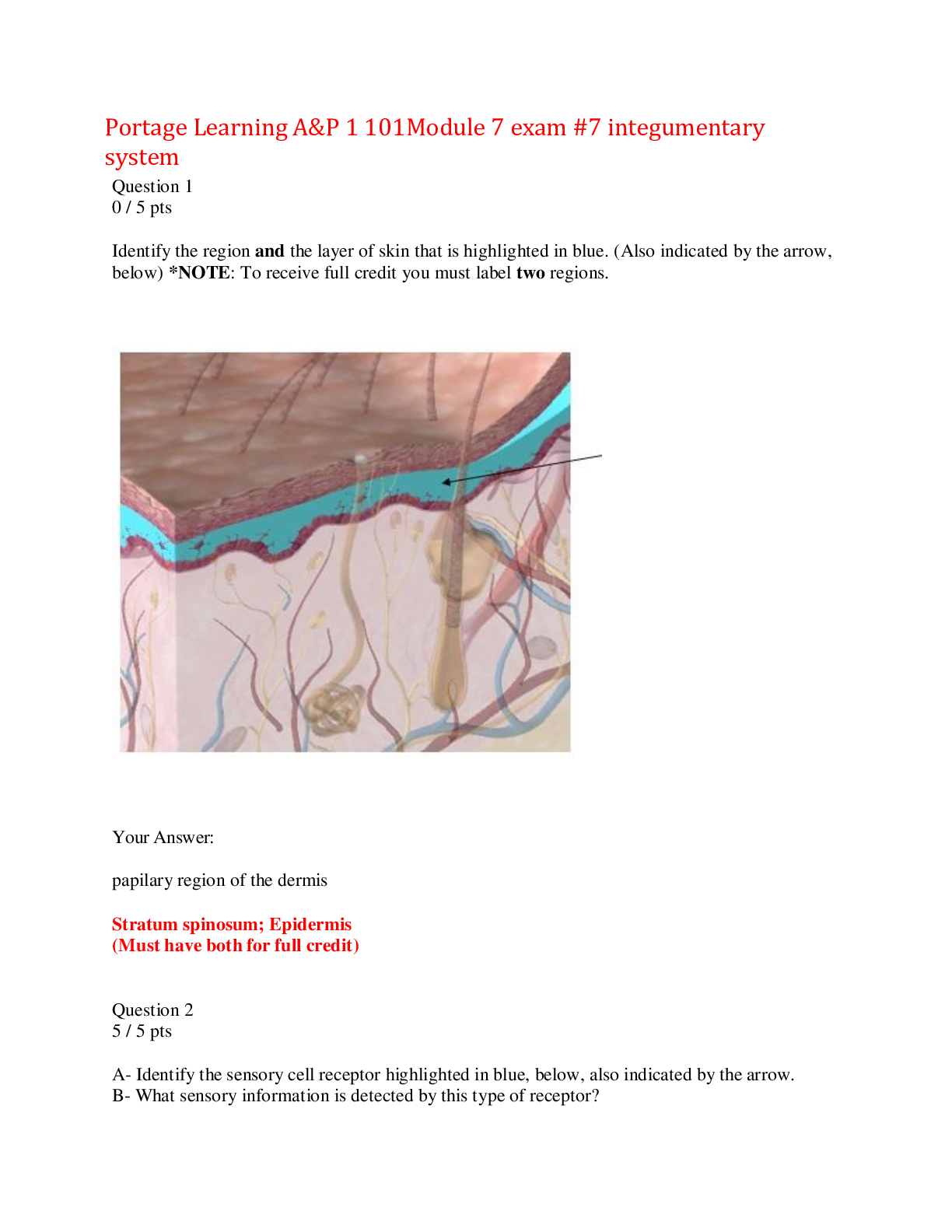
NURS 6670 Midterm Questions and Answers ,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
NURS 6670 Midterm Questions and Answers ● Question 1 Sally is a 54-year-old female who presents for care at the urging of her employer. She says that she doesn’t think she needs to be there, ... but the manager of her division at work strongly suggested that she make an appointment. She is the evening shift manager in the accounting department of a major online sales organization. Her role requires meticulous accountability of a complex system of production statistics, and she has done this exceedingly well for years. She has been a valued employee, and her work is above reproach. A few months ago, the 0 out of 1 points company adopted a new software program that required a complete revamping of Sally’s department. She has not adapted well, and her resulting anxiety is almost prohibitive of functioning in her role. During her interview, Sally is very somber and serious, and is clearly having difficulty with this change. She is distraught over the potential of not being able to do her job well and meet her immediate supervisor’s expectations. Recognizing the likely diagnosis, the PMHNP knows that Sally is likely to respond best to: Selected Answer: [None Given] Answers: Pharmacotherapy with clonazepam Free-association, nondirective therapy Interpersonal therapy Serotonergic agents Response Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. These patients often recognize that there is a problem and will do well with this form of therapy, although it is a long and complex process. Clonazepam and serotonergic agents are effective with obsessive-compulsive disorder, but their utility with obsessive-compulsive personality disorder is less clear. Interpersonal therapy is not among the therapeutic modalities with any demonstrated success with this personality disorder. ● Question 2 Becci is a 31-year-old female who presents to the PMHNP for evaluation after being referred by her friend who is a patient of the practice. She describes a relatively acute, recent onset of panic attacks. Becci says that “out of the blue” her heart starts to race, her mouth gets dry, she gets shaky, and feels like she cannot get her breath. She is afraid because her friend has panic disorder and Becci knows that before her friend got treatment, she basically would not leave 1 out of 1 points the house in case an attack happened. The PMHNP recognizes that the immediate priority in assessment for Becci is: Selected Answer: A thorough physical examination Answers: A thorough physical examination A family history of mental health disease A urine drug screen An assessment for phobic disorder Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. While these are elements of a panic attack, there are a variety of organic conditions that can cause these symptoms. Becci needs a physical examination and appropriate laboratory assessment to rule out physiologic causes of her symptoms, such as thyroid disease. The remaining elements above will all be part of the mental health assessment once physical health is determined. ● Question 3 Mrs. Bowen is a 33-year-old female who presents as a new patient requesting 0 out of 1 points medication for depression. She reports a long history of mood disorders on and off going back to adolescence. She is very articulate in describing her history and reports that neither sertraline nor fluoxetine “worked for her.” She was unable to remember the dose or how long she took the medication. With respect to considering Mrs. Bowen’s medication history, the PMHNP knows that: Selected Answer: Some forms of recurrent depression are best managed with nonpharmacologic strategies Answers: An SNRI will likely be the most appropriate choice if pharmacotherapy is indicated for this episode This may be an inaccurate characterization, as depressed patients tend to overemphasize negatives In some circumstances patients will purposefully mischaracterize the efficacy of medications they feel were ineffective Some forms of recurrent depression are best managed with nonpharmacologic strategies Respons e Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. A common mistake among clinicians is to accept the depressed patient’s self-report of medication accuracy. Depressed patients frequently overemphasize the negative and minimize the positive and may genuinely have a misimpression of their medications effectiveness; similarly, unrealistic expectations may skew their impression of medication response. An SNRI may ultimately be the most appropriate choice, but the PMHNP should not base this primarily on the patient’s self-report of SSRI response. This should not be perceived as a purposeful mischaracterization – the patients are not usually trying to misrepresent thing; they are reporting their genuine impression. Finally, recurrent depressions spanning decades will most likely require pharmacotherapy along with some form of nonpharmacologic intervention for best outcomes. ● Question 4 1 out of 1 points Danielle is a 31-year-old female who is having a psychiatric evaluation at the insistence of her husband. They have been married for 4 years, and her husband has finally become so frustrated by her jealous behavior that he threatened to leave her if she didn’t “get help.” Her husband insists that he has never been unfaithful, but Danielle repeatedly accuses him of having an affair. If he is even a few minutes late getting home from work, she demands an explanation and then does not believe anything he says. She does not have any real friends—her sister is her closest social contact, but Danielle has been angry with her for several weeks and won’t answer phone calls. Reportedly she does this often, and according to her husband can “hold a grudge forever.” During the interview, Danielle is calm, responsive, but distant. She says she really doesn’t understand why she is there—there is not a problem. The PMHNP considers the most likely diagnosis and discusses with Danielle that the treatment of choice is: Selected Answer: Psychother apy Answers: Diazepam Pimozide Psychother apy Group therapy Response Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. Danielle’s symptoms and history are consistent with paranoid personality disorder. Psychotherapy is the treatment of choice for this condition. These patients often do not do well in group therapy as a rule, although for some it can increase social skills. Pharmacotherapy is not a primary mechanism of treatment, but when comorbid agitation and anxiety occur, diazepam may be used. In some patients with quasidelusional thinking, pimozide has been helpful. ● Question 5 A 22-year-old male patient is started on sertraline 50 mg p.o. daily after 1 out of 1 points presenting with a major depressive episode. After tolerating without difficulty for 2 weeks, his dose is increased to 100 mg p.o. daily. Approximately 4 weeks later he reports an unusual set of new symptoms for the last week and a half. He says he feels “amped up” and just very generally agitated and nervous. He was short- tempered at work and home and was snapping at people for no good reason. He also reports difficulty concentrating at work. Last week he expressed disproportionate anger at his work and his boss told him that he was bipolar and should be put on medication. The PMHNP discusses with the patient that: Selected Answer: When symptoms are preceded by antidepressant therapy, a diagnosis of bipolar does not apply Answers: When symptoms are preceded by antidepressant therapy, a diagnosis of bipolar does not apply His symptoms may be consistent with bipolar disorder if they persist for at least 2 weeks A formal assessment of the social and occupational implications of his symptoms should be performed The symptoms are most likely a physiologic adaptation to the sertraline and most often normalize Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. Consistent with DSM-5 criteria, a manic episode that emerges in response to an antidepressant does not constitute bipolar disorder. If these symptoms occur beyond the natural washout period of the sertraline, then bipolar may be appropriate. Symptoms have occurred long enough, as diagnostic criteria require 1 week of symptoms most of the day. An assessment of social and occupation impact will be helpful, but as his boss has already commented, this appears possible. While there is a physiologic adaptation to sertraline, that does not include symptoms described here. ● Question 6 Darius is a 26-year-old male who presents for care as part of couple therapy with his wife, who is being seen for dependency issues. Darius himself seems very 1 out of 1 points anxious to “do the right thing” and appears to want to please the therapist. During the evaluation, Darius is impeccably dressed, very formal in his presentation and interaction, and is watchful of time because he has an appointment after the interview and states several times that he cannot be late. The PMHNP considers that Darius may have obsessive compulsive personality disorder (OCPD). In differentiating this from obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), she explores his history further for: Selected Answer: Significant impairment at work Answers: A history of racing thoughts Difficulty interacting with others Extremely high expectations of self Significant impairment at work Response Feedback : (d) is the correct answer. OCD frequently leads to difficulty at work because the symptoms interfere with the patient’s ability to successfully complete the workday; conversely, patients with OCPD frequently are praised at work because of their devotion to perfectionism. Other differences include that persons with OCPD are usually impeccably dressed, know their thoughts and actions are unreasonable or inappropriate. Conversely, there are many similarities between the personality disorder and the anxiety disorder, and they include (a) through (c). ● Question 7 1 out of 1 points In documenting a mental status exam (MSE) for Janet, a 54-year-old female, the PMHNP notes that she is bradykinesic, has poverty of speech, is depressed, and appears flat. This includes all the following elements of physical examination except: Selected Answer: Appearanc e Answers: Appearanc e Motor activity Mood Affect Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. Appearance and behavior refer to a general description, such as apparent age, style of dress, jewelry, grooming and hygiene. None of these are noted here. Janet’s motor activity is bradykinesia, her mood is depressed, and her affect is flat. ● Question 8 When performing a psychiatric assessment of an elderly patient with Alzheimer’s dementia, the PMHNP recognizes that: 1 out of 1 points Selected Answer: All of the above. Answers: An important part of the history will come from the caregiver The patient must also be interviewed alone to preserve privacy of the relationship A sexual history is not necessary in patients who are not sexually active All of the above. Response Feedback : (d.) is the correct answer. Even in clearly impaired patients, in which a big part of the history may come from a caregiver, the patient should be interviewed alone to preserve the privacy of the relationship and allow the patient the opportunity to discuss things that he or she would not discuss in front of others, such as suicidal or paranoid ideation. While some of the history may come from a caregiver, all elements are equally important, and the demented patient’s contribution may easily be more important to the chief complaint. A sexual history is important as history and fantasies may contribute to the current issue. ● Question 9 When differentiating a major depressive episode from dysthymic disorder, the PMHNP considers that: Selected Answer: Dysthymia is more subjective in its presentation than depression Answers: The cognitive theory of depression does not apply to dysthymia Hospitalization is typically indicated early in the course of dysthymia Dysthymia is more subjective in its presentation than depression Insight-oriented therapy is the most effective treatment for dysthymia 1 out of 1 points Respons e Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. While dysthymia overlaps with depression, it is different in that symptoms tend to be more prevalent than physical findings; disturbances in appetite, libido, and psychomotor function rarely occur. The cognitive theory of depression also applies to dysthymia; hospitalization is rarely indicated in dysthymia, and while insight-oriented therapy has been historically utilized, objective evidence supports cognitive, behavioral, or pharmacotherapy. ● Question 10 During the interview of Kevin, a 42-year-old male who presents for treatment 1 out of 1 points because of marital problems, the PMHNP responds to his tears by gently moving a box of tissues toward him. This is a facilitating intervention of interview known as: Selected Answer: Acknowledgem ent Answers: Reinforcement Reassurance Encouragemen t Acknowledgem ent Respons e Feedback : (d) is the correct answer. This is a form of nonverbal acknowledgement of emotion and often leads the patient to sharing more feelings. Reinforcements are those brief phrases that urge the patient to continue, such as “I see” or “go on.” Reassurance is a technique by which the therapist provides accurate information about the illness that can decrease anxiety. Encouragement characterized by providing a realistic assessment of the patient’s progress or positive contribution to the interview. ● Question 11 1 out of 1 points The psychological sciences have contributed theoretical foundations to the etiology and management of anxiety disorders from both conceptual and practical perspectives. The concept that anxiety develops in persons who feel as though they are living in a world devoid of meaning is an example of which theoretical foundation? Selected Answer: Existential Answers: Psychoanal ytic Behavioral Existential Cognitive Response Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. From an existential perspective, there is no specific identifiable stimulus for anxiety; a patient is chronically anxious as they sense that their lives and the universe have no purpose. Psychoanalytic theory suggests that anxiety is a product of an unconscious sense of danger. Behavioral theory suggests that anxiety is a learned, classic-conditioning response. Cognitive theory suggests anxiety may be related to maladaptive thought patterns. ● Question 12 Which of the following is a true statement with respect to the treatment of narcissistic personality disorder? Selected Answer: Both serotonergic drugs and lithium are useful Answers: Psychoanalytic psychotherapy has strong empiric support Both serotonergic drugs and lithium are useful Group therapy is rarely helpful Immobilized patients (hospitalized or incarcerated) have the best outcomes 1 out of 1 points Response Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. Treatment of this disorder is very difficult as patients must acknowledge and eschew their narcissism before any real therapeutic progress can be made; however, these patients are prone to both depression and mood swings for which both serotonergic drugs and lithium have been successful. Psychoanalytic therapy has been advocated, but there is no validating research. Group therapy has been advocated for by some clinicians, although more research is needed. There is no evidence that immobilized patients do better—this concept is true of antisocial personality disorder. ● Question 13 0 out of 1 points Fletcher is a 29-year-old male referred for court-ordered counseling. He has a long history of repeated offenses including DUI, domestic violence, battery, and other violent acts that fortunately have not yet caused any serious injury or death to the recipients. An interview with his wife reveals that he has lied about almost everything for the last few years; he is able to get hired for jobs because he is very engaging and likeable, and then invariably he gets fired because he misses work and doesn’t do his job properly when he is there. According to the wife, they have known each other since high school, where Fletcher was very happy and well-adjusted. He was on the soccer team, liked by teachers, and never demonstrated the tendencies he does now. Apparently in college he got involved with a fraternity that was notorious for alcohol and drug abuse, and he started drinking heavily; it was “all downhill from there.” The PMHNP considers that: Selected Answer: History and symptoms are most consistent with antisocial personality disorder Answers: History and symptoms are most consistent with antisocial personality disorder Fletcher needs a neurological workup to include an EEG and assessment for neurological soft signs Consistent with his symptoms, Fletcher will likely respond well to a stress interview It is likely that substance abuse is the underlying cause of symptoms and should be explored further Response Feedback : (d) is the correct answer. Typical antisocial personality disorder history extends into adolescence. Fletcher’s behavior appears to have changed following his substance-abuse behaviors, consistent with a diagnosis of substance-abuse disorder—when this is the case, a diagnosis of antisocial personality disorder is not warranted. Abnormal EEG and neurological soft signs are more common in antisocial personality disorder. A stress interview is a technique in which the patient is confronted aggressively with the inconsistencies in his own history and is a therapeutic technique in antisocial personality disorder —again, not appropriate in Fletcher’s case. ● Question 14 1 out of 1 points Anne is a 32-year-old female who presented to care after a random drug screening at work was positive for cocaine. She was initially resistant to therapy, maintaining that her use is not a problem and she could stop at any time. Upon further discussion in session, it appears that she uses cocaine every day at work, sometimes 2–3 times, other days more. She also uses it occasionally at home and most weekends. During her third session, she admitted that it is a financial burden, and she basically cannot afford any other form of recreation. She understands that if she uses again she will lose her job, and she admits that she loves her job and that cocaine is not worth losing it. When counseling her about cessation strategies, the PMHNP advises all the following except: Selected Answer: The physiologic symptoms of withdrawal may require a short-term hospitalization Answers: The physiologic symptoms of withdrawal may require a short-term hospitalization Unlike other substances of abuse, there are no medications to help reduce the intensity of withdrawal She will need to be monitored for depression Overcoming the intense craving for cocaine is the biggest issue Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. Unlike opiates, alcohol, or sedative-hypnotics, cocaine withdrawal does not produce physiologic symptoms that require inpatient withdrawal; occasionally a patient may need to be placed in a residential or inpatient setting just to keep them away from social settings where they can obtain the drug. There are no medications to help with withdrawal. The patient does need to understand that fatigue, dysphoria, and depression may occur. The depression can be severe, and patients should be followed for its development. The primary barrier to withdrawal is the intense cravings that patients experience, particularly as there are no other drugs to help with these symptoms and the patients know that even a small dose of cocaine will attenuate the symptoms they are having. ● Question 15 1 out of 1 points Which of the following personality disorders is associated with females with fragile X syndrome? Selected Answer: Schizoty pal Answers: Borderlin e Narcissis tic Depende nt Schizoty pal Response Feedback: (d) is the correct answer. Schizotypal personality disorder is frequently diagnosed in females with fragile X syndrome. This association is not evident among the other 9 personality disorders. ● Question 16 0 out of 1 points Alexa is a 27-year-old female who has come to group therapy while she is in the city jail. She was arrested for vagrancy because she was sleeping in her car in a parking lot at a local shopping center. She could not post bail, so she is sentenced to 14 days in jail. During group, she contributes that none of this is her fault. Her mother is totally evil because she would not let Alexa stay in the family home. She has some other family. but they are all jerks because they won’t help her. Alexa’s friend Melanie is the absolute best person in the world, but she can’t help because her boss fired her for no reason. Alexa has a history of arrests for buying illegal drugs and prostitution. The last time she was in jail, her sentence was extended for 30 days because she got into a fight with another inmate and beat her up so badly she had to be admitted to the hospital for 6 days. The PMHNP considers which of the following personality disorders? Selected Answer: Narcissis tic Answers: Histrioni c Narcissis tic Borderlin e Schizoid Response Feedback : (c) These behaviors are most consistent with borderline personality disorder. Histrionic personalities are often extreme, flamboyant, and sexually aggressive, but do not typically have this pattern of law breaking or incarceration. Narcissistic personalities are not characterized by splitting behaviors—the grandiose sense of self- importance is the dominant feature. Schizoid personalities are much more aloof and withdrawn, not prone to these extremes of emotion. ● Question 17 The professional relationship between therapist and patient with schizoid personality disorder is a challenge because these patients do not typically seek care independently. However, once a trusting relationship develops, this type of patient may: Selected Answer: Describe an active fantasy life with imaginary friends Answers: Reveal a very strong desire for an intimate relationship Become very engaged in group therapy Describe an active fantasy life with imaginary friends Demonstrate psychotic or delusional features 1 out of 1 points Response Feedback : (c) is the correct answers. If a trusting relationship develops, patients may eventually discuss an active fantasy life. They genuinely do not have much, if any, interest in sex or intimacy. Schizoid patients may become involved in group therapy settings, although they remain very quiet and appear disengaged. These patients do not have psychotic of delusional episodes; that would constitute a different diagnosis. ● Question 18 1 out of 1 points The major defensive mechanisms employed by patients with histrionic personality disorder include: Selected Answer: Repression and dissociation Answers: Repression and dissociation Projective identification Fantasy and isolation Splitting Response Feedback: (a) is the correct answer. These are most commonly used by histrionic personalities. Projective identification and splitting are more commonly used by borderline personalities, whereas fantasy and isolation. ● Question 19 0 out of 1 points Jen is a 31-year-old female who presents for care complaining of depressed mood. During the interview, it becomes apparent that she has a long history of depressive symptoms, as well as a long history of being socially isolated and feeling generally inadequate. When considering a diagnosis of dysthymia, the PMHNP considers that the core concept of dysthymia refers to sub-affective or subclinical depressive disorder with all of the following except: Selected Answer: Strong family history of depression and bipolar disorder Answers: Low-grade chronicity for at least 2 years Insidious onset, usually in childhood or adolescence Strong family history of depression and bipolar disorder Long asymptomatic periods between episodes Response (d) is the correct answer. Dysthymia is characterized by its chronicity, Feedback : and there is typically a persistent or intermittent course; long asymptomatic periods are not consistent with diagnostic criteria. Conversely, there must be a 2-year history, insidious onset that is virtually always in childhood or adolescence, and the family history of depression and bipolar disorder strongly supports the diagnosis. ● Question 20 Cory is a 23-year-old male recently incarcerated in the county correction facility for a 9-month sentence following his third conviction for battery. As part of an 1 out of 1 points early release program, he is required to participate in the therapy program. During his initial interview, he is very pleasant and engaged, expressing no anxiety or distress with his current circumstances. His psychiatric history is significant for numerous adolescent episodes of running away, truancy, and substance abuse. As a young adult, he reportedly has not held a steady job but rather is constantly coming up with money-making schemes. According to family reports is a personality disorder are very likely to: Selected Answer: Have a family history of the same disorder Answers: Have a family history of the same disorder Respond well to dialectical behavioral therapy Have impaired emotional defense mechanisms Come from smaller nuclear families Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. Cory’s history and current findings are consistent with antisocial personality disorder. Antisocial personality disorder is five times more common in first-degree relatives of men with this disorder as compared to controls. DBT is used to treat borderline personality disorder, not antisocial. Patients with personality disorders tend to have heightened defense mechanisms; this is what is responsible for symptoms and behaviors, and the inability to penetrate those defenses presents a challenge to successful therapy. Boys with antisocial personality disorder tend to come from larger families. ● Question 21 1 out of 1 points Assessment of the manic state in a patient with bipolar disorder is likely to include all the following except: Selected Answer: Suicidal or homicidal ideation Answers: Mood-congruent delusions of grandeur Suicidal or homicidal ideation Impaired judgment with no insight Unrestrained flow of ideas Response Feedback: (b) is the correct answer. While most manic patients are assaultive or threatening, the incidence of suicidal and homicidal ideation is unknown. Conversely, the other answer choices are all classic in the manic patient and are present most of the time. ● Question 22 1 out of 1 points From a biological perspective, all of the following neurotransmitters are implicit in the anxiety response except: Selected Answer: Dopamine Answers: Gamma-aminobutyric acid Norepinephrine Serotonin Dopamine Response Feedback: (d) is the correct answer. While dopamine is clearly implicit in other mental health disorders, such as schizophrenia, it is not among the neurotransmitters linked to the anxiety response. ● Question 23 The International Study of Expert Judgment on Therapeutic Use of Benzodiazepines and Other Psychotherapeutic Medications was designed to gather systematic data on the opinions of leading clinicians concerning the 0 out of 1 points benefits and risks of benzodiazepines and alternative anxiety treatments. Which of the following best characterizes the majority opinion of this group? Selected Answer: The panel supports increased federal and/or state restrictions on benzodiazepine prescribing Answers: Patients who require long-term benzodiazepine management should be maintained on long-acting agents The use of benzodiazepines long term for anxiety does not pose a high risk of dependence and abuse The panel supports increased federal and/or state restrictions on benzodiazepine prescribing When detoxifying from therapeutic dosages, daily intake should be decreased by 10–25% Respons e (b) is the correct answer. Most of the panel members opine that the benefit of benzodiazepines in long-term anxiety management Feedback : outweighs risk and that therapeutic use does not pose high risk of dependence or abuse. This group does not support increased federal or state prescribing restrictions. There is no suggestion that short- vs. long-acting agents are superior with respect to abuse potential. Detoxification from therapeutic doses should begin with a 10–25% reduction, but that is not the purview of this panel and it is not their recommendation. ● Question 24 1 out of 1 points Which of the following is a true statement with regard to the etiology of substance abuse? Selected Answer: Neurotransmitters or receptors have been identified with most substances of abuse except for alcohol Answers: Neurotransmitters or receptors have been identified with most substances of abuse except for alcohol Twin and sibling studies do not support a genetic component with respect to the etiology of substance abuse Substances of abuse decrease activity in the amygdala and anterior cingulate The WHO schematic of drug use and dependence identifies immediate antecedents as the central element of abuse Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. No receptor or transmitter has been identified for alcohol; most other substances of abuse have these identified. Studies of twins, adoptees, and sibling raised separately support a genetic component to substance abuse. Substances of abuse stimulate or increase activity in the limbic regions. The WHO schematic identifies the drug-using behavior itself as the central element. ● Question 25 Marlene is a 35-year-old female who is in therapy primarily to develop coping 0 out of 1 points mechanisms for living with her husband, who has narcissistic personality disorder. She is committed to the marriage and loves her husband, but finds his inflated sense of self-importance and complete lack of empathy to be especially difficult. She believes he has a good side, but most of her friends have only ever seen extreme arrogance, and she is embarrassed by that. While counseling Marlene, the PMHNP advises her that patients with narcissistic personality disorder have extremely fragile: Selected Answer: Sense of self- importance Answers: Sense of self- importance Defense mechanisms Self-esteem Interpersonal relationships Response Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. Patients with narcissistic personality disorder have an extremely fragile sense of self-esteem, which makes them vulnerable to depression when it is assaulted. They have an inflated sense of self-importance, a central feature of this disorder. Their defense mechanisms are intact; this is part of the pathophysiology of this disorder. They do have difficulties with interpersonal relationships because of their self-aggrandizing nature—not due to fragility. ● Question 26 Cory J. is a 23-year-old male being seen by the PMHNP today for an initial evaluation. He says that he does not think anything is wrong, but his family, including his mother, grandmother, and aunt, have all told him that he must be 1 out of 1 points “mentally ill.” He has been unable to hold a job and has worked as a cook at more than five chain restaurants in the last 6 months. He has no real friends—he says his “friends” only call him when they need something but never help him. He is currently staying with his grandmother but reportedly will soon be homeless “unless things change.” While he is telling his story, the PMHNP appreciates that Cory repeatedly includes details that make it hard to understand his point. When asked why he thinks he will be homeless, he responds by talking about how many hours he has worked and how everything was going well but then his car broke down and he couldn’t afford to fix it because his tax return was held by the IRS. The PMHNP recognizes that this represents an abnormal: Selected Answer: Thought process Answers: Affect Cognition Thought process Abstract reasoning Respons e Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. Overinclusion of trivial or irrelevant details that make it difficult to get to the point is indicative of circumstantiality, which is an abnormal thought process. Affect is an expression of mood and may be described as happy, irritable, tearful, etc. Cognition describes the patient’s level of consciousness, orientation, memory, and attention..Abstract reasoning is the ability to expand a concrete or specific concept to a general idea or application. ● Question 27 1 out of 1 points A variety of pharmacologic agents have demonstrated effectiveness in the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder. Which of the following does not have any evidenced-based support in the literature? Selected Answer: Antipsychoti cs Answers: SSRIs TCAs Antiadrener gics Antipsychoti cs Response Feedback : (d) is the correct answer. There are no data to support the efficacy of antipsychotics, and these are only indicated acutely for severe agitation or aggression. Conversely, SSRIs; TCAs; antiadrenergics, such as clonidine propranolol; as well as MAOIs and mood stabilizers all have demonstrated utility. ● Question 28 The PMHNP is on call at the local county correctional facility. He is asked to 1 out of 1 points evaluate M.S., a 21-year-old male who was just arrested following an altercation at a local bar. M.S. has never been incarcerated before and apparently has no psychiatric or medical history available. His toxicology screen was negative for alcohol or any drugs of abuse. His mother says that he has in the past had some occasions when he got kind of agitated, but this is the first time it’s been a problem. Reportedly some people from his office were at the bar celebrating a birthday, and before anyone knew what happened an argument escalated into M.S. getting very loud, yelling, and acting “crazy” before he punched a coworker and started breaking bottles. When considering a manic or hypomanic episode, the PMHNP expects that his speech would most likely be: Selected Answer: Increas ed Answers: Stutter ed Increas ed Childlik e Confus ed Response Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. Speech is described in terms of fluency, amount, speed, tone, and volume. Patients who are experiencing a manic or hypomanic episode most often (although not always) will demonstrate increased, pressured speech. Stuttered speech is more consistent with social phobias and anxiety. Childlike speech may have many causes, but it is more often associated with personality disorders. Confusion may occur in manic episodes, but it is more consistent with dementing or psychotic disorders. While there are a variety of reasons for each of these speech patterns, (b) is the best answer of those provided here. ● Question 29 0 out of 1 points The PMHNP is considering pharmacotherapeutic options for Ana, a 28-year-old female with generalized anxiety disorder. Ana is very concerned about becoming “addicted” to medication, but she is open to pharmacotherapy because there are a lot of things going on in her life and she worries all the time. Her husband is deployed overseas, she has just started a new job, and her only child has just started kindergarten. Ana denies any panic-type symptoms; her primary concern is that she is worried about everything and it is making it hard to sleep and concentrate on learning the skills for her new job. Ana may best benefit from: Selected Answer: Venlafaxi ne Answers: Lorazepa m Venlafaxi ne Propranol ol Buspiron e Response Feedback : (d) is the correct answer. Buspirone is not physically addictive, and it is particularly useful for the cognitive (vs. physiologic) manifestations of anxiety, which seems to be Ana’s primary concern. While benzodiazepines do have a role in generalized anxiety disorder, they must be used very judiciously, and Ana’s circumstances—along with her concerns—make them not a good first choice. Venlafaxine is an alternative, but its action on the physiologic symptoms makes buspirone a better choice. Propranolol does not impact the cognitive symptoms at all and is more useful for physiologic symptoms such as performance anxiety. ● Question 30 The PMHNP is evaluating Jared, a 47-year-old male who is brought to care by his 0 out of 1 points wife because “he’s not the man I married 20 years ago.” According to his wife, she and Jared have been married for 20 years, have two children, and have lived a “normal” life. Jared owns a local construction company and their marriage has been a solid one, characterized by the typical day-to-day issues that occur in most marriages, but otherwise happy. For the last 2–3 months, she says Jared has completely changed. He will get angry for no apparent reason and even broke a lamp once. He tells stupid and offensive jokes that no one else thinks are funny, and even had someone call the police when he continued to make inappropriate remarks to a woman in a restaurant. Jared seems unsure what to say, but his wife is adamant that this is a totally different man from the one she has known. The PMHNP knows that Jared should be evaluated for: Selected Answer: Substance abuse disorder Answers: Borderline personality disorder Structural brain damage Substance abuse disorder Cognitive impairment Response Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. Personality changes that occur later in the lifespan, have rapid onset, and include impaired control of behaviors and emotions are most likely due to structural damage related to head injury; neoplasms and cerebral vascular disease are also considerations. Personality disorders are usually evident well before the 5th decade. Substance abuse will be assessed in the history, but there is no report of that here. Cognitive impairment is usually not an early feature of personality disorder due to general medical condition. ● Question 31 1 out of 1 points Tim is a 20-year-old male who has been referred for care by his college counselor. The counselor has noted that Tim engages in virtually no social activities in college, and for that matter avoids day-to-day activities that require social interaction. By his own admission, Tim never participates in class discussions, even in online discussion boards. Tim is so afraid of rejection that he confines himself to his room and his studies. When differentiating schizoid personality from avoidant personality, the PMHNP knows that a primary difference is that: Selected Answer: Avoidant personalities have a strong desire for personal relationships Answers: Avoidant personalities have a strong desire for personal relationships Avoidant personalities may have an active fantasy life Schizoid personalities are perceived as distant and aloof Schizoid personalities may be very attached to animals Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. Avoidant personalities do have a desire for interpersonal relationships; schizoid personalities do not. Both types of personalities may have an active fantasy life, be perceived as distant and aloof, and be attached to animals; none of these things differentiate one type from the other. ● Question 32 0 out of 1 points Clare’s history of personal relationships is characterized by complete intolerance of being alone. Whether it is an intimate-partner relationship or a close friend, Clare appears to always need someone in her life. She had a live-in boyfriend of 3 years, and while they were together, he took care of everything. The PMHNP expects all of the following to be additional features of Clare’s history except: Selected Answer: Has difficulty disagreeing with others Answers: Has difficulty disagreeing with others Needs reassurance to support even mundane decisions Volunteers to do unpleasant tasks to obtain nurturance Has disproportionate anger toward an abusive spouse Response Feedback : (d) is the correct answer. Not only do these patients not express anger, they are more likely to tolerate abusive behavior as preferable to being alone. Conversely, dependent personalities do have difficulty disagreeing with others, need constant support and affirmation for even routine daily decision making, and will often put themselves in unpleasant situations or volunteer for undesirable tasks to be liked. ● Question 33 The PMHNP is conducting an initial interview with a patient whose history is 0 out of 1 points consistent with avoidant personality disorder. The PMHNP understands that one of the most striking features of this interview is likely to be centered upon the patient’s: Selected Answer: Speech pattern Answers: Clothing Speech pattern Anger Anxiety Response Feedback : (d) is the correct answer. Patients with avoidant personality disorder tend to be extremely anxious about talking with the interviewer. Their mannerisms during the interview change depending upon whether they think the interviewer likes them. Clothing and speech are more likely to be notable with histrionic personality disorder, and anger is more likely with borderlines. ● Question 34 1 out of 1 points Patients on lithium carbonate for management of bipolar disorder should be subject to routine assessment of: Selected Answer: TSH and serum Na+ Answers: CBC and BMP TSH and serum Na+ CMP and ECG LFTs and EEG Response Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. Lithium, as an iodine-containing medication, presents a risk of both hypothyroidism and hyponatremia. Patients on lithium should have routine monitoring of these labs as well as lithium levels. CBC is not routinely indicated; this is appropriate for drugs that can cause pancytopenia, such as valproic acid. ECG, LFT, and EEG are not routinely indicated. ● Question 35 Mr. Henderson is a 69-year-old man who presents for evaluation and care for depression. His wife died 6 months ago following a difficult 2 years with breast cancer. His primary complaint is that he just does not look forward to anything 0 out of 1 points anymore. He cannot get interested in his children and grandchildren, he no longer enjoys any of his hobbies because he and his wife used to do them together. He does not sleep well, and wakes up frequently during the night. He also admits to thinking more and more about dying himself, although he expressly denies suicidal ideation. His medical history is significant for coronary artery disease, osteoarthritis, hypothyroidism, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. He also has atrial fibrillation and is on warfarin for emboli prophylaxis, but he does not remember the names of all of his other medications. When considering pharmacotherapy for Mr. Henderson, the PMHNP considers that which of the following SSRIs is safest with respect for potential drug interactions? Selected Answer: Fluoxetine Answers: Fluoxetine Paroxetine Escitalopr am Sertraline Response Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. Escitalopram is the only medication of those listed that has no inhibitory impact on any CYP450 isoenzymes. Since Mr. Henderson does not know the names of his other drugs, it is best to avoid CYP450 inhibitors. All of the other choices have some degree of inhibition on several isoenzymes, including the 2C9 isoenzyme, which metabolizes warfarin. ● Question 36 The PMHNP is asked to evaluate the parent of one of her existing patients, a 49- 1 out of 1 points year-old woman named Sheri. Sheri reports that her father, a 78-year-old man who lives alone, has always been in good health. However, when Sheri went to have breakfast with him this past Sunday, she found her father overtly confused and he did not even seem to recognize her at first. Sheri is concerned that he has Alzheimer’s disease, and she is amazed because two days prior he was “completely fine.” The PMHNP knows that the most likely cause of this presentation is: Selected Answer: Urinary tract infection Answers: Urinary tract infection Mild cognitive impairment Normal pressure hydrocephalus Depression Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. The acute nature of this mental status change without any preexisting conditions or deficits is consistent with infection, most likely of the urinary tract. This is not mild cognitive impairment as his current symptoms clearly interfere with ADLs. Normal pressure hydrocephalus is remotely possible but much less likely. Depression may mimic dementia, but the acute and global nature of this presentation is more consistent with delirium. ● Question 37 Differentiating post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) from panic disorder and generalized anxiety disorder can be challenging. Which of the following provides the strongest support for PTSD vs the other two differential diagnoses? Selected Answer: Reexperiencing the event Answers: The time course of symptoms Presence of physiologic arousal Reexperiencing the event Response to pharmacotherapy 1 out of 1 points Response Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. PTSD, unlike generalized anxiety disorder or panic disorder, is characterized by reexperiencing of the traumatic event. The time course of symptoms is not specific; while PTSD does occur after a traumatic event, symptoms may occur 1 week or 30 years after the event. All of these conditions are characterized by physiologic arousal, and SSRIs are indicated for all of them as well. ● Question 38 0 out of 1 points The PMHNP is seeing a patient who has been referred by primary care. The patient was diagnosed with major depressive disorder and trialed on both an SSRI and SNRI by the primary care provider. The patient appears refractory to therapy and has not had any appreciable clinical response. A more detailed psychiatric history is significant for indicators of bipolar disease, as well as a family history of bipolar disease in both the patient’s father and paternal aunt. This patient will most likely benefit from: Selected Answer: Lithium Answers: Lamotrigin e Valproic acid Lithium Amitriptyli ne Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. Patients who are in the depressed state of bipolar disorder may not respond to typical antidepressants. Depressive episodes in these patients respond best to lamotrigine or low-dose ziprasidone. Valproic acid and lithium are appropriate for acute mania, and amitriptyline, a tricyclic antidepressant, is not likely to be any more successful in this patient as compared to the antidepressants he has tried. ● Question 39 John is a 41-year-old male who presents for management of heroin addiction. He has a long history of opiate abuse spanning decades and has had several unsuccessful attempts at recovery. Because of his lifestyle, he has developed a 1 out of 1 points variety of chronic health problems, including cardiomyopathy and stage 2 chronic kidney disease. He currently takes several psychiatric medications for mood disorder. When considering methadone maintenance as a mechanism of treating his opiate addiction, the PMHNP knows that if he requires more than 100 mg of methadone at the start of therapy he should have a baseline: Selected Answer: 12-lead ECG Answers: Urine drug screen Hepatic function test Pulmonary function test 12-lead ECG Response Feedback : (d) is the correct answer. In patients who are at high risk, such as those with cardiomyopathy, a 12-lead ECG should be assessed prior to starting methadone at doses > 100 mg daily as it may prolong the QT interval predisposing to ventricular dysrhythmia. A urine drug screen is typically performed prior to treatment, but this is not related to the dose of methadone. Hepatic function profile is appropriate only if there is concern about liver disease, and pulmonary function test does not have any routine indication. ● Question 40 Karen is a 19-year-old female who has been referred to care after being seen in the emergency department following a violent sexual assault. She was working 0 out of 1 points late one evening at the shopping mall and walked alone to her car after dark. She was assaulted, beaten, and thankfully a passerby saw her lying in some bushes and called 911. Initially she was resistant to mental health care, but now, 2 months later, she feels as though she needs help because she is experiencing a collection of symptoms including flashbacks, dreams of the assault, palpitations, anxiety, and a sense that she is watching the assault happen to her This sense of watching the assault as if she was an observer is characteristic of which diagnostic domain of PTSD? Selected Answer: Intrusion symptoms Answers: Intrusion symptoms Avoiding stimuli Autonomic arousal Clinical significance Response Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. There are three domains in which patients show symptoms, represented by a–c above. Depersonalization and derealization are characteristic of avoidance. Diagnostic criteria do require clinically significant distress, but this is not among the three domains. ● Question 41 Validated and reliable instruments are an important part of assessment for both clinical practice and research in psychiatrics. Which of the following tools is currently considered the standard for assessing clinical outcomes in treatment studies of schizophrenia? Selected Answer: BPRS Answers: SCID 0 out of 1 points BPRS PANS S HAM- D Response Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. This tool was designed in the late 1980s to improve upon deficits in the BPRS. The BPRS was developed in the 1960s and was widely used for assessing schizophrenia symptoms but has been essentially replaced by the PANSS. The SCID is a lengthy diagnostic tool that is used in research but, due to its length, is not practical for clinical practice. The HAM-D is a depression tool. ● Question 42 The PMHNP is working on a graduate program in which he is hoping to develop a new personality assessment tool. After an exhaustive review of the literature and 1 out of 1 points many months of work, he developed a tool to use in a research study and needs to establish its psychometric properties. He distributes the tool to four different professionals in the field and asks that they assess whether the questions appear to measure what they are purported to measure. This is an assessment of: Selected Answer: Face validity Answers: Internal consistency reliability Parallel form reliability Construct validity Face validity Response Feedback: (d) is the correct answer. Assessing whether the items measure what they appear to measure is face validity. Construct validity uses data outside of the test to measure validity. Reliability evaluates whether the tests measure what it is supposed to measure consistently. ● Question 43 The difference between a manic and hypomanic episode is best characterized by all the following except: Selected Answer: Hypomanic episodes do not cause marked impairment in function Answers: The duration of symptoms is shorter for hypomanic episodes Hypomanic episodes do not cause marked impairment in function There are no psychotic features with hypomanic episodes 0 out of 1 points Hypomanic episodes may occur as a response to antidepressants Response Feedback : (d) is the correct answer. Both manic and hypomanic episodes cannot be diagnosed when the change in mood is a response to antidepressant therapy. In both types of episodes, the patient must either not be in treatment for depression or enough time must have passed that treatment is not a factor. The duration of symptoms is shorter, as hypomanic episodes require 4 days for diagnosis and manic episodes 1 week. Full manic episodes cause marked social or occupational impairment; hypomanic episodes are noticeable to others but do not necessarily lead to such dysfunction. Manic episodes may include psychosis, whereas hypomanic episodes do not. ● Question 44 Which among the following neurotransmitters is decreased in depression and increased in mania? Selected Answer: Serotonin Answers: 0 out of 1 points Dopamine Norepinephri ne Serotonin Glutamate Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. Norepinephrine and serotonin are clearly implicit in depression, but their relationship or concentration in mania is not established. Although glutamate is being explored as a neurotransmitter implicit in mood disorders, its role is emerging and not well articulated now. ● Question 45 Dependence is a common feature of many psychiatric disorders. One of the 1 out of 1 points primary distinguishing features that differentiates dependent personality disorder from histrionic and borderline personalities is that: Selected Answer: Dependent personalities tend to have long-term relationships with one person Answers: The treatment of dependent personality is rarely successful Occupational dysfunction is rarely impaired Dependent personalities tend to have long-term relationships with one person This disorder tends to be more common in men Response (c) is the correct answer. Unlike other personality disorders, dependent Feedback : personalities tend to have long-term relationships with one person rather than a series. Treatment is often successful; insight-oriented therapies enable patients to understand their behavior and become more successful. With dependent personality disorder, occupational functioning tends to be impaired because these patients cannot act independently or without close supervision. This disorder is more common in women. ● Question 46 Trudy L. is a 29-year-old female patient who initiated care because she feels like she has no energy. She just had her annual wellness exam and her primary care provider told her that she is in excellent health. Because she complained about this excessive fatigue, her PCP performed a CBC, CMP, UA and thyroid function tests and was told, along with her physical examination, that everything looks normal. Further discussion reveals that Trudy is having some relationship challenges with her boyfriend of 2 years and this seems to be “spilling over” at work, where she is having persistent conflict with her supervisor. Ultimately the 1 out of 1 points PMHNP diagnoses Trudy with major depressive disorder, mild, single episode. The PMHNP and Trudy discuss treatment options, and Trudy would really like to try nonpharmacologic interventions. Which of the following represents the best approach for Trudy? Selected Answer: Interpersonal therapy Answers: Family therapy Behavior therapy Psychoanalytic therapy Interpersonal therapy Response Feedback : (d) is the best answer. Family therapy is not regarded as a primary therapy choice for major depressive disorder. While some data suggests that it may prevent relapse by lessening stressors, it is not among the best options presented here. There are limited data on the efficacy of behavior therapy. Psychoanalytic therapy may be helpful for depression, although it is typically a very long process and not practical for acute symptom management. Interpersonal therapy has a body of evidence to support its efficacy for major depressive disorder and may simultaneously help Trudy with her current relationship concerns. Interpersonal therapy is a goal-oriented program constructed of approximately 12 to 16 sessions, making it more practical for Trudy. ● Question 47 0 out of 1 points The PMHNP is considering a diagnosis of paranoid personality disorder in a new patient. When reviewing the history and physical examination, which of the following findings would be most consistent with this diagnosis? Selected Answer: The presence of fixed delusional thought Answers: The presence of fixed delusional thought Disdain for weak or sickly people A history of antisocial behavior Extreme “drama” in most personal relationships Response Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. Patients with paranoid personality disorder tend to be disdainful of those they perceive as weak, sickly, or otherwise imperfect; conversely, they are impressed with power. Fixed delusional thought is not present in paranoid personality disorder and would be more consistent with delusional disorder. A history of antisocial behavior is not present in these patients, and tumultuous personal relationships are more suggestive of borderline personalities. ● Question 48 The PMHNP is called to the acute care unit to evaluate a patient who is admitted after being brought in by his friends. They were at a party where there were 1 out of 1 points numerous drugs of abuse as well as alcohol. The patient cannot provide a history, and his friends are unclear as to which drugs he used. Physical examination reveals a patient who is diaphoretic, tremulous, has a pulse of 130 bpm, dilated pupils, and cannot perform fine motor tasks. These physical findings are most consistent with which type of intoxication? Selected Answer: Hallucinog en Answers: Alcohol Cannabis Opiate Hallucinog en Response Feedback : (d) is the correct answer. These findings are suggestive of hallucinogen intoxication. Alcohol is a CNS depressant and would not cause tremor or tachycardia; that is more likely with alcohol withdrawal. Cannabis intoxication does cause impaired coordination and motor function but not tremor or tachycardia. Opiates are a SNS antagonist and produces pupillary constriction, constipation, and apathy as well as euphoria. ● Question 49 1 out of 1 points Jeffrey T. is a 27-year-old man who has presented for care after being required to do so by the county court. He was involved in a car accident, and while he was not at fault for the accident, routine blood alcohol screening revealed that he was driving while intoxicated. He is a bit resentful at being required to attend therapy; he is very vocal that his driving was not impaired and that he is able to function normally even after drinking what others might consider excess amounts of alcohol. His wife confirms this; they both admit that what began as one or two beers after work a few years ago has evolved to where he now drinks at least a 12 pack of beer nightly. Regardless, they both confirm that he never “seems drunk,” and this does not interfere with his job or fulfilling his family functions. Jeffrey’s ability to function normally despite high blood alcohol is likely a result of: Selected Answer: Adaptatio n Answers: Depende nce Abuse Adaptatio n Addiction Respons e Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. Cellular or pharmacodynamic adaptation refers to the ability of the CNS to function despite high blood levels of the substance of abuse. Dependence refers to repeated use of a substance with or without physical dependence, but does not specifically encompass the concept of functioning normally with increased doses. Abuse generally refers to using drugs or alcohol in a manner deviant from societal norms, and while Jefferey may be doing that, adaptation is the phenomenon described in this scenario. Addiction refers to a situation in which deprivation of the substance produces distress and mental or physical deterioration—something not described in this scenario. While these may be present for Jeffrey, the phenomenon specifically described here is adaptation. ● Question 50 1 out of 1 points Sarah is a 23-year-old patient who presents for a follow-up of her major depressive episode. She was titrated up to maximal dose fluoxetine 6 weeks ago after demonstrating tolerance without side effects at lower doses. Today in follow-up, she reports that she still has no sides effects but no therapeutic effect either. There does not appear to be any measurable improvement of her initial presenting symptoms. The PMHNP knows that the most appropriate approach at this point is to: Selected Answer: Change to another antidepressant medication Answers: Reconsider the diagnosis of major depressive episode Add bupropion to her medication regimen Increase the dose of fluoxetine Change to another antidepressant medication Response Feedback : (d) is the correct answer. Although each patient’s history must be considered individually, as a rule, if there is no response at all to the initial agent after an appropriate trial of an appropriate dose, changing to another agent is recommended. Reconsidering the diagnosis is not an initial strategy— presumably the PMHNP was confident in the diagnosis before beginning medication therapy—although this may be appropriate in some cases, it would be the exception rather than the rule. Adding bupropion (or another augmenting agent) is preferable when there has been some therapeutic response to the initial medication. Increasing the dose of fluoxetine is not appropriate as she is at maximal dose. ● Question 51 M.T. is a 39-year-old female being seen by the PMHNP for a major depressive episode. She is being managed with SNRI therapy in combination with cognitive behavioral therapy. She is having difficulty achieving remission, and her husband comes with her to this office visit because he is becoming very frustrated. He wants to be supportive, but he is finding it very difficult to understand why she is so depressed. M.T. had an episode of depression approximately 2 years ago, but that was when her sister died in an accident. After 6 months of treatment, she seemed to return to normal. This time, her husband points out that she “has nothing to be depressed about,” but she has become so depressed that she has 1 out of 1 points essentially withdrawn from the family. In trying to help M.T.’s husband understand the disease process, the PMHNP discusses with him that: Selected Answer: The physiologic stress accompanying her first episode of depression may have produced changes in brain biology that makes her susceptible to subsequent episodes without an external trigger Answers: The physiologic stress accompanying her first episode of depression may have produced changes in brain biology that makes her susceptible to subsequent episodes without an external trigger The pharmacotherapy required to achieve remission with her first episode resulted in neuroplastic changes that increased her likelihood of experiencing additional depressive episodes The scientific literature suggests that the loss of a sibling is the life event most closely associated with recurrent episodes of major depressive disorder throughout adulthood Response to pharmacotherapy often takes a minimum of 8 weeks and that M.T. is much more likely to achieve remission if he can continue to provide the necessary support throughout her remission period. Response (a) is the correct answer. Stressful life events often precede a first Feedback : episode of depression, and one theory suggests that the physiologic changes that accompany this episode place patients at higher risk for subsequent episodes. There is no evidence that pharmacotherapy increases this risk. The most compelling data for life events suggests that losing a parent before age 11 is the greatest life event risk factor for major depressive disorder. While response to pharmacotherapy does take up to 8 weeks, this is not an etiology. ● Question 52 Marcus is an 18-year-old male presented for care by his parents. It is time for Marcus to begin exploring colleges and he flat out refuses to do so. Both Marcus and his parents admit that he has had a rather solitary lifestyle. He has been home-schooled since the eighth grade. According to his parents, he is extremely intelligent and in junior high it became very difficult for him to be in school. He was very uncomfortable in the school setting and it was counterproductive to learning, so the parents were amenable to home schooling. However, now they 0 out of 1 points want him to go to college, but he will not discuss it. When considering differential diagnosis, the PMHNP considers all of the following except: Selected Answer: Social anxiety Answers: Schizophrenia Social anxiety Schizoid personality Agoraphobia Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. There is no report of positive symptoms of schizophrenia, which would be required for this differential. However, social anxiety, schizoid personality, agoraphobia, as well as avoidant personality and depression, should all be considered here. A more detailed psychiatric interview is necessary to differentiate among them. ● Question 53 Mrs. Maxwell is a 75-year-old patient with moderate Alzheimer’s dementia. She lives with her son and his wife and generally does very well with her day to day activities. The family understands the importance of routine and Mrs. Maxwell 0 out of 1 points maintains a regular schedule of activities including her meals, timed toileting, and recreational activities. Which of the following behaviors should prompt and immediate depression screening for Mrs. Maxwell? Selected Answer: An unplanned weight loss despite consistent oral intake Answers: An acute change in mental status Angry verbal outbursts that seem unwarranted Death of her best friend An unplanned weight loss despite consistent oral intake Response Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. Mood disorders in demented patients often present as seemingly disproportionate anger. When a patient with a dementing disorder develops increasing irritability or anger, a depression screening should be among the first assessments. An acute mental status change is delirium and urinary tract infection is the first thing to rule out. Death of a best friend may trigger a depressive episode but, absent symptoms, a screening is not indicated. Unplanned weight loss, in the absence of decreased intake, warrants evaluation for organic disease. Conversely, decreased intake with concomitant weight loss may be symptomatic of a mood disorder. ● Question 54 1 out of 1 points Anthony is a 41-year-old male patient who presents for evaluation. His wife made the appointment because she is worried about him and he would not seek care on his own. Anthony has become progressively withdrawn over the last few months and is in danger of losing his job because he misses so many days. He has been evaluated by his primary care provider and has no apparent medical conditions. His wife reports that he has been diagnosed with depression in the past, and has even taken medication that seemed to help. This time he just refused to pursue care. After a comprehensive assessment, the PMHNP diagnoses the patient with major depressive episode with psychotic features. Consistent with the Texas Algorithm Medication Project (TAMP), the appropriate choice of initial medication therapy would be: Selected Answer: Fluoxetine and olanzapine Answers: Venlafaxine and clozapine Fluoxetine and olanzapine Amitriptyline and haloperidol Paroxetine and buspirone Response Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. According to TAMP, the appropriate initial medication choice for depression with psychotic features is an SSRI/SNRI with an atypical antipsychotic—the only one with evidenced- based support is fluoxetine and olanzapine. Clozapine, due to its high adverse-effect profile, is not used as the initial atypical but may be substituted later if psychotic features persist despite safer atypical agents. Tricyclic antidepressants and typical antipsychotics have a role in the management of patients who do not respond to first-line choices. Buspirone has no routine role in the management of this type of depression. ● Question 55 A PMHNP student is reviewing his notes from his clinical experience over the past 0 out of 1 points week to prepare his first required case presentation on a patient suffering a major depressive episode. Which of the following patients best represents the DSM-5 criteria for major depressive episode? Selected Answer: A 41-year-old male with a history of childhood sexual abuse, loss of interest in both his professional and personal life, an unplanned 10 lb. weight loss in the last 3 months, and perceptual disturbances Answers: A 27-year-old female with a 1-month history of social withdrawal, anorexia, hypersomnia, unprovoked outbursts of anger, and a strong family history of endogenous depression A 41-year-old male with a history of childhood sexual abuse, loss of interest in both his professional and personal life, an unplanned 10 lb. weight loss in the last 3 months, and perceptual disturbances A 65-year-old male whose wife died 2 months ago and he reports a 3- week history of generally depressed mood, guilt about his wife’s death, insomnia, difficulty focusing on daily tasks, with increasing thoughts of dying A 72-year-old female who just relocated across country to live with her adult son and daughter-in-law who is despondent about leaving her home and reports forgetfulness, loss of appetite, new onset bowel problems, and extreme loss of energy Response Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. DSM-5 criteria for a major depressive episode includes 5 of 9 primary symptoms most of the time over the preceding 2-week period, one of which must be depressed mood or loss of interest or pleasure. While each of these patients manifests some of the symptoms, the only one who meets these criteria (depressed mood, loss of interest or pleasure, significant unplanned weight loss of gain, sleep alterations, psychomotor agitation or retardation, fatigue or loss of energy, feelings of worthlessness or guilt, inability to concentrate, recurrent thoughts of suicide) is option (c). Additionally, loss of a spouse is the single most prevalent environmental risk factor for major depressive episode. ● Question 56 When developing a pharmacologic treatment plan for the management of major depressive disorder, the PMHNP counsels the patient that the medication will be titrated up to the appropriate dose and then continued for a minimum of 3 0 out of 1 points months; medication must not be stopped abruptly or without provider supervision. This is because the physiologic consequence of abrupt cessation is likely to result in: Selected Answer: Rebound depressive symptoms Answers: Antidepressant discontinuation syndrome Rebound depressive symptoms A manic or hypomanic episode Unresponsiveness to medication with future episodes Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. Antidepressant discontinuation syndrome is a collection of symptoms represented by the mnemonic FINISH (flu-like symptoms, insomnia, nausea, imbalance, sensory disturbances, hyperarousal). These are most abrupt when the patient has been on medication for > 6 weeks. While depressive symptoms may occur, (a) is the best answer as this is the most likely concern. Manic symptoms are not any more likely to occur with discontinuation of an antidepressant—antidepressants may precipitate a manic or hypomanic episode if the patient has undiagnosed bipolar disorder. While subsequent episodes of major depression are more challenging to treat than initial episodes for a variety of reasons, there is no direct correlation to abrupt cessation of medication. ● Question 57 Chantel is a 19-year-old female who presents for care because she thinks she is bipolar. During her initial interview, she admits that she has a long history of feeling like she was the person in the family of whom there were always high expectations, and she was never able to express concerns or feelings of inadequacy. When asked why she thinks she is bipolar, she says she gets very 0 out of 1 points moody. She was at the grocery store last week and slipped and fell. While waiting for help, she could not control her anger and reached up to swipe all the food off of the shelves. She has been fired from jobs because of her uncontrollable temper; she sometimes “just can’t be around certain people.” Chantel also reports that at times she will go two full days and nights being unable to sleep, and that her mind keeps racing and she can’t “shut it down.” When this happens, she just gets up and does things around the house. Finally, Chantel reports that she cannot hold onto money at all. Whenever she gets a paycheck, she immediately spends it on things that she acknowledges she doesn’t even need. When considering a diagnosis of bipolar disorder, the PMHNP specifically assesses for: Selected Answer: Manic symptoms that are sustained most of the day for at least 2 weeks Answers: Any history of suicidal attempts or serious ideation History and current patterns of substance abuse Concomitant psychotic features such as hallucination or delusion Manic symptoms that are sustained most of the day for at least 2 weeks Response Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. DSM-5 criteria for bipolar disorder require a single or multiple manic episode that meets four criteria. Chantel meets the first three; (1) a distinct period of abnormal and persistently elevated mood for at least 1 week, (2) at least 3 of 7 specific behaviors described in the question, and (3) the symptom causes marked impairment (she has been fired). The fourth criteria is that symptoms are not the result of a substance of abuse. Chantel’s history of substance abuse needs to be documented. ● Question 58 0 out of 1 points Joe W. is a 28-year-old male who is currently having an acute manic episode. He has not slept for 3 days, is extremely irritable, and is prone to violent outbursts of anger. He reports what is clearly a sustained episode of racing thoughts and has experienced psychotic episodes. According to his history, Joe has been on mood stabilizing medication in the past, but he is very unreliable when it comes to follow-up. When considering medication therapy for Joe, the PMHNP knows that: Selected Answer: Joe would be best managed with injectable antipsychotics Answers: Lithium carbonate is the drug of choice for Joe Joe would be best managed with injectable antipsychotics Risperidone is an appropriate choice when mania is characterized by anger and violence Symbyax (olanzapine/fluoxetine) is the safest choice for Joe given his psychosis Response Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. Although Joe W. requires further history to determine if inpatient management is appropriate, among these answer choices, risperidone is the best choice as his mania is characterized by anger and violent outbursts. Lithium is the gold standard, but requires close follow-up and frequent monitoring, which Joe has not historically followed. Injectable antipsychotics are not the first-line choice here as there is no evidence of imminent harm to self or others. Symbyax is appropriate for the depressive episodes of bipolar but not for acute manic episodes. ● Question 59 0 out of 1 points When evaluating the laboratory assessment of a patient with alcohol use disorder, the PMHNP may reasonably expect to find all of the following abnormalities due to chronic alcohol use except: Selected Answer: Transaminitis Answers: Macrocytosis Transaminitis Uremia Hypertriglyceride mia Response Feedback (c) is the correct answer. While chronic daily alcohol use may include macrocytosis, transaminitis, and hypertriglyceridemia, there is no : association between chronic alcohol use and uremia. When patients with alcohol use disorder have uremia, another etiology should be pursued. ● Question 60 Kevin is a 24-year-old male who seeks treatment for anxiety. He thinks he has an anxiety disorder because he has a lot of the same symptoms that his mother 1 out of 1 points does, and she takes medications for anxiety. He reports being “constantly wired,” irritable, and not sleeping well. Kevin says he always has energy, but it’s not a good kind of energy. He does not have isolated panic attacks; he is always just “amped up.” He denies any substance abuse, and he does not smoke cigarettes. When considering organic causes of his symptoms, the PMHNP must evaluate his: Selected Answer: Caffeine intake Answers: Caffeine intake Use of dietary supplements Testosterone level Liver function tests Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. These symptoms, which sound like anxiety disorder, may all be caused by excess use of caffeine; his daily caffeine intake should be evaluated. Dietary supplements can cause organic problems, but not typically anxiety symptoms. A low testosterone level would not cause anxiety levels but rather symptoms of fatigue, malaise, and weight gain. Elevated liver functions tests may cause nausea and feelings of generally being unwell, but anxiety symptoms are less likely. ● Question 61 Among the various types of therapeutic intervention for patients with borderline personality disorder, which of the following is characterized as polymodal, including group skills training, individual therapy, telephone consultation, and a 1 out of 1 points consultation team with a goal of improving interpersonal skills and decreasing self- destructive behavior? Selected Answer: Dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT) Answers: Mentalization-based treatment (MBT) Transference-focused psychotherapy (TFP) Countertransference-focused psychotherapy (CTFP) Dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT) Response Feedback (d) is the correct answer. DBT is the form of therapy that has the most empiric support. It is characterized by the stated four modes of : treatment and five essential functions of treatment. MBT is another form of therapy that fosters patient awareness of mental state of self and others. TFP is a form of psychodynamic psychotherapy that is also used. CTFP is not a defined therapeutic approach. ● Question 62 1 out of 1 points Maurice is a 22-year-old male who is being treated for major depressive episode. He presents today for a follow up visit. He was started on sertraline 50 mg daily 4 weeks ago, and 2 weeks ago, his dose was increased to 150 mg daily. Today he is concerned because he doesn’t really feel much symptom improvement, and he thinks he needs something else. The best response to Maurice is to tell him that: Selected Answer: He needs to be increased to 200 mg today and follow up in 4 weeks Answers: He needs to be increased to 200 mg today and follow up in 4 weeks He should maintain this dose for 4 weeks and reassess He should change his therapy to an SNRI Addition of cognitive behavioral therapy would likely improve response Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. Absent adverse events, his medication should be maintained at maximal doses for 4–5 weeks before considering the drug trial ineffective; 50–200 mg is the typical dose range of his medication for major depressive disorder. It is not appropriate to change drug class yet, and while CBT may improve response overall, the best answer in this scenario is to maximize his medication dose. ● Question 63 Melissa is a family nurse practitioner who is enrolled in a PMHNP program and is beginning her first clinical rotation. After being oriented to the practice processes and procedures, she is preparing for her first solo interview of a patient who is presenting to the practice to establish care. Melissa knows that, unlike her experience as a primary care nurse practitioner, the first office visit with a psychiatric patient should be: Selected Answer: Comprehensive Answers: At least 90 minutes Person- centered Comprehensive Insight- oriented 0 out of 1 points Response Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. Unlike primary care, where the reason for care is often based on the reason for visit (e.g., sore throat, wellness exam, chest pain), the psychiatric interview should be person- centered. The patient’s life experience is the central theme. Initial interviews may extend to 90 minutes, although this is not typical and in many cases the patient may not be able to tolerate that much; 45 to 90 minutes is generally allotted for an initial interview. While initial psychiatric visits are comprehensive, this is not unlike an initial medical visit. Both are comprehensive, it is the focus that is different (person-centered vs. complaint-centered). Not all therapy is insight- oriented; some people present as court-appointed or with a primary goal of changing behavior rather than developing insight. ● Question 64 Mariel is a middle-aged woman who is referred by her primary care provider for management of agoraphobia. Mariel has had this fear as long as she can remember, but now that her children have moved away from home she will need to be more independent and is very committed to trying to manage her fear. The PMHNP counsels Mariel that the most successful therapy for phobic disorders is: Selected Answer: Insight-oriented psychotherapy Answers: Insight-oriented psychotherapy Behavior therapy Virtual therapy Pharmacotherapy 0 out of 1 points Respons e Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. Behavior therapy is the most studied therapy and has the widest evidenced-based support. Insight-oriented therapy has not demonstrated resolution of the phobia. There is no clear role for pharmacotherapy in specific phobias, although it is sometimes useful in social phobia. Virtual therapy is the use of computer- generated simulations to expose the patient, and while this currently demonstrates variable success, it is considered among the cutting- edge therapies of the future. ● Question 65 Janel is a 37-year-old woman who is being interviewed as part of a family assessment. Her 10-year-old son is having some behavioral issues in school and 1 out of 1 points has been referred for evaluation. While interviewing Janel, the PMHNP appreciates that she appears very emotional. She expresses extreme distress at her son’s behavior and says she will do anything to help him; they are “best friends.” She is very demonstrative during the assessment and seems unhappy when she is not the center of attention during the evaluation process. She repeatedly talks about her own medical problems, such as recurrent headache and abdominal pain, which her doctors cannot diagnose. Her appearance is very flamboyant, and her dress is more appropriate to a nightclub than a family assessment. In addition to managing her son’s needs, Janel would likely benefit from: Selected Answer: Psychoanalytic psychotherapy Answers: Pharmacotherapy Psychoanalytic psychotherapy Transference-focused psychotherapy A stress interview Response Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. Patients with histrionic personality disorder are typically not aware of their own feelings and will benefit from clarifying their own true feelings. Pharmacotherapy may be helpful if there are additional symptoms such as depression or anxiety, but it is not primary therapy for histrionic personality disorder. Transference- focused psychotherapy is an approach used for borderline personality disorder, and stress interview is among the techniques for antisocial personality disorder. ● Question 66 Hugo is a 39-year-old male who has encouraged his wife to come to counseling because he is worried about her wine drinking. Hugo says that he and his wife have shared a bottle of wine with dinner most nights for the last couple of years, 0 out of 1 points but in the last few months he has become worried that she drinks too much. They both agree that she never really becomes intoxicated, but he does not like the fact that evening wine has become the most important part of her meal. If he wants to go out, she will only go to a place that has a wine she likes. Last month they went on a week-long vacation, and she insisted on packing enough of her wine to last the whole time. If they go to a restaurant that does not have a wine she likes, she will take her own in a disposable coffee cup. It seems like for the last few months, she has been drinking more and more, occasionally finishing the bottle alone when he doesn’t want any. Both partners agree that there is no interference with work or any activities or responsibilities, but it is causing some tension in their marriage. When considering a diagnosis of substance use disorder, the PMHNP considers that: Selected Answer: The family history should be assessed for genetic tendency Answers: Hugo’s wife meets diagnostic criteria for this disorder A trial period with no wine ingestion is necessary to assess for withdrawal symptoms The family history should be assessed for genetic tendency Hugo may have unreasonable expectations Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. Diagnostic criteria for substance use disorder includes a maladaptive pattern of substance use leading to clinically significant impairment or distress as manifested by 2 of 11 circumstances that include (1) a great deal of time is spent in activities necessary to obtain the substance and (2) use continues despite knowledge of having a persistent or recurrent physical or psychologic problem caused by the substance. Hugo’s wife’s behavior is consistent with both. Withdrawal symptoms are not necessary to support this diagnosis, and while family history will round out the clinical assessment, it is not necessary to support the diagnosis. Her preoccupation with wine is not an unreasonable concern for Hugo. ● Question 67 0 out of 1 points Cannabis intoxication delirium is characterized by all of the following except: Selected Answer: [None Given] Answers: Impaired memory Perception Psychosis Motor coordination Response Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. Cannabis intoxication syndrome, which is not uncommon, is characterized by marked impairment of cognition and performance tasks, memory, reaction time, perception, attention, and motor coordination. It is not associated with psychosis. Cannabis- induced psychotic disorder, which is very rare, is more likely in countries where people have long-term access to very high-potency cannabis. ● Question 68 Margo is a 47-year-old female who admits to a history of fairly heavy alcohol use over many years. She admits that she has had periods in the past where she 0 out of 1 points stopped drinking for a brief time, but she has always gone back to it. At this point she says she has been drinking a fifth of bourbon every 2–3 days for over a year. She has a new boyfriend and really wants to stop drinking, but she is afraid she will “go into the DTs.” She has been reading about it on the Internet, and she knows it can be fatal. Other than her drinking, Margo is amazingly healthy. She had a complete physical exam with blood work through her primary doctor, and he says that her drinking does not appear to have affected her physical health at all. While counseling Margo about alcohol withdrawal delirium (delirium tremens), the PMHNP advises Margo that: Selected Answer: [None Given] Answers: She should be admitted for inpatient detoxification People in good physical health rarely have DTs A beta adrenergic antagonist medication can minimize her risk of DTs Women rarely experience DTs Response Feedback : (b) is the correct answer. Physical illness predisposes to DTs, and people in good physical health rarely experience it. Since Margo’s current alcohol pattern is approximately 1 year and she is in good physical health, her risk of DTs is low and she can be safely managed as an outpatient. Beta adrenergic antagonists can be used for sympathetic nervous system hyperactivity but they do not treat or prevent delirium. There is not gender predisposition for DTs. ● Question 69 Laura T. is a 27-year-old female who has been referred for psychiatric evaluation. She has no significant psychiatric or medical history and denies any history of substance abuse, but she is here because she is persistently having olfactory hallucinations. For the last 3 months, she has been having this progressive sense of smelling particularly foul odors—feces, rotting food, trash— with no obvious cause. She made the appointment because she had an uncle who had schizophrenia and he used to have hallucinations too, although he was mostly hearing voices. The PMHNP knows that a priority of assessment includes a: 0 out of 1 points Selected Answer: [None Given] Answers: BPRS Toxicology screen Head imaging Family history Response Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. In North American culture, nonauditory hallucinations are a clue that there is a medical or substance abuse etiology; as the patient denies substance abuse, a priority of assessment is head imaging. The BPRS (brief psychiatric rating scale) measures psychiatric symptomatology and may be appropriate if a physical cause of symptoms is ruled out. A family history is also helpful, but the priority here—and best answer—is imaging to help rule out an organic cause. ● Question 70 Among the various psychotherapeutic techniques available for treating post- 0 out of 1 points traumatic stress disorder, which mechanism achieves its effect by having patients work through the traumatic event while in a deep state of relaxation? Selected Answer: Answers: [None Given] Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing therapy Implosive therapy Systematic desensitization Relaxation and cognitive techniques Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. EMDR is a technique in which the patient focuses on the lateral movement of the clinician’s finger while maintaining a mental image of the trauma. Implosive therapy is an intense desensitization program, while systematic desensitization is graded exposure via video or other methods of simulation. Relaxation and cognitive techniques teach coping mechanisms as well as thought- altering approaches. ● Question 71 0 out of 1 points While preparing a class on personality disorders for a class of PMHNP students, the instructor is presenting case studies of patients with cluster A personalities. One of these cases is Clark M., a 41-year-old man who is described as a life-long “loner.” In high school and college, he kept to himself, excelling in his studies in the sciences. Currently described as a brilliant computer programmer, he clearly prefers solitary pursuits and the company of his cat over people. He knows he is socially isolated, but he is just more comfortable this way. This description is most consistent with: Selected Answer: Answers: [None Given] Schizoid personality disorder Schizotypal personality disorder Paranoid personality disorder Delusional disorder Response Feedback : (a) is the correct answer. Schizotypal personalities are more likely to be characterized by disordered thinking and communication, and less of a capacity for reality. Paranoid personalities tend to be more socially engaged, and delusional disorders are characterized by delusions with no basis in reality. ● Question 72 0 out of 1 points The PMHNP is preparing a presentation for a primary care conference on geriatric health care. The topic is geriatric depression, and this presentation is designed to increase recognition of community-dwelling elders at risk. An important talking point in this presentation will include all of the following about geriatric depression except: Selected Answer: [None Given] Answers: Depression presents with more somatic symptoms as compared to younger age groups Ageism may cause primary care clinicians to accept depressive symptoms in the elderly as normal Risk factors include loss of spouse, physical illness, and social isolation Incidence of geriatric depression is estimated at 60–75% of the population Response Feedback : (d) is the correct answer. The incidence of geriatric depression is estimated to be between 25–50%. There is a greater prevalence of somatic symptoms; ageism is a documented factor in under diagnosis; and loss of spouse, social isolation, and physical illness are the primary risk factors. ● Question 73 Marie is a 30-year-old woman who presents for follow-up after starting treatment for bipolar disorder. She had been treated on and off for depression for years and had a history of alcohol abuse. After her marriage, she decided to stop drinking and was successful in eliminating alcohol from her life; unfortunately, she then went on to have a manic episode and was finally started on a mood stabilizer 1 month ago. She tolerated medication very well, and within 2 weeks symptoms were much improved. Now, 4 weeks later, she feels much better and wants to come off medication. The PMHNP tells her that: 0 out of 1 points Selected Answer: [None Given] Answers: Discontinuing medication presents a marked risk of return to alcohol A program of psychotherapy should be started before stopping medication She needs to continue medication for a minimum of 3 months Cessation of mood stabilizers prematurely increases risk for a depressive episode Response Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. An untreated manic episode lasts an average of 3 months; medications should not be discontinued prior to this time. The primary risk of early medication discontinuance is recurrent mania; there are no data with respect to return to alcohol. A program of psychotherapy may augment mood stabilizers, but it is not requisite to stopping medication. ● Question 74 Mr. Kendall is a 47-year old male who is presented to care by his younger sister, Megan. Mr. Kendall has spent his entire adult life living in an apartment that was 0 out of 1 points attached to his parents’ home. His mother died a few weeks ago, and the property is listed for sale. Mr. Kendall will have to move, and while discussing this with him, Megan became very concerned. He has apparently been considered odd all his life, has never married or even dated as far as Megan knows, but she had no idea how odd he was. When his mother died, he seemed disconnected from reality and had episodes of talking to people who weren’t present. Megan says that sometimes she does not even understand what he is talking about. He seems to think he has psychic powers, and that he doesn’t need to move because he knows the house will not be sold. When considering a diagnosis of schizotypal disorder, the PMHNP expects which of the following to be present in the history? Selected Answer: Answers: [None Given] A history of schizophrenia of a first-degree relative Sustained psychosis predating his mother’s death Comorbid Asperger’s syndrome Apparent frank thought disorder Response Feedback : (c) is the correct answers. If a trusting relationship develops, patients may eventually discuss an active fantasy life. They genuinely do not have much, if any, interest in sex or intimacy. Schizoid patients may become involved in group therapy settings, although they remain very quiet and appear disengaged. These patients do not have psychotic of delusional episodes; that would constitute a different diagnosis. ● Question 75 0 out of 1 points Depressive personality disorder exists along the spectrum of dysthymia and major depressive disorder, but it is different from these two in that: Selected Answer: [None Given] Answers: Pharmacologic treatment is not indicated The etiology is different Perfectionism is common Physical symptoms are lacking Respons e Feedback : (c) is the correct answer. Unlike patients with dysthymia or MDD who may lack the drive or ability to attend to personal or work-related details, patients with depressive personality are often meticulous, over- conscientious, and preoccupied with work. While the etiology is unknown, it is generally regarded to include the same psychosocial and physiologic causes. Patients may benefit from low-dose SSRIs or psychostimulants. Physical symptoms, such as psychomotor retardation, may be present. Tuesday, October 10, 2017 11:11:17 PM EDT [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 43 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 02, 2023
Number of pages
43
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 02, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
232