Mathematics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Questions and Answers > Colorado Technical University Math451_Unit 3_Notes Sensitivity: Graphs (All)
Questions and Answers > Colorado Technical University Math451_Unit 3_Notes Sensitivity: Graphs
Document Content and Description Below
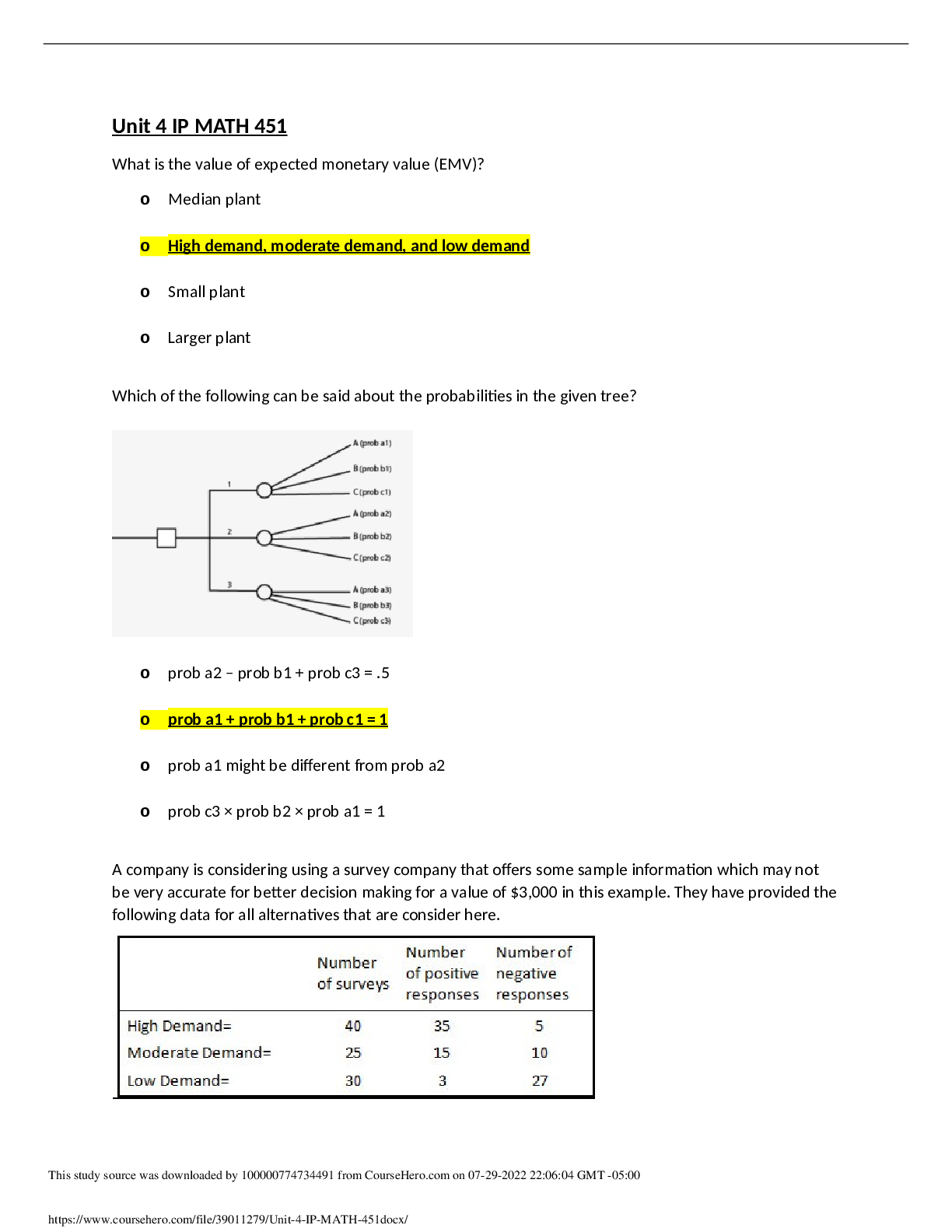
Colorado Technical University MATH 451 Math451_Unit 3_notes Sensitivity: Graphs 1. The corner points are __________ of the feasible region. The cost and availability of __________ fluctuate. T... he __________ of the graph is formed by the constraints of the model. The goal of sensitivity analysis is to determine a(n) __________ of values for the optimal solution. The __________ of the model are graphed and shaded as boundaries. Sensitivity analysis indicates how sensitive the __________ is to the model assumptions and input data changes. With the use of computers, the change to a model formulation is not too __________. The corner points are __________ of the feasible region. A __________ approach to the concept of sensitivity analysis is invaluable in larger problems. Sensitivity analysis studies __________ to the input values. Solving the model for various selling prices is __________. The optimal __________ in the graph can indicate the optimal solution. Types of Sensitivity Analysis If it was expected that the maximum assembly time of a product would be 2,000 hours and the assembly time for one product L was 1 hour and for one product T was 0.7 hours, what would the linear expression be for an LP model? In the business world, input values are not __________. The profit function in a model is referred to as the __________. In sensitivity analysis, changes to right-hand side values applies to? OFC is the coefficient of the __________ variable. Which of these choices is an advantage of using Solver for LP problems? The RHS is the __________ requirement of a criterion needed for a ≥ constraint. In the business world, input values are not __________. There are __________ types of input parameter values. The __________ value is the amount of resource for a ≤ constraint. The chance of changes to a constraint coefficient is __________ likely than OFC and RHS values. Profit or cost can be measured in __________. Which of the following is one of the ways to solve linear programming models? Profit or cost can be measured in __________. The types of input parameter values are OFC, __________, and constraint coefficients. The most common resource variable to modify in sensitivity analysis is? The software associated with Excel for determining an optimum solution in an LP model is? The correct answer is Solver If you had an objective function of P = $20L + $15T where L stands for laptop and T stands for tablet and the LP model showed that you should produce 1,350 laptops and 500 tablets, what would the expected profit be? Sensitivity analysis is not simply the analysis of a change to a(n) __________ input value for a model. Sensitivity analysis is not normally related to which of these variables? The __________ coefficients are defined as the coefficients for the decision variables. In the inequality, 4x + 5y ≤ 300, __________ is the RHS constraint. RHS Value - Nonbinding Constraint An optimal solution value can have what kind of relationship to a RHS constraint. Some __________ changes are limited to the slack or surplus. Nonbinding constraints can be described as? If the production level is reduced to more than the slack, then the corner point is no longer __________. The nonbinding constraint may only be __________ to its slack without impacting the optimal solution. The RHS nonbinding can be? Unit 3: Solution Development Changes to a business model are __________. If the sum of the ratios of proposed changes to the maximum allowable changes in a sensitivity report exceeds 1, then __________. The 100% rule is intended to be used in which of the following situations? According to the 100% Rule, the changes to assembly of an increase of 500 and a decrease of electronics to __________ would guarantee the information in the Sensitivity Report. In a sensitivity report, to use the 100% rule, __________. According to the 100% Rule, the increase of electronics of 1,500 components would __________ another change to either nonelectronic or assembly. The 100% rule is equal to __________. According to the 100% Rule, the information in the Sensitivity Report would not be guaranteed for __________. The 100% rule is __________. If proposed changes to the usage of two resources were 20 and 150, and the maximum allowable changes to the right-hand side (RHS) values to the constraints for the respective resources were 250 and 500, what would be the result of a 100% rule calculation? Select the change that would pass the 100% Rule. If proposed changes to the objective function coefficient (OFC) of two variables were 1 and 2, and the maximum allowable changes for the respective two variables were 4.67 and 3.33, which of the following would be the 100% rule calculation? Solution D increased to $36 and Solution C increased by 10 would result as __________ in the 100% Rule. In a sensitivity report, to use the 100% rule, __________. In simultaneous changes to values in a model, the changes must be to the __________ type of values. The 100% Rule for an increase of 300 for the electronics and decrease of 300 for assembly would be __________%. According to the 100% Rule, if the OFC of Solution A was modified to 30, the electronics would __________. Pricing Out New Variables What is a 100% Rule sum for this additional product? The minimum selling price is the __________ of the cost to make the product and the worth of the resources diverted from existing products. In using the 100% rule, what is compared? Which of the following question is to be considered in a pricing out study? For a proposed product to be viable, using the pricing out procedure, the final result must be __________. A company is considering the addition of product D with a worth of resources of $11.00 and a cost to produce of $27.00, if the marketing company suggested selling price is $35, you would decide to __________. Pricing out analyzes the impact of __________ to the existing LP model. The required profits contribution for the new product of Unit D is __________. The actual costs for the resources of the new product D are __________. The worth of the resources needed by the new product is __________. If the company produces 50 of Unit D, their profit will be reduced __________. Using the __________, the exact impact of the loss of resources from the existing products can be calculated. In pricing out, which of the following is used to study the impact of a new variable in a model? Sensitivity for Minimization The cost of the drink for an ounce of ingredient B added is __________. If the cost of ingredient A is $0.45, then the solution remains optimal for __________. In the following Solver model for the Diet Drink Company, what is the optimal per ounce minimization formula? The total cost will increase if the amount of __________ increases. | Ingredient | A | B | C | D | Requirement | Chemical 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ≥ 100 units | Chemical 2 2 4 1 2 ≥ 150 units | | | | | | Chemical 3 3 1 2 1 ≤ 300 units | | | | | The constraint for the model for chemical 2 would be __________. In a minimization problem where the shadow price on the Constraints portion of a sensitivity report is negative, if the use of the right-hand side (RHS) value of that constraint is increased within allowable limits, the optimum result will __________. Maximization linear programming (LP) problems often deal with maximizing profit. Minimization problems, on the other hand, often deal with which of the following? In the following Solver report for the Diet Drink Company, what is the constraint formula for Chemical Z? A minimization model __________ some ≥ constraints. Which of the following is true about the reduced cost under the variable section of a sensitivity report? The correct answer is It is the difference between the marginal contribution of the objective function value and the marginal worth of resources. | A | B | C | D | | Number of ounces | 0 | 33.33333 | 0 | 8.333333 | Cost $0.40 $0.20 $0.45 $0.30 | | | | The cost per drink is __________. A feasible region in a representative graph is The total cost of the drink will be increase by __________ if 2oz. of ingredient B are added. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 14 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 02, 2022
Number of pages
14
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 02, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
75