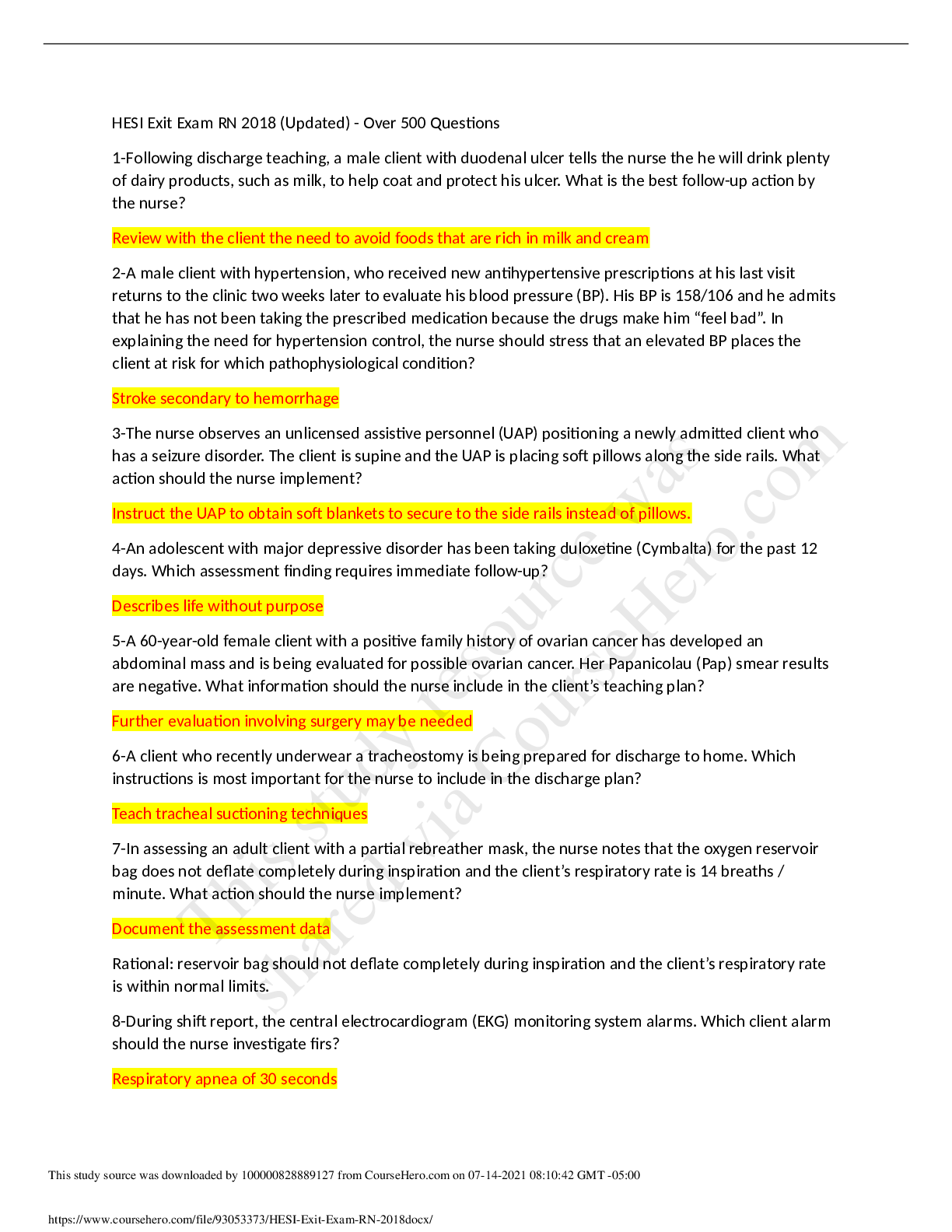Olivia_Jones_Preeclampsia_Case_Study,WITH VERIFIED ANSWERS GRADED A,
Document Content and Description Below
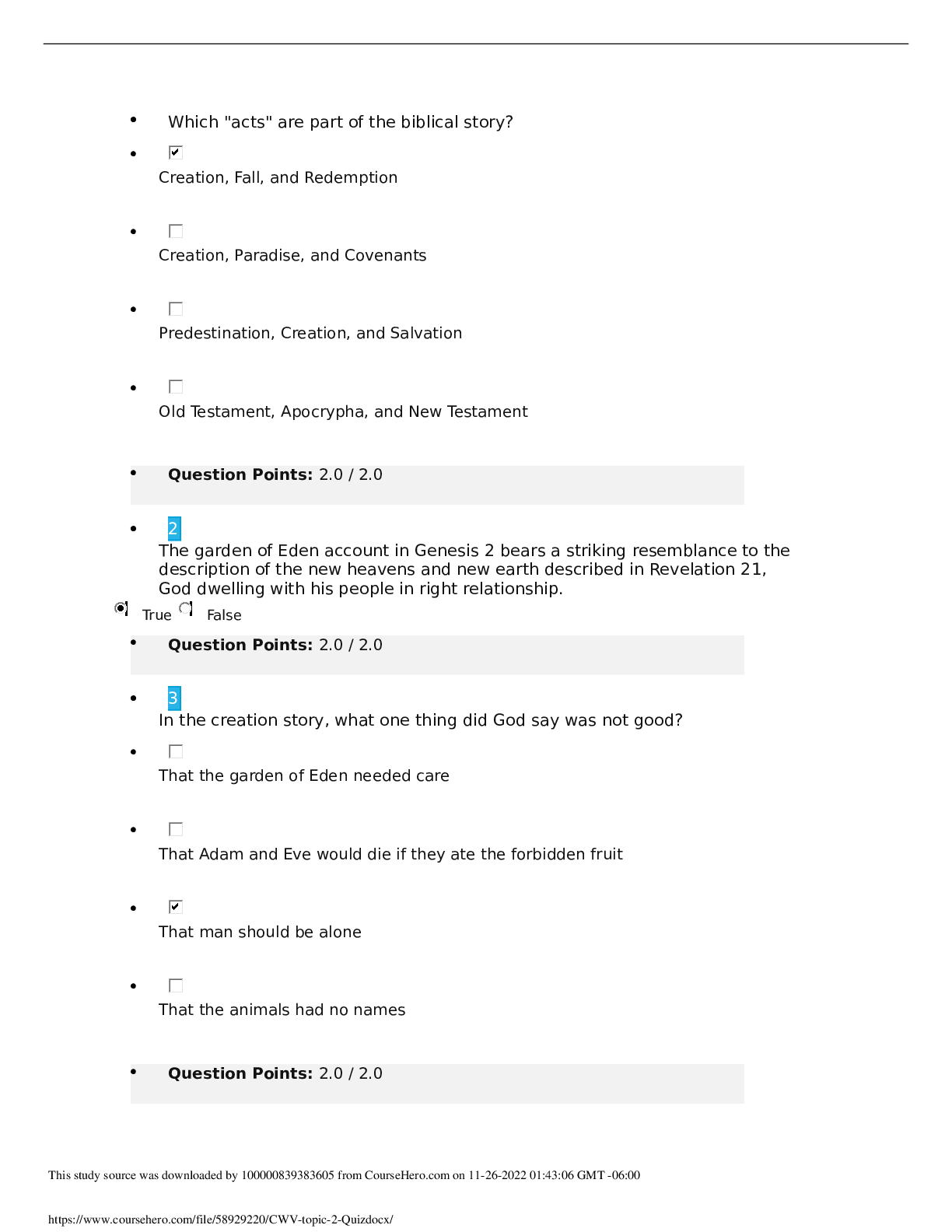
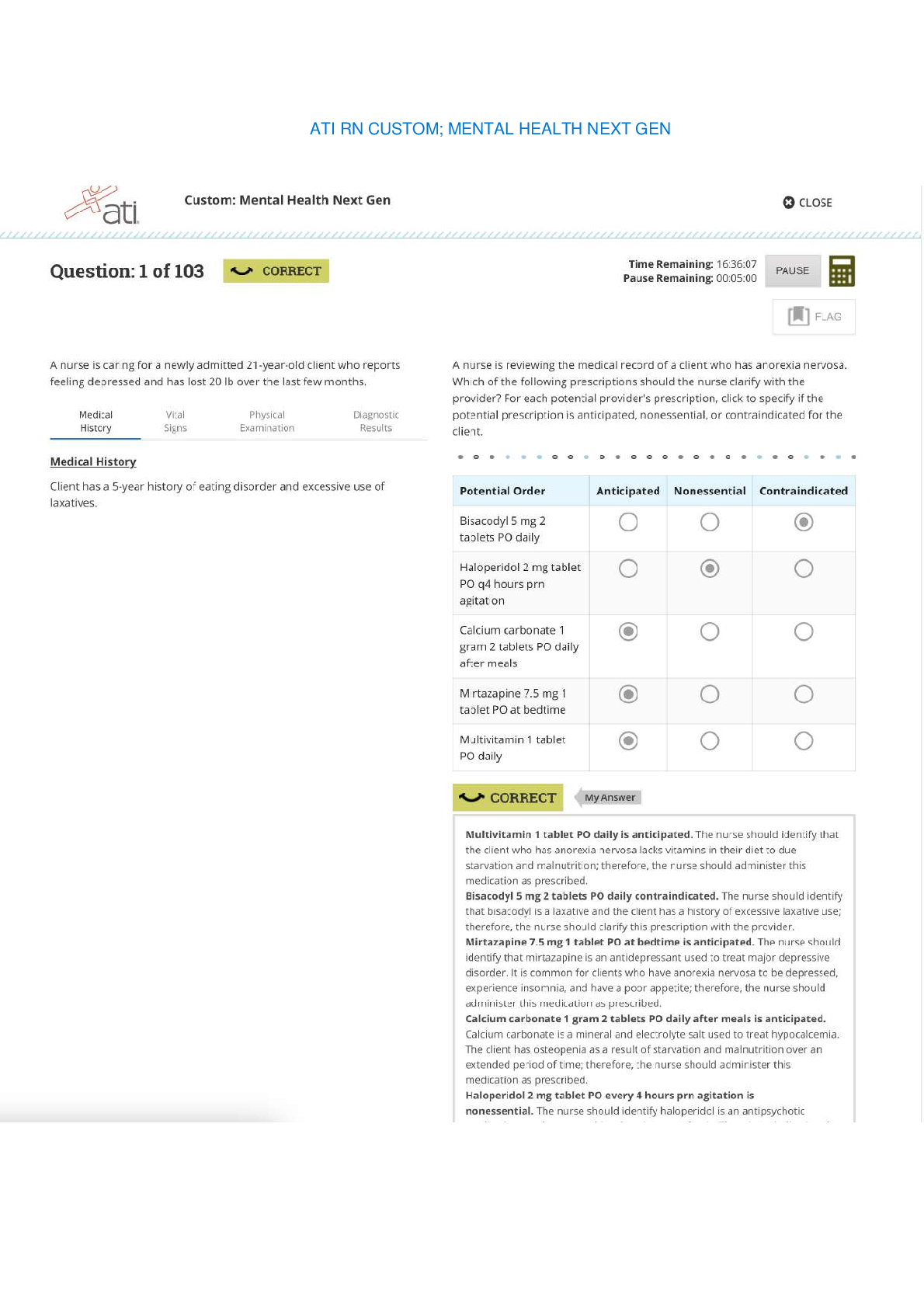
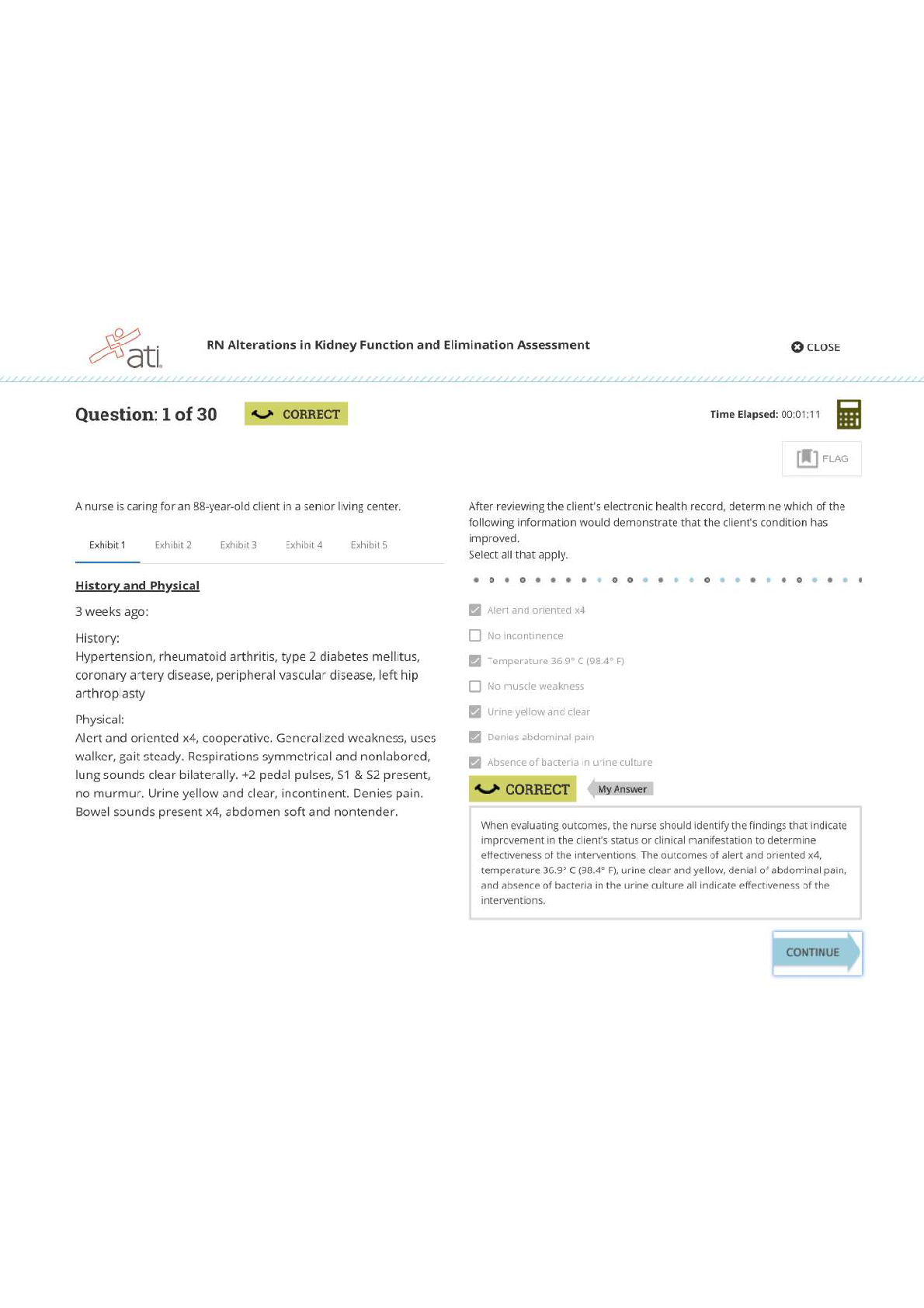
Date: 4th June 2020 Student Name: Adedayo Helen Temitope Assigned VSim: Olivia Jones Initials: Age: 23 M/F: Female Code Status: Diagnosis: severe preeclampsia Length of stay: 2 hours Allerg... ies: None HCP: Yes Consults: Recommende d Isolation: No Fall Risk: Moderate Transfer: Bed rest / bathroom priviledges IV Type: Lactated Ringer Location: Labor and delivery unit Fluid/Rate: 125 mL per hour continuous or 500ml IV bolus for nonreassuri ng fetal heart rate pattern Critical Labs: BUN, Creatinine, Triglyceride, LDH Other Services: Hypoxemia Consults needed: Yes Why is your patient in the hospital (Answer in your own words and include the History of Present Illness)? high blood pressure, unrelieved headache even with acetaminophen, visual changes, chest tightness nausea and vomiting, protein in urine, increased weight gain and generalized swelling noted in face and lower extremities Health History/Comorbidities (that relate to this hospitalization): N/A Shift Goals/ Patient Education Needs: Patient education needed on the importance of bed rest, call light use/signaling for help, NPO until serum lab result is received, provision and suggestion of diversional activities while on bed rest, information on tests and procedures to evaluate maternal-fetal status, e.g laboratory tests, sonogram, NST, Encouraging the support of family or friends while on bed rest Path to Discharge: fetal heart rate within normal range, no evidence of pulmonary edema, adequate urine output, no seizure activity, expresses concern for self and the fetus, maintaining bed rest and pursuing diversional activities, Blood pressure and other vital signs within parameters of plan of care and stable. Path to Death or Injury: Abruptio placentae, DIC, HELLP syndrome, maternal or fetal death, hypertensive crisis, pulmonary edema, oliguria, thrombocytopenia, hemorrhage, blindness, fetal intolerance of labor, hypoglycemia, hepatocellular dysfunction, prematurity Alerts: What are you on alert for with this patient? (Signs & Symptoms) 1. Elevated BP 2. Proteinuria 3. increased serum creatinine 4. hyperreflexia 5. persistent epigastric pain 6. low platelet count What Assessments will focus on for this patient? (How will I identify the above signs & Symptoms?) 1) lab result on urine dipstick 2) Serum Creatinine and BUN result 3) vital signs assessment 4) persistent headache, visual disturbances, altered level of conciousness What nursing or medical interventions may prevent the above Alert or complications? 1) Bed rest 2) Maintaining fluid balance Management of Care: What needs to be done for this Patient Today? 1) Delivery of baby if uncontrolled hypertension, eclampsia, pulmonary edema, compromised renal function Priorities for Managing the Patient’s Care Today 1) Maintaining fluid balanc 2) Promoting adequate tissue perfusion. 3) preventing injury. List Complications may occur related to dx, procedure, comorbidities: Abruptio placentae, DIC, HELLP syndrome, maternal or fetal death, hypertensive crisis, pulmonary edema, oliguria, thrombocytopenia, hemorrhage, blindness, fetal intolerance of labor, hypoglycemia, hepatocellular dysfunction, prematurity 4) decreasing anxiety and increasing knowledge 5) maintaining cardiac output What aspects of patient care can be Delegated and who can do it? 1) Respiratory therapist Plan of Care Concept Map of the etiology include the exposure to chorionic villi for the first time or in large amounts along with immunologic, genetic and endocrine factors. The disease is more commonly seen in primigravidas. Chronic hypertension, hydatidiform mole, multiple gestation, polyhydramnios, preexisting vascular disease, obesity, and diabetes mellitus may predispose a patient to preeclampsia. Adolescents and women older than age 35 are at higher risk. Diagnostic Tests Patient Information Anticipated Physical (Reason for Test and Results) - 24-hour urine for protein of more than 0.3 g (mild); more than 2.0g (severe). - Serum BUN, serum creatinine, and serum uric acid to evaluate renal function and glomerular filtration capability, specifically creatinine clearance, uric acid clearance, and urea clearance. - 23 year old African American female, G1P0 at 36 weeks of gestation Findings - High blood pressure reading - visual disturbances, headache, altered level of consciousness, scotomata or blurry vision - persistent epigastric pain - seizures or coma - Liver function tests (AST, ALT). - Coagulation studies, specifically platelets, antithrombin III and factor VIII levels. - Lipid panel to assess high- density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL): HDL levels are decreased in preeclamptic women whereas LDL levels are elevated. - Sonogram, NST to evaluate placenta and fetus. - DTRs and clonus evaluation to assess level of disease process Anticipated Nursing Interventions - As a nurse, i must monitor intake and output strictly and notify health care provider if urine output is less than 30ml/hour. - Monitor vital signs every hour. - Position patient on side to promote placental perfusion. - Monitor fetal activity - keep the environment quiet and as calm as possible. - assess DTRs and clonus every 2 hours. increase frequency of assessment as indicated by patient’s condition. - explain the disease process and plan for treatment including signs and symptoms of the disease process. - explain the need for bed rest to the woman and her support persons. - control I.V. fluid intake using a continuous infusion pump - assess edema status and report piting edema of +2 to primary care provider - monitor oxygen saturation levels with pulse oximeter. VSim ISBAR Activity Introduction Your name, position (RN), unit you are working on Name: Adedayo Helen Temitope Position: Registered Nurse (Student) Unit: Labor and delivery unit Situation Patient's name, age, specific reason for the visit Patient name: Olivia Jones Age: 23 Years Reason for Visit:unresolved headache even with medication, nausea and vomiting, fatigue, epigastric pain, visual changes and chest tightness Background Patient’s primary diagnosis, date of admission, current orders for patient Patient’s primary diagnosis: severe preeclampsia Date of admission: 06/04/2020 Current orders for the patient: vital signs assessment every hour, deep tendon reflexes every hour, head to toe assessment, continuous pulse oximetry, initiate IV care protocol, insert foley catheter, obtain ultrasound, FHR monitoring Assessment Current pertinent assessment data using the head to toe approach, pertinent diagnostics, - Symptoms identified include headache, blurry vision, fatigue, nausea/vomiting, visual disturbances, and epigastric pain. vital signs Recommendation Any orders or recommendations you may have for this patient - The patient requires bed rest. NPO Patient Education Worksheet Name of Medication, Classification, and include Prototype Medication: Magnesium Sulfate Classification: Antidysrhythmics, Electrolytes Prototype: Magnesium Hydroxide Safe Dose or Dose Range, Safe Route - 0.8 mEq/mL, 1 mEq/mL, 4 mEq/mL injection The purpose for Taking this Medication - Orally to relieve acute constipation and to evacuate bowel in preparation for x-ray of intestines. Parenterally to control seizures in toxemia of pregnancy, epilepsy, and acute nephritis and for prophylaxis and treatment of hypomagnesemia. Topically to reduce edema, inflammation, and itching. Patient Education while Taking this Medication - Drink sufficient water during the day when the drug is administered orally to prevent net loss of body water. - Recommended daily allowances of magnesium are obtained in a normal diet. Rich sources are whole-grain cereals, legumes, nuts, meats, seafood, milk, most green leafy vegetables, and bananas. - Do not breast feed while taking this drug without consulting a physician. - References Black, J. M., & Hawks, J. H. (2009). Medical-surgical nursing: Clinical management for positive outcomes (Vol. 1). Saunders Elsevier. Gibson, V. (2015). Recognising and managing community-acquired pneumonia. Nurs Stand, 30(12), 53-59. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26576915. Williams & Wilkins, Lippincott (2006) Manual of Nursing Practice 8th edition [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 10 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 10, 2021
Number of pages
10
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 10, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
74