Physics > Lab Report > Florida Atlantic University - PHY 2048LLab Report 7: Experiment 7. Static Equilibrium of a rigid bod (All)
Florida Atlantic University - PHY 2048LLab Report 7: Experiment 7. Static Equilibrium of a rigid body. Verify the conditions for the static equilibrium of a rigid body.
Document Content and Description Below
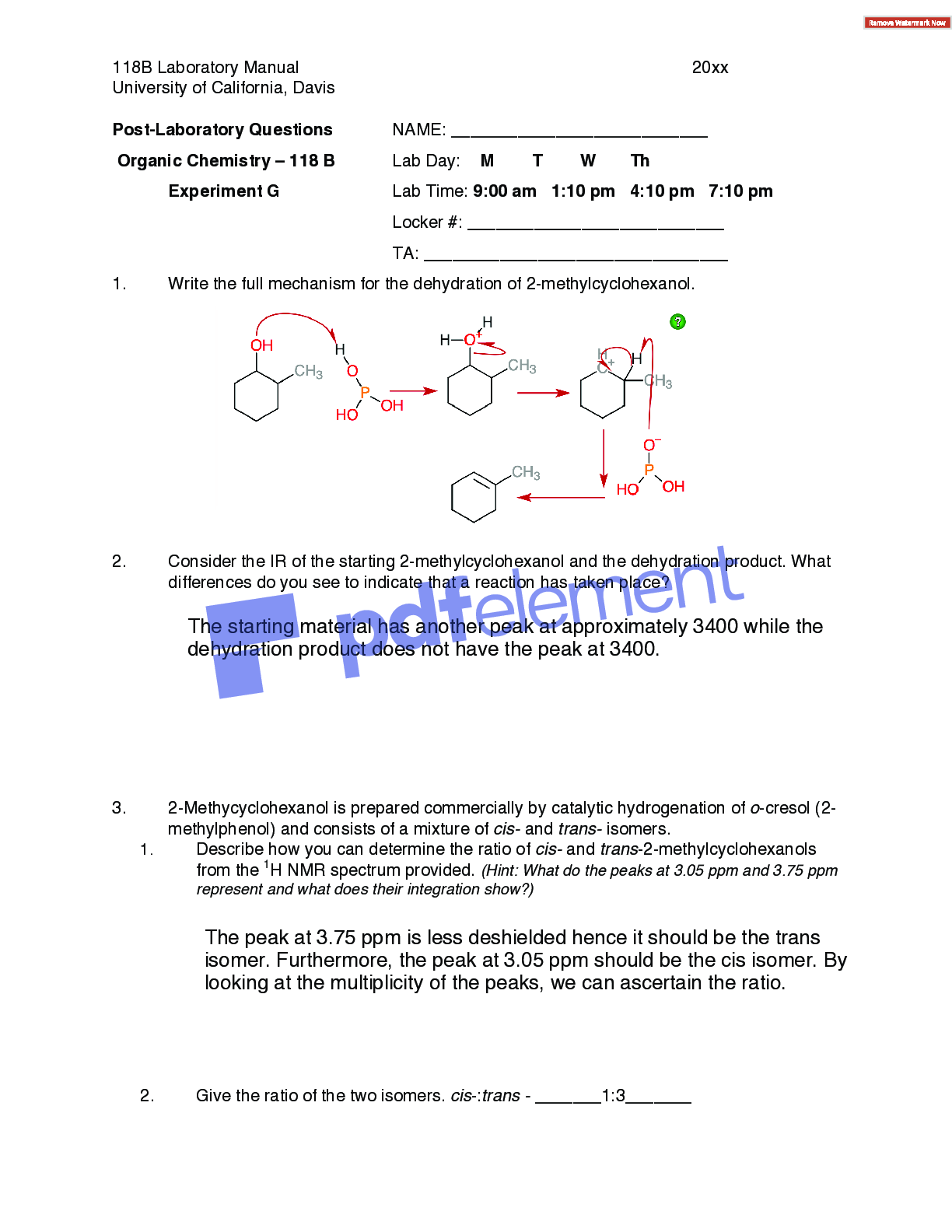
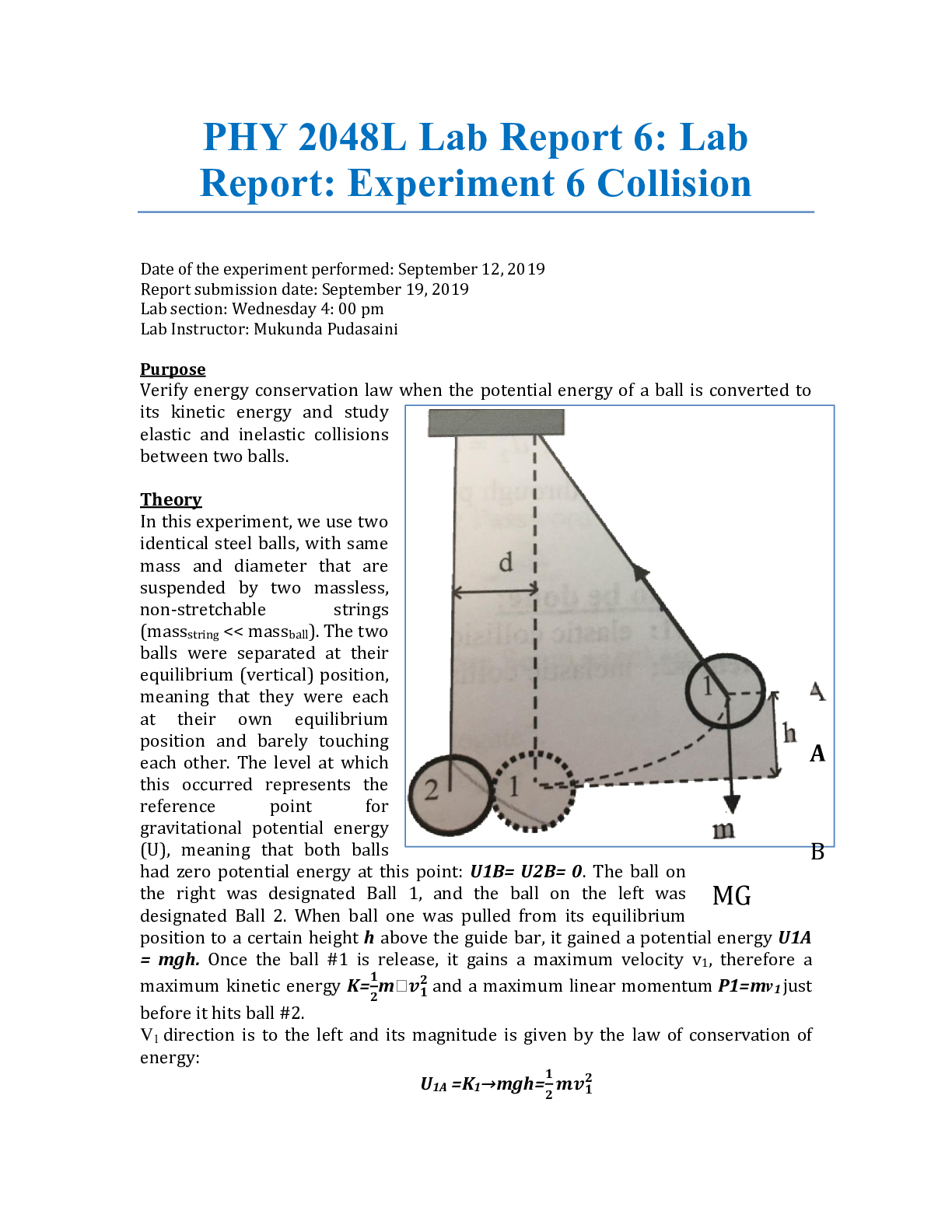
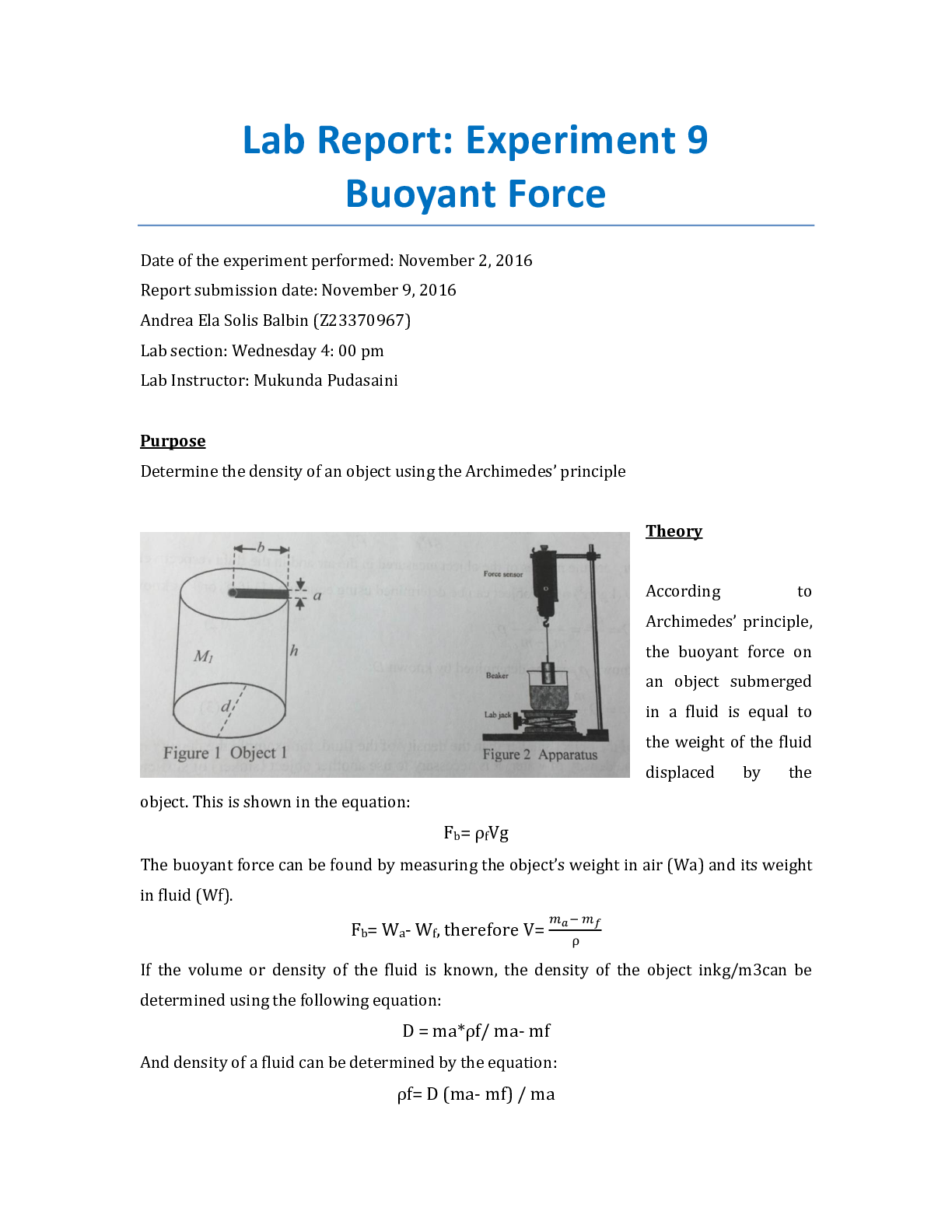
Lab Report: Experiment 7 Static Equilibrium of a rigid body Date of the experiment performed: September 19, 2019 Report submission date: September 26, 2019 Lab Instructor: Mukunda Pudasaini P... urpose Verify the conditions for the static equilibrium of a rigid bocy Theory A torque (T) is the quantitative measure of the tendency of a force to cause or change the rotational motion of a body. When a force F acts at a point P having a position vector r with respect to an origin O, the torque r of the force with respect to O is the vector quantity., represented in this equation: T = r x F. The direction of T is perpendicular to r and F. The magnitude of the T is: T=r x F x sinΦ, where Φ is the angle between r and F (0< Φ < π) or also, T = F(r x sinΦ) = FL, where L = r x sinΦ, is the perpendicular distance from O to the acting line of F and L is called lever arm or moment arm of force F about O. In particular, if both r and F lie in a place perpendicular to the axis of rotation, then the torque r is directed along the axis of rotation, with a sense given by the righ-hand rule. Additionally, the conditions for the mechanical equilibrium of a rigid body is F net= 0 and T net= 0 about any rotating axis. In this experiment, it is only consider a special equilibrium situation in which a rigid body is at rest. Such a body is said to be in static equilibrium. With the convention sigh rule of torque, the vector sum in the previous equation becomes an algebraic sum in the case that all forces in the same plan and the axis of rotation are perpendicular to this plane Questions and exercises 1. Do the equilibrium conditions meet in Measurement #1 and #2? If error exists, what are the main sources? 2. Torque is everywhere in everyday life. Explain why the torques, not the forces, play essential roles in the following actions 3. a. The condition is satisfied because the toque net would be zero due to its b. There is rotational acceleration, so the sum of the torques is not zero. c. The individual torque does not depend on the position of the rotational axis. If the total torque is equal to zero, then because there is not ratating and the distance does not matter because of static equilibrium [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 4 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 01, 2020
Number of pages
4
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 01, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
215


 (1).png)