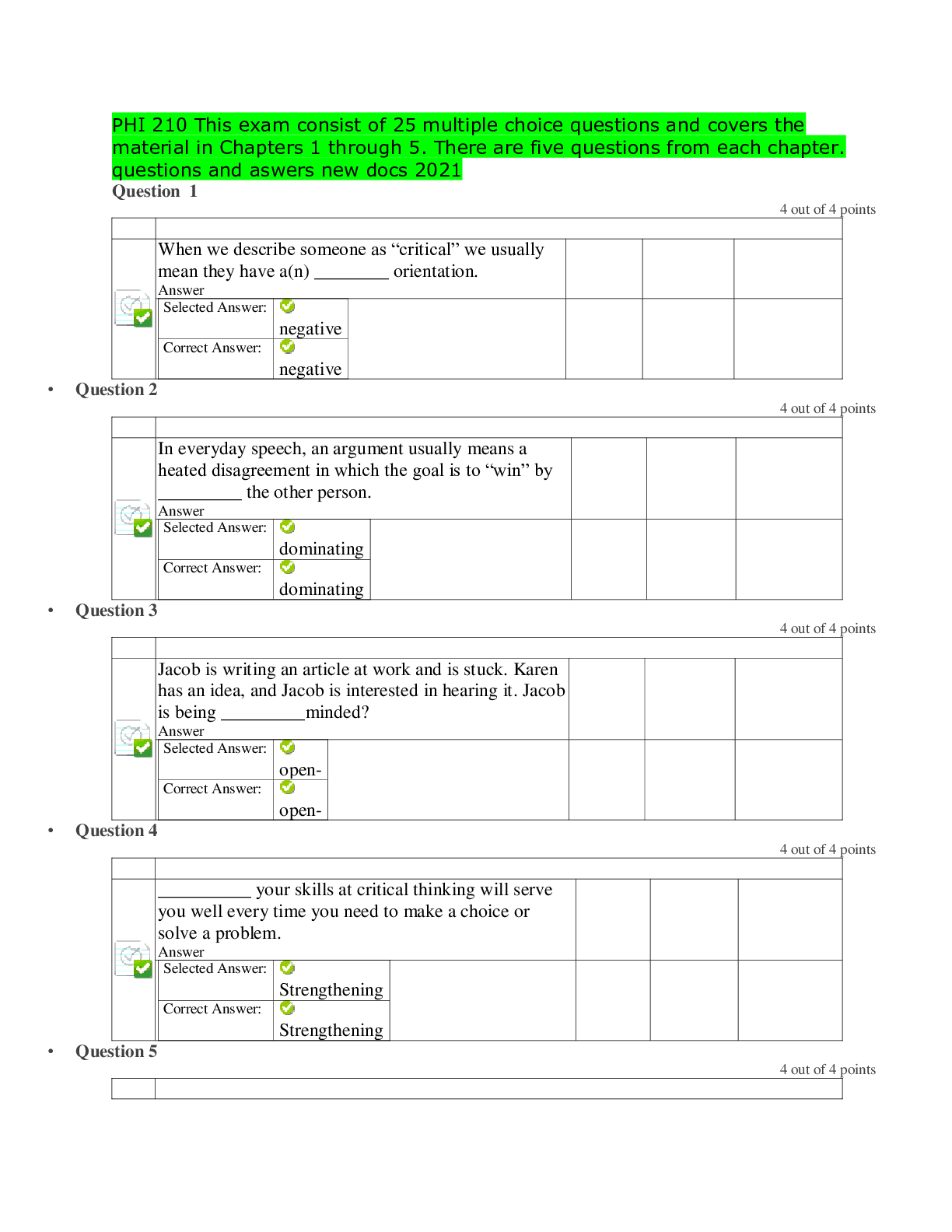
Financial Accounting > EXAM > Park University - AC 202AC202 Final Study Guide> Fully Worked Questions and Solutions (47 Pages) (All)
Park University - AC 202AC202 Final Study Guide> Fully Worked Questions and Solutions (47 Pages)
Document Content and Description Below
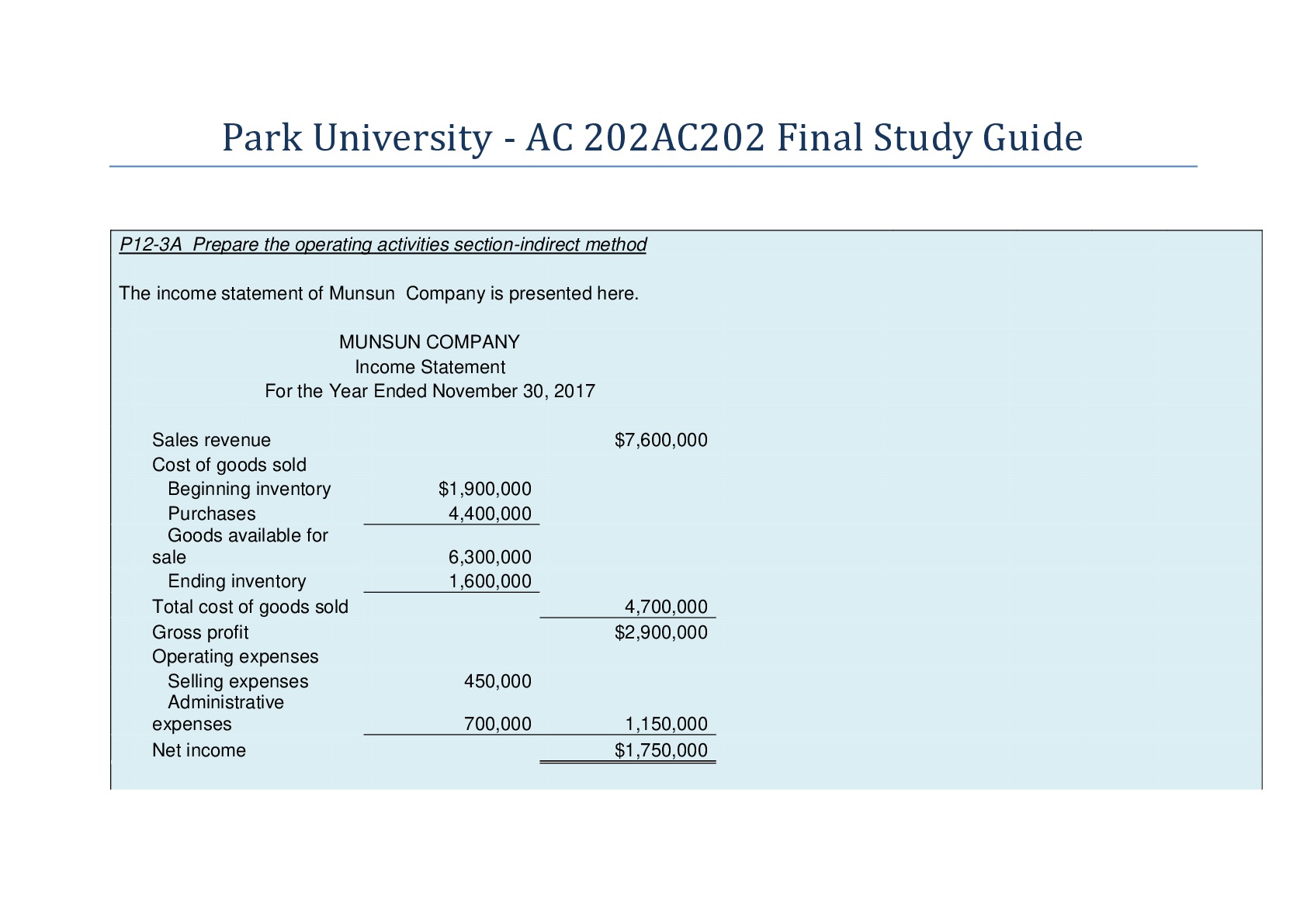
P12-3A Prepare the operating activities section-indirect method The income statement of Munsun Company is presented here. MUNSUN COMPANY Income Statement For the Year Ended November 30, 20... 17 Additional information: 1. Accounts receivable decreased $380,000 during the year, and inventory decreased $300,000. 2. Prepaid expenses increased $150,000 during the year. 3. Accounts payable to suppliers of merchandise decreased $350,000 during the year. 4. Accrued expenses payable decreased $100,000 during the year. 5. Administrative expenses include depreciation expense of $110,000. Instructions Prepare the operating activities section of the statement of cash flows for the year ended November 30, 2017, for Munsun Company, using the indirect method. NOTE: Enter a number in cells requesting a value; enter either a number or a formula in cells with a "?" . MUNSUN COMPANY Partial Statement of Cash Flows For the Year Ended November 30, 2017 Cash flows from operating activities Net income Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: Depreciation expense Decrease in accounts receivable Decrease in inventory Increase in prepaid expenses Decrease in accounts payable Decrease in accrued expenses payable After you have completed P12-3A, consider the additional question. Assume that depreciation expense, accounts receivable and accounts payable changed to $98,000, $320,000 and $300,000. Show the impact of these changes on the operating section of the statement of cash flows. P12-6A Prepare the operating activities section-indirect method Rewe Company's income statement contained the condensed information below. REWE COMPANY Income Statement For the Year Ended December 31, 2017 Accounts payable pertain to operating expenses. Instructions Prepare the operating activities section of the statement of cash flows using the direct method NOTE: Enter a number in cells requesting a value; enter either a number or a formula in cells with a "?" . REWE COMPANY Partial Statement of Cash Flows For the Year Ended December 31, 2017 Cash flows from operating activities Cash receipts from customers $960,000 Less cash payments: For operating expenses $605,000 (2) For income taxes 50,000 (3) 655,000 Net cash provided by operating activities $305,000 After you have completed P12-6A, consider the additional question. 1. Assume that the 2017 balance of accounts receivable, accounts payable, and income taxes payable changed to $75,000, $39,000 and $4,500 respectively, Show the impact of these changes on the operating section of the statement of cash flows. E15-9 Prepare a cost of goods manufactured schedule and partial financial statements At May 31, 2017, the accounts of Lopez Company show the following. 1. May 1 inventories - finished goods $12,600, work in process $14,700 and raw materials $8,200. 2. May 31 inventories - finished goods $9,500, work in process, $15,900, and raw After you have completed P12-6A, consider the additional question. 1. Assume that the 2017 balance of accounts receivable, accounts payable, and income taxes payable changed to $75,000, $39,000 and $4,500 respectively, Show the impact of these changes on the operating section of the statement of cash flows. E15-9 Prepare a cost of goods manufactured schedule and partial financial statements At May 31, 2017, the accounts of Lopez Company show the following. 1. May 1 inventories - finished goods $12,600, work in process $14,700 and raw materials $8,200. 2. May 31 inventories - finished goods $9,500, work in process, $15,900, and raw materials $7,100. materials $7,100. Debit postings to work in process were direct materials, $62,400, direct labor $50,000, and manufacturing overhead applied $40,000. Sales revenue totaled $215,000. Instructions Prepare a condensed cost of goods manufactured schedule. Prepare an income statement for May through gross profit. Indicate the balance sheet presentation of the manufacturing inventories at May 31, 2017. NOTE: Enter a number in cells requesting a value; enter either a number or a formula in cells with a "?" . Prepare a condensed cost of goods manufactured schedule. LOPEZ COMPANY Cost of Goods Manufactured Schedule For the Month Ended May 31, 2017 Prepare an income statement for May through gross profit. LOPEZ COMPANY (Partial) Income Statement For the Month Ended May 31, 2017 After you have completed E15-9, consider the following additional question. 1. Assume that the total costs for direct materials, direct labor and overhead changed to $81,400, 63,600 and $45,000 respectively. Show the impact of these changes on the cost of goods manufactured schedule, income statement and balance sheet. P15-5A Analyze manufacturing accounts and determine missing amounts Phillips Corporation's fiscal year ends on November 30. The following accounts are found in its job order cost accounting system for the first month of the new fiscal year. Other data: 1. On December 1, two jobs were in process: Job No. 154 and Job No.155. These jobs had combined direct materials costs of $9,750 and direct labor costs of $15,000. Overhead was applied at a rate that was 75% of direct labor cost. 2. During December, Job Nos. 156, 157 and 158 were started. On December 31, Job No. 158 was unfinished. This job had charges for direct materials $3,800 and direct labor $4,800 plus manufacturing overhead. All jobs, except for Job No. 158, were completed in December. 3. On December 1, Job No. 153 was in the finished goods warehouse. It had a total cost of $5,000. On December 31, Job No. 157 was the only job finished that was not sold. It had a cost of $4,000. 4. Manufacturing overhead was $1,470 underapplied in December. Instructions List the items (a) through (m) and indicate the amount pertaining to each letter. NOTE: Enter a number in cells requesting a value; enter either a number or a formula in cells with a "?" . When you have completed P15-5A, consider the following additional question. 1. Assume that requisitions changed to $17,600. Show the impact of this change on the items listed. E16-11 Compute equivalent units, unit costs, and costs assigned The Polishing Department of Major Company has the following production and manufacturing cost data for September. Materials are entered at the beginning of the process. Production: Beginning inventory 1,600 units that are 100% complete as to materials and 30% complete as to conversion costs; units started during the period ar 42,900; ending inventory of 5,000 units 10% complete as to conversion costs. Manufacturing costs: Beginning inventory costs, comprised of $20,000 of materials and $43,180 of conversion costs; material costs added in Polishing during the month, $175,800; labor and overhead applied in Polishing during the month, $125,680 and $257,140, respectively. Instructions (a) Compute the equivalent units of production for materials and conversion costs for the month of September. (b) Compute the unit costs for materials and conversion costs for the month. (c ) Determine the costs to be assigned o the units transferred out and in process. NOTE: Enter a number in cells requesting a value; enter either a number or a formula in cells with a "?" . (a) Compute the equivalent units of production for materials and conversion costs for the month of September. After you have completed the requirements of E16-11, consider this additional question. 1. Assume that 3,750 units remained in ending work in process and total conversion costs added during September changed to $359,695. Show the impact of this change on the calculation of equivalent units, unit cost, and on the cost reconciliation schedule. (Round calculation of cost per equivalent units to 3 decimal points.) (a) Compute the equivalent units of production for materials and conversion costs for the month of September. E17-1 Assign overhead using traditional costing and ABC Saddle Inc. has two types of handbags: standard and custom. The controller has decided to use a plantwide overhead rate based on direct labor costs. The president has heard of activity-based costing and wants to see how the results would differ if this system was used. Two activity cost pools were developed: machining and machine setup. Presented below is information related to the company's operations. Standard Custom Direct labor costs $50,000 $100,000 Machine hours 1,000 1,000 Setup hours 100 400 Total estimated overhead costs are $240,000. Overhead cost allocated to the machining activity cost pool is $140,000 and $100,000 is allocated to the machine setup activity cost pool. Instructions (a) Compute the overhead rate using the traditional (plantwide) approach. (b) Compute the overhead rates using the activity-based costing approach. (c) Determine the difference in allocation between the two approaches. NOTE: Enter a number in cells requesting a value; enter either a number or a formula in cells with a "?" . After you have completed E17-1, consider the additional question. Assume that total estimated overhead costs are $285,000. Overhead cost allocated to the machining activity cost pool is$150,000 and $135,000 is allocated to the machine setup activity cost pool. Redo instructions (a) to (c). P18-2A Prepare a CVP income statement, compute break-even point, contribution margin ratio, margin of safety ratio and sales for target net income Jorge Company bottles and distributes B-Lite, a diet soft drink. The beverage is sold for 50 cents per 16-ounce bottle to retailers, who charge customers 75 cents per bottle. For the year 2017, management estimates the following revenues and costs. Sales $1,800,000 Selling expenses - variable Direct materials 430,000 Selling expenses - fixed Direct labor 360,000 Administrative expenses - variable Manufacturing overhead- variable 380,000 Administrative expenses - fixed Manufacturing overhead -fixed 280,000 Instructions (a) Prepare a CVP income statement for 2017 based on management estimates. (show column for total amounts only.) (b) Compute the break-even point in (1) units and (2) dollars. (c ) Compute the contribution margin ratio and the margin of safety ratio. (Round to the nearest full percent.) (d) Determine the sales dollars required to earn net income of $180,000. NOTE: Enter a number in cells requesting a value; enter either a number or a formula in cells with a "?" . (a) Prepare a CVP income statement for 2017 based on management estimates. (show column for total amounts only.) JORGE COMPANY CVP Income Statement (Estimated) For the Year Ending December 31, 2017 Sales Variable expenses Cost of goods sold Selling expenses Administrative expenses Total variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses Cost of goods sold Selling expenses Administrative expenses Total fixed expenses (c ) Compute the contribution margin ratio and the margin of safety ratio. (Round to the nearest full percent.) After you have completed P18-2A, consider the following additional question 1. Assume that the unit selling price per bottle changed to $0.60 each, and fixed manufacturing costs increased to $300,000. Show impact of these changes on calculations. E20-10 Determine whether to sell or process further, joint products Stahl Inc. produces three separate products from a common process costing $100,000. Each of the products can be sold at the split-off point or can be processed further and then sold for a higher price. Shown below are cost and selling price data for a recent period. Sales Value Cost to Sales Value at Split-off Process after Further Point Further Processing $60,000 $100,000 $190,000 15,000 30,000 35,000 55,000 150,000 215,000 Determine total net income if all products are sold at the split-off point. Determine total net income if all products are sold after further processing. Using incremental analysis, determine which products should be sold at the split-off point and which should be processed further. Determine total net income using the results from (c ) and explain why the net income is different from that determined in (b). NOTE: Enter a number in cells requesting a value; enter either a number or a formula in cells with a "?" . Using incremental analysis, determine which products should be sold at the split-off point and which should be processed further. Determine total net income using the results from (c ) and explain why the net income is different from that determined in (b). After you have completed E20-10, consider the additional question. 1. Assume that sales value at split-off point for Product 10 changed to $75,000 and the cost to process Product 14 further changed to $162,000. What impact do these changes have on total net income at split-off point and after further processing? E20-15 Use incremental analysis concerning elimination of division. Veronica Mars, a recent graduate of Bell's accounting program, evaluated the operating performance of Dunn Company's six divisions. Veronica made the following presentation to Dunn's board of directors and suggested the Percy Division be eliminated. "If the Percy Division is eliminated," she said, "our total profits would increase by $26,000." In the Percy Division, cost of goods sold is $61,000 variable and $15,000 fixed, and operating expenses are $30,000 variable and $20,000 fixed. None of the Percy Division's fixed costs will be eliminated if the division is discontinued. Instructions Is Veronica right about eliminating the Percy Division? Prepare a schedule to support your answer. NOTE: Enter a number in cells requesting a value; enter either a number or a formula in cells with a "?" . Is Veronica right about eliminating the Percy Division? Prepare a schedule to support your answer. After you have completed E20-15, consider the following additional question. Assume that variable cost of goods sold for the Percy Division changed to $68,000 and fixed operating expenses changed to $27,500. There was no change to variable operating costs. How would these changes impact your answer? P21-1A Prepare budgeted income statement and supporting budgets. Cook Farm Supply Company manufactures and sells a pesticide called Snare. The following data are available for preparing budgets for Snare for the first 2 quarters of 2017. 1. Sales: quarter 1, 40,000 bags; quarter 2, 56,000 bags. Selling price is $60 per bag. 2. Direct materials: each bag of Snare requires 4 pounds of Gumm at a cost of $3.80 per pound and 6 pounds of Tarr at $1.50 per pound. 3. Desired inventory levels: Type of Inventory January 1 April 1 Snare (bags) 8,000 15,000 Gumm (pounds) 9,000 10,000 Tarr (pounds) 14,000 20,000 4. Direct labor: direct labor time is 15 minutes per bag at an hourly rate of $16 per hour. 5. Selling and administrative expenses are expected to be 15% of sales plus $175,000 per quarter. 6. Interest Expense is $100,000. 7. Income taxes are expected to be 30% of income before income taxes. Your assistant has prepared two budgets: (1) The manufacturing overhead budget shows expected costs to be 125% of direct labor cost, and (2) The direct materials budget for Tarr shows the cost of Tarr purchases to be $297,000 in quarter 1 and $439,500 in quarter 2. Instructions Prepare the budgeted multi-step income statement for the first 6 months and all required operating budgets by quarters. (Note: Use variable and fixed in the selling and administrative expense budget.) Do not prepare the manufacturing overhead budget or the direct materials budget for Tarr. NOTE: Enter a number in cells requesting a value; enter either a number or a formula in cells with a "?" . COOK FARM SUPPLY COMPANY Sales Budget For the Six Months Ending June 30, 2017 After you have completed P21-1A consider the following additional question. 1. Assume that the expected unit sales in Quarter 1 changed to 36,000 bags of Snare. Also assume that the amount of direct material (Gumm) used changed to 5 pounds per bag; and, that the direct labor rate changed to $18 per hour. Revise the budgets and budgeted income statement to reflect these changes. COOK FARM SUPPLY COMPANY Sales Budget For the Six Months Ending June 30, 2017 P22-1A Prepare flexible manufacturing overhead budget Bumblebee Company estimates that 300,000 direct labor hours will be worked during the coming year, 2017, in the Packaging Department. On this basis, the budgeted manufacturing overhead cost data, shown below, are computed for the year. Fixed Overhead Costs Variable Overhead Costs VC Supervision $96,000 Indirect labor $126,000 $0.42 Depreciation 72,000 Indirect materials 90,000 $0.30 Insurance 30,000 Repairs 69,000 $0.23 Rent 24,000 Utilities 72,000 $0.24 Property taxes 18,000 Lubricants 18,000 $0.06 $240,000 $375,000 $1.25 It is estimated that direct labor hours worked each month will range from 27,000 to 36,000 hours. During October 27,000 direct labor hours were worked and the following overhead costs were incurred. Fixed overhead costs: supervision $8,000, depreciation $6,000, insurance $2,460, rent $2,000, and property taxes $1,500. Variable overhead costs: indirect labor $12,432, indirect materials $7,680, repairs $6,100, utilities $6,840, and lubricants $1,920. Instructions (a) Prepare a monthly manufacturing overhead flexible budget for each increment of 3,000 direct labor hours over the relevant range for the year ending December 31, 2017. (b) Prepare a flexible budget report for October. (c ) Comment on management's efficiency in controlling manufacturing overhead costs in October. NOTE: Enter a number in cells requesting a value; enter either a number or a formula in cells with a "?" . (a) Prepare a monthly manufacturing overhead flexible budget for each increment of 3,000 direct labor hours over the relevant range for the year ending December 31, 2017. BUMBLEBEE COMPANY Packaging Department Monthly Manufacturing Overhead Flexible Budget For the Year 2017 BUMBLEBEE COMPANY Packaging Department Manufacturing Overhead Flexible Budget Report For the Month Ended October 31, 2017 Comment on management's efficiency in controlling manufacturing overhead costs in October. After you have completed P22-1A consider the following additional question. 1. Assume that during October, the actual direct labor hours worked changed to 27,500 hours. In addition, actual variable overhead costs incurred for indirect labor and indirect materials also changed to $13,500 and $8,200 respectively. Revise the flexible budget report for October. (a) Prepare a monthly manufacturing overhead flexible budget for each increment of 3,000 direct labor hours over the relevant range for the year ending December 31, 2017. BUMBLEBEE COMPANY Packaging Department Monthly Manufacturing Overhead Flexible Budget For the Year 2017 Prepare a flexible budget report for October. BUMBLEBEE COMPANY Packaging Department Manufacturing Overhead Flexible Budget Report For the Month Ended October 31, 2017 Comment on management's efficiency in controlling manufacturing overhead costs in October P23-2A Compute variances, and prepare income statement Ayala Corporation accumulates the following data relative to jobs started and finished during the month of June 2017. Cost and Production Data Actual Standard Raw materials unit cost $2.25 $2.10 Raw materials units used 10,600 10,000 Direct labor payroll $120,960 $120,000 Direct labor hours worked 14,400 15,000 Manufacturing overhead incurred $189,500 Manufacturing overhead applied $189,000 Machine hours expected to be used at normal capacity 42,500 Budgeted fixed overhead for June $55,250 Variable overhead rate per machine hour $3.00 Fixed overhead rate per machine hour $1.30 Overhead is applied on the basis of standard machine hours. Three hours of machine time are required for each direct labor hour. The jobs were sold for $400,000. Selling and administrative expenses were $40,000. Assume that the amount of raw materials purchased equaled the amount used. Instructions (a) Compute all of the variances for (1) direct materials and (2) direct labor. (b) Compute the total overhead variance. (c) Prepare an income statement for management. (Ignore income taxes.) NOTE: Enter a number in cells requesting a value; enter either a number or a formula in cells with a "?" . (a)(1) Total Materials Variance: [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 47 pages
Instant download
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 01, 2020
Number of pages
47
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 01, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
119