Pathophysiology > STUDY GUIDE > HSC 3555 pathophysiology Study Guide Chapter 1-4 (GRADED A) Questions and Answers (Revised 2021 Exam (All)
HSC 3555 pathophysiology Study Guide Chapter 1-4 (GRADED A) Questions and Answers (Revised 2021 Exam Study Guide)
Document Content and Description Below
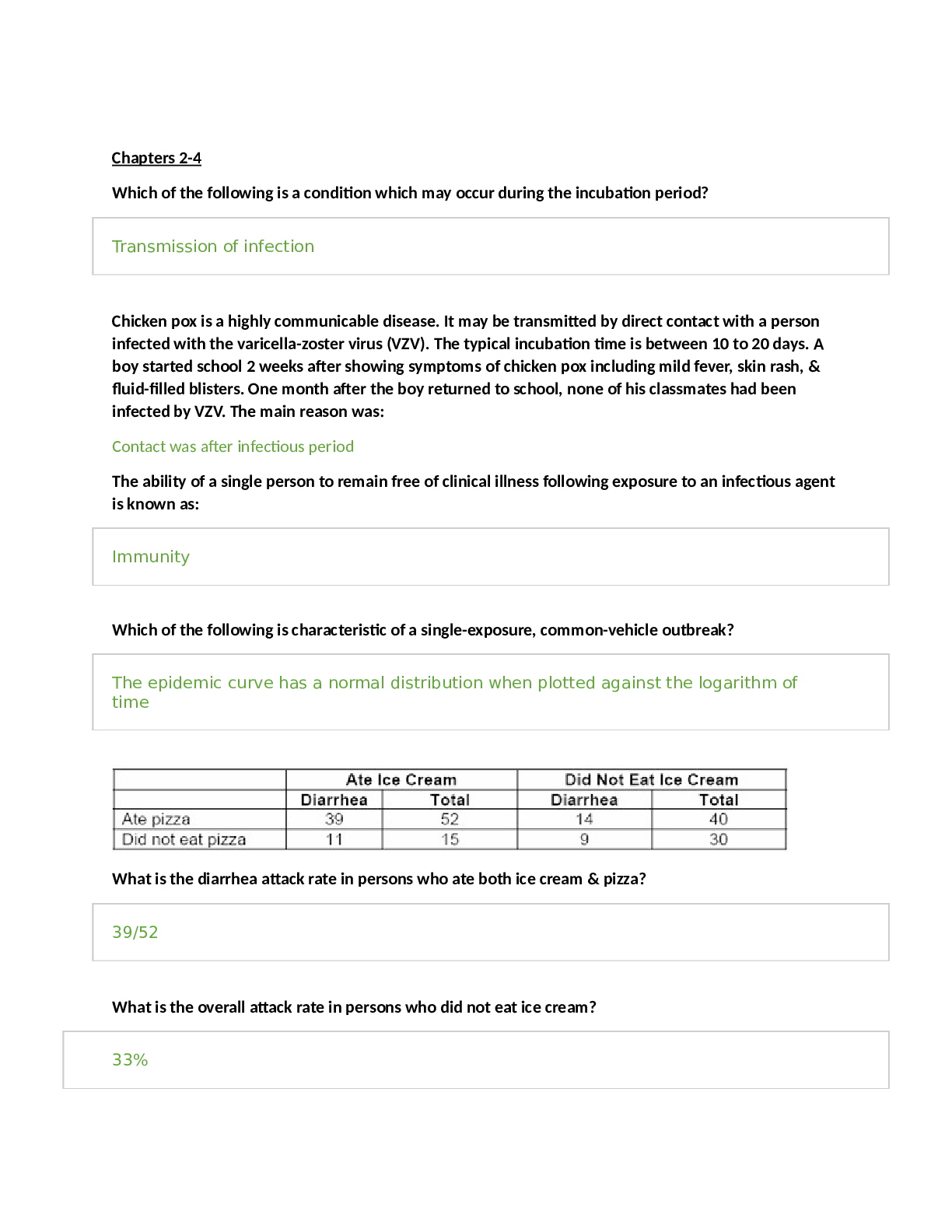
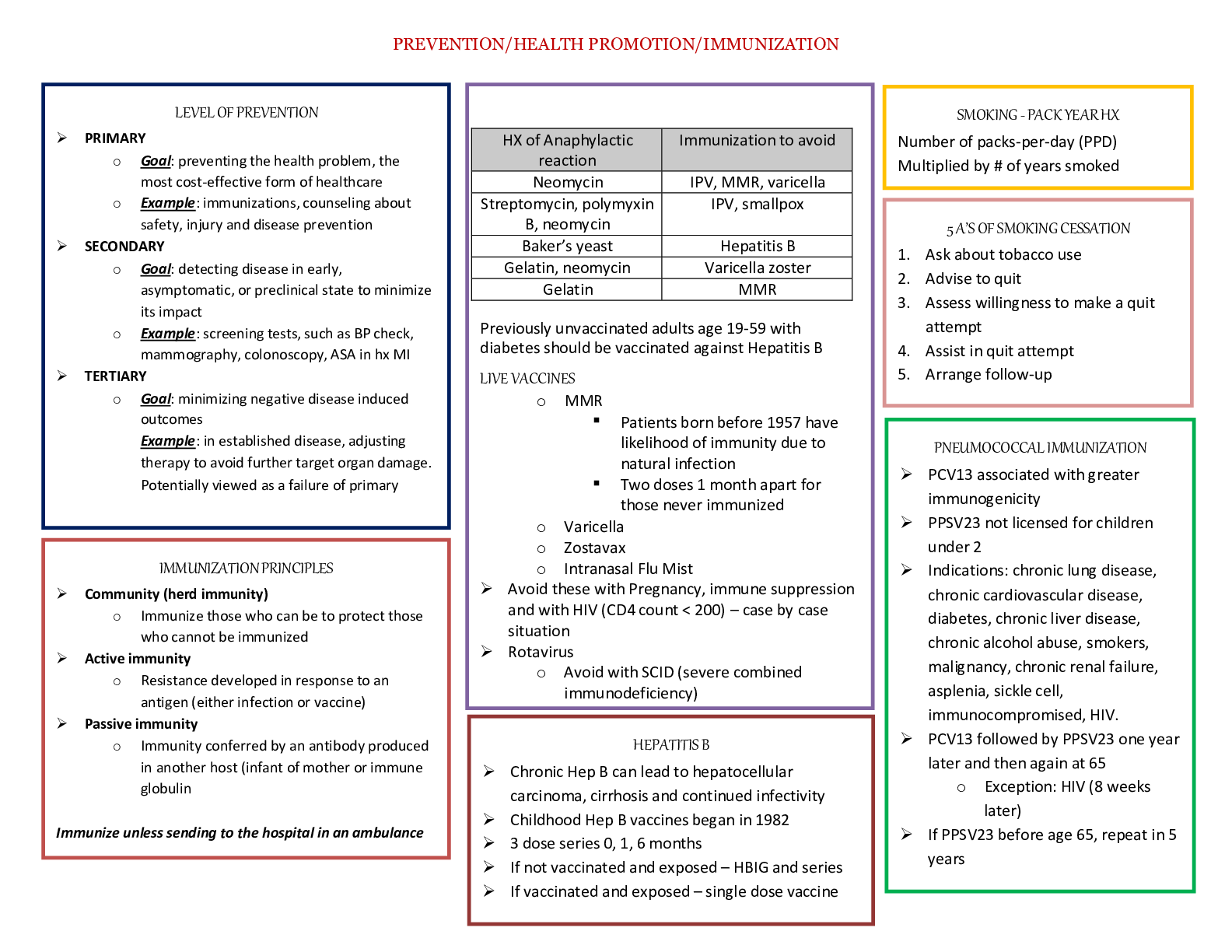
Pathophysiology Study Guide Chapter 1-4 Chapter 1 & 2: 1. The term homeostasis refers to: • Maintenance of an optimal internal environment 2. To which of the following does the term apoptosi... s refer? • Preprogrammed cell self-destruction 3. Pathophysiology involve the study of: • Functional structural changes resulting from disease processes 4. Which of the following statements is true? • Damaged cells may be able to repair themselves 5. What is a period of increased intensity of a chronic disease called? • An exacerbation 6. The term disease refers to: • A deviation from the normal state of health and function 7. The best definition of ischemia is: • A deficit of oxygen supply to the cells, due to circulatory obstruction 8. Which of the following statements best describes reversible cell injury? • The initial stage of cell damage often causes an alteration in metabolic reaction and loss of function 9. The term homeostasis refers to: • Acute 10. The term prognosis refers to the: • Expected outcome of the disease 11. When prolonged ischemia occurs to an area the resulting damage is referred to as: • Infarction 12. Why are the predisposing factors for a specific disease important to health professionals? • To develop preventative measures 13. Disordered cellular growth or abnormal adaptation observable in cervical epithelium is: • Dysplasia 14. Which type of cell injury is irreversible? • Lysis 15. Systemic effects of severe inflammation include: • Fatigue, anorexia, and mild fever 16. During an inflammatory response, erythema is caused by: • Vasodilation in the area 17. Purulent exudates usually contain: • Numerous leukocytes, bacteria, and cell debris 18. A serous exudate is best described as a: • Thin, watery, colorless exudate 19. Systemic manifestations of an inflammatory response include: • Leukocytosis 20. Application of ice to an injured knee reduces edema by: • Causing local vasoconstriction 21. Prostaglandins are released from and cause • Damaged cell membranes, vasodilation and pain 22. The number of neutrophils in the blood is increased significantly: • In order to promote phagocytosis 23. An abscess contains: • Purulent exudate 24. The most common cause of cell injury and inflammation: • Ischemia 25. The cardinal signs of inflammation include all of the following except: • Fever 26. Which of the following cellular elements found in the inflammatory responses are responsible for phagocytosis? • Neutrophils 27. The cell type responsible for synthesis of scar tissue • Fibroblasts 28. Which of the following statements regarding inflammation is incorrect? • Only bacterial and viral infections cause inflammation 29. Which of the following is a plasma-derived mediator? • Clotting system 30. Scar tissue is: • Nonfunctional collagenous and fibrotic tissue 31. Histamine is a chemical mediator primarily released from which cell type: • Mast Cell 32. Swelling during acute inflammation is caused by: • Increased capillary permeability 33. The inflammatory response: • Minimizes injury and promotes healing 34. The sequence of events within the vasculature during the onset of inflammation: • Arteriolar vasoconstriction, vasodilation, increase capillary permeability, plasma leakage, and site of injury edema 35. Which of the following would be the most likely cause of an iatrogenic disease? • An unwanted effect of prescribed drug 36. The manifestations of a disease are best defined as the • Signs and symptoms of disease 37. The best definition of the term prognosis is • Predicted outcome or like-hood of recovery from a specific disease 38. Which of the following is considered a systemic sign of disease? • Fever 39. Etiology is defined as the study of the • Causes of a disease 40. Hypertrophy of the heart would be related to • An increase in the size of the individual cells 41. A tissue in which the cells vary in size and shape and show increased mitotic figures would be called • Dysplasia 42. When a group of cells in the body dies, the change is called • Necrosis 43. Lack of exercise during an illness may cause skeletal muscle to undergo • Atrophy 44. The inflammatory process is caused by: • Any tissue injury 45. Chemical mediators released during the inflammatory response include • Histamine and prostaglandins 46. Which of the following result directly from the release of chemical mediators following a moderate burn injury? 1. Pain 2. Systemic Vasoconstriction 3. Increased Capillary Permeability 4. Pallor • 1 & 3 47. The warmth and redness related to the inflammatory response results from • Increased blood flow into the area 48. The process of phagocytosis involves the • Ingestion of foreign material or cell debris by leukocytes 49. The term leukocytosis means • Increased white blood cells in the blood 50. Replacement of damaged tissue by similar cells is termed • Regeneration 51. A sequelae refers to: • A potential unwanted outcome of the primary condition 52. All of the following are symptoms of a disease except: • A fever 53. The hyperemia that occurs during an inflammatory response is the result of: • Vasodilation 54. Chemotaxis involves the: • Attraction of leukocytes to a chemical signal 55. The movement of fluid that occurs at the site of an acute inflammatory response is of benefit to the host because it: • Dilutes and neutralizes the offending force 56. A potential complication of an exaggerated inflammatory response with excessive fluid and protein in the interstitial space: • Ischemia 57. Aspirin and NSAID's act by: • Decreasing prostaglandin synthesis at the site of inflammation Chapter 3: 1. All of the following characterize the adaptive immune response except: • Provides barrier defense by shedding of surface epithelial cells 2. Which of the following statements is false about self-antigens? • Used to provide a close match for an organ transplant 3. Which of the following is characteristic of all hypersensitivity disorders? • Stimulate the inflammatory response 4. Immunodeficiencies can be caused by all of the following except: • Loss of self-tolerance 5. DiGeorge’s syndrome is a primary immunodeficiency caused by: • A congenital lack of thymic tissue 6. Adaptive immunity is characterized by all of the following except: • Present from birth 7. Placental passage during pregnancy or ingestion of breast milk is referred to as immunity: • Natural passive 8. A child with a rabies exposure bite and is given immune globulin. This type of immunity is referred to as: • Artificial passive 9. The type of immunoglobulin involved in type 1 hypersensitivity reaction is: • IgE 10. The type of immunoglobulin that is transferred from mother to fetus is: • IgG 11. Which of the following antigens stimulates the production of IgE antibodies? • Allergens 12. Which of the following statements best describes an antigen? • A substance that induces an immune response 13. Which reaction is associated with antigen-stimulated T-lymphocytes? • Cell mediated response 14. Diminished immunoglobulin levels can be related to: • A deficit of plasma cells 15. An immunoglobulin deficiency in a child could be suggested if the child has: • Recurrent bacterial infections 16. The true statements about macrophages include which of the following: (1) tissue monocytes (2) process and present antigens to appropriate T or B cell (3) release histamine (4) originate from T cells (5) present in lymph nodes • 1, 2, 5 17. Which of the following combinations are correct? • T-helper lymphocyte: CDA receptor 18. In an atopic person the first exposure to an antigen results in: • Development of IgE antibodies that attach to mast cells 19. All of the following are associated with anaphylaxis except: • Blood loss 20. Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis is characterized by: • A type 3 hypersensitivity reaction 21. The causative mechanism of autoimmune disease is: • Loss of self-tolerance 22. Unique characteristics of HIV include all these features except: • Only cellular immunity is defective 23. T-helper lymphocytes function by: • Facilitating all immune system activity 24. The most critical consequence of HIV infection and progression to AIDS is: • Appearance of opportunistic infections and cancers 25. Which cells are required to process and present antigens from foreign material as the initial step in immune response? • Macrophages 26. Humoral immunity mediated by: • B lymphocytes 27. A patient experienced an episode of influenza 6 months ago. A recent exposure to a mutated form of the same virus results in: • A primary immune response 28. Which type of immunity is provided by a vaccination? • Active artificial 29. When an allergen binds with IgE antibodies on mast cells, resulting in release of chemical mediators, this reaction is called: • Type 1 hypersensitivity 30. The role of memory cells is to: • Support the immune response by recognizing certain antigens 31. The laboratory is indispensable in the diagnosis of immune disorders by all of the following tests except? • Detection of numbers of macrophages 32. Anaphylaxis results from: • Massive release of histamine 33. Anaphylaxis is considered a critical situation because: • Bronchoconstriction and systemic vasodilation develop rapidly 34. Incompatible blood transfusions result in: • Hemolysis of erythrocytes 35. An autoimmune disease means: • Autoantibodies are directed against self-antigens 36. The diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus is confirmed by the presence of in the blood • Presence of antinuclear antibodies 37. Distinguishing clinical features of systemic lupus erythematosus include: • Inflammation in multiple organs 38. The primary target cells for HIV are the: • T-helper lymphocytes 39. A diagnosis of HIV positive means that: • The virus and its antibodies are in the blood 40. HIV infection impairs: • Both humoral and cell-mediated immunity 41. HIV is transmitted by: • Blood, semen, and vaginal secretions from an infected person 42. Loss of cellular immunity results in the following types of disorders: (1) proliferation of viral infections inside the cells (2) development of certain types of cancer (3) bacterial infections (4) viral infectious outside the cells • 1 & 2 43. The most frequently observed selective antibody-dependent immunodeficiency is a deficit of: • IgA 44. Match the disease with the appropriate immunologic mechanism: • Glomerulonephritis: type 3 hypersensitivity 45. Contact dermatitis is the most common form of • Type 4 hypersensitivity 46. The effector cells of adaptive immune responses are: • Lymphocytes 47. Recognition of major histocompatibility complex molecules plays an important role in: • Avoiding transplant rejections 48. Once T cells are activated, they secrete chemical messengers known as: • Cytokines 49. During the latent period before antibodies are detected in the humoral immune response, B cells differentiate first into cell • Plasma 50. A child’s thymus gland is fully formed and proportionately larger than an adult’s. Which of the following processes that contribute to immunity takes place in the thymus gland? • Development of cellular immunity 51. A three-day old infant was exposed to whooping cough prior to discharge home from the hospital, but was able to effect a sufficient immune response in the hours and days following exposure. This immune response may have been due to the presence of which of the following immunoglobulins from the infant’s mother? • IgG 52. The mediators in type 1 hypersensitivity allergic responses are released from: • Mast cells 53. Mismatched blood transfusion reactions with hemolysis of blood cells is an example of type 2, mediated hypersensitivity reaction • Antibody 54. The incubation period of HIV infections refers to the period of time between infection and: • Initial symptoms 55. A patient was diagnosed as HIV positive several years ago. Which of the following blood tests is most clinically useful for determining the stage and severity of their disease? • CD4 cell counts 56. One of the self-regulatory actions of the immune system is to identify self-antigens and to be nonreactive to them. What is this ability of the immune system defined as? • Tolerance 57. Hypersensitivity reactions are the result of: • Abnormal, damaging immune response to normally harmless substances 58. Some people are so sensitive to certain antigens that they react within minutes by developing hives and bronchospasm. What is this commonly known as? • Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction 59. Which of the following can result in an immunodeficiency primarily involving B-cells? • Hypogammaglobulinemia Chapter 4: 1. Bacteria that form in clumps of spheres are called: • Staphylococci 2. All of the following are true endotoxins except: • Release enzymes that cause local damage 3. All of the following are viral mechanisms of host cell damage except: • Releases destructive enzymes 4. Which statement about viruses is not true? • Possess a cell wall and cell membrane 5. Identify the causative agent for pelvic inflammatory disease and sterility in women • Gonorrhea 6. Identify a common causative agent for pelvic inflammatory disease and sterility in women • Gonorrhea 7. Identify the causative agent responsible for a common infection in the oral cavity • Candida 8. The ability of a microbe to cause disease is called: • Pathogenicity 9. An opportunistic infection is: • Microbes that are usually harmless in healthy people 10. Transmission of infectious agents include all of the following except: • Hand washing 11. When bacteria overcome body defenses and are circulating in the blood threatening life • Septicemia 12. Which of the following sequences accurately describes the stages of a disease? • Incubation, prodromal, acute, convalescent, and resolution 13. The major factors affecting the pathogenesis of infectious disease include all of the following except: • Variations in signs and symptoms 14. Bacterial virulence depends on all of the following except: • Intergrading into host cell DNA 15. All of the following factors create a high risk for TB except: • Allergy 16. The most significant event in the mode of transmission of infectious agents is: • Unwashed hands 17. The local clinical signs and symptoms of infection are usually those of inflammation and include all of the following except: • Ischemia 18. The most reliable laboratory test used to identify the presence of tuberculosis organisms in a sputum sample would be: • Culture and sensitivity 19. An anaerobe thrives and reproduces best in: • The absence of oxygen 20. The presence of pili: • Promotes attachment of the bacteria to tissue 21. Microbial mutation means that: • Genetic information and some microbial characteristics have changed 22. Most microbes exhibit a preference for a particular type of cell. This is referred to as: • Tropism 23. A virus that persists in infectious form and continues to replicate and cause chronic injury: • A productive virus 24. All of the following are characteristics of fungi except: • Deep mycosis are acquired by skin contact 25. Which of the following is not classified as a protozoa? • Clostridium difficile 26. A local sign most suggestive of a bacterial infection: • A suppurative inflammatory reaction 27. An example of a gram negative bacillus responsible for urinary tract infection is: • E. coli 28. The most significant virulence factor of gram negative bacteria is: • Release of endotoxins 29. The term nosocomial infection means: • Infection acquired in a hospital or medical facility 30. Transmission of microbes by direct contact includes: • Sexual intercourse 31. The laboratory test most appropriate for determining the causative bacterial organism and directing treatment: • Culture and sensitivity tests 32. One of the stages in the course of an infectious disease that is characterized by vague, non-specific signs and symptoms: • Prodromal stage 33. The incubation period refers to the time period between: • Entry of the pathogen into the body and the first signs of infectious disease 34. Bacteria that forms in pairs are called: • Diplococci 35. Limiting factors in growth of bacteria include insufficient nutrients and oxygen. An example of an anaerobic microorganism would be: • Clostridium tetani 36. Release of endotoxins initially results in: • Increased capillary permeability and vascular collapse 37. All of the following viruses are causative agents of pneumonia except: • Rhinovirus 38. A fomite refers to: • Inanimate objects that carry microorganisms 39. The potency of a microbe refers to: • Virulence 40. The infection cycle may be broken by all of the following methods except: • Decreasing host resistance 41. Infection may be eradicated without antimicrobial treatment: • When host defenses are at their peak 42. Resident flora refers to non-pathogenic microbes normally present in all of the following locations except: • Stomach 43. An example of certain intracellular viruses that can alter host cell DNA thus leading to the development of malignant cells or cancer • Human papilloma virus 44. Transmission of cholera to humans from oysters growing in waters contaminated by human feces is called: • Indirect contact 45. Infections in healthcare facilities may be caused by all of the following except: • Overuse of antiseptics 46. Serologic blood tests used in the laboratory help determine the cause of an infection by the measurement of which of the following? • Antigens and antibodies 47. The course of any infectious disease progresses through several distinct stages after the pathogens enter the host. Although the duration may vary, the hallmark of the prodromal stage is: • Initial appearance of symptoms 48. A 9-month old infant has been diagnosed with botulism after he was fed honey. The child developed neuromuscular deficits which were attributed to the release of substances by Clostridium botulinum bacteria, a gram positive organism. Which virulence factor contributed to this child’s illness? • Neurotoxin [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 13 pages
Instant download

Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 15, 2021
Number of pages
13
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 15, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
199













.png)







.png)
.png)

.png)





