Linguistics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > 3120 Chpt 9 Review Questions & Answers. Latest updates. 2022/2023 (All)
3120 Chpt 9 Review Questions & Answers. Latest updates. 2022/2023
Document Content and Description Below
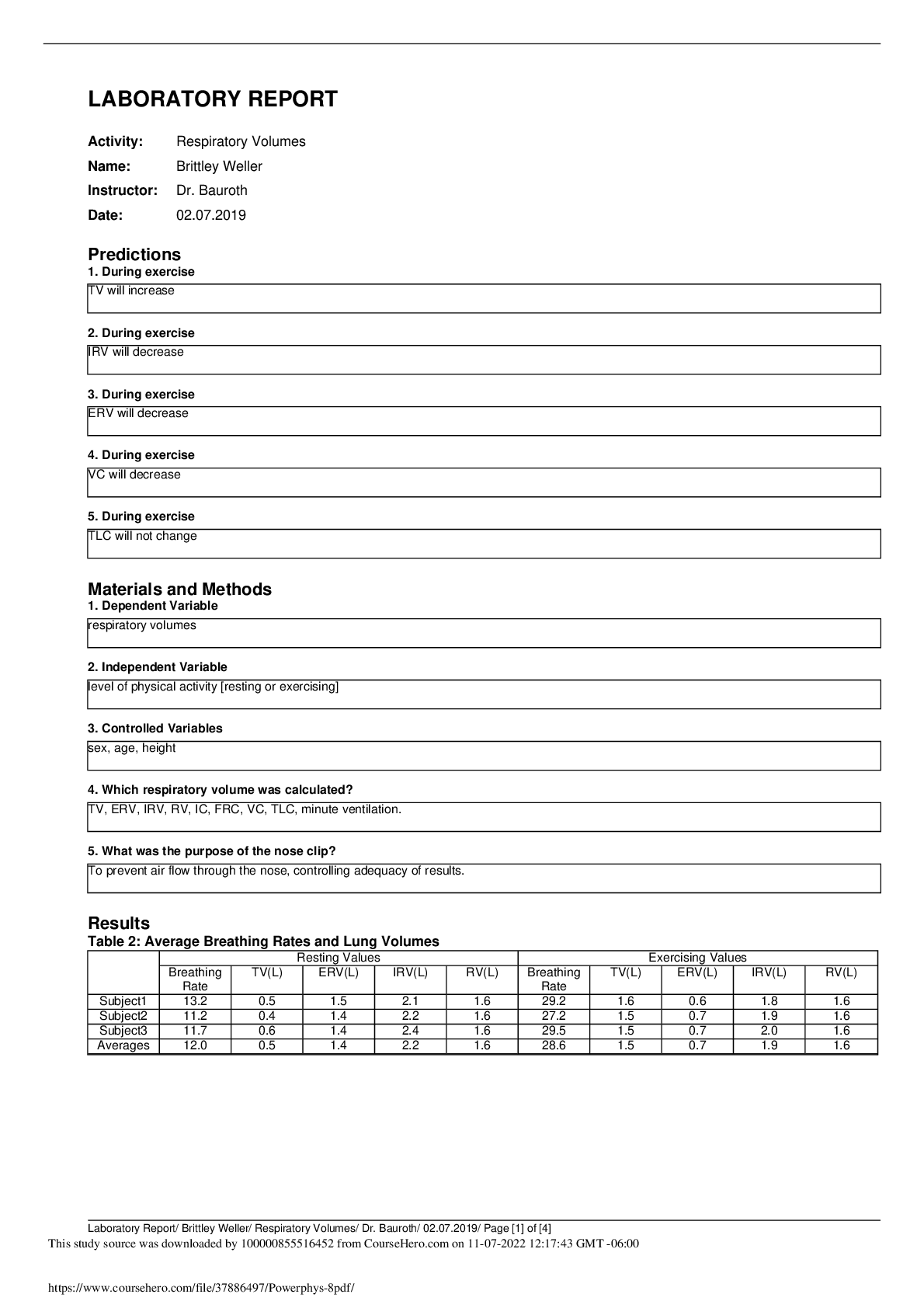
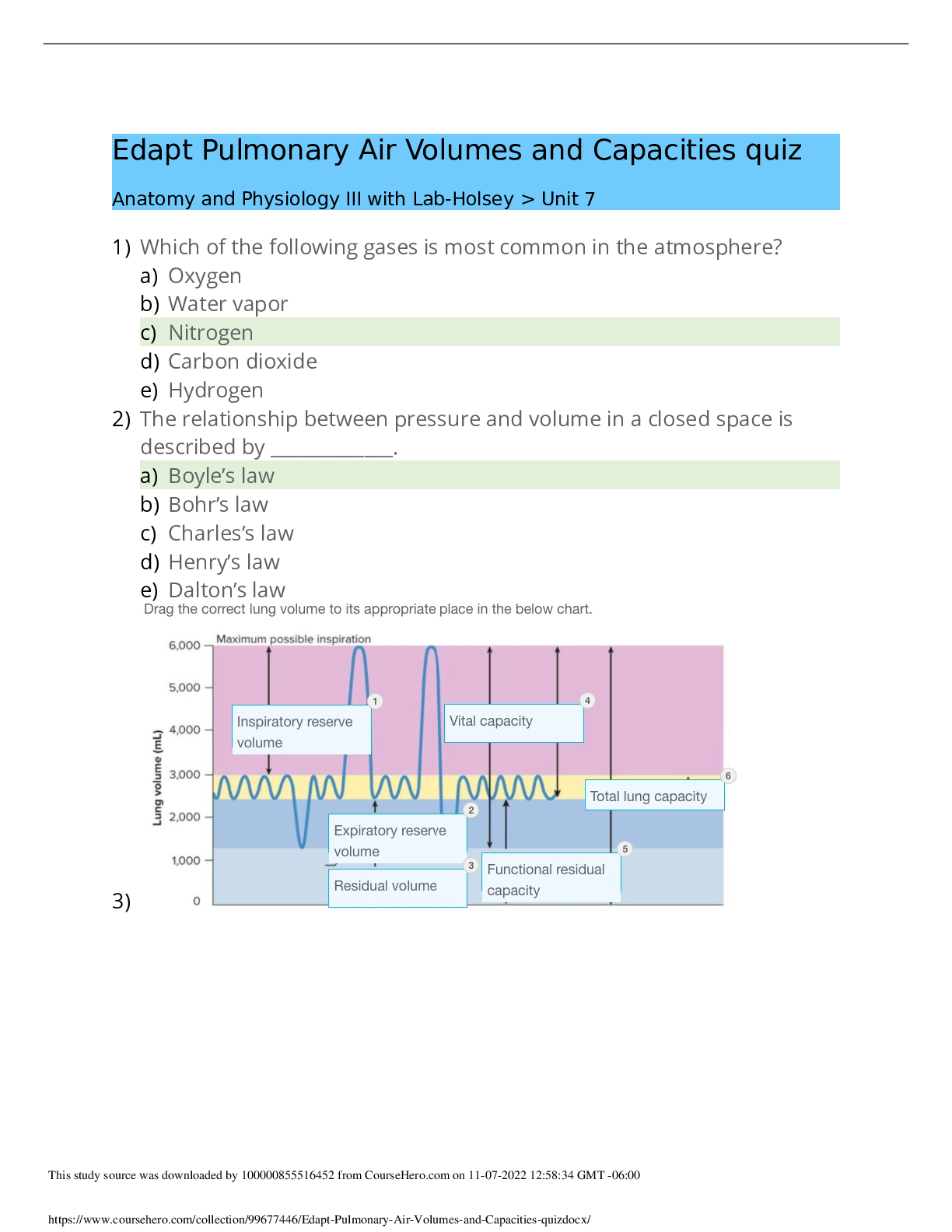
3120 Chpt 9 Review Questions & Answers. Latest updates. 2022/2023 Although children accomplish the basics of language development by the age of 4 to 5 years, language development does not stop at... that point. Evidence for continued phonological development in the school years, for example, may include all of the following EXCEPT _______________________. A. Children continue to improve their ability to perform tasks such as repeating novel sound sequences, rapid naming, and phonological awareness, all of which depend on the quality of their phonological representations. B. Children may change or acquire new accents through exposure to peers who speak a dialect different from the dialect spoken at home. C. Changes in both the size and the composition of children's lexicons continues after early childhood. D. Phonological awareness, i.e., awareness of the sounds and sound structure of the language, becomes important and develops substantially in the school years. - ✔✔C. Changes in both the size and the composition of children's lexicons continues after early childhood. Payne (1980) followed four children from the same family that moved to Philadelphia when the children were 3, 5, 6, and 8 years old. Payne examined the children's speech 5 years later, when they were 8, 10, 11, and 13, respectively, and she found that the 10- and 11-year-olds had the strongest Philadelphia accents. The 8-year-old and the 13-year-old had fewer features of the Philadelphia dialect. The results of this study suggests that ___________________. A. the rapid naming task can be used to assess the ability to rapidly retrieve and produce known words. B. learning to read an alphabetic writing system affects phonological awareness C. By the age of 14 or 15, adolescents start to move away from the peer group dialect and toward the more prestigious form of speech, especially in formal situations. D. the particular accent of their caregivers that children acquire is not permanently fixed, but may be altered due to peer influence. - ✔✔D. the particular accent of their caregivers that children acquire is not permanently fixed, but may be altered due to peer influence. Liberman, Shankweiler, Fischer, & Carter (1974) found that about 50 percent of 4- and 5-year-olds can tap out the number of syllables in a mutisyllabic word. By contrast, Liberman and associates (1974) found that no 4-year-olds and only 17 percent of 5-year-olds were able to tap out the number of phonemes in words. The contrast suggests that ___________________. A. awareness of phonemes as units is a later development than awareness of syllables, onset, and rimes. B. like other aspects of style such as how one dresses and the music one listens to, speech style is a means of stating one's identity. C. children who know more nursery rhymes at age 3 are better readers at age 6. D. Chinese adults, who read a logographic system in which characters stand for meanings and only secondarily for syllables, were found to have very low levels of phonemic awareness - ✔✔A. awareness of phonemes as units is a later development than awareness of syllables, onset, and rimes. Factors which contribute to lexical development in children after over the school years include all of the following except __________________. A. children's increasing ability to use quick, incidental learning. B. children's increasing ability to make use of direct instruction of word meanings. C. children all over the world (many without benefit of literacy) invent secret languages such as pig latin, which depend on the manipulation of phonemes. D. children's increasing knowledge of word formation processes and morphological organization. - ✔✔C. children all over the world (many without benefit of literacy) invent secret languages such as pig latin, which depend on the manipulation of phonemes. Figure 9.1 shows the estimated vocabulary size of first-, third-, and fifth-graders. According to these estimates, children's vocabularies increased by 9000 words from first to third grade and by 20,000 words from third to fifth grade. These data suggest that vocabulary growth proceeds at an even more rapid pace than during the preschool years. Here is the question. These estimated were obtained by asking first-, third-, and fifth-graders to _____________. A. complete the PPVT (Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test) B. choose the best definition for each word in a sample of entries from a dictionary C. complete the rapid naming task D. complete a word formation task - ✔✔B. choose the best definition for each word in a sample of entries from a dictionary Box 9.1 presents some expository texts produced by English-speaking children in fourth, seventh, and eleventh grade. These examples illustrate developmental changes in all of the following except _______________. A. lexical density (i.e., the ratio of content words to total words) B. lexical innovation (i.e., coining novel words such as when a child says 'try to be more rememberful, Mon") C. lexical complexity (i.e., the frequency of polysyllabic words) D. lexical diversity (i.e., the number of different words used) - ✔✔B. lexical innovation (i.e., coining novel words such as when a child says 'try to be more rememberful, Mon") Consider the morpheme -ist, which means a person who performs an action: an illusionist is someone who performs illusions and a typist is someone who types. What kind of morpheme is this and why? A. It is an inflectional morpheme because it doesn't change the topic of the word: both typing and a typist are part of the same activity. B. It is derivational morpheme because it changes the kind (the syntactic category) of word it is on: type is a verb but typist is a noun. C. It is a compounding morpheme because it adds meaning to the original word: typist provides more information than typing. - ✔✔B. It is derivational morpheme because it changes the kind (the syntactic category) of word it is on: type is a verb but typist is a noun. Affixing (i.e., adding an affix '-er' to a root word 'preach' to form the word 'preacher') and compounding (i.e., combining two existing words 'tree' and 'house' to form 'treehouse') are two important word formation processes. Clark and Hecht (1982) found that when asked questions such as "What could we call someone who gives things?" 3-year-olds were likely to produce compounds like giveman, whereas 5-year-olds consistently used the -er suffix to derive forms like giver. The observation from this study suggests that _________________________. A. The ability of QUIL (for Quick Incidental Learning) seems to emerge only after children have been in the business of learning words for a couple of years. B. It supports a highly nativist view of the development of morphology because it shows that children obey a distinction between inflections and derivations that is not provided in input. C. Most of the time in English inflectional morphemes (e.g., the plural s) are added to words after derivational morphemes, but not the other way around. D. Compounding appears to be an earlier acquired word formation process than affixing. E. The grammatical complexity of children's speech continues to increase after the age of 5. - ✔✔D. Compounding appears to be an earlier acquired word formation process than affixing. Consider the following narrative produced by a 4-year-old based on a picture book with no text [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages
Instant download

Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 06, 2022
Number of pages
9
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 06, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
79






















.png)