Pharmacology > STUDY GUIDE > MDC1/NUR2356 - Fundamentals Exam 1 (All)
MDC1/NUR2356 - Fundamentals Exam 1
Document Content and Description Below
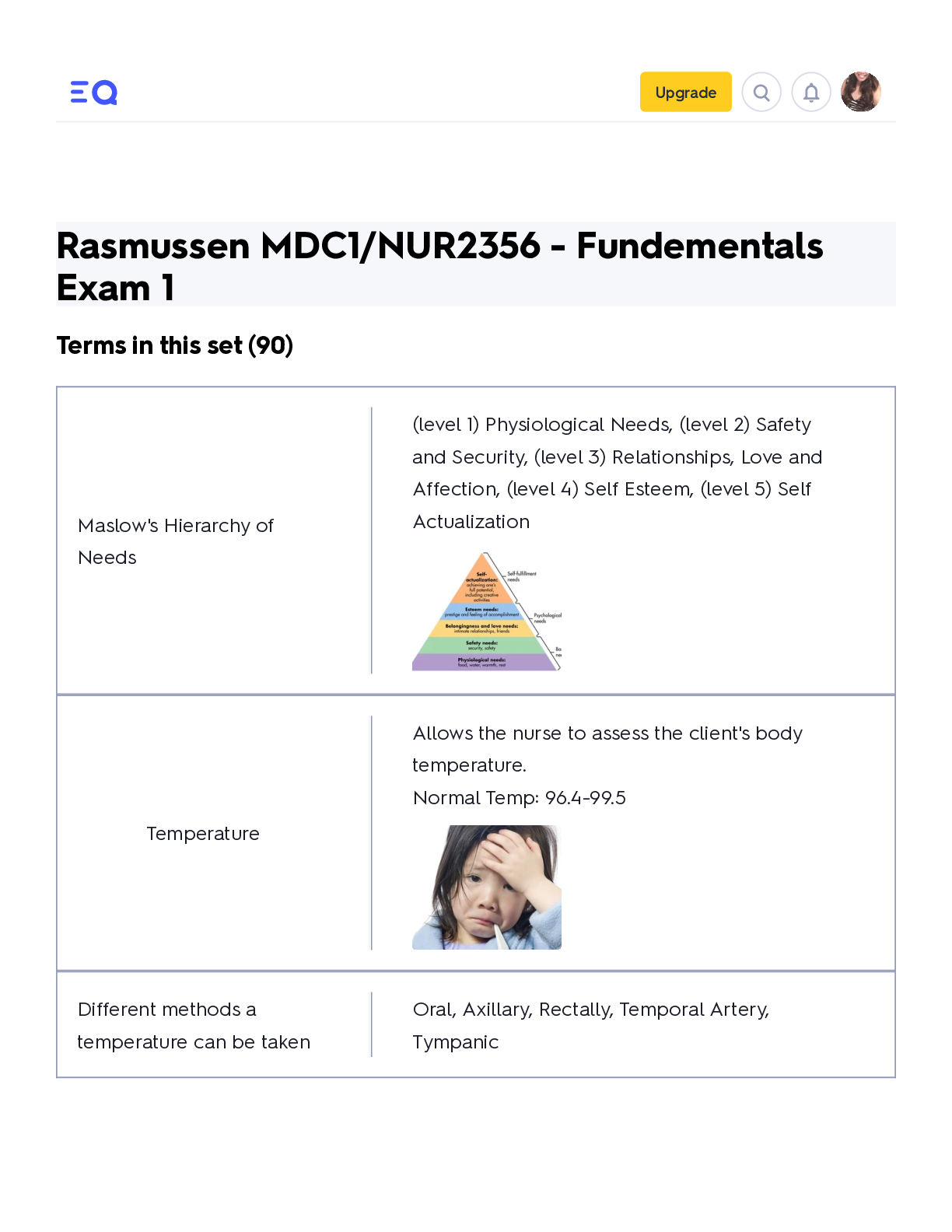
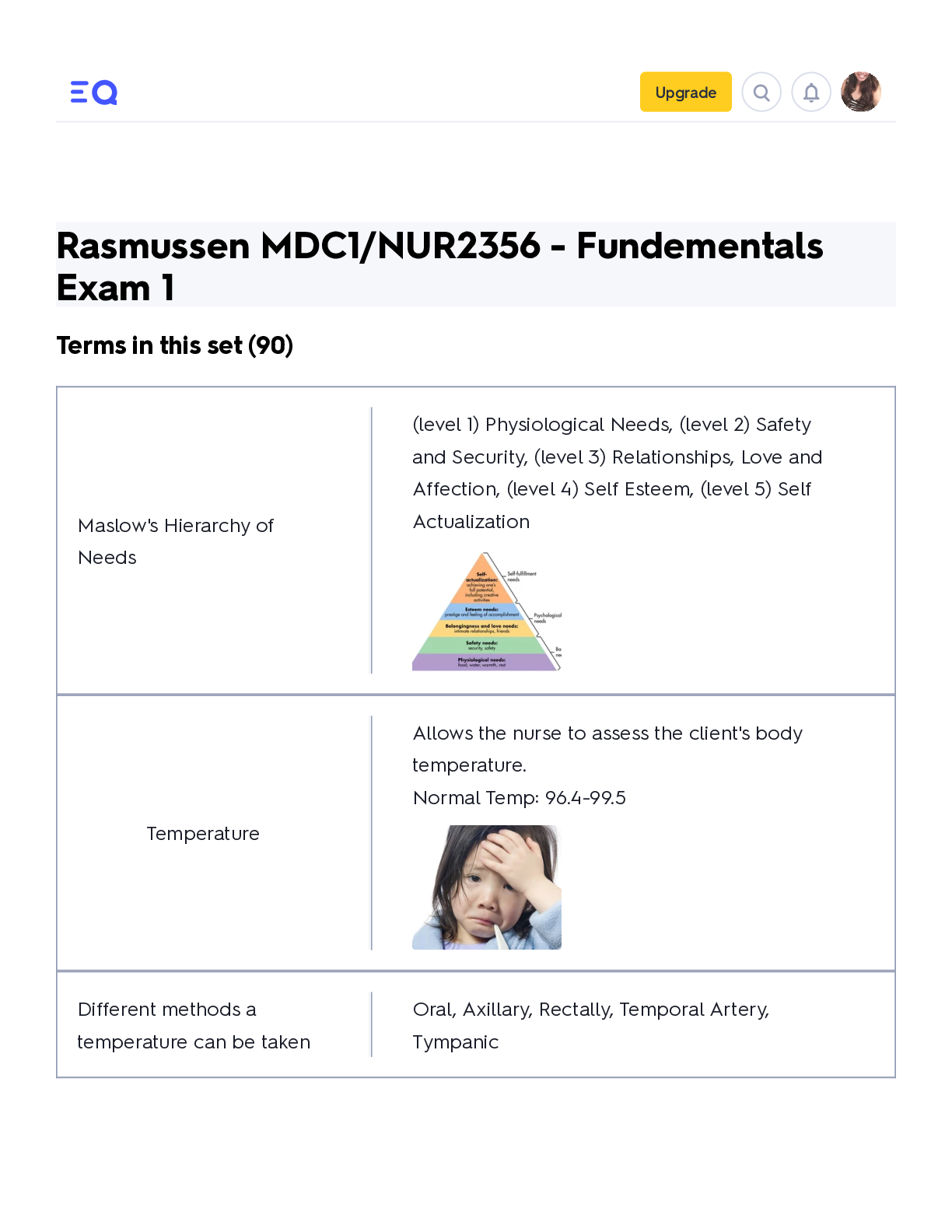
MDC1/NUR2356 - Fundamentals Exam 1 Upgrade Rasmussen MDC1/NUR2356 - Fundementals Exam 1 Terms in this set (90) Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs (level 1) Physiological Needs, (level 2) Safety and ... Security, (level 3) Relationships, Love and Affection, (level 4) Self Esteem, (level 5) Self Actualization Temperature Allows the nurse to assess the client's body temperature. Normal Temp: 96.4-99.5 Different methods a temperature can be taken Oral, Axillary, Rectally, Temporal Artery, TympanicHypothermia abnormally low body temperature Hyperthermia Abnormally high body temperature What does the Pulse allow the nurse to assess? It allows us to assess how adequate the heart is pumping blood through the body Normal Pulse: 60-100 bpm Where are the different Pulse points? Carotid, Radial, Femoral, Popliteal, Posterior Tibial, Dorsalis Pedis What does the Blood Pressure allow the nurse to assess? It allows the nurse to assess the force required to pump blood through the body Normal BP: 120/80Hypotension lower than normal blood pressure Hypertension higher than normal blood pressure What do Respirations allow the nurse to assess? It allows the nurse to assess the effort of breathing Normal Respirations: 12-20 Pulse Oximetry (SpO2) Measures the oxygen level in the blood Hypoxia Low oxygen saturation of the body, not enough oxygen in the bloodPain Assessment Provocative or Palliative (what makes it worse/better) Quality or Quantity (For example, is the pain sharp or dull, throbbing?) Region or Radiation(Location) Severity Scale (Numeric pain intensity scale) Timing (Onset) Understand Patient's Perception (Activities of Daily Living assessment) What are the major energy sources of Nutrition for the body? Carbohydrates, Fats and Proteins What are the different forms of Nutrition? Oral: Intake by mouth Enteral: Intake through MG Tube, Peg Tube, Jejunostomy Tube, G-Tube Parenteral: Taking nutrition through a centrally inserted IV line such as a PICC or Central Venous Access DeviceCommunication A process through which you send messages to and receive messages from others. Sharing of information between 2 individuals. Communication Strategies Empathy: A desire to understand and be sensitive to the feelings and situation of another person. Put yourself in the client's place mentally and emotionally. Respect: Allow the client to make choices. Be flexible when meeting the needs of each client. Genuineness: Respond honestly. Do not try to guess the answer. Let client know you will need assistance in answering a question you do not know the answer to. Concreteness: Provide your answers in specific and understandable terms. Confrontation: Request the client express his or her thoughts clearly so you can understand the meaning of the communication.Forms of Communication Verbal: Written or spoken word Non-Verbal: Body language that accompanied by the spoken word Intrapersonal: Self talk Interpersonal: Between 2 or more people with the goal of exchanging messages. Group: Organizational communication What should staff know about Fire Response Procedures? Location of Exits, Alarms, Fire Extinguishers, and Oxygen turn-off valves Do not block fire doors Know your evacuation plan! RACE acronym for fire R= Rescue A= Activate alarm C= Contain fire E= Extinguish PASS acronym Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep What are the 3 Classes of Fire Extinguishers? Class A: paper, wood, upholstery, rags, other types of trash fires Class B: flammable liquids, and gas fires Class C: electrical fires Older Adult - Increased Risk for Falls CAUSES: Decrease in strength Impaired Mobility and Balance Endurance limitations combined w/decreased sensory perceptionOther clients with increased risk for falls 1) Those with decreased visual acuity 2) Generalized weakness 3) Gait and balance problems (CP, Injury, MS) and cognitive dysfunctions 4) Side effects of medication (orthostatic hypotension, drowsiness) GENERAL MEASURES to PREVENT FALLS -be sure the client knows how to use call light, it is within reach, and encourage its use -respond to call lights in a timely manner -orient client to setting and assistive devices -place clients at risk for falls near the nursing station -ensure bedside table and frequently used items are within the client's reach -maintain the bed in the low position -for clients who are sedated, unconscious, or otherwise compromised, bed rails are kept up and the bed kept in a low position -avoid the use of full side bed rails for clients who get out of bed or attempt to get out of bed without assistance -provide nonskid footwear -keep the floor free of clutter with a clear path to the bathroom -keep assistive devices nearby after validation of safe use by client and family -educate client and family/caregivers on identified risks and plan of care -lock wheels on beds, wheelchairs, and carts -use chair or bed sensors for clients at risk for getting up unattended Rasmussen MDC1/NUR… StudyBasic First Aid - Bleeding Apply direct pressure to wound, do NOT remove impaled objects Basic First Aid - Fractures and Splinting Assess the site for swelling, deformity, and skin integrity Assess temp, distal pulses, and mobility Apply a splint to immobilize the fx and cover open areas with a sterile cloth Reassess neurovascular status after splinting Basic First Aid - Sprains RICE Acronym: REFRAIN from weight bearing/REST, ICE applied to to decrease inflammation, COMPRESSION dressing to minimize swelling, ELEVATE the affected limb Basic First Aid - Heat Stroke Manifestations: Hot, dry skin, hypotension, tachypnea, tachycardia, anxiety, confusion, seizure, and coma Rapid Cooling must be achieved: Remove client clothes, ice packs placed on major arteries(armpit, chest, groin, neck), immerse in cold water bath, wet the client's body and fan with rapid air Basic First Aid - Frostnip and Frostbite Frostnip can be treated by warming Frostbite presents as white, waxy areas on exposed skin, and tissue injury occurs; May be FULL or PARTIAL thickness, warm area 100.4 - 105.8 degrees, give pain meds, administer tetanus vaccineBasic First Aid - Burns Causes: Electrical current, chemicals, radiation, and flames Remove the agent and smother flames Cover the client and maintain NPO Elevate the extremity if no fx present Estimate surface area of burn Administer fluids and tetanus toxoid Basic First Aid - Altitude Illness Clients may become hypoxic S/S:Throbbing headache, N/V, Dyspnea, Anorexia Nursing Interventions: Administer O2, Descend to lower altitude, provide pharacological therapy such as steroids or diuretics if indicated *Altitude sickness can progress to cerebral and pulmonary edema! Infant Safety- Suffocation Prevention Place infant on back to rest Keep plastic bags out of reach Crib mattress fits snug, slats are no more than 2 3/8 inches apart Never leave alone in the bathtub Remove toys/mobiles from crib when an infant begins to push up Fence swimming pools and use a locked gate Begin swimming lessons Teach Caregivers CPR and Heimlich maneuver Keep toilet lids down and bathroom doors closedInfant Burn Prevention Test the temperature of formula and bath water Place pots on back burner and turn handle away from front of stove Supervise the use of faucets Keep matches and lighters out of reach Pre-school and School Age Children - Motor Vehicle Safety Booster seat for children who are less than 4 feet 9 inches tall and weigh less than 40lb If car has airbag, children under 12 in back seat Use seat belts properly Use protective equipment when playing sports, riding a bike, or riding as a passenger on a bike Supervise and teach safe use of equipment Teach child to play in safe areas Teach child safety rules of the road Teach child what to do if approached by a stranger Begin sex education for school-aged children Infant Motor Vehicle Safety Place infants and toddlers in rear facing car seat until 2 years of age, or until they exceed height and weight of the car seat. They can then sit in fwd facing car seat. Use car seat with 5 Point Harness for infants and children All car seats should be federally approved and be place in the back seatPre-School and School Age - Firearm Safety Keep firearms unloaded, locked up, and out of reach Teach to never touch a gun or stay at a friend's house where a gun is accessible Store bullets in a different location from guns Pre-School and School Age - Poison Safety Teach child about the hazards of alcohol, cigarettes, and prescription, non-prescription, and illegal drugs Keep potentially dangerous substances out of reach Fall Prevention in the Home Remove items that could cause client to trip, such as throw rugs and loose carpets Place electrical cords and extensions against the wall and behind furniture Monitor gait and balance and provide aids as needed Make sure that steps and sidewalks are in good repair Place grab bars near toilet and in the tub or shower Use nonskid mat in the tub or shower Place shower chair in the shower and bedside commode if needed Make sure that lighting is adequate both inside and outside of the homeSpirituality Can play an important role in clients' abilities to achieve balance in life, to maintain health, to seek health care, and to deal with illness and injury. Hope, Faith, and Transcendence are integral components of spirituality Spiritual Distress A challenge to belief systems or spiritual wellbeing. It often arises as a result of catastrophic events. When faced with health care issues such as acute, chronic, or life-limiting illness, clients often find ways to cope through the use of spiritual practices. Clients who begin to question their belief systems and are unable to find support from those belief systems may experience spiritual distress.Culturally Responsive Nursing Care Delivery of care that transcends cultural boundaries and considers a client's culture as it affects health, illness, and lifestyle. Communication, Dietary preferences, and dress are influenced by culture. Culturally sensitive means nurse is knowledgeable about the cultures in which they practice. Culturally appropriate means the nurse applies the client's culture to their care delivery. Culturally competent means nurses understand and address the entire cultural context of each client within the realm of the care they deliver. Improves communication, fosters mutual respect, promotes sensitive and effective care, and increases the likelihood of client to follow the tx plan Encourage clients in the decision-making for their care Understand your own culture and any biases you might have Accommodate each client's cultural beliefsBarriers to Culturally Responsive Nursing Care Language, communication, and perception of time Culturally inappropriate tests and tools that lead to misdiagnosis Ethnic variations in drug metabolism related to genetics Ethnocentrism is the belief that one's culture is superior to others. Bathing Client Purpose: To cleanse the body, relax it, and enhance healing. Perform a skin assessment and wound care at this time Bathe clients whose health problems have exhausted them or limited their mobility. Give a Complete Bath to clients who can tolerate it and whose hygiene needs warrant it. Partial Baths are useful for clients who can perform part of the bath independently. Oral Hygeine Helps to decrease the risk of infection for clients in LTC facilities especially for the transmission of pathogens that can cause pneumonia.Foot Care Prevents skin breakdown, pain, and infection. Extremely important for clients with diabetes mellitus, and a qualified professional must perform it. Instruct clients at risk for injury to: Inspect feet daily Dry feet thoroughly Apply moisturizer to feet, NOT between toes Avoid OTC products with alcohol or strong chemicals Wear clean, cotton socks Check shoes for objects, rough seams, or edges that may cause injury Cut nails straight across and use emery board to file Avoid self-treating Do not apply heat unless prescribed Contact provider if signs of infection/inflammation appearPerineal Care Helps to maintain skin integrity, relieve discomfort, and prevent transmission of microorganisms (catheter care). Shaving Safety Clients prone to bleeding should use electric razor Apply soap or shaving cream to warm, moist skin Move the razor over the skin in the direction of hair growth using long strokes on large areas of the face and short strokes around the chin and lips. Communicate with clients about personal shaving preferences. Narcolepsy A sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks. The sufferer may lapse directly into REM sleep, often at inopportune times.Factors that interfere with Sleep Illness Current life events Emotional stress or mental illness Diet Exercise Fatigue Sleep environment Medications Positioning (Mobility/Immobility) techniques to reduce the compression of leg veins Clients should avoid the following: Crossing legs Sitting for long periods Wearing restrictive clothing on the lower extremities Putting pillows behind the knees Massaging legs Non-verbal signs of Pain HR BPM BP BS Groaning Grimacing Guarding What is pain? Whatever the patient says it is, and it exists whenever the patient says it does. Client's report is the most reliable diagnostic measure of painPain Meds: Types Analgesics are the mainstay for relieving pain. 3 Classes of Analgesics: Non-opioids, opioids, and adjuvant Non-opioid analgesics Mild to Moderate Pain Acetaminophen NSAIDs Opioid Analgesics Synthetic pain-relieving substances that were originally derived from the opium poppy, Naturally occurring opium derivatives are called opiates. Moderate to Severe Pain Drug names:Morphine sulfate, Fentanyl, Codeine Adjuvant analgesic drugs Drugs that are added as a second drug for combined therapy with a primary drug and may have additive or independent analgesic properties, or both PCA Patient-controlled anesthesia is a medication delivery system that allows clients to selfadminister safe doses of opioids Pain Management Complications Undertreatment of Pain can lead to increased anxiety with acute pain, and depression with chronic pain. *Assess the client's pain frequently Sedation, respiratory depression, and coma can occur d/t overdosing.What are the different TYPES OF PAIN? Cutaneous: Pain that exists at the level of the skin Visceral: Deep, Internal pain Deep Somatic: Originates from ligaments, tendons, nerves, blood vessels, and bones; fx or sprain Radiating: Begins at 'origin', but extends to another location Phantom: Perceived pain from the amputation of a limb Neuropathic: Results from injury of one or more nerves Acute: Sudden onset Chronic: Pain lasting longer than 6 months, or interferes with ADLs Idiopathic: Unknown cause Natural Products and Herbal Remedies Aloe: Wound healing Chamomile: Anti-Inflammatory, Calming Echinacea: Enhances immunity Garlic: Inhibits platelet aggregation Ginger: Antiemetic Ginkgo Biloba: Improves memory Ginseng: Increases physical endurance Valerian: Promotes sleep, reduces anxiety What is COMPLIMENTARY THERAPY? Treatment approaches used IN ADDITION to or to enhance conventional medical careCOMPLIMENTARY THERAPY EXAMPLES Guided imagery/visualization, Healing Intention, Breathing, Humor, Meditation, Simple Touch, Music/Art, Therapeutic Communication, Relaxation Techniques, Elevation, Massage, Pet Therapy What is Alternative Therapy? Therapy used instead of conventional treatment What are some Urinary Elimination Complications? CAUTI: Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection UTI Decreases Output d/t BPH, Fluid retention, Bladder or Kidney issues Patient Education about Urinary Elimination Maintain regular bowel movements Try to empty bladder completely with each void Keep an incontinence diary Perm Kegel exercises Perform bladder compression techniques Avoid caffeine and alcohol consumption bc they can irritate the bladder and increase diuresis and the urge to urinate Adverse effects of meds Conduct vaginal cone therapy to strengthen pelvic muscles (for stress incontinence)What is Culture? The body of customary beliefs, material traits, and social forms that constitute the distinct tradition of a group of people. Can be adopted by Assimilation What is Ethnicity? Identity with a group of people who share the cultural traditions of a particular homeland Refers to groups whose members share a common social and cultural heritage that is passed down from generation to generation Steroetype Over generalized belief that a certain trait, behavior, or attitude, characterizes all members of some identifiable groupLanguage barriers Foreign languages, Street talk, Jargon, Dialects, Regionalisms Native Americans Family bonding is important. Acceptance of nature, tradition, sharing, belief of a spiritual power, respect of elders. Health means living in harmony with nature, body is treated with respect, illness may be associated with disharmony or evil spirits. Rituals and ceremonies, chanting, purification, meditation and herbs are common practiceAsian and Pacific Islanders Health is a state of physical and spiritual harmony. Illness is disharmony of basic principles: Yin/Yang Extended family, respect for elders, group orientation, self respect and self control, love of the land, conformity, and subordination to authority Black and African American Family bonding, Matriarch (Women in charge), Spiritual persons. Health is Mind, Body, and Spirit working together Prayer, laying of hands, magic rituals, voodoo, and herbs are practiced in this ethnic groupHispanic or Latino Family oriented, Faith and Spirituality are important, Health is a gift from God, Illness is body imbalance Prayer, belief in miracles, wearing of religious metals or amulets, religious relics in the home, herbs and spices used, Hot and Cold therapy used Verbal Communication Communication that uses written or spoken words to send a message Non-Verbal Communication Exchange of messaging without the use of words. Facial Expression, Posture, Gait, Personal appearance, Gestures, and TouchPersonal space refers to The distance we like to maintain between ourselves and other people while communicating. Enhancing Therapeutic Communication Listen actively Establish trust Be assertive Restate, clarify, and validate message Interpret body language Share your observations to clarify Use open-ended questions Use silence Summarize the conversation Barriers to Therapeutic Communication -Too many questions -Closed-ended questions -Asking "Why?" -Changing the subject abruptly -Failing to listen -Failing to explore issues in detail -Expressing approval or disapproval -Offering advice -Giving false reassurance -Stereotyping -Using patronizing languageNever Events Preventable errors, which may include falls, urinary tract infections from improper use of catheters, and pressure ulcers Incident Reporting -Tell what happened (state the time and condition of resident) -Tell how resident tolerated the incident -State facts only -Do not write anything in the incident report on the medical record (they are confidential) -Describe action taken to give care -Include suggestions for change OSHA stands for Occupational Safety and Health Administration Ensures the safety of workers Nation Patient Safety Goals JOINT COMMISION: Bringing pt safety issues into the spotlight so that we can fix themTeaching Speak Up to patients S - Speak up if you have questions/concerns P - Pay attention to care you are receiving E - Educate yourself about your diagnosis, medical tests A - Ask friend or family to be your advocate K - Know your medications U - Use a medical facility that has been approved by Joint Commission P - Participate in all decisions about your care What are the steps in the Nursing Process? ADPIE A=assessment D=diagnosis P=planning I=implementation E=evaluation Vital Signs Ranges BP 90/60 to 120/80 Pulse - 60-100 bpm Respiratory - 12-20 per min Temperature - 96.4 - 99.5 *Rectal is +1 more than oral, and Axillary is -1 less than oral O2 saturation = 95%-100% Pain - 1-10 [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 28 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 08, 2022
Number of pages
28
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 08, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
40















_2nd_E_Completed.png)











.png)







