Health Care > EXAM > NR 601 Midterm Exam Study guide (Version 2), NR 601 Question Bank NR601 Test Bank (All)
NR 601 Midterm Exam Study guide (Version 2), NR 601 Question Bank NR601 Test Bank
Document Content and Description Below
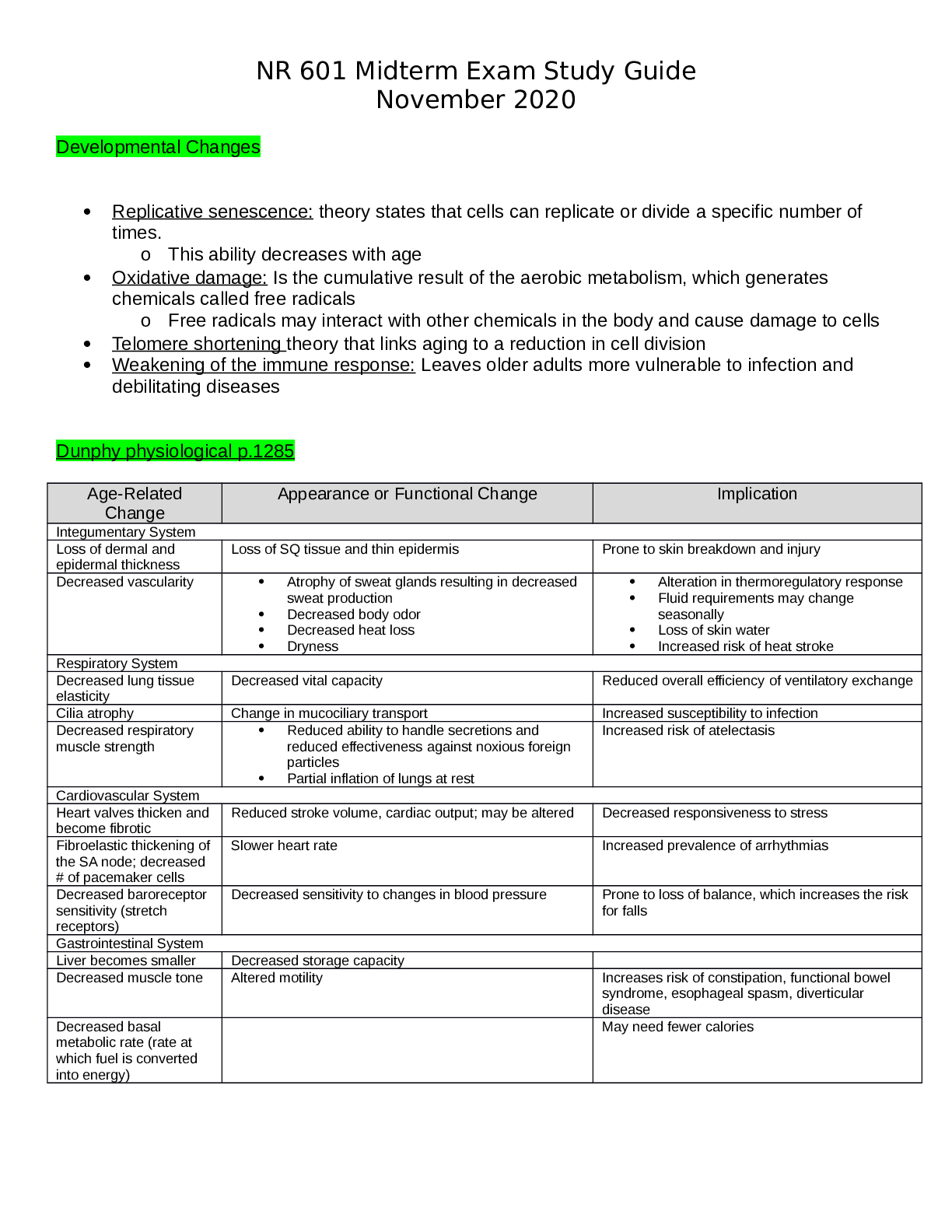
GERONTOLOGY CLASS Week 1: 1. Question: The major impact of the physiological changes that occur with aging is: Reduced physiological reserve Reduced homeostatic mechanisms Impaired immunological... response CORRECT All of the above Instructor Explanation: The major impact of all of these physiological changes can be highlighted with three primary points. First, there is a reduced physiological reserve of most body systems, particularly cardiac, respiratory, and renal. Second, there are reduced homeostatic mechanisms that fail to adjust regulatory systems such as temperature control and fluid and electrolyte balance. Third, there isimpaired immunological function: infection risk is greater, and autoimmune diseases are more prevalent. (Kennedy-Malone 3) Kennedy-Malone, Laurie, Kathleen Fletcher, Lori Martin-Plank. Advanced Practice Nursing in the Care of Older Adults. F.A. Davis Company, 2014-01-14. Vital Book file. Question 2. Question: Men have faster and more efficient biotransformation of drugs and this is thought to be due to: Less obesity rates than women Prostate enlargement CORRECT Less estrogen than women Instructor Explanation: Men have faster and more efficient biotransformation, presumably because ofserum testosterone. Conditions of increased or decreased liver perfusion alter the overall level of the drug that is absorbed and how it is metabolized. (Kennedy-Malone 5) Kennedy-Malone, Laurie, Kathleen Fletcher, Lori Martin-Plank. Advanced Practice Nursing in the Care of Older Adults. F.A. Davis Company, 2014-01-14. VitalBook file. Question 3. Question : The cytochrome p system involves enzymes that are generally: Inhibited by drugs South University 2 NSG6420 Induced by drugs CORRECT Inhibited or induced by drugs Associated with decreased liver perfusion Instructor Explanation: Biotransformation occurs in all body tissues but primarily in the liver, where enzymatic activity (cytochrome P [CYP] system) alters and detoxifies the drug and prepares it for excretion. (Kennedy-Malone 5) Kennedy-Malone, Laurie, Kathleen Fletcher, Lori Martin-Plank. Advanced Practice Nursing in the Care of Older Adults. F.A. Davis Company, 2014-01-14. VitalBook file. Question 4. Question : Functional abilities are best assessed by: Self-report of function CORRECT Observed assessment of function A comprehensive head-to-toe examination Family report of function Instructor Explanation: Two well-established tools used to evaluate function in older adults are the Katz Activities of Daily Living Scale (Katz et al., 1963) and the Lawton and Brody scale for Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (Lawton & Brody, 1969). It is important to be cautious about selfreport of function (rather than direct observation of function) and to ask, “Do you …?” instead of “Can you …?” in order to determine if patients actually perform the activity. (Kennedy-Malone 40) Kennedy-Malone, Laurie, Kathleen Fletcher, Lori Martin-Plank. Advanced Practice Nursing in the Care of Older Adults. F.A. Davis Company, 2014-01-14. VitalBook file. Question 5. Question : Iron Deficiency Anemia (IDA) is classified as a microcytic, hypochromic anemia. This classification refers to which of the following laboratory data? Hemoglobin and Hematocrit CORRECT Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) and Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH) Serum ferritin and serum iron Total iron binding capacity and transferrin saturation South University 3 NSG6420 Instructor Explanation: RBC indices reveal an MCV (mean corpuscular volume/RBC size) that will be decreased to <80 fL in adults; MCH (mean corpuscular hemoglobin/RBC color) will show hypochromia or pale cells; RBC distribution width (RDW)/volume variation will be increased. (Kennedy-Malone page 519) Kennedy-Malone, Laurie, Kathleen Fletcher, Lori Martin-Plank. Advanced Practice Nursing in the Care of Older Adults. F.A. Davis Company, 2014-01-14. VitalBook file. Question 6. Question : When interpreting laboratory data, you would expect to see the following in a patient with Anemia of Chronic Disease (ACD): Hemoglobin <12 g/dl, MCV decreased, MCH decreased Hemoglobin >12 g/dl, MCV increased, MCH increased CORRECT Hemoglobin <12 g/dl, MCV normal, MCH normal Hemoglobin >12 g/dl, MCV decreased, MCH increased Instructor Explanation: Hemoglobin (Hgb): <12 g/dL (120 g/L) women <13 g/dL (130 g/L) men Rarely <10 g/dL (100 g/L) Mean corpuscular volume: 80–96 mcm3 (normocytic) Mean corpuscular hemoglobin Normochromic (normal color) RBC distribution width: normal (Kennedy-Malone page 517) Kennedy-Malone, Laurie, Kathleen Fletcher, Lori Martin-Plank. Advanced Practice Nursing in the Care of Older Adults. F.A. Davis Company, 2014-01-14. VitalBook file. Question 7. Question : The pathophysiological hallmark of ACD is: Depleted iron stores CORRECT Impaired ability to use iron stores Chronic uncorrectable bleeding Reduced intestinal absorption of iron Instructor Explanation: The pathophysiological hallmark of ACD is a disregulation of iron homeostasis, characterized by an increased uptake and retention of iron within the cells of the reticuloendothelial system (liver/spleen), resulting in decreased RBC production. Essentially, iron is present but inaccessible for use in the production of Hgb with the erythrocytes (Bross et al., 2010). A shortened RBC survival is also a contributing factor to ACD. (Kennedy-Malone page 516-517) South University 4 NSG6420 Kennedy-Malone, Laurie, Kathleen Fletcher, Lori Martin-Plank. Advanced Practice Nursing in the Care of Older Adults. F.A. Davis Company, 2014-01-14. VitalBook file. Question 8. Question : The main focus of treatment of patients with ACD is: Replenishing iron stores Providing for adequate nutrition high in iron CORRECT Management of the underlying disorder Administration of monthly vitamin B12 injections Instructor Explanation: Treatment: Treatment of ACD focuses on management of the underlying disorder. Iron supplementation is of no benefit in ACD, except in cases of coexisting IDA. A therapeutic trial of iron supplementation of no longer than 1 month may be useful in delineating between ACD and IDA. In ACD, there would be no hematological response to iron therapy (Chen & Gandhi, 2004). (Kennedy-Malone page 518) Kennedy-Malone, Laurie, Kathleen Fletcher, Lori Martin-Plank. Advanced Practice Nursing in the Care of Older Adults. F.A. Davis Company, 2014-01-14. VitalBook file. Question 9. Question : In addition to the complete blood count (CBC) with differential, which of the following laboratory tests is considered to be most useful in diagnosing ACD and IDA? Student Answer: Serum iron Total iron binding capacity Transferrin saturation CORRECT Serum ferritin Instructor Explanation: Treatment: Treatment of ACD focuses on management of the underlying disorder. Iron supplementation is of no benefit in ACD, except in cases of coexisting IDA. A therapeutic trial of iron supplementation of no longer than 1 month may be useful in delineating between ACD and IDA. In ACD, there would be no hematological response to iron therapy (Chen & Gandhi, 2004). (Kennedy-Malone page 518) Kennedy-Malone, Laurie, Kathleen Fletcher, Lori Martin-Plank. Advanced Practice Nursing in the Care of Older Adults. F.A. Davis Company, 2014-01-14. VitalBook file South University 5 NSG6420 Question 10. Question : Symptoms in the initial human immunodeficiency virus(HIV) infection include all of the following except: Sore throat Fever CORRECT Weight loss Headache Instructor Explanation: Signal symptoms: The initial HIV infection is characterized by mononucleosis-like illness with fever, sore throat, lymphadenopathy, headache, and fatigue. A roseolalike rash may also develop. These initial symptoms are followed by an asymptomatic phase, which may last 10 years or more. Later, if untreated, lymphadenopathy, weight loss, myalgias, and diarrhea may develop (Cohen, Kuritzkes, & Sax, 2011). In advanced disease, malignancies and opportunistic infections occur. Co-infection with hepatitis B or C is common (25% to 30%) in IV drug users, so hepatitis symptoms may also appear (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC], 2010a). (Kennedy-Malone page 521) Kennedy-Malone, Laurie, Kathleen Fletcher, Lori Martin-Plank. Advanced Practice Nursing in the Care of Older Adults. F.A. Davis Company, 2014-01-14. VitalBook file. Question 11. Question : Essential parts of a health history include all of the following except: Chief complaint History of the present illness CORRECT Current vital signs All of the above are essential history components Instructor Explanation: Vital signs are part of the physical examination portion of patient assessment, not part of the health history. Question 12. Question : Which of the following clinical reasoning tools is defined as evidence-based resource based on mathematical modeling to express the likelihood of a condition in selectsituations,settings, and/or patients? South University 6 NSG6420 Clinical practice guideline CORRECT Clinical decision rule Clinical algorithm Clinical recommendation Instructor Explanation: Clinical decision (or prediction) rules provide another support for clinical reasoning. Clinical decision rules are evidence-based resources that provide probabilistic statements regarding the likelihood that a condition exists if certain variables are met with regard to the prognosis of patients with specific findings. Decision rules use mathematical models and are specific to certain situations, settings, and/or patient characteristics. Goolsby page 7 Question 13. Question : The firststep in the genomic assessment of a patient is obtaining information regarding: CORRECT Family history Environmental exposures Lifestyle and behaviors Current medications Instructor Explanation: A critical firststep in genomic assessment, including assessment of risk, is the use of family history. Family history is considered the first genetic screen (Berry & Shooner 2004) and is a critical component of care because it reflects shared genetic susceptibilities, shared environment, and common behaviors (Yoon, Scheuner, & Khoury 2003). Goolsby page 18 Question 14. Question : In autosomal recessive (AR) disorders, individuals need: Only one mutated gene on the sex chromosomes to acquire the disease Only one mutated gene to acquire the disease CORRECT Two mutated genes to acquire the disease Two mutated genesto become carriers Instructor Explanation: In autosomal recessive (AR) disorders, the offspring inherits the condition by receiving one copy of the gene mutation from each of the parents. Autosomal recessive disorders must be inherited through both parents (Nussbaum et al. 2007). Individuals who have an AR disorder have two mutated genes, one on each locus of the chromosome. Parents of an affected person South University 7 NSG6420 are called carriers because each carries one copy of the mutation on one chromosome and a normal gene on the other chromosome. Carriers typically are not affected by the disease. Goolsby page 28 Question 15. Question : In AR disorders, carriers have: Two mutated genes; two from one parent that cause disease A mutation on a sex chromosome that causes a disease A single gene mutation that causes the disease CORRECT One copy of a gene mutation but not the disease Instructor Explanation: Individuals who have an AR disorder have two mutated genes, one on each allele of the chromosome. Parents of an affected person are called carriers because each parent carries one copy of the mutation on one chromosome and a normal gene on the other chromosome. Carriers typically are not affected by the disease. In pedigrees with an AR inheritance patterns, males and females will be equally affected because the gene mutation is on an autosome. Goolsby page 28 Question 16. Question : A woman with an X-linked dominant disorder will: Not be affected by the disorder herself CORRECT Transmit the disorder to 50% of her offspring (male or female) Not transmit the disorder to her daughters Transmit the disorder to only her daughters Instructor Explanation: Everyone born with an X-linked dominant disorder will be affected with the disease. Transmission of the disorder to the next generation varies by gender, however. A woman will transmit the mutation to 50% of all her offspring (male or female). Goolsby page 29 Question 17. Question : According to the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA): Nurse Practitioners (NPs) should keep all genetic information of patients confidential NPs must obtain informed consent prior to genetic testing of all patients Employers cannotinquire about an employee’s genetic information South University 8 NSG6420 CORRECT All of the above Instructor Explanation: On May 21, 2008, President George W. Bush signed the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA) to protect Americans against discrimination based upon their genetic information when it comes to health insurance and employment, paving the way for patient personalized genetic medicine without fear of discrimination (National Human Genome Research Institute 2012). Goolsby page 43 Question 18. Question : Which of the following would be considered a “red flag” that requires more investigation in a patient assessment? Colon cancer in family member at age 70 Breast cancer in family member at age 75 CORRECT Myocardial infarction in family member at age 35 All of the above Instructor Explanation: Early onset cancer syndromes, heart disease, or dementia are red flags that warrant further investigation regarding hereditary disorders. Goolsby page 36 Question 19. Question : Your 2-year-old patientshowsfacial features,such as epicanthal folds, up-slanted palpebral fissures, single transverse palmar crease, and a low nasal bridge. These are referred to as: Variable expressivity related to inherited disease CORRECT Dysmorphic featuresrelated to genetic disease De novo mutations of genetic disease Different penetrantsigns of genetic disease Instructor Explanation: Assessing for dysmorphic features may enable identification of certain syndromes or genetic or chromosomal disorders (Jorde, Carey, & Bamshad 2010; Prichard &Korf 2008). Dysmorphology is defined as “the study of abnormal physical development” (Jorde, Carey, & Bamshad 2010, 302). Goolsby page 37 Question 20. Question : In order to provide a comprehensive genetic history of a patient, the NP should: Ask patients to complete a family history worksh [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 157 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 28, 2022
Number of pages
157
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 28, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
29



.png)



















 RATED A+.png)

.png)