Economics > EXAM > Middle Tennessee State University MBAE 6865 Economic Decisions for Managers. Quiz CHAPTER 16. All An (All)
Middle Tennessee State University MBAE 6865 Economic Decisions for Managers. Quiz CHAPTER 16. All Answers Correct.
Document Content and Description Below
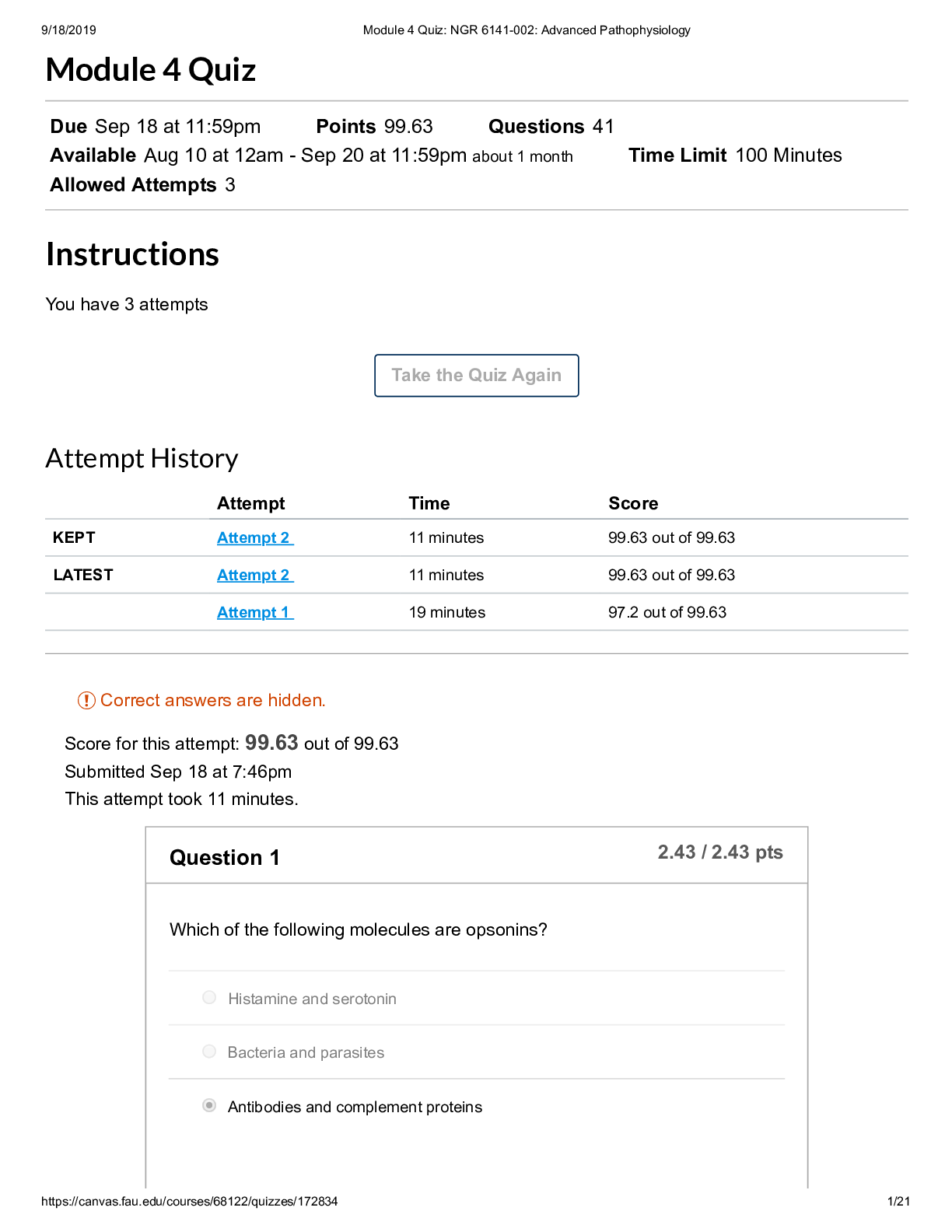
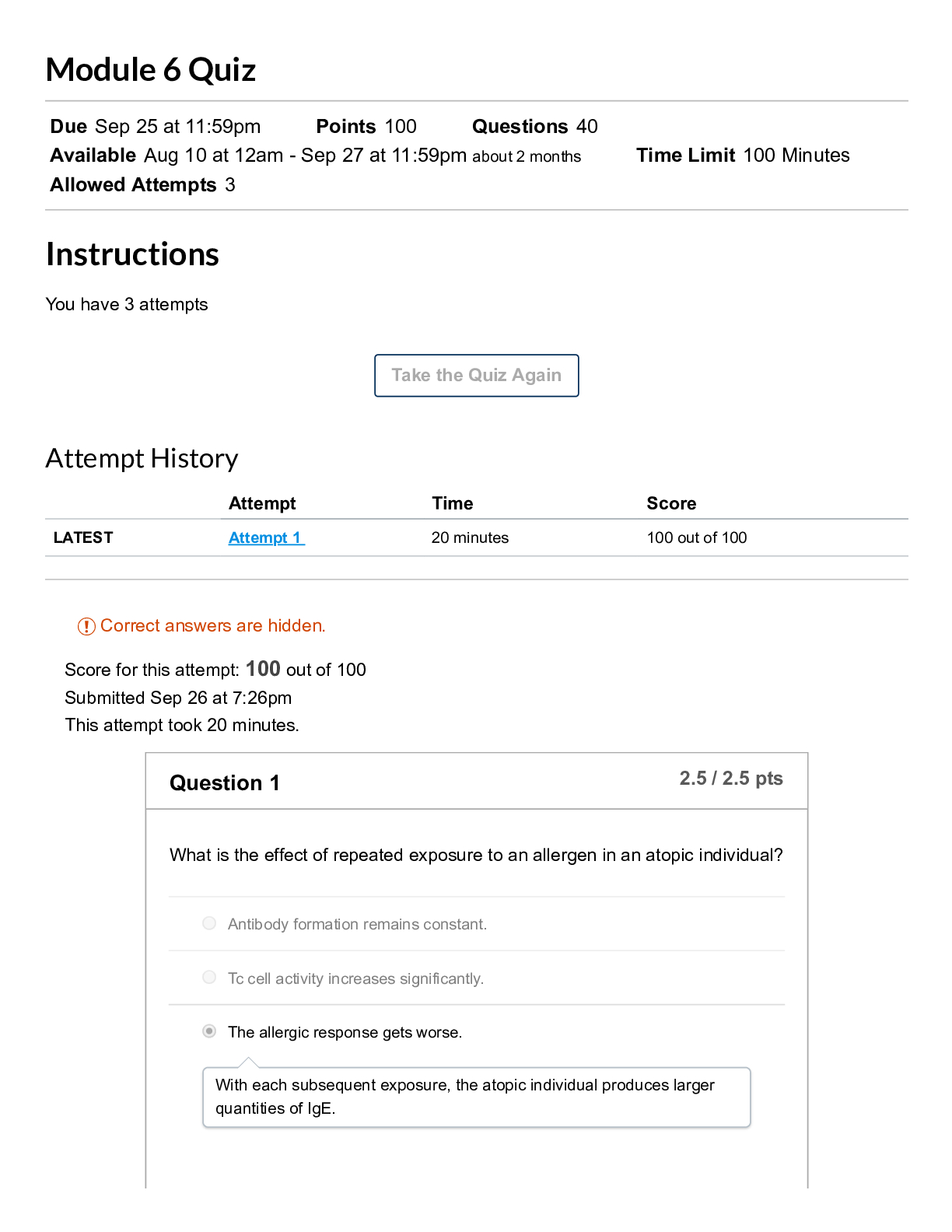
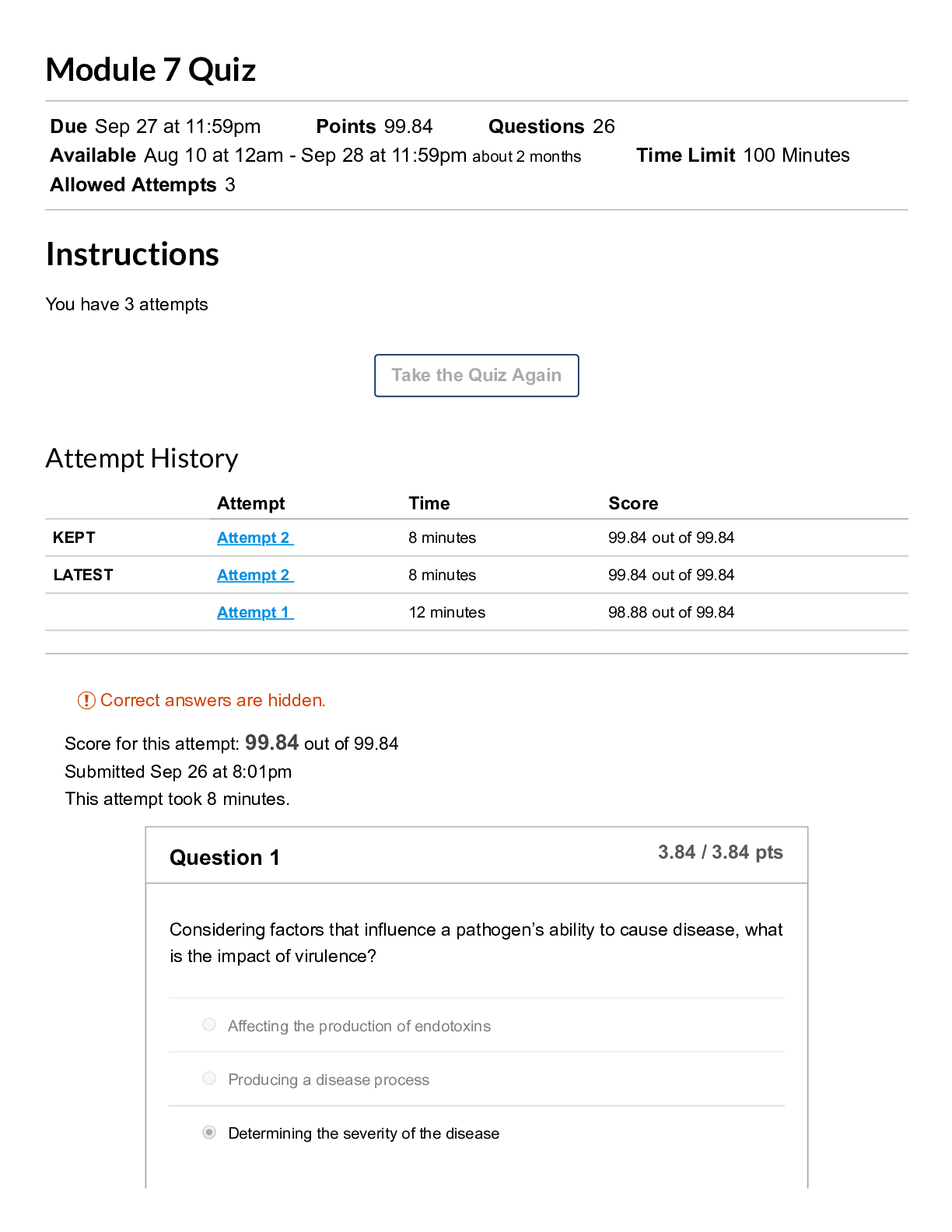
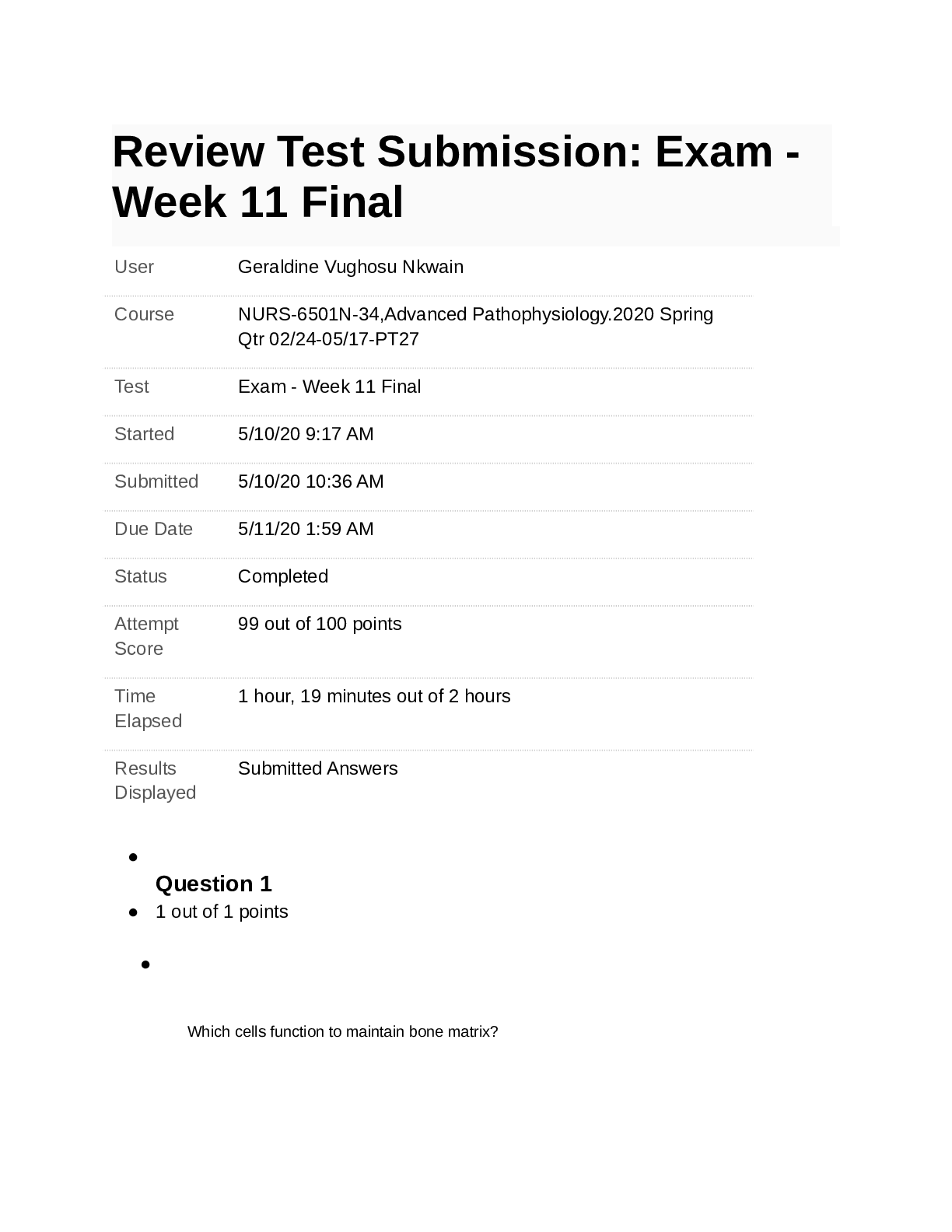
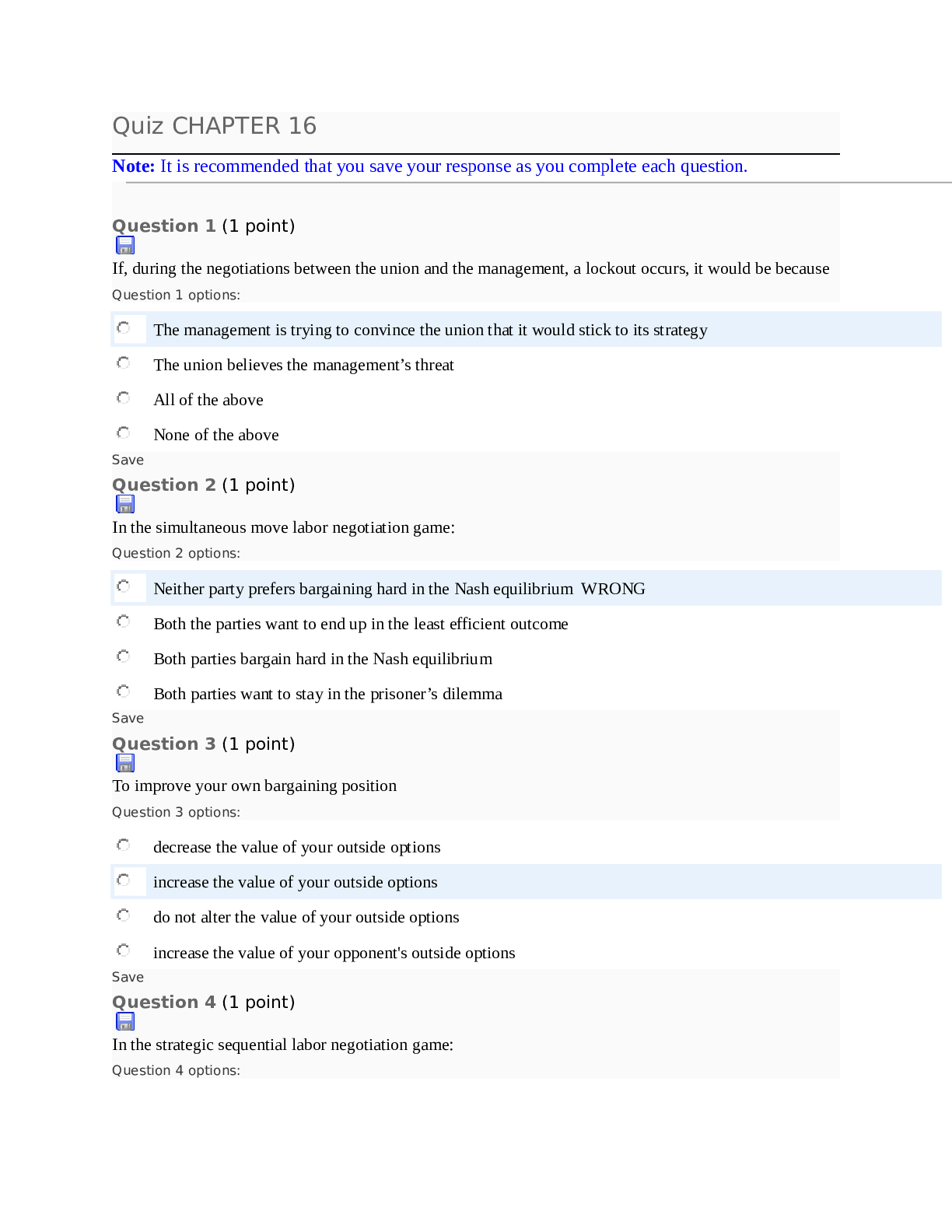
Quiz CHAPTER 16 Note: It is recommended that you save your response as you complete each question. Question 1 (1 point) If, during the negotiations between the union and the management, a lockout o... ccurs, it would be because Question 1 options: The management is trying to convince the union that it would stick to its strategy The union believes the management’s threat All of the above None of the above Save Question 2 (1 point) In the simultaneous move labor negotiation game: Question 2 options: Neither party prefers bargaining hard in the Nash equilibrium WRONG Both the parties want to end up in the least efficient outcome Both parties bargain hard in the Nash equilibrium Both parties want to stay in the prisoner’s dilemma Save Question 3 (1 point) To improve your own bargaining position Question 3 options: decrease the value of your outside options increase the value of your outside options do not alter the value of your outside options increase the value of your opponent's outside options Save Question 4 (1 point) In the strategic sequential labor negotiation game: Question 4 options:The first mover has an advantage The second mover has an advantage There is no advantage to either mover None of the above Save Question 5 (1 point) In the nonstrategic view of bargaining Question 5 options: The games are played without identifying the specific strategies Both the parties usually get some positive surplus The bargaining outcome is affected by both the parties’ disagreement values All of the above Save Question 6 (1 point) If, during the negotiations between the union and the management a strike occurs, it would be because Question 6 options: The union is trying to convince the management that it will stick to its strategy The management doesn’t believe the union’s threat All of the above None of the above Save Question 7 (1 point) When buying a car from a dealership, to get the best bargain Question 7 options: Never stick to the first offer you make Allow room for bargaining Threaten to walk out if the dealer does not accept your offer Quote your highest willingness to pay Save Question 8 (1 point) If a union threatens to strike during a slow demand period, it is more likely toQuestion 8 options: Have its conditions accepted Have its conditions rejected Get laughed at All of the above Save Question 9 (1 point) The disagreement value in a nonstrategic game is most closely associated with Question 9 options: opportunity costs fixed costs variable costs accounting costs Save Question 10 (1 point) Which of the following will improve your salary bargaining position Question 10 options: Wait until the large project you were integral to is completed Wait until your employer has hired many others with similar skills as yours' Wait until your employer has invested greatly into a long-term project you lead Wait until your employer buys new machinery that you are incapable of operating Save Question 11 (1 point) The “axiomic” view of bargaining is the Question 11 options: Strategic view of bargaining Non-strategic view of bargaining All of the above None of the above Save Question 12 (1 point)When buying a car from a dealer, to get a better bargaining position Question 12 options: Always carry your check book to show willingness to buy Carry only blank checks to ease the transaction Carry a cashier check that cannot be modified All of the above Save Question 13 (1 point) In the nonstrategic view of bargaining Question 13 options: The first-mover usually gains more The second-mover usually gains more The third-mover usually gains more The outcome depends on which mover can commit to a strategy Save Question 14 (1 point) In the simultaneous move labor negotiation game: Question 14 options: The payoffs are always higher if you accommodate The payoffs are always higher if you bargain hard The payoffs from accommodating are only higher if your opponent bargains hard CORRECT The payoffs from accommodating are only higher if your opponent accommodates WRONG Save Question 15 (1 point) When buying a car from a commission salesman you improve your bargaining position by Question 15 options: shopping for last year's model when the new model year cars are arriving shopping when the showroom is full of customers shopping when the car lot has few cars left unsold shopping toward the beginning of the month SaveQuestion 16 (1 point) Sam is responsible for ordering office supplies for the firm gets a bonus if the firm stays well-stocked at all times. The bonus implies he is more likely to Question 16 options: Pay lower prices for the supplies Pay higher prices for the supplies Have more stock outs Resign from the position Save Question 17 (1 point) Under the non-strategic view of bargaining, the terms of agreement are determined by Question 17 options: Each parties outside options Your gain from agreement Your opponents gain from agreement All of the above Save Question 18 (1 point) Jill, a bookkeeper, just received an attractive offer from an outside firm and so she asks for a raise from her current employer. She would be in a strong bargaining position because Question 18 options: Her value for disagreement has increased Her value for disagreement has decreased Her value for disagreement has not changed Her value for agreement has not changed Save Question 19 (1 point) When buying a car from a commission salesman you improve your bargaining position by Question 19 options: shopping when the new model year cars have just arrivedshopping when the showroom is empty of customers shopping when the car lot has only few cars left unsold shopping toward the beginning of the month Save Question 20 (1 point) When buying a car from a commission salesman you improve your bargaining position by Question 20 options: shopping when the new model year cars have just arrived shopping when the showroom is full of customers shopping when the car lot has very few cars left unsold shopping toward the end of the month Save CHAPTER 17 Quiz Chapter 17 Note: It is recommended that you save your response as you complete each question. Question 1 (1 point) Expected values are Question 1 options: Values that you expect from an individual Mean values Weighted average outcomes Both B&C Save Question 2 (1 point)When a variable can take on different values Question 2 options: it is a random variable it is a dependent variable it is an dummy variable it is an endogenous variable Save Question 3 (1 point) Expected value is Question 3 options: (Probability of state A+Value in state A) (Probability of state B+Value in state B) (Probability of state A*Value in state A)+(Probability of state B*Value in state B) (Probability of state A*Value in state A)-(Probability of state B*Value in state B) (Probability of state A-Value in state A) (Probability of state B-Value in state B) Save Question 4 (1 point) The key distinction between risk and uncertainty is Question 4 options: Risk cannot be quantified, priced or traded Uncertainty refers to not knowing possible outcomes or their probabilitiesUncertainty is modeled by listing the possible outcomes and assigning probabilities to the outcomes Risk has to do with not knowing the probability distribution of a random variable Save Question 5 (1 point) Type I errors are Question 5 options: False negatives False positives True negatives True positives Save Question 6 (1 point) A manager may over-research the appropriateness of a decision Question 6 options: Because the costs of a false positive are usually larger Because the costs of a false negative are usually larger WRONG Because it is important to be 100% certain before making a decision Because managers can face inordinate censure from agreeing to a bad decision CORRECT Save Question 7 (1 point)A "false positive" is Question 7 options: When you incorrectly conclude that your hypothesis is true CORRECT When you incorrectly conclude that your hypothesis is false WRONG When you correctly conclude that your hypothesis is true When you correctly conclude that your hypothesis is false Save Question 8 (1 point) A "false negative" is Question 8 options: When you incorrectly conclude that your hypothesis is true WRONG When you incorrectly conclude that your hypothesis is false CORRECT When you correctly conclude that your hypothesis is true When you correctly conclude that your hypothesis is false Save Question 9 (1 point) Type II errors are Question 9 options: False negatives False positivesTrue negatives True positives Save Question 10 (1 point) We worry that false negatives occur too often relative to false positives due to Question 10 options: Most hypotheses being false It being appropriate to set a high standard for acceptance of a hypothesis Managers having an incentive to make a false negative conclusion because they are harder for superiors to observe CORRECT? istinction between risk and uncertainty ver-research They are not too common WRONG Save Question 11 (1 point) If a deal looks too good to be true Question 11 options: The seller most likely made a mistake Be cautious. It probably is too good to be true Trust the seller to give you a good deal A good deal is a good deal. Go for it. Save Question 12 (1 point)A random variable is Question 12 options: A variable that takes of values that are uncertain A variable that takes on known values A variable that is always zero A variable that takes on null values only Save Question 13 (1 point) While working under uncertain conditions, it is better to Question 13 options: Maximize total profits Minimize error costs Maximize error costs Minimize profits Save Question 14 (1 point) At a fair carnival roulette wheel, a player can either win $10, $30, or $80. Assuming that the wheel is fair, what is the expected value of the play? Question 14 options: $20$40 $60 $80 Save Question 15 (1 point) The VP in charge of product launches hypothesizes that a particular product would be profitable, then launching an unprofitable product is a Question 15 options: Type I error Type II error Type III error Type IV error Save Question 16 (1 point) Three possibilities are equally likely and have payoffs of $3, $6, and $9. The expected value is: Question 16 options: $4 $5 $6 $7 SaveQuestion 17 (1 point) Six possibilities are equally likely and have payoffs of $2, $4, $6, $8, $10, and $12. The expected value is: Question 17 options: $4 $5 $6 $7 Save Question 18 (1 point) At a carnival roulette wheel, a player can either win $10, $30, or $80. If it costs $20 to play, should the player expect the game to be fair? Question 18 options: Yes, because it costs to play No, because on average the individual would be earning money on the wheel No, because all the carnival attractions are unfair Need more information Save Question 19 (1 point) You are considering buying a store. In order to better access your return on the investment, you must ask the storeowner for the figures on days when Question 19 options:Sales are high, costs are low Sales are low, costs are high Both sales and costs are high All of the above Save Question 20 (1 point) Four possibilities have probabilities 0.4, 0.2, 0.2 and 0.2 and values $20, $20, $40, and $40 respectively. The expected value is: Question 20 options: $22 $24 $26 $28 SaveQuiz CHAPTER 18 Note: It is recommended that you save your response as you complete each question. Question 1 (1 point) With which choice are you more likely to avoid Bid-rigging cartels? Question 1 options: Winning bids are not identified Winning bidders are not identified Cheaters do not fear punishment from other cartel members All of the above Save Question 2 (1 point) With which choice are you more likely to avoid Bid-rigging cartels? Question 2 options: Holding oral auctions Holding Vickery auctions Holding sealed-bid auctions Both B&C Save Question 3 (1 point) More bidders tend to increase the selling price in a second-price auction because Question 3 options:bidders bid less aggressively the true value of the losers is lower the true values of the losers is higher Both A&C Save Question 4 (1 point) To attract more bidders, and more aggressive bidders, to your common-value auction Question 4 options: withhold relevant information about the value of the object allow bidders to know how others are bidding do not allow potential bidders to examine the object too closely do not hold oral auctions Save Question 5 (1 point) _______losing bidders lead to _____winning bids Question 5 options: Stronger; raise Weaker; reduce Stronger; raiseNone of the above Save Question 6 (1 point) In a sealed-bid first price auction, if you notice that your competition is weaker, you should Question 6 options: Shade your bid more Shade your bid less Bid more aggressively Both B&C Save Question 7 (1 point) To attract more aggressive bidding in a common-value auction, as an auctioneer, you should Question 7 options: Release no information about the item Do not let the bidders examine the item closely Do not release any adverse information about the item Release maximum information about the item, even if it is adverse Save Question 8 (1 point) In a sealed-bid first price auction, if you notice that your competition is stronger, you should Question 8 options:Shade your bid more Shade your bid less Bid more aggressively Both B&C Save Question 9 (1 point) With which choice are you more likely to avoid Bid-rigging cartels? Question 9 options: Holding smaller auctions Holding larger auctions Holding frequent auctions Both B&C Save Question 10 (1 point) In Vickery auctions, the item is awarded to the highest bidder at a price set by Question 10 options: Highest bid Second highest bid Third highest bidCost Save Question 11 (1 point) Katy is holding an English auction. If she estimates the values of her bidders to be $2, $4, $10, $15 and $25, she should expect to be able to make ____ off the auction Question 11 options: Just above $10 Just below $10 Just above $15 Just below $15 Save Question 12 (1 point) With which choice are you more likely to avoid Bid-rigging cartels? Question 12 options: Holding Vickery auctions Holding sealed-bid auctions Holding English auctions Both A&B Save Question 13 (1 point) With which choice are you more likely to avoid Bid-rigging cartels?Question 13 options: The winning bids are announced The winning bids are not announced Winning bids are announced right after the auction Both A&C Save Question 14 (1 point) In oral auctions, the price that the winner pays depends on Question 14 options: The winner’s willingness to pay The highest willingness to pay among the losers The lowest willingness to pay among the losers None of the above Save Question 15 (1 point) Releasing more information, in a common-value auction is Question 15 options: Good for the bidders because it reduces the risk that they face Good for the auctioneer because it attracts more bidders Good for the bidders because they are less likely to bid more on the item than it’s worthBoth A&B Save Question 16 (1 point) To attract more bidders, and more aggressive bidders, to your common-value auction Question 16 options: reveal all of the relevant information about the value of the object don't allow bidders to know how others are bidding do not allow potential bidders to examine the object too closely do not hold oral auctions Save Question 17 (1 point) If the bidders at a first-price auction have true values of $8, $7, $6, and $5, the item will sell for Question 17 options: $8 $7 just over $8 just under $7 Save Question 18 (1 point) With which choice are you more likely to avoid Bid-rigging cartels?Question 18 options: Holding English auctions Holding sealed-bid auctions Holding oral auctions All of the above Save Question 19 (1 point) To attract more bidders, and more aggressive bidders, to your common-value auction Question 19 options: withhold relevant information about the value of the object don't allow bidders to know how others are bidding allow potential bidders ample time to examine the object being sold do not hold oral auctions Save Question 20 (1 point) With which choice are you more likely to avoid Bid-rigging cartels? Question 20 options: Holding smaller auctions Holding larger auctions Holding infrequent auctionsBoth B&C Save Quiz CHAPTER 19 Note: It is recommended that you save your response as you complete each question. Question 1 (1 point) Which firm is not dealing with adverse selection Question 1 options: a manufacturer requires a 90 day probationary period for new employees a temporary clerical agency hires without verifying typing skills a manufacturer requires suppliers to be ISO 9000 certified Smokers get the worse life insurance rates as non-smokers Save Question 2 (1 point) Trades between risk lovers and risk takers Question 2 options: Move assets to lower-value use Move assets to higher value use Create wealth Both B&CSave Question 3 (1 point) An individual who is a risk lover Question 3 options: values a lottery at more than its expected value values a lottery at exactly its expected value values a lottery at less than its expected value tends to play lots of lotteries Save Question 4 (1 point) Which firm is not dealing with adverse selection Question 4 options: a manufacturer forgoes a usual 90 day probationary period for new employees a temporary clerical agency requires a typing test a manufacturer requires suppliers to be ISO 9000 certified Smokers get the worse life insurance rates as non-smokers Save Question 5 (1 point) An indication that Insurance companies anticipate adverse selection is Question 5 options: they do not require a deductiblethey do not classify clients into different risk types according to their claim history they do not classify clients into different risk types according to pre-existing conditions they require a co-payment Save Question 6 (1 point) Which is a screen against adverse selection Question 6 options: Insurance companies require homeowners to have smoke detectors Rearview cameras in cars Installing engine monitors to track driving habits of the insured Prospective secretaries must take a typing test before being hired Save Question 7 (1 point) Adverse selection represents Question 7 options: Profitable transaction Unconsummated transaction WRONG Wealth creating transaction All of the above CORRECT??? SaveQuestion 8 (1 point) Signaling is Question 8 options: actions by the informed party to reveal her true risks actions by the informed party to conceal her true risks actions by the uninformed party to uncover the true risks actions by the uninformed party to conceal the true risks Save Question 9 (1 point) Which of the following is NOT a way to signal high quality Question 9 options: wearing everyday clothes to a job interview leaving a big tip for the waiter after a dinner date offering an expensive engagement ring to your bride Visiting the beauty salon before a big date Save Question 10 (1 point) Individuals who face greater risks Question 10 options: are more likely to purchase insuranceare less likely to purchase insurance are neither more nor less likely to purchase insurance are risk neutral Save Question 11 (1 point) Most people buy insurance because they Question 11 options: are risk lovers enjoy the gamble are risk neutral are risk averse Save Question 12 (1 point) The following is not an example of risk aversion Question 12 options: you don’t lock your garage when you have expensive workshop tools you are more careful when you buy a more expensive car Individuals tend to gamble more with their money when the future is certain you only go swimming when the lifeguard is on duty SaveQuestion 13 (1 point) The following is an example of adverse selection Question 13 options: A majority of those applying for well paid jobs are well qualified More reckless drivers opt for cars with more safety devices Individuals living in less secure neighborhoods want to buy less insurance Individuals with a strong family history of heart diseases opt to buy less insurance Save Question 14 (1 point) Adverse selection in insurance requires that Question 14 options: potential customers face different levels of risk potential customers facing more risk are no more interested in purchasing insurance people are not risk averse insurers can tell higher risk people from lower risk people Save Question 15 (1 point) Insurance companies create wealth by Question 15 options: reducing the amount of risk that risk averse individuals must bearreducing the amount of risk that risk loving individuals must bear increasing the amount of risk that risk averse individuals must bear moving an asset from low to high value use Save Question 16 (1 point) To signal to your insurance company that you are a low risk individual, to secure a lower premium, you should Question 16 options: Accept an insurance policy with a high deductible Accept an insurance policy with a low deductible Accept an insurance policy with a co-payment Both A&C Save Question 17 (1 point) One of the solutions to the adverse selection problem in insurance is Question 17 options: Is to require that only the high risk individuals to buy insurance Is to require that only the low risk individuals buy insurance Is to require everyone to buy insuranceIs to completely ban insurance companies Save Question 18 (1 point) Sally would only agree to a second date with Andy if she sees him leave a generous tip for the waiter on their first dinner date. This is an example of a Question 18 options: Screening mechanism Signaling mechanism Way to waste money None of the above Save Question 19 (1 point) A firm hiring only MBAs, regardless of the self-professed skill set is an example of Question 19 options: Screening mechanism Signaling mechanism Way to waste money None of the above Save Question 20 (1 point) Leaving a handsome tip for the waiter in full view of your dinner date is aQuestion 20 options: Screening mechanism Signaling mechanism Way to waste money None of the above Save Quiz Note: It is recommended that you save your response as you complete each question. Question 1 (1 point) Individuals who are more risk averse Question 1 options: buy less insurance buy more insurance are not more or less inclined to buy insurance are philosophically opposed to insurance Save Question 2 (1 point) Offering an expensive engagement ring to your (future) bride is a Question 2 options: Screening mechanism Signaling mechanism Way to waste money None of the above Save Question 3 (1 point)Adverse selection is Question 3 options: when people act differently because they are insured when more risk averse people want to be insured more when people at a greater risk want to be insured more when your guess at a test question is wrong Save Question 4 (1 point) Adverse selection happens because Question 4 options: One of the parties has more information about itself then the other party Individuals that the principle want to least select are the ones more likely to apply Parties most likely to accept an offer would be least qualified All of the above Save Question 5 (1 point) Which of the following is NOT a way to signal high quality Question 5 options: wearing a business suit on a job interview leaving a big tip for the waiter after a dinner date offering a cheap engagement ring to your bride Visiting the beauty salon before a big date Save Question 6 (1 point) A risk neutral individual Question 6 options: Values a lottery at more than its expected value Values a lottery at less than its expected value Values a lottery at its expected level Tends to play a lot of lotteries SaveQuestion 7 (1 point) As a way to still be able to transact with the low-risk individuals, insurance companies can Question 7 options: Offer them partial insurance Offer them insurance with deductibles Offer them insurance with co-payments All of the above Save Question 8 (1 point) Someone who values a lottery at more than the expected value is Question 8 options: a risk lover risk neutral risk averse one who tends to play lots of lotteries Save Question 9 (1 point) Which of the following is a possible solution to the adverse selection problem? Question 9 options: Screening Signaling All of the above None of the above Save Question 10 (1 point) The "lemons" problem is that Question 10 options: cars of verifiable high quality are withheld from the used car market cars of verifiable low quality are withheld from the used car market cars of unverifiable high quality are withheld from the used car marketcars of unverifiable low quality are withheld from the used car market Save Question 11 (1 point) Grooming well for a big date is a Question 11 options: Screening mechanism Signaling mechanism Way to waste money None of the above Save Question 12 (1 point) An indication that Insurance companies anticipate adverse selection is Question 12 options: they do not require a deductible they classify clients into different risk types according to their claim history they do not classify clients into different risk types according to pre-existing conditions they do not require a co-payment Save Question 13 (1 point) Screening is Question 13 options: actions by the informed party to reveal her true risks actions by the informed party to conceal her true risks actions by the uninformed party to uncover the true risks actions by the uninformed party to conceal the true risks Save Question 14 (1 point) For a screen to be successful, Question 14 options: High risk individuals must not be able to pose as low risk individuals WRONG It must not be profitable for high risk individuals to pose as low risk individualsHigh risk individuals should be able to pose as low risk individuals None of the above Save Question 15 (1 point) Which firm is not dealing with adverse selection Question 15 options: a manufacturer requires a 90 day probationary period for new employees a temporary clerical agency requires a typing test a manufacturer contracts with suppliers regardless of ISO 9000 status Smokers get the worse life insurance rates as non-smokers Save Question 16 (1 point) Potential buyers of older homes form their bids from imperfect estimates of a house’s value. As a consequence, Question 16 options: High-value houses would remain unsold Low value houses would remain unsold Both of the houses would be sold All of the above Save Question 17 (1 point) A bride accepting a proposal only if the ring is expensive enough is a Question 17 options: Screening mechanism Signaling mechanism Way to waste money None of the above Save Question 18 (1 point) To signal to your insurance company that you are a low risk individual, you shouldQuestion 18 options: Accept an insurance policy with a high deductible Accept an insurance policy with a low deductible Accept an insurance policy with no co-payments None of the above Save Question 19 (1 point) Lara will agree to a second date with Tom only if, on their first date, Tom is well mannered and well dressed. Lara is using a Question 19 options: Screening mechanism Signaling mechanism All of the above None of the above Save Question 20 (1 point) If you buy an insurance policy with a low deductible and no co-payments, you would end up paying Question 20 options: A higher premium A lower premium The premium of a low risk individual Both B&C Save Quiz CHAPTER 20 Note: It is recommended that you save your response as you complete each question. Question 1 (1 point) The following is NOT an example of a potential monitoring solution to moral hazard Question 1 options:blocking social network sites on company computers rejecting a job candidate that fails to show up at the allotted interview time GPS tracking devices in repair trucks listening in on call center conversations Save Question 2 (1 point) ________is the problem of separating good from bad drivers Question 2 options: Moral hazard Adverse selection Decision making None of the above Save Question 3 (1 point) The following is NOT an example of a potential monitoring solution to moral hazard Question 3 options: blocking social network sites on company computers closed circuit TVs throughout a warehouse GPS tracking devices in repair trucksrequiring physicians to be 'board certified' Save Question 4 (1 point) An example of moral hazard is Question 4 options: A taxi driver paid per mile taking the shortest route a piece-rate garment worker shirking more than a per hour worker an hourly salesman working less hard than a commission salesman an author on contract going to as many book signings as one with a percentage royalty rate Save Question 5 (1 point) One difference between moral hazard and adverse selection is Question 5 options: Adverse selection has to do with unobservable characteristics of individuals Adverse selection has to do with unobservable actions of individuals Adverse selection is when individuals most appropriate for positions are most likely to apply for them Adverse selection is when you choose the wrong answer on a test Save Question 6 (1 point) Which is NOT an example of moral hazard Question 6 options:people eat less at all-you-can-eat buffets loggers clear-cut a tract of land when paying a fixed price rather than when paying per tree felled Drivers of heavier, safer cares are more likely to run stop signs workers on commission work harder than those paid an hourly wage Save Question 7 (1 point) Solving a moral hazard problem in a transaction would benefit Question 7 options: The seller only The buyer only Both the parties None of the parties Save Question 8 (1 point) One difference between moral hazard and adverse selection is Question 8 options: Moral hazard has to do with unobservable characteristics of individuals Adverse selection has to do with unobservable actions of individuals Adverse selection is when individuals change their behaviors because of a contract WRONGAdverse selection is when you choose the wrong answer on a test Save Question 9 (1 point) An example of moral hazard is Question 9 options: A taxi driver paid per mile taking the shortest route a piece-rate garment worker shirking more than a per hour worker an hourly salesman working harder than a commission salesman an author on contract going to fewer book signings as one with a percentage royalty rate Save Question 10 (1 point) An example of moral hazard is Question 10 options: workers working diligently even though the boss is not looking health care insured employees forgoing their diet and exercise drivers of safer cars turning their phones off before driving borrowers investing their loan proceeds exactly as the bank requires Save Question 11 (1 point) An example of moral hazard is Question 11 options:people drive as carefully in icy conditions with antilock brakes as without people drive as safely with more airbags as without football players with safer helmets 'spear' with their heads more often when tackling people read the medicine warnings as carefully when self-medicating as with a doctor's prescription Save Question 12 (1 point) An example of moral hazard is Question 12 options: workers working diligently even though the boss is not looking health care insured dieting and exercising drivers of safer cars turning their phones off before driving borrowers investing their loan proceeds differently than the bank requires Save Question 13 (1 point) To keep employees from shirking, invest in greater monitoring Question 13 options: when monitoring is expensive relative to its benefits especially when monitoring is not very efficient when employees fail to respond to incentive contractswhen incentives solve both moral hazard and adverse selection problems with employees Save Question 14 (1 point) An example of moral hazard is Question 14 options: A taxi driver paid per mile taking the shortest route a piece-rate garment worker shirking less than a per hour worker an hourly salesman working harder than a commission salesman an author on contract going to as many book signings as one with a percentage royalty rate Save Question 15 (1 point) Economists discourage homeowner bailouts because Question 15 options: They encourage irresponsible borrowings It increases moral hazard among borrowers It punishes responsible borrowers All of the above Save Question 16 (1 point)You offer an extended warranty for your product that is purchased by a few customers. If the product typically fails 2% of the time, the claim rate will exceed 2% of warranty purchasers because Question 16 options: adverse selection will lead those who are more reckless to purchase the warranty moral hazard will lead those who purchase to be more reckless you systematically underestimate product failure rates Both A&B Save Question 17 (1 point) There is an influenza epidemic at Sally’s office. If she got the flu shot this winter, how does this affect her decision of going to work or working from home? Question 17 options: She would choose to work from home since the marginal cost of going to the office is high She would choose to go to work since the marginal benefit of working from home is too low She would stay home since the marginal cost of going to work so is too low She would stay home-who wants to go to work Save Question 18 (1 point) Children who play in playgrounds with rubber surfaces instead of gravel surfaces tend to Question 18 options: Play saferPlay rougher Not change their play patterns Not like playing in the playground Save Question 19 (1 point) Progressive Insurance’s 'Tripsense' monitors driving patterns of the people who purchase the related insurance policy. This lowers insurance costs because Question 19 options: only less reckless drivers will accept the device only more reckless drivers will accept the device drivers will believe they can now drive more recklessly it does not affect care in driving Save Question 20 (1 point) US law was recently changed so that some airplane manufacturers are immune from liability from accidents involving their decades old aircraft, laying all the responsibility on the pilots. As a result Question 20 options: accident rates fell due to less adverse selection accident rates fell due to less moral hazard accident rates rose due to less adverse selectionaccident rates rose due to less moral hazard Save [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 45 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 15, 2022
Number of pages
45
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 15, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
49