*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NUR 2474 Exam 1 study guide MDC2 (All)
NUR 2474 Exam 1 study guide MDC2
Document Content and Description Below
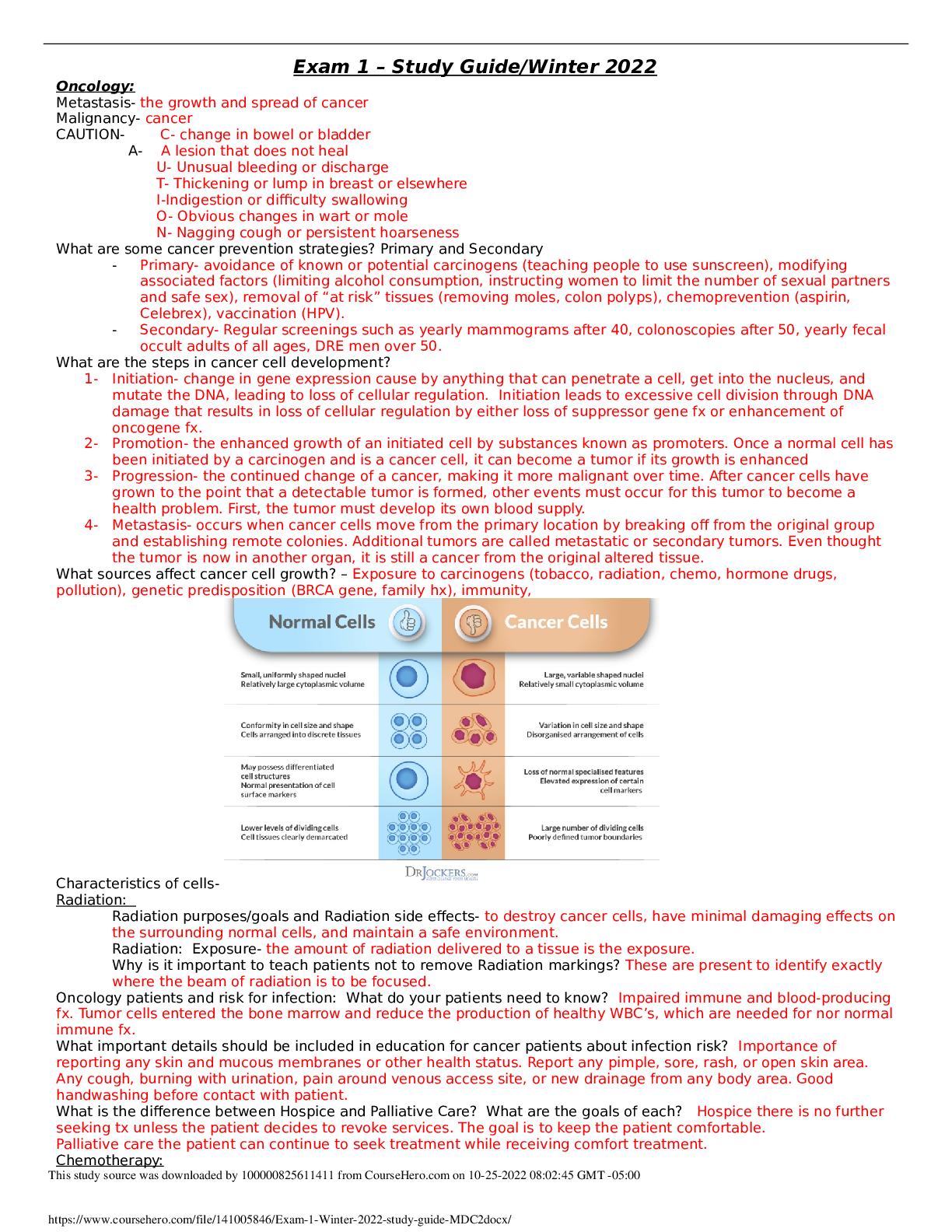
NUR 2474 Exam 1 study guide MDC2 Exam 1 – Study Guide/Winter 2022 Oncology: Metastasis- the growth and spread of cancer Malignancy- cancer CAUTION- C- change in bowel or bladder A- A lesion th... at does not heal U- Unusual bleeding or discharge T- Thickening or lump in breast or elsewhere I-Indigestion or difculty swallowing O- Obvious changes in wart or mole N- Nagging cough or persistent hoarseness What are some cancer prevention strategies? Primary and Secondary - Primary- avoidance of known or potential carcinogens (teaching people to use sunscreen), modifying associated factors (limiting alcohol consumption, instructing women to limit the number of sexual partners and safe sex), removal of “at risk” tissues (removing moles, colon polyps), chemoprevention (aspirin, Celebrex), vaccination (HPV). - Secondary- Regular screenings such as yearly mammograms after 40, colonoscopies after 50, yearly fecal occult adults of all ages, DRE men over 50. What are the steps in cancer cell development? 1- Initiation- change in gene expression cause by anything that can penetrate a cell, get into the nucleus, and mutate the DNA, leading to loss of cellular regulation. Initiation leads to excessive cell division through DNA damage that results in loss of cellular regulation by either loss of suppressor gene fx or enhancement of oncogene fx. 2- Promotion- the enhanced growth of an initiated cell by substances known as promoters. Once a normal cell has been initiated by a carcinogen and is a cancer cell, it can become a tumor if its growth is enhanced 3- Progression- the continued change of a cancer, making it more malignant over time. After cancer cells have grown to the point that a detectable tumor is formed, other events must occur for this tumor to become a health problem. First, the tumor must develop its own blood supply. 4- Metastasis- occurs when cancer cells move from the primary location by breaking off from the original group and establishing remote colonies. Additional tumors are called metastatic or secondary tumors. Even thought the tumor is now in another organ, it is still a cancer from the original altered tissue. What sources affect cancer cell growth? – Exposure to carcinogens (tobacco, radiation, chemo, hormone drugs, pollution), genetic predisposition (BRCA gene, family hx), immunity, Characteristics of cellsRadiation: Radiation purposes/goals and Radiation side effects- to destroy cancer cells, have minimal damaging effects on the surrounding normal cells, and maintain a safe environment. Radiation: Exposure- the amount of radiation delivered to a tissue is the exposure. Why is it important to teach patients not to remove Radiation markings? These are present to identify exactly where the beam of radiation is to be focused. Oncology patients and risk for infection: What do your patients need to know? Impaired immune and blood-producing fx. Tumor cells entered the bone marrow and reduce the production of healthy WBC’s, which are needed for nor normal immune fx. What important details should be included in education for cancer patients about infection risk? Importance of reporting any skin and mucous membranes or other health status. Report any pimple, sore, rash, or open skin area. Any cough, burning with urination, pain around venous access site, or new drainage from any body area. Good handwashing before contact with patient. What is the difference between Hospice and Palliative Care? What are the goals of each? Hospice there is no further seeking tx unless the patient decides to revoke services. The goal is to keep the patient comfortable. Palliative care the patient can continue to seek treatment while receiving comfort treatment. Chemotherapy: This study source was downloaded by 100000825611411 from CourseHero.com on 10-25-2022 08:02:45 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/141005846/Exam-1-Winter-2022-study-guide-MDC2docx/How does it work? Treatment of cancer with chemical agents, is used to cure and to increase survival time. It has some selectivity for killing cancer cells over normal cells. This killing effect on cancer cells is related to the ability of chemotherapy to damage DNA and interfere with cell division. How does treatment work? IV or oral regimen set by Dr. patient/family education needs? Patient-specifc information, tx regimen, how and what to communicate to health care providers, patient resources. Are there side effects? Hemorrhagic cystitis, cardiac muscle damage, loss of bone density. Anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, alopecia, mucositis, skin changes, anxiety, sleep disturbances, altered bowel eliminations, changes in cognitive fx. Emergent situations in Cancer treatment: Tumor Lysis Syndrome- Most of the time happens with the initial dose of chemotherapy. Their intracellular contents, including potassium and purines form uric acid, causing hyperuricemia. Severe or untreated TLS can cause tissue damage, AKI, and death. Hydration prevents and manages TLS by diluting the serum potassium level and increasing the kidney flow rates. SIADH- A condition where the body produces excess antidiuretic hormone leading to water retention and low sodium levels in the body. This causes hallucinations, disorientation, nausea and in severe cases coma. SVC syndrome – What is a common treatment/intervention? Compression or obstruction by tumor growth or by clots in the vessel leads to congestion of the blood. TX: Radiation, chemotherapy, surgery(rare), a metal stent placed by interventional radiology to relieve swelling SCC- Needs immediate intervention to alleviate pain and prevent neurologic damage. Damage occurs either when a tumor directly enters the spinal cord or spinal column or when the vertebrae collapse from tumor degradation of the bone. Surgical treatment classifcations – curative, prophylactic, diagnostic, palliativeCurative- removes all cancer tissues. Prophylactic- removes “at risk” tissue to prevent cancer development. Diagnostic (biopsy)- removal of all or part of a suspected lesion for examination and testing. . [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 3 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$13.50
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 07, 2022
Number of pages
3
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 07, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
37












_2nd_E_Completed.png)









.png)


