*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NR 661:APEA TEST BANK, Latest Updated (2019/2020) Complete Guide;Chamberlain. (All)
NR 661:APEA TEST BANK, Latest Updated (2019/2020) Complete Guide;Chamberlain.
Document Content and Description Below
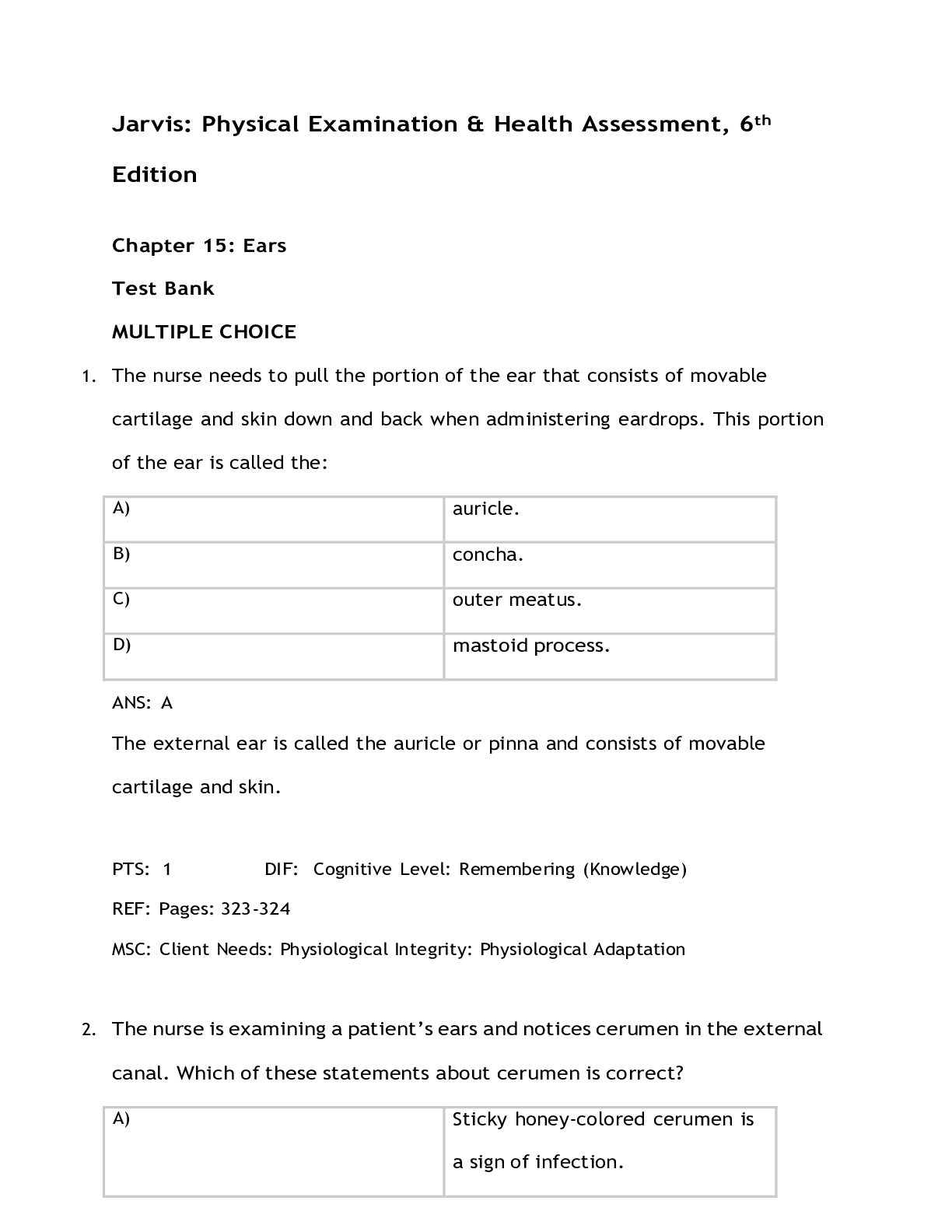
APEA TEST BANK A patient with iron deficiency anemia takes iron supplementation daily. What should he be advised to avoid within a couple of hours of taking iron? ... Leukemia may have varied clinical presentations. Which characteristic would be unusual to find in a patient with leukemia? Correct A 66 year-old African American male complains of pain in his trunk, especially his ribs. Cardiovascular disease is ruled out. He has a normocytic, normochromic anemia with hypercalcemia. The differential diagnosis should include: Incorrect What hallmark finding is associated with both B12 and folate deficiencies? Incorrect A patient demonstrates leukocytosis. This means: What statement is true about anemia in older adults? A patient has been treated for HIV infection with anti-retroviral therapy. He is stable. How often should CD4 counts be repeated? Correct A patient presents with hematuria, RBC casts, and proteinuria. What is a likely explanation? Correct A patient demonstrates leukocytosis. This means: A patient is having an allergic reaction to seafood. Which white cell will probably be increased? Correct A female patient has been diagnosed with Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD). What should be done to prevent lysis of red cells in this patient? Correct A 75 year-old patient who has multiple chronic diseases has been in very poor health for a decade. What type of anemias is he most likely to exhibit? Incorrect A patient has been diagnosed with HIV. The patient’s viral load was ordered. What other test may be ordered to assess the status of the patient’s immune system? Correct A 70 year-old male has lymph nodes in his axillary and inguinal areas that are palpable but non-tender. He states that he feels well today. What should be included in a differential diagnosis for this patient? L Correct A two year-old with sickle cell anemia (SCA) should receive which immunizations? Correct A three year-old child presents with hematuria, petechiae, and a platelet count of 50,000 (Normal = 150,000-450,000/ml). The rest of his CBC is normal. He had an upper respiratory infection about 2 weeks ago. On exam today, he is found to have petechiae and bruises. The most likely diagnosis is: Correct A child and father live in an old house. They both are found to be lead toxic. What type anemia is typically observed in patients who are lead toxic? Incorrect A patient with diarrhea has a stool specimen positive for WBCs. What does this indicate? Incorrect A 26 year-old female has thalassemia minor. What should be limited in her diet to avoid hepatotoxicity? Correct A patient is found to have eosinophilia. An expected finding is: An African American male complains of pain in his back and trunk. He is diagnosed with multiple myeloma. He is probably: . Correct A patient has heavy menses. Which lab value below reflects an iron deficiency anemia? Incorrect An obese 78 year-old male with poorly controlled hypertension and diabetes has a normocytic, normochromic anemia. This anemia is likely: . Correct An elderly male diagnosed with a microcytic, hypochromic anemia: Which suggestion below is the standard for treating iron deficiency anemia in infants and children? Correct A patient with pernicious anemia may be observed to have: Incorrect Lead toxicity can be associated with: Incorrect A patient is being treated for iron deficiency anemia. Iron is better absorbed: Incorrect What choice below can be attributed to the two most common causes of iron deficiency anemia in adults? Incorrect The laboratory identifies metamyelocytes in a 50 year-old patient who had a CBC performed. What might be an expected finding in this patient? Incorrect A patient is found to have an anemia. The patient’s MCH is normal. The patient’s anemia can be described as: Correct Which statement is true about Vitamin B-12? Correct A serum ferritin level: Correct Which anemias are described as microcytic, hypochromic anemias? Incorrect The nurse practitioner sees a child who presents with fatigue and purpura on his lower extremities. His temperature is normal. The differential includes: Correct An older adult has suspected B12 deficiency. Which of the following lab indices is most indicative of a B12 deficiency? Incorrect A patient with anemia of chronic disease probably has a: Correct A vitamin B-12 deficiency might be suspected in an older patient with what complaints? Correct A measure of the degree of variation in red cell size is indicated by: Incorrect A definitive diagnosis of sickle cell anemia can be made: An example of a macrocytic anemia is: Correct An older adult has suspected B12 deficiency. Which of the following lab indices is more indicative of a B12 deficiency? Correct Besides inadequate intake of Vitamin D in elder adults, what other factor contributes to deficiencies? Incorrect Which white cell should be present in the greatest number in a patient who is healthy today? A patient has CBC results that indicate a microcytic, hypochromic anemia. The nurse practitioner should suspect: Correct A 12 month-old was screened for iron deficiency anemia and found to be anemic. The nurse practitioner ordered oral iron. In one month, the child’s hemoglobin was re-assessed. It increased greatly. What choice might account for this? Correct A patient is found to have an anemia. The patient’s MCV is normal. The patient’s anemia can be described as: Correct A B-12 deficiency can produce: Correct Thalassemia minor can be recognized by: Correct A patient had a splenectomy after an automobile accident 3 months ago. Patients who are asplenic are: An example of a first generation cephalosporin used to treat a skin infection is: cephalexin. Correct A 4 year-old has been diagnosed with measles. The nurse practitioner identifies Koplik’s spots. These are: spots on the skin that are pathognomonic for measles. Incorrect The main difference between cellulitis and erysipelas is the: . infecting organism. Incorrect A patient reports that he found a tick on himself about one month ago. He reports that there is a red circle and a white center near where he remembers the tick bite. He did not seek treatment at the time. Today he complains of myalgias and arthralgias. What laboratory test can be used to help diagnose Lyme disease? Lyme titer Incorrect A patient who is at high risk for skin cancer should: examine his skin monthly for changes. Correct A patient has a “herald patch” and is diagnosed with pityriasis rosea. Where is the “herald patch” found? On the chest Correct Which of the following antibiotics may increase the likelihood of photosensitivity? Fluoroquinolones Correct A 60 year-old patient is noted to have rounding of the distal phalanx of the fingers. What might have caused this? Coronary artery disease Incorrect A patient exhibits petechiae on both lower legs but has no other complaints. How should the NP proceed? Order a CBC Correct When can a child with chickenpox return to daycare? After all lesions have crusted over Correct Hand-foot-and-mouth disease and herpangina: are viral infections caused by Coxsackie viruses. Correct What is the proper technique to safely remove a tick from a human? Pull it off with tweezers Correct Most cases of atopic dermatitis exacerbation are treated with: topical steroids. Correct The primary therapeutic intervention for patients who present with hives is: anti-histamines. Correct A patient is diagnosed with tinea pedis. A microscopic examination of the sample taken from the infected area would likely demonstrate: hyphae. Correct A patient has been diagnosed with scabies. What is the medication of choice to treat this? Permethrin Correct An adolescent has acne. The nurse practitioner prescribed a benzoyl peroxide product for him. What important teaching point should be given to this adolescent regarding the benzoyl peroxide? Photosensitivity of the skin can occur Correct A patient presents with plaques on the extensor surface of the elbows, knees, and back. The plaques are erythematous and there are thick, silvery scales. This is likely: plaque psoriasis. Correct An infant is diagnosed with diaper dermatitis. Satellite lesions are visible. This should be treated with a: topical anti-fungal agent. Correct A key component of the approach to a patient who has atopic dermatitis is hydration. Which agent should be avoided? Ointments Incorrect Patients with atopic dermatitis are likely to exhibit: Itching. Correct A 16 year-old has been diagnosed with Lyme disease. Which drug should be used to treat him? Doxycycline Correct A 28 year-old has thick, demarcated plaques on her elbows. Which features are suggestive of psoriasis? Silvery scales that are not pruritic Correct A 71 year-old female presents with a vesicular rash that burns and itches. Shingles is diagnosed. An oral antiviral: will nearly eliminate the risk of post-herpetic neuralgia. Incorrect A patient was burned with hot water. He has several large fluid filled lesions. What are these termed? Bullae Correct A patient with a primary case of scabies was probably infected: 1-3 days ago. Incorrect A patient has a lower leg wound that appears infected. It is red, warm to touch and edematous. He had an acute onset of pain, symptoms, and low grade fever. What is this? Cellulitis Incorrect A 15 year-old male has worked this summer as a lifeguard at a local swimming pool. He complains of itching in the groin area. He is diagnosed with tinea cruris. The nurse practitioner is likely to identify: maceration of the scrotal folds with erythema of the penis. Incorrect A patient has been diagnosed with MRSA. She is sulfa allergic. Which medication could be used to treat her? Doxycycline Correct A skin lesion which is a solid mass is described as a: papule. Correct Impetigo is characterized by: honey-colored crusts. honey-colored crusts. Correct A 10 year-old has thick, demarcated plaques on her elbows. Which features are suggestive of psoriasis? Silvery scales that are not pruritic Silvery scales that are not pruritic Correct The agent commonly used to treat patients with scabies is permethrin. How often is it applied to eradicate scabies? Once Once Correct Which test is NOT suitable to diagnose shingles if the clinical presentation is questionable? Complete blood count (CBC) Complete blood count (CBC) Correct A 74 year-old is diagnosed with shingles. The NP is deciding how to best manage her care. What should be prescribed? An oral antiviral agent An oral antiviral agent plus an oral steroid Incorrect The term caput succedaneum refers to: scalp edema. cradle cap. Incorrect A pregnant mother in her first trimester has a 5 year-old who has Fifth Disease. What implication does this have for the mother? There is a risk of fetal death if she becomes infected. She does not have to worry about transmission to the fetus. Incorrect A topical treatment for basal cell carcinoma is: 5-fluorouracil. 5-fluorouracil. Correct The most common form of skin cancer is: basal cell carcinoma. basal cell carcinoma. Correct A skin disorder has a hallmark finding of silvery scales. What word below describes this common condition? Chronic Chronic Correct The most common place for basal cell carcinoma to be found is the: face. face. Correct A low potency topical hydrocortisone cream would be most appropriate in a patient who has been diagnosed with: atopic dermatitis. atopic dermatitis. Correct A patient with a positive history of a tick bite about 2 weeks ago and erythema migrans has a positive ELISA for Borrelia. The Western blot is positive. How should he be managed? He should receive doxycycline for Lyme disease. Correct A 16 year-old male has nodulocystic acne. What might have the greatest positive impact in managing his acne? Isotretinoin (Accutane®) Correct A patient who has been in the sun for the past few weeks is very tanned. He has numerous 3-6 mm light colored flat lesions on his trunk. What is the likely etiology? Tinea unguium Incorrect A skin lesion fluoresces under a Wood’s lamp. What microscopic finding is consistent with this? Hyphae Correct An example of a premalignant lesion that develops on sun-damaged skin is: squamous cell carcinoma. Incorrect A 9 year-old female has presented to your clinic because of a rash on the left, upper area of her anterior trunk. She is embarrassed and very reticent to lift her blouse because her nipple will be exposed. How should the NP proceed? Examine all other areas of the trunk, then ask the child to lift her blouse Correct A patient reports to the minor care area of the emergency department after being bitten by a dog. The patient states that the dog had a tag around his neck and had been seen roaming around the neighborhood. The dog did not exhibit any odd behavior. How should this be managed? care. Report the bite to animal control and administer appropriate medical care. Correct A patient has seborrheic dermatitis. Which vehicle would be most appropriate to use in the hairline area to treat this? Foam Correct A 68 year old female adult with pendulous breasts complains of “burning” under her right breast. The nurse practitioner observes a malodorous discharge with mild maceration under both breasts. What is this? Tinea corporis Incorrect A patient is found to have koilonychia. What laboratory test would be prudent to perform? Complete blood count Correct Which of the following areas of the body has the greatest percutaneous absorption? Genitalia Correct A patient calls your office. He states that he just came in from the woods and discovered a tick on his upper arm. He states that he has removed the tick and the area is slightly red. What should he be advised? No treatment is needed. Correct A patient will be taking oral terbinafine for fingernail fungus. The NP knows that: Terbinafine is a potent inhibitor of the CYP 3A4 enzymes. Correct An elderly patient has been diagnosed with shingles on the right lateral aspect of her trunk. It appeared initially yesterday. It is very painful. How should she be managed? An oral antiviral agent and pain medication. Correct A young child has developed a circumferential lesion on her inner forearm. It is slightly raised, red and is pruritic. It is about 2.5 cm in diameter. This is probably related to: the child’s new cat. Correct Which chronic skin disorder primarily affects hairy areas of the body? Seborrheic dermatitis Correct A microscopic examination of the sample taken from a skin lesion indicates hyphae. What type infection might this indicate? Fungal Correct A 40 year-old female patient presents to the clinic with multiple, painful reddened nodules on the anterior surface of both legs. She is concerned. These are probably associated with her history of: ulcerative colitis. Correct What advice should be given to a parent who has a child with Fifth Disease? He can return to school when the rash has disappeared. Incorrect What finding characterizes shingles? Unilateral dermatomal rash Correct A 70 year-old is diagnosed with multiple cherry angiomas. The nurse practitioner knows that: these may bleed profusely if ruptured. Correct A patient with diabetes has a right lower leg that has recently become edematous, erythematous, and tender to touch over the anterior shin. There is no evidence of pus, but the leg is warm to touch. What is the most likely diagnosis to consider? Cellulitis Correct The American Cancer Society uses an ABCDE pneumonic to help patients develop awareness of suspicious skin lesions. What does the “B” represent? Border Correct A 9 year-old has been diagnosed with chickenpox. A drug that should be avoided in him is: penicillin. Incorrect Mr. Johnson is a 74 year old who presents with a pearly-domed nodular looking lesion on the back of the neck. It does not hurt or itch. What is a likely etiology? Basal cell carcinoma Correct A 3 year-old female had a fever of 102 degrees F for 3 days. Today she woke up from a nap and is afebrile. She has a maculopapular rash. Which statement is true? This could be Kawasaki disease. Incorrect The lesions seen in a patient with folliculitis might be filled with: pus. Correct A child has 8-10 medium brown café au lait spots > 1 cm in diameter. The differential diagnosis should include: neurofibromatosis. Correct A patient presents with small vesicles on the lateral edges of his fingers and intense itching. On close inspection, there are small vesicles on the palmar surface of the hand. What is this called? Herpes zoster Incorrect The nurse practitioner examines a patient who has had poison ivy for 3 days. She asks if she can spread it to her family members. The nurse practitioner replies: “no, transmission does not occur from the blister’s contents.” Correct A patient who is at high risk for skin cancer should: examine his skin monthly for changes. Correct A patient has used a high potency topical steroid cream for years to treat psoriasis exacerbations when they occur. She presents today and states that this cream “just doesn’t work anymore.” What word describes this? Tachyphylaxis Correct Topical 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is used to treat: basal cell carcinoma. Correct A “herald patch” is a hallmark finding in which condition? Pityriasis rosea Correct The nurse practitioner identifies satellite lesions in a 6 month-old infant. These are: indicative of candidal infection. Correct The nurse practitioner is examining a 3-month old infant who has normal development. She has identified an alopecic area at the occiput. What should be done? Encourage the caregiver to change the infant’s head position Correct A 6 year-old has been diagnosed with Lyme disease. Which drug should be used to treat him? Doxycycline Incorrect A child with a sandpaper textured rash probably has: strept infection. Correct An adolescent takes isotretinoin for nodulocystic acne. She is on oral contraceptives. Both were prescribed by the dermatologist. The adolescent arrives in your clinic with a sinus infection. Her temperature is 99.5 degrees F and her blood pressure is 160/100. How should this be managed? Call the dermatologist to report the elevated BP Correct Which of the following skin lesions in the elderly is a premalignant condition? Actinic keratosis Correct A patient has suspected scarlet fever. He likely has a sandpaper rash and: a positive rapid strept test. Correct A 6 year-old patient with sore throat has coryza, hoarseness, and diarrhea. What is the likely etiology? Viral etiology Correct A 74 year-old male patient has sustained a laceration to his foot. His last tetanus shot was more than 10 years ago. He has completed the primary series. What should be recommended? Tetanus and diphtheria only Incorrect The best way to evaluate jaundice associated with liver disease is to observe: blanching of the hands, feet, and nails. Incorrect more susceptible to bacterial infection. Question: A 40 year-old female patient presents to the clinic with multiple, painful reddened nodules on the anterior surface of both legs. She is concerned. These are probably associated with her history of: Question: A patient reports that he found a tick on himself about one month ago. He reports that there is a red circle and a white center near where he remembers the tick bite. He did not seek treatment at the time. Today he complains of myalgias and arthralgias. What laboratory test can be used to help diagnose Lyme disease? Question: An adolescent takes isotretinoin for nodulocystic acne. She is on oral contraceptives. Both were prescribed by the dermatologist. The adolescent arrives in your clinic with a sinus infection. Her temperature is 99.5 degrees F and her blood pressure is 160/100. How should this be managed? Question: The agent commonly used to treat patients with scabies is permethrin. How often is it applied to eradicate scabies? Question: An infant is diagnosed with diaper dermatitis. Satellite lesions are visible. This should be treated with a: Question: A 16 year-old has been diagnosed with Lyme disease. Which drug should be used to treat him? Question: An elderly patient has been diagnosed with shingles on the right lateral aspect of her trunk. It appeared initially yesterday. It is very painful. How should she be managed? Question: What advice should be given to a parent who has a child with Fifth Disease? Question: A low potency topical hydrocortisone cream would be most appropriate in a patient who has been diagnosed with: Question: Mr. Johnson is a 74 year old who presents with a pearly-domed nodular looking lesion on the back of the neck. It does not hurt or itch. What is a likely etiology? Question: A patient is found to have koilonychia. What laboratory test would be prudent to perform? Question: A 60 year-old patient is noted to have rounding of the distal phalanx of the fingers. What might have caused this? Question: Impetigo is characterized by: Question: A skin lesion fluoresces under a Wood’s lamp. What microscopic finding is consistent with this? Question: A skin disorder has a hallmark finding of silvery scales. What word below describes this common condition? Question: A patient will be taking oral terbinafine for fingernail fungus. The NP knows that: Question: Which of the following areas of the body has the greatest percutaneous absorption? Question: A patient who has been in the sun for the past few weeks is very tanned. He has numerous 3-6 mm light colored flat lesions on his trunk. What is the likely etiology? Question: The nurse practitioner is examining a 3-month old infant who has normal development. She has identified an alopecic area at the occiput. What should be done? Question: A patient calls your office. He states that he just came in from the woods and discovered a tick on his upper arm. He states that he has removed the tick and the area is slightly red. What should he be advised? Question: An example of a first generation cephalosporin used to treat a skin infection is: Question: Which of the following skin lesions in the elderly is a premalignant condition? Question: A 74 year-old is diagnosed with shingles. The NP is deciding how to best manage her care. What should be prescribed? Question: A child with a sandpaper textured rash probably has: Question: Patients with atopic dermatitis are likely to exhibit: Question: The most common place for basal cell carcinoma to be found is the: Question: A key component of the approach to a patient who has atopic dermatitis is hydration. Which agent should be avoided? Question: A young child has developed a circumferential lesion on her inner forearm. It is slightly raised, red and is pruritic. It is about 2.5 cm in diameter. This is probably related to: Question: A patient has used a high potency topical steroid cream for years to treat psoriasis exacerbations when they occur. She presents today and states that this cream “just doesn’t work anymore.” What word describes this? Question: A 28 year-old has thick, demarcated plaques on her elbows. Which features are suggestive of psoriasis? Question: What finding characterizes shingles? Question: A patient presents with small vesicles on the lateral edges of his fingers and intense itching. On close inspection, there are small vesicles on the palmar surface of the hand. What is this called? Question: A patient exhibits petechiae on both lower legs but has no other complaints. How should the NP proceed? Question: A 16 year-old male has nodulocystic acne. What might have the greatest positive impact in managing his acne? Question: A patient with a positive history of a tick bite about 2 weeks ago and erythema migrans has a positive ELISA for Borrelia. The Western blot is positive. How should he be managed? Question: A pregnant mother in her first trimester has a 5 year-old who has Fifth Disease. What implication does this have for the mother? Question: A patient is diagnosed with tinea pedis. A microscopic examination of the sample taken from the infected area would likely demonstrate: Question: A topical treatment for basal cell carcinoma is: Question: The best way to evaluate jaundice associated with liver disease is to observe: Question: A patient has been diagnosed with MRSA. She is sulfa allergic. Which medication could be used to treat her? Question: An adolescent has acne. The nurse practitioner prescribed a benzoyl peroxide product for him. What important teaching point should be given to this adolescent regarding the benzoyl peroxide? Question: Which of the following lesions never blanches when pressure is applied? Question: A patient with a primary case of scabies was probably infected: Question: The lesions seen in a patient with folliculitis might be filled with: Question: The term caput succedaneum refers to: Question: The primary therapeutic intervention for patients who present with hives is: Question: A patient has a lower leg wound that appears infected. It is red, warm to touch and edematous. He had an acute onset of pain, symptoms, and low grade fever. What is this? Question: The main difference between cellulitis and erysipelas is the: Question: A “herald patch” is a hallmark finding in which condition? Question: Most cases of atopic dermatitis exacerbation are treated with: : Question: A patient has suspected scarlet fever. He likely has a sandpaper rash and: Question: A 68 year old female adult with pendulous breasts complains of “burning” under her right breast. The nurse practitioner observes a malodorous discharge with mild maceration under both breasts. What is this? Question: A patient presents with plaques on the extensor surface of the elbows, knees, and back. The plaques are erythematous and there are thick, silvery scales. A child has 8-10 medium brown café au lait spots > 1 cm in diameter. The differential diagnosis should include: Question: The most common form of skin cancer is: Question: The nurse practitioner identifies satellite lesions in a 6 month-old infant. These are: Question: A patient has seborrheic dermatitis. Which vehicle would be most appropriate to use in the hairline area to treat this? Question: An example of a premalignant lesion that develops on sun-damaged skin is: Question: A 9 year-old female has presented to your clinic because of a rash on the left, upper area of her anterior trunk. She is embarrassed and very reticent to lift her blouse because her nipple will be exposed. How should the NP proceed? Question: A 6 year-old patient with sore throat has coryza, hoarseness, and diarrhea. What is the likely etiology? Question: A 9 year-old has been diagnosed with chickenpox. A drug that should be avoided in him is: Question: Which of the following antibiotics may increase the likelihood of photosensitivity? Question: A patient with diabetes has a right lower leg that has recently become edematous, erythematous, and tender to touch over the anterior shin. There is no evidence of pus, but the leg is warm to touch. What is the most likely diagnosis to consider? Question: A 70 year-old is diagnosed with multiple cherry angiomas. The nurse practitioner knows that: Question: A 15 year-old male has worked this summer as a lifeguard at a local swimming pool. He complains of itching in the groin area. He is diagnosed with tinea cruris. The nurse practitioner is likely to identify: Question: Which chronic skin disorder primarily affects hairy areas of the body? Question: A patient reports to the minor care area of the emergency department after being bitten by a dog. The patient states that the dog had a tag around his neck and had been seen roaming around the neighborhood. The dog did not exhibit any odd behavior. How should this be managed? Question: A 3 year-old female had a fever of 102 degrees F for 3 days. Today she woke up from a nap and is afebrile. She has a maculopapular rash. Which statement is true? Question: A patient has a “herald patch” and is diagnosed with pityriasis rosea. Where is the “herald patch” found? Question: Which test is NOT suitable to diagnose shingles if the clinical presentation is questionable? Question: A 4 year-old has been diagnosed with measles. The nurse practitioner identifies Koplik’s spots. These are: Question: A 74 year-old male patient has sustained a laceration to his foot. His last tetanus shot was more than 10 years ago. He has completed the primary series. What should be recommended? Question: Hand-foot-and-mouth disease and herpangina: Question: A 6 year-old has been diagnosed with Lyme disease. Which drug should be used to treat him? Question: The nurse practitioner examines a patient who has had poison ivy for 3 days. She asks if she can spread it to her family members. The nurse practitioner replies: Question: Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm should take place: Question: What would be age appropriate anticipatory guidance for the parent of a 9 month-old infant? . Question: How often should hearing be screened with audiometry in older adults? Question: Which recommendation below reflects CDC’s recommendation for administration of the zoster vaccine? Question: A one year-old patient’s mother reports allergy to gelatin. The mother describes the reaction as “lips swelling and breathing difficulties which necessitated a trip to the emergency department”. Which immunizations should be avoided? Question: A 20 year old student has an MMR titer that demonstrates an unprotective titer for rubella. She is HIV positive. Which statement is true? Question: Two common causes of weight loss in the elderly are: Question: An older adult has osteopenia. Her healthcare provider has recommended calcium 500 mg three times daily. What is the most common side effect of calcium supplementation? Question: A contraindication to giving MMR is: Question: MMR immunization is safe in children: Question: The Framingham study of cardiovascular disease initiated in the early 1970s is an example of a: Question: What should the nurse practitioner recommend to any elder taking medications? Question: What pharmacokinetic factor is influenced by a decrease in liver mass in an elderly adult? Question: In elderly females, which screening test has demonstrated greatest reduction in mortality from cancer? Question: A seven year-old entered the clinic one month ago. There was no evidence that he had any immunizations. He was given hepatitis B, DTaP, IPV, varicella, and MMR. If he returns today, which immunizations can he receive? Question: A patient who is 62 years old asks if she can get the shingles vaccine. She has never had shingles but states that she wants to make sure she doesn’t get it. What should the nurse practitioner advise? Question: A 58 year-old patient has an annual exam. A fecal occult blood test was used to screen for colon cancer. Three were ordered on separate days. The first test was positive; the last two were negative. How should the nurse practitioner proceed? Question: A pregnant patient is concerned because her 12 month-old needs an MMR immunization. What should the NP advise this patient? Question: A patient is 86 years-old and functions independently. He has hypertension, hyperlipidemia, BPH, and flare-ups of gout. His last colonoscopy was at age 76 years. What should he be advised about having a colonoscopy? Question: A criterion for medication choice in an older adult is: Question: An oral antifungal agent is commonly used to treat tinea unguium. The difficulty in treating an older adult with this is infection is: Question: Head circumference should be measured until a child has attained: Question: What is true regarding the “shingles” vaccine given to adults at or after age 50? Question: What is the most common nutrition syndrome in elderly patients? Question: A mammogram in a healthy 50 year-old female patient is considered to be an example of: Question: A 12 month-old is here today to be vaccinated with varicella. A patient’s mother reports that her 12 month- Question: A side effect of DTaP that should be reported is: Question: The incidence of osteoporosis in the elderly is high. Which characteristics below would increase the risk of osteoporosis in an elderly male patient? Question: A 76 year-old patient who is very active has elevated cholesterol and LDLs. He had been treated for hypertension for > 10 years with near normal blood pressures. What is the current recommendation for managing his lipids? Question: Which finding below is considered “within normal limits”? Question: A patient who has been treated for hypothyroidism presents for her annual exam. Her TSH is 4.1 (normal = 0.4- 3.8). She feels well. How should she be managed? Question: A 6-month old child comes into the clinic for immunizations. Which item below allows a delay in his getting immunizations today? Question: What is the recommendation from American Cancer Society for assessment of the prostate gland in a man who is 45 years old and of average risk for development of prostate cancer? He should have: Question: A patient who wrote a living will has changed his mind about the initiation of life-sustaining measures. What statement is true about this? Question: What is the recommendation for daily multivitamin supplementation in older adults? Question: A 7 year-old enters the nurse practitioner clinic. There is no evidence that he has received any immunizations. What should be administered today? Question: An octogenarian asks the nurse practitioner if it is OK for him to have an alcoholic beverage in the evenings. There is no obvious contraindication. How should the nurse practitioner respond? Question: A nurse practitioner examined a patient who had been bitten by her husband during an assault. There were numerous bite marks and lacerations on the patient’s forearms. The nurse practitioner sutured the lacerations, though this was contraindicated because of the highly infectious nature of human bites. The patient suffered no ill effects after suturing. How can this be described? Question: A nurse practitioner is working in a minor care area of an emergency department. An illegal immigrant has a puncture wound caused by an unknown sharp object in a trash container. A dirty needle is suspected. The nurse practitioner: Question: Laura admits to Anne that she keeps the medications and takes them occasionally. She states that sometimes she gives them to patients who can’t afford these medications. What is Anne’s first professional responsibility? Question: A nurse practitioner gives a patient 2 weeks of sample medications that will be taken once daily by the patient. The sample medications are packaged by the drug manufacturer. The nurse practitioner’s actions are an example of: Question: A patient that you are caring for in your clinic has Medicare Part B. What does this mean? Question: An elderly male with moderately severe dementia presents with his caregiver daughter. His BMI is 18. His clothes have food stains on them and he looks as though he hasn’t been bathed in days. How should the nurse practitioner handle this? Question: Prescriptive authority: authority, other much narrower authority. Question: A nurse practitioner examined a patient who had been injured by a cat. There was a 4 centimeter gaping laceration on the patient’s forearm. The nurse practitioner sutured the laceration. The patient subsequently became infected, needed hospital admission, and required IV antibiotics with incision and drainage. How can this situation be characterized? Question: The next two questions relate to each other. 18. Anne and Laura work as nurse practitioner (NP) partners in an NP practice. Anne learns that Laura frequently changes patient’s narcotic prescriptions to a different dosage, and then requests that the patient give her the remaining narcotic medications. Some patients have called Anne aside to tell her of this. How can Laura’s actions best be characterized? Question: You are volunteering at a clinic that cares for homeless patients. What’s the most important aspect of a patient’s first visit? Question: The legal authority to practice as a nurse practitioner in any state is determined by: Question: Mr. Bowers, a 97 year old, is not able to make an informed decision due to mental incapacity. He does not have advanced directives but only a durable power of attorney (DPA). How should the nurse practitioner proceed? Question: How would you create a therapeutic relationship with a patient? Question: A nurse practitioner knows that she is HIV positive. She is employed in a private clinic and performs wellness exams on ambulatory adults. The nurse practitioner: Question: A nurse practitioner’s scope of practice is influenced by a number of factors. Which one does not influence scope of practice? Question: A nurse practitioner is working in a minor care clinic. She realizes that a patient with a minor laceration does not have insurance and is using his brother’s insurance information today so that his visit will be covered. How should she proceed? Question: What would be the study of choice to determine the cause of a cluster of adult leukemia cases found in an isolated area of a rural state? Question: Standards of practice are established to: Question: The nurse practitioner decides to study a group of patients who are trying to quit smoking. They all will be taking the same type of medication for 42 days to help them stop smoking. The patients have agreed to return to the clinic once weekly for the study’s duration. This type of study design is termed: Question: The nurse practitioner is examining an elderly patient with dementia. She is noted to have bruises on her arms and on her posterior thoracic area. The nurse practitioner suspects elder abuse, but cannot be certain. The daughter of this elderly patient is her caregiver. The daughter is a patient of the nurse practitioner. What should the nurse practitioner do? Question: The Medicaid funded health program is: Question: A nurse practitioner has worked for a large hospital as an RN. As a new nurse practitioner, she has developed a nurse practitioner managed clinic for hospital employees and is employed by the hospital. This nurse practitioner is described as a(n): Question: Which study listed below is considered an experimental study? Question: Certification: is required by all 50 states.validates competence Question: Who certifies nurse practitioners? Question: The name given to subjects in a research study who do not have the disease or condition being studied, but who are included in the study for comparison are: Question: A nurse practitioner has agreed to participate in the Medicare health insurance program. Medicare paid 80% of the charges billed for a clinic visit. What can be done about the other 20% that is owed? Question: Licensure is: Question: A patient you are examining in the clinic states that he has Medicare Part A only. What does this mean? Question: An older adult was screened for colorectal cancer and had a positive screen. She went on to have a colonoscopy that was normal. She does not have colorectal cancer. The screen was a: Question: A liability policy that pays claims only during the period that the policy is active is termed: Question: A liability policy which pays claims even after the policy is no longer active is termed: Question: A nurse practitioner is volunteering in a homeless clinic to gain clinical experience. Which statement is true about this? Question: A nurse practitioner is taking care of a patient with health insurance and allergic complaints. The NP is aware that the patient is not using the prescribed allergy medication for her. Instead, the patient is giving the medication to her husband because he does not have insurance. What should the NP do? Question: In a research study, the difference between the smallest and largest observation is the: Question: The research design that provides the strongest evidence for concluding causation is: Question: A nurse practitioner (NP) works in an HIV exclusive practice. In talking with a patient, the NP learns that the patient’s sister lives next door to the NP. When the NP sees her neighbor (the patient’s sister), the NP states that she met her sister in the clinic today. The neighbor replies, “Don’t you work in an HIV clinic?” How can this situation be characterized? Question: What is the usual age for vision screening in young children? Question: A patient has nasal septal erosion with minor, continuous bleeding. There is macerated tissue. What is a likely etiology? Question: The nurse practitioner performs a fundoscopic exam on a patient who has recently been diagnosed with hypertension. What is the significance of AV nicking? Question: Which statement about serous otitis media is correct? Question: A medication considered first line for a patient with allergic rhinitis is a: Question: What clinical finding necessitates an urgent referral of the patient to an emergency department? Question: A patient stated that his ears felt stopped up. He pinched his nose and blew through it forcefully. The nurse practitioner diagnosed a ruptured left tympanic membrane. What would indicate this? Question: A 70 year-old patient in good health is found to have a large, white plaque on the oral mucosa of the inner cheek. There is no pain associated with this. What is a likely diagnosis? Question: Which of the following will decrease the risk of acute otitis media in a 6 month old? Question: Swimmer’s ear is diagnosed in a patient with tragal tenderness. What other symptom might he have? Question: In a patient with mononucleosis, which laboratory abnormality is most common? Question: A common complaint in older patients who have cataracts is: Question: A 70 year-old female states that she sees objects better by looking at them with her peripheral vision. She is examined and found to have a loss of central vision, normal peripheral vision, and a normal lens. This best characterizes: Question: Arcus senilis is described as: Question: A patient who is 52 years old presents to your clinic for an exam. You notice a yellowish plaque on her upper eyelid. It is painless. What should the NP assess? Question: The most common cause of acute pharyngitis in children is: Question: In a patient who is diagnosed with mastoiditis, which of the following is most likely? Question: A patient has 2 palpable, tender, left pre-auricular nodes that are about 0.5 cm in diameter. What might also be found in this patient? Question: A 45 year-old patient describes a spinning sensation that has occurred intermittently for the past 24 hours. It is precipitated by position changes like rolling over in bed. During these episodes, he complains of intense nausea. Which symptom is most characteristic of vertigo with a peripheral etiology? Question: On routine exam, a 15 year-old patient's tympanic membrane (TM) reveals a tiny white oblong mark just inferior to the umbo on the surface of the TM. The patient has no complaints of ear pain and gross hearing is intact. What is this? Question: Papilledema is noted in a patient with a headache. What is the importance of papilledema in this patient? Question: A patient diagnosed with Strept throat received a prescription for azithromycin. She has not improved in 48 hours. What course of action is acceptable? Question: A teenager with fever and pharyngitis has a negative rapid strept test. After 24 hours, the throat culture reveals “normal flora". Which conclusion can be made? Question: A 4 year-old child with otitis media with effusion: Question: A patient with environmental allergies presents to your clinic. She takes an oral antihistamine every 24 hours. What is the most effective single maintenance medication for allergic rhinitis? Question: A patient describes a sensation that "there is a lump in his throat". He denies throat pain. On exam of the throat and neck, there are no abnormalities identified. What is the most likely reason this occurs? Question: The most common complication of influenza is: Question: Which of the following is most likely observed in a patient with allergic rhinitis? Question: A nurse practitioner performs a fundoscopic exam. He identifies small areas of dull, yellowish-white coloration in the retina. What might these be? Question: The throat swab done to identify Streptococcal infection was negative in a 12 year-old female with tonsillar exudate, fever, and sore throat. What statement is true regarding this? Question: A 6 month-old infant has a disconjugate gaze. The nurse practitioner observes that the 6 month old tilts his head when looking at objects in the room. Which statement is true? Question: Group A Strept pharyngitis: Question: A 3 year-old has fluid in the middle ear that does not appear infected. The eardrum appears normal. This is referred to as: Question: Conjunctivitis: Question: A patient who presents with a complaint of sudden decreased visual acuity has a pupil that is about 4 mm, fixed. The affected eye is red. What might be the etiology? Question: Which long-acting antihistamine listed below is sedating? Question: A 2 year-old has a sudden onset of high fever while at daycare. The daycare attendant describes a seizure in the child. The child is brought to the clinic; neurologically he appears normal. His body temperature is 99.9 degrees F after receiving ibuprofen. He is diagnosed with otitis media. How should the nurse practitioner manage this? Question: At what age should screening for oral health begin? Question: A patient with diarrhea has a positive enzyme immunoassay for C. difficile. He is on clindamycin for a tooth abscess. How should he be managed? Question: Which medication listed below is considered ototoxic? Question: A patient has been diagnosed with acute rhinosinusitis. Symptoms began 3 days ago. Based on the most likely etiology, how should this patient be managed? Question: A patient has been diagnosed with mononucleosis. Which statement is correct? Question: An older adult has a cold. She calls your office to ask for advice for an agent to help her runny nose and congestion. She has hypertension, COPD, and glaucoma. What agent is safe to use? Question: A patient reports a penicillin allergy. What question regarding the allergy should the nurse practitioner ask to determine whether a cephalosporin can be safely prescribed? Question: A 6 day-old has a mucopurulent eye discharge bilaterally. What historical finding explains the etiology of the discharge? Question: A 4 month-old infant has thrush. The mother is breastfeeding. She reports that her nipples have become red, irritated, and sensitive. What should the nurse practitioner advise the mother of this baby to treat thrush? Question: How should the class effect of the nasal steroids be described? Question: A 70 year-old male has a yellowish, triangular nodule on the side of the iris. This is probably: Question: A patient with allergic rhinitis developed a sinus infection 10 days ago. He takes fexofenadine daily. What should be done with the fexofenadine? Question: A patient who is 65 years old states that she has “hayfever” and has had this since childhood. What agent could be safely used to help with rhinitis, sneezing, pruritis, and congestion? Question: A patient presents to your clinic with a painless red eye. Her vision is normal, but her sclera has a blood red area. What is this termed? Question: A 30 year old male has been diagnosed with non-allergic rhinitis. What finding is more likely in non-allergic rhinitis than allergic rhinitis? Question: An elderly patient who has a red eye with tearing was diagnosed with conjunctivitis. What characteristics below indicate viral conjunctivitis? Question: An NP examines a screaming 2 year-old. A common finding is: Question: When examining the vessels of the eye: Question: A patient presents with severe toothache. She reports sensitivity to heat and cold. There is visible pus around the painful area. What is this termed? Question: What medication should always be avoided in patients with mononucleosis? Question: A 3 year-old has been diagnosed with acute otitis media. She is penicillin allergic (Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction). How should she be managed? Question: Acute otitis media can be diagnosed by identifying which otic characteristic(s)? Question: The hearing loss associated with aging involves: Question: A 32 year-old patient is a newly diagnosed diabetic. She has developed a sinus infection. Her symptoms have persisted for 10 days. Six weeks ago she was treated with amoxicillin for an upper respiratory infection. It cleared without incident. What should be recommended today? Question: Which of the following symptoms is more indicative of a bacterial sinusitis than viral? Question: A 70 year-old patient is concerned and comes into the clinic with complaints of headache, slurred speech, and onset of symptoms within the last 60 minutes. When the patient is examined, her complaints are confirmed by the examiner. What is the likely etiology of this event? Question: A 2 month-old infant has an asymmetric Moro reflex. What statement is true? Question: The classic description of transient ischemic attack is “ a sudden onset of focal neurological symptoms that lasts less than”: one minute.five minutes.one hour. Incorrect24 hours. Correct Question: Which reflexes might a one month-old infant be expected to exhibit? Question: The "get up and go" test in an elderly patient is used to evaluate: Question: A patient complains of right leg numbness and tingling following a back injury. He has a diminished right patellar reflex and his symptoms are progressing to both legs. What test should be performed? Question: An elderly patient is at increased risk of stroke and takes an aspirin daily. Aspirin use in this patient is an example of: Question: A patient presents to the NP clinic with a complaint of nocturnal paresthesias. What is the likely underlying etiology? Question: Mrs. Jopson is unable to name a familiar object. How is this described? Question: Mrs. Johnson is an 89 year-old resident at a long-term care facility. Her state of health has declined rapidly over the past 2 months, and she can no longer make her own decisions. Her daughter requests a family conference with the nurse practitioner. Some important principles that need discussion at this time, if not previously documented, are: Question: A patient diagnosed with cluster headaches: Question: A patient who had a stroke has recovered and is performing all of her activities of daily living. Taking aspirin for stroke prevention is an example of: Question: An elderly patient with organic brain syndrome is at increased risk of elder abuse because she: Question: When should medications be started in a patient diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease? Question: The Snellen chart is used to assess: distant vision Question: A 26 year-old patient with long history of chronic sinusitis presents today with temperature of 103.2 F, headache, and stiff neck. Which finding below should make the nurse practitioner suspect meningitis? Question: A patient is diagnosed with carpal tunnel syndrome. Which finger is not affected by carpal tunnel syndrome? Question: A 62 year-old female patient presents to the clinic with very recent onset of intermittent but severe facial pain over the right cheek. She is diagnosed with trigeminal neuralgia. What assessment finding is typical of this? Question: In a three year-old with fever, which finding might precipitate a febrile seizure? Question: An elderly patient has an audible carotid bruit. He has a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and a myocardial infarction 5 years ago. The finding of a bruit indicates that the patient: Question: A family member of a newly diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease patient asks how long the patient will have to take donepezil, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, before learning whether it is beneficial or not. You reply: Question: All of the following characteristics may be found in an older adult with dementia. Which one is common in a patient with Alzheimer’s disease, but uncommon in a patient with another type of dementia? Question: A patient with migraine headaches and hypertension should receive which medication class with caution? Question: A patient who is 60 years old complains of low back pain for the last 5-6 weeks. She states that the severity is about 4/10 and that she gets no relief from sitting, standing, or lying. The NP should consider: Question: Most patients with migraine headache symptoms do not need imaging for diagnosis. Which finding in a patient with migraine headache symptoms would compel the examiner to order an imaging study? Question: A patient reports a history of transient ischemic attack (TIA) 6 months ago. His daily medications are lisinopril, pravastatin, and metformin. After advising him to quit smoking, what intervention is most important in helping to prevent stroke in him? Question: A patient who is 82 years old is brought into the clinic. His wife states that he was working in his garden today and became disoriented and had slurred speech. She helped him back into the house, gave him cool fluids, and within 15 minutes his symptoms resolved. He appears in his usual state of health when he is examined. He states that although he was scared by the event, he feels fine now. How should the nurse practitioner proceed? Question: A 72 year-old patient with a relatively benign medical history complains of new onset headache associated with abrupt onset of visual disturbances. Her sedimentation rate is elevated. Her neuro exam is otherwise normal. What is the most likely reason for her symptoms? Question: A nurse practitioner is assessing a 3 day old infant’s head. What would be a normal observation in a healthy 3 day old infant who is crying? Question: What is the earliest age that an average child would appropriately receive construction paper and a pair of scissors with rounded points? Question: Which reflex may be present at 9 months of age during sleep? Question: A 68 year-old smoker with a history of well controlled hypertension, describes a syncopal episode which occurred yesterday while mowing his lawn. Today, he has no complaints. Initially, the NP should: . Question: The most common polyneuropathy in the elderly is: Question: Restless legs syndrome is part of the differential diagnosis for Mr. Wheaton. What should be part of the laboratory workup? Question: A 70 year-old male who is diabetic presents with gait difficulty, cognitive disturbance, and urinary incontinence. What is part of the nurse practitioner’s differential diagnosis? Question: Which symptom is INCONSISTENT with irritable bowel syndrome in older adults? Question: A 70 year-old patient states that he had some bright red blood on the toilet tissue this morning after a bowel movement. What is the most likely cause in this patient? Question: A 24 year-old male has recently returned from a weekend camping trip with friends. He has ulcerative colitis and history of migraine headaches. He reports a two-day history of headache, nausea, and vomiting with weakness. Which of the following is least likely as a possible cause? Question: A patient has suspected peptic ulcer disease. Her symptoms occur a few hours after eating. She likely has a: Question: An 84 year-old presents with a stated involuntary weight loss. He states that he’s lost about 6 pounds in the last 6 or 8 weeks. What statement below is NOT part of the assessment? Question: Which choice contains 3 medications that should have liver function tests measured prior to initiation of the medications? Question: A 20 year-old female patient presents with tenderness at McBurney’s point. Appendicitis is considered. What laboratory test would be LEAST helpful to the nurse practitioner in excluding appendicitis as part of the differential? Question: A patient has the following laboratory values. What does this mean? Question: A 6 week-old male infant is brought to the nurse practitioner because of vomiting. The mother describes vomiting after feeding and feeling a “knot” in his abdomen especially after he vomits. The child appears adequately nourished. What is the likely etiology? Question: A mother of a 4 week-old infant visits your office. She states that her baby is vomiting after feeding and then cries as if he is hungry again. What should the nurse practitioner assess? Question: The relationship between colon polyps and colon cancer is: Question: Which of the following is appropriate for initiation of an 8 week-old with gastroesophageal reflux? Question: A patient has a positive hepatitis B surface antibody. This means: Question: An elderly adult has chronic constipation. How should this be managed initially? Question: GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) and physiologic reflux have similar characteristics. However, physiologic reflux: Question: Children with an inguinal hernia: Question: Which of the following would be usual in a patient with biliary colic? Question: A 40 year-old patient has the following laboratory values. How should they be interpreted? HBsAg (-), Question: A 95 year-old male has lost muscle mass as he has aged. He does not have any underlying disease that has caused this loss. What is this termed? Question: Hirschsprung's disease is characterized by: Question: A patient is in the clinic with a 36 hour history of diarrhea and moderate dehydration. Interventions should include: Question: A 63 year-old male has been your patient for several years. He is a former smoker who takes simvastatin, ramipril, and an aspirin daily. His blood pressure and lipids are well controlled. He presents to your clinic with complaints of fatigue and “just not feeling well” for the last few days. His vital signs and exam are normal. His hepatitis panel is negative for infectious hepatitis. What is the most likely cause of his elevated liver enzymes? Question: A patient with a suspected inguinal hernia should be examined: Question: An elderly adult with an appendicitis is unlikely to exhibit: Question: A patient with gall bladder disease has classic symptoms. Which symptom below is NOT classic of gallbladder disease? Question: A fecal occult blood test (FOBT) obtained during a rectal examination: Question: Which description is more typical of a patient with acute cholecystitis? Question: A 14 year-old patient has an acute, painless groin swelling. What tool would yield the most information to identify the etiology of the swelling? Question: The most common place for indirect inguinal hernias to develop is: Question: A patient has a positive anti-HCV test. This means: Question: A 5 year-old has been diagnosed with pinworms. He lives with his mother. There are no other members of the household. How should his mother be managed? Question: Older adults frequently complain of constipation. Which medication listed below does NOT increase chance of constipation in an older adult? Question: What medication used to treat patients who have GERD provides the fastest relief of heartburn symptoms? Question: The most common cause of diarrhea in adults is: Question: A patient has hepatitis B. He probably has a predominance of: Question: A 19 year-old female presents with lower abdominal pain that began about 12 hours ago. She is febrile. She denies vaginal discharge. Which choice below is the least likely cause of her symptoms? Question: What medication may be used to treat GERD if a patient has tried over the counter ranitidine without benefit? Question: A 56 year-old male patient has been diagnosed with an inguinal hernia. What symptom would make the nurse practitioner suspect an incarcerated hernia? Question: The two tests which can indicate with certainty that a patient has hepatitis B at present are: Question: Many older adults have cachexia. What characterizes this? Question: A patient has been diagnosed with Hepatitis B. The most common reported risk factor is: Question: A mother presents with her one-month old infant. She reports that he cries inconsolably every evening after his first evening feeding. She asks for help. What should be done? Question: A 3 day-old infant weighed 8 pounds at birth. Today he weighs 7.5 pounds. How should this be managed? Question: What choice below is most commonly associated with pancreatitis? Question: What medication listed below could be used to increase appetite in an anorexic patient? Question: A 15 year-old is about 10% below her ideal body weight. She complains of dizziness when she stands up. Laboratory studies were performed. Besides malnutrition, what else could account for her dizziness? Question: A 40 year-old patient has the following laboratory values. How should they be interpreted? HBsAg (-), Question: What is true regarding overweight states in older adults? Question: A 45 year-old patient has the following laboratory values. How should they be interpreted? HBsAg (+), HBsAb (-), HBcAb (+) Question: Which medication listed below can exacerbate the symptoms of GERD? Question: A patient has been prescribed metronidazole for treatment of C. difficile. What should be avoided in this patient? Question: A 50 year-old with a history of consumption of 3-4 alcoholic drinks daily and weekend binges has elevated liver enzymes. Which set of enzymes is most representative of this patient? Question: The most common risk factor for developing hepatitis B is: Question: An inguinal hernia is palpated on a male patient by an examiner. Which word below best describes what the hernia feels like when touched by the examiner? . Question: The most common symptoms associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) are heartburn and: Question: Which patient has NO indication for further evaluation of his diarrhea? One with: Question: A patient has elevated liver enzymes. ALT = 642 U/L; AST= 150 U/L. What is the likely etiology of the elevation? Question: Which of the following symptoms is typical of GERD? Question: An 83 year-old patient is diagnosed with diverticulitis. Where is her pain typically located? Question: A 10 year-old female presents with a three-month history of abdominal pain. She has been diagnosed with recurrent abdominal pain. During the interview the nurse practitioner is likely to elicit a finding of: Question: The most common reason that older adults develop peptic ulcer disease is: Question: An older adult has suspected Vitamin B12 deficiency. Which of the following lab indices is more indicative of a Vitamin B12 deficiency? Question: A patient with diarrhea is tested for C. difficile. How soon should the enzyme immunoassay (EIA) yield results? Question: A patient has the following laboratory value. What is the clinical interpretation? Question: A 35 year-old patient has the following laboratory values. How should they be interpreted? HBsAg (-), HBsAb (-), HBcAb (-) Question: An older patient presents with left lower quadrant pain. If diverticulitis is suspected, how should the NP Question: Which set of symptoms is most likely in a patient infected with C. difficile? Question: Which characteristic does not describe hemorrhoids? Question: LFTs should be checked initially in patients who take: Question: A patient has the following laboratory value. What does this mean? Hepatitis B surface antigen (+) Question: The three most common causes of bacterial diarrhea in the US are Salmonella, Campylobacter, and: Question: Most patients who have acute hepatitis B infection: Question: A patient has been diagnosed with viral gastroenteritis. He has nausea, vomiting, and has started having lower abdominal cramps. What is the most effective intervention for him? Question: The initial step in the management of encopresis is: Question: A patient has been diagnosed with Hepatitis A. The most common reported risk factor is: Question: A healthcare provider (“the HCP”) was stuck with a needle from a patient suspected to be infected with HIV (“the patient”). A rapid HIV test was performed and was found to be positive. This means that the: Question: A 70 year-old presents to the nurse practitioner’s office for a well exam today. What medication probably has no affect on screening for occult blood in the stool? Question: A patient with eczema asks for a recommendation for a skin preparation to help with xerosis. What should the NP respond? Question: The early signs and symptoms of appendicitis in an adult: Question: An elderly adult has constipation. A supplement known to cause constipation is: Question: Which imaging study of the abdomen would be LEAST helpful in diagnosing an acute appendicitis? Question: Which of the following is NOT part of the prescription for management of weight loss in older adults? Question: Most patients who have acute hepatitis A infection: Question: A patient has a positive hepatitis B surface antibody. His core antibody is negative. This indicates: Question: A 37 year-old has routine blood work performed during an annual exam. He is found to have elevated liver enzymes. On exam he has a tender, enlarged liver. How should the nurse practitioner proceed? Question: Mrs. Lovely, an 84 year old complains of fecal incontinence. A likely cause is: Question: An 83 year-old patient is diagnosed with diverticulitis. The most common complaint is: Question: A patient had an acute onset of right upper quadrant pain that has lasted for the past 3 days. He has low-grade fever. Which lab test(s) will be elevated if he has pancreatitis? Question: A 48 year-old patient has the following laboratory values. How should they be interpreted? HCV IgG (+), RIBA (radio immuno blot assay) (+) Question: A 43 year-old patient who has been diagnosed with hepatitis B has the following laboratory values. How should they be interpreted based on these values? HCV IgG (-), RIBA (radio immuno blot assay) (-) Question: A 26 year-old female with low-grade fever and nausea has pain at McBurney’s point. The most appropriate action by the NP is to: Question: What is the simplest screen for nutritional adequacy in elderly patients? Question: A 44 year-old non-smoker is diagnosed with pneumonia. He is otherwise healthy and does not need hospitalization at this time. Which antibiotic can be used for empirical treatment according to the 2007 Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society? Question: An independent 82 year-old male patient is very active but retired last year. His total cholesterol and LDLs are moderately elevated. How should the NP approach his lipid elevation? Question: A characteristic of an ACE inhibitor induced cough is that it: Question: A patient with newly diagnosed heart failure has started fosinopril in the last few days. She has developed a cough. What clinical finding can help distinguish the etiology of the cough as heart failure? Question: A 28 year-old has a Grade 3 murmur. Which characteristic indicates a need for referral? Question: You are managing the warfarin dose for an older adult with a prosthetic heart valve. Which situation listed requires that warfarin be discontinued now? Question: According to the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, which characteristic listed below is a coronary heart disease (CHD) risk equivalent; that is, which risk factor places the patient at similar risk for CHD as a history of CHD? Question: A 40 year-old patient who has aortic stenosis wants to know what symptoms indicate worsening of his stenosis. The nurse practitioner replies: Question: How often should lipids be screened in patients who are 65 years and older if they have lipid disorders or cardiovascular risk factors? Question: A common, early finding in patients who have chronic aortic regurgitation (AR) is: Question: In older adults, the three most common ailments are: Question: Which choice below characterizes a patient with aortic regurgitation? Family Nurse Practitioner Exam Topics Just know all your lab values, screening guidelunes. Derm n what they look like plus treatment, management and propitiation, levels of research Fitzgerald has a good hierarchy that was helpful. • 53 questions on clinical management • 7 questions on professional role and policy • 16 questions on nurse practitioner and patient relationship • 39 questions on assessment of acute and chronic illness • 4 questions on research • 31 questions on health promotion and disease prevention The questions cover a range of life stages from birth to aging adult (including pregnant women), although some questions may not be precise about the stage of life. Family Nurse Practitioner Certification Exam Practice Questions 1. The nurse practitioner should order which diagnostic study to confirm a suspected diagnosis of colorectal cancer? a. Stool Hematest b. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) c. Colonoscopy d. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan 2. The nurse practitioner is determining if a client's lesions are indicative of herpes zoster. The best way to determine this is that herpes zoster lesions are typically: a. grouped vesicles occurring on lips and oral mucous membranes. b. grouped vesicles occurring on the genitalia. c. rough, fresh, or gray skin protrusions. d. grouped vesicles in linear patches along a dermatome. 3. A client with left-sided heart failure comes into the clinic complaining of increasing shortness of breath and is agitated and coughing up pink-tinged, foamy sputum. The nurse practitioner recognizes these findings as signs and symptoms of: a. right-sided heart failure. b. acute pulmonary edema. c. pneumonia. d. cardiogenic shock. 4. A nurse practitioner is assessing a client with suspected pneumothorax. To confirm the diagnosis, the nurse practitioner should order: a. arterial oxygen saturation (SaO20) monitoring. b. arterial blood gas (ABG) studies. c. hourly chest auscultation. d. a chest X-ray. 5. What diagnostic study finding helps make a diagnosis of multiple myeloma? a. Decreased serum creatinine level b. Hypocalcemia c. Bence Jones protein in the urine d. Low serum protein level 6. A nurse practitioner suspects neglect in a 3-year-old child seen in the office. What assessment findings should the nurse practitioner look for? a. Slapping, kicking, and punching others b. Poor hygiene and weight loss c. Loud crying and screaming d. Pulling hair and hitting 7. A 2-year-old child is brought clinic with a history of upper airway infection that has worsened over the past 2 days. The nurse practitioner suspects the child has croup. Signs of croup include a hoarse voice, inspiratory stridor, and a. a barking cough. b. a high fever. c. sudden onset. d. dysphagia. 8. A mother brings her 5-year-old son who is complaining of a fever and sore throat to the clinic. A nurse practitioner documents the client's tonsils as 3+. This rating means the tonsils are: a. barely visible outside the tonsillar pillar. b. halfway between the tonsillar pillar and the uvula. c. touching the uvula. d. touching each other. 9. A nurse practitioner is conducting a well-baby examination of an 8-month-old infant. Which reflex does the nurse practitioner anticipate to be present? a. Stepping b. Moro c. Plantar grasp d. Palmar grasp 10. An obese 14-year-old adolescent says that he wants to lose weight. Besides dietary intake and physical activity, what's the most important factor to assess? a. The adolescent's metabolic rate b. Who prepares the adolescent's meals c. How food is used in his home d. His educational interests NP Family Certification Risk Factors of Infection [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 100 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$20.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 15, 2020
Number of pages
100
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 15, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
74

.png)