*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NESTA PFT Top Exam Questions and answers, 100% Accurate, rated A+ (All)
NESTA PFT Top Exam Questions and answers, 100% Accurate, rated A+
Document Content and Description Below
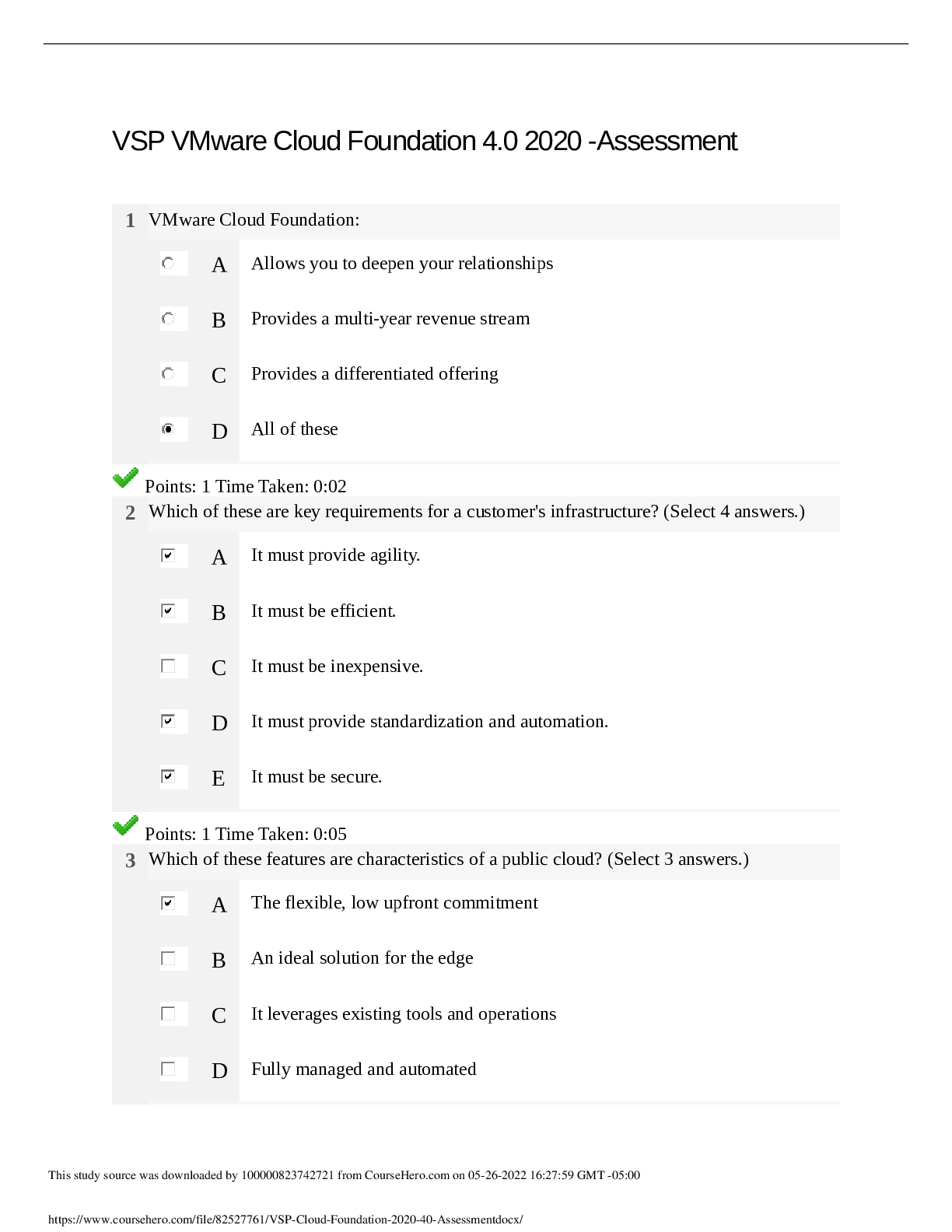
NESTA PFT Top Exam Questions and answers, 100% Accurate, rated A+ What are the four steps in "Bridging the Gap" between current client health & fitness levels, & their future goals & needs? - ✔... ✔-Assess - Design - Instruct - Re-assess What is the difference between implicit & explicit goals? - ✔✔-Implicit - implied, but not necessarily mentioned. Explicit - goals that are mentioned by your client. What is the kinetic chain? What is its function? - ✔✔-3 separate systems which work together to create human movement. (nerous system, muscular system, skeletal system) What is the difference between smooth, cardiac & skeletal muscle? - ✔✔-Smooth - muscles that are capable of involuntary actions/no striations. (digestive tract, bladder, uterus, blood vessel walls) Cardiac - muscles that are capable of involuntary actions/some striations. (heart only) Skeletal - muscles that are capable of voluntary contraction. (all muscles controlling movement) What are the 3 layers of fascia? What is their significance? - ✔✔-Epimysium - outer layer/surrounds muscle completely. Perimysium - next layer/groups muscle fibers in bundles. Endomysium - innermost layer/surrounds individual muscle fibers. What is the structure of the motor unit? - ✔✔-A motor neuron & all of the fibers it activates. What is the sliding filament theory? - ✔✔-The Sacromere is composed of thin & thick filaments, these elements slide over each other resulting in the shortening of all the sacromeres together causing the muscle to contract. Know the difference between eccentric, isometric & concentric muscle actions. Which is the strongest? Which is the weakest? - ✔✔-Eccentric - as the muscles attempt to control the downward phase or decelerate load. (the strongest) Concentric - as the muscles attempt the contraction or lifting phase of a load. (weakest) Isometric - static/the muscle fires, but there is no change in the length of the muscle & no movement in the joints. What is the difference between hypertrophy, hyperplasia & atrophy? - ✔✔-Hypertrophy - increase in the size of the muscle/the myofibrils inside the muscle fibers. Hyperplasia - increase in the number of muscle cells in the body w/a corresponding increase in muscular size. (extremely rare) Atrophy - the wasting or loss of muscle tissue resulting from disease or lack of use. What are the 3 different skeletal muscle types? Be able to identify which type is dominate in an exercise. - ✔✔-Type I - Aerobic Fibers Fatigue resistant - tend toward stabilizing functions rather than prime movers - endurance related (longer than 3 mins) Type IIA - Tend to help in activities lasting between 30 sec & 2 mins using a moderate level of strength & aerobic activity. Type IIB/IIX - Anaerobic fibers Larger in diameter & suited for brief powerful contractions. Prime movers of joints - tend to excel in maximal lifts, sprinting or jumping. What are the various roles of muscle? Be able to identify various roles during movement. - ✔✔-Prime Mover/Agonist - a muscle that acts directly to bring about a desired movement through concentric muscle action. Assistant Mover/Synergist - a muscle that assists indirectly to bring about a desired movement. Antagonist - a muscle responsible for opposing the concentric muscle action of the agonist. Stabilizer - a muscle responsible for stabilizing an adjacent segment. Neutralizer - a muscle responsible for eliminating or canceling out an undesired movement. What are the various types of strength? Be able to identify exercises which emphasize a particular type of strength. - ✔✔-Absolute Strength - the maximum amount of force an individual can produce in a one repetition maximum lift, irrespective of bodyweight & time of force development. (shot putters or lineman) Relative Strength - the maximum force that muscles can generate in relation to one's bodyweight. (gymnast) Strength Endurance/Muscular Endurance - the ability to sustain muscular contractions for a long duration of time. (cycling or rowing) What factors contribute to muscle soreness? - ✔✔-Post Exercise Muscle Soreness/PEMS - normal & not necessarily harmful. 24 - 48 hrs Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness/DOMS - should be avoided. Lasts more than 1-2 days. The goal is to gain muscular, joint & nervous system benefits, not tissue microtrauma & soreness. It is normal for a muscle & connective tissue to tear & rebuild. It is not normal to create excessive trauma to muscle fibers & connective tissue by creating pain that lasts more than 1-2 days. What are the basic structure & functions of joints? - ✔✔-Joint - an articulation between two bones which is used to connect one component of a structure with one or more other components. What are the different types of diarthrodial joints? Be able to give examples of each. - ✔✔-Saddle - two saddle shaped surfaces allowing two degrees of freedom. (ex. carpo - metacarpal joint of the thumb) Condyloid - biaxial, one plane of movement that dominates two planes of motion. (ex. tibiofemoral joint, interphalangeal joint) Hinge - one degree of motion. (ex. humeroulnar) Plane "gliding" - flat surface that allows translation between two bones. (ex. acromioclavicular joint) Pivot - one degree of freedom. (ex. antlantoaxial joint) Multiaxial - "Ball & Socket" - three degrees of freedom, freely movable, allowing motion in all three planes of human movement. (ex. hip joint) What is the Epiphyseal Plate? What is Epiphyseal Plate slippage? - ✔✔-Growth plate - disk of cartilaginous cells separating diaphysis & epiphysis - site of longitudinal growth. Slippage is more likely to occur in pre-pubescent chidlren... may inhibit the grown of bone at a joint, but will not necessarily affect growth of the entire body. What is ATP? - ✔✔-Adenosine Triphosphate - the immediate source of energy for muscle contractions/the muscles primary energy source. What are the 3 different energy systems? - ✔✔-Anaerobic Pathway I: ATP/PCr System (aka Phosphagen System) - Does not use oxygen nor produce lactic acid. Used for very short durations up to 10 sec. (ie. golf swing - powerlifting) Anaerobic Pathway II: Glycolysis - Breakdown of glycogen in a multi-step process into pyruvate which is converted to lactate - used for exercises lasting less than 2 minutes. (ie 400m sprint) Aerobick Pathway: Aerobic Glycolysis & Oxidative Phosphorylation - Long duration energy system - all exercises for 2 min or longer utilize the oxidative system for energy production & the oxidative energy system supplies almost all cellular energy for the muscles. Lactate is a by-product of what energy system? - ✔✔-Anaerobic Pathway II/Glycolisis What is "aerobic exercise"? - ✔✔-Processes utilizing oxygen in the processes of breaking down & syntheses. (occuring in the mitochondria or the muscle cells) What is blood pressure? - ✔✔-The measure of the force that blood exerts on the walls of the blood vessels. What are the different phases that make up the heartbeat? - ✔✔-Systolic Phase - cardiac muscle contraction, whereby the ventricles contract, pushing blood away from the heart. Diastolic Phase - cardiac muscle relaxation. What is considered normal BP? High BP? - ✔✔-Normal - 120/80 High - 140/90 What is the valsalva maneuver? - ✔✔-When an individual holds their breath by closing the glottis of the throat in an attempt to briefly increase muscular power. What happens when exercise is abruptly stopped? - ✔✔-Blood can potentially pool in the extremities leaving the individual feeling light headed or dizzy. What is RHR? THR? HRR? MHR? How is each determined? - ✔✔-RHR - Resting Heart Rate Ideally measured 1st thing in the morning or after at least 5 min of quiet rest & no caffeine. (60-80 bpm) MHR - Maximum Heart Rate The maximum number of contractions the heart will beat in one minute. Reached through maximum physical exercise. (must estimate w/out MHR test) HRR - Heart Rate Reserve The difference between MHR & RHR. (where training occurs) THR - Target Heart Rate Ideal heart rate intensity during exercise. Calculated as percentage of VO2 max or percentage of HRR. (50-85% of HRR) (THR = RHR + HRR x % desired) Be able to use the Karvonen equation. - ✔✔-HRR = MHR - RHR MHR = 220 - age What is overreaching? Overtraining? Detraining? - ✔✔-Overreaching - a state where a few days of rest or light exercise enables the body to recover & return to a normal physiological state. Overtraining - a state of fatigue or physical malfunctioning where it may take weeks, months or even years to return to a normal physiological state & be able to progress & improve significantly. Detraining - Diminishing physiological capacity as training becomes infrequent or ceases altogether. What is the most efficient way to breathe? - ✔✔-2:1 exhale to inhale - it increases oxygen utilization & encourages greater cardiovascular efficiency. How does high altitude affect breathing? - ✔✔-The partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere declined, making it more difficult to get sufficient oxygen to diffuse into the cappillaries... the body compensates by increasing the rate of venillation through hyperventilating, increasing the rate of cellular respiration & decreasing the capacity to do work. In most cases, should one exhale or inhale on the exertion phase of an exercise? - ✔✔-Exhale What is anatomical position? Anatomical neutral? - ✔✔-Anatomical - a position of standing erect with the palms facing forward or externally rotated. Anatomical Neutral - a position of standing erect with the palms facing the body. (aka fundamental starting position) What are the planes of movement? How do they divide the body? - ✔✔-Sagittal Plane - divides the body into right & left halves. Frontal Plane - divides the body into front & back halves. (aka coronal plane) Horizontal Plane - divides the body into top & bottom halves. (aka transverse plane) Be able to identify & properly use all the anatomical movement descriptors. - ✔✔-Anterior (aka ventral) - the front of the body relative to another reference point. Posterior (aka dorsal) - the back of the body relative to another reference point. Superior - above a reference point. Inferior - below a reference point. Medial - a position relatively closer to the midline of the body. Lateral - a position relatively farther away from the midline. Proximal - a position closer to a reference point. Distal - a position farther from the reference point. Unilateral - refers to only one side. Superficial - near the surface. Deep - further beneath the surface. Cephalic - toward the head. Caudal - toward the bottom. Supine - lying on one's backside. Prone - lying face down. What are the primary movement descriptors? What planes do each move in? - ✔✔-Sagittal Plane/Coronal Axis: Flexion - a bending movement where the relative angle between two adjacent segments decreases. Extension - a bending movement where the relative angle between two adjacent segments increases. Frontal Plane/Anterior-Posterior Axis: Abduction - movement away from the midline of the body. Adduction - movement towards the midline of the body. Transverse Plane/Longitudinal Axis: Internal/Medial Rotation - the rotation of a body part towards the midline (spine or vertebrae column) of the body. External/Lateral Rotation - the rotation of a body part away from the midline of the body. If an individual's foot is externally rotated when standing, which parts of the leg will most likely also externally rotate? - ✔✔-... What are the 4 main movements of the Scapula? - ✔✔-Protraction - abduction of the scapula. Retraction - adduction of the scapula. Elevation - raising of the scapula. (shrug) Depression - lowering of the scapula. What is pronation & supination at the wrist? At the ankle? - ✔✔-At wrist: Pronation - movement of the forearm where the palm rotates to face backward. Supination - movement of the forearm where the palm rotates to face forward. At ankle: Pronation - a triplane motion consisting of simultaneous movements of eversion, abduction, dorsiflexion. Supination - a triplane motion which combines the movements of inversion, adduction, plantarflexion. What are the 3 main parts of a muscle? - ✔✔-Belly - the bulging part of a muscle. Origin (or head) - the less moveable attachment (there can be more than 1 origin) Insertion - the movable attachment. What is the job of the sternocleidomastoid? - ✔✔-Flex head. What is the primary function of the gastrocnemius on soleus during a calf raise? - ✔✔-Primary function is concentric: Gastrocnemius - plantarflexion & knee flexion. Soleus - plantarflexion. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 31 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Also available in bundle (1)

NESTA PFT EXAM BUNDLE, VERIFIED.
NESTA PFT EXAM 3, Questions with Accurate answers, 100% Accurate, rated A+. EXAM PREDICTOR PAPERS.
By Topmark 1 year ago
$36
21
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 13, 2023
Number of pages
31
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 13, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
73

















.png)




