Mathematics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Questions and Answers > Colorado Technical University MATH 451-1404B-Network Flow Models (All)
Questions and Answers > Colorado Technical University MATH 451-1404B-Network Flow Models
Document Content and Description Below
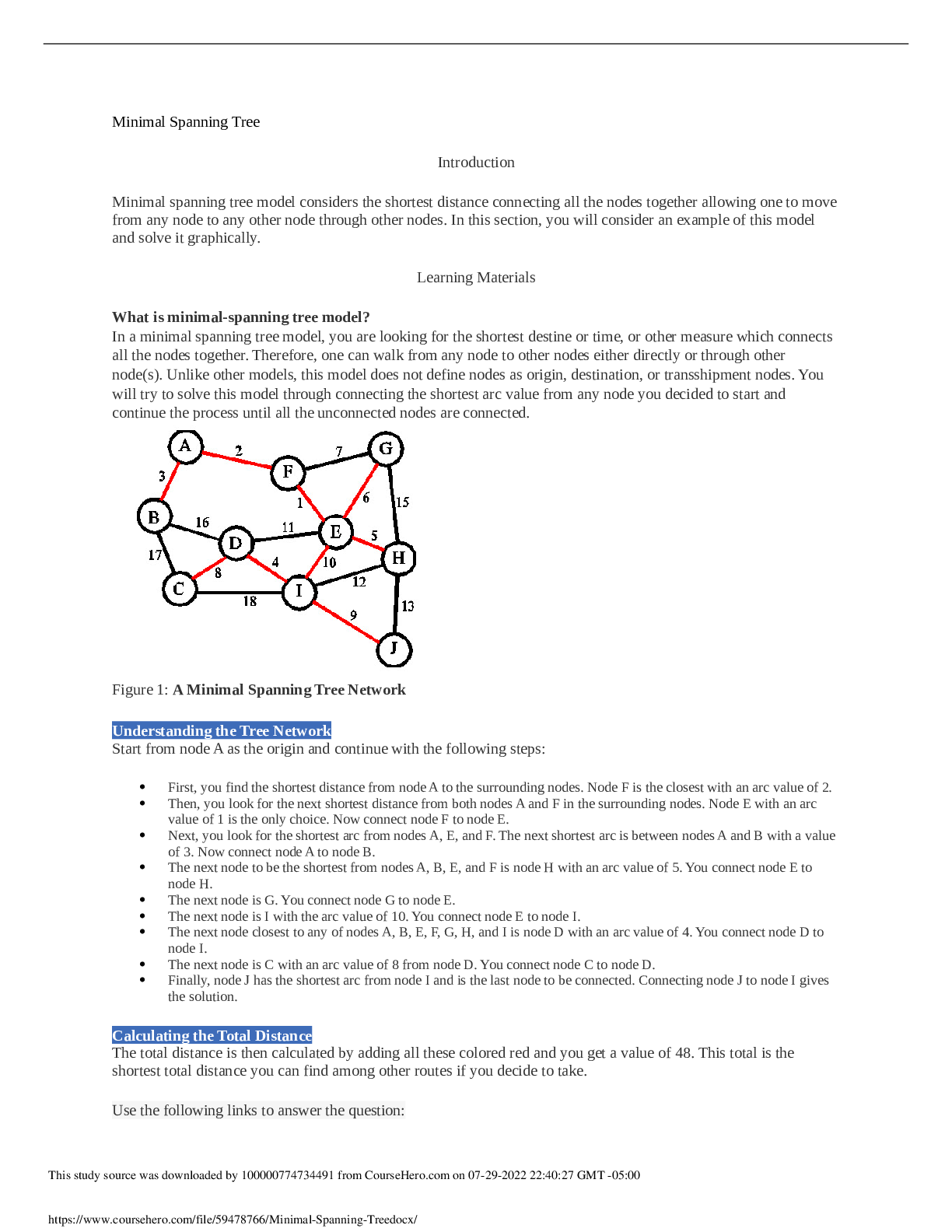
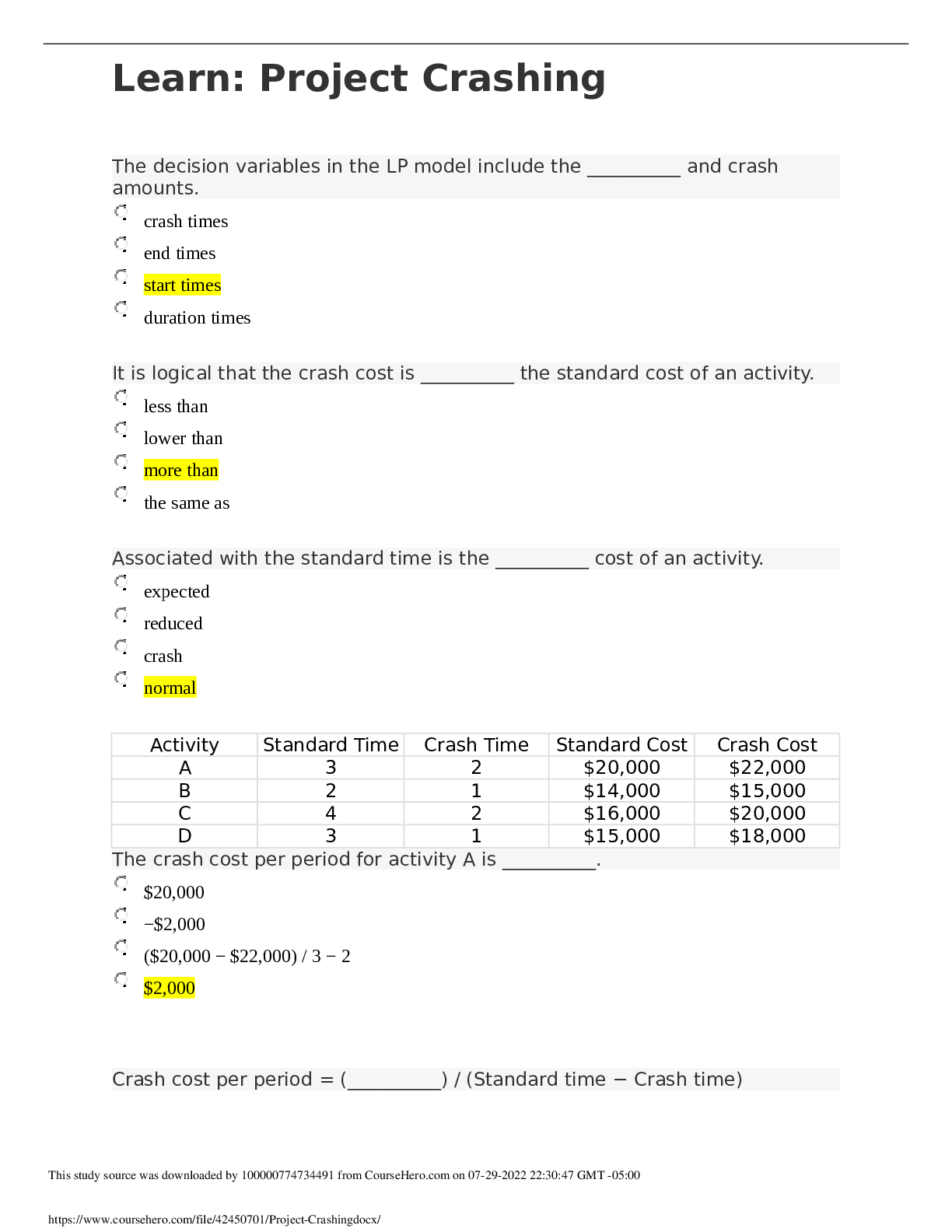
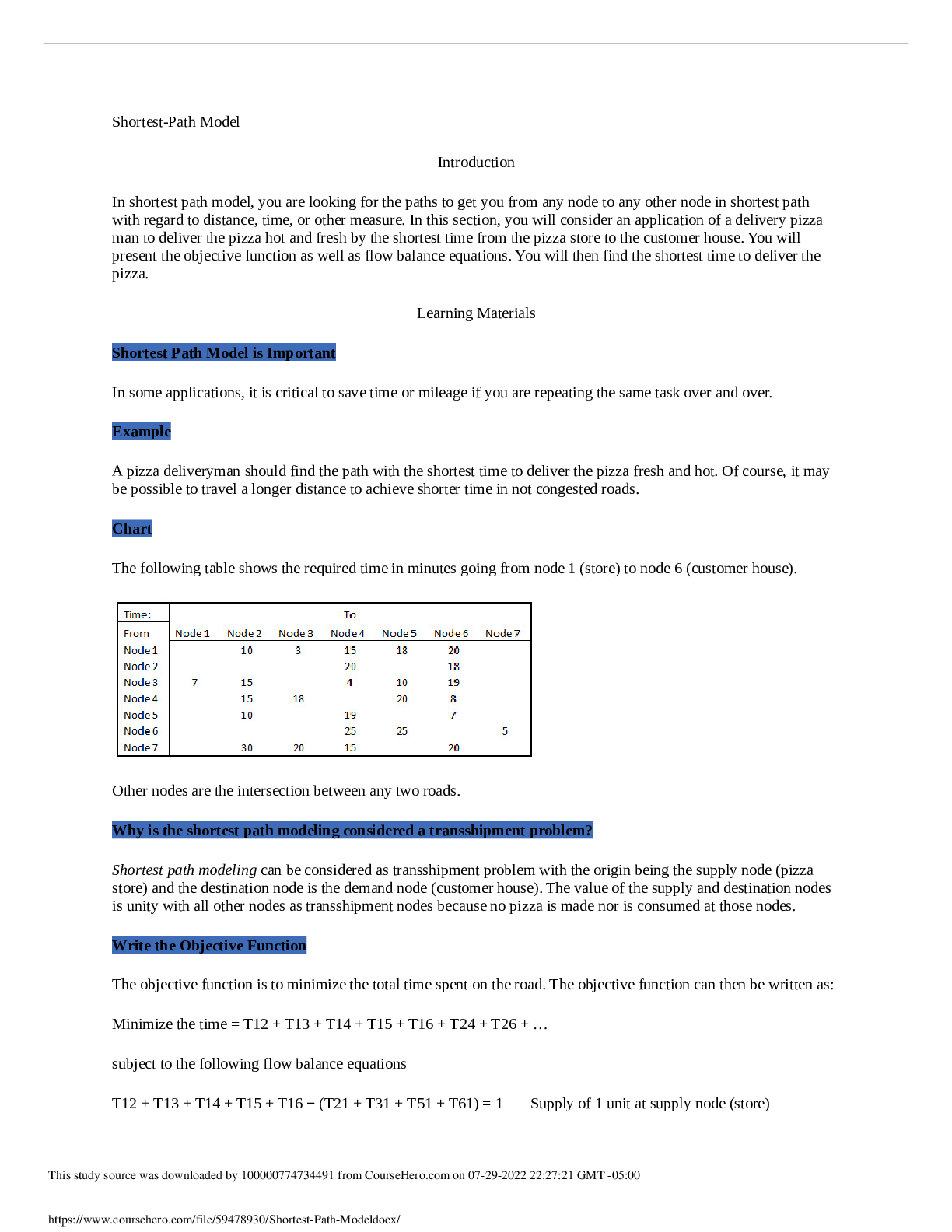
Colorado Technical University MATH 451-1404B- Network Flow Models Network Flow Models Introduction Network flow models are special cases of linear programming models. Networks consist of nodes a... nd arcs that connect the nodes together. Most of transportation applications are involved in a minimization model minimizing the transportation of good among locations. Learning Materials Different Network Flow Modeling Network flow modeling involves the following: · transportation · transshipment · assignment · maximal flow · shortest path · minimal spanning tree models Transportation Model In transportation model, you will consider the distribution of goods from several locations called supply points, origins, or sources to other locations called destinations, demand points, or sinks. The objective of these kinds of applications is to minimize the total cost of the shipment. You can also consider it as a maximization problem by seeking the total profit for the shipment. In transportation model, goods leave supply points and arrive at demands points. Transportation modeling can also be used to identify a new site or facility among several options for expansion of the company. Transshipment Model An extension of transportation model is transshipment model. In transshipment, there are points in which shipments can be received and departed. This type of problems is based on hub and spoke. The benefit of transshipment is that it may reduce the total shipping cost by receiving goods from several supply points and then divert them to destinations. An excellent example of transshipment is airline industry in which passengers arrive from some flights and then leave by other flights or continue on the same flight. Assignment Model Assignment modeling determines the most efficient assignment of people to projects. It mostly involves minimization of total cost or time performing the tasks at hand. In assignment model, you assign each job or person to at most one project or machine and vice versa. Maximal Flow Model Another special case of linear programming model is the maximal flow model. In this model, one considers the flow capacity from sources to destinations according to their limitations. The model can find the maximum flow that can happen from a source to the destination. Shortest Path Model Shortest path model deals with finding the shortest path or route in a network. The length of arcs can be functions of distance, time, cost, or any other measure. Minimal Spanning Tree Model Finally, minimal spanning tree model determines the path through the network that connects all the points. Most of its applications deal with minimizing the total cost or distance to cover the entire network connected together. Node A node is a specific point on the network. It can be classified as supply, demand, or transshipment node. At supply nodes, the goods are created and entered the network. At demand nodes, the goods are consumed and exited the network. A transshipment node allows the goods to be received from supplies and then to be delivered to other destinations. No goods are created or consumed at these nodes. The decision variables represent the amounts of the flows through unidirectional arcs. Flow balance constraints calculate the net flow for each node. Net flow is the difference between the total flow into the node and out of the node. At supply node, the total flow out of the node is more than the total flow into the node. In a pure supply node, there is no in flow and all you have is the outgoing flow. In a demand node, the total flow out of the node is less than the total flow into the node. A pure demand node does not have any outgoing flow. In a pure transshipment node, the net flow is always zero because it neither creates nor consumes any goods and just is used to flow in and then flow out the goods. If all the supply and demand values are whole numbers, the solutions to the linear programming are also integers. Suppose that you have three sources, three transshipment nodes, and three destination nodes, where each source can ship to any of the transshipment nodes, and any transshipment node can ship to any destination node. If you set this up as shown in the examples, there may be decision variables that really cannot be used. How many real decision variables are there in this problem? 243 18 9 81 Which of the following is true regarding a supply node? Total flow out of the node is more than total flow into the node. There is no flow into the node. Total flow out of the node is less than total flow into the node. Total flow out of the node is equal to total flow into the node. How many nodes and type of nodes can a network modeling application have? Only one demand node You should not have any transshipment node As many as you wish in each type of nodes, At least one source and one demand node Only one supply node In a shortest path problem, each link will be assigned a number, and in the solution, each decision variable will also be assigned a number. What do those numbers represent? Link: cost; variable: link traversed, Link: length; variable: this link is taken Link: length; variable: distanced traveled on the link Link: position in path; variable: distance traveled on the link Link: capacity; variable: this link is taken Which of the following is true regarding a pure demand node? Total flow out of the node is equal to total flow into the node. There is no flow into the node. There is no flow out of the node. Total flow out of the node is more than total flow into the node. Click on the graph that looks like a 3 × 3 assignment problem. Picture 1 What other name is supply point denoted by? Origin, Source End point(s) Destination Demand Link costs are positive integers. Source, demand, and link capacities are likewise positive. Click on the conditions that are necessary? blue Network flow models can solve the problem of assigning agents to tasks. An example of this would be assigning drivers to truck routes. What does a flow in this model represent? The completion of a task The assignment of a task to an agent The pairing of two agents How agents get to the tasks What type of node can a network model have? Assignment Transportation Maximal flow Source, transshipment, and demand, Supply, transshipment, and sink What is the numerical value of net flow at a transshipment point? It can be a positive or negative nonzero number It should be a positive number 0 It should be a negative number What is the important characteristic of assignment model? Several workers are assigned to several joint projects. Each project is assigned to at most one worker. Each worker is assigned to at most one project. A worker can work on several projects. Which of the following kinds of model would be used to assess the effect of adding a new distribution point to a network? Transportation Transshipment Shortest path Minimal spanning tree What other name is demand point denoted by? Origin Transshipment Supply Destination, Sink Counting is an important aspect of mathematics. Suppose that you have two sources and two sinks, with each source capable of producing two units and each sink requiring two units. Assume that the units are indistinguishable. The following diagram shows the connections: How many different ways are there to satisfy the demand for two units at each of the blue sinks? 9 4 3 2 What is net flow? Total flow entering the node Total flow exiting the node Sum of the total flow entering and exiting the node Total flow in -Total flow out Which one of the following happens at transshipment node? Goods are neither created nor consumed at this node. Goods are created at this node. Goods are created and consumed at this node. Goods are received from some node(s) and passed on to other node(s). Which one of the following happens at a supply point? Goods are created at this node. Goods are created and consumed at this point. Goods are passing through this point. Goods are consumed at this point. What is included in shortest path models? Shortest cost Shortest distance Shortest distance, shortest time, and shortest cost, Shortest of any measure you are trying to solve for Shortest time For a minimal spanning tree, what can be said about links and variables? The link capacityis ,andthe variableis . The link cost is positive, and the variable is 0 or 1. The variable is , and the link cost is The variable is , and the link cost is If cis the link cost andvisthe corresponding decision variable, then . The variable is positive, and the link cost is 0 or 1. Suppose that you have three sources, three transshipment nodes, and three destination nodes. If you set this up as shown in the examples, how many decision variables will you have? 18 27 9 243 In a general network flow model, what does each link have? A length and a maximum cost A length and a delay A maximum flow and a total cost A maximum flow and a per unit cost [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download

Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 02, 2022
Number of pages
6
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 02, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
54