Finance > EXAM > University of Phoenix - FIN 370Week 3 practice problems. 37 Questions and Answers. 100% Correct. (All)
University of Phoenix - FIN 370Week 3 practice problems. 37 Questions and Answers. 100% Correct.
Document Content and Description Below
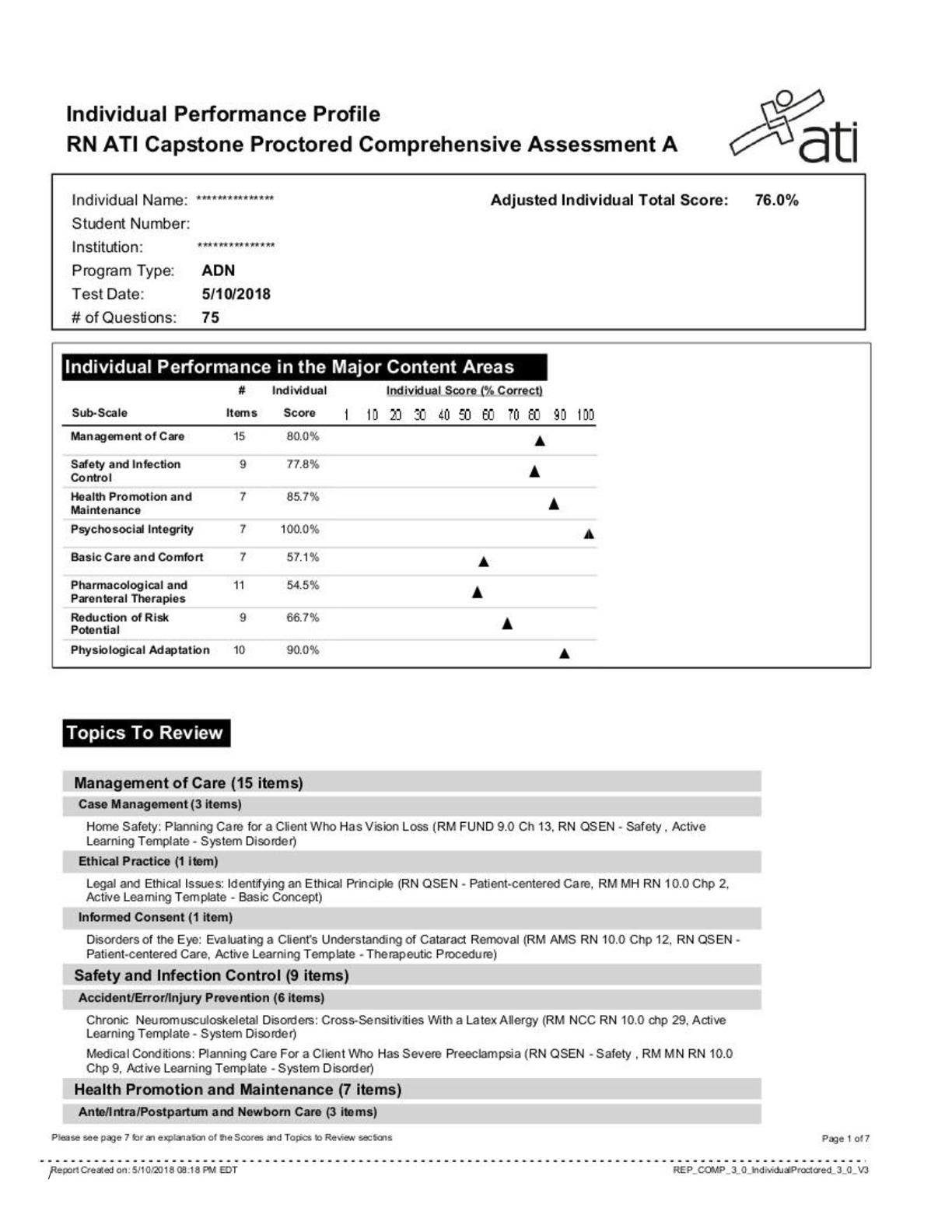
FIN 370 Week 3 Practice Problems. 1. Which one of these is the correct formula for computing the current value of a $1,000, 10-year, zero coupon bond if the discount rate is 8%? a. PV = $1,000 X [1 ... + (0.08/2)]20th b. PV = $1,000 X (1.08)10th c. PV = $1,000 / 1.08 10th d. PV = $1,000 / [1 + (0.08 / 2)]20th 2. Which one of these represents correct calculator input for computing the current value of a 5% coupon compounded semi-annually? The corporate bond matures in 12.5 years. The current discount rate is 6.5 percent. Assume the face value of the bond as $1,000. PMT = (0.05 / 2) X $1,000 = $25 a. PMT = 25 b. I = 6.5 c. FV = 10,000 d. N = 12.5 3. Assume a corporate bond pays a 5% coupon and matures in ten years. What will be the change in current price of this bond if market interest rates increase from 5% to 5.5%? When the coupon rate matches the market rate, a bond sells at par, which is assumed to be $1,000. Using a financial calculator, the price at 5.5% is: N = 20, I = 2.75; PMT = 25; FV = 1000, CPT PV; PV = -961.93 – 1000 = -38.07 a. -38.07 b. 38.07 c. 19.04 d. -19.04 4. Corporate bond A has a 6 percent coupon and matures in 3 years. Corporate bond B has a 6 percent coupon and matures in 15 years. The current interest rate is 6 percent. By how much will Bond A and Bond B change in price if the market rate increases to 6.5 percent? Assume both bonds are currently selling at par which is $1000. Bond A: N = 6, I = 3.25, PMT = 30, FV = 1000, PV = 986.57; Bond B: N = 30; I = 3.25, PMT = 30’FV = 1000, PV = 952.55 a. -13.43; -47.45 b. -11.89; -47.56 c. -14.76; -52.33 d. -12.08; -49.19 5. A corporate bond pays $45 in interest every six months and matures in 11 years. What is the yield to maturity if the bond currently sells for $1,213? N=22; PV=-1,213; PMT=45; FV=1,000; I=3.144 a. 5.93 b. 6.29 c. 4.58 d. 3.14 6. A 7.5% corporate bond matures in 16 years and has a price quote of 102.3. what is the yield to maturity? N=32; PV=-1,023; PMT=37.50; FV=1,000; I=3.62735 x 2 a. 7.2524% b. 7.2547% c. 6.8309% d. 6.8414% 7. A corporate bond has a yield to maturity of 6.48%, an current price of $916.58, and matures in 5 years. What is the coupon rate? N=10; I=3.24; PV=-916.58; FV=1,000; PMT=22.50 – coupon rate (2 x 22.50) / 1000 = 0.045 or 4.50% a. 6.25% b. 4.25% c. 6.50% d. 4.50% 8. Which of the following affect the coupon rate a firm must set on its bonds if the bonds are to be sold at par? Select all that apply? a. Face amount b. Bond term c. Default risk d. Market rates of interest 9. Which of these statements correctly applies to the NYSE bond market? Select all that apply. a. Corporate bonds are the primary source of bond trading volume on the NYSE b. Treasury bonds are the primary source of bond trading volume on the NYSE transactions on the NYSE indicate the volume of trading in corporate bonds is quite high c. The NYSE operates the largest centralized U.S. bond market 10. You want to compute the value of a 5-year zero-coupon corporate bond given a market rate of 5.5%. which of these represent correct calculator inputs? Select all that apply. a. I – 5.5 b. PV = 1000 c. N=10 d. FV=1000 11. How does the yield to call differ from the yield to maturity for the same bond? Select all that apply. a. There are fewer periods in the yield to call b. The interest payment will vary as the coupon rate is applied to the call price rather than the par value in the yield to call c. The interest payments are annual in the yield to call and semiannual in the yield to maturity d. The call price used in the yield to call usually exceeds the face value used in the yield to maturity 12. Which of the following apply to high-yield bonds? Select all that apply. a. Increased credit risk b. Low risk c. Low-quality d. High-quality 13. A 10-year treasury bond has a 4% coupon and a yield to maturity of 4.62%. a 10- year, A-rated corporate bond has a 4.5% coupon and a yield to maturity of 5.98%. what is the yield spread between these two bonds? a. 1.98% b. 0.50% c. 1.36% d. 1.48% 14. Which of the following are commonly included in an indenture agreement? Select all that apply a. Call premium b. Bond price c. Par value d. Coupon rate 15. What are the taxable equivalent yields (ETY) at tax rates of 25% and 35% if the muni yield is 3.5%? ETY = 0.035 / (1 - 0.25) = 0.0467 and 0.035 / (1 – 0.35) = 0.0538 a. 4.67; 5.38 b. 2.63; 2.28 c. 2.80; 2.59 d. 4.38; 4.73 16. The market rate of interest that is used to compute the present value of a bond is affected by which of the following? Select all that apply. a. Bond’s face value b. Credit quality of the bond c. Tax status of the bond d. Bond’s coupon rate 17. A typical municipal bond is selling at a price of $5,114.20. what is the price quote for this bond? Price quote = $5,114.20 / $5,000 = 1.02284 = 102.284% or 102.284 price quote a. 100.114 b. 114.200 c. 102.284 d. 100.228 18. A TIPS was issued with a face value of $1000 and a reference CPI of 204.89. The current par value of this TIPS is $1001.37. what is the current CPI? Current price = $1000 X (current CPI / 204.89) a. 207.70 b. 205.17 c. 202.12 d. 204.61 19. Assume a $1,000 Treasury inflation-protected bond has a 2% coupon and a face value at issuance of $1,000. The reference CPI is 202.34 and the current CPI is 203.18. what do you know for certain about this bond? a. The current par value is $1,000 b. The coupon rate is still 2% but the interest payment have increase c. The current semiannual interest payment is $10 d. The current par value is $1,000 but the coupon rate is currently greater than 2% 20. A bond has a par value of $1,000, a call premium of one year’s interest, a call provision after 5 years, a coupon rate of 5%, semiannual interest payments, and a maturity of 20 years. Which of these is (are) correct? Select all that apply. a. Each interest payment will be $25 b. The bond will pay a total of 20 payments c. The bond will pay $1,050 at maturity d. The bond can be paid off in year 6 for a price of $1,050, plus any unpaid interest 21. A TIPS was issued with a face value of $5,000, a coupon rate of 3%, and a reference CPI of 201.42. the current CPI is 203.14. what is the current interest payment? Current interest payment = $5,000 X (203.14 / 201.42) X (0.03 / 2) = $75.64 a. $148.73 b. $74.36 c. 151.28 d. 75.64 22. Which of these is the current yield formula? a. Annual interest / face value b. Annual interest / principal value c. Annual interest / current value d. Annual interest / par value 23. What rate does an investor need to earn on a corporate bond to earn the same return as he can on a 3.5% muni if his tax rate is 28%? Equivalent taxable yield = 0.035 / (1 – 0.28) = 0.0486 a. 4.86 b. 2.73 c. 4.48 d. 6.02 24. Which of the following bonds is subject to the greatest interest rate risk? a. 10 year, 5% coupon b. 5 year, 5% coupon c. 10 year, zero coupon d. 5 year, zero coupon 25. A corporate bond matures in 14.5 years and pays a 6.75% coupon. What is its current value if the market rate of interest is 7.5%? a. $843.83 b. 1,524.94 c. 934.38 d. 1,330.90 26. At what tax rate will an investor be indifferent between a 4.2% municipal bond and a 7% corporate bond? 0.07 = 0.042 / (1 – tax rate) a. 60% b. 40% c. 67% d. 33% 27. Which of these apply to publicly-issued common stock? Select all that apply. a. Value determined on the stock exchanges b. Stock value depends on the issuer’s business success c. Ownership position d. Valueless security unless dividends are currently being paid 28. What is the key difference between a floor broker on AMEX and a dealer on NASDAQ? a. A dealer sells securities and a broker buys them b. A dealer operates on a trading floor while a broker deals only with electronic trades c. A dealer buys and sells only from his own inventory while a floor broker executes trades both for himself and others d. A broker is a market maker while a dealer is not 29. Which statements are correct? Select all that apply a. A limit sell order will only execute at the limit price or higher b. A limit sell order may never be executed c. A limit buy order will execute as soon as the market price reaches or exceeds the limit price d. A market order will execute immediately, regardless of the price 30. A stock has a dividend yield of 1.4%. what is the expected return if the growth rate is 4%? What if the growth rate is 8%? Expected return = 1.4 + 4 = 5.4; expected return = 1.4 + 8 = 9.4 a. 2.6%; 6.6% b. 4; 8 c. 5.4; 9.4 d. 5.4; 8.4 31. A stock just paid an annual dividend of $0.70. the dividend is expected to increase by 10% per year for the next three years and by 2% per year thereafter. What is the current price at a discount rate of 9%? a. $11.58 b. 11.92 c. 13.47 d. 12.62 32. A firm is expected to have net earnings of $1,480,000 three years from now. There are 500,000 shares of stock outstanding. The firm’s current P/E ratio is 18 and it is expected to remain at that level. What is the firm’s expected stock price for year 3? P3 = 18 X ($1,480,000 / 500,000) = $53.28 a. $49.16 b. 55.07 c. 44.29 d. 53.28 33. Which of these firms are considered to be incorrectly priced? Select all that apply. a. Low growth, high P/E b. High growth, high P/E c. Low growth, low P/E d. High growth, low P/E 34. Why are dividends an important part of a common stock’s rate of return? Select all that apply. a. Dividends tend to be more stable than capital gains b. Dividends represent the total return that can be earned from owning a common stock c. Dividends are guaranteed while capital gains are not d. Dividends increase the return for stocks with capital gains and reduce the loss for stocks with capital losses 35. Which of these is correct? a. Investors earn the spread b. Dealers are willing to sell stocks at the ask price c. Deals are willing to purchase stocks at the ask price d. Investors buy stocks at the bid price 36. Which of these is the primary basis for a stock’s value? a. The overall level of market activity b. Market supply c. Market demand d. The profitability and success of the issuer [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Dec 19, 2020
Number of pages
6
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Dec 19, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
64