Biology > LECTURE NOTES > Strayer University - BIOLOGY MISC;NCLEX-1-DAY-Review (All)
Strayer University - BIOLOGY MISC;NCLEX-1-DAY-Review
Document Content and Description Below
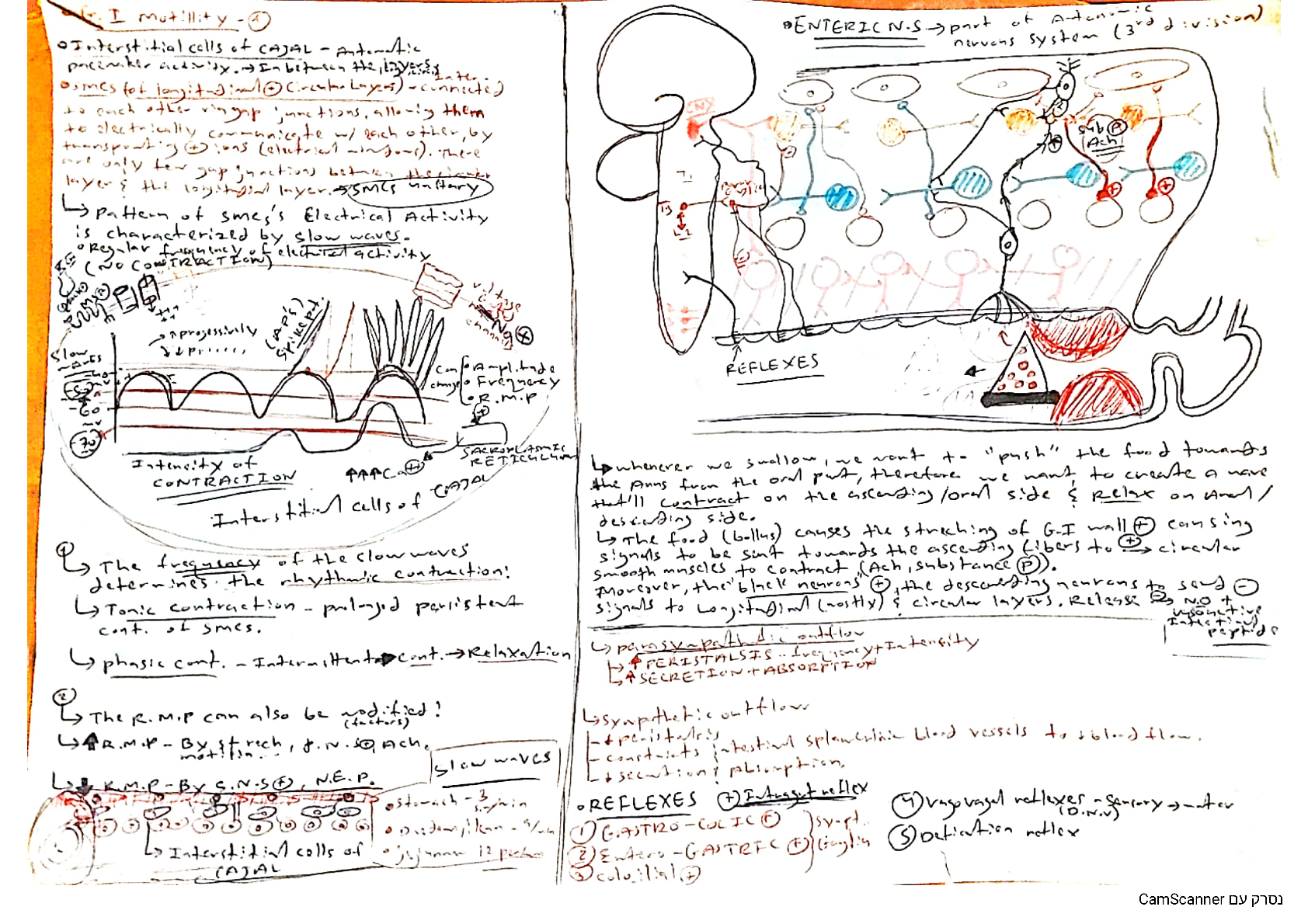
ANTICHOLINERGIC vs. CHOLINERGIC EFFECTS ANTICHOLINERGIC CHOLINERGIC Mucus Bronchodilation Dry mouth Dry eyes Urinary retention Dry skin Constipation Shut d... own GI Prevents V when trying to intubate Bronchorrhea (large amounts of mucus in airway) Bronchoconstriction Salivation Lacrimating Urination Diaphoresis/Diarrhea GI Upset Emesis ACID BASE GASES A. ABG Interpretation a. Rule of the B’s i. If the pH and the BICARB (HCO3) ii. Are BOTH in the same direction, iii. Then it is METABOLIC b. pH = acidosis c. pH= alkaline B. Values a. Normal pH = 7.35 – 7.45 b. Normal Bicarb= 22-26 c. PaO2= 80-100 mmHg d. PaCO2= 35-45 mmHg e. SaO2= 95-100% C. Signs & Symptoms of Acid-Base Imbalance a. As the pH goes, so goes the patient except for Potassium (bc it will try to compensate) pH UP K [ALKALOSIS] pH DOWN K [ACIDOSIS] Tachycardia Tachypnea Diarrhea Tremors Seizure Hyperreflexia Agitated Borborygmi ( bowel sounds) Bradycardia Bradypnea Hypotension lucidity anorexia coma lethargy cardia arrest Hypertension Palpitations Tetany Anxiety/Panic Poly suppressed, decreased, falling D. Causes of Acid-Base Imbalance a. First ask, “Is it Lung?” i. If YES- then it is Respiratory b. Then ask yourself: i. Are they Overventilating or Underventilating? 1. If Overventilating pick Alkalosis 2. If Underventilating pick Acidosis c. If not lung, then it’s Metabolic i. If the patient has prolonged gastric vomiting or suction, pick Metabolic Alkalosis ii. For everything else that isn’t lung, pick Metabolic Acidosis 1. Also, if you don’t know what to pick choose Metabolic Acidosis VENTILATOR ALARMS 1. High Pressure Alarms are triggered by resistance to air flow and can be caused by obstructions of three types: a. Kinked Tube i. NRS ACTION: Unkink it b. Water in tubing (caused by condensation) i. NRS ACTION: Empty it/Remove H2O c. Mucus in airway i. NRS ACTION: Turn, C&DB; only use suction if C&DB fails, as a last resort 2. Low Pressure Alarms are triggered by resistance to air flow and can be caused by disconnections of the: a. Tubing i. NRS ACTION: Pay attention to where tubing is… (contamination) ii. If on floor, change out iii. If on chest, clean with alcohol then put back on 3. Respiratory Alkalosis (Overventilation) means ventilator settings may be too HIGH. 4. Respiratory Acidosis (Underventilation) means ventilator settings may be too LOW. 5. To “Wean” To gradually and incrementally decrease with the goal of ridding all together [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 57 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 03, 2021
Number of pages
57
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 03, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
83









.png)
.png)
.png)










.png)












