BioChemistry > EXAM > University of South Florida BIOCHEMIST 3023 Biochem Exam 2 all in all/ Biochem Exam 2: Most commonly (All)
University of South Florida BIOCHEMIST 3023 Biochem Exam 2 all in all/ Biochem Exam 2: Most commonly tested and essential questions. Contains more than 60 questions and Answers.
Document Content and Description Below
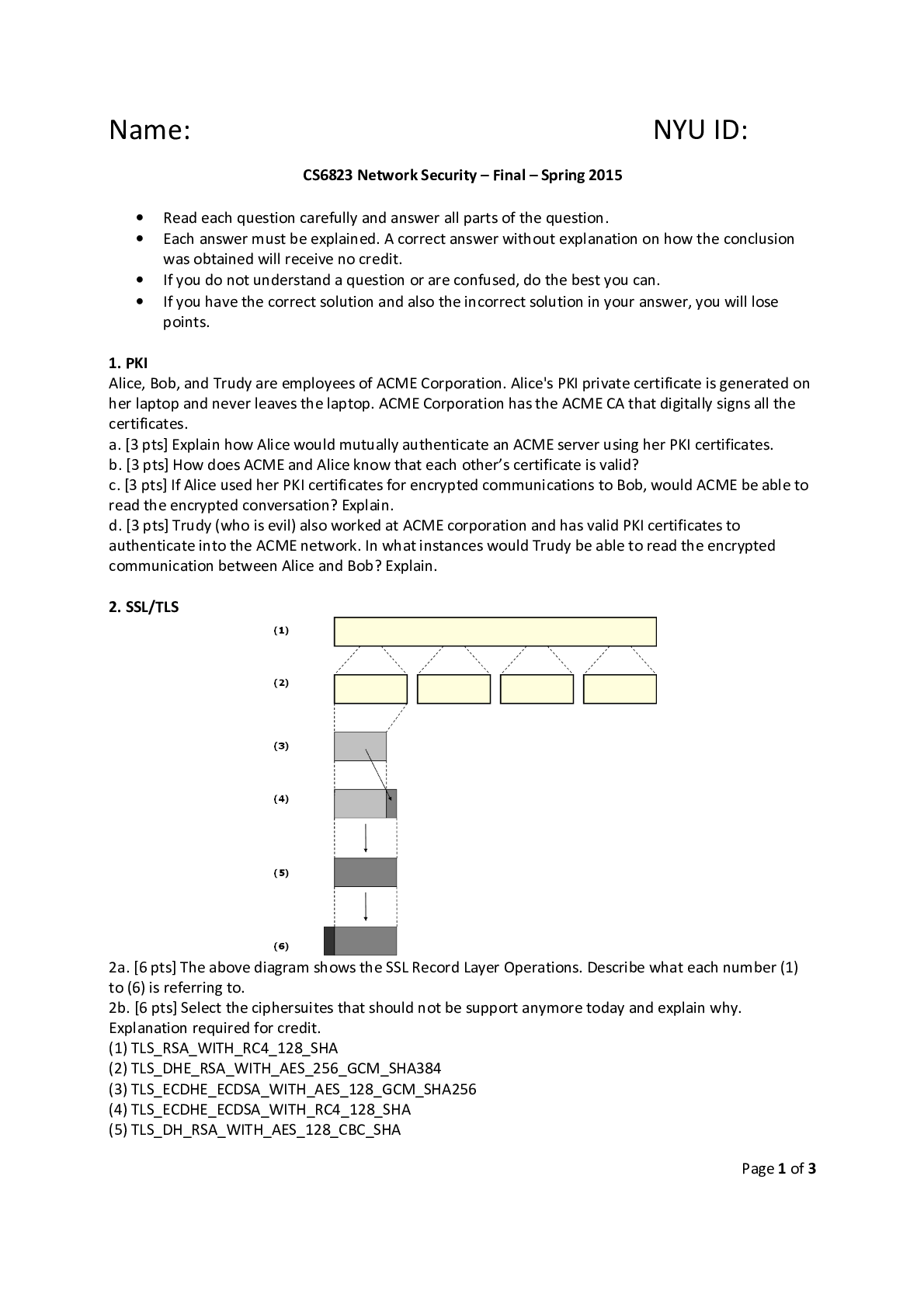
Biochem Exam 2: 1. Which enzyme is considered part of TCA and ETC? a. Malate dehydrogenase b. Citrate synthase c. Isocitrate dehydrogenase d. NADH- ubiquinone oxidoreductase e. FADH2- ubiquinone... oxidoreductase 2. A solution at pH 7 contains a weak acid, HA. The pKa of the acid is 6.5 what is the ratio of [A-/HA]? Answer: 3.16:1 3. In mitochondria, what is the expected pH of the matrix compared to the inter-membrane space? a. More acidic b. The same c. More neutral d. More basic e. Greater proton concentration 4. Compound C gives electrons to compound D, then compound D is a(n) ____ and compound C is _____ a. Oxidant, reductant b. Reductant, oxidant c. Oxidized, reduced d. Reduced, oxidized 5. When compound C gives electrons to Compound D, then Compound D was _______and Compound C was ______ a. Oxidant, reductant b. Reductant, oxidant c. Oxidized, reduced d. Reduced, oxidized 6. What provides the energy to the ATP synthase for the formation of ATP? a. Electron flow b. Proton flow c. GTP d. Phosphoryl transfer e. Equilibrium shift (km change) 7. What do cristae structures in the mitochondria provide? a. Pores for the movement of proteins b. These are the proteins found in the outer membrane c. These proteins seal the inner membrane d. These structures increase surface area of the inner membrane 8. (True / False) The amino acid T at pH 7.4 has two charged groups but is actually a net zero charge.9. 10. Which species is the reductant for the proposed ETC? a. Ickygreenol b. Barsoom c. Barstool d. Ickygreenone 11. Which species is the oxidant for the proposed ETC? a. Ickygreenol b. Barsoom c. Barstool d. Ickygreenone 12. Which series of voltages represents the correct voltages to trace the electron flow for the free calculation? a. -0.5 and -1.25 V b. +0.5 and -1.25 V c. -0.5 and +1.25 d. +0.5 and +1.25 V 13. What is the free energy gained from the electron transport chain presented? a. -34.5 kcal/mol b. +80.5 kcal/mol c. +34.5 kcal/mol d. -80.5 kcal/mol e. It cannot be determined from the information given 14. From one run of the proposed electron transport chain, how may ATP equivalents to be generated? a. 3 b. 4 c. 5 d. 6 e. 7 15.(True/False) 16.Material in figure 4? 17. What is the rate-limiting enzyme of the TCA cycle? a. Malate dehydrogenase b. Phosphofructokinase c. Citrate synthase d. Fumarase e. None of the above18. What is the material above? (FIGURE 1) a. Citrate b. Succinate c. Malate d. Acetyl CoA e. Oxaloacetate 19. What is the material in figure 2? a. Citrate b. Succinate c. Malate d. Acetyl CoA e. Oxaloacetate 20. What is the material above? (figure 3) a. Citrate b. Succinate c. Malate d. Acetyl CoA e. Oxaloacetate 21. Given radiolabeled citrate, what is the first enzyme that will produce radioactive carbon dioxide? a. Malate dehydrogenase b. Alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase c. Isocitrate dehydrogenase d. Succinate dehydrogenase e. Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase 22. Ammonium has a pKa of 9.25. 45mL of 1.00 M HCl is added to 75 mL of a 1.00 M buffer solution of this ammonium at pH 10. The resulting solution is at pH: a) 7.4 b) 8.0 c) 8.5 d) 9.0 e) This is an explosive reaction 23. In a test organism that possesses a normal TCA cycle, you determine that malate is elevated compared to control samples. Which enzymatic failure could best explain this observation?A. Citrate synthase B. Malate dehydrogenase C. Isocitrate synthase D. Fumarase E. Succinyl CoA synthetase 24. What type of reaction does the rate-liming step of the TCA perform? A. Phosphoryl transfer B. Carboxylation C. Reduction D. Oxidative decarboxylation E. Hydrolysis 25. Which enzyme activity in TCA is powered by thioester bond cleavage and makes a nucleotide triphosphate as a product? A. Citrate synthase B. Fumarase C. Succinate dehydrogenase D. Succinyl CoA synthetase E. None of the above 26. (True/False) it is reasonable to say that TCA does not make ATP directly 27. a 28. Alpha ketoglutarate can become what amino acid? A. G B. E C. N D. Q E. K 29. A 30. Using glycolysis, given that one mole of glucose is converted to one mole of pyruvate, how many ATP are generated? a. 4 b. 2 c. 3 d. 1 e. 0 31. A mad-scientist wishes to make a glycolysis inhibitor to treat gerbilitis, why is this a bad idea? A. Expect toxicity to the eye B. Expect toxicity to red blood cells C. Expect toxicity to the kidney medulla D. All of the above 32. What does regulation of hexokinase protect against A. Protection from depletion of NADH B. Protection from depletion of NAD+ C. Protection from depletion of ADP D. Protection from depletion of Pi E. Protection from accumulation of fructose 1,6-biphosphate33. Which of the following glycolytic enzymatic reactions is freely reversible in cellular conditions? A. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate B. Phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate C. Glucose to glucose 6-phosphate D. Fructose-6 phosphate to fructose 1, 6 biphosphate E. None of the above reactions are freely reversible 34. What is the name of the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of the correct answer to the previous question? a. Phosphoglycerate mutase b. Phosphoglycerate kinase c. Enolase d. Triose phosphate isomerase e. None of the above are correct because none of the previous reactions were reversible 35. If ATP is elevated in cells, what is the effect on the glycolysis pathway in those cells? a. Glycolysis is unaffected by ATP b. Levels of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate will decrease c. Phosphofructokinase activity will be increased d. Pyruvate kinase activity will be increased e. Citrate synthase activity will be decreased 36. Which of the following structures is the product made by the rate-limiting step of glycolysis? Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate because the rate limiting step is phosphofructose kinase. 37. Which enzyme in glycolysis is the first one to produce ATP? a. Hexokinase b. Phosphoglycerate kinase c. Pyruvate kinase d. Phosphofructokinase e. Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase 38. Dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate produces a. Phosphoenolpyruvate b. Pyruvate c. 3-phosphoglycerate d. 2-phosphoglycerate e. dihydroxacetone phosphate 39. Consider the experiment from the previous question. An inhibitor is added to the experiment to determine the activity of the inhibitor. It is hypothesized that the inhibitor acts only on the enzymesubstrate complex and not at any other time. What is the predicted change upon addition of the inhibitor? a) Km would increase, Vmax would decrease. b) Km would decrease, Vmax would increase. c) Km would decrease, Vmax would decrease. d) Km would remain unchanged, Vmax would decrease. e) Km would increase, Vmax would remain unchanged. 40. During anaerobic conditionsa. Glycolysis risks failing due to lack of a key metabolite b. Lactate dehydrogenase begins to function c. NADH is consumed d. All of the above complete the statement 41. Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate increases in the cell, what would we expect? a. Decreased activity of hexokinase b. Decreased activity of lactate dehydrogenase c. Increased activity of pyruvate kinase Test #2 1. From the structures shown, select the structure of the nitrogenous base that is found only in RNA. 2. Using the structures in the previous question, which one is adenine? a) a b) b c) c d) d e) e 3. (True / False) From the structures above, (a) is a pyrimidine derivative. 4. (True / False) From the structures above, (a) would be expected to form 2 hydrogen bonds with € in a DNA double helix. 5. Which of the following statements above comparing DNA to RNA is true? a) RNA contains thymine, DNA contains uracil. b) Phosphate groups are not found on the sugar of RNA. c) Gerbils do not contain DNA. d) The sugar in DNA is a derivative of ribose that lacks a hydroxyl group. e) DNA is found in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes. 6. Which experiment used pathogenic bacteria to determine that dead bacteria that still possessed Dna could transform non-pathogenic bacteria? a) Mcleod and McCarty b) Hershey and Chase c) Meselson and Stahl d) Daniel and Gerbil 7. Which experiment used differential centrifugation and “heavy” nitrogen to identify the mode of DNAreplication? a) McLeod and McCarty b) Hershey and Chase c) Meselson and Stahl d) Daniel and Gerbil 8. Which experiment used radiolabeling of sulfur and phosphorous to identify genetic material? a) McLeod and McCarty b) Hershey and Chase c) Meselson and Stahl d) Daniel and Gerbil For the questions 9 to 12 use the following diagram. Notice that different features are pointed out by number (e.g. 1.(5’ or 3’ end) use these guides to answer the questions: 9. Indicator (2) is pointing to an enzyme, which one is it based on the clue provided? a) Helicase b) SSBPase c) Telomerase d) Polymerase e) Topoisomerase 10. Indicator (3) is pointing to an enzyme, notice its position in the replication fork. Which enzyme is this? a) Gyrase b) Polymerase c) Helicase d) Ligase e) Topoisomerase 11. Indicator (6) is asking which enzyme joins the nick in the DNA backbone after replication is completed on this strand. Which one is it? a) Polymerase I b) DNA Ligase c) RNA Primase d) DNA Hamsterase e) None of the above12. As shown by arrow (5) one side of DNA replication is always fragmented at first. What is the name of those fragments? a) Okazaki Fragments b) Leading Fragments c) Primers d) Meselson Fragments e) Ligation Fragments 13. Given the structure at the right, what is the name and distance of (A)? a) Minor groove, 22 A b) Major groove, 34 A c) Major groove, 22 A d) Minor groove, 34 A e) None of the above 14. Given the nature of the backbone of DNA in a double helix, which one of the following amino acids is most likely to be found in a protein site that interacts with the DNA backbone? a) K b) D c) E d) V e) F 15. Given the structure on the right, what is that molecule? a) Palmitic Acid b) Palmitoleic Acid c) Linoleic Acid d) Linolenic Acid e) Cholesterol 16. What type of reaction does lipase perform? a) Phosphoryl transfer b) Hydration c) Decarboxylation d) Oxidation e) Hydrolysis17. After lipases act on their substrate as much as possible, what molecule remains of the initial substrate? a) Acyl b) Acetyl c) Glycerol d) Pyrophosphate e) Coenzyme A 18. Consider that the lipase phosphorylation site is mutated from Y to S, what happens? a) Nothing is anticipated to change. b) Lipase now lacks an amino acid that can be phosphorylated. c) Lipase is now inactivated by phosphorylation. d) Lipase does not respond to glucagon. 19. (True / False ) Every part of a triacylglyceride can be used for energy production. 20. What type of molecule is dihydroxyacetone phosphate? a) Ester b) Carboxylic Acid c) Aldehyde d) Fatty acid e) Ketone 21. Acyl CoA Synthetase, is an enzyme that requires ATP to function. However, the reaction that charge CoA with the acyl group is freely reversible with an equilibrium constant of 1. Why is charging the CoA freely reversible with splitting the acyl from the CoA molecule? a) The phosphate group on the CoA can provide energy for hydrolysis. b) The enzyme actually favors the reverse reaction (positive Delta G). c) The question is flawed, this reaction is not reversible. d) The thioester bond on Acyl CoA provides energy for the reverse reaction. e) There is a second enzyme that uses ATP to un-charge the acyl CoA. 22. Since the action of Acyl CoA Synthetase is freely reversible with an equilibrium constant of 1. How is the reaction prevented from reversing? a) This question is flawed, the reaction is not freely reversible. b) The enzyme strongly favors the forward reaction (positive Delta G). c) A second enzyme removes a key reactant. d) There is not enough ATP to drive the reverse reaction. e) The enzyme is degraded after use. 23. How does and Acyl CoA enter the matix of a mitochondrion? a) The energy of the CoA bond allows the Acyl group to pass through the membrane. b) Acyl carnitine translocates with carnitine. c) Passive diffusion is all that is necessary since Acyl CoA is hydrophobic. d) Acyl CoA translocates with carnitine. e) Acyl CoA translocates with acetyl CoA 24. Which of the following molecules has a carbon-carbon double bond (ignoring the structure of CoA)? a) Hydroxyacyl CoA b) Ketoacyl CoA c) Acetyl CoAd) Palmitate CoA e) Enoyl CoA 25. Which of the following molecules comes from a hydration reaction in B-oxidation? a) Acetyl CoA b) Enoyl CoA c) Ketoacyl CoA d) Hydroxyacyl CoA e) Acyl CoA 26. Which enzyme creates Acetyl CoA as the end product in B-oxidation a) Acyl CoA Dehydrogenase b) B-ketothiolase c) Enoyl CoA Hydratase d) Hydroxyacyl CoA Dehydrogenase e) None of the above 27. Which of the following enzymes provides Acetyl CoA for palmitate synthesis? a) Malic Enzyme b) ATP-Citrate Lyase c) Acyl-Malonyl ACP reducing enzyme d) Acyl CoA Dehydogenase 28. What provides the energy for the enzyme in the previous question? a) Reducing equivalent (i.e. NADPH) b) Phosphoryl Transfer c) Oxidation (i.e. NADP+) d) No energy input is needed e) Product depletion by splitting pyrophosphate (i.e. dG shift) 29. What is the rate limiting enzyme of palmitate biosynthesis? a) Thioesterase b) Enoyl ACP reductase c) Acetyl CoA Carboxylase d) 3-hydroxyacyl ACP dehydratase e) Acyl-malonyl ACP reducing enzyme 30. Which of the following is the key building block of palmitate? B. 31. What enzyme recognizes palmitate for release in the mammalian fatty acid synthase? a) Thioesterase b) Enoyl ACP reductase c) Acetyl CoA Carboxylase d) 3-hydroxyacyl ACP dehydratase e) Acyl-malonyl ACP reducing enzyme32. What enzyme perform the rate-limiting step of cholesterol biosynthesis? a) Mevalonate Synthase b) HMG-CoA Reductase c) Squalene Synthase d) Geranyl Transferase e) Pyrophosphomevalonate Decarboxylase 33. Which of the following is the primary building block of cholesterol biosynthesis? C. 34. What molecule combine with farnesyl to make squalene? a) Geranyl Pyrophosphate b) Isopentenyl pyrophosphate c) Acetyl CoA d) Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate e) None of the above 35. What type of chemical reaction results in the product that is the basic building block of cholesterol biosynthesis? a) Decarboxylation b) Phosphorylation c) Hydration d) Hydrolysis e) Oxidation 36. How many of the building blocks are needed to create cholesterol? a) 2 b) 3 c) 4 d) 5 e) 6 37. How many carbons are in cholesterol? a) 27 b) 25 c) 17 d) 29 e) 3038. How is cholesterol oxidized to CO2 and water in humans? a) Glycolysis b) B-oxidation c) TCA Cycle d) Any of the above e) It isn’t 39. What is the structure on the right? a) Cholesterol b) Triacylglyceride c) Palmitate d) Lineolic Acid e) None of the above 40. Consider water in a beaker. Phospholipid is added to the water at the water / air interface. What happens? a) Phosphates are solubilized, the lipids remain in the air or entangled with each other. b) Lipids are solubilized, the phosphates remain in the air. c) The entire molecule enters into solution. d) The entire molecule rests on the surface of the water. e) It cannot be determined from the information given. 41. Consider octane in a beaker. Phospholipid is added to the octane at the octane / air interface. What happens? a) Phosphates are solubilized, the lipids remain in the air or entangled with each other. b) Lipids are solubilized, the phosphates remain in the air. c) The entire molecule enters into solution. d) The entire molecule rests on the surface of the water. e) It cannot be determined from the information given. 42. What is atelectasis? a) Collapse of an alveolus due to overabundance of surfactant. b) Over inflation of an alveolus due to overabundance of surfactant. c) Damage to the gall bladder due to overabundance of cholesterol. d) Damage to the gall bladder due to lack of cholesterol. e) None of the above. 43. What is the underlying cause of Respiratory Distress Syndrome in a premature infant? a) Overgrowth of cells lining the lung. b) Over production of cholesterol. c) Immature type II cells in the lung. d) Cell death of type II cells in the lung. e) Overabundance of lecithin. 44. Why do humans have an absolute requirement for cholesterol? a) It is a precursor for bile acids. b) It is a precursor for certain hormones. c) It is needed to absorb fat soluble vitamins. d) It is needed to protect the gall bladder.e) All of the above. 45. What is the product of the non-enzymatically driven light reaction that is one way in which humans photosynthesize? a) Prostaglandin 3 b) Vitamin b c) Cyclization of Cholesterol d) Vitamin D e) Vitamin K 46. Given the following: Excess acetoacetyl CoA is available All the acetyl CoA made in the beta oxidation of a palmitate goes directly for cholesterol biosynthesis Each acetyl CoA is used sequentially All of the steps of cholesterol biosynthesis occur sequentially and not in parallel The 7th carbon on palmitate CoA is radiolabeled From the list below, select the first material that appears with the radiolabel in the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway: a) Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate b) geranyl pyrophosphate c) farnesyl pyrophosphate d) squalene e) gerbyne d. Immediate conversion of dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate f. Decreased activity of pyruvate kinase 42. Which of the following allosterically inhibits phosphofructokinase? a. AMP b. Fructose-2,6-bisphophate c. Glucose d. Hydroxyl e. Citrate 43. How is glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate converted to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate? a. ATP is used provide phosphate b. Pi is used to provide phosphate c. Phosphate is transferred from fructose-2,6-bisphosphate d. NADH provides the phosphate e. This reaction does not occur in glycolysis, the question is invalid 44. How is glucose-6-phosphate converted to fructose-6-phosphate a. Isomerization b. Decarboxylation c. Oxidative decarboxylation d. Phosphoryl transfer e. Reductive carboxylation 45. Which of the following is a cause of hemolytic anemia?a. Failure of glucose kinase b. Failure of phoshphofructokinase c. Failure of triosephosphate isomerase d. Failure of pyruvate kinase e. Failure of lactate dehydrogenase Exam 2 1) Which enzyme is considered part of TCA and ETC? ● FADH2 - Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase 2) A solution at pH 6.7 contains a weak acid, HA. The pKa of the acid is 7.0. What is the ratio of [A]:[HA]? ● 1:2 3) In mitochondria, what is the expected pH of the intermembrane space compared to matrix? ● More Acidic 4) When Compound C gives electrons to Compound D, then Compound D is an _____ and Compound C is a _____. ● Oxidant, reductant 5) When Compound C takes electrons from Compound D; Compound D was _____ and Compound C was _____. ● Oxidized, reduced 6) What provides the energy to ATP Synthase for the formation of ATP? ● Proton Flow 7) What do cristae in the mitochondria do? (Select all that apply) ● Increase surface area of the inner membrane, these structures house the f1 and f0 ATP Synthase 8) (True / False) The amino acid R at pH 7.4 has has 3 charged groups. ● True --- Congratulations! Due to your success in Dr. Daniel’s Biochemistry class. You have been selected by NASA to do the biochemical write up on a new organism recovered from aMartian probe! During your analysis you have discovered a brand new electron transport chain! The organism appears to use electron transport as its primary source of energy rather than ATP. This leaves you with a couple of questions to answer: (9-13) During your analysis you discover a new electron transport chain based on: 1. Ickygreenone + H+ +2e- → Ickygreenol [REDACTED] V 0.5 V 2. Barsoom + H+ +2e- → Barsool [REDACTED] V 1.25V 9) Which species is the reductant for the proposed ETC? ● Ickygreenol 10) Which species is the oxidant for the proposed ETC? ● Barsoom 11) Which series of voltages represents the correct voltage to trace the electron flow for the free energy calculation? ● -0.500 V and + 1.25 V 12) What is the free energy gained from the ETC presented? ● -34.5 kcal/mol 13) From one run of the proposed electron transport chain, how many ATP equivalents in energy could theoretically be generated? ● 4 14) (True/False) Given metabolic pathways in the class so far, malate can be directly converted to pyruvate in one step by a single enzyme. ● False 15) What is the material in Figure 4 (bottom of this page)? (PYRUVATE) ● None of the above 16) What is the rate limiting enzyme of the TCA cycle? ● Isocitrate dehydrogenase 17) What is the material on the right (Figure 1)? ● Citrate 18) What is the material on the right (Figure 2)? ● Oxaloacetate 19) What is the material on the right (Figure 3)? ● Succinate 20) The asterisk shows a radiolabeled carbon. This glycolytic intermediate will be converted to enter the TCA cycle. What product will be radiolabeled?● CO2 21) Ammonium has a pKa of 9.25. 45 ml of 1.00 M HCl is added to 75 mL of a 1.00 M buffer solution of this ammonium at pH 10. The resulting solution is at pH: ● 8.8 22) In a test organism that possesses a normal TCA cycle, you determine that malate is elevated compared to control samples. Which enzymatic failure would best explain this observation? ● Citrate synthase 23) What type of reaction does the rate-limiting step of TCA perform? (Hint: consider all products made, including side products) ● Oxidative decarboxylation 24) Which enzyme activity in TCA is powered by thioester bond cleavage and makes a nucleotide triphosphate as a product? ● Succinyl CoA Synthetase 25) (A = True / B = False) It is reasonable to say that TCA does not make ATP directly. ● True 26) The asterisk shows a radiolabeled carbon, after one round of TCA where is this carbon found? ● Oxaloacetate carbone 1 or 4 27) Alpha-ketoglutarate can become what amino acid? ● Glutamate 28) Which of the following amino acids is/are likely positive at physiological pH? (Select all that apply) ● R, K 29) Using glycolysis, given that 1 mole of glucose is converted to 1 mole of pyruvate, how many moles of ATP are [REDACTED]? (Hint: Read this question carefully) ● 2 30) A mad-scientist wishes to make a glycolysis inhibitor to treat gerbilitis, why is this a bad idea? (Select all that apply) ● Expect severe toxicity to eye, RBCs, kidney and medulla31) What does regulation of hexokinase protect against? ● Protection from depletion of Pi 32) Which of the following glycolytic enzymatic reactions is freely reversible by the same enzyme in cellular conditions? ● G3P to DHAP 33) What is the name of the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of the correct answer to the previous question? ● Triose phosphate isomerase 34) If ATP is elevated in cells, what is the effect on the glycolysis pathway in those cells? ● Levels of fructose- 1,6 - bisphosphate will decrease 35) Which of the following structures is the product made by the rate limiting step of glycolysis? ● Fructose - 1,6 - biphosphate 36) What enzyme in glycolysis is the first one to produce ATP? a) Hexokinase b) Phosphoglycerate Kinase c) Pyruvate Kinase d) Phosphofructokinase e) Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 37) Dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate produces: [2-Phosphoglycerate] ---> Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) ● Phosphoenolpyruvate 38) Consider an allosteric inhibitor. What would be the changes expected in a LWB plot? (Select all that apply) ● One intercept does not change (either x or y) 39) During anaerobic conditions … (Select all that apply) ● Glycolysis risks failing due to lack of a key metabolite; NADH is consumed 40) Fructose 1,6 bisphosphate increases in the cell, what would we expect? ● Increased activity of pyruvate kinase 41) Which of the following allosterically inhibits phosphofructokinase?● Citrate 42) How is glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate converted to 1, 3- biphosphoglycerate? ● Pi is used to provide phosphate 43) How is glucose-6-phosphate converted to fructose-6-phosphate? ● Isomerization 44) Which of the following is a cause of hemolytic anemia? [hemolytic anemia/pyruvate kinase deficiency] ● Failure of pyruvate kinase 45) Does this span of amino acids possess a residue typically used in phosphorylation: D-K-Y-F-W-Q-N ● Yes, it contains tyrosine [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 27 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 28, 2021
Number of pages
27
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 28, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
39