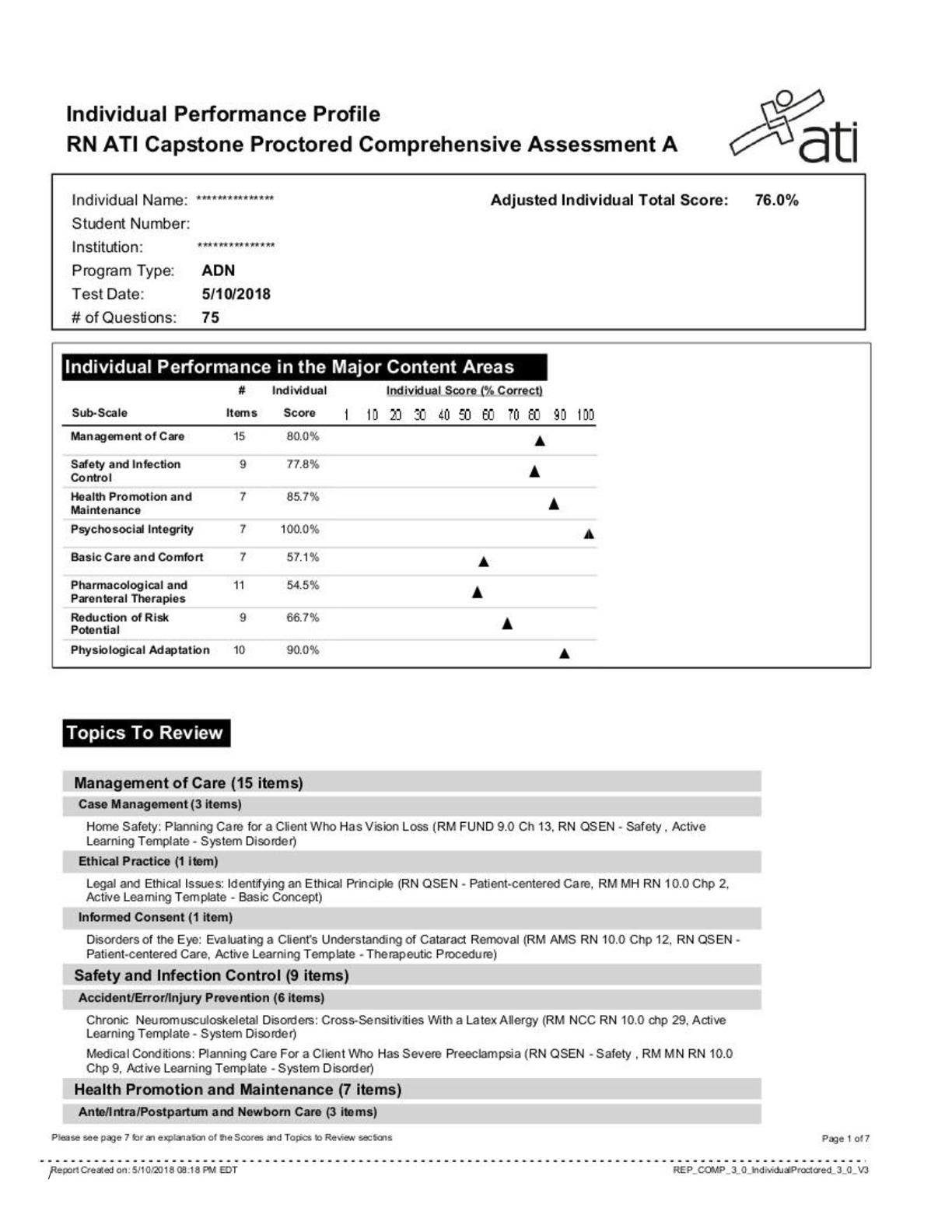
NSG 5003 week_5_midterm_questions. Graded A
Document Content and Description Below
NSG 5003 week_5_midterm_questions Question 1 (2 points) In examination of the nose, the clinician observes gray, pale mucous membranes with clear, serous discharge. This is most likely indicati... ve of: Question 1 options: a) Bacterial sinusitis b) Allergic rhinitis c) Drug abuse d) Skull fracture Save Question 2 (2 points) Your patient complains of a feeling of heaviness in the lower legs daily. You note varicosities, edema, and dusky color of both ankles and feet. Which of the following is the most likely cause for these symptoms? Question 2 options: a) Femoral vein thrombosis b) Femoral artery thrombus c) Venous insufficiency d) Musculoskeletal injury Save Question 3 (2 points) Which of the following is the most important question to ask during cardiovascular health history? Question 3 options: a) Number of offspring b) Last physical exam c) Sudden death of a family member d) Use of caffeine Save Question 4 (2 points) Rheumatic heart disease is a complication that can arise from which type of infection? Question 4 options: a) Epstein-Barr virus b) Diphtheria c) Group A beta hemolytic streptococcus d) Streptococcus pneumoniae Save Question 5 (2 points) A cough is described as chronic if it has been present for: Question 5 options: a) 2 weeks or more b) 8 weeks or more c) 3 months or more d) 6 months or more Save Question 6 (2 points) A key symptom of ischemic heart disease is chest pain. However, angina equivalents may include exertional dyspnea. Angina equivalents are important because: Question 6 options: a) Women with ischemic heart disease many times do not present with chest pain b) Some patients may have no symptoms or atypical symptoms; diagnosis may only be made at the time of an actual myocardial infarction c) Elderly patients have the most severe symptoms d) A & B only Save Question 7 (2 points) A woman with an X-linked dominant disorder will: Question 7 options: a) Not be affected by the disorder herself b) Transmit the disorder to 50% of her offspring (male or female) c) Not transmit the disorder to her daughters d) Transmit the disorder to only her daughters Save Question 8 (2 points) A 55-year-old post-menopausal woman with a history of hypertension complains of jaw pain on heavy exertion. There were no complaints of chest pain. Her ECG indicates normal sinus rhythm without ST segment abnormalities. Your plan may include: Question 8 options: a) Echocardiogram b) Exercise stress test c) Cardiac catheterization d) Myocardial perfusion imaging Save Question 9 (2 points) The aging process causes what normal physiological changes in the heart? Question 9 options: a) The heart valve thickens and becomes rigid, secondary to fibrosis and sclerosis b) Cardiology occurs along with prolapse of the mitral valve and regurgitation c) Dilation of the right ventricle occurs with sclerosis of pulmonic and tricuspid valves d) Hypertrophy of the right ventricle Save Question 10 (2 points) It is important to not dilate the eye if ____ is suspected Question 10 options: a) Cataract b) Macular degeneration c) Acute closed-angle glaucoma d) Chronic open-angle glaucoma Save Question 11 (2 points) Your patient is a 78-year-old female with a smoking history of 120-pack years. She complains of hoarseness that has developed over the last few months. It is important to exclude the possibility of: Question 11 options: a) Thrush b) Laryngeal cancer c) Carotidynia d) Thyroiditis Save Question 12 (2 points) In examining the mouth of an older adult with a history of smoking, the nurse practitioner finds a suspicious oral lesion. The patient has been referred for a biopsy to be sent for pathology. Which is the most common oral precancerous lesion? Question 12 options: a) Fictional keratosis b) Keratoacanthoma c) Lichen planus d) Leukoplakia Save Question 13 (2 points) A 20-year-old engineering student complains of episodes of abdominal discomfort, bloating, and episodes of diarrhea. The symptoms usually occur after eating, and pain is frequently relieved with bowel movement. She is on a “celiac diet” and the episodic symptoms persist. Physical examination and diagnostic tests are negative. Colonoscopy is negative for any abnormalities. This is a history and physical consistent with: Question 13 options: a) Inflammatory bowel disease b) Irritable bowel syndrome c) Giardiasis d) Norovirus gastroenteritis Save Question 14 (2 points) The most common cause of eye redness is: Question 14 options: a) Conjunctivitis b) Acute glaucoma c) Head trauma d) Corneal abrasion Save Question 15 (2 points) In AR disorders, carriers have: Question 15 options: a) Two mutated genes; one from each parent that cause disease b) A mutation on a sex chromosome that causes a disease c) A single gene mutation that causes the disease d) One copy of a gene mutation but not the disease Save Question 16 (2 points) According to the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA): Question 16 options: a) Nurse Practitioners (NPs) should keep all genetic information of patients confidential b) NPs must obtain informed consent prior to genetic testing of all patients c) Employers cannot inquire about an employee’s genetic information d) All of the above Save Question 17 (2 points) Aortic regurgitation requires medical treatment for early signs of CHF with: Question 17 options: a) Beta blockers b) ACE inhibitors c) Surgery d) Hospitalization Save Question 18 (2 points) Which of the following is the most common cause of heartburn-type epigastric pain? Question 18 options: a) Decreased lower esophageal sphincter tone b) Helicobacter pylori infection of stomach c) Esophageal spasm d) Peptic ulcer disease Save Question 19 (2 points) The best way to diagnose structural heart disease/dysfunction non-invasively is: Question 19 options: a) Chest X-ray b) EKG c) Echocardiogram d) Heart catheterization Save Question 20 (2 points) Essential parts of a health history include all of the following except: Question 20 options: a) Chief complaint b) History of the present illness c) Current vital signs d) All of the above are essential history components Save Question 21 (2 points) Men have faster and more efficient biotransformation of drugs and this is thought to be due to: Answer is Testosterone (one option is repeated) Question 21 options: a) Less obesity rates than women b) Prostate enlargement c) Prostate enlargement d) Less estrogen than women Save Question 22 (2 points) The main focus of treatment of patients with ACD is: Question 22 options: a) Replenishing iron stores b) Providing for adequate nutrition high in iron c) Management of the underlying disorder d) Administration of monthly vitamin B12 injections Save Question 23 (2 points) A 72-year-old woman and her husband are on a cross-country driving vacation. After a long day of driving, they stop for dinner. Midway through the meal, the woman becomes very short of breath, with chest pain and a feeling of panic. Which of the following problems is most likely? Question 23 options: a) Pulmonary edema b) Heart failure c) Pulmonary embolism d) Pneumonia Save Question 24 (2 points) Your patient has been using chewing tobacco for 10 years. On physical examination, you observe a white ulceration surrounded by erythematous base on the side of his tongue. The clinician should recognize that very often this is: Question 24 options: a) Malignant melanoma b) Squamous cell carcinoma c) Aphthous ulceration d) Behcet’s syndrome Save Question 25 (2 points) The first assessment to complete related to the eyes is: Question 25 options: a) Eye lids b) Visual acuity c) Extraocular movements d) Peripheral vision Save Question 26 (2 points) A 66-year-old patient presents to the clinic complaining of dyspnea and wheezing. The patient reports a smoking history of 2 packs of cigarettes per day since age 16. This would be recorded in the chart as: Question 26 options: a) 50 x 2-pack years b) 100-pack years c) 50-year, 2-pack history d) 100-pack history Save Question 27 (2 points) Which disease process typically causes episodic right upper quadrant pain, epigastric pain or chest pain that can last 4-6 hours or less, often radiates to the back (classically under the right shoulder blade) and is often accompanied by nausea or vomiting and often follows a heavy, fatty meal. Question 27 options: a) Acute pancreatitis b) Duodenal ulcer c) Biliary colic d) Cholecystitis Save Question 28 (2 points) Which of the following conditions is the most common cause of nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea? Question 28 options: a) Viral gastroenteritis b) Staphylococcal food poisoning c) Acute hepatitis A d) E coli gastroenteritis Save Question 29 (2 points) Which of the following findings should trigger an urgent referral to a cardiologist or neurologist? Question 29 options: a) History of bright flash of light followed by significantly blurred vision b) History of transient and painless monocular loss of vision c) History of monocular severe eye pain, blurred vision, and ciliary flush d) All of the above Save Question 30 (2 points) In order to provide a comprehensive genetic history of a patient, the NP should: Question 30 options: a) Ask patients to complete a family history worksheet b) Seek out pathology reports related to the patient’s disorder c) Interview family members regarding genetic disorders d) All of the above Save Question 31 (2 points) Patients that have atopic disorders are mediated by the production of Immunoglobulin E (IgE) will have histamine stimulated as an immediate phase response. This release of histamine results in which of the following? Question 31 options: a) Sinus pain, increased vascular permeability, and bronchodilation b) Bronchospasm, vascular permeability, and vasodilatation c) Contraction of smooth muscle, decreased vascular permeability, and vasoconstriction d) Vasodilatation, bronchodilation, and increased vascular permeability Save Question 32 (2 points) A 56-year-old male complains of anorexia, changes in bowel habits, extreme fatigue, and unintentional weight loss. At times he is constipated and other times he has episodes of diarrhea. His physical examination is unremarkable. It is important for the clinician to recognize the importance of: Question 32 options: a) CBC with differential b) Stool culture and sensitivity c) Abdominal X-ray d) Colonoscopy Save Question 33 (2 points) (*There are multiple questions on this exam related to the following scenario. Be sure to read the whole way through to the question.) Mr. Keenan is a 42-year-old man with a mild history of GERD and a remote history of an appendectomy, presenting with an acute onset of significant right upper-quadrant abdominal pain and vomiting. His pain began after a large meal, was unrelieved by a proton-pump inhibitor, was unlike his previous episodes of heartburn, but upon questioning, reports milder, prodromal episodes of similar post-prandial pain. His pain seems to radiate to his back. Despite a family history of cardiac disease, he reports no classic anginal signs or chest pain. He furthermore denies respiratory or pleuritic signs and denies fever, night sweats, and unintended weight loss. Finally, there are no dermatologic signs, nor genitourinary symptoms. When all lab work is returned within normal limits, what is the most practical imaging study to order, considering cost, availability, and sensitivity? Question 33 options: a) Abdominal upright and flat plate x-ray b) Abdominal MRI c) Abdominal CT scan with contrast d) Abdominal ultrasound Save Question 34 (2 points) A common auscultatory finding in advanced CHF is: Question 34 options: a) Systolic ejection murmur b) S3 gallop rhythm c) Friction rub d) Bradycardia Save Question 35 (2 points) Mr. A presents to your office complaining of chest pain, mid-sternal and radiating to his back. He was mowing his lawn. He reports the pain lasting for about 8 minutes and went away after sitting down. What is his most likely diagnosis based on his presenting symptoms? Question 35 options: a) Acute MI b) GERD c) Pneumonia d) Angina Save Question 36 (2 points) (*There are multiple questions on this exam related to the following scenario. Be sure to read the whole way through to the question.) Mr. Keenan is a 42-year-old man with a mild history of GERD and a remote history of an appendectomy, presenting with an acute onset of significant right upper-quadrant abdominal pain and vomiting. His pain began after a large meal, was unrelieved by a proton-pump inhibitor, was unlike his previous episodes of heartburn, but upon questioning, reports milder, prodromal episodes of similar post-prandial pain. His pain seems to radiate to his back. Despite a family history of cardiac disease, he reports no classic anginal signs or chest pain. He furthermore denies respiratory or pleuritic signs and denies fever, night sweats, and unintended weight loss. Finally, there are no dermatologic signs, nor genitourinary symptoms. The chosen imaging study reveals: “GB normal in size without wall-thickening, but with 5-6 stones with shadowing. Common bile duct not dilated. Liver is homogenous and normal in size. Pancreas and kidneys are normal.” What is the most effective therapeutic/management option at this point? Question 36 options: a) Trial of ursodiol b) ‘Watchful waiting’ c) Surgical consult d) HIDA scan Save Question 37 (2 points) A nurse practitioner reports that your patient’s abdominal X-ray demonstrates multiple air-fluid levels in the bowel. This is a diagnostic finding found in: Question 37 options: a) Appendicitis b) Cholecystitis c) Bowel Obstruction d) Diverticulitis Save Question 38 (2 points) The most common etiologic organism for community-acquired pneumonia is: Question 38 options: a) Streptococcus pneumoniae b) Beta hemolytic streptococcus c) Mycoplasma d) Methicillin resistant staphylococcus Save Question 39 (2 points) What test is used to confirm the diagnosis of appendicitis? Question 39 options: a) CBC b) Flat plate of abdomen c) Rectal exam d) CT of abdomen with attention to appendix Save Question 40 (2 points) A 76-year-old patient with a 200-pack year smoking history presents with complaints of chronic cough, dyspnea, fatigue, hemoptysis, and weight loss over the past 2 months. The physical exam reveals decreased breath sounds and dullness to percussion over the left lower lung field. The chest X-ray demonstrates shift of the mediastinum and trachea to the left. These are classic signs of: Question 40 options: a) Lung cancer b) Tuberculosis c) Pneumonia d) COPD Save Question 41 (2 points) Jeff, 48 years old, presents to the clinic complaining of fleeting chest pain, fatigue, palpitations, lightheadedness, and shortness of breath. The pain comes and goes and is not associated with activity or exertion. Food does not exacerbate or relieve the pain. The pain is usually located under the left nipple. Jeff is concerned because his father has cardiac disease and underwent a CABG at age 65. The ANP examines Jeff and hears a mid-systolic click at the 4th ICS mid-clavicular area. The ANP knows that this is a hallmark sign of: Question 41 options: a) Angina b) Pericarditis c) Mitral valve prolapse d) Congestive heart failure Save Question 42 (2 points) Which of the following is considered a “red flag” when diagnosing a patient with pneumonia? Question 42 options: a) Fever of 102 b) Infiltrates on chest X-ray c) Pleural effusion on chest X-ray d) Elevated white blood cell count Save Question 43 (2 points) (*There are multiple questions on this exam related to this scenario. Be sure to read the whole way through to the question.) Mr. Keenan is a 42-year-old man with a mild history of GERD and a remote history of an appendectomy, presenting with an acute onset of significant right upper-quadrant abdominal pain and vomiting. His pain began after a large meal, was unrelieved by a proton-pump inhibitor, was unlike his previous episodes of heartburn, but upon questioning, reports milder, prodromal episodes of similar post-prandial pain. His pain seems to radiate to his back. Despite a family history of cardiac disease, he reports no classic anginal signs or chest pain. He furthermore denies respiratory or pleuritic signs and denies fever, night sweats, and unintended weight loss. Finally, there are no dermatologic signs, nor genitourinary symptoms. Of the following lab studies, which would provide little help in determining your differential diagnosis? Question 43 options: a) Abdominal plain films b) Liver function tests c) Amylase/lipase d) Urinalysis Save Question 44 (2 points) In addition to the complete blood count (CBC) with differential, which of the following laboratory tests is considered to be most useful in diagnosing ACD and IDA? Question 44 options: a) Serum iron b) Total iron binding capacity c) Transferrin saturation d) Serum ferritin Save Question 45 (2 points) What is the most common valvular heart disease in the older adult? Question 45 options: a) Aortic regurgitation b) Aortic stenosis c) Mitral regurgitation d) Mitral stenosis Save Question 46 (2 points) Iron Deficiency Anemia (IDA) is classified as a microcytic, hypochromic anemia. This classification refers to which of the following laboratory data? Question 46 options: a) Hemoglobin and Hematocrit b) Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) and Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH) c) Serum ferritin and Serum iron d) Total iron binding capacity and transferrin saturation Save Question 47 (2 points) A 22-year-old female comes to your office with complaints of right lower quadrant abdominal pain, which has been worsening over the last 24 hours. On examination of the abdomen, there is a palpable mass and rebound tenderness over the right lower quadrant. The clinician should recognize the importance of: Question 47 options: a) Digital rectal examination b) Endoscopy c) Pelvic examination d) Urinalysis Save Question 48 (2 points) Which of the following details are NOT considered while staging asthma? Question 48 options: a) Nighttime awakenings b) Long-acting beta agonist usage c) Frequency of symptoms d) Spirometry findings Save Question 49 (2 points) Dan G., a 65-year-old man, presents to your primary care office for the evaluation of chest pain and left-sided shoulder pain. Pain begins after strenuous activity, including walking. Pain is characterized as dull, aching; 8/10 during activity, otherwise 0/10. Began a few months ago, intermittent, aggravated by exercise, and relieved by rest. Has occasional nausea. Pain is retrosternal, radiating to left shoulder, definitely affects quality of life by limiting activity. Pain is worse today; did not go away after he stopped walking. BP 120/80. Pulse 72 and regular. Normal heart sounds, S1 and S2, no murmurs. Which of the following differential diagnoses would be most likely? Question 49 options: a) Musculoskeletal chest wall syndrome with radiation b) Esophageal motor disorder with radiation c) Acute cholecystitis with cholelithiasis d) Coronary artery disease with angina pectoris Save Question 50 (2 points) The following criterion is considered a positive finding when determining whether a patient with asthma can be safely monitored and treated at home: Question 50 options: a) Age over 40 b) Fever greater than 101 c) Tachypnea greater than 30 breaths/minute d) Productive cough Save Question 51 (2 points) Your 2-year-old patient shows facial features, such as epicanthal folds, up-slanted palpebral fissures, single transverse palmar crease, and a low nasal bridge. These are referred to as: Question 51 options: a) Variable expressivity related to inherited disease b) Dysmorphic features related to genetic disease c) De novo mutations of genetic disease d) Different penetrant signs of genetic disease Save Question 52 (2 points) A 26-year-old, non-smoker, male presented to your clinic with SOB with exertion. This could be due to: Question 52 options: a) Exercise-induced cough b) Bronchiectasis c) Alpha-1 deficiency d) Pericarditis Save Question 53 (2 points) Your patient has been treated for glaucoma for 5 years. Which of the following will provide indication of the level of progression during the funduscopic examination for this patient? Question 53 options: Checking the macula Estimating cup-to-disk ratio Verifying a red reflex Extraocular movements Save Question 54 (2 points) Which of the following medications are commonly associated with the side effect of cough? Question 54 options: a) Beta blocker b) Diuretic c) ACE inhibitor d) Calcium antagonist Save Question 55 (2 points) When interpreting laboratory data, you would expect to see the following in a patient with Anemia of Chronic Disease (ACD): Ans is Hemoglobin <12 g/dl, MCV normal, MCH normal option missing Question 55 options: a) Hemoglobin b) Hemoglobin >12 g/dl, MCV increased, MCH increased c) Hemoglobin d) Hemoglobin >12 g/dl, MCV decreased, MCH increased Save Question 56 (2 points) The first step in the genomic assessment of a patient is obtaining information regarding: Question 56 options: a) Family history b) Environmental exposures c) Lifestyle and behaviors d) Current medications Save Question 57 (2 points) In assessing the eyes, which of the following is considered a “red flag” finding when associated with eye redness? Question 57 options: a) History of prior red-eye episodes b) Grossly visible corneal defect c) Exophthalmos d) Photophobia Save Question 58 (2 points) During physical examination of a patient, you note resonance on percussion in the upper lung fields. This is consistent with: Question 58 options: a) COPD b) Pneumothorax c) A normal finding d) Pleural effusion Save Question 59 (2 points) Which test is the clinical standard for the assessment of aortic stenosis? Question 59 options: a) Cardiac catheterization b) Stress test c) Chest X-ray d) Echocardiography Save Question 60 (2 points) Which of the following would be considered a “red flag” that requires more investigation in a patient assessment? Question 60 options: a) Colon cancer in family member at age 70 b) Breast cancer in family member at age 75 c) Myocardial infarction in family member at age 35 d) All of the above Save Question 61 (2 points) When counseling clients regarding the use of antidiarrheal drugs such as Imodium anti-diarrheal and Kaopectate, the nurse practitioner advises patients to: Question 61 options: a) Use all the medication b) Do not use for possible infectious diarrhea c) Use should exceed one week for effectiveness d) These drugs provide exactly the same pharmaceutical effects Save Question 62 (2 points) Which of the following imaging studies should be considered if a pulmonary malignancy is suspected? Question 62 options: a) Computed tomography (CT) scan b) Chest X-ray with PA, lateral, and lordotic views c) Ultrasound d) Positron emission tomography (PET) scan Save Question 63 (2 points) A 75-year-old patient complains of pain and paresthesias in the right foot that worsens with exercise and is relieved by rest. On physical examination you note pallor of the right foot, capillary refill of 4 seconds in the right foot, +1 dorsalis pedis pulse in the right foot, and +2 pulse in left foot. Which of the following is a likely cause of the signs and symptoms? Question 63 options: a) Arterial insufficiency b) Femoral vein thrombus c) Venous insufficiency d) Peripheral neuropathy Save Question 64 (2 points) Emphysematous changes in the lungs produce the following characteristic in COPD patients? Question 64 options: a) Asymmetric chest expansion b) Increased lateral diameter c) Increased anterior-posterior diameter d) Pectus excavatum Save Question 65 (2 points) Which of the following findings would indicate a need for another endoscopy in clients with peptic ulcer disease? Question 65 options: a) Cases of dyspepsia with constipation b) Symptoms persisting after six to eight weeks of therapy c) All clients with dyspepsia who smoke and drink alcohol d) When a therapeutic response to empiric treatment is obtained Save Question 66 (2 points) Your patient has just returned from a 6-month missionary trip to Southeast Asia. He reports unremitting cough, hemoptysis, and an unintentional weight loss of 10 pounds over the last month. These symptoms should prompt the clinician to suspect: Question 66 options: a) Legionnaires' disease b) Malaria c) Tuberculosis d) Pneumonia Save Question 67 (2 points) The cytochrome p system involves enzymes that are generally: Question 67 options: a) Inhibited by drugs b) Induced by drugs c) Inhibited or induced by drugs d) Associated with decreased liver perfusion Save Question 68 (2 points) Functional abilities are best assessed by: Question 68 options: a) Self-report of function b) Observed assessment of function c) A comprehensive head-to-toe examination d) Family report of function Save Question 69 (2 points) Epistaxis can be a symptom of: Question 69 options: a) Over-anticoagulation b) Hematologic malignancy c) Cocaine abuse d) All of the above Save Question 70 (2 points) Which of the following is not a contributing factor to the development of esophagitis in older adults? Question 70 options: a) Increased gastric emptying time b) Regular ingestion of NSAIDs c) Decreased salivation d) Fungal infections such as Candida Save Question 71 (2 points) A 24-year-old patient presents to the emergency department after sustaining multiple traumatic injuries after a motorcycle accident. Upon examination, you note tachypnea, use of intercostal muscles to breathe, asymmetric chest expansion, and no breath sounds over the left lower lobe. It is most important to suspect: Question 71 options: a) Pulmonary embolism b) Pleural effusion c) Pneumothorax d) Fracture of ribs Save Question 72 (2 points) You have a patient complaining of vertigo and want to know what could be the cause. Knowing there are many causes for vertigo, you question the length of time the sensation lasts. She tells you several hours to days and is accompanied by tinnitus and hearing loss. You suspect which of the following conditions? Question 72 options: a) Ménière’s disease b) Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo c) Transient ischemic attack (TIA) d) Migraine Save Question 73 (2 points) An 82-year-old female presents to the emergency department with epigastric pain and weakness. She admits to having dark, tarry stools for the last few days. She reports a long history of pain due to osteoarthritis. She self-medicates daily with ibuprofen, naprosyn, and aspirin for joint pain. On physical examination, she has orthostatic hypotension and pallor. Fecal occult blood test is positive. A likely etiology of the patient’s problem is: Question 73 options: a) Mallory-Weiss tear b) Esophageal varices c) Gastric ulcer d) Colon cancer Save Question 74 (2 points) The major impact of the physiological changes that occur with aging is: Question 74 options: a) Reduced physiological reserve b) Reduced homeostatic mechanisms c) Impaired immunological response d) All of the above Save Question 75 (2 points) The pathophysiological hallmark of ACD is: Question 75 options: a) Depleted iron stores b) Impaired ability to use iron stores c) Chronic uncorrectable bleeding d) Reduced intestinal absorption of iron Save Question 76 (2 points) Which symptom is more characteristic of Non-Cardiac chest pain? Question 76 options: a) Pain often radiates to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, shoulder, or arm b) Pain tends to occur with movement, stretching or palpation c) Pain usually lasts less than 10 minutes and is relieved by nitroglycerine d) Pain is aggravated by exertion or stress Save Question 77 (2 points) A 23-year-old patient who has had bronchiectasis since childhood is likely to have which of the following: Question 77 options: a) Barrel-shaped chest b) Clubbing c) Pectus excavatum d) Prolonged capillary refill Save Question 78 (2 points) Upon assessment of respiratory excursion, the clinician notes asymmetric expansion of the chest. One side expands greater than the other. This could be due to: Question 78 options: a) Pneumothorax b) Pleural effusion c) Pneumonia d) Pulmonary embolism Save Question 79 (2 points) A specific exam used to evaluate the gall bladder is: Question 79 options: a) Psoas sign b) Obturator sign c) Cullens sign d) Murphy’s sign Save Question 80 (2 points) Susan P., a 60-year-old woman with a 30 pack year history, presents to your primary care practice for evaluation of a persistent, daily cough with increased sputum production, worse in the morning, occurring over the past three months. She tells you, “I have the same thing, year after year.” Which of the following choices would you consider strongly in your critical thinking process? Question 80 options: a) Seasonal allergies b) Acute bronchitis c) Bronchial asthma d) Chronic bronchitis Save Question 81 (2 points) Your 35-year-old female patient complains of feeling palpitations on occasion. The clinician should recognize that palpitations are often a sign of: Question 81 options: a) Anemia b) Anxiety c) Hyperthyroidism d) All of the above Save Question 82 (2 points) A 59-year-old patient with history of alcohol abuse comes to your office because of ‘throwing up blood”. On physical examination, you note ascites and caput medusa. A likely cause for the hematemesis is: Question 82 options: a) Peptic ulcer disease b) Barrett’s esophagus c) Esophageal varices d) Pancreatitis Save Question 83 (2 points) A 74-year-old obese female presents complaining of persistent right upper quadrant pain. She reports that she has not had any prior abdominal surgeries. Which of the following laboratory studies would be most indicative of acute cholecystitis? Question 83 options: C-reactive protein level of 3 mg White blood cell count of 11,000 Direct serum bilirubin level of 0.3 mg/dl Serum amylase level of 145 U/L Save Question 84 (2 points) In a patient presenting with suspected recurrence of diverticulitis, abdominal pain usually presents where in the abdomen? Question 84 options: a) Left upper quadrant b) Right upper quadrant c) Left lower quadrant d) Right lower quadrant Save Question 85 (2 points) Which of the following statements is true concerning anti-arrhythmic drugs? Question 85 options: a) Amiodarone is the only one not associated with increased mortality and it has a very favorable side effect profile. b) Both long-acting and short-acting calcium channel blockers are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. c) Most anti-arrhythmics have a low toxic/therapeutic ratio and some are exceedingly toxic. d) Anti-arrhythmic therapy should be initiated in the hospital for all patients. Save Question 86 (2 points) In autosomal recessive (AR) disorders, individuals need: Question 86 options: a) Only one mutated gene on the sex chromosomes to acquire the disease b) Only one mutated gene to acquire the disease c) Two mutated genes to acquire the disease d) Two mutated genes to become carriers Save Question 87 (2 points) Which of the following clinical reasoning tools is defined as evidence-based resource based on mathematical modeling to express the likelihood of a condition in select situations, settings, and/or patients? Question 87 options: a) Clinical practice guideline b) Clinical decision rule c) Clinical algorithm d) Clinical recommendation Save Question 88 (2 points) Symptoms in the initial human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection include all of the following except: Question 88 options: a) Sore throat b) Fever c) Weight loss d) Headache Save Question 89 (2 points) An 86-year-old patient who wears a hearing aid complains of poor hearing in the affected ear. In addition to possible hearing aid malfunction, this condition is often due to: Question 89 options: a) Acoustic neuroma b) Cerumen impaction c) Otitis media d) Ménière’s disease Save Question 90 (2 points) A patient complains of fever, fatigue, and pharyngitis. On physical examination there is pronounced cervical lymphadenopathy. Which of the following diagnostic tests should be considered? Question 90 options: a) Mono spot b) Strep test c) Throat culture d) All of the above Save Question 91 (2 points) Which of the following symptoms is common with acute otitis media? Question 91 options: a) Bulging tympanic membrane b) Bright light reflex of tympanic membrane c) Increased tympanic membrane mobility d) All of the above Save Question 92 (2 points) A 64-year-old male presents with erythema of the sclera, tearing, and bilateral pruritus of the eyes. The symptoms occur intermittently throughout the year and he has associated clear nasal discharge. Which of the following is most likely because of the inflammation? Question 92 options: a) Bacterium b) Allergen c) Virus d) Fungi Save Question 93 (2 points) An obese middle-aged client presents with a month of nonproductive irritating cough without fever. He also reports occasional morning hoarseness. What should the differential include? Question 93 options: a) Atypical pneumonia b) Peptic ulcer disease c) Gastroesophageal reflux d) Mononucleosis (Epstein-Barr) Save Question 94 (2 points) When teaching a group of older adults regarding prevention of gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms, the nurse practitioner will include which of the following instructions? Question 94 options: a) Raise the head of the bed with pillows at night and chew peppermints when symptoms of heartburn begins. b) Raise the head of the bed on blocks and take the proton pump inhibitor medication at bedtime. c) Sit up for an hour after taking any medication and restrict fluid intake. d) Avoid food intolerances, raise head of bed on blocks, and take a proton pump inhibitor before a meal. Save Question 95 (2 points) Jenny is a 24 year old graduate student that presents to the clinic today with complaints of fever, midsternal chest pain and generalized fatigue for the past two days. She denies any cough or sputum production. She states that when she takes Ibuprofen and rest that the chest pain does seem to ease off. Upon examination the patient presents looking very ill. She is leaning forward and states that this is the most comfortable position for her. Temp is 102. BP= 100/70. Heart rate is 120/min and regular. Upon auscultation a friction rub is audible. Her lung sounds are clear. With these presenting symptoms your initial diagnosis would be: Question 95 options: a) Mitral Valve Prolapse b) Referred Pain from Cholecystitis c) Pericarditis d) Pulmonary Embolus Save Question 96 (2 points) A 75-year-old patient with community-acquired pneumonia presents with chills, productive cough, temperature of 102.1, pulse 100, respiration 18, BP 90/52, WBC 12,000, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 22 mg/dl. He has a history of mild dementia and his mental status is unchanged from his last visit. These findings indicate that the patient: Question 96 options: a) Can be treated as an outpatient b) Requires hospitalization for treatment c) Requires a high dose of parenteral antibiotic d) Can be treated with oral antibiotics Save Question 97 (2 points) The best evidence rating drugs to consider in a post myocardial infarction patient include: Question 97 options: ASA, ACE/ARB, beta-blocker, aldosterone blockade ACE, ARB, Calcium channel blocker, ASA Long-acting nitrates, warfarin, ACE, and ARB ASA, clopidogrel, nitrates Save Question 98 (2 points) Your patient complains of lower abdominal pain, anorexia, extreme fatigue, unintentional weight loss of 10 pounds in last 3 weeks, and you find a positive hemoccult on digital rectal examination. Laboratory tests show iron deficiency anemia. The clinician needs to consider: Question 98 options: a) Diverticulitis b) Colon cancer c) Appendicitis d) Peptic ulcer disease Save Question 99 (2 points) An older patient reports burning pain after ingestion of many foods and large meals. What assessment would assist the nurse practitioner in making a diagnosis of GERD? Question 99 options: a) Identification of a fluid wave b) Positive Murphy’s sign c) Palpable spleen d) Midepigastric pain that is not reproducible with palpation Save Question 100 (2 points) During auscultation of the chest, your exam reveals a loud grating sound at the lower anterolateral lung fields, at full inspiration and early expiration. This finding is consistent with: Question 100 options: a) Pneumonia b) Pleuritis c) Pneumothorax d) A and B [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 49 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 10, 2019
Number of pages
49
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 10, 2019
Downloads
0
Views
76