*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NURS 8022 Chapter 37: Alterations of Digestive Function in Children (All)
NURS 8022 Chapter 37: Alterations of Digestive Function in Children
Document Content and Description Below
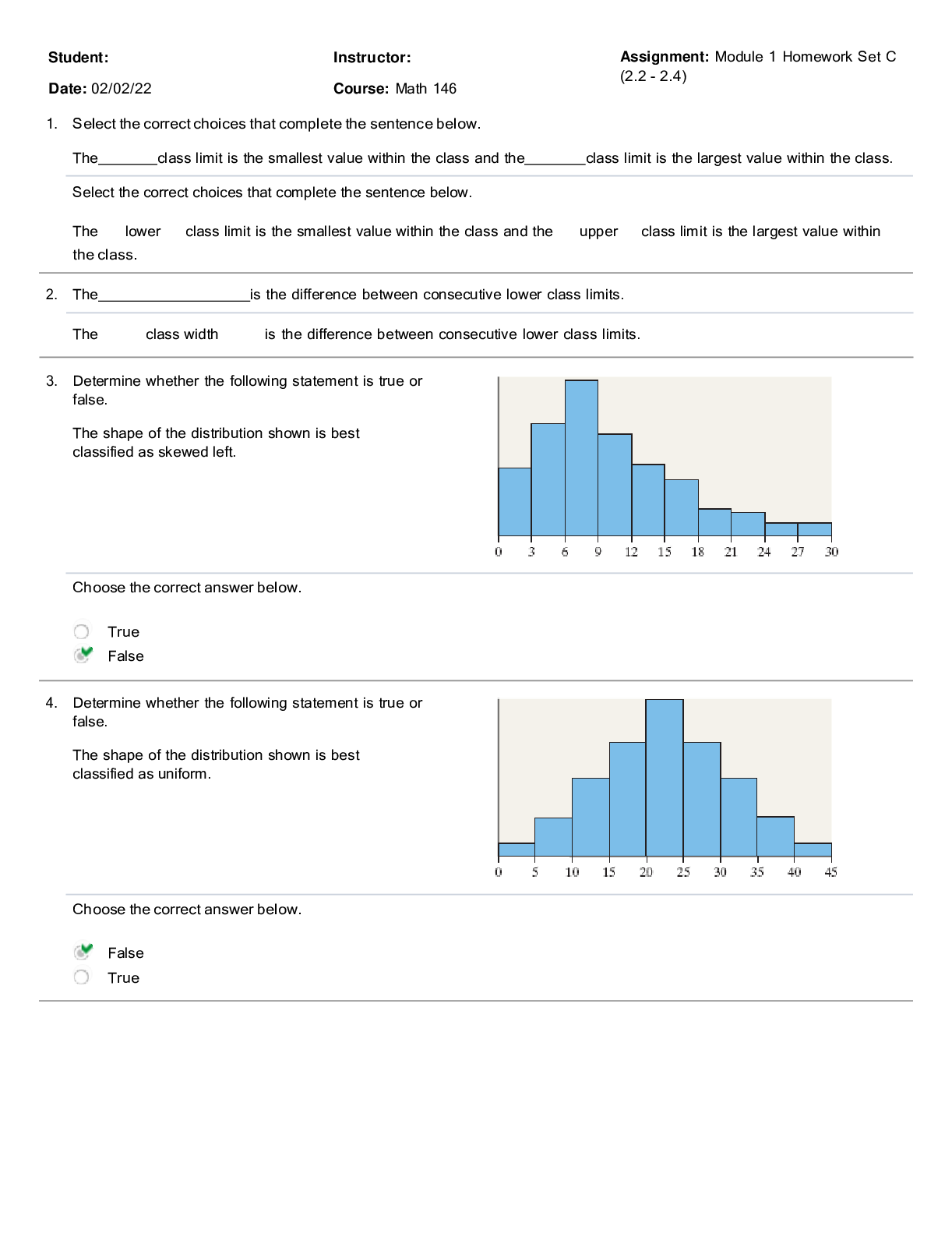
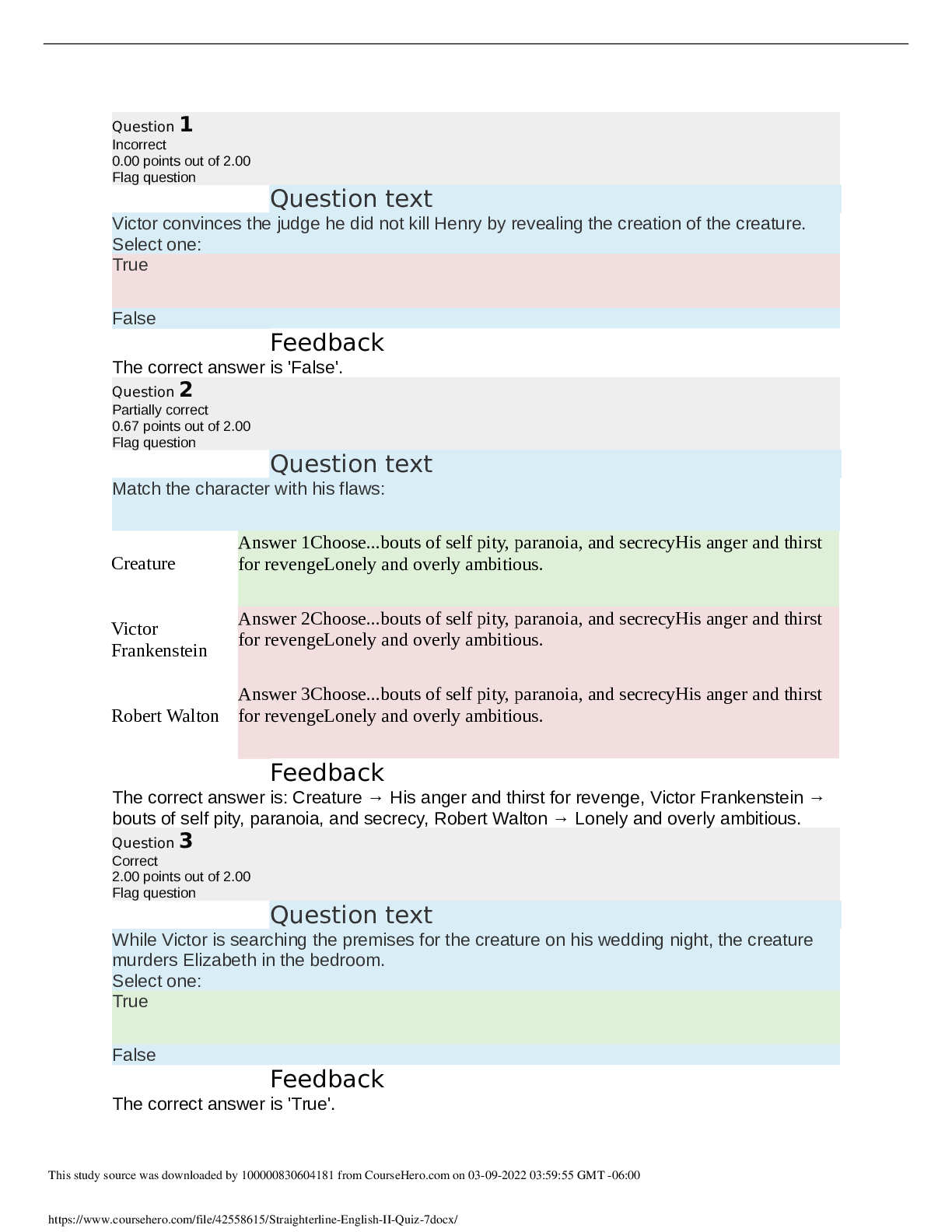
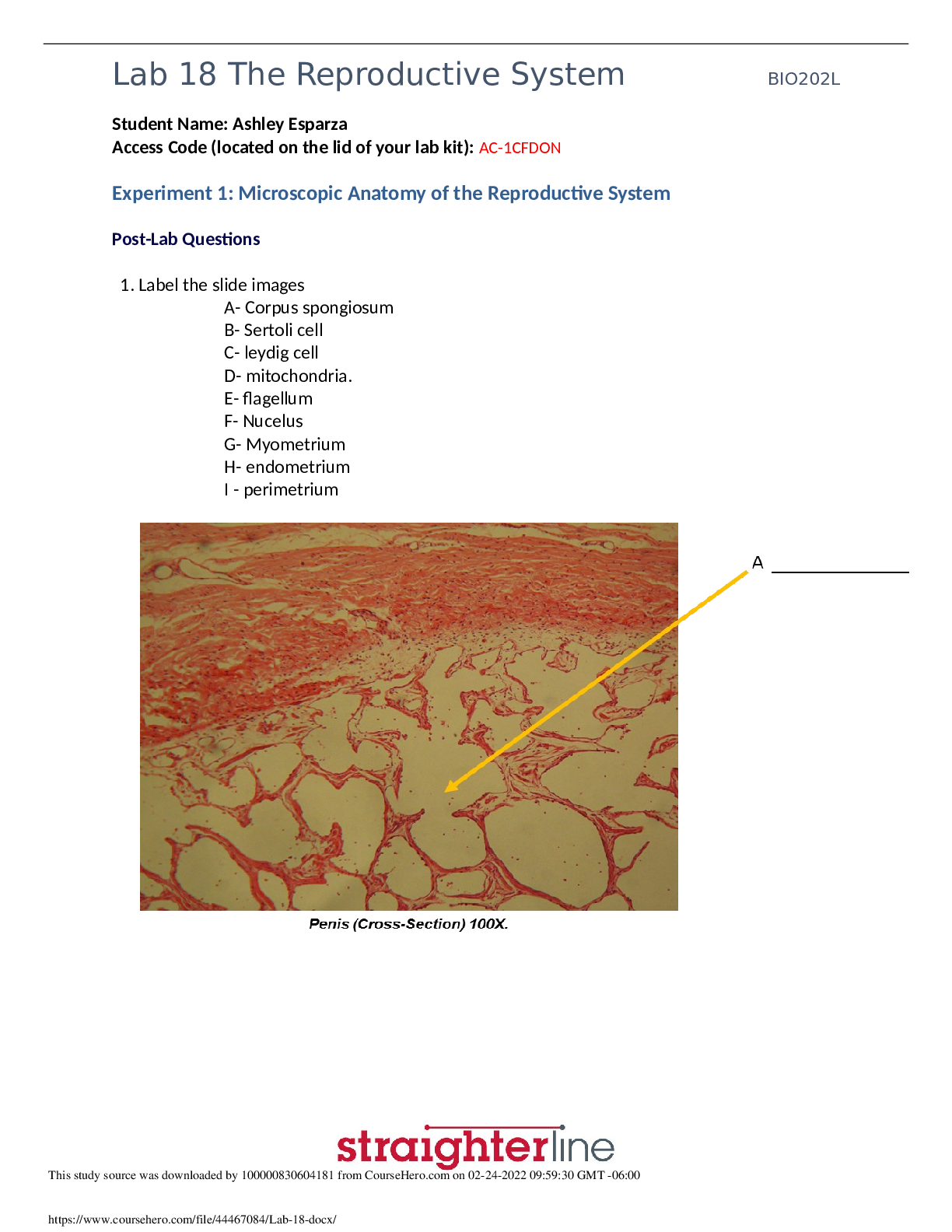
1. The family learns that a 3D ultrasound of a 9-week fetus shows incomplete fusion of the nasomedial process. What is this defect commonly called? a. Cleft lip b. Nasal passage atresia c. Esophag... eal atresia d. Lack of dentition ANS: A Cleft lip, not nasal passage atresia, occurs when there is lack of or incomplete fusion of the nasomedial or intermaxillary process. In esophageal atresia, the esophagus ends in a blind pouch. Lack of dentition is not due to incomplete fusion of the processes. REF: p. 950 2. What term is used to document the condition that exists when the esophagus ends in a blind pouch? a. Esophageal atresia b. Tracheoesophageal stenosis c. Esophagitis d. Pyloric stenosis ANS: A When the esophagus ends in a blind pouch, the condition is referred to as esophageal atresia; the trachea is not involved. Esophagitis is inflammation of the esophagus. Pyloric stenosis is a narrowing of the connection between the stomach and the duodenum. REF: p. 951 3. Which condition should the nurse assess for in mothers carrying fetuses affected by esophageal malformations? a. Enlarged placentas b. Excessive amniotic fluid c. Short umbilical cords d. Foul-smelling vaginal discharge ANS: B Polyhydramnios (excessive amniotic fluid) is reported to occur in mothers of affected infants because of alterations in fetal swallowing. Esophageal malformations are not associated with enlarged placentas, short umbilical cords, or vaginal discharge. REF: p. 951 4. A 2-week-old infant vomits forcefully immediately after feeding for no apparent reason and is frequently constipated. These signs support which diagnosis? a. Pyloric stenosis This study source was downloaded by 100000827039679 from CourseHero.com on 07-15-2021 02:40:29 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/21067772/c37/ This study resource was shared via CourseHero.comb. Meconium ileus c. Esophageal atresia d. Galactosemia ANS: A Between 2 and 8 weeks after birth, an infant who has fed well and gained weight begins forceful, nonbilious vomiting immediately after feeding. Constipation occurs because little food reaches the intestine. The signs do not support a diagnosis of meconium ileus, esophageal atresia, or galactosemia. REF: p. 952 5. A sign that a newborn infant may have pyloric stenosis is: a. diarrhea. b. bile regurgitation. c. olive-sized mass in the upper abdomen. d. ascites with a fluid wave visible across the abdomen. ANS: C A firm, small, movable mass, approximately the size of an olive, is felt in the right upper quadrant in 70-90% of infants with pyloric stenosis. Pyloric stenosis is not associated with diarrhea, bile regurgitation, or ascites. REF: p. 952 6. A 2-month-old female is brought to the emergency room (ER) for persistent bile-stained vomiting after feeding. Physical examination reveals dehydration, and x-ray reveals gas bubbles in the intestines. What is the most likely cause of this condition? a. Malrotation b. Ileocecal displacement c. Pyloric stenosis d. Meconium ileus ANS: A In infants, malrotation obstruction causes intermittent or persistent bile-stained vomiting after feedings. Radiographic films of the abdomen and barium studies show intestinal gas bubbles and distention proximal to the site of obstruction. This assessment data does not support a diagnosis of ileocecal displacement. Pyloric stenosis is manifested by vomiting, but it is not bile stained and the colon is not displaced. In meconium ileus, there is an intestinal obstruction caused by meconium formed in utero. REF: p. 953 7. Meconium ileus (MI) is associated with which of the following disorders? a. Pyloric stenosis b. Esophageal atresia c. Cystic fibrosis d. Esophagitis ANS: C Meconiu [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages
Instant download
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 15, 2021
Number of pages
9
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 15, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
74
.png)





.png)

.png)



.png)

