SCIENCE 101 > GIZMOS > GIZMO LEARNING: American College of International Academics, Lahore - Student Exploration: Chicken G (All)
GIZMO LEARNING: American College of International Academics, Lahore - Student Exploration: Chicken Genetics SE. allele, codominant, dominant, genotype, heterozygous, homozygous, phenotype, probability, Punnett square, recessive, trialAll Questions Answered.
Document Content and Description Below
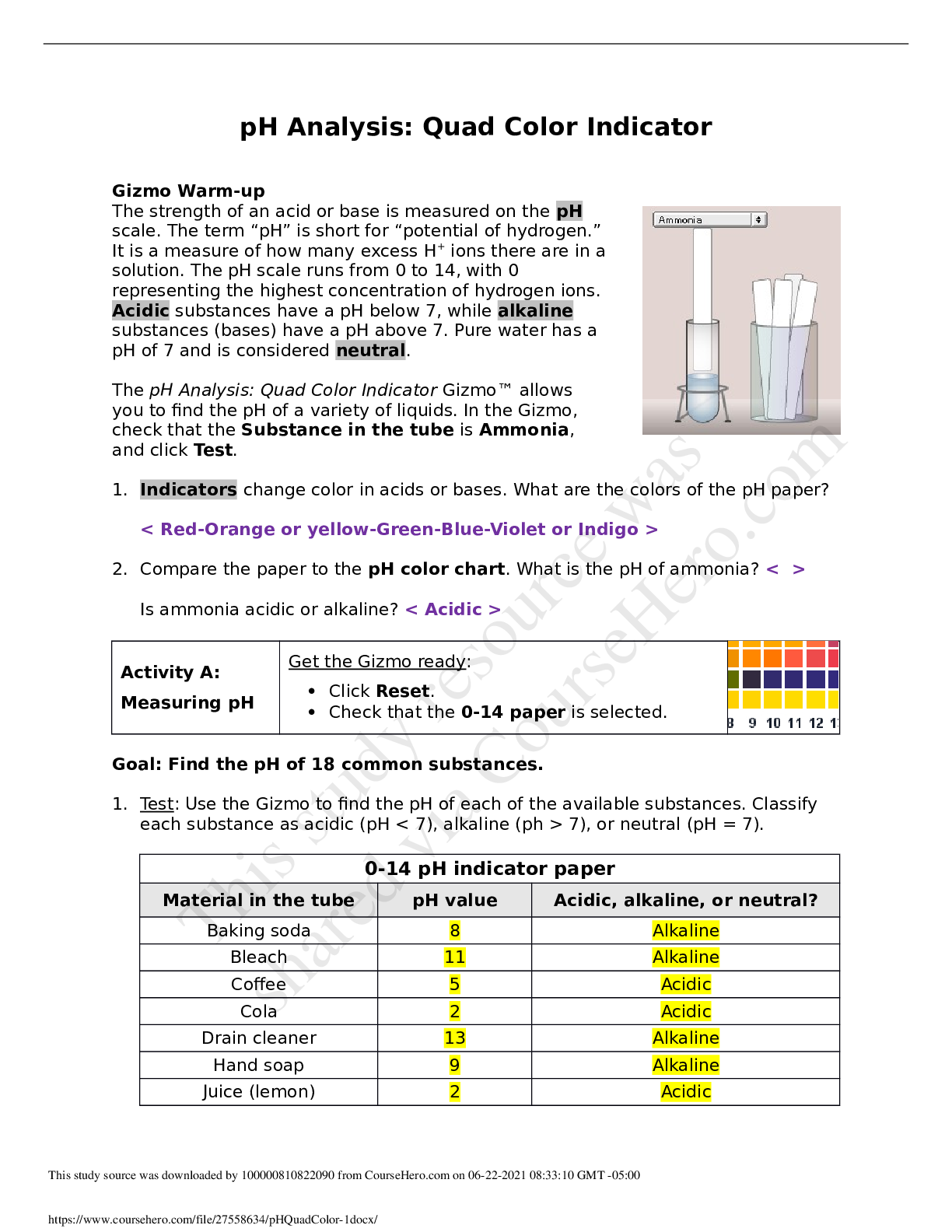
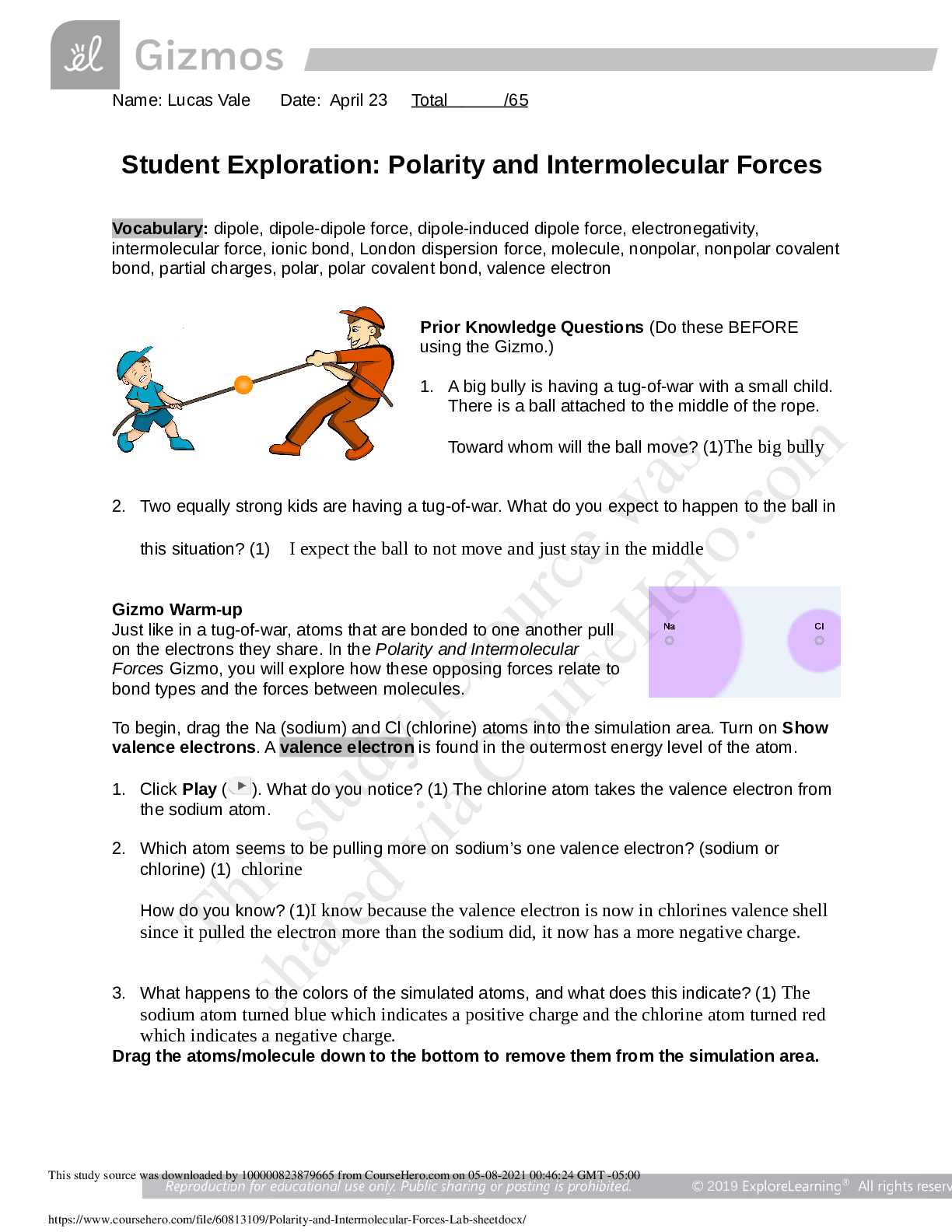
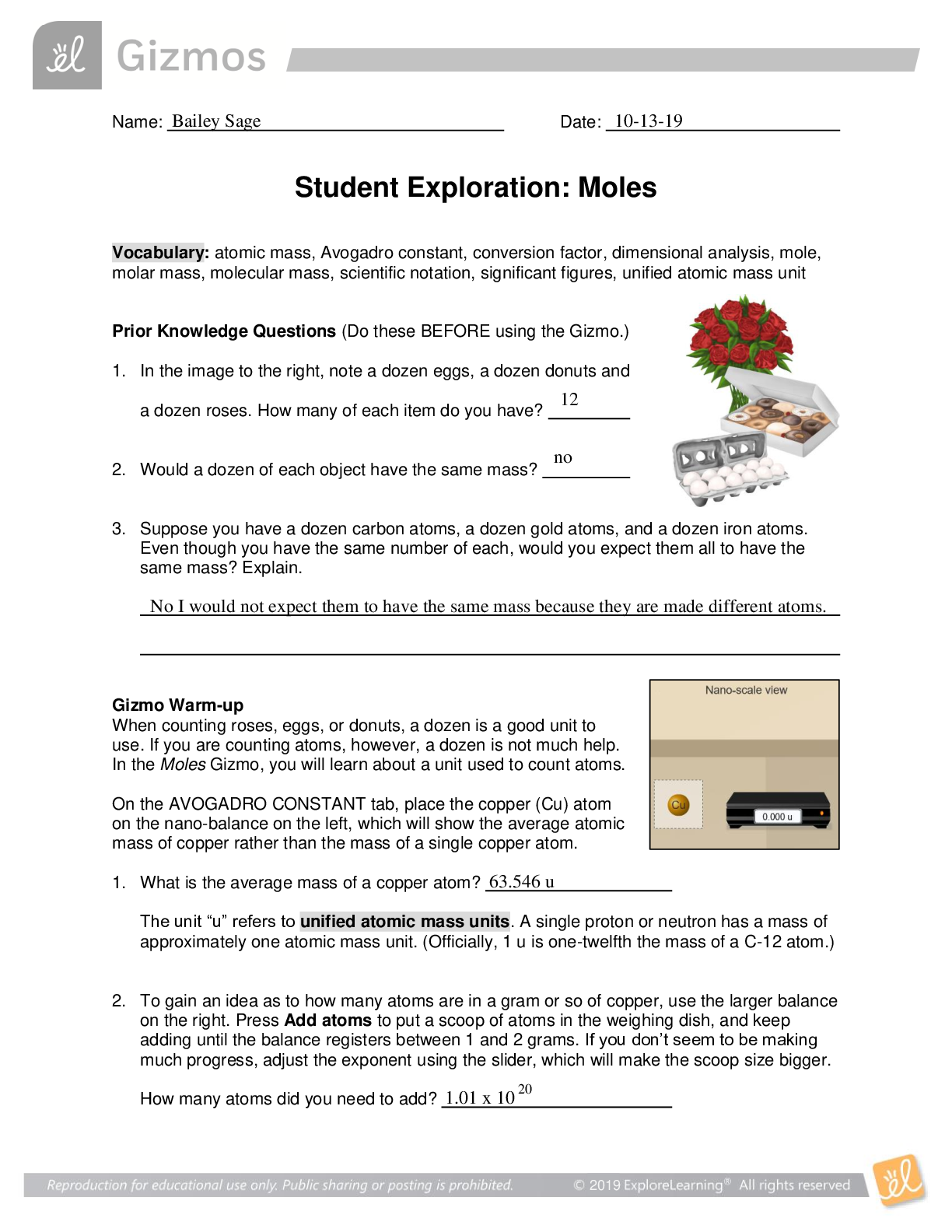
Student Exploration: Chicken Genetics Vocabulary: allele, codominant, dominant, genotype, heterozygous, homozygous, phenotype, probability, Punnett square, recessive, trial Prior Knowledge Qu... estions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. The image shows a flower that was produced by crossing a pure red flower with a pure white flower. Which do you think is the dominant petal color: red or white? Explain. 2. How is the inheritance pattern shown by this flower different from other inheritance patterns you have seen or studied? Gizmo Warm-up There are many different ways traits can be inherited. Some traits are governed by alleles that are dominant over other alleles. Other traits are governed by alleles that share dominance. These alleles follow a pattern of inheritance called codominance. With the Chicken Genetics Gizmo™, you will study how codominance affects the inheritance of certain traits. 1. Turn on Show genotype. The genotype is the allele combination an organism has. Point to the red chicken. A. What is the red chicken’s genotype? B. What is the white chicken’s genotype? 2. What do you think the letters F, R, and W stand for in the genotypes? | Activity A: Codominant traits | Get the Gizmo ready: ● Drag a red chicken and a white chicken into the parent boxes, but don’t click Breedyet. Question: What inheritance patterns do codominant traits display? 1. Predict: What do you think the offspring of a red chicken and a white chicken will look like? 2. Observe: Click Breed. What are the offspring genotypes? An organism’s appearance is its phenotype. Describe the offspring’s phenotype. 3. Experiment: Drag four offspring to the Holding Cages. Click Clear, and then drag one of the offspring to a parent box. Drag a white chicken to the other box. Click Breed several times. Describe the resulting genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. 4. Revise and Repeat: Click Clear. Drag another chicken from the Holding Cages to the parent box. Drag a red chicken to the other box. Click Breed several times. Describe the resulting genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. 5. Explain: In dominant/recessive inheritance patterns, the dominant allele is always expressed when present. The recessive allele is only expressed when the dominant allele is not present. Use your observations from this activity to describe how codominant inheritance patterns differ from dominant/recessive inheritance patterns. | Activity B: Codominant crosses | Get the Gizmo ready: ● Click Clear. ● Drag the remaining chickens from the Holding Cagesinto the parent boxes. Introduction: Probability is the likelihood that a specific event will occur. Scientists use probability to predict the outcomes of different genetic crosses. Question: How can you use probability to predict the outcome of a codominant cross? W 1. Model: A Punnett square is used to model the possible offspring genotypes from a genetic cross. The parent genotypes are written at the top and side of the square, as shown. The possible offspring genotypes are then filled in. The first square is filled in for you. Fill in the remaining squares. (Note: FR FW is equivalent to FW FR.) 2. Analyze: A homozygous chicken will have the same alleles for feather color. A heterozygous chicken will have two different alleles for feather color. A. Are the parents homozygous or heterozygous? Explain how you know. B. What are the possible genotypes of the offspring? C. Will the offspring be homozygous or heterozygous? 3. Calculate: Punnett squares can be used to predict probable outcomes of genetic crosses. To calculate probability, divide the number of one kind of possible outcome by the total number of all possible outcomes. For example, if you toss a coin, the chance it will land on heads is equal to 1 ÷ 2. This probability can be expressed as ½, 0.5, or 50%. Look at the Punnett square above. A. How many total possible outcomes are there? B. How many of the possible outcomes are for each of the following genotypes? | | | | C. What is the probability for each of the following outcomes? (Record answers as both | | | fractions and percentages.) | | | | (Activity B continued on next page) Activity B (continued from previous page) 4. Test: Use the Gizmo to test your predicted outcomes. Turn on Show statistics and Show as approximate percentage. Click Breed. What are the results of the cross? 5. Evaluate: Did the results of the cross match your prediction? If not, why do you think that was the case? 6. Collect data: Click Breed 19 more times until you have generated 100 offspring. How do the percentages match your prediction now? Have they gotten to be more or less similar to your original prediction? 7. Compare: Click Breed until you have generated at least 1,000 offspring. Compare the statistics on the Gizmo with your original predictions. How close are they? 8. Draw conclusions: Each time you bred the parent chickens, you completed a trial. A trial is single time that you conduct an experiment. Random chance often causes identical trials to have different outcomes. Because of this, scientists repeat experiments many times in order to make sure that chance alone is not responsible for the results of a trial. How did your results change as the number of trials you completed increased? Why was it important for you to breed the chickens repeatedly in this experiment? [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 21, 2021
Number of pages
6
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 21, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
414






.png)






.png)
.png)