiencies are improving. This is a positive sign, but not the best indicator of compliance with the treatment plan of care. A weekly weight gain of 1 kg (2.2 lb) Daily bowel movements that are soft Return of regular menstrual periods Improvement of the oral mucosa 15 An assistive personnel (AP) is caring for a child diagnosed with leukemia and undergoing chemotherapy. In which of the following clinical situations should a nurse intervene? Chemotherapy can damage gastrointestinal mucosal cells. Using a soft toothbrush will provide mouth care and will be gentle on the mucous membranes in order to prevent ulceration. Hair loss is a common side effect of chemotherapy. Children often feel better if their heads are covered so no one can see that they have lost their hair. A soft cap is most comfortable and won't increase perspiration or cause itching as do other materials. Chemotherapy will put children at risk for infection secondary to immunosuppression, so all visitors with infections are restricted. The rectal area is prone to ulceration from various drugs, feces, and urine. Urine and feces must be removed immediately and the perianal area washed. Using rectal temperatures is avoided to prevent trauma. The AP offers a soft toothbrush for oral care. The AP applies a soft cotton cap to the child's head. The AP maintains a restriction of all visitors and health personnel with infections. The AP prepares to take a rectal temperature. ???16 A nurse is preparing to administer an intramuscular (IM) injection to a 2-month-old infant. Which of the following is the preferred injection site? (PICTURE HERE) The vastus lateralis is the preferred site for IM injections in infants. The deltoid muscle is not the preferred site for IM injections in infants. It is recommended that the ventrogluteal site not be used until infants begin walking. 17 A nurse is reinforcing teaching with the parent of an infant who has club feet with bilateral casts. Which of the following statements should be included in the teaching? If a cast is too tight, circulation will be impaired and the toes will swell. Serial manipulation and casting allows for the gradual stretching of skin and accommodates the rapid growth in early infancy, and is performed every week for 8 to 12 weeks. If normal alignment is not achieved by 3 months, surgical intervention is indicated and will take place at about 6 to 12months of age. It can take 24 to 48 hr for the cast to dry completely. A regular fan or cool-air hair dryer to circulate air may facilitate drying when humidity is high. Heated fans and dryers should not be used because they can cause the cast to dry on the outside but remain wet on the inside. They may also cause burns from the conduction of heat from the cast to the underlying tissue. Pain is not a problem associated with casting for club feet. "Check the toes for any swelling or discoloration." "Monthly recasting should be scheduled with the orthopedist." "Use a heated fan or dryer to facilitate the drying of the cast." "Give the baby Tylenol every 4 hr to help with pain." 18 A nurse is caring for a child with measles. Which of the following actions is appropriate supportive care? Photophobia accompanies rubeola; therefore, diversional activities with bright lights are contraindicated. Dimming the room lights is soothing for the child. Isolation should be until day 5of the rash. The period of communicability is from 4 days before the appearance of the rash until5 days following the appearance of the rash. An elevated temperature is common. Overheating, which increases itching, should be avoided. The child should wear lightweight, loose, and nonirritating clothing, and keep out of the sun. Antipyretics should also be administered. Vitamin A supplementation reduces the morbidity and mortality in children with the measles. Children with measles should be given vitamin A supplements. Nurses need to instruct parents on safe storage and administration of vitamin A to prevent excessive administration and possible toxicity. Provide diversional activities such as video games. Maintain isolation for 48 hr after the rash resolves. Keep the child warm with adequate undergarments and bedding. Administer vitamin A supplements as prescribed. 19 A nurse is caring for a 14-year-old client diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. The nurse is discussing the ongoing monitoring needed with this diagnosis. Which of the following should be included in the discussion? When children are ill their fluid intake should be monitored. They often drink less, leading to dehydration. When children are hyperglycemic, dehydration from illness leads to increased hyperglycemia and requires extra fluid intake. Exercise results in increased movement of glucose into the cells and decreased blood glucose levels. The client should have a snack, not additional insulin. There is poor correlation between glycosuria and blood glucose. Blood glucose monitoring is much more accurate than urine glucose monitoring. Children with diabetes should increase the amount of whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, which contain complex carbohydrates, in their diets. Concentrated sweets are avoided to prevent hyperglycemia. The illness requires careful attention to fluid balance since hyperglycemia contributes to dehydration. Exercise requires additional insulin since glucose will be released from the cells during activity. Urine glucose must be monitored because there is a correlation between simultaneous glycosuria and blood glucose concentrations. The diet needs to include fewer complex carbohydrates because they quickly raise blood glucose. 20 A nurse is reinforcing teaching with the parent of a 4-year-old child with influenza. Which of the following should the nurse include in the teaching? Influenza is spread by direct contact. This means it can be spread from one person to another or by touching an object that has been contaminated by nasopharyngeal secretions. The most infectious period for influenza is 24 hr before and after the onset of symptoms. There is a possible link between aspirin and Reye syndrome, so children with influenza or other viral illnesses should not be given aspirin. Most cases of Reye syndrome follow a common viral illness such as chickenpox or influenza. The immunization vaccine can be given at the same time as other vaccines, but must be given in a separate syringe and at a different injection site. Influenza is transmitted by airborne means, so handwashing will not prevent transmission. Children are not infectious after 12 hr from the onset of influenza symptoms. Aspirin should not be given to children with influenza for relief of discomfort. The influenza vaccine may not be given at the same time as other immunizations. 21 A nurse is discussing nutrition with an adolescent who is pregnant. The adolescent's parent is in the room. Which of the following statements made by the parent indicates a need for further dietary instruction? This statement needs clarification. Snacks containing sugar are often eaten by the adolescent who is pregnant, but are not a good source of calories for energy and nutrition for the developing fetus. Whether pregnant or not, an adolescent's nutritional needs include an increase in calcium, protein, and iron. Nutritious between-meal snacks are a good source of energy. Complex carbohydrates of wheat and whole grains and fruits are appropriate snacks. This is a good suggestion because the adolescent does need additional calories in the second and third trimester. "I told my daughter that any calories ingested are a source of energy and nutrition." "I try to provide foods with an increased amount of calcium, protein, and iron." "I encourage between-meal snacks that are complex carbohydrates and fruits." "I have planned meals and snacks for additional calories in the second and third trimester." 22 A nurse is caring for a 14-year-old child with appendicitis who has a pain rating of 8 on a scale of 1 to 10. The child has just returned to the unit after a computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and tells the nurse the pain just stopped. Which of the following should the nurse do first? Even though continued pain assessment is important, this is not the first priority with the sudden relief of pain. The child's vital signs will need to be taken before surgery, but this is not the priority at this time. The sudden cessation of pain in a child with appendicitis should cause the nurse to suspect a ruptured appendix. The primary care provider should be notified immediately since the client is at increased risk for developing peritonitis, which can cause death if appropriate interventions are not immediately taken. The nurse would assess bowel sounds as the child is prepared for surgery, but this is not the priority at this time. Continue with the pain assessment. Take the child's vital signs. Notify the primary care provider. Auscultate the child's bowel sounds. 23 A nurse is monitoring a 9-year-old child on the first postoperative day following abdominal surgery. The nurse notes the child grimacing and guarding her abdomen. Which of the following pain assessment tools should the nurse use based on its acceptance by children? The poker chip scale is used by children, but is not rated as the most preferred by that age group. The FACES pain rating scale is the best choice for a 9-year-old child because it includes visual face, numerical correspondence, and text stating feelings. This is the most preferred scale for children. The visual analog scale allows a child to mark a line stating the length of pain; however, this scale is difficult to determine and clarification is needed. The numerical 1 to 10 rating scale is used for adults. It has too many options and often requires clarification when used with children. Poker chip tool FACES rating scale Visual analog scale Numerical 1 to 10 rating scale 24 A nurse is reinforcing teaching to a group of parents about preventing accidental poisoning in preschoolers. Which of the following should the nurse include? This does not prevent accidental poisoning. Parents should caution against eating inedible items such as houseplants. Never remove labels from containers of toxic substances. Store toxic agents in a locked cabinet. All potentially toxic agents should be placed out of reaching a locked cabinet. Toddlers may be able to climb onto the sink and get into the cabinet. Have syrup of ipecac available in the home. Explain to preschool children that plants can be eaten only after they are cooked. Keep labels on containers of toxic substances and never remove them. Place medications in a cabinet above the sink. 25 A nurse is caring for a 4-month-old infant with thrush (candidiasis) who is breastfed. Which of the following is an appropriate nursing action? To prevent relapse, therapy with nystatin should be continued for at least 2 days after the lesions disappear. No change in feeding is needed as part of the care for a client with thrush. No change in feeding is needed as part of the care for a client with thrush. Sucking may be painful, but changing to a formula or another method of feeding will not alleviate the discomfort. Oral candidiasis cannot be removed with a tongue blade and attempting to do so will cause bleeding and discomfort for the infant. Administer the prescribed nystatin (Mycostatin) for 2 to 3 days after the lesions disappear. Place the infant on a soy-based formula to supplement breastfeeding until thrush is resolved. Discontinue breastfeeding and resume 48 hr after the last lesion disappears. Scrape off the white patches of thrush from the oral mucous membrane with a tongue depressor. 26 A nurse is caring for an adolescent with inadequate weight gain. Which of the following nutritional considerations is important to reinforce when talking with the client about appropriate nutrition? Generally, adolescents obtain or exceed the recommended carbohydrate consumption. Limiting fat consumption is important to overall health. Adolescence is a time of accelerated physical growth, which can include doubling the adolescent requirements of calcium, iron, zinc, and protein. Maximum bone mass is acquired during adolescence making calcium intake during these years essential. Just increasing calories will not ensure adequate consumption of the necessary vitamins and minerals necessary to assure good health. Identify food preferences high in complex carbohydrates. Identify food preferences high in saturated and unsaturated fats. Identify food preferences high in calcium and protein. Identify food preferences high in calories. 27 A primary care provider prescribes amoxicillin suspension to a child with otitis media who weighs 22 lb. The prescription reads: 30 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hr. The pharmacy carries the medication as 200 mg/5 mL. How may mL should the nurse give in one dose? Answer in mL. mL First, convert the client's weight to kg: 2.2 lb = 1 kg, so 22 lb = 10 kg. 24 hr/day = 3 doses/day 8 hr/dose 30 mg/kg/day = 10 mg/kg/dose 3 doses 10 mg x 10 kg = 100 mg every 8 hr The desired dose is 100 mg. The medication is available as 200 mg/5 mL. 100 mg/x mL = (½)5 mL 200 mg/5 mL 5 mL = 2.5 mL/dose  2 First, convert the client's weight to kg: 2.2 lb = 1 kg, so 22 lb = 10 kg. 24 hr/day = 3 doses/day 8 hr/dose 30 mg/kg/day = 10 mg/kg/dose3 doses 10 mg x 10 kg = 100 mg every 8 hr The desired dose is 100 mg. The medication is available as 200 mg/5 mL. 100 mg/x mL = (½)5 mL200 mg/5 mL 5 mL = 2.5 mL/dose 2 28 Which of the following approaches is the most accurate way to measure the heart rate of a 10month-old infant? The apical heart rate is auscultated and is the most accurate measurement for an infant. The radial pulse is not palpable in an infant. The ulnar vein is deep in the arm and is not palpable. The brachial pulse is palpable in an infant. It provides a quick check of circulation status, but it is not the most accurate approach. Apical Radial Ulna Brachial 29 A nurse is caring for a 4-year-old child diagnosed with leukemia who is admitted with myelosuppression. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? High carbohydrates will not provide the proper nutrients for protection against infection. The child needs a diet high in protein for defense against infection. Chemotherapy can cause injury to mucous cells lining the rectal area, making this area prone to ulceration and tears. Rectal temperatures should be avoided to prevent trauma to this fragile tissue. Lemon and glycerin swabs are abrasive and can irritate tissue. A break in the skin is a potential source of infection. Provide a diet high in carbohydrates. Monitor rectal temperature every 4 hr. Use lemon or glycerin swabs for oral care. Inspect the skin daily for lesions. 30 The parents of a 4-year-old child state that they had an infant die 2 months ago during childbirth. They are concerned about their 4-year-old child's response to the infant's death. Which of the following statements by the parents indicates an expected response about death from the 4- year-old child? This expresses a more adult understanding of death. Preschoolers tend to think that the sibling is still alive. This kind of question would be appropriate for a school-age child. These responses are most characteristic of adolescents who have the most difficulty coping with death. Young children often feel guilty and responsible for a sibling's death, or may view illness or injury as a punishment for their thoughts about the sibling. "Our child wants to go to the cemetery to be with his sister." "Our child asks many questions about what happened to the baby's body." "Our child is not sleeping, eating, or playing lately and we are worried." "Our child blames himself for the baby's death because he said he didn't want a baby brother or sister." 31 A nurse is preparing a room for the admission of a client with sickle cell anemia who is in vasoocclusive crisis. Which type of equipment should the nurse place in the client's room? Wheelchairs are used to decrease energy expenditures; however, this is not the most important equipment needed at this time. It would be nice to have these available in the room, but these are not priority measures at this time. It would be nice to have these available in the room, but these are not priority measures. Exchange transfusion is an important part of the treatment for vaso- occlusive crisis. One of the main objectives when managing a sickle cell crisis is blood replacement to treat anemia and hydration to reduce the viscosity of the sickled blood. Wheelchair with adjustable leg rests A radio and age-appropriate reading materials Extra blankets and pillows Blood transfusion equipment 32 An 8-year-old child is admitted to a pediatric unit with a fractured femur and is placed in skeletaltraction. Which of the following nursing interventions is the most appropriate? Weights should hang freely to promote the forward force of traction. High-fat meals are not recommended. When a client is immobile, a high-fiber diet may be recommended to keep stools soft and prevent complications. The pulses on the side that are in traction are compared to the pulses on the contralateral side to assure that circulation in the affected side is not compromised. Color of the skin and nailbeds can also be assessed to observe for any neurovascular changes. The child's position should be changed at least every 2 hr to relieve frictional pressure on the bed and minimize skin breakdown. Passive, active, or active-with resistance exercises of the uninvolved extremities and joints should be performed to maintain strength and range of motion. Dependent upon the type of traction, varying degrees of position changes can be made without interfering with the traction. Position the weights securely against the foot of the bed. Provide small, frequent, high-fat meals to the child. Compare pulses on affected site to contralateral side. Provide diversional activities to minimize the child's movement. 33 A nurse on a pediatric unit is assigned to care for a child with Reye syndrome. Which of the following is the most serious clinical manifestations for which the nurse should monitor? Reye syndrome results in children secondary to a mitochondrial insult sustained following a viral infection and the administration of aspirin. It is not associated with an anaphylactic reaction. Cerebral edema with increased intracranial pressure presents the most significant threat to life. Vital functions and neurologic status need to be monitored by the nurse. Secondary to related liver dysfunction, coagulation impairment with prolonged bleeding time is a sign of Reye syndrome. This complication is not the most serious clinical manifestation of Reye syndrome. The possibility of hypovolemic shock is a constant threat in children with controlled fluid intake and osmotic diuresis. Monitoring of intake and output is necessary for adjusting fluid volumes to prevent dehydration. Anaphylaxis Cerebral edema Impaired coagulation Hypervolemia 34 A nurse is preparing to take a rectal temperature on a 7-month-old infant. Which of the following should the nurse keep in mind when preparing to take the temperature? A rectal thermometer should be well-lubricated prior to insertion, but the maximum depth of tip insertion is 2.5 cm into the rectum, not inches. Rectal temperatures are approximately 1° Chigher than an oral temperature. To convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius: (5/9)(x-32)=° C. For example, a rectal temperature of 99.6° F is converted to Celsius by performing (5/9)(99.6-32)=(5/9) (67.6)=338/9=37.5° C. Next, the oral temperature of 97.7° F is converted to Celsius by performing (5/9)(97.7-32)=(5/9)(65.7)=328.5/9=36.5° C. The rectal temperature of 37.5° C is 1° higher than the oral temperature of 36.5° C. Therefore, a rectal temperature of 99.6° F is equivalent to an oral temperature of 97.7° F. Rectal temperatures are more accurate, but infants should have their temperature taken by axillary or tympanic membrane because of the danger of damaging rectal mucosa. Rectal temperatures should only be obtained on infants and children when no other route can be used. Rectal thermometers should be left in place for 4min, but the use of mercury thermometers is losing favor. Mercury thermometers should not be used because if broken, inhaled vapors from the mercury can cause significant toxicity. A well-lubricated thermometer tip should be inserted a maximum of 2.5 in into the rectum. A rectal temperature of 99.6° F is equal to an oral temperature of 97.7° F. Infants should have temperatures taken rectally for accuracy and thermoregulation. Mercury thermometers are the thermometers of choice to obtain the rectal temperature, holding it in place for 4 min. 35 A nurse is talking to the parents of a 3-year-old child about water safety precautions. Which of the following statements made by the parents indicates a need for clarification? Toddlers are curious and can fall headfirst and be trapped. Toddlers can drown in bathtubs while being left unattended. Toddlers can drown in unusual places due to their curiousness and fascination with water. All standing amounts of water should be drained. Teaching swimming and water safety are beneficial, but insufficient for protection against drowning. When the child is near the swimming pool, the parent needs to be supervising the toddler. Statistics show that 90% of all drownings occur in the swimming pool. Water is fascinating to children and drowning can occur quickly. "We keep the toilet seat down at all times." "We don't answer the phone during bath time." "We empty all buckets filled with water." "We have our child in swimming lessons." 36 A nurse is caring for a child with Wilms' tumor. The parents ask why the sign "Do not palpate the abdomen" has to be placed on their child's bed. Which of the following is the correct response by the nurse? This is not the reason the abdomen should not be palpated. Wilms' tumor is characteristically nontender. Palpation will not cause the tumor to grow. Tumors grow from multiplication of cells, not manipulation of the mass. Palpation of the abdomen is avoided because manipulation of the mass may cause cancer cells to spread to other sites. The tumor is on the kidney, not the bladder. Palpation will not cause urinary leakage. "Any manipulation of the abdomen can result in pain for your child." "Palpation of the abdomen could cause the tumor to grow." "Palpation of the abdomen could result in some of the tumor cells breaking loose, causing it to spread." "Any manipulation of the abdomen will put pressure on the bladder and cause urine to leak." 37 A nurse is caring for a child with muscular dystrophy. Which of the following priority actions should the nurse include in the care of this child? Maintaining function of muscles is the goal of treatment for muscular dystrophy. Stretching, range-of-motion exercises, and strength and muscle training should be performed to help maintain function. Children who remain active can delay the eventual confinement in wheelchair for a great length of time. Duchenne muscular dystrophy occurs from mother-to-son transmission of the defective gene. It is inherited from an X-linked trait. Therefore, genetic counseling is an important aspect of supportive family care and it is recommended for the parents, female siblings, maternal aunts, and their female offspring. This is not the priority nursing action. Flu and pneumococcal vaccines are encouraged as well as the avoidance of persons with respiratory infections because children with muscular dystrophy are at an increased risk for respiratory infections. Incentive spirometer use and breathing exercises should be performed daily to increase and maintain vital lung capacity. Limit physical activity and plan frequent rest periods to avoid overexertion and exhaustion of muscle groups. Recommend genetic counseling for parents, male siblings, and paternal uncles and their male offspring. Advise against flu and pneumococcal vaccines due to a compromised respiratory system. Have the child use an incentive spirometer and perform breathing exercises routinely. 38 A nurse is caring for a child with acute glomerulonephritis. The child has edema, hypertension, and gross hematuria. Which of the following is the most appropriate nursing intervention? Children with glomerulonephritis require frequent monitoring of vital signs, but oxygen saturation is not necessary. For children with hypertension and edema, moderate sodium and fluid restrictions may be instituted. Foods high in potassium are restricted during oliguric periods. Due to the edema present in the disease process, the child is weighed and fluid balances monitored daily to check the fluid balance. This is not the first priority in the child's care. Most children recover completely. However, health supervision following hospitalization should be continued weekly and then monthly for evaluation and urinalysis. Monitor the oxygen saturation every 4 hr. Teach the parents dietary restrictions regarding protein. Weigh the child daily and record intake and output. Counsel the parents about the need for follow-up. 39 A nurse is performing a routine physical examination on an adolescent client who asks, "Why do I have to use a condom if my girlfriend is on the pill? I thought the pill was enough protection against pregnancy." Which of the following is the most appropriate response by the nurse? Using two forms of birth control may be effective against pregnancy, but this response does not explain why one form must be a condom. Having both partners share responsibility for birth control is a positive situation, but this is not the reason the client should use a condom along with birth control pills. When used correctly, contraceptives are as effective in adolescents as in adults. Condoms are the only birth control method that protect against sexually transmitted diseases. "You need to use two forms of birth control so if one fails you have a second form of protection against pregnancy." "Using a condom allows you to share the responsibility for birth control." "Oral contraceptives are less than 99 percent effective in adolescents. Therefore, a second form of contraception is needed." "Oral contraceptives are highly effective in preventing pregnancy but do not prevent sexually transmitted diseases." 40 A nurse is preparing to admit a 15-year-old client with HIV/AIDS. Based on the client's diagnosis, which of the following nursing actions is appropriate? HIV/AIDS is transmitted through blood and body fluids. The precautions necessary for blood and body fluid transmission are standard precautions. The client and the client's family should be educated regarding the transmission of infectious disease. Basic information about standard precautions should be presented in a manner that is age-appropriate and considers educational levels for the client and the client's family. The combination of hot water and detergents used in hospital dishwashers is sufficient to decontaminate dishes, glasses and cups, and eating utensils. Disposable dishes are not necessary. Airborne precautions require a negative pressure room. Tuberculosis, not HIV, is a disease that would require this precaution. Visitors do not need to wear either a gown or mask. A mask and gown are required during procedures and client care activities that are likely to generate splashes or sprays of blood, body fluids, secretions, or excretions to provide protection from contact transmission of pathogenic organisms. Contribute to planning client education on standard precautions in age-appropriate manner. Contact the dietary department to request foods be delivered on disposable dishes. Prepare for infection control in a negative pressure room for this client. Instruct visitors to wear gowns and masks when entering the client's room. 41 A nurse is reinforcing home care instructions with the parents of a 5-year-old child who has acute bronchitis. In order to prevent the transmission of the virus, which of the following should the nurse include in the instructions? Acute bronchitis is generally caused by a virus. Transmission is via direct contact; therefore, isolation is not required. Careful handwashing is important when caring for children with respiratory infections. They should be taught to use a tissue to cover their nose and mouth when they cough or sneeze and to wash their hands. Bronchitis is transmitted via articles contaminated with nasopharyngeal secretions. The virus will not live if dishes are washed properly. The combination of hot water and detergent is sufficient to decontaminate dishes, glasses, cups, and eating utensils. Clients wear masks when they are immunocompromised and a health care professional is trying to prevent the client from acquiring a secondary infection. A client with bronchitis is not considered immunocompromised. Isolate the child in a bedroom separated from the rest of the family. Teach the child to wash his hands after coughing secretions into a tissue. Serve food to the child on disposable dishes with plastic utensils. Have the child wear a mask whenever leaving the bedroom. 42 A nurse is monitoring a 6-month-old infant who is diagnosed with pneumonia. The nurse observes an absence of respirations and peripheral cyanosis. After determining unresponsiveness, which of the following is the next nursing action? This should be done after establishing an open airway. This is not the next nursing action. Following cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) techniques, the nurse should determine unresponsiveness and reposition the infant to dislodge an obstruction or open the airway. For infants, help is called after 1 min of CPR. Look, listen, and feel for normal breathing. Give two rescue breaths. Position the infant to open the airway. Immediately call for assistance. 43 Which of the following emotional manifestations demonstrates an improvement in a 7-month- oldinfant diagnosed with nonorganic failure to thrive? The absence of separation anxiety and fear of strangers is a clinical manifestation of failure to thrive. Most infants develop separation anxiety and fear of strangers from 6 to 8months of age. Radar scan of the environment with a wide-eyed gaze is a clinical manifestation of failure to thrive. Infants with nonorganic failure to thrive are detached and show less interest in social interactions. Signs of nonorganic failure to thrive include the infant being passive, sleepy, and lethargic. Infants with nonorganic failure to thrive do not like to be held or touched, so this would be a sign of improvement. Infant has no fear of strangers. Infant scans environment with wide-eyed gaze. Infant is passive and sleeps well. Infant likes to be held and touched. 44 During an outpatient clinic visit a 13-year-old client is diagnosed with infectious mononucleosis. The nurse should expect which of the following to be included in the client's plan of care? A simple nonnarcotic analgesic is usually sufficient to relieve the headache, fever, and malaise of mononucleosis. Gargling alleviates the pain from sore throat. Warm water is soothing to the inflamed throat and rinses the pharynx of secretions. Sometimes a short course of penicillin is prescribed for sore throat, but ampicillin is contraindicated because it frequently triggers a maculopapular rash. The child and family should be advised to limit exposure to persons outside of the family, especially during the acute phase to prevent secondary infection. Take acetaminophen (Tylenol) with codeine as prescribed for pain. Encourage gargling with warm water to alleviate pain. Start a short course of ampicillin. Encourage social activity to prevent depression. 45 A nurse is reinforcing teaching with the parents of an infant diagnosed with recurrent otitis media. Which of the following is appropriate teaching to include? The use of steroids, decongestants, and antihistamines to treat acute otitis media is not recommended. The upright position prevents formula from draining into the middle ear through the eustachian tube. Equalizing tubes are used to treat otitis media, not tonsillectomy or an adenoidectomy. These have not been found to be effective treatments. An ice compress placed over the affected ear may provide comfort and reduce edema and pressure. "Give the child an over-the-counter antihistamine when the symptoms begin." "Hold the child in an upright position while feeding." "Talk with the primary health care provider about performing a tonsillectomy." "Apply a warm compress over the affected ear to provide comfort." 46 A nurse is caring for a child who has hemophilia. The nurse should expect abnormal results in which of the following diagnostic tests? Tests that measure serum fibrinogen level are all normal in persons with hemophilia. Hemoglobin serves as the vehicle for transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Itis not a test that relates to the cause of hemophilia.PT measures prothrombin activity and bypasses the intrinsic-extrinsic mechanism. It detects deficiencies in factor V, VII, X, and fibrinogen as well as prothrombin. This laboratory test reveals that a client with hemophilia has prolonged PTT. PTT measures the activity of thromboplastin, which depends on intrinsic clotting factors. Factor VIII and IX are needed for the formation of thromboplastin, and it is factor VIII or IX that is deficient in hemophilia or hemophilia B respectively. Fibrinogen Hemoglobin level Prothrombin time (PT) Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) 47 A nurse is caring for a 4-year-old child who is prescribed an intravenous medication preoperatively. Which of the following therapeutic play techniques is most appropriate when reinforcing the teaching for this procedure? Role playing is best when it involves the child and enables the child to handle equipment. This option has the nurse’s role playing with passive involvement of the child. Stories can be helpful to introduce the topic; however, this does not diminish the anxiety of seeing the equipment for the first time. Movies may scare a preschool child, especially if the child in the Movie cries during the procedure. Allowing the child to see, hold, and collect the supplies familiarizes the child with the frightening aspects of the procedure. Instruction can be based on the child's questions in a nonthreatening environment. The child can gain an understanding of the procedure by pretending to start an IV on a doll. Role play with another nurse the technique of IV placement and how the medication is infused. Read a story that explains the basics of how IVs are placed. Watch a movie narrated by nurses and children about IV placement. Explain the basic procedure and give the child IV supplies to play with, minus the needle. 48 A nurse is monitoring a child whose parents are suspected of child neglect. Which of the following is an expected finding of neglect? Physical neglect involves the deprivation of necessities such as clothing, food, shelter, supervision, medical care, and education. Lack of parental education is not correlated with physical neglect. Socioeconomic group is not a factor in child neglect. If the child is clean, faded clothing with large shoes may be a sign of financial difficulties and not a sign of physical neglect. Lack of required immunizations Parental lack of education Lower socioeconomic group Faded clothing with large shoes 49 A nurse is initiating a plan of care for a toddler who is hospitalized. Which of the following instructions is important to communicate to the nursing assistant? Toddlers are able to undress themselves, but do not have the fine motor development skills required for dressing. Allowing the child to feed himself provides opportunities for autonomy and motor skill development. Toddlers view everything in relation to self only and are involved in parallel play. One way of dealing with negativism is to decrease opportunities for "no" answers. Have the toddler dress himself. Offer the toddler finger foods for snacks. Provide opportunities to share toys with others. Ask the child simple yes or no questions. 50 A nurse is caring for a 3-year-old child with strabismus. Which of the following actions should the nurse advise the parents to implement to help prevent amblyopia? Biconcave lenses are used to correct myopia. While trauma should be avoided to prevent eye damage, this is not an implementation to prevent amblyopia (impairment of vision or blindness) from strabismus. Strabismus, or cross eye, is when one eye deviates from the point of fixation. If the misalignment is constant, the weak eye becomes lazy and the brain eventually suppresses the image. If not corrected by the age of 4 to 6 years, blindness from disuse or amblyopia may result. Treatment includes covering the strong eye to strengthen the muscles in the weak eye. Dry eyes are not a manifestation of strabismus. Wear corrective biconcave lenses. Prevent trauma to the eyes. Patch the strong eye. Instill artificial tears. 51 A nurse is caring for an infant with a history of vomiting due to gastroenteritis. Which of the following nursing interventions is considered the priority? Maintaining the infant's airway is of the highest priority. A child who is vomiting should be positioned on the side or in a semi-reclining position to prevent aspiration. Administration of fluids and electrolytes is important to prevent or correct dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, but is not of the highest priority. Antiemetic medications are administered as prescribed if necessary. This is not the first priority. Of major importance is avoiding ketosis. A dietary intake high in carbohydrates spares the body protein and avoids ketosis which can result from exhaustion of the glycogen stores. This is not the highest priority. Place the infant in a side or semi-reclined position. Administer oral rehydration and electrolyte therapy. Administer antiemetic medications as prescribed. Maintain a high-carbohydrate intake to prevent ketosis. 52 A nurse has reinforced teaching to the parent of a 9-month-old infant who has redness in the diaper area and inner thighs. Which of the following statements by the parent indicates a correct understanding of this teaching Hair dryers can burn the skin and thus are not recommended. Powder should not be used. It tends to cake when the skin is wet, and there is also the danger of inhalation. Applying a skin cream barrier is much more effective. Rubber pants should not be used because they do not allow air to circulate. Thus, they promote skin irritation and breakdown. Exposing the skin allows it to air dry completely which helps prevent breakdown. "I can use a hair dryer on the reddened skin to help with the drying." "I can use powder after diaper changes to absorb excess moisture." "I can use cloth diapers with rubber outer pants until the rash clears." "I can keep the diaper off to expose the skin to air." 53 A 6-year-old child is brought to the emergency department after falling down the outdoor steps. The parent's account of the incident appears different than the neighbor's account of the incident. Upon questioning the child, the nurse should recognize which of the following as usual pattern of behavior exhibited by an abused child? The child would answer questions but would not contradict the parent's story. The typical reaction of the child is to repeat the same story as the parent. Children rarely betray the parent even when the parent is abusive. The child will even defend the parent. While children have creative imaginations, they do not make up stories in this scenario. Stress of the situation and the fear of losing what security they have with the parent keeps children who have been abused clinging to the parent's story. Children are afraid of losing the parent, so they do not implicate the parent in the abusive behavior. The child refuses to answer questions. The child repeats the same story as the parent. The child will fabricate an obviously false story. The child tells what really happened at the time. 54 A nurse is providing care for a 2-day-old neonate with a cleft lip and palate. The nurse evaluates the parents' understanding of correct feeding methods. Which of the following observations indicates a need for further teaching? Large, soft nipples reach back further in the mouth. The large holes make sucking less of an effort, and thus these types of devices appear to work well for nipple feedings after a cleft lip and palate repair. When breastfeeding, the nipple is positioned back in the oral cavity so that the action of the tongue can make the expression of milk easier. When an infant has trouble with a nipple feeding, a rubber-tipped eye dropper makes feeding easier. The rubber tip extends the length of the feeding device and has a larger hole so the infant doesn't have to create as much suction. Infants with a cleft lip and palate have difficulty creating the suction required to get the formula from the bottle. A "gravity flow" nipple with a squeezable bottle allows the formula to be deposited directly into the mouth. Uses a long, soft nipple with a cross-cut opening attached to a bottle When breastfeeding, positions the nipple toward the front of the mouth Uses an eyedropper with a piece of rubber tubing on the tip Obtains a "gravity flow" nipple and attaches it to a squeezable plastic bottle 55 A nurse is holding an infant during a lumbar puncture for a suspicion of meningitis. The infant is in a sitting position with the buttocks at the edge of the table and the neck flexed, and the nurses is immobilizing the infant's arms and legs. Which assessment takes priority during the procedure? This is important to note anytime a spinal tap is done, but it is not the priority assessment. This is important to note anytime a spinal tap is done, but it is not the priority assessment. Based on the child's position, the nurse should be concerned about limiting chest expansion and movement of the diaphragm. Based on the bending of the neck, the nurse should be concerned about the infant's soft, pliable trachea, which may collapse. This is important to note anytime a spinal tap is done, but it is not the priority assessment. Circulation checks of the lower extremities Heart rate and crying pattern Chest expansion and diaphragm excursion Clarity of spinal fluid and level of consciousness 56 A nurse is reinforcing teaching given to the parent of a 1-year-old child who has had a high temperature, vomiting, and diarrhea for 48 hr. The child has sunken eyes and cracked lips. Which of the following should the nurse tell the parent? This is contraindicated because this diet has little nutritional value (it is low in energy and protein) and is high in carbohydrates and low in electrolytes. These soups contain excessive sodium and inadequate carbohydrates. Infants and children with acute diarrhea and dehydration should be treated first with oral rehydration solutions. These help the child replace the sodium and water that are being lost through the vomiting. Water has no electrolytes and will not help compensate for the diarrhea and dehydration. "Give the infant applesauce and rice cereal because these have been found to have high nutritional value." "Encourage the child to take sips of chicken or beef broth because they will replace the fluid losses your child is experiencing." "Give the infant oral rehydration solutions that are available commercially. They replace some of the electrolytes lost through vomiting." "Give the child nothing by mouth for 4 hr. Once the vomiting has decreased you can introduce sips of clear water." 57 A nurse is caring for a 4-year-old client with full-thickness burns. Which of the following nursing actions are essential for the care of this child? (Select all that apply.) Monitor level of consciousness is correct. Symptoms of confusion or seizures can result from alterations in the electrolyte balance. Disorientation is one of the first signs of sepsis or may indicate inadequate hydration. Maintain intravenous fluids is correct. Fluid shifts that occur after a burn injury make intravenous fluids very important. Intravenous fluid therapy compensates for loss of water and sodium, reestablishes electrolyte balance, and corrects acidosis. IV therapy restores circulating volume, provides sufficient perfusion, and improves renal function. Document vital signs is correct. Management of pulmonary and cardiovascular status is apriority, especially in the acute phase of burn injury treatment. The respiratory system is monitored for burn involvement and if suspected or evident, then 100% oxygen is administered. An endotracheal tube may need to be inserted to maintain the airway. Blood gas values including carbon monoxide levels are obtained. Heart rate helps to determine the adequacy of fluid resuscitation. Provide a low-calorie, high carbohydrate diet is incorrect. Clients who have suffered burns should have a high-protein, high-calorie diet. This helps to avoid protein breakdown as the body's metabolism increases after a burn injury. Monitor urinary output is correct. Urinary output helps to determine the adequacy of fluid resuscitation. Urine output and specific gravity help to establish adequate hydration and guide the rate of fluid administration. Administer morphine subcutaneously for pain is incorrect. Morphine sulfate is the preferred medication for severe burn injuries. It is administered continuously by IV infusion. The unstable circulatory status, edema, and tissue damage make intramuscular and subcutaneous injections contraindicated in burn injuries. Monitor level of consciousness is correct. Symptoms of confusion or seizures can result from alterations in the electrolyte balance. Disorientation is one of the first signs of sepsis or may indicate inadequate hydration. Maintain intravenous fluids is correct. Fluid shifts that occur after a burn injury make intravenous fluids very important. Intravenous fluid therapy compensates for loss of water and sodium, reestablishes electrolyte balance, and corrects acidosis. IV therapy restores circulating volume, provides sufficient perfusion, and improves renal function. Document vital signs is correct. Management of pulmonary and cardiovascular status is a priority, especially in the acute phase of burn injury treatment. The respiratory system is monitored for burn involvement and if suspected or evident, then 100% oxygen is administered. An endotracheal tube may need to be inserted to maintain the airway. Blood gas values including carbon monoxide levels are obtained. Heart rate helps to determine the adequacy of fluid resuscitation. Provide a low-calorie, high carbohydrate diet is incorrect. Clients who have suffered burns should have a high-protein, high-calorie diet. This helps to avoid protein breakdown as the body's metabolism increases after a burn injury. Monitor urinary output is correct. Urinary output helps to determine the adequacy of fluid resuscitation. Urine output and specific gravity help to establish adequate hydration and guide the rate of fluid administration. Administer morphine subcutaneously for pain is incorrect. Morphine sulfate is the preferred medication for severe burn injuries. It is administered continuously by IV infusion. The unstable circulatory status, edema, and tissue damage make intramuscular and subcutaneous injections contraindicated in burn injuries. Monitor level of consciousness. Maintain intravenous fluids. Document vital signs. Provide a low-calorie, high-carbohydrate diet. Monitor urinary output. Administer morphine subcutaneously for pain. 58 A nurse is caring for a 7-month-old infant with acute bronchiolitis. The infant has a persistent, dry, hacking cough that worsens at night, tachypnea, and weakness. Which of the following actions should the nurse implement? Cough suppressants may be useful to allow rest but can interfere with clearance of secretions. They have not proven to be of benefit for this condition. Bronchiolitis is caused by a virus and is transmitted via direct contact. Therefore, contact precautions are required rather than droplet precautions. Antibodies and corticosteroids are not effective in uncomplicated bronchiolitis. Fluids by mouth may be contraindicated to prevent aspiration if the child has tachypnea, weakness, and fatigue. Therefore, IV fluids are preferred to maintain hydration and dilute secretions. Administer prescribed cough suppressants as needed. Place the child on droplet precautions. Administer antibiotics and corticosteroids as prescribed. Provide intravenous fluids as prescribed. 59 A nurse is caring for an infant with hypospadias. Which of the following is an expected finding? This defect describes epispadias, a condition in which the meatal/urethral opening is on the dorsal/back surface of the penis. With hypospadias, the urethral opening can be anywhere on the underside/ventral surface of the penile shaft or the perineum. Fluid in the scrotal sac is referred to as hydrocele. testes that are not palpable within the scrotal sac are an indication of cryptorchidism. This is a failure of one or both testes to descend through the inguinal canal. The meatal opening is on the dorsal surface of the penis. The urethral opening is on the underside of the penis. Fluid is present in the scrotal sac containing the testes. The testes are not palpable within the scrotal sac. 60 A nurse is caring for a 3-year-old child who is diagnosed with a urinary tract infection (UTI). The parent is concerned about recognizing the signs and symptoms of future UTIs. Which of the following statements made by the parent indicates a correct understanding of the manifestations of a UTI? A child who has frequent urination and exhibits strong-smelling urine should be evaluated for a UTI. These are signs of glomerulonephritis, not UTI. These symptoms are seen in acute renal failure and are not signs of a UTI. Hematuria, not abdominal pain, is a sign of a UTI. "I should look for more frequent urination and strong-smelling urine." "My child would have tea-colored urine and puffiness around the eyes." "I should observe for episodes of nausea and less frequent urination." "My child would have pale-colored urine and abdominal tenderness and pain." ATI.CHILD CARE 1.0 1 A child diagnosed with asthma begins corticosteroid treatments. The nurse explains to the parents that the purpose of corticosteroid treatment is to produce which therapeutic effect? Incorrect: Dilation of the bronchial airways is common in treating asthma. Albuterol is a common medication. Incorrect: Bronchospasms are usually reduced by B-2 agonists and bronchodilators. Incorrect: Infections are treated by antibiotics but not indicated in the treatment of asthma unless lung congestion is noted. Correct: Corticosteroid usage is common for decreasing inflammation of the bronchial airways. Dilation of bronchial airways Decrease bronchospasms Prevention of infection Anti-inflammatory effect 2 Which is the recommended treatment for moderate to severe lead poisoning? Incorrect: IV fluids are typically not used in the treatment of lead poisoning. IV fluids area conservative treatment regimen and are not indicated for treatment of lead poisoning; a more radical therapy is needed to remove the lead from the body. Incorrect: Treatment with antiemetic is not effective in the treatment of lead toxicity because the heavy metal is absorbed into the body. Lead ingestion usually occurs more than one time. Correct: The heavy metal antagonist, edetate calcium disodium, is frequently the drug of choice for the removal of the lead toxin from the body. Chelating agents inactivate the toxicity of the lead and cause excretion through the urine. Others drugs may treat the symptoms of toxicity rather than remove the lead from the body. Untreated lead toxicity can lead to a wide array of neurobehavioral problems include: attention deficit- hyperactivity disorder, reduced cognitive performance, irritability or lethargy, aggressiveness, and hearing impairment. The most serious and irreversible side effect of lead poisoning is encephalopathy, which is associated with lead levels > 100 mg/ dL. Incorrect: Antibiotics have no effect on the removal of the toxin. IV fluids Antiemetics Heavy metal antagonist Antibiotics 3 Which treatment is a nursing priority when providing care for an infant diagnosed with bacterial meningitis? Incorrect: Cardiorespiratory monitoring is standard for care of the child with bacterial meningitis as a means of establishing the baseline parameters for vital signs. The infant with meningitis may have a low baseline heart rate, tachypnea or fever. This however, is not the priority nursing intervention. Incorrect: The initiation of IV fluids for hydration and nutrition is a primary concern for the care of the infant with bacterial meningitis. However, the most important intervention is starting antibiotic therapy. Incorrect: Meningococcal meningitis is the only type of meningitis spread through air-born droplets and therefore, respiratory precautions need to be initiated as soon as possible. Respiratory isolation is important for the control of transmission of the disease after the child receives the first doses of antibiotics. Correct: The first nursing priority is the implementation of antibiotic therapy, which prohibits the microbial damage to the neurologic system through the cerebral spinal fluid. Bacterial meningitis has a high rate of infant morbidity (illness) or mortality (death). Immediate treatment with antibiotics can prevent: death, deafness, reduced cognitive ability, attention deficit-hyperactive disorder, seizures and various other complications. Initiate cardiorespiratory monitoring. Initiate intravenous fluids. Observe respiratory isolation. Administer antibiotic therapy. 4 The dosage of a pediatric medication is 120mg/kg/day to be give t.i.d. The patient weighs 12 pounds. What is the correct dose for the nurse to administer? Incorrect: The dose of 120 mg is half the indicated dose. The erred dosage represents a failure to divide the total daily dose by the number of individual dosages required per day. The failure to use the weight in the calculation is evident. Incorrect: The dosage of 480 mg is an excessive dose for the child. The calculation error is likely a failure to convert pounds to kilograms. Correct: The patient weighs twelve pounds. This weight converts to kilograms by dividing 12 by 2.2 (1 kg. = 2.2 lb.). In this example, the child's weight converts to 5.4 kg. The daily dose of 120 mg is given t.i.d: each individual dose is 40 mg/kg. Then multiply the weight in kilograms by the individual dose (40mg). The individual dose is 218 mg. Incorrect: The dose of 650 mg is too large of a dose. The weight of the child when converting from pounds to kilograms is 5.45 kg. The dose is ordered to be given t.i.d.. Therefore, the daily dose of 120 mg/kg/day is divided by 3 to yield an individual dose of 40 mg/kg/dose. The error is this dosage was likely a failure to divide the total daily dose by the number of doses required per day. 120 mg 480 mg 218 mg 651 mg 5 In a child diagnosed with Tetralogy of Fallot, which of the following is a compensatory mechanism to decrease venous return to the heart? Correct: Squatting is a compensatory mechanism that decreases venous return (deoxygenated blood) to the heart. The clinical sign is commonly seen in young children with Tetralogy of Fallot (a type of cyanotic heart disease). The signs associated with cyanotic heart disease include hypoxia, poor growth, low tolerance for physical exertion, cardiomegaly, murmur and acute, intermittent blue spells that occur after crying or feeding (tet spells). Incorrect: Clubbing is found in children with chronic respiratory disease and cyanotic heart disease. However, this finding is rare in young children. Incorrect: Shortness of breath, retractions and increased respiratory effort occur with lung dysfunction. Generally, the child with impaired oxygenation due to a cardiac lesion does not exhibit signs of respiratory distress. Incorrect: Polycythemia is common in children with hypoxia due to respiratory or cardiac dysfunction. This compensatory mechanism increases the oxygen-. carrying capacity in the body. The effect is not related to the venous return of unoxygenated blood to the heart. Squatting Clubbing Shortness of breath Polycythemia 6 A 1-year-old receives routine health maintenance care at the pediatric clinic. The child receives an MMR immunization. The mother asks the nurse, "When will my child get the next dose of MMR vaccine?" Which is the correct response by the nurse? Incorrect: The DPT vaccine is routinely given in six months. Incorrect: An additional dose of MMR vaccine is needed in the middle school years to maintain full immunity from the diseases. Incorrect: The first dose of Hepatitis B vaccine (HBV) is given in the hospital prior to discharge home. A follow-up HBV is given in 1-2 months and followed up in 6-12 months following the second does. The schedule does not coordinate with the routine immunization schedule for MMR. Correct: A second MMR, often called a booster, will be needed when the child enters middle school at age eleven or twelve years of age. In six months with the next DPT No further vaccination needed With the Hepatitis B series After the child is 10 years of age 7 Which is a major difference in the clinical manifestation of adolescents with anorexia nervosa compared to bulimia? Incorrect: Binge eating is a common manifestation of both disorders. Incorrect: Purging can be associated with both disorders. Correct: The major difference between adolescents with anorexia nervosa and adolescents with bulimia is body image distortion. Clients with anorexia see themselves as being overweight no matter how underweight they become. Clients with bulimia see their weight realistically but have psychological problems that manifest in an eating disorder. Incorrect: Decreased self-esteem is often a catalyst of both disorders. Binge eating Purging Body image distortion Decreased self esteem 8 Which is the most common factor associated with non-organic failure to thrive? Incorrect: A cool, drafty sleeping area is not a comfortable environment for sleep, but is unrelated as a cause of failure to thrive. Correct: The most significant factor associated with non-organic failure to thrive is typically a disturbance in the mother/child relationship. A situation involving dysfunctional family relationships is often complex; characterized by marital discord, economic pressures, and parental immaturity with a low stress tolerance. Incorrect: Lack of interest in the surroundings is a symptom of failure to thrive but not an etiologic factor. Incorrect: The financial hardship related to the expense of infant formula is not usually a primary cause of non-organic failure to thrive. The Women's Infant and Children program (WIC) provides infant formula at a low or no cost with eligibility. Therefore, the disorder is not likely to be related to obtaining adequate nutrition but instead related to the ability of the infant to consume, digest, and utilize the nutritive source. A cool, drafty area for sleeping Disturbance of mother/child relationship Lack of interest in the surroundings Financial hardship causing poor nutritional care 9 An adolescent recovering from substance abuse is diagnosed with hepatitis B. Which nursing instruction should be included when planning the client's care? Incorrect: During periods of acute hepatitis, the client needs plenty of rest. Correct: The mode of the transmission in hepatitis B is via the parenteral route through blood products, intravenous injection and maternal-fetal trans placental transmission. It is extremely important for the nurse to educate the family about the relationship between intravenous exposure and the transmission of the disease. Incorrect: Fluid intake is not limited in the treatment of hepatitis B. Incorrect: Eating a diet high in fat is contraindicated because of the liver involvement. Increase exercise. Avoid sharing needles. Limit fluid intake. Eat a diet high in fat. 10 Changes in the growth and development of the preschooler are characterized by: Incorrect: Continued rapid physical growth is not common for this developmental level. Incorrect: Major changes in weight, height and head circumference have usually already taken place prior to this developmental level. Correct: Physical growth slows in the preschool years. Preschoolers enjoy social contacts. Preschoolers are gaining control of their muscles and participate in vigorous activities with other children. Incorrect: Improvement in motor ability is rapid at this developmental level as the children are gaining control of their muscles. Preschoolers' gait resembles that of an adult. Rapid physical growth and a persistent curiosity. Major changes in weight, height and head circumference. A slowing of physical growth and expansion of social contacts. A slow improvement in motor ability. 11 A teacher asks the school nurse to assess the behavior of a child with attention deficit- hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Which situation best facilitates an effective nurse/child interaction? Incorrect: Playground time for the discussion is desirable because the child would not miss classroom instruction. However, recess is an appropriate time for the child to expel energy.The playground offers many opportunities for distraction and the child may have difficulty concentrating on the discussion in this environment. Incorrect: A discussion between the nurse and student in the classroom would be brief and impersonal due to the presence of other students. At the end of the day, this environment is noisy, chaotic and rushed and may be one of the least desirable locations for a meaningful dialogue between the nurse and student. The child will most likely be distracted. Correct: A characteristic of attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder is distractibility and impulsivity. A quiet and calm environment is necessary to engage the child in focused discussion. Incorrect: Although a physical education class provides the structured environment for the release of energy in an appropriate manner, this is not a place for the nurse to provide education to the child with ADHD. This setting also lacks the privacy necessary for a confidential exchange of information. Playground during recess In the classroom at the end of the day Nurse's office before school Physical education class 12 The health care provider orders 60% oxygen to be administered with a partial rebreather mask and bag reservoir. Which error regarding the oxygen delivery system requires correction? Incorrect: Moisture collecting in the mask is the result of humidification of the air. Oxygen can be very drying to the tissue and alveoli; damage can result to the airways without humidification. Incorrect: To optimize the delivery of oxygen via mask, a snug head strap is necessary. Incorrect: The mask covering the nose and mouth is a correct application of the mask. Correct: The reservoir bag on the non-rebreather mask should remain partially filled during inspiration to provide positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP). If the bag collapses the equipment may be faulty. Moisture collects inside the mask The strap around the head is snug The mask covers the nose and mouth The reservoir bag collapses during inspiration 13 A toddler is admitted to the hospital for treatment of acute gastroenteritis and dehydration. The mother states that she must go home to make arrangements for the care of her other children. To reduce the child's separation anxiety, which nursing intervention is most appropriate? Incorrect: Placing the child in the crib may make the child feel more alone and afraid. At this developmental stage, the child is not likely to be comfortable enough with the surroundings to adjust and begin to play. Correct: Anxiety is the child's predominant emotion with the separation from a parent. Activities that calm and comfort the child are appropriate. Often a toddler will fall asleep in the nurse's arms due to the stress of a parent's leaving the child alone in the hospital. Incorrect: The video may serve as a distraction, but does not provide the security of human contact. Incorrect: The nurse's station may allow an opportunity for social contact. Many toddlers may be overwhelmed or frightened by the activity at this central location. Place the child in the crib with toys. Rock the child in a rocking chair. Turn on an age-appropriate video. Take the child to the nurse's station. 14 Which technique is most appropriate when assessing the circulation of a child's leg in traction? Incorrect: The movement of the toes is a neurological assessment and does not relate to circulation. Correct: The best way to assess circulation is to palpate the dorsalis pedal pulse located on the top of the foot. If a peripheral pulse is not palpable, a Doppler may be necessary to ascertain loss of circulation and pulse. Incorrect: Assessing pain sensation in the lower extremities is a neurological assessment and does not relate to circulation. Incorrect: Range of motion to the affected area is usually contraindicated while in traction. Determine if the child can wiggle the toes. Palpate the dorsalis pedis artery. Assess for pain sensation in the lower extremity. Perform range of motion in the lower extremity. 15 Initially, which solid food is generally recommended for an infant's diet? Correct: Rice cereal is bland, easily digested and fortified with iron. Rice cereal is the first food introduced into the diet at approximately six months. Incorrect: Strained vegetables are introduced after the infant tolerates rice cereal. The order that various foods are initiated is controversial and dependent on regional, generational, cultural and personal factors. Incorrect: Strained fruits are introduced generally after the infant tolerates strained vegetables. Incorrect: Meats are introduced between 8-10 months of age. Infant meats are generally denser in texture and less preferred by many infants. The coordination of the muscles of the tongue and pharynx must be more developed for the introduction of solid meat. Infant rice cereal Strained vegetables Strained fruits Infant meats 16 A boy diagnosed with hemophilia falls while roller-blading and injures his knee. The nurse is most likely to assess which physical finding? Correct: Hemophilia is a group of bleeding disorders in which there is a deficiency of one of the clotting factors. After a child sustains a traumatic injury to a joint, hemarthrosis is likely to result. Incorrect: Thrombocytopenia, is a decreased number of platelets in the circulating blood, and is not related to hemophilia. Incorrect: Petechiae are pinpoint non-raised, purplish spots on the skin, which are characteristic of low platelets. Incorrect: Neutropenia, which is the diminished number of neutrophils, is not associated with hemophilia. Hemarthrosis Thrombocytopenia Petechiae Neutropenia 17 A toddler is admitted to the emergency department following a febrile seizure. Which information does the nurse provide to the family regarding febrile seizures? Correct: There is little chance that future seizures will occur as a result of a febrile seizure. Febrile seizures are the body's reaction to an immature thermoregulation system. This reaction is not indicative of an epileptic disorder. Incorrect: There is no familial tendency noted in febrile seizures. Incorrect: Neurological defects are not commonly seen in children with febrile seizures. Incorrect: Children who experience a febrile seizure are not at risk of developing a seizure disorder. There is no relationship to seizure disorders. There must be a familial tendency toward seizures. The child most likely has a neurological defect or brain tumor. The child is likely to develop a seizure disorder as he grows. 18 The nurse assesses Koplik spots on the lingual and buccal mucosa of a 4-year-old. Which disease is likely to appear within the next two to three days? Correct: Koplik spots are small red spots with bluish white centers on the lingual and buccal mucosa. These spots are characteristic of an outbreak of measles. The measles rash usually erupts a day or two after the appearance of the Koplik spots. Incorrect: Mumps are an acute viral disease characterized by the swelling of the parotid glands. Incorrect: Varicella virus (chickenpox) is a contagious viral disease characterized by vesicular eruptions on the skin. Incorrect: Pertussis is a highly contagious respiratory disease characterized by paroxysmal coughing with dyspnea on inspiration. Rubeola (measles) Mumps (epidemic parotitis) Varicella (chickenpox) Pertussis (whooping cough) 19 Which is the most appropriate pain scale to use for a Spanish speaking 5-year-old child who communicates very little in English? Incorrect: The Poker Chip Tool uses four red poker chips to indicate the degree of pain. The child must be able to count and have some concept of numbers for correct use of the tool. Incorrect: The Eland Color Tool directs the child to use colored markers to fill in an outline of the body with a color that describes their pain. This scale is used for children over four years of age. Correct: The FACES Pain Rating Scale is intended for use in the child ages 1-7 years. This scale uses a pictorial face that represents the child's level of pain. The smile face indicates that the child has no pain and the tearful face represents the highest level of pain. This scale is useful to the non-English speaking child because words are not necessary for reporting pain level. Incorrect: The Word Graphic Rating Scale uses descriptive words to rate the intensity of pain (no pain to worst possible pain) and aids the child in answering various questions about the nature and degree of pain. It would not be appropriate for a child who speaks little English and may not yet read. Poker Chip Tool Eland Color Tool FACES Pain Rating Scale Word Graphic Rating Scale 20 If a child with Type I diabetes mellitus takes regular insulin at 0800, which time during the day should the parents be taught to expect the peak action of regular insulin? Incorrect: At 0830 the onset, not the peak, of the regular insulin should be occurring. Correct: Regular insulin peaks in two to four hours. The onset of the insulin begins in 30 minutes. A snack should be planned to avoid any symptoms of hypoglycemia. Incorrect: At 1300 the peak time of the insulin has already passed. Incorrect: At 1500 the peak effect of insulins achieved. 0830 1100 1300 1500 21 The nurse evaluates the effectiveness of care for the school-aged child with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA). Which clinical outcome does the nurse expect the child to demonstrate after nursing care interventions are implemented? Incorrect: JRA is treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen, to reduce inflammation to the joints. Slower-acting antirheumatic drugs may be added. Cytotoxic drugs are reserved for the child with severe, debilitating disease. Antibiotics are not used for JRA. Correct: The nurse observes the movements of the child and uses pain assessment tools to determine the intensity of pain. Nonpharmacologic modalities and anti-inflammatory and analgesic medication are provided to promote comfort and relieve pain associated with JRA. By modifying pain perception, joint mobility is likely to improve with reduced discomfort. Incorrect: Children are encouraged to maximize their efforts for self-care and activities of daily living. Exercise enhances the mobility and strength of the supporting muscles, which is necessary in pain prevention. However, overexertion should be avoided. Incorrect: Children with JRA, like many with chronic illness or disability, develop personality traits including: manipulativeness, hostility, and passive aggressiveness. Although it is the goal for care of the family to promote an understanding of the child's disease and altered lifestyle and have compassion for the situation, it is important that family members do not enable the negative behaviors to persist. Efforts need to be made to intervene early and prevent permanent ineffective coping techniques. The symptoms will subside with use of antibiotics. The child is able to move with minimal or no discomfort. The child limits his own physical activity to prevent pain. The family copes with the child's manipulative behaviors. 22 The nurse providing care to the child with pediculosis capitus (head lice) educates the family about the condition, transmission, and treatment. Which condition is necessary for survival of the louse on the host? Correct: Survival of the louse is dependent upon blood that is extracted from the host. Incorrect: The louse feeds on the blood of the human host. Warmth is not necessary for survival. Incorrect: The louse feeds on the blood of the human host. Moisture is not necessary for survival. Incorrect: The louse feeds on the blood of the human host. Mucous is not necessary for survival. Blood Warmth Moisture Mucous 23 An adolescent with Type I diabetes mellitus asks her mother for permission to go with friends to get pizza and ice cream. Which response by the adolescent's mother indicates that previous nursing instruction has been effective? Incorrect: It is not necessary to reinforce to the adolescent that he/she is unable to eat similar to the friends. Peer groups and being accepted are very important at this age. The adolescent who can manage the insulin needs in accordance with the diet is allowed to have a variety of foods. Incorrect: It is not realistic or therapeutic to expect the friends to know the diabetic diet. This type of expectation may alienate the child from the peer group. The adolescent typically values the similarity to the peer group. Incorrect: By avoiding the situation, the adolescent does not directly deal with the underlying task of adapting the chronic illness into the lifestyle. An important part of developing relationships among adolescents is spending leisure time together. The child alienates him or herself and suppresses feelings of anger towards self, others and/or the disease. Correct: The standard diabetic diet and appropriate nutritional education are flexible and incorporates many preferred foods at various times. The dose of insulin will need to be adjusted for this altered schedule, type and amount of food. Close glucose monitoring is very important to the safety of the diabetic child whose metabolic needs are variable. "It is important for you to spend time with friends but you cannot eat what they are eating." "Your friends need to learn that there are certain foods that you cannot have. They will understand that you can't go with them." "You must stay away from those foods. It is easier for you to avoid the situation. You can go with your friends another time." "It is important for you to spend time with your friends. I will help you select your food and determine your next insulin dose." 24 When obtaining a health history, which significant event may precede a diagnosis of rheumatic fever? Incorrect: Chickenpox is caused by varicella virus. Rheumatic fever is a complication of group A beta hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis. Correct: There is evidence that rheumatic feverish associated with group A beta hemolytic streptococci, which is a common cause of pharyngitis. Incorrect: The presence of a heart murmur is not reason enough to diagnose rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever is associated with streptococcal infections. Incorrect: Vomiting and diarrhea are frequently caused by intestinal viruses, not bacteria. The primary symptoms of group A beta hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis include: fever, malaise, dysphagia, lymphadenopathy and occasionally diarrhea in the young child. Rheumatic fever is a complication of “strep throat” that can cause cardiac damage. Exposure to chickenpox Recent severe sore throat Presence of a heart murmur Vomiting and diarrhea 25 Which intervention is most appropriate when providing nursing care for the child diagnosed with Duchenne's muscular dystrophy? Incorrect: Limitation of physical activity may accelerate the process of muscular deterioration and atrophy. Incorrect: Increased weight gain becomes more likely as the activity level diminishes. The care of the child with a progressive, incapacitating disease becomes increasingly more demanding for the caregivers at home. As a loss of mobility and independence occurs, the child will require more lifting, dressing and physical care. Excessive weight would aggravate the situation. Correct: The most important way for the nurse to impact the family of the child with Duchenne's muscular dystrophy is to assist the child and family in coping with the progressive, incapacitating and incurable disease. As muscular weakness progresses, wasting and contractures develop. A loss of ambulance occurs usually be 9-11 years of age. Difficult issues for the family to deal with pertain to loss of independence, mobility and self- care and, eventually, death. Incorrect: No effective pharmacologic treatment exists for Duchenne's muscular dystrophy. Corticosteroid use has been reported beneficial in improving the muscle strength and size in some children. However, there is no conclusive evidence that steroid use has palliative or curative function. The goal for treatment is to maintain as much muscular function for as long as possible. Limit physical activity. Increase caloric intake. Assist the family to cope. Administer steroids. 26 An adolescent comes to the clinic with a fever, sore throat, and fatigue. Physical assessment findings reveal enlargement of the spleen and lymph nodes. Mononucleosis is diagnosed. Which is the nurse's priority in planning the care for the child at home? Correct: The patient with splenomegaly is cautioned to avoid heavy lifting, trauma to the abdomen or vigorous athletics. Splenic rupture is a concern and requires immediate attention. Incorrect: Limitation of visitors is important for the promotion of client rest, however, isolation or visitor restriction is not needed. Incorrect: Maintenance of adequate fluid volume is a concern but not a main priority. Bland cool liquids that are not irritating to the throat are encouraged. Incorrect: Due to the fatigue, getting plenty of rest is necessary but not the main priority for instruction. Avoid vigorous athletics. Limit visitors. Maintain adequate fluids. Obtain plenty of rest. 27 The presence of which classic cell provides data for the definitive diagnosis of Hodgkin's disease? Correct: The Reed-Sternberg cell, which is seen on microscopic examination of lymph node tissue, contains two nuclei and is diagnostic of the disease. Incorrect: Sickling of the red blood cell is seen in sickle cell anemia, not Hodgkin's disease. Incorrect: T-cells are not commonly elevated with autoimmunity diseases and not definitive for the diagnosis of Hodgkin's disease. Incorrect: Epstein Barr is a virus and not related to Hodgkin's disease. Reed-Sternberg cell Sickle shaped red blood cell Floating T-cell Epstein Barr cell 28 Which is the most common complication of acetaminophen toxicity in the toddler? Incorrect: Respiratory distress is not a complication related to acetaminophen toxicity. In the latter stage, hepatic impairment, occurs which is characterized by jaundice, confusion and stupor, pain in the upper right quadrant, and coagulation abnormalities. Incorrect: Nausea and vomiting occur as a result of acetaminophen toxicity. Dehydration is possible in the toddler with frequent vomiting and may be accompanied by electrolyte disturbances. Incorrect: Due to the metabolism of acetaminophen in the liver, the most common complication is liver impairment. Correct: Acetaminophen is metabolized in the liver, therefore, hepatic damage is a major concern. Respiratory distress Fluid overload Renal failure Hepatic damage 29 During the acute phase of glomerulonephritis in a child, which intervention is the most appropriate? Incorrect: Although the child with acute glomerulonephritis is more susceptible to infection, protective isolation procedures are not indicated. Careful handwashing and avoidance of known or likely exposure to infectious organisms is reasonable and prudent. Incorrect: During the oliguric phase of glomerulonephritis, the potassium intake should be limited. The risk for hyperkalemia is increased if a high potassium intake accompanies decreased urinary output and excretion of potassium. Incorrect: Bedrest is often maintained in the acute phase. Children have malaise and fatigue with glomerulonephritis and usually restrict their own activities. Although rest and sleep are important, the most important intervention is focused on the prevention of serious complications, such as malignant hypertension. Correct: Neurologic complications, such as seizures and diminished level of consciousness may occur because of severe hypertension associated with acute glomerulonephritis. The child with edema, hypertension and gross hematuria may be subject to neurologic complications. Observe protective isolation procedures. Encourage increased potassium intake. Encourage bedrest with appropriate diversional activity. Assess the child for signs of neurologic complications. 30 An 18-year-old female diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) comes to the rheumatology clinic for a follow-up visit. The nurse assesses the client's skin and reviews the client's BUN and creatinine levels. Which is the rationale for the nurse's actions? Correct: SLE is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by injury to the skin, joints, kidneys, nervous system and mucous membranes. Clients often seek medical help for relief of fever, weight loss, joint pain, butterfly rash, pleural effusion and nephritis. Because of the kidney damage, the blood pressure will rise and protein in the urine may be evident. Edema results. Incorrect: Kidney damage is common, but does not result in dehydration or dry skin. Incorrect: The characteristic rash in SLE is on the face, not generalized over the body, and is in the shape of a butterfly. Incorrect: Urinary frequency is not a characteristic of SLE. Instead hematuria and decreased urine output are common. A "butterfly rash" and kidney damage are common characteristics of the disease. The client is prone to dry, scaly skin and dehydration related to kidney dysfunction. The generalized rash may lead to a secondary infection affecting the kidneys. The disease process is complicated by urinary frequency and a papular rash. 31 At an unscheduled clinic appointment, the mother of a 9-month-old states that she is concerned about her baby's small size and frequent crying. The mother has limited support systems and poor role modeling for parenthood from her own childhood. Which initial physical assessment data is most important for the nurse to obtain at this time? Incorrect: The measurement of head and chest circumference can provide data indicating the presence of hydrocephalus, microcephaly or neurological defects. Although these growth parameters also indicate the patterns of growth, the height and weight are more specific measures of overall growth. Incorrect: Heart rate and breath sounds are important measures for the physical assessment of the cardiorespiratory status but do not indicate growth patterns. Correct: Excessive crying may indicate a wide variety of physical or emotional problems in infancy. The nurse who suspects that the infant is failing to thrive in the home environment first obtains the data regarding the infant's pattern of growth: the height and weight. Incorrect: The suck reflex, present at birth, is vital for infant nutrition. By nine months of age, however, the child should be eating solid foods, chewing soft foods and teething. The assessment for presence of the suck reflex is most appropriate during the newborn assessment. Chest and head circumference Heart rate and breathe sounds Height and weight Sucking reflex 32 Which information regarding suspected episodes of child abuse should the nurse include in the documentation? Incorrect: Summative statements regarding the events of potential child maltreatment or sexual abuse are inappropriate. Direct quotes from interviewees are recommended to reduce bias and premature judgment. Correct: The documentation of events related to potential child abuse needs to be an objective, factual and concise. Direct quotations from interviewees are recommended to reduce personal bias, interpretation or judgment. Incorrect: Generalizations regarding the nature of actions leading to harm in a child are inappropriate. Clear, concise, and concrete information is absolutely necessary for the documentation of the events in question. Incorrect: Interpretative statements do not have an appropriate role in the delivery of care to the child with suspected maltreatment or sexual abuse. When allegations are made regarding the actions leading to harm to a child, clear, concise and factual information needs to be documented. Summative statements Exact quotes regarding the events Generalized description of events Statements related to causative factors 33 A toddler is diagnosed with impetigo and the nurse gives the toddler's mother instructions about skin care. Which statement by the mother indicates a need for further education? Incorrect: The transmission of impetigo occurs from direct contact with infected skin surfaces. The disease is highly contagious. Incorrect: Impetigo contagious is highly communicable in the toddler and preschool child. The skin is colonized with staphylococcal organisms that cause impetigo and therefore, toddlers and preschoolers are susceptible to bacterial infections from their own skin. Correct: Impetigo is a staphylococcal infection that is highly contagious. The impetigo lesions should be cleaned three to four times a day with Burrow's solution 1:20 to remove the crusts. Usually, the application of a topical bactericidal ointment (Bactroban) follows the wound debridement. With proper wound care, lesions are not likely to scar unless a secondary infection occurs. Incorrect: Cleaning the lesions three to four times daily is a correct treatment regimen. "Impetigo can be spread from one body surface to another." "Toddlers are susceptible from the bacteria on their own skin." "The crusted areas should be allowed to fall off without treatment." "The lesions need to be cleaned three to four times daily." 34 The nurse provides nutritional education for the mother of a toddler. Which information in the toddler's health history indicates a problem regarding nutrition? The toddler: Incorrect: The developmental stage of a toddler is often characterized by ritualistic behavior regarding many daily routines, including mealtime. The toddler in his effort to control the environment and create a predictable and secure life may insist on various details regarding the meal. Incorrect: Playing with food and dishes is a normal developmental finding for toddlers. Toddlers do eat some of the food they play with. Therefore, foods should be nutritious and appropriate for the age group. Incorrect: Imitating eating patterns of others is a normal finding for toddlers. Correct: The variety and volume of food in a toddler's diet is increased and the volume of milk is lessened. Cow's milk contains little iron and displaces the hunger for solid foods. The most common cause of iron deficiency anemia is related to excess cow's milk in the diet. is particular about the arrangement of food on the plate. likes to play with the food and dishes. imitates the eating habits of an older sibling. drinks 42 ounces of cow's milk per day. 35 During the mental health examination of a troubled teen, the nurse assesses for the risk of violence. Which nursing response is most appropriate? Correct: Safety for the teen is important. By asking a direct question, the youth can verbalize feelings instead of acting out the behavior against oneself or others. Incorrect: Asking a question about the past does not focus on the problems in the present. This question does not address violent behavior currently. Incorrect: Discussing impulse control is important but does not address suicidal or homicidal behavior that is at risk with violent teens. Incorrect: While family patterns are often passed from generation to generation, the priority is focusing on the client’s violent behavior and not the family's pattern of behavior. "Do you feel like hurting yourself or anyone else?" "Have you responded to stress with aggressive behavior in the past?" "Have you ever had a problem with impulse control?" "Tell me how your family deals with anger." 36 A physician orders gentamicin (Garamycin) one drop OS four times daily for a 3-year-old child. Which method of medication administration is most appropriate? Incorrect: Instilling drops into the right eye is incorrect as the doctor ordered the drops be instilled into the left eye. OD is the abbreviation for right eye. Correct: OS is the correct abbreviation for the left eye. The appropriate procedure is to pull the left lower eyelid down forming a cradle and then instilling the drop. Incorrect: Pulling down the pinna of the ear is not inappropriate technique for instilling eye drops. Incorrect: Pulling the pinna of the ear upward is not the appropriate procedure for instilling eye drops. Pull the right lower eyelid down, instill drops, and then repeat with the other eye. Pull the left lower eyelid down, forming a cradle, and instill the drops. Pull the left pinna down and back to instill the drops. Pull the right pinna upward and back and instill the drops. 37 A school-age client receives a blood transfusion. The nurse assesses shortness of breath, bulging neck veins, and a moist cough. These findings are indicative of which complication? Incorrect: An allergic reaction has signs and symptoms of urticaria, flushing, wheezing and laryngeal edema. Correct: The findings of shortness of breath, neck vein bulging and a moist cough indicate fluid overload. Incorrect: An air embolism would present with symptoms of difficulty breathing, a sharp pain in the chest and apprehension. Incorrect: A hemolytic reaction may present with symptoms of chills, fever, nausea/vomiting, headache, pain in the chest, not dyspnea, and moist cough. An allergic reaction Fluid overload An air embolism A hemolytic reaction 38 The nurse plans the preoperative care of the infant with pyloric stenosis. In feeding the infant, which measure should be implemented until surgery? Incorrect: An increase in the frequency and amount of the feedings will increase the volume of the stomach, which is already having difficulty emptying, resulting in overload within the stomach. Projectile vomiting is a common symptom. Incorrect: Burping any infant is important. The infant with pyloric stenosis is not burped any more frequently than any other infant. Care is taken that the infant is handled gently during the burping. Incorrect: The Breck feeder is used for infants with cleft lip and palate. Correct: Pyloric stenosis is a narrowing of the pyloric sphincter at the outlet of the stomach. The infant should be allowed to rest after the feeding. Handling the infant should be kept to a minimum so the feeding can advance down the digestive tract. Increase the frequency of the feedings. Burp the infant between feedings. Feed the infant with a Breck feeder. Let the infant rest after the feeding. 39 When providing instructions to a day care provider about the transmission of chickenpox, which statement by the day-care worker reflects a need for further education about the infectious phase of this disease? Incorrect: Varicella virus is transmitted through the respiratory route in the droplet form. Incorrect: Varicella virus is transmitted through direct or indirect contact. Correct: Chickenpox is a highly contagious disease caused by a primary infection with varicella-zoster virus. The characteristic feature is the generalized, vesicular rash that itches. The mode of transmission is direct contact with persons infected with the varicella and herpes zoster viruses. Respiratory spread by droplet also occurs. The disease is most contagious in the incubation period prior to or including the time of onset of prodromal symptoms and the first crop of the rash. The lesion dries and the crust falls off within 5 to 20 days. By the time the lesions scab over, children are no longer infectious and may return to the daycare setting. Seizures are not associated with chickenpox. Incorrect: Varicella lesions with drainage are contagious; the child should remain at home until all vesicles have dried and crusted. Immunosuppresses persons should not be exposed to the virus. "Chickenpox is spread through the respiratory tract." "Chickenpox is transmitted by direct contact." "When the rash first appears, we should watch for seizures." "Children that have seeping pox should remain at home." 40 Digoxin (Lanoxin) is used in the treatment of a client diagnosed with a congenital heart defect. Which is the mechanism of action? Incorrect: The mechanism of action for digoxin is increased cardiac contractility. Nitroglycerine, not digoxin, is an example of a cardiac medication that is used primarily for the effect of vasodilation of the coronary arteries. Correct: Digoxin is used to increase the contractility of the heart and improve the cardiac output. By increasing the effectiveness of the heart's pumping action, the blood supply to the body is improved. The increased tissue perfusion leads to improved oxygen delivery to the organ sites. Incorrect: Digoxin is primarily used to increase the cardiac output by improving the contractility of the heart. Incorrect: A diuretic is often used for congestive heart failure to reduce systemic overload associated with congenital heart defects. Dilates the coronary arteries Improves contractility of the heart Reduces venous return to the heart Decreases systemic overload 41 The nurse provides care for the child diagnosed with glomerulonephritis and collects a urine sample for urinalysis. Which urine color suggests the presence of red blood cells? Correct: The presence of blood in the urine gives the urine a smoky color. Incorrect: A cloudy appearance is commonly associated with the presence of white blood cells. Incorrect: Bright orange urine occurs as a result of the administration of phenazopyridine hydrochloride (Pyridium). This medication reduces the symptomatic relief or urinary burning, itching, frequency and urgency with urinary tract infection or following urologic procedures. This medication stains clothing. Incorrect: Dark yellow urine is an indication of concentrated urine with a high specific gravity. Smoky Cloudy Bright orange Dark yellow 42 A 2-month-old baby is diagnosed with cystic fibrosis. Which statement most accurately defines this disorder? Incorrect: Cystic fibrosis is not a dominant disorder and does not lead to fatty deposits on the liver. Incorrect: Cystic fibrosis is not linked on a dominant gene and is not produced by the lungs. Incorrect: Structural changes of the heart are not produced by cystic fibrosis. Correct: Cystic fibrosis is a recessive disorder that is inherited from both parents. Cystic fibrosis is a disorder of the exocrine glands causing the glands to produce abnormally thick mucus secretions. The glands most affected are those in the pancreas, respiratory system and sweat glands. Dominant disorder in which an enzyme deficiency leads to fatty deposits on the liver Dominant disorder in which secretions produced in the lungs plug the airway and induce respiratory distress Recessive disorder in which structural changes occur in the heart muscle Recessive disorder in which abnormal amounts of secretions are produced by the exocrine glands 43 Initial treatment for unilateral (talipes equinus) clubfoot includes which intervention? Incorrect: Passive range of motion may be used in later stages of healing but is not the initial treatment. Correct: Casting is implemented as soon as the diagnosis is made. The cast is changed regularly as the child grows. Incorrect: A soft brace is used to add support to an extremity but does not change the true alignment. Incorrect: The hip spica cast is used for congenital dysplasia of the hip and not for clubfoot. Passive range of motion exercises to the ankle and toes four times daily Application of a cast to the affected foot as soon as diagnosis is made A soft brace to hold the foot in the proper alignment until surgery The use of a spica cast until the newborn is ready for surgery 44 A 10-year-old is seen in the allergy clinic. The child describes itchy, watery eyes and nasal congestion after spending time outdoors. The skin is noted to be dry and scaly in patches on the back of the arms. Skin testing is ordered. Which measure by the nurse promotes the accuracy of the testing? Incorrect: Skin testing is commonly repeated with different variations of allergens included. It is still important to note past sensitivities on past medical histories, but the use of antihistamines are still more important for the test accuracy. Incorrect: Assessment of lung fields and nasal mucosa is a precautionary measure. This indicates a reaction to past allergens and could be enhanced following the skin testing. Correct: Antihistamine use suppresses skin test reactivity and should be withheld for five days prior to testing. Incorrect: The upper forearm and upper back, not the abdomen, are appropriate sites for allergy testing. Determining a site depends upon the location of choice, cooperation of child and specifics of skin. Assessing past medical history for skin testing that was previously positive Assessing the lung fields for wheezing and nasal mucosa for irritation Reviewing medications over the past five days for antihistamine use Using the child's abdomen instead of upper forearm for skin testing 45 A school-age child falls from a bicycle and sustains head trauma. Upon arrival to the emergency department, the nurse identifies signs indicating increased intracranial pressure. Which sign should the nurse document? Incorrect: A rapid response of the pupils to light is an appropriate neurological response. Pupils that are fixed and dilated or sluggish to react to light and accommodation indicate increased intracranial pressure. Retinal hemorrhages and papilledema occur with brain injury. Incorrect: Widened pulse is the increased discrepancy between the systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The pulse pressure typically widens with increased intracranial pressure. This isa late finding, occurring more often in adults. Incorrect: Elevated body temperature sometimes occurs as an indicator of increased intracranial pressure. Correct: Classic signs of increased intracranial pressure in the school-age child include: altered mental status, agitation, vomiting without nausea, diplopia (double vision), elevated body temperature and widened pulse pressure. The behavioral changes of a child are the most reliable indicators of acute intracranial pressure change. Rapid response of the pupils to light Narrowed pulse pressure Decrease in body temperature Mounting agitation 46 According to Erikson's theory of child development, the normal school-aged child masters which psychosocial stage for development of healthy personality? Incorrect: Autonomy versus shame and doubt is Erikson's stage of psychosocial development that occurs during the toddler period. The child learns of his or her ability to predictably control own actions that also have a direct effect on the reaction and behavior of others. During toddlerhood, areas of conflict regarding autonomy are typical. The toddler's will to control exists with an immature lack of understanding about natural consequences to actions. Incorrect: Identity versus role diffusion emerges during the pubescent period. A sense of group identity precedes the development of personal identity. Adolescents first engage in mastering the task of finding their place within the peer group prior to resolving issues relating towho they are in relation to the inner self, family and society. Incorrect: Initiative versus guilt is a psychosocial, developmental task of the preschool child. Children at this age begin to play and learn about the world through their own endeavors. They take pride in the new-found abilities to engage in new activities and produce some outcome. The demands of a task for a preschool child may exceed the maturity or skills and produce some degree of remorse, anxiety or guilt. Correct: The child in the middle years develops a fundamental attitude toward work. During this stage of accomplishment, the child master’s various skills that enable him/her to participate in the family or community in a meaningful way. The child who is not prepared or capable to accomplish or assume the responsibilities associated with the stage of industry may develop a sense of inferiority Autonomy versus shame and doubt Identity versus role diffusion Initiative versus guilt Industry versus inferiority 47 A preschool child is brought to the primary-care clinic because of anal itching at night. The child is diagnosed with pinworm infestation and mebendazole (Vermox) is prescribed. Which instruction to the family is most important regarding follow-up care? Incorrect: Washing the sheets in hot water is advised for hygiene measures. However, the control of the infestation occurs with the pharmacologic treatment (Vermox). Incorrect: Isolation of the child is unnecessary after treatment with Vermox. The first dose of medication is highly effective in controlling the infestation. Incorrect: Showering is recommended rather than tub-bathing during the two-week period between the initial dose of Vermox and the follow-up dose. Other measures to prevent re- infestation to the child or others include: thorough handwashing after toileting, keeping the child's fingernails short to minimize the ova collecting under the nail, and dressing the child in one piece sleep attire to minimize itching at night. Correct: All family members are treated with one dose of the medication. After treatment with the single Vermox dose, the pinworm infestation is eradicated. A second dose two weeks after the initial therapy is necessary to prevent re-infestation. All sheets must be washed in hot water. Contact with other children should be avoided for 7-10 days. Daily tub bathing is recommended during infestation. The entire family must be treated with Vermox. 48 A nurse assesses the growth and development of a 3-month-old. Which activity is undeveloped at this age? Incorrect: Holding a rattle is an appropriate motor activity for a three-month old infant due to the intact grasp reflex. The infant frequently drops a rattle because the grasp is reflexive and not purposeful. Incorrect: Attempting to roll over is an appropriate developmental function at three months of age. The infant is beginning to coordinate the movements of the body. Correct: The three-month old infant does not have the ability to use the pincher grasp. Usually this fine motor skill occurs at about eight months of age. Incorrect: Typically, smiling in response to a mother's voice and social behavior occurs at two months of age. Holds a rattle and places it in the mouth Attempts to roll over Picks up a small object using finger and thumb Smiles in response to mother's voice 49 Which diagnostic procedure is used to ascertain if a female client has gonorrhea? Incorrect: Blood specimens are not an indicator of gonorrhea. Correct: The diagnostic test for gonorrhea is a vaginal culture with microscopic examination. Incorrect: Pus in the urine may be indicative of a urinary tract infection but not gonorrhea. Incorrect: Determining the last menstrual period is not helpful with the diagnosis of gonorrhea. Take a blood specimen. Obtain a vaginal culture. Test the urine for pus. Determine the last menstrual period. 50 The nurse assesses the development of a 3-year-old child at a routine clinic visit. The nurse should expect the mastery of which developmental task? Correct: A three-year old child with normal development is able to identify five body parts. Incorrect: The dexterity necessary to copy a square does not normally develop until six years of age. Incorrect: The fine motor skills that are necessary for tying shoelaces do not normally appear until five or six years of age. Incorrect: The school-aged child, not the preschooler, is normally able to hop on one foot. Identifying five body parts Copying a square Tying shoelaces Hopping on one foot 51 The nurse providing nutritional instruction to parents of a child diagnosed with cystic fibrosis recommends which type of diet? Correct: The child with cystic fibrosis lacks the pancreatic enzyme necessary for adequate digestion and growth. A well-balanced, high-calorie, high protein diet, as much as 50%above normal, should be encouraged. The impaired intestinal absorption can lead to poor nutritional status. Additionally, the child should take supplementary pancreatic enzymes to increase nutritional availability and reduce the waste product transit time through the bowel. Incorrect: Fat is expelled in stool as a result of poor fat absorption in the intestinal tract. Incorrect: A high fiber diet is not a primary concern in the nutritional counseling for the child with cystic fibrosis. A well-balanced diet that is high in protein and calories is necessary to achieve growth. Incorrect: A vegetarian diet is not encouraged unless it contains a high caloric density, high protein and high fat components to meet the needs of the child with cystic fibrosis. High calorie Low fat High fiber Vegetarian 52 Which nursing assessment indicates bleeding in the postoperative phase after a tonsillectomy? Correct: Frequent swallowing is an indication that the operative site is bleeding. Surgical intervention or surgical packing may be needed. Incorrect: Complaints of throat pain are common after surgery. Analgesic/antipyretic drugs, such as acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID), are commonly administered to promote comfort and reduce inflammation. Incorrect: An increase in the pulse rate is common due to pain, stress, and physiologic response to surgery. Incorrect: Dark brown blood is commonly seen in the vomitus, secretions of the nose, and between the teeth related to the blood loss during the surgical procedure. Active bleeding is evidence by bright red blood or pink mucous. Oral intake is restricted until there are no signs of hemorrhage. Frequent swallowing Complaints of throat pain Increased pulse rate Dark brown blood in the emesis 53 The school nurse provides an educational program for a group of preadolescents regarding the use of birth control pills. Which is the mechanism of action for oral contraceptives? Incorrect: Oral contraceptives do not kill sperm. Correct: Oral contraceptives inhibit ovulation. If the ovum is not released from the ovary, it cannot be fertilized and pregnancy cannot occur. Incorrect: Oral contraceptives do not change the genetics of sperm. Incorrect: Oral contraceptives do not interfere with the implantation of the fertilized ovum in the uterus. Kill sperm Inhibit ovulation Cause sperm dysfunction Prevent ovum implantation 54 The mother of a school-aged child diagnosed with a terminal illness asks the nurse, “How should I explain this to my child?” Which nursing instruction is most appropriate? Incorrect: The child's physical condition may not determine how much information the child understands or wants to know. Incorrect: Although the school-aged child is in the Piaget's stage of concrete-operational thought, photographs of other children in the latter stage of the disease may provide too much detail and frighten him/her. This level of detail may be useful for health care professionals but not for an ill child. Incorrect: A full description of the disease process and contributing causes is probably more than the child is interested in learning. The school-aged child is egocentric and the explanation needs to pertain directly to the personal situation. Only information that is relevant to the child will be retained. Correct: The child's age, cognitive and emotional development set the boundaries regarding the type and extent of information and the manner for delivery. Provide an explanation of the illness depending on the child's physical condition. Show photographs of the children in the latter phase of the disease. Give a description of the disease process and contributing causes. Explain the illness honestly at an age-appropriate level. 55 The nurse prepares to administer an intramuscular injection to a 4-year-old child. Which site is most appropriate? Incorrect: The ventrogluteal is not a recommended site for young children. The sciatic nerve can be injured from a long needle injected posteriorly and medially. Incorrect: The vastus lateralis is an acceptable site for intramuscular injection in preschool children. However, often the site becomes sore and interferes with walking. The vastus lateralis site is ideal for intramuscular injection in infancy and can be accessed in a variety of sitting, lying or side-lying positions. This muscle can tolerate larger volumes of fluid because of the development of the muscle mass in infancy. Incorrect: The dorsogluteal is site that is frequently used for intramuscular injections in older children and adults. The site is contraindicated in children walking less than one year. Correct: The deltoid muscle is adequately developed in the preschool child and is likely to tolerate the fluid in an intramuscular injection. From a developmental perspective, the deltoid may be a more acceptable site for injection due to the sense of privacy that begins in the preschool age group. Ventrogluteal Vastus lateralis Dorsogluteal Deltoid 56 Which is the peak age for the occurrence of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)? Incorrect: Two to four weeks of age is early for most cases of SIDS. Unexplained death at this time could be related to many types of congenital abnormalities, such as persistent, late apnea of prematurity that exists beyond 44 weeks post-conceptual age. Correct: The peak time period for the incidence of SIDS is two to four months of age with 95% of the cases occurring by the age of six months. It is more common in low birth weight babies, males, crowded living conditions, environmental cigarette smoke, and during the winter months. Research indicates that infant positioning during sleep may be a factor in the incidence of SIDS. Supine positioning for sleep in healthy infants is recommended to reduce the risk of SIDS. Incorrect: By ten months of age, the risk for SIDS is markedly reduced. The infant has good head, neck and back control. If an obstruction of the airway occurs as a result of head positioning, the infant at 6-10 months of age can rescue him/herself. Incorrect: After ten months of age, infant death is most likely to be the result of an accidental injury. Prior to four weeks Two to six months Six to ten months After ten months 57 An adolescent seeks health care at a free clinic and states she is sexually active and concerned about AIDS. Which nursing instruction regarding transmission of sexually transmitted diseases is most appropriate? Incorrect: Diaphragms do not prevent the transmission of infection. A diaphragm serves as a barrier for the prevention of sperm penetration to the uterus. The diaphragm with spermicidal agent is an effective method to reduce the chance of pregnancy, not the spread of infection. Incorrect: The lack of symptoms of AIDS is unrelated to the infectious status as the virus may lie dormant in the body for an extended period of time prior to the onset of symptoms of infection. Correct: Condoms are the best protection against the spread of sexually transmitted disease (STD) if used correctly. Incorrect: Spermicidal do not protect the body from the exposure to the virus. “It is essential that you wear a diaphragm to prevent cross infection with your partner.” “If your partner has no symptoms of sexually transmitted disease then you do not need to worry.” “A condom is the best protection, except for abstinence, to prevent sexually transmitted disease.” “A spermicidal is used to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted disease in both partners.” 58 An adolescent girl is diagnosed with scoliosis and her mother is reluctant to pursue treatment. The nurse educates the mother that untreated scoliosis may ultimately have which outcome? Incorrect: Scoliosis is not likely to correct over time. Incorrect: Scoliosis of the thoracic region does not affect bladder control. Incorrect: Scoliosis of the thoracic region does not affect gastrointestinal function. Correct: Scoliosis is the lateral curvature of the spine, which may be congenital, idiopathic, or a result of paralysis. Scoliosis is at the level of the chest, therefore, if untreated, heart and lung function may be compromised. Correct itself over time Compromise bladder control Reduce gastrointestinal function Affect heart and lung performance 59 When assessing the heart rate for infants and small children, which pulse point should the nurse use? Correct: The apical pulse is recommended for infants and children and is heard at the apex of the heart for one full minute. Incorrect: The carotid pulse is located in the neck and is not used to assess heart rate in children. Incorrect: Brachial pulses are used to assess the absence of a pulse when performing CPR. Incorrect: Apical pulses are taken in children under one because the radial pulse rate is too faint. Apical Carotid Brachial Radial 60 A hospitalized 18-month-old is diagnosed with gastroenteritis. When providing discharge teaching for the child's parents, which food should the nurse suggest be reintroduced last? Incorrect: Bananas can be introduced into the diet early and are part of the BRAT diet. Bananas provide potassium, which may have been lost through vomiting and diarrhea. Correct: Following an acute episode of gastroenteritis, foods are reintroduced slowly. The glucose and milk within the pudding would be introduced later into the diet after the body is able to tolerate the BRAT (Bananas, Rice, Applesauce and Toast) diet. The high sugar and milk content found in the pudding may trigger further diarrhea. Incorrect: Applesauce is a part of the BRAT diet and can be introduced into the diet early. It is bland and easy to digest. Incorrect: Rice is also part of the BRAT diet, is easily digested and can be introduced into the diet early. Rice provides carbohydrates needed for energy. Bananas Pudding Applesauce Rice 61 A child with Type I diabetes mellitus experiences polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia, and has a history of diabetic ketoacidosis. The family should be instructed that ketones can appear in the urine when the blood glucose reaches which level? Incorrect: 120 mg/dl is a normal blood glucose reading. Correct: The normal blood glucose varies between 110-150 mg/dl. It is not until 250 mg/dl that blood glucose will spill over into the urine. Incorrect: 180 mg/dl is above normal limits but not far enough above normal limits for the appearance of glucose in the urine. Incorrect: 150 mg/dl is on the upper boundaries of normal but would not have any blood glucose spilling to the urine. 120 mg/dl 250 mg/dl 180 mg/dl 150 mg/dl 62 A hospitalized preschool child is recovering from surgery and is in the playroom. Which behavior should the nurse expect to observe? Correct: An imaginary friend is not uncommon for this age. The creative imagination of a preschool child is rapidly developing and acts as a way the child can practice social relationships in a non-threatening environment. independent play activity among toddlers. Playing a board game with another child Talking to an imaginary friend Throwing a ball into the air and catching it Playing with a toy beside other children 63 A 4-week-old infant with an atrial septal defect (ASD) is monitored for signs of congestive heart failure (CHF) prior to surgery. The nurse measures intake and output to determine the fluid status of the child. Which is the best method to obtain an approximation of the volume of urine output? Correct: The correct procedure for the determination of an accurate urinary output is to weigh the diaper prior to and following urination. Subtract the difference. Cloth diapers vary in weight; a baseline measurement will be necessary. However, because the weight of disposable diapers is stable with very little discrepancy among diaper weights, each diaper does not need to be weighed but the baseline for that type and size is necessary information. The conversion for volume to weight measurement is: 1cc = 1 gm. Record the weight of the wet diaper directly on the graphic flow sheet. After urination, weigh the wet diaper and divide by the birthweight. Weigh the diaper before and after urination and subtract the difference. Weigh the infant before and after urination and record the volume. 64 A 12-week-old infant requires the insertion of a ventricular peritoneal (VP) shunt for the treatment of hydrocephalus. Which is the most serious complication of VP shunts? Correct: Shunt infection is the most serious complication. Any type of invasive procedure provides a risk of infection. Shunt infections are particularly grave since they may compromise the intellect of the child. Shunt migration Obstruction of the shunt Mechanical malfunction Shunt infection 65 A mother brings her toddler into the clinic because of fussiness, fever, and pulling of the right ear. The mother states that the symptoms are the same as when the child had a previous ear infection. Which is the most appropriate nursing response? Correct: The nurse explains the structure of the infant's ear and addresses the reason for the infant's repeated ear infections. "It is good that you are concerned because frequent ear infections may lead to deafness." "It is probable that the previous ear infection did not completely resolve." "Otitis media is an infection in the outer ear canal and is common in early childhood." "Children are more prone to hear infections due to the shorter, straighter ear canal." 66 An 11-year-old receives an allergy shot during a clinic visit. Which symptom indicates the early stage of anaphylactic shock? Correct: A correlation has been found to relate reports of impending doom and anxiousness and anaphylactic reactions. Incorrect: A heart rate of 90 beats per minute is normal for a child that is eleven years old. A blood pressure reading of 100/60 A sense of impending doom A heart rate of 90 Complaints of abdominal cramping 67 When initiating a plan of care for the child with leukemia, the nurse informs the family to anticipate which diagnostic test? Correct: The test commonly used to diagnose leukemia is a bone marrow aspiration. Leukemia is the uncontrolled production of white blood cells, and is the most frequently occurring type of cancer in children. The bone marrow of the client is characterized by a high white blood cell count (leukocytosis), low platelet count (thrombocytopenia) and immature white blood cells (blast cells.) Red blood cell count Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Bone marrow aspiration Blood gas analysis 68 The administration of aspirin has been discouraged in pediatric use because of the association of which condition? Correct: Aspirin should not be given to children with influenza virus or chickenpox due to the association with Reye's Syndrome. This disorder is characterized by encephalopathy and liver dysfunction. Erb palsy Hodgkin's disease Kaposi sarcoma Reye's syndrome 69 A child diagnosed with sickle cell disease experiences an acute, vasoocclusive crisis. Which nursing intervention is the priority? Correct: The priority for the care of the child with acute vasoocclusive crisis is oxygen therapy. Sickled cells cause obstruction in the blood vessels leading to tissue ischemia and infarction. Maintain hydration. Prevent infection. Provide analgesia. Administer oxygen. 70 The nurse provides discharge instructions to the parent of a child who has a newly applied cast to the leg. Which statement by the parent indicates the need for further nursing instruction? Correct: The palms of the hands should be used when handling the wet cast to prevent depressions to the external surface "The new cast will need to air dry." "I should use my fingertips when handling the wet cast." "I need to check the toes for temperature and color." "I will place the leg above the level of the heart." 71 Which is the main difference between the male and female anatomy related to urinary tract infections? Correct: The urethra is shorter and straighter in females; therefore, pathogens can enter the bladder more readily. Due to the proximity of the rectum, the female urethra may be more easily contaminated with bacteria. The nurse can provide education to the child and/or caregiver to practice hygiene measures to reduce the spread of organisms to the genitourinary tract. Incorrect: Both the male and female tracts are lined with mucous membranes. The male urethra is straighter, allowing more rapid elimination of pathogens. The female urethra is shorter so the pathogens can enter the bladder more quickly. The male urethra is lined with mucous membranes to trap microorganisms. The female urethra is larger in diameter, allowing for the rapid entrance of pathogens. 72 A teenage boy commits suicide. Which is the main cause of suicide? Correct: Suicide is most commonly referred to as destructive aggression turned inward against the self. An act of defiance A psychotic act Destructive aggression turned inward A form of manipulation 73 Which signs indicate IV infiltration in a child? Correct: Erythema (redness), pain, edema and a streaking at the vein site are indications that IV fluids may be accumulating in the interstitial tissue and not going through the circulation. Also these signs may indicate an irritation of the vein that could cause IV compromise. Fever, chills, and pain Erythema, edema, and streaking at the vein site Limited ability to move the extremity Backflow of blood at the IV site and in the IV tubing 74 Following the surgical repair of a toddler's cleft palate, which method of administering fluid is most appropriate in the post-operative recovery period? Correct: Nothing should be placed inside of the mouth as palate sutures may be damaged. A cleft palate is typically repaired between 12-18 months of age. It is important to offer the cup in a manner that is appropriate for the skills of toddler age. Sippy cup Drinking straw Regular cup Breck feeder 75 The nurse planning the care for a child that has partial and full thickness burns understands that an early complication with extensive burns is Correct: The primary emphasis during the initial phase of burn care is the prevention of hypovolemic shock. dehydration. infection. hypovolemic shock. high-output renal failure. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 114 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 31, 2021
Number of pages
114
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 31, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
44





.png)
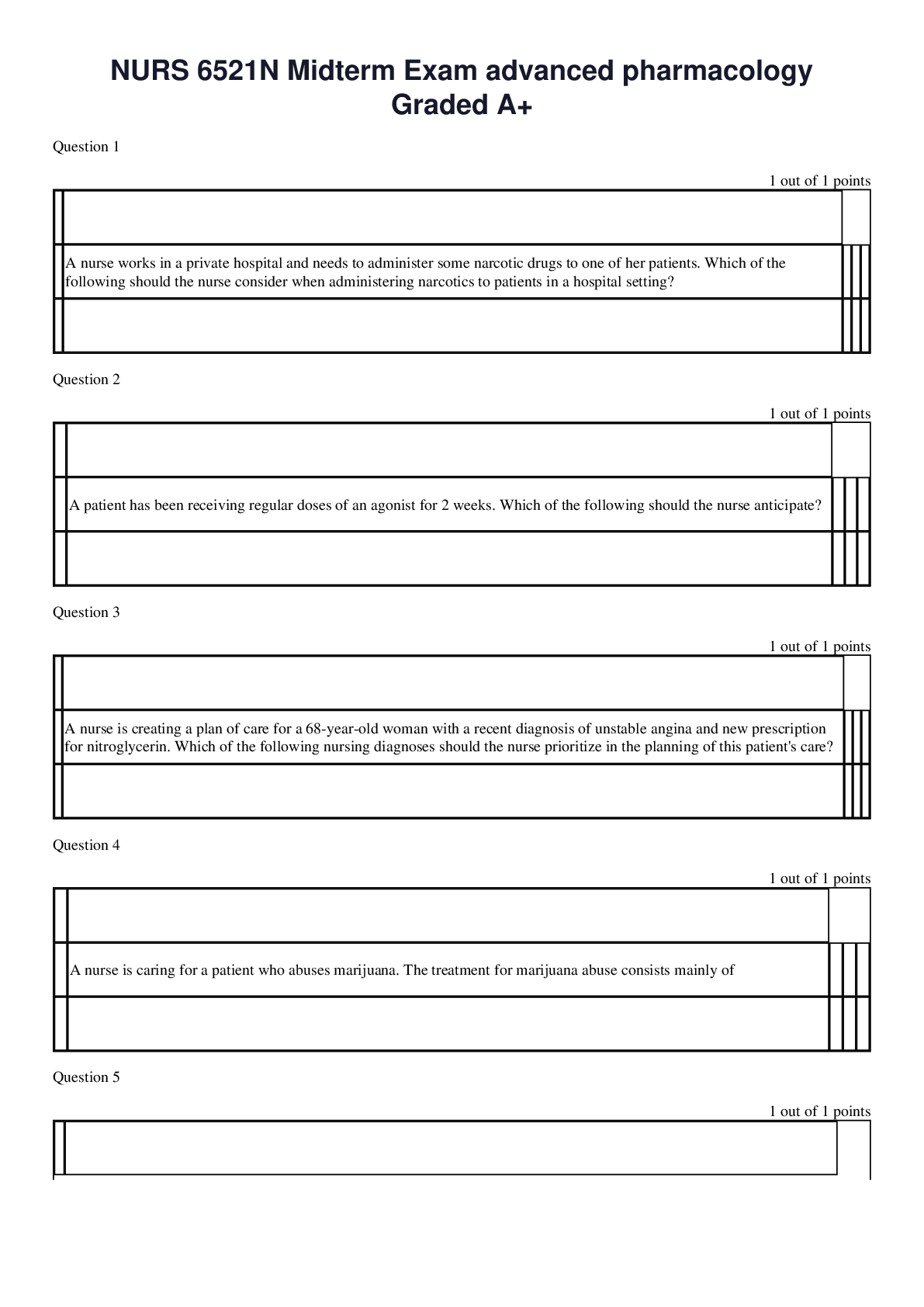

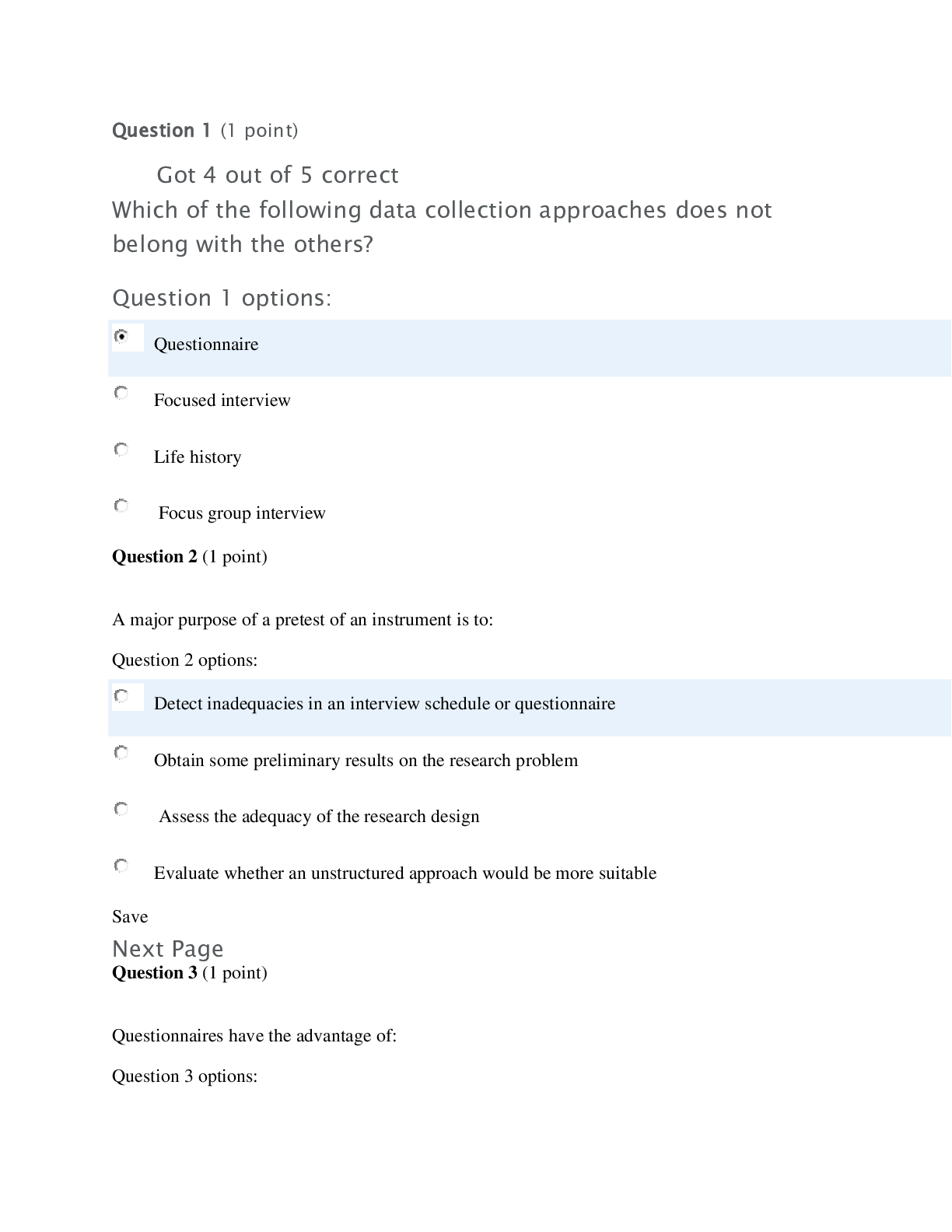


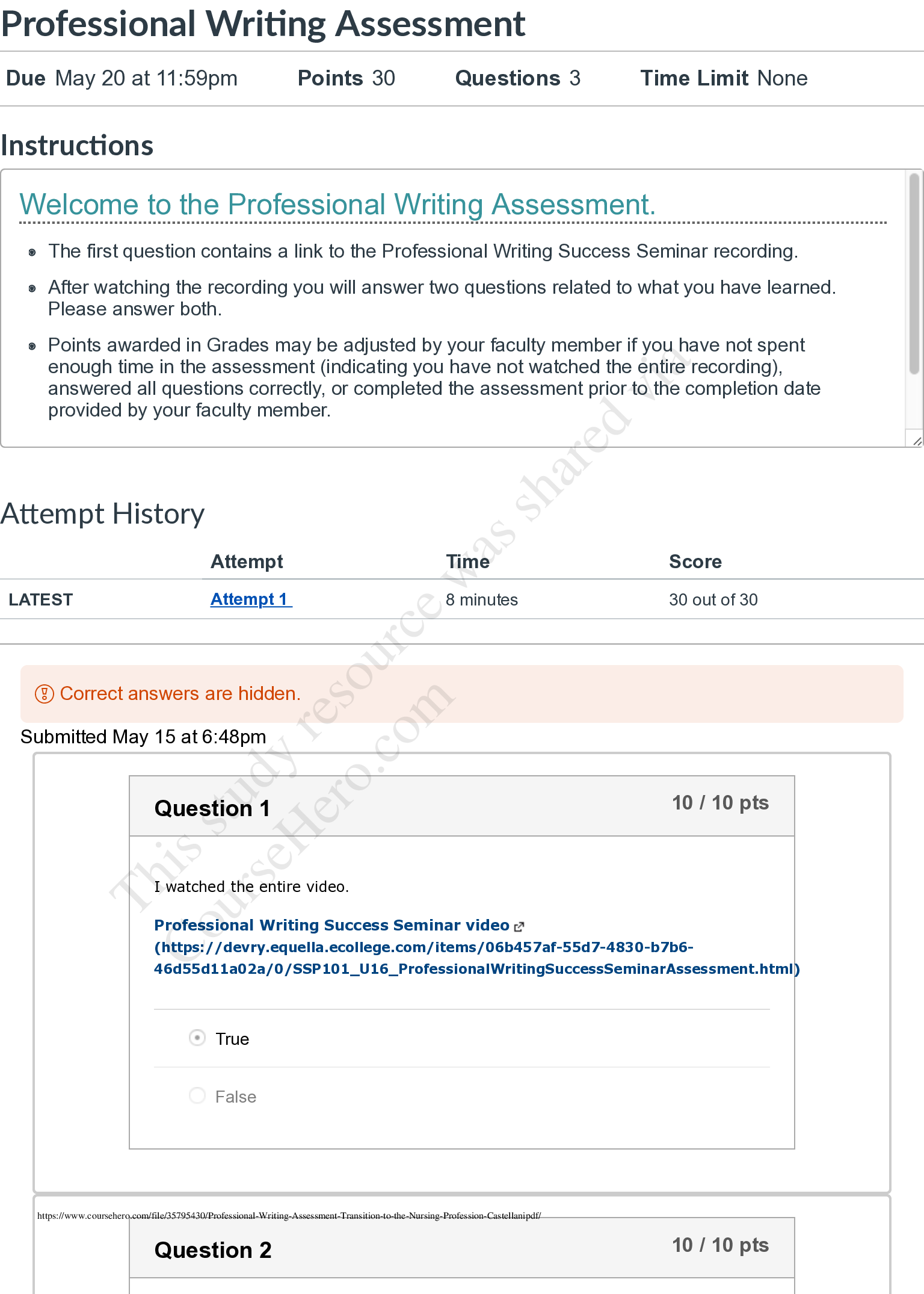













.png)











