*NURSING > iHuman > IHuman patient Darrell Johnson 64 year-old for worsening symptoms of Parkinson’s disease (All)
IHuman patient Darrell Johnson 64 year-old for worsening symptoms of Parkinson’s disease
Document Content and Description Below
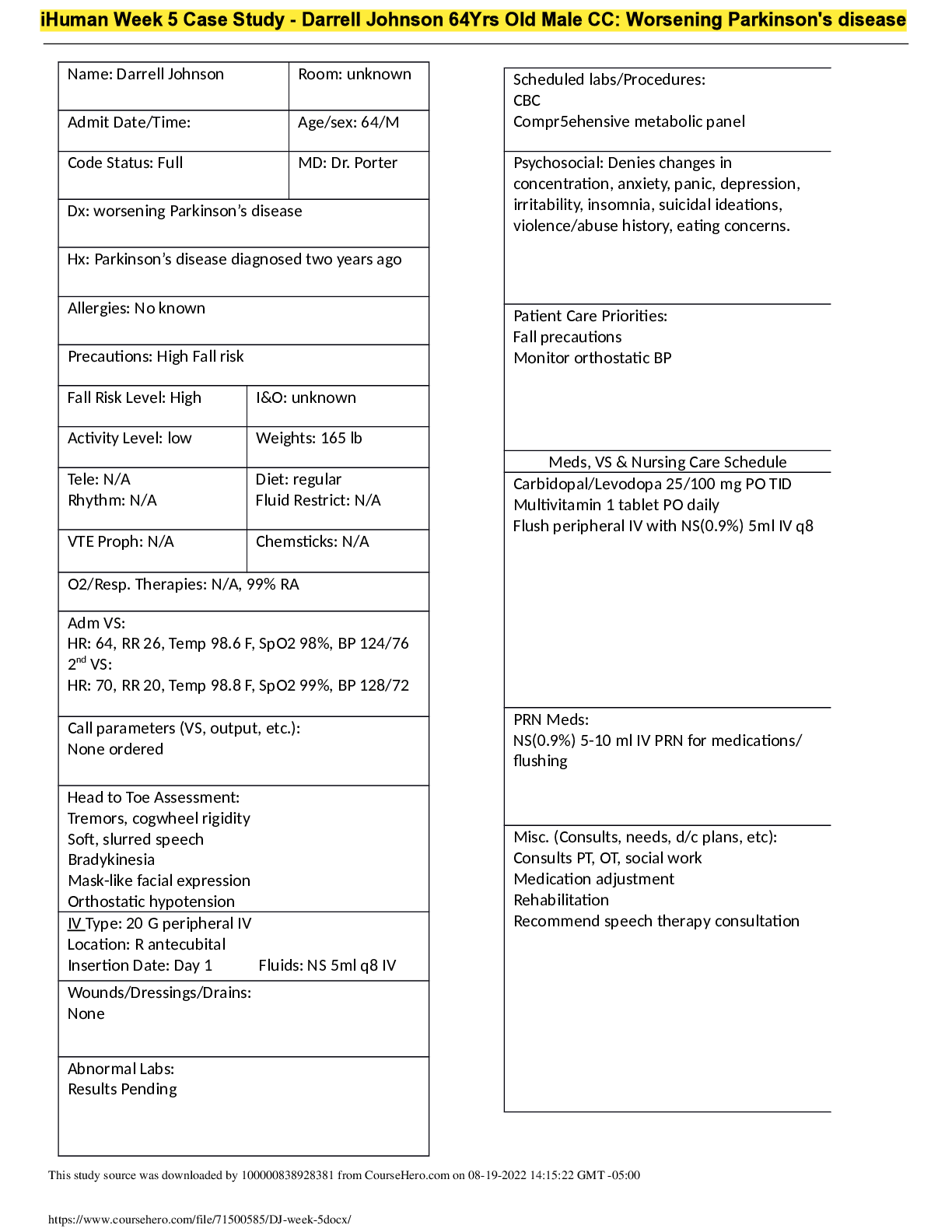
IHuman patient Darrell Johnson 64 year-old for worsening symptoms of Parkinson’s disease IHuman patient Darrell Johnson 64 year-old for worsening symptoms of Parkinson’s disease Prework A 64 ye... ar-old male who is being directly admitted to the hospital from the neurologist’s office for worsening symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. 1. What are your primary concerns for this patient and what assessments and interventions would be associated with your concerns? Why? For this patient I would assess neurological status, assess his ability to swallow and chew, muscle weakness and respiratory status. Memory lost because increase in tremors, safety, risk for falls, issues with swallowing. Interventions: • monitor for constipation • Instruct patient to raise the head of the bed and make position changes slowly. • Teach patient to dangle legs a few minutes before standing. • Avoid dehydration and maintain adequate dietary salt. • Refer patient to physical therapist He is at risk for aspiration, use thickener if appropriate, fall risk assessment tools initiated (non-slid sucks, call light within reach), inform case management to make sure he is safe at home. Lewis, S. L., Dirksen, S. R., Heitkemper, M. M., & Bucher, L. (2017). Medical surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems (10th ed.). Mosby. 2. What do you anticipate the patient’s home medications prior to admission might be? Why? • Carbidopa-levodopa • dopamine agonists • MAO B inhibitor (they help prevent breakdown of brain dopamine by inhibiting the brain enzyme monoamine oxidase B) Sinemet in early disease She asked How dopamine works in the brain? Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Quiring, C. (2019). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). F.A. Davis. 3. What medications do you anticipate the healthcare provider would prescribe while the patient is in the hospital? Why? • Carbidopa-levodopa • antihistamine with anticholinergic to manage tremors • anticholinergic such as benztropine (Cogentin) to manage PD home meds plus anticholinergic, antiemetic, some patients maybe depressed, so med for depression could be prescribed as well. Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Quiring, C. (2019). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). F.A. Davis. 4. What medications do you anticipate the healthcare provider prescribing for the patient’s discharge? Why? • Carbidopa-levodopa • Anticholinergic Same as home and hospital. (question 3 and 4) Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Quiring, C. (2019). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). F.A. Davis. Nurses notes Darrell Johnson is a 64-year old patient who presented to his neurologist with worsening parkinson’s disease symptoms that began impacting his ability to perform activities of daily living independently. He is being admitted for medication adjustment. Height/weight: 6’0 165 lbs Temp: 37.1c Pulse: 70 RR: 20 SpO2: 98% BP: 128/74 Pain: 0/10 Patient IV line is patent, no phlebitis, infiltration, extravasation or hematoma noted, device is well secured, no client concerns. Skin, hair, nails: skin is warm and dry with no lesions, hair grey and thinning on the sides and back of the head, bald on top. Nails without ridging, pitting, or peeling. Skin rapidly returns to baseline after pinch test. Capillary refill less than three seconds. HEENT Eyelids: no ptosis, erythema, or swelling, conjunctivae is pin with no discharge, sclerae is white, orbital area has no edema, redness, tenderness or lesions noted. Ears: No deformities or discharge noted. Nose: no discharge or polyps, no edema or tenderness over the frontal or maxillary sinuses. Neck: patient can swallow own secretions but drools at times. Respiratory: chest is symmetrical, excursion with respiration is symmetrical and there are no retractions or use of accessory muscles. No distention, scars, masses, or rashes. Unlabored, lungs are clear to all field, no cyanosis or clubbing noted. Cardiac: regular rhythm, 2+, no murmurs or bruits. GI: abdomen is flat and symmetric with no scars, deformities, striae or lesions, no pain, tenderness, masses, or pulsations, no guarding or rebound tenderness. Extremities: there is no swelling or deformity, there is no cyanosis clubbing or edema. Warm to touch. GI: no masses or tenderness, no urethral discharge. Musculoskeletal: full range of motion to upper and lower extremities, muscle stiffness creates jerky movements with passive ROM, movements are slow. Strength is 5/5 bilaterally. Neuro: mini mental state exam score is 22/30. Slow rapid alternating movement of arms, hands, and fingers. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 3 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 07, 2022
Number of pages
3
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 07, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
39



















 2021.png)






