Chem 103 Exam 2 Accurate Questions and Answers
Document Content and Description Below
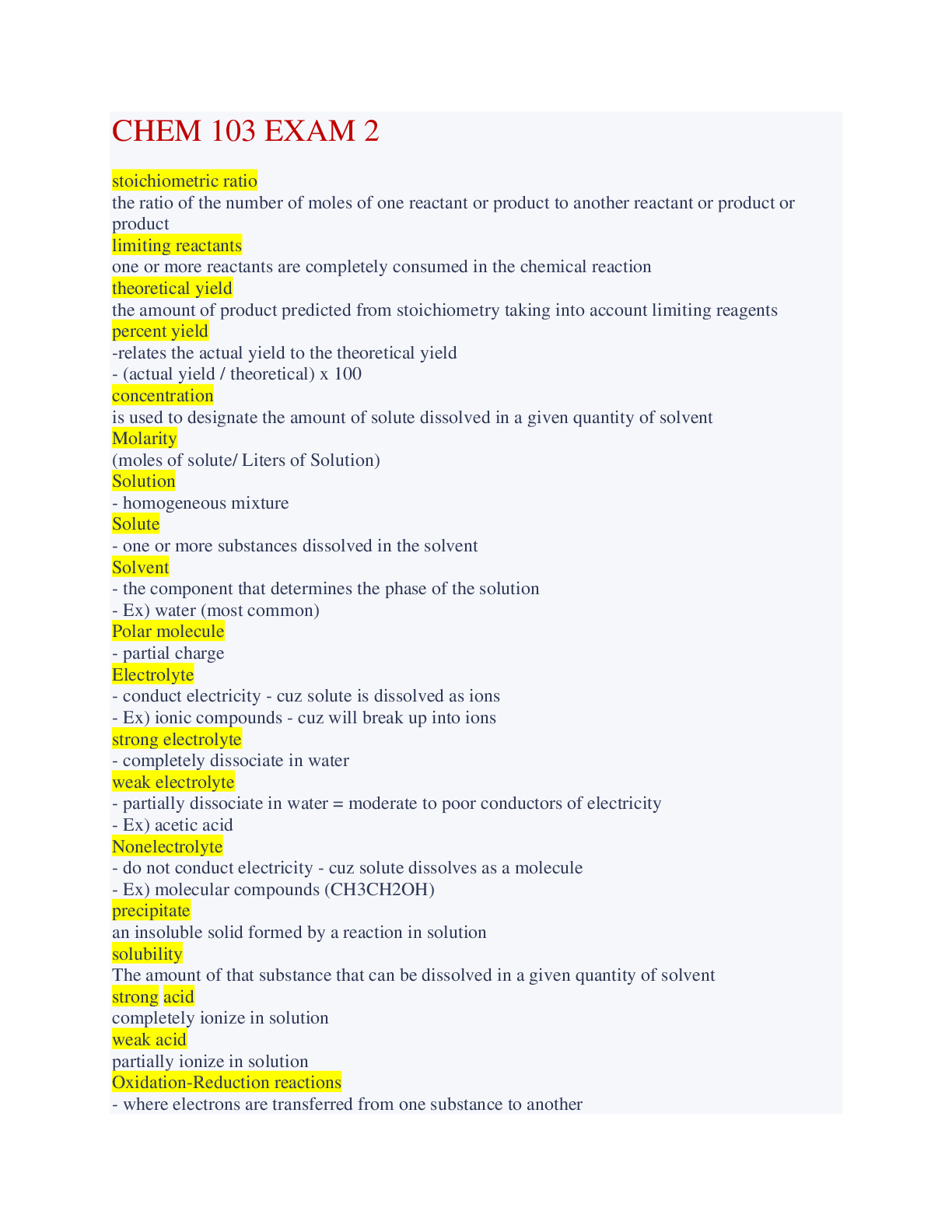
Chem 103 Exam 2 Accurate Questions and Answers stoichiometric ratio the ratio of the number of moles of one reactant or product to another reactant or product or product limiting reactants one... or more reactants are completely consumed in the chemical reaction theoretical yield the amount of product predicted from stoichiometry taking into account limiting reagents percent yield -relates the actual yield to the theoretical yield - (actual yield / theoretical) x 100 concentration is used to designate the amount of solute dissolved in a given quantity of solvent Molarity (moles of solute/ Liters of Solution) Solution - homogeneous mixture Solute - one or more substances dissolved in the solvent Solvent - the component that determines the phase of the solution - Ex) water (most common) Polar molecule - partial charge Electrolyte - conduct electricity - cuz solute is dissolved as ions - Ex) ionic compounds - cuz will break up into ions strong electrolyte - completely dissociate in water weak electrolyte - partially dissociate in water = moderate to poor conductors of electricity - Ex) acetic acid Nonelectrolyte - do not conduct electricity - cuz solute dissolves as a molecule - Ex) molecular compounds (CH3CH2OH) precipitate an insoluble solid formed by a reaction in solution solubility The amount of that substance that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent strong acid completely ionize in solution weak acid partially ionize in solution Oxidation-Reduction reactions - where electrons are transferred from one substance to another Pressure force per unit area Dissociate -when an ionic compound dissolves in water -each ion is surrounded by water molecules Molecular Compounds in Water dissolves in water but no ions are formed aqueous solution soluble in water acid a molecule that is able to ionize to produce H+ Base substances that accept hydrogen ions oxidation gaining oxidation numbers (loss of electrons) reduction decrease in oxidation numbers (gain of electrons) spectator ions -the ions that get canceled out of the Ionic equation vapors substances that are liquids or solids under ordinary conditions but may also exist as gases under different conditions Boyle Law PV = constant Charles Law V/T = constant Avogadro's Law V/n = constant Ideal Gas Law PV = nRT STP - standard temperature and pressure -0 degree C and 1 atm - 22.4 L / mol Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures P₁ = n₁RT/V Mole Fraction P₁/n₁ = P₂/n₂ Sulfur Oxides - produced from coal burning - component of acid rain - affects the respiratory system - Ex) So₂ and SO₃ Carbon monoxide - formed from incomplete combustion of fossil fuels - produced from vehicle emissions - affects respiratory system/ binds to oxygen in blood system and suffocates Nitrogen Oxides - formed in gasoline combustion/ high temp combustion process - component of acid rain and haze - lung and eye irritant - Ex) NO and NO₂ Ozone - O₃ - produced by reactions of hydrocarbons and NO in the presence of sunlight - component of smog affects respiratory system [Show More]
Last updated: 7 months ago
Preview 1 out of 3 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 30, 2023
Number of pages
3
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 30, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
53

.png)