*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NSG 6020 STUDY GUIDE GENERAL-Best Exam Prep Document (All)
NSG 6020 STUDY GUIDE GENERAL-Best Exam Prep Document
Document Content and Description Below
NSG 6020 STUDY GUIDE GENERAL NSG 6020 STUDY GUIDE GENERAL 1. Which of the following are examples of secondary prevention? (Choose all that apply) 1. Mrs. Brody has brought his 16-year-old daugh... ter, Mandy, for a school sports physical exam. Mandy's height is 65 inches, and she weighs 126 lbs. Mrs. Brody is concerned that her daughter is overweight. According to Mandy's BMI, what is your response? A. Mandy is overweight and needs to take diet pills. B. Reassure the mother that this is a normal body weight. C. Refer the patient to a nutritionist and psychologist because the patient is anorexic. D. Give the patient information about exercise and reduction of fat cholesterol in her diet because she is overweight. B - (126 X 700) / (65^2) = 20.9 Body Mass Index (BMI) = (Weight (lbs) x 700)/(height (inches)^2) - Underweight: BMI < 18.5 - Normal: BMI 18.5-24.9 - Overweight: BMI 25.0-29.9 - Obesity I: BMI 30.0-34.9 - Obesity II: BMI 35.0-39.9 - Extreme Obesity III: BMI ≥ 40 1. A sudden painless unilateral vision loss may be caused by which of the following - Retinal detachment 2. A 73 year old nurse comes to your office for evaluation of new onset of tremors. She is not on any medications and does not take herbs or supplements. She has no chronic medical conditions. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. She walks into the examination room with slow movements and shuffling steps. She has decreased facial mobility and a blunt expression without any changes in hair distribution on her face. Based on this what is the most likely diagnosis. - Parkinsons 3. You are interviewing an elderly woman in the ambulatory setting and trying to get more information about her urinary symptoms. Which of the following techniques is not a component of adaptive questioning - Reassuring the patient that the urinary symptoms are benign and that she doesn’t need to worry about it being a sign of cancer. 4. A fifteen year old high school sophomore comes to the clinical for evaluation of a three week history of sneezing itchy watery eyes clear nasal discharge ear pain and non productive cough. Which is the most likely pathologic process? 5. a light is pointed at a patients pupli, which contracts it is also noted that the other pupil contracts as well, though it is not exposed to bright light. Which of the following terms describes this latter phenomenon - Consensual reaction. 6. Which of the following is used to screen for color blindness in a seven year old boy - Ishihara test 7. You feel a small mass that you think is a lymph node. It is mobile in both up and down and side by side direction. Which of the following is most likely 8. Lymph node 9. What is the best procedure for evaluating a corneal abrasion 10. Which of the following is a symptom involving the eye - Scotomas 11. Most sensitive test to detect hearing loss ? is it whisper or tuning forks 12. HA that has lasted 5 days and he does work at a computer is it a cluster, migraine, tension headache 13. A 55 year old bank teller comes to your office for persistent episodes of dizziness. The first episode started suddenly and lasted 3-4 hours. He experienced a lot of nausea with vomiting. The episode resolved spontaneously. He has had five episodes in the past 1 ½ weeks. He does note some tinnitus that comes and goes. upon physical exam you note that he has a normal gait. The weber localized to the right side and the air conduction is equal to the bone conduction in the right ear. Nystagmus is present. Based on this description what is the most likely diagnosis - Meniere’s disease - - A 35-year-old archaeologist comes to your office (located in Phoenix, Arizona) for a regular skin check-up. She has just returned from her annual dig site in Greece. She has fair skin and reddish-blonde hair. She has a family history of melanoma. She has many freckles scattered across her skin. From this description, which of the following is not a risk factor for melanoma in this patient? - A 15-year-old high school sophomore and her mother come to your clinic because the mother is concerned about her daughter's weight. You measure her daughter's height and weight and obtain a BMI of 19.5 kg/m2. Based on this information, which of the following is appropriate? - A 32-year-old attorney comes to your office for her second prenatal visit. She has had two previous pregnancies with uneventful prenatal care and vaginal deliveries. Her only problem was that with each pregnancy she gained 50 lbs (23 kg) and had difficulty losing the weight afterward. She has no complaints today. Looking at her chart, you see she is currently 10 weeks pregnant and that her prenatal weight was 130 lbs (59 kg). Her weight today is 134 lbs (60.9 kg). Her height is 5'4", giving her a BMI of 22. Her blood pressure, pulse, and urine tests are unremarkable. The fetal heart tone is difficult to find but is located and is 150. While you give her first trimester education, you tell her how much weight you expect her to gain. How much weight should this patient gain during pregnancy? A) Less than 15 pounds (less than 7 kg) B) 15 to 25 pounds (7 to 11.5 kg) C) 25 to 35 pounds (11.5 to 16 kg) D) 30 to 40 pounds (12.5 to 18 kg) - Nice work! - You just studied 158 terms! - Now up your study game with Learn mode. - Try Learn modeStudy with Flashcards again - 3/158 - Created by - f94248 - Study Guide-Flashcards - Terms in this set (158) - - A 22-year-old advertising copywriter presents for evaluation of joint pain. The pain is new, located in the wrists and fingers bilaterally, with some subjective fever. The patient denies a rash; she also denies recent travel or camping activities. She has a family history significant for rheumatoid arthritis. Based on this information, which of the following pathologic processes would be the most correct? - A 35-year-old archaeologist comes to your office (located in Phoenix, Arizona) for a regular skin check-up. She has just returned from her annual dig site in Greece. She has fair skin and reddish-blonde hair. She has a family history of melanoma. She has many freckles scattered across her skin. From this description, which of the following is not a risk factor for melanoma in this patient? - A 15-year-old high school sophomore and her mother come to your clinic because the mother is concerned about her daughter's weight. You measure her daughter's height and weight and obtain a BMI of 19.5 kg/m2. Based on this information, which of the following is appropriate? A) Refer the patient to a nutritionist and a psychologist because the patient is anorexic. B) Reassure the mother that this is a normal body weight. C) Give the patient information about exercise because the patient is obese. D) Give the patient information concerning reduction of fat and cholesterol in her diet because she is obese. - answer- B - A 32-year-old attorney comes to your office for her second prenatal visit. She has had two previous pregnancies with uneventful prenatal care and vaginal deliveries. Her only problem was that with each pregnancy she gained 50 lbs (23 kg) and had difficulty losing the weight afterward. She has no complaints today. Looking at her chart, you see she is currently 10 weeks pregnant and that her prenatal weight was 130 lbs (59 kg). Her weight today is 134 lbs (60.9 kg). Her height is 5'4", giving her a BMI of 22. Her blood pressure, pulse, and urine tests are unremarkable. The fetal heart tone is difficult to find but is located and is 150. While you give her first trimester education, you tell her how much weight you expect her to gain. How much weight should this patient gain during pregnancy? A) Less than 15 pounds (less than 7 kg) B) 15 to 25 pounds (7 to 11.5 kg) C) 25 to 35 pounds (11.5 to 16 kg) D) 30 to 40 pounds (12.5 to 18 kg) - answer- C - You are beginning the examination of the skin on a 25-year-old teacher. You have previously elicited that she came to the office for evaluation of fatigue, weight gain, and hair loss. You strongly suspect that she has hypothyroidism. What is the expected moisture and texture of the skin of a patient with hypothyroidism? A) Moist and smooth B) Moist and rough C) Dry and smooth D) Dry and rough - answer- D - A middle-aged man comes in because he has noticed multiple small, blood-red, raised lesions over his anterior chest and abdomen for the past several months. They are not painful and he has not noted any bleeding or bruising. He is concerned this may be consistent with a dangerous condition. What should you do? A) Reassure him that there is nothing to worry about. B) Do laboratory work to check for platelet problems. C) Obtain an extensive history regarding blood problems and bleeding disorders. D) Do a skin biopsy in the office. - answer- A - Upgrade to remove ads - Only $1/month - - A 23-year-old ticket agent is brought in by her husband because he is concerned about her recent behavior. He states that for the last 2 weeks she has been completely out of control. He says that she hasn't showered in days, stays awake most of the night cleaning their apartment, and has run up over $1,000 on their credit cards. While he is talking, the patient interrupts him frequently and declares this is all untrue and she has never been so happy and fulfilled in her whole life. She speaks very quickly, changing the subject often. After a longer than normal interview you find out she has had no recent illnesses or injuries. Her past medical history is unremarkable. Both her parents are healthy but the husband has heard rumors about an aunt with similar symptoms. She and her husband have no children. She smokes one pack of cigarettes a day (although she has been chain-smoking in the last 2 weeks), drinks four to six drinks a week, and smokes marijuana occasionally. On examination she is very loud and outspoken. Her physical examination is unremarkable. Which mood disorder does she most likely have? A) Major depressive episode B) Manic episode C) Dysthymic disorder - answer- B - Jacob, a 33-year-old construction worker, complains of a "lump on his back" over his scapula. It has been there for about a year and is getting larger. He says his wife has been able to squeeze out a cheesy-textured substance on occasion. He worries this may be cancer. When gently pinched from the side, a prominent dimple forms in the middle of the mass. What is most likely? A) An enlarged lymph node B) A sebaceous cyst C) An actinic keratosis D) A malignant lesion - answer- B - A patient comes to you for the appearance of red patches on his forearms that have been present for several months. They remain for several weeks. He denies a history of trauma. Which of the following is likely? A - A patient is describing a very personal part of her history very quickly and in great detail. How should you react to this? A) Write down as much as you can, as quickly as possible. B) Ask her to repeat key phrases or to pause at regular intervals, so you can get almost every word. C) Tell her that she can go over the notes later to make sure they are accurate. D) Push away from the keyboard or put down your pen and listen. - answer- D - Mrs. Glynn is 90 years old and lives alone. She is able to bathe, dress, prepare her food, and transfer from bed to chair independently. She has children in the area who help her with her medications and transportation needs. Which of the following is considered an instrumental activity of daily living? - A young mother presents with a pregnancy confirmed by urine HCG. Her LMP was June 20. Using Naegele's rule, you estimate what day of delivery? - When using an interpreter to facilitate an interview, where should the interpreter be positioned? A) Behind you, the examiner, so that the lips of the patient and the patient's nonverbal cues can be seen B) Next to the patient, so the examiner can maintain eye contact and observe the nonverbal cues of the patient C) Between you and the patient so all parties can make the necessary observations D) In a corner of the room so as to provide minimal distraction to the interview - answer- B - Which of the following represents age-related changes in the lungs? A) Decrease in chest wall compliance B) Speed of expiration increases C) Increase in respiratory muscle strength D) Increased elastic recoil of lung tissue - answer- A - A 67-year-old retired janitor comes to the clinic with his wife. She brought him in because she is concerned about his weight loss. He has a history of smoking 3 packs of cigarettes a day for 30 years, for a total of 90 pack-years. He has noticed a daily cough for the past several years, which he states is productive of sputum. He came into the clinic approximately 1 year ago, and at that time his weight was 140 pounds. Today, his weight is 110 pounds. Which one of the following questions would be the most important to ask if you suspect that he has lung cancer? - A 19-year old-college student presents to the emergency room with fever, headache, and neck pain/stiffness. She is concerned about the possibility of meningococcal meningitis. Several of her dorm mates have been vaccinated, but she hasn't been. Which of the following physical examination descriptions is most consistent with meningitis? - A young woman comes in for a routine wellness examination. You notice that her vaginal walls have deep rugae and are slightly bluish in color. She also has a thicker white discharge. What should you suspect? - Adam is a very successful 15-year-old student and athlete. His mother brings him in today because he no longer studies, works out, or sees his friends. This has gone on for a month and a half. When you speak with him alone in the room, he states it "would be better if he were not here." What would you do next? - A 26-year-old violinist comes to your clinic, complaining of anxiety. He is a first chair violinist in the local symphony orchestra and has started having symptoms during performances, such as sweating, shaking, and hyperventilating. It has gotten so bad that he has thought about giving up his first chair status so he does not have to play the solo during one of the movements. He says that he never has these symptoms during rehearsals or when he is practicing. He denies having any of these symptoms at any other time. His past medical history is unremarkable. He denies any tobacco use, drug use, or alcohol abuse. His parents are both healthy. On examination you see a young man who appears worried. His vital signs and physical examination are unremarkable. What type of anxiety disorder best describes his situation? - A 24-year-old cashier comes to your clinic for her first OB visit. She had her last period 10 weeks before, which would mean she is 12 weeks pregnant. She did a home pregnancy urine test a month ago and it was positive. She has had some fatigue and nausea, but not in the last week. She has had no cramping or bleeding. Her vital signs, head, eyes, ears, nose, throat, thyroid, cardiac, pulmonary, and abdominal examinations are all unremarkable. On speculum examination her os is closed and there is a pinkish hue to the cervix. On bimanual examination the cervix is soft and the uterus is enlarged to the pelvic brim. Despite 20 minutes of trying, you cannot find heart tones. You repeat a urine pregnancy test and it is negative. A serum pregnancy test is ordered and is positive. You send the patient for a vaginal ultrasound. What is the most likely explanation for her presentation? - Mrs. Buckley is a 75-year-old widow who wants you to look at her teeth because over the past 2 weeks she has had right-sided jaw pain when eating. It does not occur otherwise. She also has had a headache. Which of the following should be considered? - Mrs. H. comes to your clinic, wanting antibiotics for a sinus infection. When you enter the room, she appears to be very angry. She has a raised tone of voice and states that she has been waiting for the past hour and has to get back to work. She states that she is unimpressed by the reception staff, the nurse, and the clinic in general and wants to know why the office wouldn't call in an antibiotic for her. Which of the following techniques is not useful in helping to calm this patient? - In obtaining a history, you note that a patient uses the word "largely" repeatedly, to the point of being a distraction to your task. Which word best describes this speech pattern? - A 58-year-old gardener comes to your office for evaluation of a new lesion on her upper chest. The lesion appears to be "stuck on" and is oval, brown, and slightly elevated with a flat surface. It has a rough, wartlike texture on palpation. Based on this description, what is your most likely diagnosis? - A patient presents for evaluation of a cough. Which of the following anatomic regions can be responsible for a cough? - You are seeing an older patient who has not had medical care for many years. Her vital signs taken by your office staff are: T 37.2, HR 78, BP 118/92, and RR 14, and she denies pain. You notice that she has some hypertensive changes in her retinas and you find mild proteinuria on a urine test in your office. You expected the BP to be higher. She is not on any medications. What do you think is causing this BP reading, which doesn't correlate with the other findings? - A patient tells you about her experience with prolonged therapy for her breast cancer. You comment, "That must have been a very trying time for you." What is this an example of? - A 72-year-old retired truck driver comes to the clinic with his wife for evaluation of hearing loss. He has noticed some decreased ability to hear what his wife and grandchildren are saying to him. He admits to lip-reading more. He has a history of noise exposure in his young adult years: He worked as a sound engineer at a local arena and had to attend a lot of concerts. Based on this information, what is the most likely finding regarding his hearing acuity? - You are seeing an elderly man with multiple complaints. He has chronic arthritis, pain from an old war injury, and headaches. Today he complains of these pains, as well as dull chest pain under his sternum. What would the order of priority be for your problem list? - The following information is best placed in which category? "The patient had a stent placed in the left anterior descending artery (LAD) in 1999." - A 62-year-old teacher presents to the clinic for evaluation of the following symptoms: fever, headache, sinus congestion, sore throat, green nasal discharge, and cough. This cluster of symptoms is best explained by: - Mrs. Anderson presents with an itchy rash which is raised and appears and disappears in various locations. Each lesion lasts for many minutes. What most likely accounts for this rash? - Jeannie is a 24-year-old pregnant woman who asks you today if her frequent urination is normal. Which of the following hormones is most likely responsible for this? - Mr. Kelly comes to you today for a burning pain in his lower abdomen. This has gone on for 2 months. He has received radiation for prostatic cancer for the past quarter. What assumptions could you draw from this? - On a very busy day in the office, Mrs. Donelan, who is 81 years old, comes for her usual visit for her blood pressure. She is on a low-dose diuretic chronically and denies any side effects. Her blood pressure is 118/78 today, which is well-controlled. As you are writing her script, she mentions that it is hard not having her husband Bill around anymore. What would you do next? - A new mother is concerned that her child occasionally "turns blue." On further questioning, she mentions that this is at her hands and feet. She does not remember the child's lips turning blue. She is otherwise eating and growing well. What would you do now? - An 89-year-old retired school principal comes for an annual check-up. She would like to know whether or not she should undergo a screening colonoscopy. She has never done this before. Which of the following factors should not be considered when discussing whether she should go for this screening test? - Is the following information subjective or objective? Mr. M. has a respiratory rate of 32 and a pulse rate of 120. - During cardiac examination you notice a new parasternal systolic murmur of 2/6 intensity. On palpation, the PMI is slightly higher than usual. What do you suspect? - Susanne is a 27 year old who has had headaches, muscle aches, and fatigue for the last 2 months. You have completed a thorough history, examination, and laboratory workup but have not found a cause. What would your next action be? - A 75-year-old homemaker brings her 76-year-old husband to your clinic. She states that 4 months ago he had a stroke and ever since she has been frustrated with his problems with communication. They were at a restaurant after church one Sunday when he suddenly became quiet. When she realized something was wrong he was taken to the hospital by EMS. He spent 2 weeks in the hospital with right-sided eakness and difficulty speaking. After hospitalization he was in a rehab center, where he regained the ability to walk and most of the use of his right hand. He also began to speak more, but she says that much of the time "he doesn't make any sense." She gives an example that when she reminded him the car needed to be serviced he told her "I will change the Kool-Aid out of the sink myself with the ludrip." She says that these sayings are becoming frustrating. She wants you to tell her what is wrong and what you can do about it. While you write up a consult to neurology, you describe the syndrome to her. What type of aphasia does he have? A) Wernicke's aphasia B) Broca's aphasia C) Dysarthria - answer- A - A pregnant woman is concerned by the recent onset of a midline swelling. It is soft and nontender. What does this represent? - A 22-year-old clerk, primigravida, comes to your office for a prenatal visit. She is in her second trimester and has had prenatal care since she was 8 weeks pregnant. Her only complaint is that she has a new brownish line straight down her abdomen. On examination her vital signs are unremarkable. Her urine has no protein, glucose, or leukocytes. With a Doptone the fetal heart rate is 140, and her uterus is palpated to the umbilicus. Today you are sending her for congenital abnormality screening and setting up an ultrasound. What physical finding is responsible for her new "brown line"? - A 24-year-old secretary comes to your clinic, complaining of difficulty sleeping, severe nightmares, and irritability. She states it all began 6 months ago when she went to a fast food restaurant at midnight. While she was waiting in her car a man entered through the passenger door and put a gun to her head. He had her drive to a remote area, where he took her money and threatened to kill her. When the gun jammed he panicked and ran off. Ever since this occurred the patient has been having these symptoms. She states she jumps at every noise and refuses to drive at night. She states her anxiety has had such a marked influence on her job performance she is afraid she will be fired. She denies any recent illnesses or injuries. Her past medical history is unremarkable. On examination you find a nervous woman appearing her stated age. Her physical examination is unremarkable. You recommend medication and counseling. What anxiety disorder to you think this young woman has? - A 25-year-old type 1 diabetic clerk presents to the emergency room with shortness of breath and states that his blood sugar was 605 at home. You diagnose the patient with diabetic ketoacidosis. What is the expected pattern of breathing? - Mrs. Lenzo weighs herself every day with a very accurate balance-type scale. She has noticed that over the past 2 days she has gained 4 pounds. How would you best explain this? - Jenny is one of your favorite patients who usually shares a joke with you and is nattily dressed. Today she is dressed in old jeans, lacks makeup, and avoids eye contact. To what do you attribute these changes? - A 29-year-old homemaker who is G4P3 comes to your clinic for her first prenatal check. Her last period was 2 months ago. She has had three previous pregnancies and deliveries with no complications. She has no medical problems and has had no surgeries. Her only current complaint is of severe reflux that occurs in the mornings and evenings. On examination she is in no acute distress. Her vitals are 110/70 with a pulse of 88. Her respirations are 16. Her head, eyes, ears, nose, throat, thyroid, cardiac, pulmonary, and abdominal examinations are unremarkable. On bimanual examination her cervix is soft and her uterus is 10 weeks in size. Pap smear, cultures, and blood work are pending. What is the most likely cause of her first-trimester reflux? - A 72-year-old African-American male is brought to your clinic by his daughter for a follow-up visit after his recent hospitalization. He had been admitted to the local hospital for speech problems and weakness in his right arm and leg. On admission his MRI showed a small stroke. The patient was in rehab for 1 month following his initial presentation. He is now walking with a walker and has good use of his arm. His daughter complains, however, that everyone is still having trouble communicating with the patient. You ask the patient how he thinks he is doing. Although it is hard for you to make out his words you believe his answer is "well . . . fine . . . doing . . . okay." His prior medical history involved high blood pressure and coronary artery disease. He is a widower and retired handyman. He has three children who are healthy. He denies tobacco, alcohol, or drug use. He has no other current symptoms. On examination he is in no acute distress but does seem embarrassed when it takes him so long to answer. His blood pressure is 150/90 and his other vital signs are normal. Other than his weak right arm and leg his physical examination is unremarkable. What disorder of speech does he have? - A 73-year-old retired accountant comes to your office for her annual examination. She has incontinence of urine when she coughs or sneezes. She takes several medications for control of hypertension and diabetes. You use the DIAPERS mnemonic to assess the cause of her incontinence. All of the following are items represented by the mnemonic except for: - . A 23-year-old graduate student comes to your clinic for evaluation of a urethral discharge. As the provider, you need to get a sexual history. Which one of the following questions is inappropriate for eliciting the information? - Steve has just seen a 5-year-old girl who wheezes when exposed to cats. The patient's family history is positive for asthma. You think the child most likely has asthma. What have you just accomplished? - A 37-year-old nurse comes for evaluation of colicky right upper quadrant abdominal pain. The pain is associated with nausea and vomiting and occurs 1 to 2 hours after eating greasy foods. Which one of the following physical examination descriptions would be most consistent with the diagnosis of cholecystitis? - Mr. Larson is a 42-year-old widowed father of two children, ages 4 and 11. He works in a sales office to support his family. Recently he has injured his back and you are thinking he would benefit from physical therapy, three times a week, for an hour per session. What would be your next step? - You are interviewing an elderly woman in the ambulatory setting and trying to get more information about her urinary symptoms. Which of the following techniques is not a component of adaptive questioning? - A 30-year-old sales clerk comes to your office wanting to lose weight; her BMI is 30.0 kg/m2. What is the most appropriate amount for a weekly weight reduction goal? - A 27-year-old woman is brought to your office by her mother. The mother tells you that her daughter has been schizophrenic for the last 8 years and is starting to decompensate despite medication. The patient states that she has been taking her antipsychotic and she is doing just fine. Her mother retorts that her daughter has become quite paranoid. When asked why, the mother gives an example about the mailman. She says that her daughter goes and gets the mail every day and then microwaves the letters. The patient agrees that she does this but only because she sees the mailman flipping through the envelopes and she knows he's putting anthrax on the letters. Her mother turns to her and says, "He's only sorting the mail!" Which best describes the patient's abnormality of perception? - You are observing a patient with heart failure and notice that there are pauses in his breathing. On closer examination, you notice that after the pauses the patient takes progressively deeper breaths and then progressively shallower breaths, which are followed by another apneic spell. The patient is not in any distress. You make the diagnosis of: - Which of the following is worrisome in Melissa, a woman in her 26th week of pregnancy? - It is summer and an 82-year-old woman is brought to you from her home after seeing her primary care doctor 2 days ago. She was started on an antibiotic at that time. Today, she comes to the emergency room not knowing where she is or what year it is. What could be a likely cause of this? - A 26-year-old stewardess comes in for a third trimester prenatal visit. She has had prenatal care since her sixth week of pregnancy. She has no complaints today and her prenatal course has been unremarkable. Today her blood pressure and weight gain are appropriate and her urine is unremarkable. You have a first-year medical student shadowing you, so you ask the student to get Doptones and measure the patient's uterus in centimeters. The student promptly reports fetal heart tones of 140, but he is having difficulty obtaining the correct measurement. He knows one end of the tape goes over the uterine fundus. From what inferior anatomic position should the tape be placed? - Which of the following is commonly seen in aging men? - A patient complains of knee pain on your arrival in the room. What should your first sentence be after greeting the patient? - Which of the following is true of assessment of the vascular system in the elderly? - On the way to see your next patient, you glance at the calendar and make a mental note to buy a Mother's Day card. Your patient is Ms. Hernandez, a 76-year-old widow who lost her husband in May, two years ago. She comes in today with a headaches, abdominal pain, and general malaise. This happened once before, about a year ago, according to your detailed office notes. You have done a thorough evaluation but are unable to arrive at a consistent picture to tie these symptoms together. This is an example of a: - Is the following information subjective or objective? Mr. M. has shortness of breath that has persisted for the past 10 days; it is worse with activity and relieved by rest. As you listen to him describe his symptom in more detail, you say "Go on," and later, "Mm-hmmm." This is an example of which of the following skilled interviewing techniques? - The following information is recorded in the health history: "I feel really tired." Which category does it belong to? - Alexandra is a 28-year-old editor who presents to the clinic with abdominal pain. The pain is a dull ache, located in the right upper quadrant, that she rates as a 3 at the least and an 8 at the worst. The pain started a few weeks ago, it lasts for 2 to 3 hours at a time, it comes and goes, and it seems to be worse a couple of hours after eating. She has noticed that it starts after eating greasy foods, so she has cut down on these as much as she can. Initially it occurred once a week, but now it is occurring every other day. Nothing makes it better. From this description, which of the seven attributes of a symptom has been omitted? - A 26-year-old white female comes to your clinic at 38 weeks, complaining of intermittent contractions. They last for 30 seconds and are coming every 10 minutes. Her prenatal course has so far been uneventful. You send her to labor and delivery for a labor assessment. On vaginal examination she has effaced 4 cm, but you cannot feel a presenting part. You admit her for active labor; however, you wish to assess if she is vertex (baby's head is down), so you do the Leopold's maneuver. Palpating the upper pole with your hands, you feel a firm round mass. Placing your hand along the right side of her abdomen, you feel a smooth firmness. Palpating your other hand along the left side of her abdomen, you feel irregular bumps. Above the pelvic brim you feel a firm irregular mass. While awaiting ultrasound to confirm your diagnosis, you write the pertinent orders. How is this fetus presenting? - You are excited about a positive test finding you have just noticed on physical examination of your patient. You go on to do more examination, laboratory work, and diagnostic tests, only to find that there is no sign of the disease you thought would correlate with the finding. This same experience happens several times. What should you conclude? t woman finally comes in for her prenatal checkup. She complains today of headache and abdominal pain of several months' duration. She appears somewhat hurried or nervous. What question would you ask next? - The following information is best placed in which category? "The patient has had three cesarean sections." - You have just asked a patient how he feels about his emphysema. He becomes silent, folds his arms across his chest and leans back in his chair, and then replies, "It is what it is." How should you respond? A) "You seem bothered by this question." - The following information is recorded in the health history: "The patient has had abdominal pain for 1 week. The pain lasts for 30 minutes at a time; it comes and goes. The severity is 7 to 9 on a scale of 1 to 10. It is accompanied by nausea and vomiting. It is located in the mid-epigastric area." Which of these categories does it belong to? ormation is best placed in which category? "The patient was treated for an asthma exacerbation in the hospital last year; the patient has never been intubated." A) Adult illnesses - A 26-year-old telephone operator comes to your office for her first prenatal visit. This is her first pregnancy. Her last period was about 2 months ago. She has no current complaints. She is eating healthily, taking vitamins, and exercising. She has a past medical history of an appendectomy as a teenager. Her mother had three children vaginally with no complications. On examination she appears healthy and her vital signs are unremarkable. Her head, eyes, ears, nose, throat, thyroid, cardiac, pulmonary, and abdominal examinations are also unremarkable. By speculum examination, her cervix appears bluish in color and highly vascular. A bimanual examination reveals a soft cervix and a 12-week-sized uterus. No masses are felt in either adnexal area. Results of her Pap, cultures, and - A 35-year-old stockbroker comes to your office, complaining of feeling tired and irritable. She also says she feels like nothing ever goes her way and that nothing good ever happens. When you ask her how long she has felt this way she laughs and says, "Since when have I not?" She relates that she has felt pessimistic about life in general since she was in high school. She denies any problems with sleep, appetite, or concentration, and states she hasn't thought about killing herself. She reports no recent illnesses or injuries. She is single. She smokes one pack of cigarettes a day, drinks occasionally, and hasn't taken any illegal drugs since college. Her mother suffers from depression and her father has high blood pressure. On examination her vital signs and physical examination are unremarkable. What - A mother brings her 11 month old to you because her mother-in-law and others have old her that her baby is jaundiced. She is eating and growing well and performing the developmental milestones she should for her age. On examination you indeed notice a yellow tone to her skin from head to toe. Her sclerae are white. To which area should your next questions be related? - A 70-year-old retired auto mechanic comes to your office because his neighbor is concerned about his memory. The patient himself admits to misplacing his keys more often and forgets what he is supposed to buy from the grocery store and where he has parked the car. He denies getting lost in familiar places. Upon further questioning, he states that his wife of 40 years died 8 months ago; his three children live in three different states; and he has limited his activities because the people he interacted with were "his wife's friends, not his." He drinks a six-pack of beer daily; he does not smoke or use illicit drugs. You perform a mini-mental state examination and obtain a total score of 24 out of 28. Based on this information, what is your most likely diagnosis? - A 19-year-old childcare worker comes to you for her first prenatal visit. She cannot remember when her last period was but thinks it was between 2 and 5 months ago. When she began gaining weight and feeling "something" moving down there, she did a home pregnancy test and it was positive. She states she felt the movement about a week ago. She has had no nausea, vomiting, fatigue, or fevers. Her past medical history is remarkable only for irregular periods. She has been dating the same young man for a year. She says they were not using condoms. On examination you see an overweight young lady appearing her stated age. Her head, eyes, ears, nose, throat, neck, thyroid, cardiac, and pulmonary examinations are unremarkable. Her abdomen is nontender, with normal bowel sounds, and the gravid uterus is palpated to the level of the umbilicus. Fetal tones are easily found with Doptone, and with the fetoscope a faint heart rate of 140 is heard. By speculum examination the cervix is bluish and by bimanual examination the cervix is soft. Results of Pap smear, cultures, and blood work are pending. You give the patient her due date and how far along she is, based on your clinical findings. An OB ultrasound to confirm her dates is ordered. With only the clinical examination, how many weeks pregnant did you tell this patield white female comes to your clinic, complaining of overwhelming sadness. She says for the past 2 months she has had crying episodes, difficulty sleeping, and problems with overeating. She says she used to go out with her friends from work but now she just wants to go home and be by herself. She also thinks that her work productivity has been dropping because she just is too tired to care or concentrate. She denies any feelings of guilt or any suicidal ideation. She states that she has never felt this way in the past. She denies any recent illness or injuries. Her past medical history consists of an appendectomy when she was a teenager; otherwise, she has been healthy. She is single and works as a clerk in a medical office. She denies tobacco, alcohol, or illegal drug use. Her mother has high blood pressure and her father has had a history of mental illness. On examination you see a woman appearing her stated age who seems quite sad. Her facial expression does fatigued of performing a maneuver on examination because you have never found a positive and are usually pressed for time. How should you next approach this maneuver? A) Use this test when you have a higher suspicion for a certain correlating condition. B) Omit this test from future examinations. C) Continue doing the test, but rely more heavily on laboratory work and diagnostics. D) Continue performing it on all future examinations. - Mr. Chin is an 82-year-old man who comes to your office for a routine check. On examination, you notice a somewhat high-pitched murmur in the second right intercostal space during systole. It does not radiate and the rest of his examination is normal for his age. Which is true of the most likely cause of this murmur? A) It often decreases carotid upstroke. B) It carries with it increased risk for cardiovascular disease. C) It is usually accompanied by an S3 gallop. D) It is found in 10% of otherwise normal elderly patients. - answer- B - A woman in her 24th week of pregnancy notices she feels faint when lying down for a period. What would you suspect as a cause for - Which of the following is the major effect of placental hormones? A) Insulin resistance B) Increased tidal volume brings him in today because he notes that Mr. White has not been himself lately. He seems forgetful and has not taken care of himself as he normally does. He has reported falling twice at home to his son and has telephoned late at night because of insomnia. His blood pressure and diabetes have been difficult to control and his warfarin dosing has become more difficult. - A 49-year-old truck driver comes to the emergency room for shortness of breath and swelling in his ankles. He is diagnosed with congestive heart failure and admitted to the hospital. You are the student assigned to do the patient's complete history and physical examination. When you palpate the pulse, what do you expect to feel? A) Large amplitude, forceful B) Small amplitude, weak C) Normal D) Bigeminal - answer- B - A 78-year-old retired seamstress comes to the office for a routine check-up. You obtain an ECG (electrocardiogram) because of her history of hypertension. You diagnose a previous myocardial infarction and ask her if she had any symptoms related to this. Which of the following symptoms would be more common in this patient's age group for an acute myocardial infarction? - Mr. Garcia comes to your office for a rash on his chest associated with a burning pain. Even a light touch causes this burning sensation to worsen. On examination, you note a rash with small blisters (vesicles) on a background of reddened skin. The rash overlies an entire rib on his right side. What type of pain is this? - Lucille is in her 24th week. You notice a new onset of high blood pressure readings. Today's value is 168/96. Her urine is normal. What do you suspect? A) Preeclampsia - You are speaking to an 8th grade class about health prevention and are preparing to discuss the ABCDEs of melanoma. Which of the following descriptions correctly defines the ABCDEs? old body builder is upset by a letter of denial from his life insurance company. He is very lean but has gained 2 pounds over the past 6 months. You personally performed his health assessment and found no problems whatsoever. He says he is classified as "high risk" because of obesity. What should you do next? - Mrs. Geller is somewhat quiet today. She has several bruises of different colors on the ulnar aspects of her forearms and on her abdomen. She otherwise has no complaints and her diabetes and hypertension are well managed. Her son from out of state accompanies her today and has recently moved in to help her. What should you suspect? - Which of the following accompanies decreased ovarian function? - Mrs. Kelly comes to you for her usual prenatal check-up. You measure the fundal height at 24 cm. What would you estimate the length of her gestation to be? - You are examining an elderly man and notice the following: decreased vibration sense in the feet and ankles, diminished gag reflex, right patellar reflex less than the left, and diminished abdominal reflexes. Which of these is abnormal? - An 18-year-old college freshman presents to the clinic for evaluation of gastroenteritis. You measure the patient's temperature and it is 104 degrees Fahrenheit. What type of pulse would you expect to feel during his initial examination? - A woman in her third trimester complains of shortness of breath on occasion, without other symptoms. She has a normal examination. The most likely cause of this symptom is: - The following information is recorded in the health history: "Patient denies chest pain, palpitations, orthopnea, and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea." Which category does it belong to? - A 79-year-old retired banker comes to your office for evaluation of difficulty with urination; he gets up five to six times per night to urinate and has to go at least that often in the daytime. He does not feel as if his bladder empties completely; the strength of the urinary stream is diminished. He denies dysuria or hematuria. This problem has been present for several years but has worsened over the last 8 months. You palpate his prostate. What is your expected physical examination finding, based on this description? - Mr. Curtiss has a history of obesity, diabetes, osteoarthritis of the knees, HTN, and obstructive sleep apnea. His BMI is 43 and he has been discouraged by his difficulty in losing weight. He is also discouraged that his goal weight is 158 pounds away. What would you tell him? - A 22-year-old man is brought to your office by his father to discuss his son's mental health disorder. The patient was diagnosed with schizophrenia 6 months ago and has been taking medication since. The father states that his son's dose isn't high enough and you need to raise it. He states that his son has been hearing things that don't exist. You ask the young man what is going on and he tells you that his father is just jealous because his sister talks only to him. His father turns to him and says, "Son, you know your sister died 2 years ago!" His son replies "Well, she still talks to me in my head all the time!" Which best describes this patient's abnormality of perception? - A 55-year-old bookkeeper comes to your office for a routine visit. You note that on a previous visit for treatment of contact dermatitis, her blood pressure was elevated. She does not have prior elevated readings and her family history is negative for hypertension. You measure her blood pressure in your office today. Which of the following factors can result in a false high reading? - You are asked to perform a home safety assessment for an 87-year-old retired farmer who lives by himself. Which of the following is not considered to be an increased risk for falls? - Ms. Wright comes to your office, complaining of palpitations. While checking her pulse you notice an irregular rhythm. When you listen to her heart, every fourth beat sounds different. It sounds like a triplet rather than the usual "lub dup." How would you document your examination? - The following information is recorded in the health history: "The patient completed 8th grade. He currently lives with his wife and two children. He works on old cars on the weekend. He works in a glass factory during the week." Which category does it belong to? - Blood pressure abnormalities found more commonly in Western elderly include which of the following? - Despite having high BP readings in the office, Mr. Kelly tells you that his readings at home are much lower. He checks them twice a day at the same time of day and has kept a log. How do you respond? - A young man comes to you with an extremely pruritic rash over his knees and elbows which has come and gone for several years. It seems to be worse in the winter and improves with some sun exposure. On examination, you notice scabbing and crusting with some silvery scale, and you are observant enough to notice small "pits" in his nails. What would account for these findings? - A 15-year-old high school sophomore comes to the clinic for evaluation of a 3-week history of sneezing; itchy, watery eyes; clear nasal discharge; ear pain; and nonproductive cough. Which is the most likely pathologic process? - A 68-year-old retired farmer comes to your office for evaluation of a skin lesion. On the right temporal area of the forehead, you see a flattened papule the same color as his skin, covered by a dry scale that is round and feels hard. He has several more of these scattered on the forehead, arms, and legs. Based on this description, what is your most likely diagnosis? A) Actinic keratosis B) Seborrheic keratosis C) Basal cell carcinoma D) Squamous cell carcinoma - answer- A - A 19-year-old college student, Todd, is brought to your clinic by his mother. She is concerned that there is something seriously wrong with him. She states for the past 6 months his behavior has become peculiar and he has flunked out of college. Todd denies any recent illness or injuries. His past medical history is remarkable only for a broken foot. His parents are both healthy. He has a paternal uncle who had similar symptoms in college. The patient admits to smoking cigarettes and drinking alcohol. He also admits to marijuana use but none in the last week. He denies using any other substances. He denies any feelings of depression or anxiety. While speaking with Todd and his mother you do a complete physical examination, which is essentially normal. When you question him on how he is feeling, he says that he is very worried that Microsoft has stolen his software for creating a better browser. He tells you he has seen a black van in his neighborhood at night and he is sure that it is full of computer tech workers stealing his work through special gamma waves. You ask him why he believes they are trying to steal his programs. He replies that the technicians have been telepathing their intents directly into his head. He says he hears these conversations at night so he knows this is happening. Todd's mother then tells you, "See, I told you . . . he's crazy. What do I do about it?" While arranging for a psychiatry consult, what psychotic disorder do you think Todd has? A) Schizoaffective disorder B) Psychotic disorder due to a medical illness C) Substance-induced psychotic disorder D) Schizophrenia - answer- D - Mrs. R. is a 92-year-old retired teacher who comes to your clinic accompanied by her daughter. You ask Mrs. R. why she came to your clinic today. She looks at her daughter and doesn't say anything in response to your question. This is an example of which type of challenging patient? A) Talkative patient B) Angry patient C) Silent patient D) Hearing-impaired patient - answer- C - Mrs. Stanton is a 79-year-old widow who presents to your office for a routine BP visit. You note a new pulsatile mass in the right neck at the carotid artery. Which of the following is the most likely cause for this? A) Anxiety B) Carotid artery aneurysm C) Kinking of the artery D) Tortuous aorta - answer- C - An 8-year-old girl comes with her mother for evaluation of hair loss. She denies pulling or twisting her hair, and her mother has not noted this behavior at all. She does not put her hair in braids. On physical examination, you note a clearly demarcated, round patch of hair loss without visible scaling or inflammation. There are no hair shafts visible. Based on this description, what is your most likely diagnosis? A) Alopecia areata B) Trichotillomania C) Tinea capitis D) Traction alopecia - answer- A - A 55-year-old data entry operator comes to the clinic to establish care. She has the following symptoms: headache, neck pain, sinus congestion, sore throat, ringing in ears, sharp brief chest pains at rest, burning abdominal pain with spicy foods, constipation, urinary frequency that is worse with coughing and sneezing, and swelling in legs. This cluster of symptoms is explained by: A) One disease process B) More than one disease process - answer- B - You are beginning the examination of a patient. All of the following areas are important to observe as part of the General Survey except: A) Level of consciousness B) Signs of distress C) Dress, grooming, and personal hygiene D) Blood pressure - answer- D - Common or concerning symptoms to inquire about in the General Survey and vital signs include all of the following except: A) Changes in weight B) Fatigue and weakness C) Cough D) Fever and chills - answer- C - You ask a patient to draw a clock. He fills in all the numbers on the right half of the circle. What do you suspect? A) Hemianopsia B) Fatigue C) Oppositional defiant disorder D) Depression - answer- A - A 19-year-old construction worker presents for evaluation of a rash. He notes that it started on his back with a multitude of spots and is also on his arms, chest, and neck. It itches a lot. He does sweat more than before because being outdoors is part of his job. On physical examination, you note dark tan patches with a reddish cast that has sharp borders and fine scales, scattered more prominently around the upper back, chest, neck, and upper arms as well as under the arms. Based on this description, what is your most likely diagnosis? A) Pityriasis rosea B) Tinea versicolor C) Psoriasis D) Atopic eczema - answer- B - Jason is a 41-year-old electrician who presents to the clinic for evaluation of shortness of breath. The shortness of breath occurs with exertion and improves with rest. It has been going on for several months and initially occurred only a couple of times a day with strenuous exertion; however, it has started to occur with minimal exertion and is happening more than a dozen times per day. The shortness of breath lasts for less than 5 minutes at a time. He has no cough, chest pressure, chest pain, swelling in his feet, palpitations, orthopnea, or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea. Which of the following symptom attributes was not addressed in this description? A) Severity B) Setting in which the symptom occurs C) Timing D) Associated manifestations - answer- A - Mrs. T. comes for her regular visit to the clinic. She is on your schedule because her regular provider is on vacation and she wanted to be seen. You have heard about her many times from your colleague and are aware that she is a very talkative person. Which of the following is a helpful technique to improve the quality of the interview for both the provider and the patient? A) Allow the patient to speak uninterrupted for the duration of the appointment. B) Briefly summarize what you heard from the patient in the first 5 minutes and then try to have her focus on one aspect of what she told you. C) Set the time limit at the beginning of the interview and stick with it, no matter what occurs in the course of the interview. D) Allow your impatience to show so that the patient picks up on your nonverbal cue that the appointment needs to end. - answer- B - Which of the following questions is part of the screening for physical disability? A) Are you able to go shopping for groceries or clothes? B) Are you able to walk one block? C) Are you able to pass the driver's license test? D) Are you able to perform light dusting and pick up after yourself around the house? - answer- A - A 72-year-old teacher comes to a skilled nursing facility for rehabilitation after being in the hospital for 6 weeks. She was treated for sepsis and respiratory failure and had to be on the ventilator for 3 weeks. You are completing your initial assessment and are evaluating her skin condition. On her sacrum there is full-thickness skin loss that is 5 cm in diameter, with damage to the subcutaneous tissue. The underlying muscle is not affected. You diagnose this as a pressure ulcer. What is the stage of this ulcer? A) Stage 1 B) Stage 2 C) Stage 3 D) Stage 4 - answer- C - Which of the following booster immunizations is recommended in the older adult population? A) Tetanus B) Diphtheria C) Measles D) Mumps - answer- A - You are running late after your quarterly quality improvement meeting at the hospital and have just gotten paged from the nurses' station because a family member of one of your patients wants to talk with you about that patient's care. You have clinic this afternoon and are double-booked for the first appointment time; three other patients also have arrived and are sitting in the waiting room. Which of the following demeanors is a behavior consistent with skilled interviewing when you walk into the examination room to speak with your first clinic patient? A) Irritability B) Impatience C) Boredom D) Calm - answer- D - A 35-year-old bus driver comes to your office for a prenatal visit. She is approximately 28 weeks pregnant and has had no complications. She is complaining only of heartburn and has had no fatigue, headaches, leg swelling, contractions, leakage of fluid, or bleeding. On examination her blood pressure is 142/92 and her urine shows no glucose, protein, or leukocytes. Her weight gain is appropriate, with no large recent increases. Fetal tones are 140 and her uterus measures 32 cm from the pubic bone. Looking back through her chart, you see her prenatal blood pressure was 120/70 and her blood pressures during the first 20 weeks were usually 120 to 130/70 to 80. What type of blood pressure is this? A) Normotensive for pregnancy B) Chronic hypertension C) Gestational hypertension D) Preeclampsia - answer- C - When you enter your patient's examination room, his wife is waiting there with him. Which of the following is most appropriate? A) Ask if it's okay to carry out the visit with both people in the room. B) Carry on as you would ordinarily. The permission is implied because his wife is in the room with him. C) Ask his wife to leave the room for reasons of confidentiality. D) First ask his wife what she thinks is going on. - answer- A - The components of the health history include all of the following except which one? A) Review of systems B) Thorax and lungs C) Present illness D) Personal and social items - answer- B - A patient presents for evaluation of a sharp, aching chest pain which increases with breathing. Which anatomic area would you localize the symptom to? A) Musculoskeletal B) Reproductive C) Urinary D) Endocrine - answer- A - A woman in her 30th week has a cervical length estimated at 1 cm. Should you be concerned? A) Yes; she may be at risk for preterm labor. B) Yes; she most likely has a bicornuate uterus. C) No; this is a normal measurement for this gestational age. - answer- A - Ms. Whiting is a 68 year old who comes in for her usual follow-up visit. You notice a few flat red and purple lesions, about 6 centimeters in diameter, on the ulnar aspect of her forearms but nowhere else. She doesn't mention them. They are tender when you examine them. What should you do? A) Conclude that these are lesions she has had for a long time. B) Wait for her to mention them before asking further questions. C) Ask how she acquired them. D) Conduct the visit as usual for the patient. - answer- C - You have recently returned from a medical missions trip to sub-Saharan Africa, where you learned a great deal about malaria. You decide to use some of the same questions and maneuvers in your "routine" when examining patients in the midwestern United States. You are disappointed to find that despite getting some positive answers and findings, on further workup, none of your patients has malaria except one, who recently emigrated from Ghana. How should you next approach these questions and maneuvers? A) Continue asking these questions in a more selective way. B) Stop asking these questions, because they are low yield. C) Question the validity of the questions. D) Ask these questions of all your patients. - answer- A - On routine screening you notice that the cup-to-disc ratio of the patient's right eye is 1:2. What ocular condition should you suspect? A) Macular degeneration B) Diabetic retinopathy C) Hypertensive retinopathy D) Glaucoma - answer- D - Which of the following brief screening measures is useful in assessing memory? A) Three-item recall B) Serial 7s C) Spelling "world" backward D) Copying intersecting pentagrams - answer- A - Claire's daughter brings her in today after Claire fell at her home. Which assessments are indicated at this time? A) Orthostatic vital signs B) Review of her medications C) Assessment of gait and balance D) All of the above - answer- D - A woman has a positive pregnancy test and comes to you with left lower quadrant pain. On bimanual examination, you feel a tender mass. Which of the following should you suspect? A) Threatened abortion B) Appendicitis C) Ovarian cyst D) Tubal pregnancy - answer- D - For which of the following patients would a comprehensive health history be appropriate? A) A new patient with the chief complaint of "I sprained my ankle" B) An established patient with the chief complaint of "I have an upper respiratory infection" C) A new patient with the chief complaint of "I am here to establish care" D) A new patient with the chief complaint of "I cut my hand" - answer- C - A 20-year-old college student comes in with symptoms of fatigue, nausea, and an increase in urination. Her last period was 3 months ago (June 20, 2008). She is sexually active and always uses condoms. Her past medical history is unremarkable. On examination you see a young, anxious-appearing woman. Her vital signs are unremarkable. Her head, eyes, ears, throat, neck, thyroid, cardiac, pulmonary, and abdominal examinations are unremarkable. On pelvic examination a soft cervix is palpated and a 14-week-sized uterus is palpated. A urine pregnancy test is positive. You then inform the patient that she is expecting and, using Naegele's rule, give her the estimated date of confinement (EDC, or due date). What was the due date you gave her? A) March 27, 2009 B) March 13, 2009 C) September 27, 2009 D) March 20, 2009 - answer- A - Mr. Q. is a 45-year-old salesman who comes to your office for evaluation of fatigue. He has come to the office many times in the past with a variety of injuries, and you suspect that he has a problem with alcohol. Which one of the following questions will be most helpful in diagnosing this problem? A) You are an alcoholic, aren't you? B) When was your last drink? C) Do you drink 2 to 3 beers every weekend? D) Do you drink alcohol when you are supposed to be working? - answer- B - Mrs. Hill is a 28-year-old African-American with a history of SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus). She has noticed a raised, dark red rash on her legs. When you press on the rash, it doesn't blanch. What would you tell her regarding her rash? A) It is likely to be related to her lupus. B) It is likely to be related to an exposure to a chemical. C) It is likely to be related to an allergic reaction. D) It should not cause any problems. - answer- A - Ms. Washington is a 67-year-old who had a heart attack last month. Now she complains of shortness of breath and not being able to sleep in a flat position (orthopnea). On examination you note increased jugular venous pressure, an S3 gallop, crackles low in the lung fields, and swollen ankles (edema). This is an example of a: A) Pathophysiologic problem B) Psychopathologic problem - answer- A - Suzanne, a 25 year old, comes to your clinic to establish care. You are the student preparing to go into the examination room to interview her. Which of the following is the most logical sequence for the patient-provider interview? A) Establish the agenda, negotiate a plan, establish rapport, and invite the patient's story. B) Invite the patient's story, negotiate a plan, establish the agenda, and establish rapport. C) Greet the patient, establish rapport, invite the patient's story, establish the agenda, expand and clarify the patient's story, and negotiate a plan. D) Negotiate a plan, establish an agenda, invite the patient's story, and establish rapport. - answer-C - You are examining for fetal heart tones with a fetoscope and are unable to hear any. Using a Doptone, you measure the rate as 164. Which gestational age is most likely? A) 8 weeks B) 14 weeks C) 20 weeks D) 26 weeks - answer- B - You arrive at the bedside of an elderly woman who has had a stroke, affecting her entire right side. She cannot speak (aphasia). You are supposed to examine her. You notice that the last examiner left her socks at the bottom of the bed, and although sensitive areas are covered by a sheet, the blanket is heaped by her feet at the bottom of the bed. What would you do next? A) Carry out your examination, focusing on the neurologic portion, and then cover her properly. B) Carry out your examination and let the nurse assigned to her "put her back together." C) Put her socks back on and cover her completely before beginning the evaluation. D) Apologize for the last examiner but let the next examiner dress and cover her. - answer- C - A 47-year-old contractor presents for evaluation of neck pain, which has been intermittent for several years. He normally takes over-the-counter medications to ease the pain, but this time they haven't worked as well and he still has discomfort. He recently wallpapered the entire second floor in his house, which caused him great discomfort. The pain resolved with rest. He denies fever, chills, rash, upper respiratory symptoms, trauma, or injury to the neck. Based on this description, what is the most likely pathologic process? A) Infectious B) Neoplastic C) Degenerative D) Traumatic - answer- C - You are performing a young woman's first pelvic examination. You make sure to tell her verbally what is coming next and what to expect. Then you carry out each maneuver of the examination. You let her know at the outset that if she needs a break or wants to stop, this is possible. You ask several times during the examination, "How are you doing, Brittney?" What are you accomplishing with these techniques? A) Increasing the patient's sense of control B) Increasing the patient's trust in you as a caregiver C) Decreasing her sense of vulnerability D) All of the above - answer- D - A young woman comes to you with a cut on her finger caused by the lid of a can she was opening. She is pacing about the room, crying loudly, and through her sobs she says, "My career as a pianist is finished!" Which personality type exhibits these features? A) Narcissistic B) Paranoid C) Histrionic D) Avoidant - answer- C - A 28-year-old patient comes to the office for evaluation of a rash. At first there was only one large patch, but then more lesions erupted suddenly on the back and torso; the lesions itch. On physical examination, you note that the pattern of eruption is like a Christmas tree and that there are a variety of erythematous papules and macules on the cleavage lines of the back. Based on this description, what is the most likely diagnosis? A) Pityriasis rosea B) Tinea versicolor C) Psoriasis D) Atopic eczema - answer- A - Dakota is a 14-year-old boy who just noticed a rash at his ankles. There is no history of exposure to ill people or other agents in the environment. He has a slight fever in the office. The rash consists of small, bright red marks. When they are pressed, the red color remains. What should you do? A) Prescribe a steroid cream to decrease inflammation. B) Consider admitting the patient to the hospital. C) Reassure the parents and the patient that this should resolve within a week. D) Tell him not to scratch them, and follow up in 3 days. - answer- B - Which of the following changes are expected in vision as part of the normal aging process? A) Cataracts B) Glaucoma C) Macular degeneration D) Blurring of near vision - answer- D - A 29-year-old woman comes to your office. As you take the history, you notice that she is speaking very quickly, and jumping from topic to topic so rapidly that you have trouble following her. You are able to find some connections between ideas, but it is difficult. Which word describes this thought process? A) Derailment B) Flight of ideas C) Circumstantiality D) Incoherence - answer- B - A patient comes to the emergency room for evaluation of shortness of breath. To which anatomic region would you assign the symptom? A) Reproductive B) Urinary C) Cardiac D) Hematologic - answer- C - A 25-year-old radio announcer comes to the clinic for an annual examination. His BMI is 26.0 kg/m2. He is concerned about his weight. Based on this information, what is appropriate counsel for the patient during the visit? A) Refer the patient to a nutritionist because he is anorexic. B) Reassure the patient that he has a normal body weight. C) Give the patient information about reduction of fat, cholesterol, and calories because he is overweight. D) Give the patient information about reduction of fat and cholesterol because he is obese. - answer- C - An 85-year-old retired teacher comes to your office for evaluation of weakness. You obtain a complete history, perform a thorough physical examination, and order laboratory tests. You diagnose her with hyperthyroidism. Based on her age, which of the atypical symptoms of hyperthyroidism is more likely to be seen? A) Fatigue B) Weight loss C) Tachycardia D) Anorexia - answer- D - You are examining an unconscious patient from another region and notice Beau's lines, a transverse groove across all of her nails, about 1 cm from the proximal nail fold. What would you do next? A) Conclude this is caused by a cultural practice. B) Conclude this finding is most likely secondary to trauma. C) Look for information from family and records regarding any problems which occurred 3 months ago. D) Ask about dietary intake. - answer- C - 1. When performing a physical assessment, the technique the nurse will always use first is: 1. palpation. 2. inspection. 3. percussion. 4. auscultation. - inspection. - 2. The inspection phase of the physical assessment: 1. yields little information. 2. takes time and reveals a surprising amount of information. 3. may be somewhat uncomfortable for the expert practitioner. 4. requires a quick glance at the patient's body systems before proceeding on with palpation. - takes time and reveals a surprising amount of information. - 3. The nurse is assessing a patient's skin during an office visit. What is the best technique to use to best assess the patient's skin temperature? 1. Use the fingertips because they're more sensitive to small changes in temperature. 2. Use the dorsal surface of the hand because the skin is thinner than on the palms. 3. Use the ulnar portion of the hand because there is increased blood supply that enhances temperature sensitivity. 4. Use the palmar surface of the hand because it is most sensitive to temperature variations because of increased nerve supply in this area. - Use the dorsal surface of the hand because the skin is thinner than on the palms. - 4. Which of the following techniques uses the sense of touch when assessing a patient? 1. Palpation 2. Inspection 3. Percussion 4. Auscultation - Palpation - 5. The nurse is preparing to assess a patient's abdomen by palpation. How should the nurse proceed? 1. Avoid palpation of reported "tender" areas because this may cause the patient pain. 2. Quickly palpate the area to avoid any discomfort that the patient may experience. 3. Begin the assessment with deep palpation, encouraging the patient to relax and take deep breaths. 4. Start with light palpation to detect surface characteristics and to accustom the patient to being touched. - Start with light palpation to detect surface characteristics and to accustom the patient to being touched. - 6. The nurse would use bimanual palpation technique in which situation? 1. Palpating the thorax of an infant 2. Palpating the kidneys and uterus 3. Assessing pulsations and vibrations 4. Assessing the presence of tenderness and pain - Palpating the kidneys and uterus - Upgrade to remove ads - Only $1/month - - 7. The nurse is preparing to percuss to assess the underlying: 1. tissue turgor. 2. tissue texture. 3. tissue density. 4. tissue consistency. - tissue density. - 8. The nurse is preparing to percuss the thorax of an adult. Which technique is correct? 1. Use the direct percussion technique. 2. Use the indirect percussion technique. 3. Use the ulnar surface of the hand to percuss the thorax. 4. Use the dorsal surface of the hand to percuss the thorax. - Use the indirect percussion technique. - 9. When percussing over the ribs of a patient, the nurse notes a dull sound. The nurse would: 1. consider this a normal finding. 2. palpate this area for an underlying mass. 3. reposition the hands and attempt to percuss in this area again. 4. consider this an abnormal finding and refer the patient for additional treatment. - consider this a normal finding. - 10. The nurse is unable to identify any changes in sound when percussing over the abdomen of an obese patient. What should the nurse do next? 1. Ask the patient to take deep breaths to relax the abdominal musculature 2. Consider this a normal finding and proceed with the abdominal assessment. 3. Increase the amount of strength used when attempting to percuss over the abdomen. 4. Decrease the amount of strength used when attempting to percuss over the abdomen. - Increase the amount of strength used when attempting to percuss over the abdomen. - 11. The nurse hears bilateral louder, longer, and lower tones when percussing over the lungs of a 4-year-old child. What should the nurse do next? 1. Palpate over the area for increased pain and tenderness. 2. Ask the child to take shallow breaths and percuss over the area again. 3. Refer the child immediately because of an increased amount of air in the lungs. 4. Consider this a normal finding for a child this age and proceed with the examination. - Consider this a normal finding for a child this age and proceed with the examination. - 12. A patient has suddenly developed shortness of breath and appears to be in significant respiratory distress. Which of the following is the best action for the nurse to take? 1. Count the respirations and put a call in to the physician. 2. Percuss the thorax bilaterally, noting any differences in percussion tones. 3. Call for a chest x-ray and wait for the results before beginning an assessment. 4. Inspect the thorax for any new masses and bleeding associated with respirations. - Percuss the thorax bilaterally, noting any differences in percussion tones. - 13. Which of the following statements is true regarding the stethoscope and its use? 1. The slope of the earpieces should point posteriorly (toward the occiput). 2. The stethoscope does not magnify sound but does block out extraneous room noise. 3. The fit and quality of the stethoscope are not as important as its ability to magnify sound. 4. The ideal tubing length should be 22 inches long to dampen distortion of sound. - The stethoscope does not magnify sound but does block out extraneous room noise. - 14. Which statement is true regarding the diaphragm of the stethoscope? 1. Use the diaphragm to listen for high-pitched sounds. 2. Use the diaphragm to listen for low-pitched sounds. 3. Hold the diaphragm lightly against the person's skin to block out low-pitched sounds. 4. Hold the diaphragm lightly against the person's skin to listen for extra heart sounds and murmurs. - Use the diaphragm to listen for high-pitched sounds. - 15. Before auscultating the abdomen for the presence of bowel sounds on a patient, the nurse will: 1. warm the end piece of the stethoscope by placing it in warm water. 2. leave the gown on so that the patient does not get chilled during the examination. 3. make sure that the bell side of the stethoscope is turned to the "on" position. 4. check the temperature of the room and offer blankets to the patient if he or she feels cold. - check the temperature of the room and offer blankets to the patient if he or she feels cold. - 16. Which technique of assessment is used to determine the presence of crepitus, swelling, and pulsations? 1. Palpation 2. Inspection 3. Percussion 4. Auscultation - Palpation - 17. Which of the following statements is true regarding the otoscope? 1. The otoscope is often used to direct light onto the sinuses. 2. The otoscope uses a short broad speculum to visualize the ear. 3. The otoscope is used to examine the structures of the internal ear. 4. The otoscope directs light into the ear canal and onto the tympanic membrane. - The otoscope directs light into the ear canal and onto the tympanic membrane. - 18. An examiner is using an ophthalmoscope to examine a patient's eyes. The patient has astigmatism and is nearsighted. Which of the following techniques would indicate the examination is being performed correctly? 1. Using the large full circle of light when assessing pupils that are not dilated 2. Rotating the lens selector dial to the black numbers to compensate for astigmatism 3. Using the grid on the lens aperture dial to visualize the external structures of the eye 4. Rotating the lens selector dial to the red numbers to compensate for nearsightedness - Rotating the lens selector dial to the red numbers to compensate for nearsightedness - 19. The nurse is unable to palpate the right radial pulse on a patient. The best action would be to: 1. auscultate over the area with a fetoscope. 2. use a goniometer to measure the pulsations. 3. use a Doppler device to check for pulsations over the area. 4. check for the presence of pulsations with a stethoscope. - use a Doppler device to check for pulsations over the area. - 20. When performing the physical assessment, the examiner should: 1. perform the examination from the left side of the bed. 2. examine tender or painful areas first to help relieve the patient's anxiety. 3. follow the same examination sequence regardless of the patient's age or condition. 4. organize the assessment so that the patient does not change positions too often. - organize the assessment so that the patient does not change positions too often. - 21. A man is at the clinic for a physical examination. He states that he is "very anxious" about the physical exam. What steps can the examiner take to make him more comfortable? 1. Appear unhurried and confident when examining him. 2. Stay in the room when he undresses in case he needs assistance. 3. Ask him to change into an examining gown and take off his undergarments. 4. Defer measuring vital signs until the end of the examination, which allows him. time to become comfortable. - Appear unhurried and confident when examining him. - 22. When performing a physical examination, safety must be considered to protect the examiner and the patient against the spread of infection. Which of the following statements describes the most appropriate actions the examiner should take when performing a physical examination? 1. There is no need to wash one's hands after removing gloves, as long as the gloves are still intact. 2. Wash hands at the beginning of the examination and any time that one leaves and re-enters the room. 3. Wash hands between the examination of each body system to prevent the spread of bacteria from one part of the body to another. 4. Wear gloves throughout the entire examination to demonstrate to the patient concern regarding the spread of infectious diseases. - Wash hands at the beginning of the examination and any time that one leaves and re-enters the room. - 23. The nurse is examining a patient's lower leg and notes a draining ulceration. Which of the following actions is most appropriate in this situation? 1. Wash hands and contact the physician. 2. Continue to examine the ulceration and then wash hands. 3. Wash hands, put on gloves, and continue with the examination of the ulceration. 4. Wash hands, proceed with rest of the physical examination, and then continue with the examination of the leg ulceration. - Wash hands, put on gloves, and continue with the examination of the ulceration. - 24. During the examination, it is often appropriate to offer some brief teaching about the patient's body or one's findings. Which of the following statements by the nurse is most appropriate? 1. "Your hypertension is under control." 2. "You have pitting edema and mild varicosities." 3. "Your pulse is 80 beats per minute. This is within the normal range." 4. "I'm using my stethoscope to listen for any crackles, wheezes, or rubs." - "Your pulse is 80 beats per minute. This is within the normal range." - 25. The most important reason to share information and offer brief teaching while performing the physical examination is to help: 1. the examiner feel more comfortable and gain control of the situation. 2. build rapport and increase the patient's confidence in the examiner. 3. the patient understand his or her disease process and treatment modalities. 4. the patient identify questions about his or her disease and potential areas of patient education. - build rapport and increase the patient's confidence in the examiner. - 26. In infants, the nurse knows to elicit the Moro reflex: 1. when the infant is sleeping. 2. at the end of the examination. 3. before auscultation of the thorax. 4. halfway through the examination. - at the end of the examination. - 27. When preparing to perform a physical examination on an infant, the examiner should: 1. have the parent remove all clothing except the diaper on a boy. 2. instruct the parent to feed the infant immediately before the exam. 3. encourage the infant to suck on a pacifier during the abdominal exam. 4. ask the parent to briefly leave the room when assessing the infant's vital signs. - have the parent remove all clothing except the diaper on a boy. - 28. A 6-month-old infant has been brought to the well-child clinic for a check-up. She is currently sleeping. What should the examiner do first? 1. Auscultate the lungs and heart while the infant is still sleeping. 2. Examine the infant's hips because this procedure is uncomfortable. 3. Begin with the assessment of the eye and continue with the remainder of the examination in a head-to-toe approach. 4. Wake the infant before beginning any portion of the examination to obtain the most accurate assessment of body systems. - Auscultate the lungs and heart while the infant is still sleeping. - 29. A 2-year-old child has been brought to the clinic for a well-child check-up. How should the examiner proceed with the assessment? 1. Ask the parent to place the child on the examining table. 2. Have the parent remove all the child's clothing before the examination. 3. Allow the child to keep a security object such as a toy or blanket during the examination. 4. Initially focus interactions on the child, essentially "ignoring" the parent, until the child's trust has been obtained. - Allow the child to keep a security object such as a toy or blanket during the examination. - 30. The nurse is examining a 2-year-old child and asks, "May I listen to your heart now?" Which critique of her technique is most accurate? 1. Asking questions enhances the child's autonomy. 2. Asking the child for permission helps to develop a sense of trust. 3. This is an appropriate statement because children at this age like to have choices. 4. Children at this age like to say "No." The examiner should not offer a choice when there is none. - Children at this age like to say "No." The examiner should not offer a choice when there is none. - 31. With which of the following patients would it be most appropriate to use games during the assessment, such as, having the patient "blow out" the light on the penlight? 1. An infant 2. A preschool child 3. A school-age child 4. An adolescent - A preschool child - 32. The nurse is preparing to examine a 4-year-old child. Which action is appropriate first? 1. Explain procedures in detail to alleviate the child's anxiety. 2. Give the child feedback and reassurance during the examination. 3. Do not ask the child to remove his clothes because children at this age are usually very private. 4. Perform an examination of the ear, nose, and throat first and then examine the thorax and abdomen. - Give the child feedback and reassurance during the examination. - 33. When examining a 16-year-old male teenager, the examiner should: 1. discuss health teaching with the parent because the teen is unlikely to be interested in promoting wellness. 2. ask his parent to stay in the room during the history and physical examination to answer any questions and alleviate his anxiety. 3. talk to him the same as one would talk would a younger child because a teen's level of understanding may not match his or her speech. 4. provide feedback that his body is developing normally and discuss the wide variation among teenagers on the rate of growth and development. - provide feedback that his body is developing normally and discuss the wide variation among teenagers on the rate of growth and development. - 34. When examining the aging adult, the nurse should: 1. avoid touching the patient too much. 2. attempt to perform the entire physical during one visit. 3. speak loudly and slowly because most aging adults have hearing deficits. 4. arrange the sequence to allow as few position changes as possible. - arrange the sequence to allow as few position changes as possible. - 35. The most important step that the nurse can take to prevent transmission of nosocomial infections in the hospital setting is to: 1. wear protective eye wear at all times. 2. wear gloves during any and all contact with patients. 3. wash hands before and after contact with each patient. 4. clean the stethoscope with an alcohol swab between patients. - wash hands before and after contact with each patient. - During an assessment, the nurse notices that a patient is handling a small charm that is tied to a leather strip around his neck. Which action by the nurse is appropriate? - Depression - A female patient has denied any abuse when answering the Abuse Assessment Screen, but the nurse has noticed some other conditions that are associated with intimate partner violence, examples of such conditions include: - To provide a data base of subjective information about the patient's past and current health - The nurse is preparing to conduct a health history. Which of these statements best describes the purpose of a health history? - Learned through language acquisition and socialization - The nurse is reviewing the development of culture. Which statement is correct regarding the development of one's culture? Culture is: - Clustering related cues - Which critical thinking skill helps the nurse to see relationships among the data? - Give him the Four Unrelated Words Test - The nurse is planning to assess new memory with a patient. The best way for the nurse to do this would be to - Plan to perform a complete mental status examination - A woman brings her husband to the clinic for an examination. She is particularly worried because after a recent fall, he seems to have lost a great deal of his memory of recent events. Which statement reflects the nurse's best course of action? The nurse should: - Woman who follows the traditions that her mother followed regarding meals - The nurse recognizes that an example of a person who is heritage consistent would be a: - Whipping from an extension cord - During an examination, the nurse notices a patterned injury on a patient's back. Which of these would cause such an injury? - Marijuana - During a session on substance abuse, the nurse is reviewing statistics with the class. For persons aged 12 years and older, which of these illicit substances was the one most commonly used? - May take a little longer to respond, but his general knowledge and abilities should not have declined. - The nurse is assessing a 75 year old man. As the nurse begins the mental status portion of the assessment, the nurse expects that this patient: - Inappropriate affect - A patient has been diagnosed with schizophrenia. During a recent interview, he shows the nurse a picture of a man holding a decapitated head. He describes this picture as horrifying and laughs loudly at the content. This behavior is a display of: - Hispanic - When reviewing the demographics of ethnic groups in the United States, the nurse recalls that the largest and fasting growing population is: - That more information should be gathered to decided whether her dress is appropriate - A 19 year old woman comes to the clinic at the insistence of her brother. She is wearing black combat boots and black lace nightgown over the top of her other clothes. Her hair is dyed pink with black streaks throughout. She has several pierced holes in her nares and ears and is wearing an earring through her eyebrow and heavy black makeup. The nurse concludes: - Assessment, diagnosis, outcome identification, planning, implementation, evaluation - The nursing process is a sequential method of problem solving that nurse use, and includes which steps? - Breathing, pain, sleep - A newly admitted patient is in acute pain, has not been sleeping well lately, and is having difficulty breathing. How should the nurse prioritize these problems? - "When was the last time you used marijuana?" - The nurse is asking an adolescent about illicit substance abuse. The adolescent answers, "Yes I used marijuana at parties with my friends." What is the next question the nurse should ask? - Note-taking may impede the nurse's observation of the patient's nonverbal behaviors? - In an interview, the nurse may find it necessary to take notes to aid his or her memory later. What statement is true regarding note-taking? - As a routine part of each health care encounter - The nurse is aware that intimate partner violence screening should occur with which situation - Red - The nurse is assessing bruising on an injured patient. Which color indicates a new bruise that is less than 2 hours old? - Denies color change - Which of these statements represents subjective data the nurse obtained from the patient regarding the patient's skin? - A personal effort to find purpose and meaning in life - The nurse is comparing the concepts of religion and spirituality. Which of the following is an appropriate component of one's spirituality? - Will be oriented to place and person but may not be certain of the date - A patient has been in the intensive care unit for 10 days. He has just been moved to the medical-surgical unit, and the admitting nurse is planning to perform a mental status examination on him. During the tests of cognitive function the nurse would expect that he: - Opening or introduction - The nurse asks, "I would like to ask you some questions about your health and your usual daily activities sot hat we can better plan your stay here." This question is found at the ______ phase of the interview process. - Unintentional physical neglect - During a home visit, the nurse notices that an elderly woman is caring for her bedridden husband. The woman states that this is her duty, she does the best she can, and her children come to help when they are in town. Her husband is unable to care for himself, and she appears thin, weak, and exhausted. The nurse notices that several of his prescription medication bottles are empty. This situation is best described by the term: - "Please describe what happens to you when you take penicillin." - A patient tells the nurse that he is allergic to penicillin. What would be the nurse best response to this information? - Requires an increase amount of the substance to produce the same effect. - The nurse is reviewing aspects of substance abuse in preparation for a seminar. Which of these statements illustrates the concept of "tolerance" to an illicit substance? The person: - Medical - The nurse knows that developing appropriate nursing interventions for a patient relies on the appropriateness of the _______ diagnosis. - "We ask the following questions because domestic violence is so common in our society." - Which statement is best for the nurse to use when preparing to administer the Abuse Assessment Screen - Provided consistent information and therefore is reliable - When the nurse is evaluation the reliability of a patient's responses, which of these statements would be correct? The patient: - Data base - The patient's record, laboratory studies, objective data, and subjective data combine to form the: - Be silent and allow him to continue when he is ready. - When taking a history from a newly admitted patient, the nurse notices that he is pausing often and looking at the nurse expectantly. What would be the nurse's best response to this behavior? - "Can you point to where it hurts?" - A patient tells the nurse that she has had abdominal pain for the past week. What would be the best response by the nurse? - Photographic documentation of injury - When documenting intimate partner violence and elder abuse, the nurse should include: - Decreased liver and kidney functioning - When reviewing the use of alcohol by older adults, the nurse notes that older adults have several characteristics that can increase the risk of alcohol use. Which would increase the bioavailablity of alcohol in the blood for longer periods of time in the older adult? - Use the words the child has given to describe how the injury occurred - The nurse suspects abuse when a 10 year old child is taken to the urgent care center for a leg injury. The best way to document the history and physical findings is to: - Their sensory-perceptive abilities - When assessing aging adults, the nurse knows that one of the first things that should be assessed before making judgments about their mental status is: - Objective - After completing an initial assessment on a patient, the nurse has charted that his respiration's are eupneic and his pulse is 58. This type of data would be: - Holistic health views the mind, body, and spirit as interdependent - When reviewing concepts of health, the nurse recalls that components of holistic health include which of these? - "No amount of alcohol has been determined to be safe during pregnancy" - A woman who has just discovered that she is pregnant is in the clinic for her fist obstetric visit. She asks the nurse, "How many drink a day is safe for my baby?" The nurse's best response is: - "How would you say the pain affects your ability to do your daily activities?" - A 29 year old woman tells the nurse that she has "excruciating pain" in her back. Which would be an appropriate response by the nurse to the woman's statement? - "How do you feel today?" - During a mental status examination, the nurse wants to assess a patient's affect. The nurse should ask the patient which question? - It is usually sufficient to gather mental status information during the health history interview - The nurse is preparing to do a mental status examination. Which statement is true regarding the mental status examination? - "Mrs. H., my name is Mrs. C. I'll need to ask you a few questions about what happened." - A woman has just entered the emergency department after being battered by her husband. The nurse needs to get some information from her to begin treatment. What is the best choice for an opening with this patient? - Financial neglect - During a home visit, the nurse notices that an elderly woman has very little food in her cabinets or refrigerator and that most of her prescription bottles are empty. She says that she has enough money, but her nephew has her checkbook and he "takes care of everything." She says, "Oh, my nephew will get around to getting groceries and my medicine when he can. He's very busy." This is an example of: - Reduces noise by turning off televisions and radios - The nurse makes which adjustment in the physical environment in order to promote the success of an interview - Exhibiting verbal and nonverbal behavior that does not match - The nurse is conducting an interview with a woman who has recently learned that she is pregnant and who has come to the clinic today to begin prenatal care. The woman states that she and her husband are excited about the pregnancy but have a few question. She looks nervously at her hands during the interview and sighs loudly. Considering the concept of communication, the nurse knows that which statement is most accurate? The woman is: - Subjective - A patient tells the nurse that he is very nervous, that he is nauseated, and that he "feels hot." This type of data would be: - An individual with shortness of breath and respiratory distress - The nurse is conducting a class on priority setting for a group of new graduate nurses. Which is an example of a first-level priority problem? - Suspicion of elder abuse and/or neglect - As a mandatory reporter of elder abuse, which of these must be present before a nurse notifies the authorities? - - 1. For which of the following patients would a comprehensive health history be appropriate? A) A new patient with the chief complaint of "I sprained my ankle" B) An established patient with the chief complaint of "I have an upper respiratory infection" C) A new patient with the chief complaint of "I am here to establish care" D) A new patient with the chief complaint of "I cut my hand" - C. This patient is here to establish care, and because she is new to you, a comprehensive health history is appropriate - 2. The components of the health history include all of the following except which one? A) Review of systems B) Thorax and lungs C) Present illness D) Personal and social items - B The thorax and lungs are part of the physical exam, not part of the health history. - Nice work! - You just studied 133 terms! - Now up your study game with Learn mode. - Try Learn modeStudy with Flashcards again - 1/133 - Created by - leroylewis884 - Terms in this set (133) - - 1. For which of the following patients would a comprehensive health history be appropriate? A) A new patient with the chief complaint of "I sprained my ankle" B) An established patient with the chief complaint of "I have an upper respiratory infection" C) A new patient with the chief complaint of "I am here to establish care" D) A new patient with the chief complaint of "I cut my hand" - C. This patient is here to establish care, and because she is new to you, a comprehensive health history is appropriate - 2. The components of the health history include all of the following except which one? A) Review of systems B) Thorax and lungs C) Present illness D) Personal and social items - B The thorax and lungs are part of the physical exam, not part of the health history. - Is the following information subjective or objective? Mr. M. has shortness of breath that has persisted for the past 10 days; it is worse with activity and relieved by rest. A) Subjective B) Objective - A. Subjective This is information given by the patient about the circumstances of his chief complaint. - Is the following information subjective or objective? Mr. M. has a respiratory rate of 32 , and a pulse rate of 120. A. Subjective B. Objective - B This is a measurement obtained by the examiner, so it is considered objective data. - The following information is recorded in the health history: "The patient has had abdominal pain for 1 week. The pain lasts for 30 minutes at a time; it comes and goes. The severity is 7 to 9 on a scale of 1 to 10. It is accompanied by nausea and vomiting. It is located in the mid-epigastric area." Which of these categories does it belong to? A) Chief complaint B) Present illness C) Personal and social history D) Review of systems - B. Present Illness. This information describes the problem of abdominal pain, which is the present illness. The interviewer has obtained the location, timing, severity, and associated manifestations of the pain. The interviewer will still need to obtain information concerning the quality of the pain, the setting in which it occurred, and the factors that aggravate and alleviate the pain. You will notice that it does include portions of the pertinent review of systems, but because it relates directly to the complain, it is included in the history of the present illness. - The following information is recorded in the health history: "The patient completed 8th grade. He currently lives with his wife and two children. He works on old cars on the weekend. He works in a glass factory during the week." Which category does it belong to? - Personal and social history Personal and social history information includes educational level, family of origin, current household status, personal interests, employment, religious beliefs, military history, and lifestyle (including diet and exercise habits; use of alcohol, tobacco, and/or drugs; and sexual preferences and history). All of this information is documented in this example. - Upgrade to remove ads - Only $1/month - - The following information is recorded in the health history: "I feel really tired." Which category does it belong to? - Chief complaint The chief complaint is an attempt to quote the patient's own words, as long as they are suitable to print. It is brief, like a headline, and further details should be sought in the present illness section. - The following information is recorded in the health history: "Patient denies chest pain, palpitations, orthopnea, and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea." Which category does it belong to? - Review of Systems Review of systems documents the presence or absence of common symptoms related to each major body system. The absence of cardiac symptoms is listed in the above example. - The following information is best placed in which category? "The patient has had three cesarean sections." - Surgeries A cesarean section is a surgical procedure. Approximate dates or the age of the patient at time of the surgery should also be recorded. - "The patient had a stent placed in the left anterior descending artery (LAD) in 1999" Category? - Adult Illnesses The adult illness category is reserved for chronic illnesses, significant hospitalizations, significant injuries, and significant procedures. A stent is a major procedure but does not involve a surgeon. - "The patient was treated for an asthma exacerbation in the hospital last year; the patient has never been intubated." - Adult illnesses This information is about a significant hospitalization and should be placed in the adult illnesses section. If the patient is being seen for an asthma exacerbation, you may consider placing this information in the present illness section, because it relates to the chief complaint at that visit. - A patient presents for evaluation of a sharp, aching chest pain which increases with breathing. Which anatomic area would you localize the symptom to? - Musculoskeletal Chest pain may be due to a musculoskeletal condition, such as costochondritis, or intercostal muscle cramp. This would be worsened by motion of the chest wall. Pleuritic chest pain is also a sharp chest pain which increases with a deep breath. This type of pain can occur with inflammation of the pleura from pneumonia or other conditions and pulmonary embolus. - A patient comes to the emergency room for evaluation of shortness of breath. To which anatomic region would you assign the symptom? - Cardiac Cardiac disorders such as CHF are the most likely on this list to result in shortness of breath. There are cases within the other categories which may also result in shortness of breath, such as anemia in the hematologic category, pregnancy in the reproductive category, or sepsis with UTI in the urinary category. This demonstrates the "tension" in clinical resigning between making sure all possibilities are covered while still being able to pick the most likely cause. - A patient presents for evaluation of a cough. Which of the following anatomic regions can be responsible for a cough? A) Ophthalmologic B) Auditory C) Cardiac D) Endocrine - C The cardiac system can cause a cough if the patient has congestive heart failure. This results in fluid buildup in the lungs, which in turn can cause a cough that produces pink, frothy sputum. A foreign body in the ear may also cause a cough by stimulating Arnold's branch of the vagus nerve, but this is less likely to be seen clinically than heart failure. - A 22-year-old advertising copywriter presents for evaluation of joint pain. The pain is new, located in the wrists and fingers bilaterally, with some subjective fever. The patient denies a rash; she also denies recent travel or camping activities. She has a family history significant for rheumatoid arthritis. Based on this information, which of the following pathologic processes would be the most correct? A) Infectious B) Inflammatory C) Hematologic D) Traumatic - The description is most consistent with an inflammatory process, although all the other etiologies should be considered. Lyme disease is an infection which commonly causes arthritis, hemophilia is a hematologic condition which can cause bleeding in the joints, and trauma can obviously cause joint pain. Your clinical reasoning skills are important for sorting through all of the data to arrive at the most likely conclusion. - A 47-year-old contractor presents for evaluation of neck pain, which has been intermittent for several years. He normally takes over-the-counter medications to ease the pain, but this time they haven't worked as well and he still has discomfort. He recently wallpapered the entire second floor in his house, which caused him great discomfort. The pain resolved with rest. He denies fever, chills, rash, upper respiratory symptoms, trauma, or injury to the neck. Based on this description, what is the most likely pathologic process? A) Infectious B) Neoplastic C) Degenerative D) Traumatic - C The description is most consistent with degenerative arthritis in the neck. The patient has had intermittent symptoms and the questions asked to elicit pertinent negative and positive findings are negative for infectious, traumatic, or neoplastic disease. - A 15-year-old high school sophomore comes to the clinic for evaluation of a 3-week history of sneezing; itchy, watery eyes; clear nasal discharge; ear pain; and nonproductive cough. Which is the most likely pathologic process? A) Infection B) Inflammation C) Allergic D) Vascular - C - A 19-year old-college student presents to the emergency room with fever, headache, and neck pain/stiffness. She is concerned about the possibility of meningococcal meningitis. Several of her dorm mates have been vaccinated, but she hasn't been. Which of the following physical examination descriptions is most consistent with meningitis? A) Head is normocephalic and atraumatic, fundi with sharp discs, neck supple with full range of motion B) Head is normocephalic and atraumatic, fundi with sharp discs, neck with paraspinous muscle spasm and limited range of motion to the right C) Head is normocephalic and atraumatic, fundi with blurred disc margins, neck tender to palpation, unable to perform range of motion D) Head is normocephalic and atraumatic, fundi with blurred disc margins, neck supple with full range of motion - C Blurred disc margins are consistent with papilledema, and neck tenderness and lack of range of motion are consistent with neck stiffness, which in this scenario is likely to be caused by meningeal inflammation. Later, you will learn about Kernig's and Brudzinski's signs, which are helpful in testing for meningeal irritation on examination. - A 37-year-old nurse comes for evaluation of colicky right upper quadrant abdominal pain. The pain is associated with nausea and vomiting and occurs 1 to 2 hours after eating greasy foods. Which one of the following physical examination descriptions would be most consistent with the diagnosis of cholecystitis? A) Abdomen is soft, nontender, and nondistended, without hepatosplenomegaly or masses. B) Abdomen is soft and tender to palpation in the right lower quadrant, without rebound or guarding. C) Abdomen is soft and tender to palpation in the right upper quadrant with inspiration, to the point of stopping inspiration, and there is no rebound or guarding. D) Abdomen is soft and tender to palpation in the mid-epigastric area, without rebound or guarding. - C in cholecystitis, the pain, which originates from the gallbladder, is located in the right upper quadrant. Severity of pain with inspiration that is sufficient to stop further inhalation is also known as Murphy's sign, which, if present, is further indicative of inflammation of the gallbladder. - A 55-year-old data entry operator comes to the clinic to establish care. She has the following symptoms: headache, neck pain, sinus congestion, sore throat, ringing in ears, sharp brief chest pains at rest, burning abdominal pain with spicy foods, constipation, urinary frequency that is worse with coughing and sneezing, and swelling in legs. This cluster of symptoms is explained by: A) One disease process B) More than one disease process - b The patient appears to have several possible conditions: allergic rhinitis, arthritis, conductive hearing loss, pleuritic chest pains, heartburn, stress urinary incontinence, and venous stasis, among other conditions. Although we always try, it is very difficult to assign all of these symptoms to one cohesive diagnosis. - A 62-year-old teacher presents to the clinic for evaluation of the following symptoms: fever, headache, sinus congestion, sore throat, green nasal discharge, and cough. This cluster of symptoms is best explained by: A) One disease process B) More than one disease process - A This cluster of symptoms is most consistent with sinusitis. The chance that all of these symptoms are caused by multiple synchronous conditions in the same patient is much less than the possibility of having one problem which accounts for all of them. - Steve has just seen a 5-year-old girl who wheezes when exposed to cats. The patient's family history is positive for asthma. You think the child most likely has asthma. What have you just accomplished? A) You have tested your hypothesis. B) You have developed a plan. C) You have established a working diagnosis. D) You have created a hypothesis. - D As you go through a history and examination, you will start to generate ideas to explain the patient's symptoms. It is best to keep an open mind and make as many hypotheses as you can, to avoid missing a possibility. A common mistake is to latch onto one idea too early. Once you have committed your mind to a diagnosis, it is difficult to change to another. To think about looking for wheezes on examination would be an example of testing your new hypothesis. Starting a patient on an inhaled medicine would be a plan. It is too early to commit to a working diagnosis, given the amount of information you have gathered. - Ms. Washington is a 67-year-old who had a heart attack last month. Now she complains of shortness of breath and not being able to sleep in a flat position (orthopnea). On examination you note increased jugular venous pressure, an S3 gallop, crackles low in the lung fields, and swollen ankles (edema). This is an example of a: A) Pathophysiologic problem B) Psychopathologic problem - A This is an example of a pathophysiologic problem because Ms. Washington's symptoms are consistent with a pathophysiologic process. The heart attack reduced the ability of her heart to handle her volume status and subsequently produced the many features of congestive heart failure. - On the way to see your next patient, you glance at the calendar and make a mental note to buy a Mother's Day card. Your patient is Ms. Hernandez, a 76-year-old widow who lost her husband in May, two years ago. She comes in today with a headaches, abdominal pain, and general malaise. This happened once before, about a year ago, according to your detailed office notes. You have done a thorough evaluation but are unable to arrive at a consistent picture to tie these symptoms together. This is an example of a: A) Pathophysiologic problem B) Psychopathologic problem - B It is not uncommon for patients to experience psychopathologic symptoms around the anniversary of a traumatic event. The time of year and the lack of an obvious connection between Ms. Hernandez's symptoms would make you consider this as a possibility. You will note that although this might have been an early consideration in your hypothesis generation, it is key to convince yourself that there is not a physiologic explanation for these symptoms, by performing a careful history and examination. - Mr. Larson is a 42-year-old widowed father of two children, ages 4 and 11. He works in a sales office to support his family. Recently he has injured his back and you are thinking he would benefit from physical therapy, three times a week, for an hour per session. What would be your next step? A) Write the physical therapy prescription. B) Have your office staff explain directions to the physical therapy center. C) Discuss the plan with Mr. Larson. D) Tell Mr. Larson that he will be going to physical therapy three times a week. - C you should discuss your proposed plan with the patient before implementing it. In this case, you and Mr. Larson will need to weigh the benefit of physical therapy against the ability to provide for his family. You may need to consider other ways of helping the patient, perhaps through prescribed back exercises he can do at home. It is a common mistake to implement a plan without coming to an agreement with the patient first. - You are seeing an elderly man with multiple complaints. He has chronic arthritis, pain from an old war injury, and headaches. Today he complains of these pains, as well as dull chest pain under his sternum. What would the order of priority be for your problem list? A) Arthritis, war injury pain, headaches, chest pain B) War injury pain, arthritis, headaches, chest pain C) Headaches, arthritis, war injury pain, chest pain D) Chest pain, headaches, arthritis, war injury pain - D The problem list should have the most active and serious problem first. This new complaint of chest pain is almost certainly a higher priority than his other, more chronic problems. - You are excited about a positive test finding you have just noticed on physical examination of your patient. You go on to do more examination, laboratory work, and diagnostic tests, only to find that there is no sign of the disease you thought would correlate with the finding. This same experience happens several times. What should you conclude? A) Consider not doing this test routinely. B) Use this test when you have a higher suspicion for a certain correlating condition. C) Continue using the test, perhaps doing less laboratory work and diagnostics. D) Omit this test from future examinations. - C This is an example of a sensitive physical finding that lacks specificity. This does not make this a useless test, because the purpose of a screening physical is to find disease. This finding made you consider the associated condition as one of your hypotheses, and this in itself has value. Other possibilities are that you may be doing the maneuver incorrectly or using it on the wrong population. It is important to ask for hands-on help from your instructor when you have a question about a maneuver. Make sure that your information about the maneuver comes from a reliable source as well. All of this information also applies to history questions. - You are growing fatigued of performing a maneuver on examination because you have never found a positive and are usually pressed for time. How should you next approach this maneuver? A) Use this test when you have a higher suspicion for a certain correlating condition. B) Omit this test from future examinations. C) Continue doing the test, but rely more heavily on laboratory work and diagnostics. D) Continue performing it on all future examinations. - A This is an example of a specific test that lacks sensitivity. With this scenario, when you finally find a positive, you might be very certain that a given condition is present. We generally develop our examinations to fit our clinical experiences. Sensitive tests are performed routinely on the screening examination, while specific tests are usually saved for the detailed or "branched" examinations. Branched examinations are further maneuvers we can perform to investigate positive findings on our screening examinations. Save this type of maneuver to confirm your hypothesis. All of this information also applies to history questions. - You have recently returned from a medical missions trip to sub-Saharan Africa, where you learned a great deal about malaria. You decide to use some of the same questions and maneuvers in your "routine" when examining patients in the midwestern United States. You are disappointed to find that despite getting some positive answers and findings, on further workup, none of your patients has malaria except one, who recently emigrated from Ghana. How should you next approach these questions and maneuvers? A) Continue asking these questions in a more selective way. B) Stop asking these questions, because they are low yield. C) Question the validity of the questions. D) Ask these questions of all your patients. - A The predictive value of a positive finding depends upon the prevalence of a given disease in a population. The prevalence of malaria in the Midwest is almost zero, except in people immigrating from areas of high prevalence. You will waste time and resources applying these questions and maneuvers to all patients. It would be wise to continue applying what you learned to those who are from areas of high prevalence of a given disease. Likewise, physicians from Ghana should not ask about signs or symptoms of multiple sclerosis, as it is found almost exclusively in northern latitudes. You will learn to tailor your examination to the population you are serving. - Alexandra is a 28-year-old editor who presents to the clinic with abdominal pain. The pain is a dull ache, located in the right upper quadrant, that she rates as a 3 at the least and an 8 at the worst. The pain started a few weeks ago, it lasts for 2 to 3 hours at a time, it comes and goes, and it seems to be worse a couple of hours after eating. She has noticed that it starts after eating greasy foods, so she has cut down on these as much as she can. Initially it occurred once a week, but now it is occurring every other day. Nothing makes it better. From this description, which of the seven attributes of a symptom has been omitted? A) Setting in which the symptom occurs B) Associated manifestations C) Quality D) Timing - Associated Manifestations The interviewer has not recorded whether or not the pain has been accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, weight loss, and so on. Associated manifestations are additional symptoms that may accompany the initial chief complaint and that help the examiner to start refining his or her differential diagnosis. - Jason is a 41-year-old electrician who presents to the clinic for evaluation of shortness of breath. The shortness of breath occurs with exertion and improves with rest. It has been going on for several months and initially occurred only a couple of times a day with strenuous exertion; however, it has started to occur with minimal exertion and is happening more than a dozen times per day. The shortness of breath lasts for less than 5 minutes at a time. He has no cough, chest pressure, chest pain, swelling in his feet, palpitations, orthopnea, or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea. - Severity The severity of the symptom was not recorded by the interviewer, so we have no understanding as to how bad the symptom is for this patient. The patient could have been asked to rate his pain on a 0 to 10 scale or used one of the other standardized pain scales available. This allows the comparison of pain intensity before and after an intervention. k - You are interviewing an elderly woman in the ambulatory setting and trying to get more information about her urinary symptoms. Which of the following techniques is not a component of adaptive questioning? A) Directed questioning: starting with the general and proceeding to the specific in a manner that does not make the patient give a yes/no answer B) Reassuring the patient that the urinary symptoms are benign and that she doesn't need to worry about it being a sign of cancer C) Offering the patient multiple choices in order to clarify the character of the urinary symptoms that she is experiencing D) Asking her to tell you exactly what she means when she states that she has a urinary tract infection - b Reassurance is not part of clarifying the patient's story; it is part of establishing rapport and empathizing with the patient. - Mr. W. is a 51-year-old auto mechanic who comes to the emergency room wanting to be checked out for the symptom of chest pain. As you listen to him describe his symptom in more detail, you say "Go on," and later, "Mm-hmmm." This is an example of which of the following skilled interviewing techniques? A) Echoing B) Nonverbal communication C) Facilitation D) Empathic response - c This is an example of facilitation. Facilitation can be posture, actions, or words that encourage the patient to say more. - Mrs. R. is a 92-year-old retired teacher who comes to your clinic accompanied by her daughter. You ask Mrs. R. why she came to your clinic today. She looks at her daughter and doesn't say anything in response to your question. This is an example of which type of challenging patient? A) Talkative patient B) Angry patient C) Silent patient D) Hearing-impaired patient - c This is one example of a silent patient. There are many possibilities for this patient's silence: depression, dementia, the manner in which you asked the question, and so on. - Mrs. T. comes for her regular visit to the clinic. She is on your schedule because her regular provider is on vacation and she wanted to be seen. You have heard about her many times from your colleague and are aware that she is a very talkative person. Which of the following is a helpful technique to improve the quality of the interview for both the provider and the patient? A) Allow the patient to speak uninterrupted for the duration of the appointment. B) Briefly summarize what you heard from the patient in the first 5 minutes and then try to have her focus on one aspect of what she told you. C) Set the time limit at the beginning of the interview and stick with it, no matter what occurs in the course of the interview. D) Allow your impatience to show so that the patient picks up on your nonverbal cue that the appointment needs to end. - b You can also say, "I want to make sure I take good care of this problem because it is very important. We may need to talk about the others at the next appointment. Is that okay with you?" This is a technique that can help you to change the subject but, at the same time, validate the patient's concerns; it also can provide more structure to the interview. - A 23-year-old graduate student comes to your clinic for evaluation of a urethral discharge. As the provider, you need to get a sexual history. Which one of the following questions is inappropriate for eliciting the information? A) Are you sexually active? B) When was the last time you had intimate physical contact with someone, and did that contact include sexual intercourse? C) Do you have sex with men, women, or both? D) How many sexual partners have you had in the last 6 months? - a This is inappropriate because it is too vague. Given the complaint, you should probably assume that he is sexually active. Sometimes patients may respond to this question with the phrase "No, I just lie there." A specific sexual history will help you to assess this patient's risk for other sexually transmitted infections. - Mr. Q. is a 45-year-old salesman who comes to your office for evaluation of fatigue. He has come to the office many times in the past with a variety of injuries, and you suspect that he has a problem with alcohol. Which one of the following questions will be most helpful in diagnosing this problem? A) You are an alcoholic, aren't you? B) When was your last drink? C) Do you drink 2 to 3 beers every weekend? D) Do you drink alcohol when you are supposed to be working? - b This is a good opening question that is general and neutral in tone; depending on the timing, you will be able to ask for more specific information related to the patient's last drink. The others will tend to stifle the conversation because they are closed-ended questions. Answer D implies negative behavior and may also keep the person from sharing freely with you. - On a very busy day in the office, Mrs. Donelan, who is 81 years old, comes for her usual visit for her blood pressure. She is on a low-dose diuretic chronically and denies any side effects. Her blood pressure is 118/78 today, which is well-controlled. As you are writing her script, she mentions that it is hard not having her husband Bill around anymore. What would you do next? A) Hand her the script and make sure she has a 3-month follow-up appointment. B) Make sure she understands the script. C) Ask why Bill is not there. D) Explain that you will have more time at the next visit to discuss this. - c Sometimes, the patient's greatest need is for support and empathy. It would be inappropriate to ignore this comment today. She may have relied heavily upon Bill for care and may be in danger. She may be depressed and even suicidal, but you will not know unless you discuss this with her. Most importantly, you should empathize with her by saying something like "It must be very difficult not to have him at home" and allow a pause for her to answer. You may also ask "What did you rely on him to do for you?" Only a life-threatening crisis with another patient should take you out of her room at this point, and you may need to adjust your office schedule to allow adequate time for her today. - A patient is describing a very personal part of her history very quickly and in great detail. How should you react to this? A) Write down as much as you can, as quickly as possible. B) Ask her to repeat key phrases or to pause at regular intervals, so you can get almost every word. C) Tell her that she can go over the notes later to make sure they are accurate. D) Push away from the keyboard or put down your pen and listen. - d This is a common event in clinical practice. It is much more important to listen actively with good eye contact at this time than to document the story verbatim. You want to minimize interruption (e.g., answer B). It is usually not appropriate to ask a patient to go over the written notes, but it would be a good idea to repeat the main ideas back to her. You should be certain she has completed her story before doing this. By putting down your pen or pushing away from the keyboard, you let the patient know that her story is the most important thing to you at this moment. - When you enter your patient's examination room, his wife is waiting there with him. Which of the following is most appropriate? A) Ask if it's okay to carry out the visit with both people in the room. B) Carry on as you would ordinarily. The permission is implied because his wife is in the room with him. C) Ask his wife to leave the room for reasons of confidentiality. D) First ask his wife what she thinks is going on. - a Even in situations involving people very familiar with each other, it is important to respect individual privacy. There is no implicit consent merely because he has allowed his wife to be in the room with him. On the other hand, it is inappropriate to assume that his wife should leave the room. Remember, the patient is the focus of the visit, so it would be appropriate to allow him to control who is in the room with him and inappropriate to address his wife first. Although your duty is to the patient, you may get optimal information by offering to speak to both people confidentially. This situation is analogous to an adolescent's visit. - A patient complains of knee pain on your arrival in the room. What should your first sentence be after greeting the patient? A) How much pain are you having? B) Have you injured this knee in the past? C) When did this first occur? D) Could you please describe what happened? - d When looking into a complaint, it is best to start with an invitation for the patient to tell you in his or her own words. More specific questions should be used later in the interview to fill in any gaps. - A patient tells you about her experience with prolonged therapy for her breast cancer. You comment, "That must have been a very trying time for you." What is this an example of? A) Reassurance B) Empathy C) Summarization D) Validation - d This is an example of validation to legitimize her emotional experience. "Now that you have had your treatment, you should not have any further troubles" is an example of reassurance. "I understand what you went through because I am a cancer survivor myself" is an example of empathy. "So, you have had a lumpectomy and multiple radiation treatments" is an example of summarization as applied to this vignette. - You are performing a young woman's first pelvic examination. You make sure to tell her verbally what is coming next and what to expect. Then you carry out each maneuver of the examination. You let her know at the outset that if she needs a break or wants to stop, this is possible. You ask several times during the examination, "How are you doing, Brittney?" What are you accomplishing with these techniques? A) Increasing the patient's sense of control B) Increasing the patient's trust in you as a caregiver C) Decreasing her sense of vulnerability D) All of the above - d These techniques minimize the effects of transitions during an examination and empower the patient. Especially during a sensitive examination, it is important to give the patient as much control as possible. - When using an interpreter to facilitate an interview, where should the interpreter be positioned? A) Behind you, the examiner, so that the lips of the patient and the patient's nonverbal cues can be seen B) Next to the patient, so the examiner can maintain eye contact and observe the nonverbal cues of the patient C) Between you and the patient so all parties can make the necessary observations D) In a corner of the room so as to provide minimal distraction to the interview - b nterpreters are invaluable in encounters where the examiner and patient do not speak the same language, including encounters with the deaf. It should be noted that deaf people from different regions of the world use different sign languages. The priority is for you to have a good view of the patient. Remember to use short, simple phrases while speaking directly to the patient and ask the patient to repeat back what he or she understands. - A 15-year-old high school sophomore and her mother come to your clinic because the mother is concerned about her daughter's weight. You measure her daughter's height and weight and obtain a BMI of 19.5 kg/m2. Based on this information, which of the following is appropriate? A) Refer the patient to a nutritionist and a psychologist because the patient is anorexic. B) Reassure the mother that this is a normal body weight. C) Give the patient information about exercise because the patient is obese. D) Give the patient information concerning reduction of fat and cholesterol in her diet because she is obese. - B The patient has a normal BMI; the range for a normal BMI is 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m2. You may be able to give the patient and her mother the lower limit of normal in pounds for her daughter's height, or instruct her in how to use a BMI table. - A 25-year-old radio announcer comes to the clinic for an annual examination. His BMI is 26.0 kg/m2. He is concerned about his weight. Based on this information, what is appropriate counsel for the patient during the visit? A) Refer the patient to a nutritionist because he is anorexic. B) Reassure the patient that he has a normal body weight. C) Give the patient information about reduction of fat, cholesterol, and calories because he is overweight. D) Give the patient information about reduction of fat and cholesterol because he is obese. - C The patient has a BMI in the overweight range, which is 25.0 to 29.9 kg/m2. It is prudent to give him information about reducing calories, fat, and cholesterol in his diet to help prevent further weight gain. - A 67-year-old retired janitor comes to the clinic with his wife. She brought him in because she is concerned about his weight loss. He has a history of smoking 3 packs of cigarettes a day for 30 years, for a total of 90 pack-years. He has noticed a daily cough for the past several years, which he states is productive of sputum. He came into the clinic approximately 1 year ago, and at that time his weight was 140 pounds. Today, his weight is 110 pounds. Which one of the following questions would be the most important to ask if you suspect that he has lung cancer? A) Have you tried to force yourself to vomit after eating a meal? B) Do you have heartburn/indigestion and diarrhea? C) Do you have enough food to eat? D) Have you tried to lose weight? - D This is important: If the patient hasn't tried to lose weight, then this weight loss is inadvertent and poses concern for a neoplastic process, especially given his smoking history. - Common or concerning symptoms to inquire about in the General Survey and vital signs include all of the following except: A) Changes in weight B) Fatigue and weakness C) Cough D) Fever and chills - C This sx is more appropriate to the respiratory review of systems - You are beginning the examination of a patient. All of the following areas are important to observe as part of the General Survey except: A) Level of consciousness B) Signs of distress C) Dress, grooming, and personal hygiene D) Blood pressure - D BP is a vital sign, not part of the general survey - A 55-year-old bookkeeper comes to your office for a routine visit. You note that on a previous visit for treatment of contact dermatitis, her blood pressure was elevated. She does not have prior elevated readings and her family history is negative for hypertension. You measure her blood pressure in your office today. Which of the following factors can result in a false high reading? A) Blood pressure cuff is tightly fitted. B) Patient is seated quietly for 10 minutes prior to measurement. C) Blood pressure is measured on a bare arm. D) Patient's arm is resting, supported by your arm at her mid-chest level as you stand to measure the blood pressure. - A. A blood pressure cuff that is too tightly fitted can result in a false high reading. The other answers are important to observe to obtain an accurate blood pressure reading. JNC-7 also mentions the importance of having the back supported when obtaining blood pressure in the sitting position. - A 49-year-old truck driver comes to the emergency room for shortness of breath and swelling in his ankles. He is diagnosed with congestive heart failure and admitted to the hospital. You are the student assigned to do the patient's complete history and physical examination. When you palpate the pulse, what do you expect to feel? A) Large amplitude, forceful B) Small amplitude, weak C) Normal D) Bigeminal - b Congestive heart failure is characterized by decreased stroke volume or increased peripheral vascular resistance, which would result in a small-amplitude, weak pulse. Subtle differences in amplitude are usually best detected in large arteries close to the heart, like the carotid pulse. You may not be able to notice these in other locations. - An 18-year-old college freshman presents to the clinic for evaluation of gastroenteritis. You measure the patient's temperature and it is 104 degrees Fahrenheit. What type of pulse would you expect to feel during his initial examination? A) Large amplitude, forceful B) Small amplitude, weak C) Normal D) Bigeminal - A Fever results in an increased stroke volume, which results in a large-amplitude, forceful pulse. Later in the course of the illness, if dehydration and shock result, you may expect small amplitude and weak pulses. - A 25-year-old type 1 diabetic clerk presents to the emergency room with shortness of breath and states that his blood sugar was 605 at home. You diagnose the patient with diabetic ketoacidosis. What is the expected pattern of breathing? A) Normal B) Rapid and shallow C) Rapid and deep D) Slow - C This is the expected rate and depth in diabetic ketoacidosis. The body is trying to rid itself of carbon dioxide to compensate for the acidosis. This is known as Kussmaul's breathing and is seen in other causes of acidosis as well - Mrs. Lenzo weighs herself every day with a very accurate balance-type scale. She has noticed that over the past 2 days she has gained 4 pounds. How would you best explain this? A) Attribute this to some overeating at the holidays. B) Attribute this to wearing different clothing. C) Attribute this to body fluid. D) Attribute this to instrument inaccuracy. - C This amount of weight over a short period should make one think of body fluid changes. You may consider a kidney problem or heart failure in your differential. The other reasons should be considered as well, but this amount of weight gain over a short period usually indicates causes other than excessive caloric intake. A rule of thumb for dieters is that an energy excess of 3500 calories will cause a 1-pound weight gain, if the increase is to be attributed to food intake. - Mr. Curtiss has a history of obesity, diabetes, osteoarthritis of the knees, HTN, and obstructive sleep apnea. His BMI is 43 and he has been discouraged by his difficulty in losing weight. He is also discouraged that his goal weight is 158 pounds away. What would you tell him? A) "When you get down to your goal weight, you will feel so much better." B) "Some people seem to be able to lose weight and others just can't, no matter how hard they try." C) "We are coming up with new medicines and methods to treat your conditions every day." D) "Even a weight loss of 10% can make a noticeable improvement in the problems you mention." - D Many patients trying to change a habit are overwhelmed by how far they are from their goal. As the proverb says: "A journey of a thousand miles begins with one step." Many patients find it empowering to know that they can achieve a small goal, such as a loss of 1 pound per week. They must be reminded that this process will take time and that slow weight loss is more successful long-term. Research has shown that significant benefits often come with even a 10% weight loss. - Jenny is one of your favorite patients who usually shares a joke with you and is nattily dressed. Today she is dressed in old jeans, lacks makeup, and avoids eye contact. To what do you attribute these changes? A) She is lacking sleep. B) She is fatigued from work. C) She is running into financial difficulty. D) She is depressed - D It is important to use all of your skills and memory of an individual patient to guide your thought process. She is not described as sleepy. Work fatigue would most likely not cause avoidance of eye contact. Financial difficulties would not necessarily deplete a nice wardrobe. It is most likely that she is depressed or in another type of difficulty. - Despite having high BP readings in the office, Mr. Kelly tells you that his readings at home are much lower. He checks them twice a day at the same time of day and has kept a log. How do you respond? A) You diagnose "white coat hypertension." B) You assume he is quite nervous when he comes to your office. C) You question the accuracy of his measurements. D) You question the accuracy of your measurements - C It is not uncommon to see differences in a patient's home measurements and your own in the office. Presuming that this is "white coat hypertension" can be dangerous because this condition is not usually treated. This allows for the effects of a missed diagnosis of hypertension to go unchecked. It is also very difficult to judge if a patient is outwardly nervous. You should always consider that your measurements are not accurate as well, but the fact that you and your staff are well-trained and perform this procedure on hundreds of patients a week makes this less likely. Ideally, you would ask the patient to bring in his BP equipment and take a simultaneous reading with you to make sure that he is getting an accurate reading. - You are observing a patient with heart failure and notice that there are pauses in his breathing. On closer examination, you notice that after the pauses the patient takes progressively deeper breaths and then progressively shallower breaths, which are followed by another apneic spell. The patient is not in any distress. You make the diagnosis of: A) Ataxic (Biot's) breathing B) Cheyne-Stokes respiration C) Kussmaul's respiration D) COPD with prolonged expiration - B Cheyne-Stokes respiration can be seen in patients with heart failure and is usually not a sign of an immediate problem. Ataxic breathing is very irregular in rhythm and depth and is seen with brain injury. Kussmaul's respiration is seen in patients with a metabolic acidosis, as they are trying to rid their bodies of carbon dioxide to compensate. Respirations in COPD are usually regular and are not usually associated with apneic episodes - Mr. Garcia comes to your office for a rash on his chest associated with a burning pain. Even a light touch causes this burning sensation to worsen. On examination, you note a rash with small blisters (vesicles) on a background of reddened skin. The rash overlies an entire rib on his right side. What type of pain is this? A) Idiopathic pain B) Neuropathic pain C) Nociceptive or somatic pain D) Psychogenic pain - B This vignette is consistent with a diagnosis of herpes zoster, or shingles. This is caused by reemergence of dormant varicella (chickenpox) viruses from Mr. Garcia's nerve root. The characteristic burning quality without a history of an actual burn makes one think of neuropathic pain. It will most likely remain for months after the rash has resolved. There is no evidence of physical injury and this is a peculiar distribution, making nociceptive pain less likely. There is no evidence of a psychogenic etiology for this, and the presence of a rash makes this possibility less likely as well. Because of your astute diagnostic abilities, the pain is not idiopathic. - A 50-year-old body builder is upset by a letter of denial from his life insurance company. He is very lean but has gained 2 pounds over the past 6 months. You personally performed his health assessment and found no problems whatsoever. He says he is classified as "high risk" because of obesity. What should you do next? A) Explain that even small amounts of weight gain can classify you as obese. B) Place him on a high-protein, low-fat diet. C) Advise him to increase his aerobic exercise for calorie burning. D) Measure his waist - D The patient most likely had a high BMI because of increased muscle mass. In this situation, it is important to measure his waist. It is most likely under 40 inches, which makes obesity unlikely (even to an insurance company). It is important that you personally contact the company and explain your reasoning. Be prepared to back your argument with data. A special diet is unlikely to be of much use, and more aerobic exercise, while probably a good idea for most, is redundant for this individual - Ms. Wright comes to your office, complaining of palpitations. While checking her pulse you notice an irregular rhythm. When you listen to her heart, every fourth beat sounds different. It sounds like a triplet rather than the usual "lub dup." How would you document your examination? A) Regular rate and rhythm B) Irregularly irregular rhythm C) Regularly irregular rhythm D) Bradycardia - C Because this unusual beat occurs every fourth set of heart sounds, it is regularly irregular. This is most consistent with ventricular premature contractions (or VPCs). This is generally a common and benign rhythm. An irregularly irregular rhythm is a classic finding in atrial fibrillation. The rhythm is very random in character. Bradycardia refers to the rate, not the rhythm. - A 35-year-old archaeologist comes to your office (located in Phoenix, Arizona) for a regular skin check-up. She has just returned from her annual dig site in Greece. She has fair skin and reddish-blonde hair. She has a family history of melanoma. She has many freckles scattered across her skin. From this description, which of the following is not a risk factor for melanoma in this patient? A) Age B) Hair color C) Actinic lentigines D) Heavy sun exposure - A The risk for melanoma is increased in people over the age of 50; our patient is 35 years old. The other answers represent known risk factors for melanoma. Especially with a family history of melanoma, she should be instructed to keep her skin covered when in the sun and use strong sunscreen on exposed areas - You are speaking to an 8th grade class about health prevention and are preparing to discuss the ABCDEs of melanoma. What are the ABCDEs? - A=asymmetry B=irregular borders C=color changes D=diameter >6,, E=evolution - You are beginning the examination of the skin on a 25-year-old teacher. You have previously elicited that she came to the office for evaluation of fatigue, weight gain, and hair loss. You strongly suspect that she has hypothyroidism. What is the expected moisture and texture of the skin of a patient with hypothyroidism? - Dry and rough A patient with hypothyroidism is expected to have skin that is dry as well as rough. - 28-year-old patient comes to the office for evaluation of a rash. At first there was only one large patch, but then more lesions erupted suddenly on the back and torso; the lesions itch. On physical examination, you note that the pattern of eruption is like a Christmas tree and that there are a variety of erythematous papules and macules on the cleavage lines of the back. Based on this description, what is the most likely diagnosis? A) Pityriasis rosea B) Tinea versicolor C) Psoriasis D) Atopic eczema - A This is a classic description of pityriasis rosea. The description of a large single or "herald" patch preceding the eruption is a good way to distinguish this rash from other conditions. - A 19-year-old construction worker presents for evaluation of a rash. He notes that it started on his back with a multitude of spots and is also on his arms, chest, and neck. It itches a lot. He does sweat more than before because being outdoors is part of his job. On physical examination, you note dark tan patches with a reddish cast that has sharp borders and fine scales, scattered more prominently around the upper back, chest, neck, and upper arms as well as under the arms. Based on this description, what is your most likely diagnosis? A) Pityriasis rosea B) Tinea versicolor C) Psoriasis D) Atopic eczema - B - Pityriasis rosea - cause unknown, self limiting illness lasting 4 weeks to 8 weeks and asymptomatic. Pt c/o oval lesions with fine scales that follow skin lines(leavage lines) of the trunk or a "christmas tree" pattern. "Herald Patch"first lesion to appear and largest in size, appears 2 weeks before full breakout. - Tinea versicolor - a fungal infection that causes painless, discolored areas on the skin - A 68-year-old retired farmer comes to your office for evaluation of a skin lesion. On the right temporal area of the forehead, you see a flattened papule the same color as his skin, covered by a dry scale that is round and feels hard. He has several more of these scattered on the forehead, arms, and legs. Based on this description, what is your most likely diagnosis? A) Actinic keratosis B) Seborrheic keratosis C) Basal cell carcinoma D) Squamous cell carcinoma - A This is a typical description of actinic keratosis -it may be easier to feel than to see. If left untreated, approximately 1% of cases can develop into squamous cell carcinoma - A 58-year-old gardener comes to your office for evaluation of a new lesion on her upper chest. The lesion appears to be "stuck on" and is oval, brown, and slightly elevated with a flat surface. It has a rough, wartlike texture on palpation. Based on this description, what is your most likely diagnosis? A) Actinic keratosis B) Seborrheic keratosis C) Basal cell carcinoma D) Squamous cell carcinoma - B THe benign, "stuck on" appearance and the rough, wart like texture are key features for the diagnosis. They often produce a greasy scale when scratched with a fingernail, which further helps to distinguish them from other lesions. Frequently, these benign lesions actually meet several of the ABCDEs of melanoma, so it is important to distinguish these lesions to prevent unnecessary biopsy. - An 8-year-old girl comes with her mother for evaluation of hair loss. She denies pulling or twisting her hair, and her mother has not noted this behavior at all. She does not put her hair in braids. On physical examination, you note a clearly demarcated, round patch of hair loss without visible scaling or inflammation. There are no hair shafts visible. Based on this description, what is your most likely diagnosis? A) Alopecia areata B) Trichotillomania C) Tinea capitis D) Traction alopecia - A This is a typical description for alopecia areata. There are no risk factors for trichotillomania or for traction alopecia. The physical examination is not consistent with tinea capitis because the skin is intact. - A mother brings her 11 month old to you because her mother-in-law and others have told her that her baby is jaundiced. She is eating and growing well and performing the developmental milestones she should for her age. On examination you indeed notice a yellow tone to her skin from head to toe. Her sclerae are white. To which area should your next questions be related? A) Diet B) Family history of liver diseases C) Family history of blood diseases D) Ethnicity of the child - A The lack of jaundice in the sclerae is an important clue. Typically, this is the first place where one sees jaundice. This examination should also be carried out in natural light (sunlight) as opposed to fluorescent lighting, which can alter perceived colors. Many infants this age have a large proportion of carrots, tomatoes, and yellow squash, which are rich in carotene. Liver and blood diseases can cause jaundice, but this should involve the sclerae. The ethnicity of the child should not cause a perceived change from her usual skin tone - A new mother is concerned that her child occasionally "turns blue." On further questioning, she mentions that this is at her hands and feet. She does not remember the child's lips turning blue. She is otherwise eating and growing well. What would you do now? A) Reassure her that this is normal B) Obtain an echocardiogram to check for structural heart disease and consult cardiology C) Admit the child to the hospital for further observation D) Question the validity of her story - A This is an example of peripheral cyanosis. This is a very common and benign condition which typically occurs when the child is slightly cold and his peripheral circulation is adjusting to keep his core warm. Without other problems, there is no need for further workup. If the lips or other central locations are involved, you must consider other etiologies. - You are examining an unconscious patient from another region and notice Beau's lines, a transverse groove across all of her nails, about 1 cm from the proximal nail fold. What would you do next? A) Conclude this is caused by a cultural practice. B) Conclude this finding is most likely secondary to trauma. C) Look for information from family and records regarding any problems which occurred 3 months ago. D) Ask about dietary intake. - C These lines can provide valuable information about previous significant illnesses, some of which are forgotten or are not able to be reported by the patient. Because the fingernails grow at about 0.1 mm per day, you would ask about an illness 100 days ago. This patient may have been hospitalized for endocarditis or may have had another significant illness which should be sought. Trauma to all 10 nails in the same location is unlikely. Dietary intake at this time would not be related to this finding. Do not assume a finding is necessarily related to a patient's culture unless you have good knowledge of that culture. - Dakota is a 14-year-old boy who just noticed a rash at his ankles. There is no history of exposure to ill people or other agents in the environment. He has a slight fever in the office. The rash consists of small, bright red marks. When they are pressed, the red color remains. What should you do? A) Prescribe a steroid cream to decrease inflammation. B) Consider admitting the patient to the hospital. C) Reassure the parents and the patient that this should resolve within a week. D) Tell him not to scratch them, and follow up in 3 days. - B Although this may not be an impressive rash, the fact that they do not "blanch" with pressure is very concerning. This generally means that there is pinpoint bleeding under the skin, and while this can be benign, it can be associated with life-threatening illnesses like meningococcemia and low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia) associated with serious blood disorders like leukemia. You should always report this feature of a rash immediately to a supervisor or teacher. - vasculitis - inflammation of a blood vessel - Mrs. Hill is a 28-year-old African-American with a history of SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus). She has noticed a raised, dark red rash on her legs. When you press on the rash, it doesn't blanch. What would you tell her regarding her rash? A) It is likely to be related to her lupus. B) It is likely to be related to an exposure to a chemical. C) It is likely to be related to an allergic reaction. D) It should not cause any problems. - A A "palpable purpura" is usually associated with vasculitis. This is an inflammatory condition of the blood vessels often associated with system rheumatic disease. It can cut off circulation to any portion of the body and can mimic many other diseases in this manner. While allergic and chemical exposures may be a possible cause of hte rash, this patient's SLE should make you consider vasculitis. - Jacob, a 33-year-old construction worker, complains of a "lump on his back" over his scapula. It has been there for about a year and is getting larger. He says his wife has been able to squeeze out a cheesy-textured substance on occasion. He worries this may be cancer. When gently pinched from the side, a prominent dimple forms in the middle of the mass. What is most likely? - A sebaceous cyst. This is a classic description of an epidermal inclusion cyst resulting from a blocked sebaceous gland. The fact that any lesion is enlarging is worrisome, but the other descriptors are so distinctive that cancer is highly unlikely. This would be an unusual location for a lymph node, and these do not usually drain to the skin. - A young man comes to you with an extremely pruritic rash over his knees and elbows which has come and gone for several years. It seems to be worse in the winter and improves with some sun exposure. On examination, you notice scabbing and crusting with some silvery scale, and you are observant enough to notice small "pits" in his nails. What would account for these findings? - Psoriasis Plaque psoriasis. Eczema is usually over the flexor surfaces and does not scale, whereas psoriasis affects the extensor surfaces. Pityriasis usually is limited to the trunk and proximal extremities. Tinea has a much finer scale associated with it, almost like a powder, and is found in dark and moist areas. - Mrs. Anderson presents with an itchy rash which is raised and appears and disappears in various locations. Each lesion lasts for many minutes. What most likely accounts for this rash? - Urticaria THis is a typical case of urticaria. The most unusual aspect of this condition is that the lesions "move" from place to place. This would be distinctly unusual for hte other causes listed. - Ms. Whiting is a 68 year old who comes in for her usual follow-up visit. You notice a few flat red and purple lesions, about 6 centimeters in diameter, on the ulnar aspect of her forearms but nowhere else. She doesn't mention them. They are tender when you examine them. What should you do? A) Conclude that these are lesions she has had for a long time. B) Wait for her to mention them before asking further questions. C) Ask how she acquired them. D) Conduct the visit as usual for the patient. - C These are consistent with ecchymoses, or bruises. It is important to ask about antiplatelet medications such as aspirin, trauma history, and history of blood disorders in the patient and her family. Because of the different ages of the bruises and the isolation of them to the ulnar forearms, these may be a result of abuse or other violence. It is your duty to investigate the cause of these lesions. - A middle-aged man comes in because he has noticed multiple small, blood-red, raised lesions over his anterior chest and abdomen for the past several months. They are not painful and he has not noted any bleeding or bruising. He is concerned this may be consistent with a dangerous condition. What should you do? A) Reassure him that there is nothing to worry about. B) Do laboratory work to check for platelet problems. C) Obtain an extensive history regarding blood problems and bleeding disorders. D) Do a skin biopsy in the office. - These represent cherry angiomas, which are very common, benign lesions. Further workup such as laboratory work, skin biopsy, or even further questions are not necessary at this time. It would be wise to ask the patient to report any changes in any of his skin lesions, and tell him that you would need to see him at that time. - A 72-year-old retired saleswoman comes to your office, complaining of a bloody discharge from her left breast for 3 months. She denies any trauma to her breast. Her past medical history includes high blood pressure and abdominal surgery for colon cancer. Her aunt died of ovarian cancer and her father died of colon cancer. Her mother died of a stroke. The patient denies tobacco, alcohol, or drug use. She is a widow and has three healthy children. On examination her breasts are symmetric, with no skin changes. You are able to express bloody discharge from her left nipple. You feel no discrete masses, but her left axilla has a hard, 1-cm fixed node. The remainder of her heart, lung, abdominal, and pelvic examinations are unremarkable. What cause of nipple discharge is the most likely in her circumstance? A) Benign breast abnormality B) Breast cancer C) Galactorrhea - B Nipple discharge in breast cancer is usually unilateral and can be clear or bloody. Although a breast mass is not palpated, in this case a fixed lymph node is palpated. - A 44-year-old female comes to your clinic, complaining of severe dry skin in the area over her right nipple. She denies any trauma to the area. She noticed the skin change during a self-examination 2 months ago. She also admits that she had felt a lump under the nipple but kept putting off making an appointment. She does admit to 6 months of fatigue but no weight loss, weight gain, fever, or night sweats. Her past medical history is significant for hypothyroidism. She does not have a history of eczema or allergies. She denies any tobacco, alcohol, or drug use. On examination you find a middle-aged woman appearing her stated age. Inspection of her right breast reveals a scaly eczema-like crust around her nipple. Underneath you palpate a nontender 2-cm mass. The axilla contains only soft, moveable nodes. The left breast and axilla examination findings are unremarkable. What visible skin change of the breast does she have? A) Nipple retraction B) Paget's disease C) Peau d'orange sign - B This uncommon form of breast cancer starts as an eczema like scaly skin change around the areola. The lesion may weep, crust, or erode. It can be associated with an underlying mass, but the skin change can also be found alone. Any eczema-like area around the nipple that does not response to topical treatment needs to evaluated for breast cancer. - A 56-year-old female comes to your clinic, complaining of her left breast looking unusual. She says that for 2 months the angle of the nipple has changed direction. She does not do self-examinations, so she doesn't know if she has a lump. She has no history of weight loss, weight gain, fever, or night sweats. Her past medical history is significant for high blood pressure. She smokes two packs of cigarettes a day and has three to four drinks per weekend night. Her paternal aunt died of breast cancer in her forties. Her mother is healthy but her father died of prostate cancer. On examination you find a middle-aged woman appearing older than her stated age. Inspection of her left breast reveals a flattened nipple deviating toward the lateral side. On palpation the nipple feels thickened. Lateral to the areola you palpate a nontender 4-cm mass. The axilla contains several fixed nodes. The right breast and axilla examinations are unremarkable. What visible skin change of the breast does she have? A) Nipple retraction B) Paget's disease C) Peau d'orange sign - A A retracted nipple is flattened or pulled inward or toward the medial, lateral, anterior, or posterior side of the breast. The surrounding skin can be thickened. This is a relatively late finding in breast cancer. - A 19-year-old female comes to your office, complaining of a clear discharge from her right breast for 2 months. She states that she noticed it when she and her boyfriend were "messing around" and he squeezed her nipple. She continues to have this discharge anytime she squeezes that nipple. She denies any trauma to her breasts. Her past medical history is unremarkable. She denies any pregnancies. Both of her parents are healthy. She denies using tobacco or illegal drugs and drinks three to four beers a week. On examination her breasts are symmetric with no skin changes. You are able to express clear discharge from her right nipple. You feel no discrete masses and her axillae are normal. The remainder of her heart, lung, abdominal, and pelvic examinations are unremarkable. A urine pregnancy test is negative. What cause of nipple discharge is the most likely in her circumstance? A) Benign breast abnormality B) Breast cancer C) Nonpuerperal galactorrhea - A Nipple discharge in benign breast abnormalities tends to be clear and unilateral. The discharge is usually not spontaneous. This patient needs to be told to stop compressing her nipple. If the problem still persists after the patient has stopped compressing the nipple, further workup is warranted. - A 23-year-old computer programmer comes to your office for an annual examination. She has recently become sexually active and wants to be placed on birth control. Her only complaint is that the skin in her armpits has become darker. She states it looks like dirt, and she scrubs her skin nightly with soap and water but the color stays. Her past medical symptoms consist of acne and mild obesity. Her periods have been irregular for 3 years. Her mother has type 2 diabetes and her father has high blood pressure. The patient denies using tobacco but has four to five drinks on Friday and Saturday nights. She denies any illegal drug use. On examination you see a mildly obese female who is breathing comfortably. Her vital signs are unremarkable. Looking under her axilla, you see dark, velvet-like skin. Her annual examination is otherwise unremarkable. What disorder of the breast or axilla is she most likely to have? A) Peau d'orange B) Acanthosis nigricans C) Hidradenitis suppurativa - B Acanthosis nigricans can be associated with an internal malignancy, but in most cases, it is a benign dermatologic condition associated with polycystic ovarian syndrome, consisting of acne, hirsutism, obesity, irregular periods, infertility, ovarian cysts, and early onset type 2 diabetes. It is also known to correlate with insulin resistance. - A 43-year-old store clerk comes to your office upset because she has found an enlarged lymph node under her left arm. She states she found it yesterday when she was feeling pain under her arm during movement. She states the lymph node is about an inch long and is very painful. She checks her breasts monthly and gets a yearly mammogram (her last was 2 months ago), and until now everything has been normal. She states she is so upset because her mother died in her 50s of breast cancer. The patient does not smoke, drink, or use illegal drugs. Her father is in good health. On examination you see a tense female appearing her stated age. On visual inspection of her left axilla you see a tense red area. There is no scarring around the axilla. Palpating this area, you feel a 2-cm tender, movable lymph node underlying hot skin. Other shotty nodes are also in the area. Visualization of both breasts is normal. Palpation of her right axilla and both breasts is unremarkable. Examining her left arm, you see a scabbed-over superficial laceration over her left hand. Upon your questioning, she remembers she cut her hand gardening last week. What disorder of the axilla is most likely responsible for her symptoms? A) Breast cancer B) Lymphadenopathy of infectious origin C) Hidradenitis suppurativa - B A lymph node enlarged because of infection is generally hot, tender, and red. CLose examination of hte skin that drains to that lymph node region is advised. Often there will be a cut or scratch over that involved arm that has an infectious agent. An example is cat scratch disease. - A 63-year-old nurse comes to your office, upset because she has found an enlarged lymph node under her right arm. She states she found it last week while taking a shower. She isn't sure if she has any breast lumps because she doesn't know how to do self-exams. She states her last mammogram was 5 years ago and it was normal. Her past medical history is significant for high blood pressure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. She quit smoking 2 years ago after a 55-packs/year history. She denies using any illegal drugs and drinks alcohol rarely. Her mother died of a heart attack and her father died of a stroke. She has no children. On examination you see an older female appearing her stated age. On visual inspection of her right axilla you see nothing unusual. Palpating this area, you feel a 2-cm hard, fixed lymph node. She denies any tenderness. Visualization of both breasts is normal. Palpation of her left axilla and breast is unremarkable. On palpation of her right breast you feel a nontender 1-cm lump in the tail of Spence. What disorder of the axilla is most likely responsible for her symptoms? A) Breast cancer B) Lymphadenopathy of infectious origin C) Hidradenitis suppurativa - A Metastatic lymph nodes tend to be hard, contender, and fixed, often to the rib cage. Although the patient has no family history of breast cancer, she is at a slightly increased risk due to her never having had children. - 8. A 40-year-old mother of two presents to your office for consultation. She is interested in knowing what her relative risks are for developing breast cancer. She is concerned because her sister had unilateral breast cancer 6 years ago at age 38. The patient reports on her history that she began having periods at age 11 and has been fairly regular ever since, except during her two pregnancies. Her first child arrived when she was 26 and her second at age 28. Otherwise she has had no health problems. Her father has high blood pressure. Her mother had unilateral breast cancer in her 70s. The patient denies tobacco, alcohol, or drug use. She is a family law attorney and is married. Her examination is essentially unremarkable. Which risk factor of her personal and family history most puts her in danger of getting breast cancer? - First-degree relative wiht premenopausal breast cancer. - Which of the following is true regarding breast self-examination? A) It has been shown to reduce mortality from breast cancer. B) It is recommended unanimously by organizations making screening recommendations. C) A high proportion of breast masses are detected by breast self-examination. D) The undue fear caused by finding a mass justifies omitting instruction in breast self-examination. - C Although self-exam has not been shown to reduce mortality and is not recommended by all groups making screening recommendations, many choose to teach women a systematic method in which to examine their breasts. A high proportion of breast masses are detected by breast self-exam - Which is true of women who have had a unilateral mastectomy? A) They no longer require breast examination. B) They should be examined carefully along the surgical scar for masses. C) Lymphedema of the ipsilateral arm usually suggests recurrence of breast cancer. D) Women with breast reconstruction over their mastectomy site no longer require examination - B A woman who has had breast cancer remains at high risk for recurrence, especially in the contralateral breast. The mastectomy site should be carefully examined for local recurrence as well. Lymphedema or swelling of the ipsilateral arm following mastectomy is common and does not usually indicate recurrence. Women with breast reconstruction must also undergo careful examination. - Which is the most effective pattern of palpation for breast cancer? A) Beginning at the nipple, make an ever-enlarging spiral. B) Divide the breast into quadrants and inspect each systematically. C) Examine in lines resembling the back and forth pattern of mowing a lawn. D) Beginning at the nipple, palpate outward in a stripe pattern. - C The vertical strip pattern has been shown to be the most effective pattern for palpation of the breast. The most important aspect, however, is to be systematic. The tail of Spence, located on the upper anterior chest, is an area commonly missed on examination. - Which of the following is most likely benign on breast examination? A) Dimpling of the skin resembling that of an orange B) One breast larger than the other C) One nipple inverted D) One breast with dimple when the patient leans forward - B Asymmetry in size of the breasts is common benign finding. - How often, according to American Cancer Society recommendations, should a woman undergo a screening breast examination by a skilled clinician? - Every 3 years. The current recommendation for screening by breast exam is every 3 years - Mrs. Patton, a 48-year-old woman, comes to your office with a complaint of a breast mass. Without any other information, what is the risk of this mass being cancerous? - 10% approx. Eleven percent of women presenting with a breast mass will have breast cancer. This statistic can be reassuring to a patient, but the importance of further studies must be emphasized. - When should a woman conduct a breast self-exam with respect to her menses? - Five to seven days following period. -least estrogen stimulation of breast tissue at this time. - What lymp node groups is most commonly involved in breast cancer? - Central The central nodes at the apex of the axilla are most commonly involved in breast cancer. The axilla can be viewed roughly as a four-sided pyramid. An examination covering all sides and the apex is unlikely to miss a significant node. - A 30-year-old man notices a firm, 2-cm mass under his areola. He has no other symptoms and no diagnosis of breast cancer in his first-degree relatives. What is the most likely diagnosis? A) Breast tissue B) Fibrocystic disease C) Breast cancer D) Lymph node - A Approx. one third of adult men will have palpable breast tissue under the areola. While males can have breast cancer, this is much less common. There are no lymph nodes in this area. - A patient is concerned about a dark skin lesion on her anterolateral abdomen. It has not changed, and there is no discharge or bleeding. On examination there is a medium brown circular lesion on the anterolateral wall of the abdomen. It is soft, has regular borders, is evenly pigmented, and is about 7 mm in diameter. What is this lesion? A) Melanoma B) Dysplastic nevus C) Supernumerary nipple D) Dermatofibroma - C Occurs along "milk line" and do not exhibit features of more concerning lesions. - A 51-year-old cook comes to your office for consultation. She recently found out that her 44-year-old sister with premenopausal breast cancer is positive for the BRCA1 gene. Your patient has been doing research on the Internet and saw that her chance of having also inherited the BRCA1 gene is 50%. She is interested in knowing what her risk of developing breast cancer would be if she were positive for the gene. She denies any lumps in her breasts and has had normal mammograms. She has had no weight loss, fever, or night sweats. Her mother is healthy and her father has prostate cancer. Two of her paternal aunts died of breast cancer. She is married. She denies using tobacco or illegal drugs and rarely drinks alcohol. Her breast and axilla examinations are unremarkable. At her age, what is her risk of getting breast cancer if she has the BRCA1 gene? A) 10% B) 50% C) 80% - B At age of 50, risk is 50% with gene - A 14-year-old junior high school student is brought in by his mother and father because he seems to be developing breasts. The mother is upset because she read on the Internet that smoking marijuana leads to breast enlargement in males. The young man adamantly denies using any tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. He has recently noticed changes in his penis, testicles, and pubic hair pattern. Otherwise, his past medical history is unremarkable. His parents are both in good health. He has two older brothers who never had this problem. On examination you see a mildly overweight teenager with enlarged breast tissue that is slightly tender on both sides. Otherwise his examination is normal. He is agreeable to taking a drug test. What is the most likely cause of his gynecomastia? A) Breast cancer B) Imbalance of hormones of puberty C) Drug use - B Approx. one third of teenage boys develop gynecomastia during puberty. It is not surprising that the two older brothers did not have this. - A 38-year-old accountant comes to your clinic for evaluation of a headache. The throbbing sensation is located in the right temporal region and is an 8 on a scale of 1 to 10. It started a few hours ago, and she has noted nausea with sensitivity to light; she has had headaches like this in the past, usually less than one per week, but not as severe. She does not know of any inciting factors. There has been no change in the frequency of her headaches. She usually takes an over-the-counter analgesic and this results in resolution of the headache. Based on this description, what is the most likely diagnosis of the type of headache? - Migraine No aura, phonophobia, photophobia, nausea, resolution with sleep, and unilateral distribution. - A 29-year-old computer programmer comes to your office for evaluation of a headache. The tightening sensation is located all over the head and is of moderate intensity. It used to last minutes, but this time it has lasted for 5 days. He denies photophobia and nausea. He spends several hours each day at a computer monitor/keyboard. He has tried over-the-counter medication; it has dulled the pain but not taken it away. Based on this description, what is your most likely diagnosis? - Tension - Which of the following is a symptom involving the eye? A) Scotomas B) Tinnitus C) Dysphagia D) Rhinorrhea - Scotomas specks in vison or areas where the patient cannot see; therefor, this is common/concerning sx of the eye - A 49-year-old administrative assistant comes to your office for evaluation of dizziness. You elicit the information that the dizziness is a spinning sensation of sudden onset, worse with head position changes. The episodes last a few seconds and then go away, and they are accompanied by intense nausea. She has vomited one time. She denies tinnitus. You perform a physical examination of the head and neck and note that the patient's hearing is intact to Weber and Rinne and that there is nystagmus. Her gait is normal. Based on this description, what is the most likely diagnosis? A) Benign positional vertigo B) Vestibular neuronitis C) Ménière's disease D) Acoustic neuroma - A This is a classic description of benign positional vertigo. The vertigo is episodic, lasting a few seconds to minutes, instead of continuous as in vestibular neuronitis. Also, there is no tinnitus or sensorineural hearing loss as occurs in Ménière's disease and acoustic neuroma. You may choose to learn about Hallpike maneuvers, which are also helpful in the evaluation of vertigo. - nystagmus - Involuntary rapid eye movements - A 55-year-old bank teller comes to your office for persistent episodes of dizziness. The first episode started suddenly and lasted 3 to 4 hours. He experienced a lot of nausea with vomiting; the episode resolved spontaneously. He has had five episodes in the past 1½ weeks. He does note some tinnitus that comes and goes. Upon physical examination, you note that he has a normal gait. The Weber localizes to the right side and the air conduction is equal to the bone conduction in the right ear. Nystagmus is present. Based on this description, what is the most likely diagnosis? A) Benign positional vertigo B) Vestibular neuronitis C) Ménière's disease D) Acoustic neuroma - C Ménière's disease is characterized by sudden onset of vertiginous episodes that last several hours to a day or more, then spontaneously resolve; the episodes then recur. On physical examination, sensorineural hearing loss is present. The patient does complain of tinnitus. - A 73-year-old nurse comes to your office for evaluation of new onset of tremors. She is not on any medications and does not take herbs or supplements. She has no chronic medical conditions. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. She walks into the examination room with slow movements and shuffling steps. She has decreased facial mobility and a blunt expression, without any changes in hair distribution on her face. Based on this description, what is the most likely reason for the patient's symptoms? A) Cushing's syndrome B) Nephrotic syndrome C) Myxedema D) Parkinson's disease - D This is a typical description for a patient with Parkinson's disease. Facial mobility is decreased, which results in a blunt expression—a "masked" appearance. The patient also has decreased blinking and a characteristic stare with an upward gaze. In combination with the findings of slow movements and a shuffling gait, the diagnosis of Parkinson's is almost clinched. - A 29-year-old physical therapist presents for evaluation of an eyelid problem. On observation, the right eyeball appears to be protruding forward. Based on this description, what is the most likely diagnosis? A) Ptosis B) Exophthalmos C) Ectropion D) Epicanthus - B Exophthalmos is the condition when the eyeball protrudes forward. If it is bilateral, it suggests the presence of Graves' disease. If it is unilateral, it could still be caused by Graves' disease. Alternatively, it could be caused by a tumor or inflammation in the orbit. - A 12-year-old presents to the clinic with his father for evaluation of a painful lump in the left eye. It started this morning. He denies any trauma or injury. There is no visual disturbance. Upon physical examination, there is a red raised area at the margin of the eyelid that is tender to palpation; no tearing occurs with palpation of the lesion. Based on this description, what is the most likely diagnosis? A) Dacryocystitis B) Chalazion C) Hordeolum D) Xanthelasma - C Hordeolum, or sty, is a painful, tender, erythematous infection in a glad at teh margin of the eyelid - A 15-year-old high school sophomore presents to the emergency room with his mother for evaluation of an area of blood in the left eye. He denies trauma or injury but has been coughing forcefully with a recent cold. He denies visual disturbances, eye pain, or discharge from the eye. On physical examination, the pupils are equal, round, and reactive to light, with a visual acuity of 20/20 in each eye and 20/20 bilaterally. There is a homogeneous, sharply demarcated area at the lateral aspect of the base of the left eye. The cornea is clear. Based on this description, what is the most likely diagnosis? A) Conjunctivitis B) Acute iritis C) Corneal abrasion D) Subconjunctival hemorrhage - D A subconjunctival hemorrhage is a leakage of blood outside of the vessels, which produces a homogenous, sharply demarcated bright red area; it fades over several days, turning yellow, then disappears. There is no associated eye pain, ocular discharge, or changes in visual acuity; the cornea is clear. Many times it is associated with severe cough, choking, or vomiting, which increase venous pressure. It is rarely caused by a serious condition, so reassurance is usually the only treatment necessary. - A 67-year-old lawyer comes to your clinic for an annual examination. He denies any history of eye trauma. He denies any visual changes. You inspect his eyes and find a triangular thickening of the bulbar conjunctiva across the outer surface of the cornea. He has a normal pupillary reaction to light and accommodation. Based on this description, what is the most likely diagnosis? A) Corneal arcus B) Cataracts C) Corneal scar D) Pterygium - D A pterygium is a triangular thickening of the bulbar conjunctiva that grows slowly across the outer surface of the cornea, usually from the nasal side. Reddening may occur, and it may interfere with vision as it encroaches on the pupil. Otherwise, treatment is unnecessary. - Which of the following is a "red flag" regarding patients presenting with headache? A) Unilateral headache B) Pain over the sinuses C) Age over 50 D) Phonophobia and photophobia - C A unilateral headache is often seen with migraines and may commonly be accompanied by phonophobia and photophobia. Pain over the sinuses from sinus congestion may also be unilateral and produce pain. Migraine and sinus headaches are common and generally benign. A new severe headache in someone over 50 can be associated with more serious etiologies for headache. Other red flags include: acute onset, "the worst headache of my life"; very high blood pressure; rash or signs of infection; known presence of cancer, HIV, or pregnancy; vomiting; recent head trauma; and persistent neurologic problems. - A sudden, painless unilateral vision loss may be caused by which of the following? A) Retinal detachment B) Corneal ulcer C) Acute glaucoma D) Uveitis - A Corneal ulcer, acute glaucoma, and uveitis are almost always accompanied by pain. Retinal detachment is generally painless, as is chronic glaucoma. - Sudden, painful unilateral loss of vision may be caused by which of the following conditions? A) Vitreous hemorrhage B) Central retinal artery occlusion C) Macular degeneration D) Optic neuritis - D In multiple sclerosis, sudden painful loss of vision may accompany optic neuritis. The other conditions are usually painless. - Diplopia, which is present with one eye covered, can be caused by which of the following problems? A) Weakness of CN III B) Weakness of CN IV C) A lesion of the brainstem D) An irregularity in the cornea or lens - d Double vision in one eye alone points to a problem in "processing" the light rays of an incoming image. The other causes of diplopia result in a misalignment of the two eyes. - You are conducting a pupillary examination on a 34-year-old man. You note that both pupils dilate slightly. Both are noted to constrict briskly when the light is placed on the right eye. What is the most likely problem? A) Optic nerve damage on the right B) Optic nerve damage on the left C) Efferent nerve damage on the right D) Efferent nerve damage on the left - b Because both pupils can constrict, efferent nerve damage is unlikely. When the light is placed on the left eye, neither a direct nor a consensual response is seen. This indicates that the left eye is not perceiving incoming light. - You feel a small mass that you think is a lymph node. It is mobile in both the up-and-down and side-to-side directions. Which of the following is most likely? A) Cancer B) Lymph node C) Deep scar D) Muscle - b A useful maneuver for discerning lymph nodes from other masses in the neck is to check for their mobility in all directions. Many other masses are mobile in only two directions. Cancerous masses may also be "fixed," or immobile. - college student presents with a sore throat, fever, and fatigue for several days. You notice exudates on her enlarged tonsils. You do a careful lymphatic examination and notice some scattered small, mobile lymph nodes just behind her sternocleidomastoid muscles bilaterally. What group of nodes is this? A) Submandibular B) Tonsillar C) Occipital D) Posterior cervical - d The group of nodes posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle is the posterior cervical chain. These are common in mononucleosis. - A young woman undergoes cranial nerve testing. On touching the soft palate, her uvula deviates to the left. Which of the following is likely? A) CN IX lesion on the left B) CN IX lesion on the right C) CN X lesion on the left D) CN X lesion on the right - d The failure of the right side of the palate to rise denotes a problem with the right 10th cranial nerve. The uvula deviates toward the properly functioning side. - A young man is concerned about a hard mass he has just noticed in the midline of his palate. On examination, it is indeed hard and in the midline. There are no mucosal abnormalities associated with this lesion. He is experiencing no other symptoms. What will you tell him is the most likely diagnosis? A) Leukoplakia B) Torus palatinus C) Thrush (candidiasis) D) Kaposi's sarcoma - b Torus palatinus is relatively common and benign but can go unnoticed by the patient for many years. The appearance of a bony mass can be concerning. Leukoplakia is a white lesion on the mucosal surfaces corresponding to chronic mechanical or chemical irritation. It can be premalignant. Thrush is usually painful and is seen in immunosuppressed patients or those taking inhaled steroids for COPD or asthma. Kaposi's sarcoma is usually seen in HIV-positive individuals and is classically a deep purple. - A patient with hearing loss by whisper test is further examined with a tuning fork, using the Weber and Rinne maneuvers. The abnormal results are as follows: bone conduction is greater than air on the left, and the patient hears the sound of the tuning fork better on the left. Which of the following is most likely? A) Otosclerosis of the left ear B) Exposure to chronic loud noise of the right ear C) Otitis media of the right ear D) Perforation of the right eardrum - a The above pattern is consistent with a conductive loss on the left side. Causes would include: foreign body, otitis media, perforation, and otosclerosis of the involved side. - A patient presents with ear pain. She is an avid swimmer. The history includes pain and drainage from the left ear. On examination, she has pain when the ear is manipulated, including manipulation of the tragus. The canal is narrowed and erythematous, with some white debris in the canal. The rest of the examination is normal. What diagnosis would you assign this patient? A) Otitis media B) External otitis C) Perforation of the tympanum D) Cholesteatoma - b These are classic history and examination findings for a patient suffering from external otitis. Otitis media would not usually have pain with movement of the external ear, nor drainage unless the eardrum was perforated. In this case the examination of the eardrum is recorded as normal. Cholesteatoma is a growth behind the eardrum and would not account for these symptoms. Otitis media would classically be accompanied by a bulging, erythematous eardrum. - 15. A patient complains of epistaxis. Which other cause should be considered? A) Intracranial hemorrhage B) Hematemesis C) Intestinal hemorrhage D) Hematoma of the nasal septum - b Although the source of epistaxis may seem obvious, other bleeding locations should be on the differential. Hematemesis can mimic this and cause delay in life-saving therapies if not considered. Intracranial hemorrhage and septal hematoma are instances of contained bleeding. Intestinal hemorrhage may cause hematemesis if there is obstruction distal to the bleeding, but this is unlikely. - Glaucoma is the leading cause of blindness in African-Americans and the second leading cause of blindness overall. What features would be noted on funduscopic examination? A) Increased cup-to-disc ratio B) AV nicking C) Cotton wool spots D) Microaneurysms - a It is important to screen for glaucoma on funduscopic examination. The cup and disc are among the easiest features to find. AV nicking and cotton wool spots are seen in hypertension. Microaneurysms are seen in diabetes. - A patient is assigned a visual acuity of 20/100 in her left eye. Which of the following is true? A) She obtains a 20% correct score at 100 feet. B) She can accurately name 20% of the letters at 20 feet. C) She can see at 20 feet what a normal person could see at 100 feet. D) She can see at 100 feet what a normal person could see at 20 feet. - c - . A light is pointed at a patient's pupil, which contracts. It is also noted that the other pupil contracts as well, though it is not exposed to bright light. Which of the following terms describes this latter phenomenon? A) Direct reaction B) Consensual reaction C) Near reaction D) Accommodation - b - On visual confrontation testing, a stroke patient is unable to see your fingers on his entire right side with either eye covered. Which of the following terms would describe this finding? A) Bitemporal hemianopsia B) Right temporal hemianopsia C) Right homonymous hemianopsia D) Binasal hemianopsia - c - You note that a patient has anisocoria on examination. Pathologic causes of this include which of the following? A) Horner's syndrome B) Benign anisocoria C) Differing light intensities for each eye D) Eye prosthesis - Ans: A Chapter: 07 Page and Header: 211, Techniques of Examination Feedback: Anisocoria can be associated with serious pathology. Remember to exclude benign causes before embarking on an intensive workup. Testing the near reaction in this case may help you to find an Argyll Robertson or tonic (Adie's) pupil. - A patient is examined with the ophthalmoscope and found to have red reflexes bilaterally. Which of the following have you essentially excluded from your differential? A) Retinoblastoma B) Cataract C) Artificial eye D) Hypertensive retinopathy - d Hypertensive retinopathy requires a careful examination of the optic fundus. It cannot be diagnosed or excluded merely from the red reflex. Typically, the red reflex would be normal in this case. The other conditions are all associated with an abnormal red reflex. - A patient presents with ear pain. She is an avid swimmer. The history includes pain and drainage from the left ear. On examination, she has pain when the ear is manipulated, including manipulation of the tragus. The canal is narrowed and erythematous, with some white debris in the canal. The rest of the examination is normal. What diagnosis would you assign this patient? A) Otitis media B) External otitis C) Perforation of the tympanum D) Cholesteatoma - Ans: B Chapter: 07 Page and Header: 225, Techniques of Examination Feedback: These are classic history and examination findings for a patient suffering from external otitis. Otitis media would not usually have pain with movement of the external ear, nor drainage unless the eardrum was perforated. In this case the examination of the eardrum is recorded as normal. Cholesteatoma is a growth behind the eardrum and would not account for these symptoms. Otitis media would classically be accompanied by a bulging, erythematous eardrum. - A young woman undergoes cranial nerve testing. On touching the soft palate, her uvula deviates to the left. Which of the following is likely? A) CN IX lesion on the left B) CN IX lesion on the right C) CN X lesion on the left D) CN X lesion on the right - d The failure of the right side of the palate to rise denotes a problem with the right 10th cranial nerve. The uvula deviates toward the properly functioning side. - YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE... - Medical Surgical Nursing | Picmonic Nursing Guide45 sets - Picmonic - $2.99 - STUDY GUIDE - Bates' Advanced Health Assessment Chapters 1-…115 Terms - DeannaSchloemer - Advanced Health Assessment Exam 3: Abdomen, M…100 Terms - DeannaSchloemer - Health assessment midterm90 Terms - jessica_laskoskie - OTHER SETS BY THIS CREATOR - Genetics12 Terms - leroylewis884 - Alternative Tx26 Terms - leroylewis884 - Addictive D/O Lecture67 Terms - leroylewis884 - Hypothalamus (notes pages 1-8) #780 Terms - leroylewis884 - THIS SET IS OFTEN IN FOLDERS WITH... - Bates review 4 and 5123 Terms - umunze - WGU-Comprehensive Health Assessment for Patie…158 Terms - johnsabrina - PD Exam 3 -Bates 8, 9, 1171 Terms - - - - Search - - Create - - - Upgrade: free 7-day trial - - Futurenp139 - - Upgrade to remove ads - Only $1/month - NSG 6020 FINAL Review (from arigaud2 mp12345678910) - STUDY - - Flashcards - - Learn - - Write - - Spell - - Test - - PLAY - - Match - - Gravity - - The main difference between cellulitis and erysipelas is the: a. organism b. length of time that infection lasts c. treatment d. area involved - d. area involved - What are the most common signs and symptoms associated with mononucleosis? a. Fatigue and lymphadenopathy b. Cough and pharyngitis c. Splenomegaly and fever d. Rash and pharyngitis - a. Fatigue and lymphadenopathy - Nice work! - You just studied 63 terms! - Now up your study game with Learn mode. - Try Learn modeStudy with Flashcards again - 1/63 - Created by - bethlewis04 - Terms in this set (63) - - The main difference between cellulitis and erysipelas is the: a. organism b. length of time that infection lasts c. treatment d. area involved - d. area involved - What are the most common signs and symptoms associated with mononucleosis? a. Fatigue and lymphadenopathy b. Cough and pharyngitis c. Splenomegaly and fever d. Rash and pharyngitis - a. Fatigue and lymphadenopathy - An older adult has suspected B12 deficiency. Which of the following lab indices is more indicative of a B12 deficiency? a. Microcytosis b. Macrocytosis c. Leukocytosis d. Thrombocytopenia - b. Macrocytosis - HIV testing during pregnancy: a. is recommended during pregnancy b. is an "opt-in" approach c. is better performed in the third trimester d. produces many false positives - a. is recommended by ACOG - A patient who is at high risk for skin cancer should: a. examine his skin monthly for changes b. be examined by a dermatologist quarterly c. use emollients regularly d. eat foods high in vitamin C - a. examine his skin monthly for changes - A patient cannot stick his tongue out of his mouth. What cranial nerve is responsible for this movement? a. Cranial Nerve III b. Cranial Nerve VII c. Cranial Nerve X d. Cranial Nerve XII - d. Cranial Nerve XII - Upgrade to remove ads - Only $1/month - AV nicking is identified in a patient with what disease? a. Glaucoma b. Cataracts c. Diabetes d. Hypertension - d. Hypertension - A patient has 2 palpable, tender, left pre-auricular nodes that are about 0.5cm in diameter. What might also be found in this patient? a. Sore throat b. Ulceration on the tongue c. Conjunctivitis d. Ear infection - c. Conjunctivitis - A 40 year-old female patient presents to the clinic with multiple, painful reddened nodules on the anterior surface of both legs. She is concerned. These are probably associated with her history of: a. deep vein thrombosis b. phlebitis c. ulcerative colitis d. alcoholism - c. ulcerative colitis - A patient is in the clinic with a 36 hour history of diarrhea and moderate dehydration. Interventions should include: a. oral rehydration with tea, cola, or Gatorade b. IV rehydration c. oral rehydration with an electrolyte replenishment solution d. resumption of usual fluid intake and solid foods intake - c. oral rehydration with an electrolyte replenishment solution - The nurse practitioner performs a fundoscopic exam on a patient who has recently been diagnosed with hypertension. The nurse practitioner identifies AV nicking. a. This is an incidental finding b. This is indicative of long standing hypertension c. The patient should be screened for diabetes d. The patient should be referred to ophthalmology - b. This is indicative of long standing hypertension - In a patient who is diagnosed with mastoiditis, which of the following is most likely? a. Recent history of pharyngitis b. Fever, cough c. Displaced pinna d. Nuchal rigidity - c. Displaced pinna - The most common risk factor for developing hepatitis B is: a. homosexual activity b. injecting drug use c. heterosexual activity d. body piercings - c. heterosexual activity - A patient who abuses alcohol will probably exhibit: a. elevated alkaline phosphatase b. decreased TSH c. elevated ALT, AST, and GGT d. elevated AST only - c. elevated ALT, AST, and GGT - A healthcare provider ("the HCP") was stuck with a needle from a patient suspected to be infected with HIV ("the patient"). A rapid HIV test was performed and was found to be positive. This means that the: a. healthcare provider has been infected with HIV b. the patient is infected with HIV c. the HIV status of the patient requires further testing d. the HIV status of the healthcare provider requires further testing - c. the HIV status of the patient requires further testing - Which of the following medications does not warrant monitoring of potassium levels? a. Fosinopril b. Candesartan c. Hydrochlorothiazide d. Amlodipine - d. Amlodipine - An unusual symptom associated with acute bronchitis is: a. fever b. cough c. pharyngitis d. purulent sputum - a. fever - A patient presents to your clinic with a painless red eye. Her vision is normal, but her sclera has a blood red area. What is this termed? a. Conjunctivitis b. Acute iritis c. Glaucoma d. Subconjuctival hemorrhage - d. Subconjunctival hemorrhage - What laboratory test could help differentiate acute bronchitis from pneumonia in a patient with a productive cough? a. CBC b. Chest x-ray c. Sputum specimen d. Pulmonary function tests - b. Chest x-ray - A 24 year-old patient presents to your clinic. She states that she has vomited for the last 5 mornings and until early afternoon. She feels better in the evenings. She denies fever. What lab tests should be monitored? a. Progesterone and ketones b. Electrolytes and serum pregnancy c. Electrolytes and hepatitis panel d. Metabolic panel and potassium level - b. Electrolytes and serum pregnancy - A 70 year-old male patient has an elevated MCV with an anemia. His triglycerides are 420. What should be suspected? a. Pernicious anemia b. Folate deficiency c. Alcohol abuse d. Hypertriglyceridemia - c. Alcohol abuse - A 39 year-old has a sudden onset of a red eye. He reports sensitivity to light and the sensation of a foreign body, though his history for a foreign body is negative. He does not wear contact lenses. How should the NP manage this? a. Refer to ophtalmology b. Treat for viral conjunctivitis c. Treat for bacterial conjunctivitis d. Observe for 24 hours if visual acuity is normal - a. Refer to ophthalmology - Which medication is contraindicated for lone use in treating asthma? a. Short-acting bronchodilator b. Long-acting bronchodilator c. Inhaled steroid d. Oral steroid - b. Long-acting bronchodilator - A patient who is 60 years old complains of low back pain for the last 5-6 weeks. She states that the severity is about 4/10 and that she gets no relief from sitting, standing, or lying. The NP should consider: a. sciatica b. ankylosing spondylitis c. disc disease d. systemic illness - d. systemic illness - A short-acting anticholinergic medication can be used alone or in combination with a short-acting beta agonist to manage symptoms of which disease? a. COPD b. Benign prostatic hyperplasia c. Glaucoma d. Tachyarrhythmias - a. COPD - The major difference between varicose veins and arteriosclerosis is the: a. limbs affected b. gender affected c. vessels affected d. degree of pain - c. vessels affected - A 70 year-old African American male complains of pain in his back and trunk. Cardiovascular disease is ruled out. He has a normocytic normochromic anemia with hypercalcemia. A likely diagnosis is: a. multiple myeloma b. lymphoma c. leukemia d. prostate cancer - a. multiple myeloma - Which of the following symptoms is typical of GERD? a. Chest pain b. Hoarseness c. Sore throat d. Pyrosis - d. Pyrosis - A patient with a positive history if a tick bite about 2 weeks ago and erythema migrans has a positive ELISA for Borrelia. The Western blot is positive. How should he be managed? a. He should receive doxycycline for Lyme disease b. He should receive penicillin for syphilis c. He does not have Lyme disease or syphilis d. He needs additional testing to confirm Lyme disease - a. He should receive doxycycline for Lyme disease - Topical 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is used to treat: a. atopic dermatitis b. hepatitis c. thalassemia d. basal cell carcinoma - d. basal cell carcinoma - A 32 year-old patient is a newly diagnosed diabetic. She has developed a sinus infection. Her symptoms have persisted for 10 days. Six weeks ago she was treated with amoxicillin for an upper respiratory infection. It cleared without incident. What should be recommended today? a. Prescribe amoxicillin again b. Prescribe amoxicillin-clavulanate today c. Do not prescribe an antibiotic; a decongestant is indicated only d. Prescribe a decongestant and antihistamine - b. Prescribe amoxicillin-clavulanate today - A 74 year-old male patient has sustained a laceration to his foot. His last tetanus shot was more than 10 years ago. He has completed the primary series. What should be recommended? a. Tetanus toxoid only b. Tetanus and diphtheria only c. His primary series will protect him d. Tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis (Tdap) - b. Tetanus and diphtheria only - The single most effective maintenance therapy for allergic rhinitis is: a. an antihistamine b. a decongestant c. a topical nasal steroid d. a topical antihistamine - c. a topical nasal steroid - A one week-old infant has mucopurulent eye discharge bilaterally. What explains the etiology of the discharge? a. The mother probably has an STD b. The infant likely has a plugged tear duct c. This is bacterial conjunctivitis d. This is viral conjunctivitis - a. The mother probably has an STD - A two year-old with sickle cell anemia (SCA) should receive which immunizations? a. All routine childhood immunizations at an accelerated rate b. All routine childhood immunizations at a decelerated rate c. All routine childhood immunizations at the usual time d. Immunizations should be limited in this group - c. All routine childhood immunizations at the usual time - The rubella vaccine is contraindicated in pregnant women because: a. it can cause rubella in the mother b. it can cause rubella in the infant c. it does not cross the placenta d. neurological toxicity may occur in the mother - b. it can cause rubella in the infant - A 43 year-old patient who has been diagnosed with hepatitis B has the following laboratory values. How should they be interpreted? HCV IgG(-), RIBA (radio immuno blot assay) (-) a. The patient has hepatitis B and hepatitis C b. The patient does not have hepatitis C c. The patient could have hepatitis C d. The results are indeterminate - b. The patient does not have hepatitis C - The risk of HIV transmission is increased: a. when other STDs are present b. in females c. when patients are aware of their HIV status d. in patients with diabetes - a. when other STDs are present - An elderly patient has been diagnosed with shingles on the right lateral aspect of her trunk. It appeared initially yesterday. It is very painful. How should she be managed? a. Treatment with a topical lidocaine patch only b. An oral antiviral agent and NSAIDs c. An oral antiviral agent and pain medication d. An oral antiviral agent, pain medication, and oral steroids - c. An oral antiviral agent and pain medication - A patient calls your office. He states that he just came in from the woods and discovered a tick on his upper arm. He states that he has removed the tick and the area is slightly red. What should be advised? a. No treatment is needed b. He should be prescribed doxycycline c. He needs a topical scrub to prevent Lyme disease d. He should come to the office for a ceftriaxone injection - a. No treatment is needed - A patient with a primary case of scabies was probably infected: a. 1-3 days ago b. 1 week ago c. 2 weeks ago d. 3-4 weeks ago - d. 3-4 weeks ago - An overweight 76 year-old female with a recent onset of diabetes has longstanding hypertension and hyperlipidemia. She has developed atrial fibrillation, The nurse practitioner knows that she will be at risk for: a. an S3 gallop b. CHF c. shortness of breath d. hypothyroidism - b. CHF - A patient is diagnosed with tinea pedis. A microscopic examination of the sample taken from the infected area would likely demonstrate: a. hyphae b. yeast c. spores d. a combination of hyphae and spores - a. hyphae - Which of the following will decrease the risk of acute otitis media in a 6 month old? a. Cigarette smoke exposure b. Breastfeeding c. Sucking on pacifiers d. Vitamin D supplementation - b. Breastfeeding - Which medication listed below can exacerbate the symptoms of GERD? a. Verapamil b. Metformin c. Ferrous sulfate d. Ceftriaxone - a. Verapamil - A nurse practitioner is working in a minor care area of an emergency department. A patient without insurance arrives that has a puncture wound caused by an unknown sharp object in a trash container. A dirty needle is suspected. The nurse practitioner: a. should administer a tetanus injection only since he has no insurance b. should prescribe appropriate medications for HIV exposure even though she knows he can't afford them c. should not mention the possibility of HIV from a dirty needle d. can offer to buy the HIV medications for $50 with her employee discount at the pharmacy next door - b. should prescribe appropriate medications for HIV exposure even though she knows he can't afford them - Classic symptoms of a deep vein thrombosis include: a. swelling, pain, redness b. calf complaints, pain with walking, history of exercise c. swelling, pain, and discoloration in lower extremity d. warmth, edema, and relief of pain with walking - c. swelling, pain, and discoloration in lower extremity - A key component of the approach to a patient who has atopic dermatitis is hydration. Which agent should be avoided? a. Lotions b. Creams c. Thick creams d. Ointments - a. Lotions - A patient was exposed to HIV through sexual intercourse. He should be followed with screening tests to identify seroconversion for: a. 4-6 weeks b. 3-4 months c. about 6 months d. one year - d. one year - A patient who is 52 years old presents to your clinic for an exam. You notice a yellowish plaque on her upper eyelid. It is painless. What should the NP assess? a. Vision in the affected eye b. Sedimentation rate c. Lipid levels d. Liver function studies - c. Lipid levels - The greatest risk of transmitting HIV is during: a. the acute phase b. the time that detectable antibody is present c. high viral load periods d. late infection phase - c. high viral load periods - A three year-old presents with hematuria, petechia, and a platelet count of 50,000 (Normal = 150,000-400,000/ml). The rest of his CBC is normal. He had an upper respiratory infection about 2 weeks ago. On exam today, he is found to have petechiae and bruises. The most likely diagnosis is: a. polycythemia vera b. acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) c. Von Willebrand's disease d. Idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP) - d. Idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP) -low platelets is thrombocytopenia. ITP is most common type in children b/t 2-4yrs old. - A homeless patient presents to the free clinic. She should be screened for disease that are most prevalent in this population. These would be: a. TB, HIV, and hepatitis b. pregnancy and STDs c. urinary tract infection and STDs d. diabetes, HIV, and foot ulcers - a. TB, HIV, and hepatitis - How should a 20 year-old college age student be screened for TB? He presents with cough, night sweats, and weight loss. a. A chest x-ray b. A TB skin test c. A sputum specimen d. Questionnaire about symptoms - b. A TB skin test - Thalassemia minor can be recognized by: a. microcytic, normochromic red cells b. normocytic, normochromic red cells c. microcytic, hypochromic red cells d. normocytic, hyperchromic red cells - c. microcytic, hypochromic red cells - A vegetarian presents to your clinic with iron deficiency anemia. What can the NP suffest to help alleviate this condition? a. Dark green leafy vegetables and dried peas and beans b. Mushrooms, oatmeal, and whole grain breads c. Beets, broccoli, and beef d. Baked potatoes, beets, and broccoli - a. Dark green leafy vegetables and dried peas and beans - Which medication listed below could potentially exacerbate CHF in a susceptible individual? a. Naproxen b. HCTZ c. Lovastatin d. Loratadine - a. Naproxen - A patient has the following laboratory values. What does this mean? Hepatitis A: (-) IgM (-) IgG a. He has hepatitis A b. He has immunity to hepatitis A c. He has no immunity to hepatitis A d. More data is needed - c. He has no immunity to hepatitis A - The pneumococcal immunization in infants has: a. decreased the episodes of acute otitis media due to H. flu b. shifted the pathogenesis to fewer cases of S. pneumoniae c. eradicated acute otitis media due to S. pneumoniae d. improved the prognosis of acute otitis media - b. shifted the pathogenesis to fewer cases of S. pneumoniae - Which group of medications would not be used to treat a patient with CHF? a. Ramipril, aspirin, metoprolol b. Digoxin, furosemide, aspirin c. Fosinopril, HCTZ, verapamil d. Furosemide, enalapril, aspirin - c. Fosinopril, HCTZ, verapamil - A patient has been prescrbed metronidazole for treatment of C. difficile. What should be avoided in this patient? a. Excess fluids b. Vitamin B12 c. Grapefuit juice d. Alcohol - d. Alcohol - A patient with diarrhea is tested for C. difficile. How soon should the enzyme immunoassay (EIA) yield results? a. Within 20 minutes b. About 24 hours c. About 3 days d. Less than one week - b. About 24 hours - A patient has a lower leg wound that appears infected. It is red, warm to touch, and edematous. He had an acute onset of pain, symptoms, and low grade fever. What is this? a. Cellulitis b. Erysipelas c. Impetigo d. An allergic reaction - b. Erysipelas What part of the heart occupies most of the anterior cardiac surface? right ventricle (it also sits behind sternum) The apical impulse (at apex) is identified during palpation of the precordium as the? PMI-point of maximal impulse Blood going from LV through AV to the aorta is called? systole Blood going from LA through MV to the LV is called? diastole S1 is produced by? closure of mitral valve S2 is produced by? closure of aortic valve LV pressure usually corresponds to what? systolic blood pressure S3 in children may arise from? rapid deceleration of the column of blood against the ventricular wall S3 in adults indicates? pathologic change S4 marks? And where do you hear it? atrial contraction, hear it immediately before S1 (it's diastolic) Jugular venous pressure reflects? right atrial pressure What's #1 reason you would have elevated JVP? Heart failure What's #1 cause of right heart failure? left heart failure Poor blood return from the head is manifested as? jugular vein distention Words to describe carotid pulse upstroke? - brisk (normal) - delayed (having hard time getting blood through) - bounding (indicates working too hard) Carotid pulse that is delayed suggests? aortic stenosis Carotid pulse that is bounding suggests? aortic insufficiency What are thrills? humming vibrations What are bruits? whooshing, that indicates turbulent flow in the blood vessels Why would you have a bruit? very abnormal vessels - mechanical vessel replacement - atherosclerosis What are the areas of the cardiac exam? Aortic Pulmonic Tricuspic Mitral Aortic landmark? 2nd ICS, right of sternum Pulmonic landmark? 2nd ICS, left of sternum Triscupic landmark? 4-5th ICS, left of sternum Mitral landmark? 5th ICS, apex of heart, along midclavicular line The PMI may be? (on palpation) - tapping (normal) - sustained - diffuse What could a sustained PMI suggest? LV hypertrophy from HTN or aortic stenosis What could a diffuse PMI suggest? dilated ventricle from congestive heart failure or cardiomyopathy The diaphragm of stethoscope is best for detecting __________ sounds like? - high-pitched sounds - S1, S2, and also S4 and most murmurs The bell of the stethoscope is best for detecting ______ sounds, like? - low-pitched - rumble of mitral stenosis Can you hear closing of tricuspid valve with S1? No, unless you have a SERIOUS problem but it does happen around the same time What is S2 splitting? It is due to aortic and pulmonic valves not closing together When is S2 splitting heard best? inspiration If S1 and S2 splitting are 3 distinct booms, then... that is BAD, not normal Regurgitate or insufficiency means? lack of full valve closure, so little bit of back flow Stenosis means? narrowing What's a normal JVD measurement? 4cm above sternal angle, 9cm above RT Atrium Why do you palpate the precordium? - for heaves or lifts from abnormal ventricular movements (use fingerpads) - thrills or turbulence transmitted to chest wall by a damaged heart valve (use ball of hand) (congestive heart failure could present with all of this) If left ventricle is having to work harder, what could happen? Example? - left ventricular hypertrophy (thickening of muscle) - such as in HTN because it has to work harder What happens ONLY in systole? MR. AS lives ONLY in systole with TRaPS - Mitral regurgitation - Aortic stenosis - Tricuspid regurgitation - Pulmonic stenosis What happens ONLY in diastole? MS. AR lives ONLY in diastole with T.SiPR - Mitral stenosis - Aortic regurgitation - Tricuspid stenosis - Pulmonic regurgitation How do you measure cardiac output? volume of blood ejected from each ventricle during 1 minute, is the product of heart rate and stroke volume What is stroke volume? - the volume of blood ejected with each heartbeat - the difference between end-diastolic volume and end-systolic volume What does preload refer to? the load that stretches the cardiac muscle before contraction (volume of blood in RV at end of diastole constitutes its preload for next beat) If you have decreased LV output or pooling of blood in capillary bed or venous system what does this do to RV preload? decreases it What does myocardial contractility refer to? ability of the cardiac muscle, when given a load, to shorten Myocardial contractility increases when stimulated by action of the ________ and decreases when? - sympathetic nervous system - blood flow or oxygen delivery to myocardium is impaired Afterload refers to? degree of vascular resistance to ventricular contraction The term __________ is now preferred over congestive heart failure because not all patients have? - heart failure - volume overload on initial presentation What factors influence arterial pressure? - left ventricular stroke volume - distensibility of the aorta and the large arteries - peripheral vascular resistance, particularly at the arteriolar level - volume of blood in the arterial system JVP can fall with? loss of blod JVP can increase when? - increase with right or left heart failure - pulmonary HTN - tricuspid stenosis - pericardial compression or tamponade When and why would you hear a midsystolic murmur? - its a click in the middle of lub dub (lub-click-dub) - usually from mitral prolapse-the mitral valve bouncing off the wall When would you hear holosystolic murmur? between S1 and S2 and its purely flat When would you hear late systolic murmur? at the end of systole When would you hear diastolic murmur? between S2 and S1 If you have a patient who is hypovolemic, how will you measure JVD? - lower bed to 0 degrees IF JVP is increased then what elevation do you want patient? - 60 or 90 degrees Increased JVP suggests? - Right-sided congestive heart failure more commonly - Also constrictive pericarditis, tricuspid stenosis, or superior vena cava obstruction In patients with obstructive lung disease, venous pressure may appear elevated on ________ only; the veins collapse during ______. This does not indicate congestive heart failure. - expiration - inspiration Where bed elevation do you start measuring JVP? 30 Degrees a PMI greater than 2.5 cm suggests what? left ventricular hypertrophy seen in HTN and aortic stenosis S3 corresponds to what pathology? abrupt deceleration and inflow across the mitral valve S4 corresponds to what pathology? left ventricular and diastolic stiffness which decreases compliance JVD in hypovolemic patient? very small, may have to lie flat in order to see veins increased JVP associated with what? acute and chronic right and left-sided HF, tricuspid stenosis, chronic PHTN, superior vena cava obstruction, pericardial disease such as tamponade or constrictive pericarditis pats w/ obstructive lung disease JVD? elevated on expiration and veins collapse on inspiration elevated JVD indicates what? increased left ventricular end diastolic pressure and low left ventricular ejection fraction unilateral distension of JVD due to what? local kinking or obstruction tortuous and kinked carotid may produce what? unilateral pulsatile bulge causes of decreased pulsations? decreased SV and factors in the artery such as atherosclerosis small, thready, or weak pulse occurs in... cardiogenic shock bounding pulse in... aortic insufficiency carotid upstroke delayed in... aortic stenosis alternatey loud and soft korotkoff sounds or a sudden doubling of the apparent heart rate as the cuff pressure declines indicates... pulsus alternans paradoxical pulse suggests what...? pericardial tamponade, constrictive pericarditis, most commonly obstructive airway disease causes of bruits... atherosclerotic narrowing of carotid artery, tortuous carotid artery with intraluminal turbulence, external carotid arterial disease, aortic stenosis, hypervascularity of hyperthyroidism, and external compression from thoracic outlet syndrome sounds heard in left lateral decubitus position... low-pitched extra sounds, S3, opening snap, diastolic rumble of mitral stenosis sounds heard sitting leaning forward, after full exhalation... soft decrescendo higher pitched diastolic murmur of aortic insufficiency S1 diminished in... first-degree heart block S2 diminished in... aortic stenosis apical impulse displaced upward and left in... pregnancy and high left diaphragm lateral displacement from cardiomegaly seen in HF, cardiomyopathy, and ischemic heart disease diffuse PMI with diameter > than 3cm seen in left lateral decubitus position indicates... left ventricular enlargement brief middiastolic impulse indicates... S3 impulse just before the systolic apical beat indicates... S4 sustained high amplitude impulse suggests... LVH from pressure overload, if displaced laterally consider volume overload sustained low amplitude impulse in.. dilated cardiomyopathy marked increase in impulse amplitude, no change duration occurs with... chronic volume overload of right ventricle as in atrial septal defect impulse w/ increased amplitude/ duration occurs in... pressure overload of right ventricle as in pulmonary stenosis or HTN palpable S2 at 2nd left ICS suggests... PHTN palpable S2 at 2nd right ICS suggests... HTN, pulsation here suggests dilated or aneurysmal aorta markedly dilated failing heart may have impulse... displaced far to the left most common extra sound in systole midsystolic click of mitral valve prolapse diastolic murmurs indicate.. valvular heart disease systolic murmurs indicate.... valvular disease but can occur when the heart valves are normal midsystolic murmurs arise from... blood flow across semilunar valves pansystolic murmurs arise from.. regurgitant backward flow across the av valves late systolic murmur arises from... mitral valve prolapse and often preceded by systolic click early diastolic murmurs from... regurgitant flow across incompetent semilunar valves middiastolic and presystolic murmur reflect... turbulent flow across the AV valves (mitral and tricuspid stenosis) continuous murmur seen in... patent ductus arteriosus, AV fistulas, dialysis patients presystolic murmur of mitral stenosis shape crescendo early diastolic aortic regurg shape decrescendo midsystolic murmur of aortic stenosis and innocent flow murmurs shape crescendo-decrescendo pansystolic murmur of mitral regurgitation shape plateau murmur murmur best heard in 2nd right ICS originates where? at or near aortic valve only systolic maneuver that increases during the strain phase of valsalva maneuver due to increased outflow tract obstruction hypertrophic cardiomyopathy sporadic or regularly irregular rhythm ventricular premature contractions irregularly irregular rhythm atrial fibrillation holosystolic murmurs mitral regurg, tricuspid regurg, ventricular septal defect (plateau shaped) midsystolic murmurs aortic stenosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, pulmonic stenosis (crescendo-decrescendo shaped) diastolic murmurs aortic regurg (decrescendo), mitral stenosis (nike check) cardiovascular sounds with systolic and diastolic components venous hum, pericardial friction rub, patent ductus arteriosus squatting valsalva: release phase causes... delay of click and murmur shortens decreased mitral valve prolapse decreased intensity of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy murmur increased intensity of aortic stenosis murmur standing valsalva: strain phase causes... click moves earlier in systole and murmur lengthens increased mitral valve prolapse increased intensity of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy murmur decreased intensity of aortic stenosis murmur Search Create Upgrade: free 7-day trial Futurenp139 Ch. 14: Eyes STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity When examining the eye, the nurse notices that the patient's eyelid margins approximate completely. The nurse recognizes that this assessment finding: Is expected During ocular examinations, the nurse keeps in mind that movement of the extraocular muscles is: Stimulated by CNs, III, IV, and VI Nice work! You just studied 39 terms! Now up your study game with Learn mode. Try Learn modeStudy with Flashcards again 1/39 Created by justine_stenberg Terms in this set (39) When examining the eye, the nurse notices that the patient's eyelid margins approximate completely. The nurse recognizes that this assessment finding: Is expected During ocular examinations, the nurse keeps in mind that movement of the extraocular muscles is: Stimulated by CNs, III, IV, and VI The nurse is performing an external eye examination. Which statement regarding the outer layer of the eye is true? The outer layer of the eye is very sensitive to touch When examining a patient's eye, the nurse recalls that stimulation of the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system: Elevates the eyelid and dilates the pupil The nurse is reviewing causes of increased intraocular pressure. Which of these factors determines intraocular pressure? Amount of aqueous produced and resistance to its outflow at the angle of the anterior chamber The nurse is conducting a visual examination. Which of these statements regarding visual pathways and visual fields is true? The image formed on the retina is upside down and reversed from its actual appearance in the outside world Upgrade to remove ads Only $1/month The nurse is testing a patient's visual accommodation, which refers to which action? Pupillary constriction when looking at a near object A patient has a normal pupillary light reflex. The nurse recognizes that this reflex indicates that: Constriction of both pupils occurs in response to bright light A mother asks when her newborn infant's eyesight will be developed. The nurse should reply: "By approximately 3 months of age, infants develop more coordinated eye movements and can fixate on an object." The nurse is reviewing in age-related changes in the eye for a class. Which of these physiologic changes is responsible for presbyopia? Loss of lens elasticity Which of these assessment findings would the nurse expect to see when examining the eyes of a black patient? Dark retinal background A 52-year-old patient describes the presence of occasional floaters or spots moving in front of his eyes. The nurse should: that floaters are usually insignificant and are caused by condensed vitreous fibers The nurse is preparing to assess the visual acuity of a 16-year-old patient. How should the nurse proceed? Use the snellen chart positioned 20 feet away from the patient A patient's vision is recorded 20/30 when the Snellen eye chart is used. The nurse interprets these results to indicate that: The patient can read at 20 feet what a person with normal vision can read at 20 feet A patient is unable to read even the largest letters on the Snellen chart. The nurse should take which action next? Shorten the distance between the patient and the chart until the letters are seen, and record the distance A patient's vision is recorded as 20/80 in each eye. The nurse interprets this finding to mean that the patient: Has poor vision When performing the corneal light reflex assessment, the nurse notes that the light is reflected at 2 O' clock in each eye. The nurse should: Consider this a normal finding The nurse is performing the diagnostic positions test. Normal findings would be which of these results? Parallel movement of both eyes During an assessment of the sclera of a black patient, the nurse would consider which of these an expected finding? Presence of small brown macules on the sclera A 60-year-old man is at the clinic for an eye examination. The nurse suspects that he has ptosis of one eye. How should the nurse check for this? Observe the distance between the palpebral fissuers During an examination of the eye, the nurse would expect what normal finding when assessing the lacrimal apparatus? Absence of drainage from the puncta when pressing against the inner orbital rim When assessing the pupillary light reflex, the nurse should use which technique? Shine a light across the pupil from one side, and observe for direct an consensual pupillary restriction The nurse is assessing a patient's eyes for the accommodation response and would expect to see which normal finding? Convergence of the axes of the eyes In using the opthalmoscope to assess a patient's eyes, the nurse notices a red glow in the patient's pupils. On the basis of this finding, the nurse would: Consider the red glow a normal reflection of the opthalmoscope light off the inner retina The nurse is examining a patient's retina with an opthalmoscope. Which finding is considered normal? Optic disc that is a yellow-orange color A 2-week-old infant can fixate on an object but cannot follow a light or bright toy. The nurse would: Consider this a normal finding The nurse is assessing color vision of a male child. Which statement is correct? The nurse should: Test for color vision once between ages of 4 and 8 years The nurse is performing an eye-screening clinic at a daycare center. When examining a 2-year-old child, the nurse suspects that the child has a "lazy eye" and should: Test for strabismus by performing the corneal light reflex test The nurse is performing an eye assessment on an 80-year-old patient. Which of these findings is considered abnormal? Unequal pupillary constriction in response to light The nurse notices the presence of periorbital edema when performing an eye assessment on a 70-year-old patient. The nurse should: Ask the patient if he or she has a history of heart failure When a light is directed across the iris of a patient's eye from the temporal side, the nurse is assessing for: Presence of shadows, which may indicate glaucoma In a patient who has aniscoria, the nurse would expect to observe: Pupils of unequal size A patient comes to the emergency department after a boxing match, and his left eye is swollen almost shut. He has bruises on his face and neck. He says he is worried because he "can't see well" from his left eye. The physician suspects retinal damage. the nurse recognizes that sings of retinal detachment include: Shadow or diminished vision in one quadrant or one half of the visual field A patient comes into the clinic complaining of pain in her right eye. On examination, the nurse sees a pustule at the lid margin that is painful to touch, red, and swollen. The nurse recognizes that this is a: Hordeolum (stye) A 68-year-old woman is in the eye clinic for a check-up. she tells the nurse that she has been having trouble reading the paper, sewing, and even seeing the faces of her grandchildren. On examination, the nurse notes that she has some loss of central vision but her peripheral vision is normal. These findings suggest that she may have: Macular degeneration A patient comes into the emergency department after an incident at work. A machine blew dust into his eyes, and he wasn't wearing safety glasses. The nurse examines his corneas by shining a light from the side across the cornea. What findings would suggest that he has suffered a corneal abrasion? Shattered look to the light rays reflecting off the cornea An ophthalmic examination reveals papilledema. The nurse is aware that this finding indicates: Increased intracranial pressure During a physical education class, a student is hit in the eye with the end of a baseball bat. When examined in the emergency department, the nurse notices the presence of blood in the anterior chamber of the eye. This finding indicates the presence of: Hyphema During an assessment, the nurse notices than an older adult patient has tears rolling down his face from his left eye. Closer examination shows that the lower lid is loose and rolling outward. The patient complains of his eye feeling "dry and itchy." Which action by the nurse is correct? Assessing for other signs of ectropion A 78-year-old retired seamstress comes to the office for a routine check-up. You obtain an electrocardiogram (ECG) because of her history of hypertension. You diagnose a previous myocardial infarction and ask her if she had any symptoms related to this. Which of the following symptoms would be more common in this patient's age group for an AMI? Chest pain Syncope Pain radiating into the left arm Pain radiating into the jaw Syncope How should you determine whether a murmur is systolic or diastolic? A. Palpate the carotid pulse. B. Palpate the radial pulse. C. Judge the relative length of systole and diastole by auscultation. D. Correlate the murmur with a bedside heart monitor. Palpate the carotid pulse. During a routine physical exam of a 90-year-old woman, a low-pitched diastolic murmur Grade II/VI is auscultated. It is located on the fifth intercostal space on the left side of the midclavicular line. Which of the following is the correct diagnosis? A. Aortic regurgitation B. Mitral stenosis C. Mitral regurgitation D. Tricuspid regurgitation Mitral stenosis Mrs. Adams would like to begin an exercise program and was told to exercise as intensely as necessary to obtain a heart rate of 60% or greater of her maximum heart rate. She is fifty-two years old. What heart rate should she achieve? A. 80 B. 100 C. 120 D. 140 100 You examine a 24-year-old woman with mitral valve prolapse (MVP). Her physical examination findings may also include: A. pectus excavatum. B. obesity. C. petite stature. D. hyperextensible joints. pectus excavatum In performing a cardiac examination in a person with MVP, you expect to find: . A. an early to mid systolic, crescendo-decrescendo murmur. B. a pansystolic murmur. C. a low-pitched, diastolic rumble. D. a mid to late systolic murmur. a mid to late systolic murmur. Upgrade to remove ads Only $1/month Additional findings in MVP include: a. Opening snap B. mid-systolic click C. a paradoxical splitting of the second heart sound (S2). D. a fourth heart sound (S4). mid-systolic click what is S1? mitral and tricuspid valve closure What is S2? Aortic and pulmonic valve closure In evaluating the person with aortic stenosis, the NP anticipates finding 12-lead ECG changes consistent with: A. right bundle branch block. B. extreme axis deviation. C. right atrial enlargement. D. left ventricular hypertrophy. left ventricular hypertrophy. Of the following patients, who is in greatest need of endocarditis prophylaxis when planning dental work? A. a 22-year-old woman with MVP with trace mitral regurgitation noted on echocardiogram B. a 54-year-old woman with a prosthetic aortic valve C. a 66-year-old man with cardiomyopathy D. a 58-year-old woman who had a three-vessel coronary artery bypass graft with drug-eluting stents 1 year ago a 54-year-old woman with a prosthetic aortic valve Of the following people, who has no significant increased risk for developing bacterial endocarditis? A. a 43-year-old woman with a bicuspid aortic valve B. a 55-year-old man who was diagnosed with a Still's murmur during childhood C. a 45-year-old woman with a history of endocarditis D. a 75-year-old man with dilated cardiomyopathy a 55-year-old man who was diagnosed with a Still's murmur during childhood You are examining an elderly woman and find a grade 3/6 crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur with radiation to the neck. This is most likely caused by: A. aortic stenosis B. aortic regurgitation. C. anemia. D. mitral stenosis. aortic stenosis Aortic stenosis in a 15-year-old is most likely: A. a sequela of rheumatic fever. B. a result of a congenital defect. C. calcific in nature. D. found with atrial septal defect. a result of a congenital defect You are examining an 18-year-old man who is seeking a sports clearance physical examination. You note a mid-systolic murmur that gets louder when he stands. This may represent: A. aortic stenosis. B. hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. C. a physiologic murmur. hypertrophic cardiomyopathy According to recommendations of the American Heart Association (AHA), which of the following antibiotics should be used for endocarditis prophylaxis in patients who are allergic to penicillin? A. erythromycin B. dicloxacillin C. azithromycin D. ofloxacin azithromycin The S4 heart sound has which of the following characteristics? A. After it is initially noted, it is a permanent finding. B. It is noted in presence of poorly controlled hypertension. C. It is heard best in early diastole. D. It is a high-pitched sound best heard with the diaphragm of the stethoscope. It is noted in presence of poorly controlled hypertension. You examine an 82-year-old woman who has a history of heart failure (HF). She is in the office because of increasing shortness of breath. When auscultating her heart, you note a tachycardia with a rate of 104 bpm and an extra heart sound early in diastole. This sound most likely represents: A. summation gallop. B. S3. C. opening snap. D. S4. S3. Mitral valve Left side, 5th ICS at the costochondral junction Pulmonic valve Left side, between 2nd and 4th ICS just above the sternum Aortic valve Left side, 4th ICS just above the costochondral junction Tricuspid valve Right side, 4-5th ICS near the costochondral junction Point of Maximum Impulse 5th IC space, 7-9cm left of midsternal You are evaluating a patient who has rheumatic heart disease. When assessing her for mitral stenosis, you auscultate the heart, anticipating finding the following murmur: A. systolic with wide radiation over the precordium B. localized diastolic with little radiation C. diastolic with radiation to the neck D. systolic with radiation to the axilla [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 119 pages
Instant download

Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 11, 2021
Number of pages
119
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 11, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
39










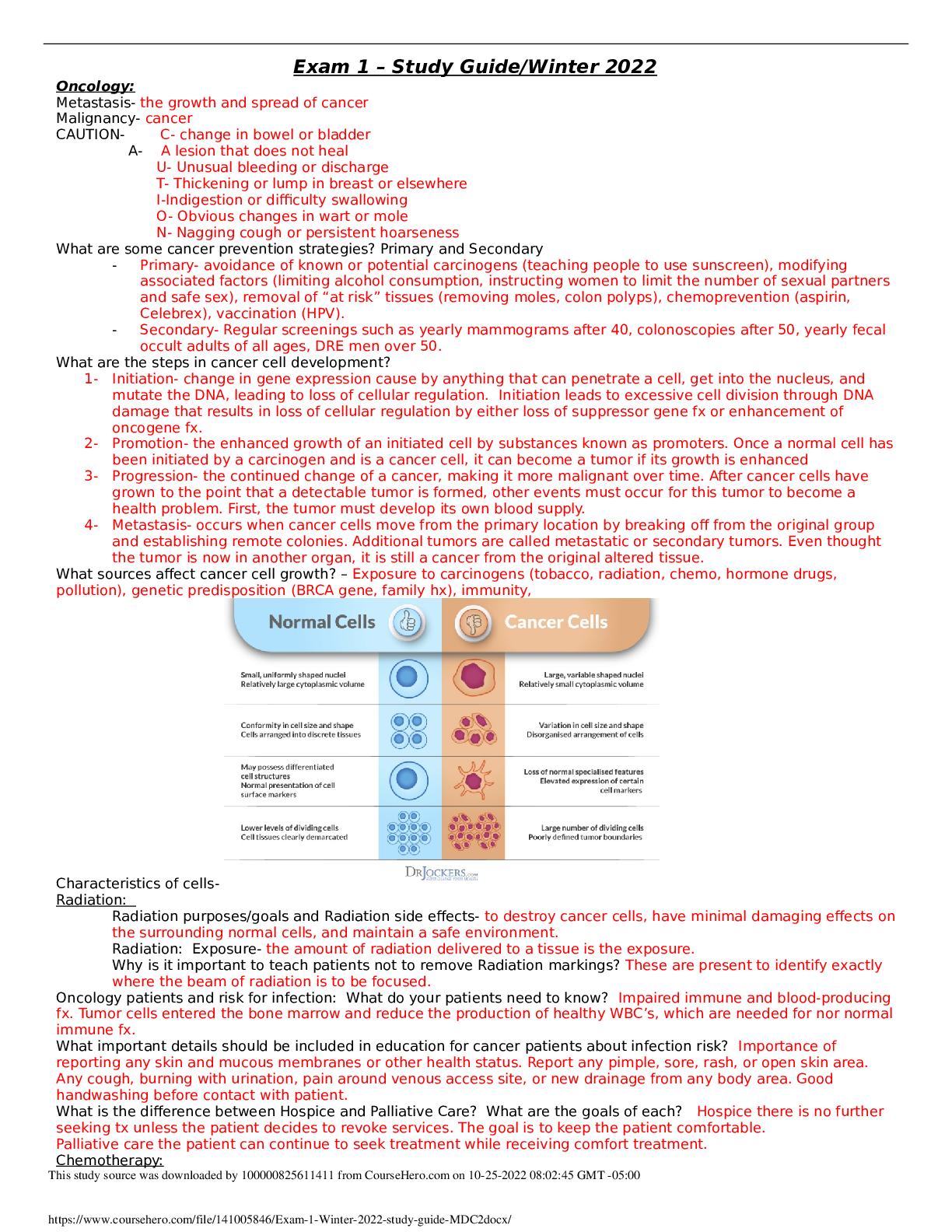




_2nd_E_Completed.png)









.png)









