Pediatric Nursing exam 1 practice 244 Questions with Answers,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
Pediatric Nursing exam 1 practice 244 Questions with Answers The nurse is seeing an adolescent and the parents in the clinic for the first time. Which should the nurse do first? a. Introduce him... - or herself. b. Make the family comfortable. c. Give assurance of privacy. d. Explain the purpose of the interview. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A The first thing that nurses must do is to introduce themselves to the patient and family. Parents and other adults should be addressed with appropriate titles unless they specify a preferred name. Clarification of the purpose of the interview and the nurse's role is the second thing that should be done. During the initial part of the interview, the nurse should include general conversation to help make the family feel at ease. The interview also should take place in an environment as free of distraction as possible. In addition, the nurse should clarify which information will be shared with other members of the health care team and any limits to the confidentiality. Which is considered a block to effective communication? a. Using silence b. Using clichés c. Directing the focus d. Defining the problem - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Using stereotyped comments or clichés can block effective communication. After the nurse uses such trite phrases, parents often do not respond. Silence can be an effective interviewing tool. Silence permits the interviewee to sort out thoughts and feelings and search for responses to questions. To be effective, the nurse must be able to direct the focus of the interview while allowing maximum freedom of expression. By using open-ended questions and guiding questions, the nurse can obtain the necessary information and maintain a relationship with the family. The nurse and parent must collaborate and define the problem that will be the focus of the nursing intervention. Which is the single most important factor to consider when communicating with children? a. Presence of the child's parent b. Child's physical condition c. Child's developmental level d. Child's nonverbal behaviors - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C The nurse must be aware of the child's developmental stage to engage in effective communication. The use of both verbal and nonverbal communication should be appropriate to the developmental level. Nonverbal behaviors vary in importance based on the child's developmental level and physical condition. Although the child's physical condition is a consideration, developmental level is much more important. The presence of parents is important when communicating with young children but may be detrimental when speaking with adolescents. Because children younger than 5 years are egocentric, the nurse should do which when communicating with them? a. Focus communication on the child. b. Use easy analogies when possible. c. Explain experiences of others to the child. d. Assure the child that communication is private - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A Because children of this age are able to see things only in terms of themselves, the best approach is to focus communication directly on them. Children should be provided with information about what they can do and how they will feel. With children who are egocentric, analogies, experiences, and assurances that communication is private will not be effective because the child is not capable of understanding. The nurse's approach when introducing hospital equipment to a preschooler who seems afraid should be based on which principle?a. The child may think the equipment is alive. b. Explaining the equipment will only increase the child's fear. c. One brief explanation will be enough to reduce the child's fear. d. The child is too young to understand what the equipment does. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A Young children attribute human characteristics to inanimate objects. They often fear that the objects may jump, bite, cut, or pinch all by themselves without human direction. Equipment should be kept out of sight until needed. Simple, concrete explanations about what the equipment does and how it will feel will help alleviate the child's fear. Preschoolers need repeated explanations as reassurance. When the nurse interviews an adolescent, which is especially important? a. Focus the discussion on the peer group. b. Allow an opportunity to express feelings. c. Use the same type of language as the adolescent. d. Emphasize that confidentiality will always be maintained. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Adolescents, like all children, need opportunities to express their feelings. Often they interject feelings into their words. The nurse must be alert to the words and feelings expressed. The nurse should maintain a professional relationship with adolescents. To avoid misunderstanding or misinterpretation of words and phrases used, the nurse should clarify the terms used, what information will be shared with other members of the health care team, and any limits to confidentiality. Although the peer group is important to this age group, the interview should focus on the adolescent. The nurse is preparing to assess a 10-month-old infant. He is sitting on his father's lap and appears to be afraid of the nurse and of what might happen next. Which initial actions by the nurse should be most appropriate? a. Initiate a game of peek-a-boo. b. Ask the infant's father to place the infant on the examination table. c. Talk softly to the infant while taking him from his father. d. Undress the infant while he is still sitting on his father's lap. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A Peek-a-boo is an excellent means of initiating communication with infants while maintaining a safe, nonthreatening distance. The child will most likely become upset if separated from his father. As much of the assessment as possible should be done with the child on the father's lap. The nurse should have the father undress the child as needed during the examination. An 8-year-old girl asks the nurse how the blood pressure apparatus works. The most appropriate nursing action is which? a. Ask her why she wants to know. b. Determine why she is so anxious. c. Explain in simple terms how it works. d. Tell her she will see how it works as it is used. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C School-age children require explanations and reasons for everything. They are interested in the functional aspect of all procedures, objects, and activities. It is appropriate for the nurse to explain how equipment works and what will happen to the child so that the child can then observe during the procedure. The nurse should respond positively for requests for information about procedures and health information. By not responding, the nurse may be limiting communication with the child. The child is not exhibiting anxiety in asking how the blood pressure apparatus works, just requesting clarification of what will occur. The nurse is having difficulty communicating with a hospitalized 6-year-old child. Which technique should be most helpful? a. Recommend that the child keep a diary. b. Provide supplies for the child to draw a picture. c. Suggest that the parent read fairy tales to the child. d. Ask the parent if the child is always uncommunicative. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Drawing is one of the most valuable forms of communication. Children's drawings tell a great deal about them because they are projections of the children's inner self. A diary should be difficult for a 6-year-old child, who is most likely learning to read. The parent reading fairy tales to the child is a passive activity involving the parent and child; it should not facilitate communication with the nurse. The child is in a stressful situation and is probably uncomfortable with strangers, not always uncommunicative. Which data should be included in a health history? a. Review of systems b. Physical assessment c. Growth measurements d. Record of vital signs - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A A review of systems is done to elicit information concerning any potential health problems. This further guides the interview process. Physical assessment, growth measurements, and a record of vital signs are components of the physical examination. The nurse is taking a health history of an adolescent. Which best describes how the chief complaint should be determined? a. Request a detailed listing of symptoms. b. Ask the adolescent, "Why did you come here today?" c. Interview the parent away from the adolescent to determine the chief complaint. d. Use what the adolescent says to determine, in correct medical terminology, what the problem is. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B The chief complaint is the specific reason for the child's visit to the clinic, office, or hospital. Because the adolescent is the focus of the history, this is an appropriate way to determine the chief complaint. Requesting a detailed list of symptoms makes it difficult to determine the chief complaint. The parent and adolescent may be interviewed separately, but the nurse should determine the reason the adolescent is seeking attention at this time. The chief complaint is usually written in the words that the parent or adolescent uses to describe the reason for seeking help. The nurse is interviewing the mother of an infant. The mother reports, "I had a difficult delivery, and my baby was born prematurely." This information should be recorded under which heading? a. History b. Present illness c. Chief complaint d. Review of systems - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A The history refers to information that relates to previous aspects of the child's health, not to the current problem. The difficult delivery and prematurity are important parts of the infant's history. The history of the present illness is a narrative of the chief complaint from its earliest onset through its progression to the present. Unless the chief complaint is directly related to the prematurity, this information is not included in the history of the present illness. The chief complaint is the specific reason for the child's visit to the clinic, office, or hospital. It should not include the birth information. The review of systems is a specific review of each body system. It does not include the premature birth but might include sequelae such as pulmonary dysfunction. Where in the health history does a record of immunizations belong? a. History b. Present illness c. Review of systems d. Physical assessment - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A The history contains information relating to all previous aspects of the child's health status. The immunizations are appropriately included in the history. The present illness, review of systems, and physical assessment are not appropriate places to record the immunization status. The nurse is taking a sexual history on an adolescent girl. Which is the best way to determine whether she is sexually active? a. Ask her, "Are you sexually active?" b. Ask her, "Are you having sex with anyone?" c. Ask her, "Are you having sex with a boyfriend?" d. Ask both the girl and her parent if she is sexually active. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Asking the adolescent girl if she is having sex with anyone is a direct question that is well understood. The phrase sexually active is broadly defined and may not provide specific information for the nurse to provide necessary care. The word "anyone" is preferred to using gender-specific terms such as "boyfriend" or "girlfriend." Using gender-neutral terms is inclusive and conveys acceptance to the adolescent. Questioning about sexual activity should occur when the adolescent is alone. When doing a nutritional assessment on a Hispanic family, the nurse learns that their diet consists mainly of vegetables, legumes, and starches. The nurse should recognize that this diet is which? a. Lacking in protein b. Indicating they live in poverty c. Providing sufficient amino acids d. Needing enrichment with meat and milk - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C A diet that contains vegetables, legumes, and starches may provide sufficient essential amino acids even though the actual amount of meat or dairy protein is low. Combinations of foods contain the essential amino acids necessary for growth. Many cultures use diets that contain this combination of foods. It is not indicative of poverty. A dietary assessment should be done, but many vegetarian diets are sufficient for growth. Which parameter correlates best with measurements of total muscle mass? a. Height b. Weight c. Skinfold thickness d. Upper arm circumference - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D Upper arm circumference is correlated with measurements of total muscle mass. Muscle serves as the body's major protein reserve and is considered an index of the body's protein stores. Height is reflective of past nutritional status. Weight is indicative of current nutritional status. Skinfold thickness is a measurement of the body's fat content. The nurse is preparing to perform a physical assessment on a 10-year-old girl. The nurse gives her the option of her mother staying in the room or leaving. This action should be considered which? a. Appropriate because of child's age b. Appropriate, but the mother may be uncomfortable c. Inappropriate because of child's age d. Inappropriate because child is same sex as mother - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A It is appropriate to give older school-age children the option of having the parent present or not. During the examination, the nurse should respect the child's need for privacy. Children who are 10 years old are minors, and parents are responsible for health care decisions. The mother of a 10-year-old child would not be uncomfortable. The child should help determine who is present during the examination. With the National Center for Health Statistics criteria, which body mass index (BMI)-for-age percentiles should indicate the patient is at risk for being overweight? a. 10th percentile b. 75th percentile c. 85th percentile d. 95th percentile - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Children who have BMI-for-age greater than or equal to the 85th percentile and less than the 95th percentile are at risk for being overweight. Children who are greater than or equal to the 95th percentile are considered overweight. Children whose BMI is between the 10th and 75th percentiles are within normal limits. Rectal temperatures are indicated in which situation? a. In the newborn period b. Whenever accuracy is essential c. Rectal temperatures are never indicated d. When rapid temperature changes are occurring - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Rectal temperatures are recommended when definitive measurements are necessary in infants older than age 1 month. Rectal temperatures are not done in the newborn period to avoid trauma to the rectal mucosa. Rectal temperature is an intrusive procedure that should be avoided whenever possible. What is the earliest age at which a satisfactory radial pulse can be taken in children? a. 1 year b. 2 years c. 3 years d. 6 years - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Satisfactory radial pulses can be taken in children older than 2 years. In infants and young children, the apical pulse is more reliable. The nurse needs to take the blood pressure of a small child. Of the cuffs available, one is too large and one is too small. The best nursing action is which? a. Use the small cuff. b. Use the large cuff. c. Use either cuff using the palpation method. d. Wait to take the blood pressure until a proper cuff can be located. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B If blood pressure measurement is indicated and the appropriate size cuff is not available, the next larger size is used. The nurse recognizes that this may be a falsely low blood pressure. Using the small cuff will give an incorrectly high reading. The palpation method will not improve the inaccuracy inherent in the cuff. Where is the best place to observe for the presence of petechiae in dark-skinned individuals? a. Face b. Buttocks c. Oral mucosa d. Palms and soles - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Petechiae, small distinct pinpoint hemorrhages, are difficult to see in dark-skinned individuals unless they are in the mouth or conjunctiva. During a routine health assessment, the nurse notes that an 8-month-old infant has a significant head lag. Which is the most appropriate action? a. Recheck head control at next visit. b. Teach the parents appropriate exercises. c. Schedule the child for further evaluation. d. Refer the child for further evaluation if the anterior fontanel is still open. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Significant head lag after age 6 months strongly indicates cerebral injury and is referred for further evaluation. Head control is part of normal development. Exercises will not be effective. The lack of achievement of this developmental milestone must be evaluated The nurse has just started assessing a young child who is febrile and appears ill. There is hyperextension of the child's head (opisthotonos) with pain on flexion. Which is the most appropriate action? a. Ask the parent when the neck was injured. b. Refer for immediate medical evaluation. c. Continue assessment to determine the cause of the neck pain. d. Record "head lag" on the assessment record and continue the assessment of the child. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Hyperextension of the child's head with pain on flexion is indicative of meningeal irritation and needs immediate evaluation. No indication of injury is present. This situation is not descriptive of head lag. During a funduscopic examination of a school-age child, the nurse notes a brilliant, uniform red reflex in both eyes. The nurse should recognize that this is which? a. A normal finding b. A sign of a possible visual defect and a need for vision screening c. An abnormal finding requiring referral to an ophthalmologist d. A sign of small hemorrhages, which usually resolve spontaneously - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A A brilliant, uniform red reflex is an important normal finding. It rules out many serious defects of the cornea, aqueous chamber, lens, and vitreous chamber. Which explains the importance of detecting strabismus in young children? a. Color vision deficit may result. b. Amblyopia, a type of blindness, may result. c. Epicanthal folds may develop in the affected eye. d. Corneal light reflexes may fall symmetrically within each pupil. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B By the age of 3 to 4 months, infants are able to fixate on one visual field with both eyes simultaneously. In strabismus, or cross-eye, one eye deviates from the point of fixation. If misalignment is constant, the weak eye becomes "lazy," and the brain eventually suppresses the image produced from that eye. If strabismus is not detected and corrected by age 4 to 6 years, blindness from disuse, known as amblyopia, may occur. Color vision is not the only concern. Epicanthal folds are not related to amblyopia. In children with strabismus, the corneal light reflex will not be symmetric for each eye. Which is the most frequently used test for measuring visual acuity? a. Snellen letter chart b. Ishihara vision test c. Allen picture card test d. Denver eye screening test - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A The Snellen letter chart, which consists of lines of letters of decreasing size, is the most frequently used test for visual acuity. The Ishihara Vision Test is used for color vision. The Allen picture card test and Denver eye screening test involve single cards for children ages 2 years and older who are unable to use the Snellen letter chart. The nurse is testing an infant's visual acuity. By which age should the infant be able to fix on and follow a target? a. 1 month b. 1 to 2 months c. 3 to 4 months d. 6 months - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Visual fixation and ability to follow a target should be present by ages 3 to 4 months. One to 2 months is too young for this developmental milestone. If an infant is not able to fix and follow by 6 months, further ophthalmologic evaluation is needed. During an otoscopic examination on an infant, in which direction is the pinna pulled? a. Up and back b. Up and forward c. Down and back d. Down and forward - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C In infants and toddlers, the ear canal is curved upward. To visualize the ear canal, it is necessary to pull the pinna down and back to the 6 to 9 o'clock range to straighten the canal. In children older than age 3 years and adults, the canal curves downward and forward. The pinna is pulled up and back to the 10 o'clock position. Up and forward and down and forward are positions that do not facilitate visualization of the ear canal. What is an appropriate screening test for hearing that the nurse can administer to a 5-year-old child? a. Rinne test b. Weber test c. Pure tone audiometry d. Eliciting the startle reflex - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Pure tone audiometry uses an audiometer that produces sounds at different volumes and pitches in the child's ears. The child is asked to respond in some way when the tone is heard in the earphone. The Rinne and Weber tests measure bone conduction of sound. Eliciting the startle reflex may be useful in infants. What is the appropriate placement of a tongue blade for assessment of the mouth and throat? a. On the lower jaw b. Side of the tongue c. Against the soft palate d. Center back area of the tongue - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B The side of the tongue is the correct position. It avoids the gag reflex yet allows visualization. On the lower jaw and against the soft palate are not appropriate places for the tongue blade. Placement in the center back area of the tongue elicits the gag reflex. When assessing a preschooler's chest, what should the nurse expect? a. Respiratory movements to be chiefly thoracic b. Anteroposterior diameter to be equal to the transverse diameter c. Retraction of the muscles between the ribs on respiratory movement d. Movement of the chest wall to be symmetric bilaterally and coordinated with breathing - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D Movement of the chest wall should be symmetric bilaterally and coordinated with breathing. In children younger than 6 or 7 years, respiratory movement is principally abdominal or diaphragmatic. The anteroposterior diameter is equal to the transverse diameter during infancy. As the child grows, the chest increases in the transverse direction, so that the anteroposterior diameter is less than the lateral diameter. Retractions of the muscles between the ribs on respiratory movement are indicative of respiratory distress. When auscultating an infant's lungs, the nurse detects diminished breath sounds. What should the nurse interpret this as? a. Suggestive of chronic pulmonary disease b. Suggestive of impending respiratory failure c. An abnormal finding warranting investigation d. A normal finding in infants younger than 1 year of age - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Absent or diminished breath sounds are always an abnormal finding. Fluid, air, or solid masses in the pleural space all interfere with the conduction of breath sounds. Further data are necessary for diagnosis of chronic pulmonary disease or impending respiratory failure. Diminished breath sounds in certain segments of the lungs can alert the nurse to pulmonary areas that may benefit from chest physiotherapy. Further evaluation is needed in all age groups. Which type of breath sound is normally heard over the entire surface of the lungs except for the upper intrascapular area and the area beneath the manubrium? a. Vesicular b. Bronchial c. Adventitious d. Bronchovesicular - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A This is the definition of vesicular breath sounds. They are heard over the entire surface of the lungs, with the exception of the upper intrascapular area and the area beneath the manubrium. Bronchial breath sounds are heard only over the trachea near the suprasternal notch. Adventitious breath sounds are not usually heard over the chest. These sounds occur in addition to normal or abnormal breath sounds. Bronchovesicular breath sounds are heard over the manubrium and in the upper intrascapular regions, where the trachea and bronchi bifurcate. The nurse is assessing a child's capillary refill time. This can be accomplished by doing what? a. Inspect the chest. b. Auscultate the heart. c. Palpate the apical pulse. d. Palpate the nail bed with pressure to produce a slight blanching. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D Capillary refill time is assessed by pressing lightly on the skin to produce blanching and then noting the amount of time it takes for the blanched area to refill. Inspecting the chest, auscultating the heart, and palpating the apical pulse will not provide an assessment of capillary refill time. Which heart sound is produced by vibrations within the heart chambers or in the major arteries from the back-and-forth flow of blood? a. S1 and S2 b. S3 and S4 c. Murmur d. Physiologic splitting - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Murmurs are the sounds that are produced in the heart chambers or major arteries from the back-and-forth flow of blood. S1 and S2 are normal heart sounds. S1 is the closure of the tricuspid and mitral valves, and S2 is the closure of the pulmonic and aortic valves. S3 is a normal heart sound sometimes heard in children. S4 is rarely heard as a normal heart sound. If it is heard, medical evaluation is required. Physiologic splitting is the distinction of the two sounds in S2, which widens on inspiration. It is a significant normal finding Examination of the abdomen is performed correctly by the nurse in which order? a. Inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation b. Inspection, percussion, auscultation, and palpation c. Palpation, percussion, auscultation, and inspection d. Inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D The correct order of abdominal examination is inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation. Palpation is always performed last because it may distort the normal abdominal sounds. Auscultation is performed before percussion. The act of percussion can influence the findings on auscultation. Superficial palpation of the abdomen is often perceived by the child as tickling. Which measure by the nurse is most likely to minimize this sensation and promote relaxation? a. Palpate another area simultaneously. b. Ask the child not to laugh or move if it tickles. c. Begin with deeper palpation and gradually progress to superficial palpation. d. Have the child "help" with palpation by placing his or her hand over the palpating hand. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D Having the child "help" with palpation by placing his or her hand over the palpating hand will help minimize the feeling of tickling and enlist the child's cooperation. Palpating another area simultaneously will create the sensation of tickling in the other area also. Asking the child not to laugh or move will bring attention to the tickling and make it more difficult for the child. Superficial palpation is done before deep palpation. During examination of a toddler's extremities, the nurse notes that the child is bowlegged. The nurse should recognize that this finding is which? a. Abnormal and requires further investigation b. Abnormal unless it occurs in conjunction with knock-knee c. Normal if the condition is unilateral or asymmetric d. Normal because the lower back and leg muscles are not yet well developed - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D Lateral bowing of the tibia (bowlegged) is an expected finding in toddlers when they begin to walk. It usually persists until all of their lower back and leg muscles are well developed. Further evaluation is needed if it persists beyond ages 2 to 3 years, especially in African American children. The nurse is caring for a non-English-speaking child and family. Which should the nurse consider when using an interpreter? a. Pose several questions at a time. b. Use medical jargon when possible. c. Communicate directly with family members when asking questions. d. Carry on some communication in English with the interpreter about the family's needs. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C When using an interpreter, the nurse should communicate directly with family members when asking questions to reinforce interest in them and to observe nonverbal expressions. Questions should be posed one at a time to elicit only one answer at a time. Medical jargon should be avoided whenever possible. The nurse should avoid discussing the family's needs with the interpreter in English because some family members may understand some English. Which action should the nurse implement when taking an axillary temperature? a. Take the temperature through one layer of clothing. b. Add a degree to the result when recording the temperature. c. Place the tip of the thermometer under the arm in the center of the axilla. d. Hold the child's arm away from the body while taking the temperature. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C The thermometer tip should be placed under the arm in the center of the axilla and kept close to the skin, not clothing. The temperature should not be taken through any clothing. The child's arm should be pressed firmly against the side, not held away from the body. The temperature should be recorded without a degree added and designated as being taken by the axillary method. The nurse is aware that skin turgor best estimates what? a. Perfusion b. Adequate hydration c. Amount of body fat d. Amount of anemia - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Skin turgor is one of the best estimates of adequate hydration and nutrition. It does not indicate amount of body fat and is not a test for anemia. The Asian parent of a child being seen in the clinic avoids eye contact with the nurse. What is the best explanation for this considering cultural differences? a. The parent feels inferior to the nurse. b. The parent is showing respect for the nurse. c. The parent is embarrassed to seek health care. d. The parent feels responsible for her child's illness. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B In some ethnic groups, eye contact is avoided. In the Vietnamese culture, an individual may not look directly into the nurse's eyes as a sign of respect. The nurse providing culturally competent care would recognize that the other answers listed are not why the parent avoids eye contact with the nurse. The nurse is performing an otoscopic examination on a child. Which are normal findings the nurse should expect? (Select all that apply.) a. Ashen gray areas b. A well-defined light reflex c. A small, round, concave spot near the center of the drum d. The tympanic membrane is a nontransparent grayish color e. A whitish line extending from the umbo upward to the margin of the membrane - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B, C, E Normal findings include the light reflex and bony landmarks. The light reflex is a fairly well-defined, cone-shaped reflection that normally points away from the face. The bony landmarks of the eardrum are formed by the umbo, or tip of the malleus. It appears as a small, round, opaque, concave spot near the center of the eardrum. The manubrium (long process or handle) of the malleus appears to be a whitish line extending from the umbo upward to the margin of the membrane. The tympanic membrane should be light pearly pink or gray and translucent, not nontransparent. Ashen gray areas indicate signs of scarring from a previous perforation. The nurse is assessing breath sounds on a child. Which are expected auscultated breath sounds? (Select all that apply.) a. Wheezes b. Crackles c. Vesicular d. Bronchial e. Bronchovesicular - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C, D, E Normal breath sounds are classified as vesicular, bronchovesicular, or bronchial. Wheezes or crackles are abnormal or adventitious sounds The nurse is performing an oral examination on a preschool child. Which strategies should the nurse use to encourage the child to open the mouth for the examination? (Select all that apply.) a. Lightly brush the palate with a cotton swab. b. Perform the examination in front of a mirror. c. Let the child examine someone else's mouth first. d. Have the child breathe deeply and hold his or her breath. e. Use a tongue blade to help the child open his or her mouth. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A, B, C, D To encourage a child to open the mouth for examination, the nurse can lightly brush the palate with a cotton swab, perform the examination in front of a mirror, let the child examine someone else's mouth first, and have the child breathe deeply and hold his or her breath. A tongue blade may elicit the gag reflex and should not be used. Which are effective auscultation techniques? (Select all that apply.) a. Ask the child to breathe shallowly. b. Apply light pressure on the chest piece. c. Use a symmetric and orderly approach. d. Place the stethoscope over one layer of clothing. e. Warm the stethoscope before placing it on the skin. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C, E Effective auscultation techniques include using a symmetric approach and warming the stethoscope before placing it on the skin. Breath sounds are best heard if the child inspires deeply, not shallowly. Firm, not light, pressure should be used on the chest piece. The stethoscope should be placed on the skin, not over clothing The nurse is assessing heart sounds on a school-age child. Which should the nurse document as abnormal findings if found on the assessment? (Select all that apply.) a. S4 heart sound b. S3 heart sound c. Grade II murmur d. S1 louder at the apex of the heart e. S2 louder than S1 in the aortic area - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A, C, E S4 is rarely heard as a normal heart sound; it usually indicates the need for further cardiac evaluation. A grade II murmur is not normal; it is slightly louder than grade I and is audible in all positions. S3 is normally heard in some children. Normally, S1 is louder at the apex of the heart in the mitral and tricuspid area, and S2 is louder near the base of the heart in the pulmonic and aortic area. The nurse understands that blocks to therapeutic communication include what? (Select all that apply.) a. Socializing b. Use of silence c. Using clichés d. Defending a situation e. Using open-ended questions - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A, C, D Blocks to communication include socializing, using clichés, and defending a situation. Use of silence and using open-ended questions are therapeutic communication techniques. 1. A 16-year-old girl comes to the pediatric clinic for information on birth control. The nurse knows that before this young woman can be examined, consent must be obtained from which source? a. Herself b. Her mother c. Court order d. Legal guardian - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A Contraceptive advice is one of the conditions that is considered "medically emancipated." The adolescent is able to provide her own informed consent. The nurse needs to take the blood pressure of a preschool boy for the first time. What action would be best in gaining his cooperation? a. Tell him that this procedure will help him get well faster. b. Take his blood pressure when a parent is there to comfort him. c. Explain to him how the blood flows through the arm and why the blood pressure is important. d. Permit him to handle the equipment and see the cuff inflate and deflate before putting the cuff in place. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D A preschooler is at the stage of preoperational thought. The nurse needs to explain the procedure in simple terms and allow the child to see how the equipment works. This will help allay fears of bodily harm. Blood pressure measurement is used for assessment, not therapy, and will not help him get well faster. Although the parent will be able to support the child, he may still be uncooperative. Also, the assessment of blood pressure may be needed before the parent is available. Explaining to a preschooler how the blood flows through the artery and why the blood pressure is important is too complex. A 4-year-old girl is admitted to outpatient surgery for removal of a cyst on her back. Her mother puts the hospital gown on her, but the child is crying because she wants to leave on her underpants. What is the most appropriate nursing action at this time?? a. Allow her to wear her underpants. b. Discuss with her mother why this is important to the child. c. Ask her mother to explain to her why she cannot wear them. d. Explain in a kind, matter-of-fact manner that this is hospital policy. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A It is appropriate for the child to leave her underpants on. If necessary, the underpants can be removed after she has received the initial medications for anesthesia. This allows her some measure of control in this procedure. The mother should not be required to make the child more upset. The child is too young to understand what hospital policy means. Using knowledge of child development, what approach is best when preparing a toddler for a procedure? a. Avoid asking the child to make choices. b. Plan for a teaching session to last about 20 minutes. c. Demonstrate on a doll how the procedure will be done. d. Show the necessary equipment without allowing child to handle it. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Prepare toddlers for procedures by using play. Demonstrate on a doll but avoid the child's favorite doll because the toddler may think the doll is really "feeling" the procedure. In preparing a toddler for a procedure, the child is allowed to participate in care and help whenever possible. Teaching sessions for toddlers should be about 5 to 10 minutes. Use a small replica of the equipment and allow the child to handle it. The nurse is preparing a 9-year-old boy before obtaining a blood specimen by venipuncture. The child tells the nurse he does not want to lose his blood. What approach is best by the nurse? a. Explain that it will not be painful. b. Suggest to him that he not worry about losing just a little bit of blood. c. Discuss with him how his body is always in the process of making blood. d. Tell the child that he will not even need a Band-Aid afterward because it is a simple procedure. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C School-age children can understand that blood can be replaced. Explain the procedure to him using correct scientific and medical terminology. The venipuncture will be uncomfortable. It is inappropriate to tell him it will not hurt. Even though the nurse considers it a simple procedure, the boy is concerned. Telling him not to worry will not allay his fears. A bone marrow biopsy will be performed on a 7-year-old girl. She wants her mother to hold her during the procedure. How should the nurse respond? a. Holding your child is unsafe. b. Holding may help your child relax. c. Hospital policy prohibits this interaction. d. Holding your child is unnecessary given the child's age. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B The mother's preference for assisting, observing, or waiting outside the room should be assessed, as well as the child's preference for parental presence. The child's choice should be respected. This will most likely help the child through the procedure. If the mother and child agree, then the mother is welcome to stay. Her familiarity with the procedure should be assessed and potential safety risks identified (mother may sit in chair). Hospital policies should be reviewed to ensure that they incorporate family-centered care. A 6-year-old child needs to drink 1 L of GoLYTELY in preparation for a computed tomography scan of the abdomen. To encourage the child to drink, what should the nurse do? a. Give him a large cup with ice so it tastes better. b. Restrict him to his room until he drinks the GoLYTELY. c. Use little cups and make a game to reward him for each cup he drinks. d. Tell him that if he does not finish drinking by a set time, the practitioner will be angry. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C One liter of GoLYTELY is difficult for many children to drink. By using small cups, the child will find the amount less overwhelming. Then a game can be made in which some type of reward (sticker, reading another page of a book) is given for each cup. A large cup of ice would make it more difficult because the child would see it as too much and ice adds additional fluid to be consumed. Negative reinforcement may work if the child wishes to be out of his room. A practitioner may or may not be angry if he does not finish drinking by a set time; this is a threat that may or may not be true. If the child is having difficulty drinking, this would most likely not be effective. A toddler is being sent to the operating room for surgery at 9 AM. As the nurse prepares the child, what is the priority intervention? a. Administering preoperative antibiotic b. Verifying that the child and procedure are correct c. Ensuring that the toddler has been NPO since midnight d. Informing the parents where they can wait during the procedure - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B The most important intervention is to ensure that the correct child is going to the operating room for the identified procedure. It is the nurse's responsibility to verify identification of the child and what procedure is to be done. If an antibiotic is ordered, administering it is important, but correct identification is a priority. Clear liquids can be given up to 2 hours before surgery. If the child was NPO (taking nothing by mouth) since midnight, intravenous fluids should be administered. Parents should be encouraged to accompany the child to the preoperative area. Many institutions allow parents to be present during induction. A 5-year-old child returns from the pediatric intensive care unit after abdominal surgery. The orders state to monitor vital signs every 2 hours. On assessment, the nurse observes that the child's heart rate is 20 beats/min less than it was preoperatively. What should be the nurse's next action? a. Follow the orders and check in 2 hours. b. Ask the parents if this is the child's usual heart rate. c. Recheck the pulse and blood pressure in 15 minutes. d. Notify the surgeon that the child is proba - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C In a 5-year-old child, this is a significant change in vital signs. The nurse should assess the child to see if his condition mirrors a drop in heart rate. The assessment and vital signs should be redone in 15 minutes to determine whether the child's condition is stable. When a disparity in vital signs or other assessment data is observed, the nurse should reassess sooner. Most parents will not know their child's heart rate. It is important to determine how the child is recovering from surgery. The nurse should collect additional information before notifying the surgeon. This includes blood pressure, respiratory rate, and pain status. A 10-year-old child requires daily medications for a chronic illness. Her mother tells the nurse that the child continually forgets to take the medicine unless reminded. What nursing action is most appropriate to promote adherence to the medication regimen? a. Establish a contract with her, including rewards. b. Suggest time-outs when she forgets her medicine. c. Discuss with her mother the damaging effects of her rescuing the child. d. Ask the child to bring her medicine containers to each appo - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A Many factors can contribute to the child's not taking the medication. The nurse should resolve those issues such as unpleasant side effects, difficulty taking medicine, and time constraints before school. If these factors do not contribute to the issue, then behavioral contracting is usually an effective method to shape behaviors in children. Time-outs provide negative reinforcement. If part of a contract, negative consequences can work, but they need to be structured. Discussing with her mother the damaging effects of her rescuing the child is not the most appropriate action to encourage compliance. For a school-age child, parents should refrain from nagging and rescuing the child. This child is old enough to partially assume responsibility for her own care. If the child brings her medicine containers to each appointment so they can be counted, this will help determine if the medications are being taken, but it will not provide information about whether the child is taking them A 7-year-old is identified as being at risk for skin breakdown. What intervention should the nursing care plan include? a. Massaging reddened bony prominences b. Teaching the parents to turn the child every 4 hours c. Ensuring that nutritional intake meets requirements d. Minimizing use of extra linens, which can irritate the child's skin - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Children who are hospitalized and NPO (taking nothing by mouth) for several days are at risk for nutritional deficiencies and skin breakdown. If NPO status is prolonged, parenteral nutrition should be considered. Massaging bony prominences can cause deep tissue damage. This should be avoided. Although parents can participate, turning the child is the nurse's responsibility. If the child is alert and can move, position shifts should be done more frequently. If the child does not move, the nurse should reposition every 2 hours. The number of linens is not an issue. The child should not be dragged across the sheet. Children should be lifted and moved to avoid friction and shearing. A 6-year-old boy is hospitalized for intravenous antibiotic therapy. He eats very little on his "regular diet" trays. He tells the nurse that all he wants to eat is pizza, tacos, and ice cream. What nursing action is the most appropriate? a. Request these favorite foods for him. b. Identify healthier food choices that he likes. c. Explain that he needs fruits and vegetables. d. Reward him with ice cream at the end of every meal that he eats. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A Loss of appetite is a symptom common to most childhood illnesses. To encourage adequate nutrition, the nurse should request favorite foods for the child. The foods he likes provide nutrition and can be supplemented with additional fruits and vegetables. Ice cream and other desserts should not be used as rewards or punishment. A 14-year-old adolescent is hospitalized with cystic fibrosis. What nursing note entry represents best documentation of his breakfast meal? a. Tolerated breakfast well b. Finished all of breakfast ordered c. One pancake, eggs, and 240 ml OJ d. No documentation is needed for this age child. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Specific information is necessary for hospitalized children. It is essential to be able to identify caloric intake and eating patterns for assessment and intervention purposes. That he tolerated breakfast well only provides information that the child did not become ill with the meal. Even if he finished all his breakfast, an evaluation cannot be completed unless the quantity of food ordered is known. Nutritional information is essential, especially for children with chronic illnesses. A child, age 7 years, has a fever associated with a viral illness. She is being cared for at home. What is the principal reason for treating fever in this child? a. Relief of discomfort b. Reassurance that illness is temporary c. Prevention of secondary bacterial infection d. Avoidance of life-threatening complications - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A The principal reason for treating fever is the relief of discomfort. Relief measures include pharmacologic and environmental intervention. The most effective is the use of pharmacologic agents to lower the set point. Although the nurse can reassure the child that the illness is temporary, the child is often uncomfortable and irritable. Intervention helps the child and family minimize the discomfort. Most fevers result from viral, not bacterial, infections. Few life-threatening events are associated with fever. The use of antipyretics does not seem to reduce the incidence of febrile seizures. A critically ill child has hyperthermia. The parents ask the nurse to give an antipyretic such as acetaminophen. How should the nurse respond to the parents? a. Febrile seizures can result. b. Antipyretics may cause malignant hyperthermia. c. Antipyretics are of no value in treating hyperthermia. d. Liver damage may occur in critically ill children. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Unlike with fever, antipyretics are of no value in hyperthermia because the set point is already normal. Cooling measures are used instead. Antipyretics do not cause seizures. Malignant hyperthermia is a genetic myopathy that is triggered by anesthetic agents. Antipyretic agents do not have this effect. Acetaminophen can result in liver damage if too much is given or if the liver is already compromised. Other antipyretics are available, but they are of no value in hyperthermia. The nurse gives an injection in a patient's room. How should the nurse dispose of the needle? a. Remove the needle from the syringe and dispose of it in a proper container. b. Dispose of the syringe and needle in a rigid, puncture-resistant container in the patient's room. c. Close the safety cover on the needle and return it to the medication preparation area for proper disposal. d. Place the syringe and needle in a rigid, puncture-resistant container in an area outside of the patient's room. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B All needles (uncapped and unbroken) are disposed of in a rigid, puncture-resistant, tamper-proof container located near the site of use. Consequently, these containers should be installed in the patient's room. Needles and syringes are disposed of uncapped and unbroken. A used needle should not be transported to an area distant from use for disposal. A child who has cystic fibrosis is admitted to the pediatric unit with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection. The nurse recognizes that in addition to a private room, the child is placed on what precautions? a. Droplet b. Contact c. Airborne d. Standard - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B MRSA is an increasingly significant source of hospital-acquired infections. This organism meets the criteria of being epidemiologically important and can be transmitted by direct contact. Gowns and gloves should be worn when exposed to potentially contagious materials, and meticulous hand washing is required. S. aureus is not an organism that is spread through airborne or droplet mechanisms. Additional precautions, beyond Standard Precautions, are needed to prevent spread of this organism. An 11-month-old hospitalized boy is restrained because he is receiving intravenous (IV) fluids. His grandmother has come to stay with him for the afternoon and asks the nurse if the restraints can be removed. What nurse's response is best? a. "Restraints need to be kept on all the time." b. "That is fine as long as you are with him." c. "That is fine if we have his parents' consent." d. "The restraints can be off only when the nursing staff is present." - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B The restraints are necessary to protect the IV site. If the child has appropriate supervision, restraints are not necessary. The nurse should remove the restraints whenever possible. When parents or staff members are present, the restraints can be removed and the IV site protected. Parental permission is not needed for restraint removal. A nurse must do a venipuncture on a 6-year-old child. What consideration is important in providing atraumatic care? a. Use an 18-gauge needle if possible. b. Show the child the equipment to be used before the procedure. c. If not successful after four attempts, have another nurse try. d. Restrain the child completely. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B To provide atraumatic care the child should be able to see the equipment to be used before the procedure begins. Use the smallest gauge needle that permits free flow of blood. A two-try-only policy is desirable, in which two operators each have only two attempts. If insertion is not successful after four punctures, alternative venous access should be considered. Restrain the child only as needed to perform the procedure safely; use therapeutic hugging. A 2-year-old child is being admitted to the hospital for possible bacterial meningitis. When preparing for a lumbar puncture, what should the nurse do? a. Set up a tray with equipment the same size as for adults. b. Apply EMLA to the puncture site 15 minutes before the procedure. c. Prepare the child for conscious sedation being used for the procedure. d. Reassure the parents that the test is simple, painless, and risk free. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Because of the urgency of the child's condition, conscious sedation should be used for the procedure. Pediatric spinal trays have smaller needles than do adult trays. EMLA should be applied approximately 60 minutes before the procedure; the emergency nature of the spinal tap precludes its use. A spinal tap is not a simple procedure and does have associated risks; analgesia will be given for the pain. Frequent urine tests for specific gravity are required on a 6-month-old infant. What method is the most appropriate way to collect small amounts of urine for these tests? a. Apply a urine collection bag to the perineal area. b. Tape a small medicine cup inside of the diaper. c. Aspirate urine from cotton balls inside the diaper with a syringe without a needle. d. Use a syringe without a needle to aspirate urine from a superabsorbent disposable diaper. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C To obtain small amounts of urine, use a syringe without a needle to aspirate urine directly from the diaper. Diapers with superabsorbent gels absorb the urine; if these are used, place a small gauze dressing or cotton balls inside the diaper to collect the urine and aspirate the urine with a syringe. For frequent urine sampling, the collection bag would be too irritating to the child's skin. It is not feasible to tape a small medicine cup to the inside of the diaper; the urine will spill from the cup. A child has a central venous access device for intravenous (IV) fluid administration. A blood sample is needed for a complete blood count, hemogram, and electrolytes. What is the appropriate procedure to implement for this blood sample? a. Perform a new venipuncture to obtain the blood sample. b. Interrupt the IV fluid and withdraw the blood sample needed. c. Withdraw a blood sample equal to the amount of fluid in the device, discard, and then withdraw the sample needed. d. Flush the line and c - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C The blood specimen obtained must reflect the appropriate hemodilution of the blood and electrolyte concentration. The nurse needs to withdraw the amount of fluid that is in the device and discard it. The next sample will come from the child's circulating blood. With a central venous device, the trauma of a separate venipuncture can be avoided. The blood sample will be diluted with either the IV fluid being administered or the saline. The nurse has just collected blood by venipuncture in the antecubital fossa. What should the nurse do next? a. Keep the child's arm extended while applying a Band-Aid to the site. b. Keep the child's arm extended and apply pressure to the site for a few minutes. c. Apply a Band-Aid to the site and keep the arm flexed for 10 minutes. d. Apply a gauze pad or cotton ball to the site and keep the arm flexed for several minutes. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Applying pressure to the site of venipuncture stops the bleeding and aids in coagulation. Pressure should be applied before a bandage or gauze pad is applied. An appropriate method for administering oral medications that are bitter to an infant or small child should be to mix them with which? a. Bottle of formula or milk b. Any food the child is going to eat c. One teaspoon of something sweet-tasting such as jam d. Carbonated beverage, which is then poured over crushed ice - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Mix the drug with a small amount (about 1 tsp) of sweet-tasting substance. This will make the medication more palatable to the child. The medication should be mixed with only a small amount of food or liquid. If the child does not finish drinking or eating, it is difficult to determine how much medication was consumed. Medication should not be mixed with essential foods and milk. The child may associate the altered taste with the food and refuse to eat this food in the future. The practitioner has ordered a liquid oral antibiotic for a toddler with otitis media. The prescription reads 1 1/2 tsp four times per day. What should the nurse consider in teaching the mother how to give the medicine? a. A measuring spoon should be used, and the medication must be given every 6 hours. b. The mother is not able to handle this regimen. Long-acting intramuscular antibiotics should be administered. c. A hollow-handled medication spoon is advisable, and the medication should be eq - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C A hollow-handled medication spoon allows the mother to measure the correct amount of medication. The order is written for four times a day; every 6 hours dosing is not necessary. There is no indication that the mother is not able to adhere to the medication regimen. She is asking for clarification so she can properly care for her child. Long-acting intramuscular antibiotics are not indicated. Household teaspoons vary greatly and should not be used. Guidelines for intramuscular administration of medication in school-age children include what standard? a. Inject medication as rapidly as possible. b. Insert needle quickly, using a dartlike motion. c. Have the child stand if at all possible and if the child is cooperative. d. Penetrate the skin immediately after cleansing the site while the skin is moist. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B The needle should be inserted quickly in a dartlike motion at a 90-degree angle unless contraindicated. Inject medications slowly. Allow skin preparation to dry completely before the skin is penetrated. Place the child in a lying or sitting position. What is an advantage of the ventrogluteal muscle as an injection site in young children? a. Easily accessible from many directions b. Free of significant nerves and vascular structures c. Can be used until child reaches a weight of 9 kg (20 lb) d. Increased subcutaneous fat, which provides sustained drug absorption - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Being free of significant nerves and vascular structure is one of the advantages of the ventrogluteal site. In addition, it is considered less painful than the vastus lateralis. The major disadvantage is lack of familiarity by health professionals and controversy over whether the site can be used before weight bearing. The vastus lateralis is a more accessible site. The ventrogluteal muscle site has safely been used from newborn through adulthood. Clinical guidelines address the need for the child to be walking. The site has less subcutaneous tissue, which facilitates intramuscular deposition of the drug rather than subcutaneous. When teaching a mother how to administer eye drops, where should the nurse tell her to place them? a. At the lacrimal duct b. On the sclera while the child looks to the outside c. In the conjunctival sac when the lower eyelid is pulled down d. Carefully under the eyelid while it is gently pulled upward - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C The lower eyelid is pulled down, forming a small conjunctival sac. The solution or ointment is applied to this area. The medication should not be administered directly on the eyeball. The lacrimal duct is not the appropriate placement for the eye medication. It will drain into the nasopharynx, and the child will taste the drug. What is the best method to verify the placement of a nasogastric tube before each use? a. Radiologic confirmation b. Auscultation of injected air c. Aspiration of stomach contents d. Verification of tape placement on tube - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Visual inspection and pH check of stomach contents is a reliable method of determining placement before each use. Radiologic examination should be obtained after initial placement but would be too cumbersome to do before each use. Auscultation is an unreliable method to confirm tube placement because of the similarity of sounds produced by air in the bronchus, esophagus, or pleural space. Verification of tape placement on the tube can be inaccurate if the tube has moved within the tape or become dislodged from the stomach Parents are being taught how to feed their infant using a newly placed gastrostomy tube (G-tube). What is essential information for the parents to receive? a. Verify placement before each feeding. b. Use a syringe with a plunger to give the infant bolus feedings. c. Position the infant on the right side during and after the feeding. d. Beefy red tissue around the G-tube site must be reported to the practitioner. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Positioning on the right side during and after feedings helps minimize the risk of aspiration. It is not necessary to verify placement before each feeing. G-tubes are inserted into the stomach and sutured in place. If the tube is through the skin, it is in the stomach. Feedings should be given by gravity flow. The plunger may be used to initiate the feeding, but then the formula should be allowed to flow. Beefy red tissue around the G-tube site is normal granulation tissue that is expected. What is a priority intervention for an infant with a temporary colostomy for Hirschsprung disease? a. Teaching how to irrigate the colostomy b. Protecting the skin around the colostomy c. Discussing the implications of a colostomy during puberty d. Using simple, straightforward language to prepare the child - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Protection of the peristomal skin is a major priority. Well-fitting appliances and skin protectants are used. Teaching how to irrigate a colostomy is not necessary because colostomies are not irrigated in infants. The colostomy is usually reversed within 6 months to 1 year. The parents, not the infant, need to be prepared for the surgery. A 1-month-old infant is admitted to the hospital. The infant's mother is 17 years old and single and lives with her parents. Who signs the informed consent for the 1-month-old infant? a. The infant's mother b. The maternal grandparents of the infant c. The paternal grandparents of the infant d. Both the infant's mother and the maternal grandparents - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A An emancipated minor is one who is legally under the age of majority but is recognized as having the legal capacity of an adult under circumstances prescribed by state law, such as pregnancy, marriage, high school graduation, independent living, or military service. A preschool child needs a dressing change. To prepare the child, what strategy should the nurse implement? a. Explain the procedure using medical terminology. b. Plan a 30-minute teaching session. c. Give choices when possible but avoid delay. d. Allow time after the procedure for questions and discussion. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Involving children helps to gain their cooperation. Permitting choices gives them some measure of control. The other options would not be appropriate for a preschool child. The nurse on a pediatric unit is writing guidelines for age-specific preparation of children for procedures based on developmental characteristics. What guideline is accurate? a. Inform toddlers about an upcoming procedure 2 hours before the procedure is to be performed. b. Inform school-age children about an upcoming procedure immediately before the procedure is scheduled to occur. c. Discourage parent presence during procedures on infants and toddlers. d. Use simple diagrams of anatomy and ph - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D To assist the school-age child in meeting Erickson's developmental stage of industry, using simple diagrams of anatomy and physiology to explain a procedure is the accurate guideline. Toddlers should be told about a procedure right before the procedure. School-age children should know about the procedure in advance, not right before, and parents should be present for procedures for infants and toddlers. A laboratory technician is performing a blood draw on a toddler. The toddler is holding still but crying loudly. The nurse should take which action? a. Have the lab technician stop the procedure until the child stops crying. b. Do nothing. It's Okay for a child to cry during a painful procedure. c. Tell the child to stop crying; it's only a small prick. d. Tell the child to stop crying because the procedure is almost over. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B The child should be allowed to express feelings of anger, anxiety, fear, frustration, or any other emotion. It is natural for children to strike out in frustration or to try to avoid stress-provoking situations. The child needs to know that it is all right to cry. At which age should a nurse keep teaching time short (5 minutes)? a. Infant b. Toddler c. Preschool d. School age - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Toddlers have limited time concept, and teaching time should be kept short (5-10 minutes). The nurse is preparing to give acetaminophen (Tylenol) to a child who has a fever. What nursing action is appropriate? a. Retake the temperature in 15 minutes after giving the Tylenol. b. Place a warm blanket on the child so chilling does not occur. c. Check to be sure the Tylenol dose does not exceed 15 mg/kg. d. Use cold compresses instead of Tylenol to control the fever. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Nurses must have an understanding of the safe dosages of medications they administer to children, as well as the expected actions, possible side effects, and signs of toxicity. The recommended doses of acetaminophen should never be exceeded. The nurse is administering an IM injection into a vastus lateralis muscle of a 6-month-old infant. What should the length of the needle and amount to be given be? a. 5/8 to 1 inch; 0.5 to 1.0 ml b. 1 inch to 1 1/2 inch; 1.0 to 2.0 ml c. 1 inch to 1 1/2 inch; 0.5 to 1.0 ml d. 5/8 to 1 inch; 0.75 to 2 ml - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A The length of a needle for an infant should be 5/8 to 1 inch, and the amount of solution should not exceed 1 ml. The nurse needs to start an intravenous (IV) line on an 8-year-old child to begin administering intravenous antibiotics. The child starts to cry and tells the nurse, "Do it later, okay?" What action should the nurse take? a. Postpone starting the IV until the next shift. b. Start the IV line and then allow for expression of feelings. c. Change the route of the antibiotics to PO. d. Postpone starting the IV line until the child is ready. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B A school-age child may try to delay the procedure, but it is best to complete the procedure and allow time for the child to express his or her feelings. The nurse should not postpone administering the antibiotic, change it to PO, or wait to start the IV line until the child is ready. The nurse is preparing to administer a liquid medication by a nasogastric feeding tube. What is the first thing the nurse should do? a. Check placement of the tube. b. Check the pH of the gastric aspirate. c. Flush the tube with a small amount of water. d. Give the medication and then flush with a small amount of water. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B The most accurate way to check the position of the nasogastric tube is by checking the pH. Auscultation as a verification tool is reliable only 60% to 80% of the time and should not be used without additional methods. The tube should not be flushed or the medication administered until placement of the tube is checked. To facilitate the administration of an oral medication to a preschool-age child, what action should the nurse take? a. Dilute the medication in a large amount of favorite liquid and allow the child to hold the cup. b. Set limits about the need to take medication and offer praise immediately after the task is accomplished. c. Mix the medication in a moderate amount of the child's favorite food. d. Explain the purpose of the medication and allow the child time to express resistance before giving t - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Nurses who approach children with confidence and who convey the impression that they expect to be successful are less likely to encounter difficulty. It is best to approach a child as though cooperation is expected. The medication should not be placed in a favorite liquid or food. Allowing the child time to express resistance will delay administration of the medication. A 2-year-old child has to receive Rocephin IM injections every 12 hours. What nursing intervention should be implemented for the child? a. Hold the child while rocking in a chair after each injection. b. Prepare the child several hours before the injection is given. c. Allow the child to watch a younger child receive an injection. d. Encourage the child to draw a picture of the pain experienced when an injection is given. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A After the procedure, the child continues to need reassurance that he or she performed well and is accepted and loved. The other options are not appropriate for a toddler. When checking the intravenous (IV) site on a child, the nurse should take which action? a. Look at the site. b. Ask the child if the site "hurts." c. Look at the site while palpating the area. d. Take all the tape off, assess the site, and redress. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C To appropriately check the intravenous (IV) site, the nurse should look at the site and palpate the area. The other options would not be adequate assessments of the site. The nurse is caring for a 12-year-old child who is on fall precautions secondary to seizures. What interventions should be included in the child's care plan? (Select all that apply.) a. Place a call light and desired items within reach. b. Keep the bed in the highest position with the two side rails up. c. Turn off the lights and television at night. d. Keep personal belongings and clutter contained in one area of the floor. e. Have the child wear an appropriate-size gown and nonskid footwear. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A, E Prevention of falls requires alterations in the environment, including keeping call light and desired items within reach and having the child wear appropriate-size gowns and nonskid footwear. The bed should be in the lowest position possible with all the side rails up; at least a dim light should be left on at night; and personal belongings and clutter should not be on the floor—they should be in a cabinet. What methods should the nurse use to measure compliance to a treatment plan? (Select all that apply.) a. Pill counts b. Chemical assays c. Direct observation d. Third-party reporting e. Monitoring therapeutic response - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A, B, C, E Assessment of compliance must include direct measurement techniques. Pill counts, chemical assays, direct observation, and monitoring therapeutic response are direct measurement techniques. Third-party reporting would not always be available and would not be a method to measure compliance. What interventions should the nurse implement to prevent a pressure ulcer in a critically ill child? (Select all that apply.) a. Nutrition consults b. Using skin moisturizers c. Turning the child every 2 hours d. Using plastic disposable underpads e. Using draw sheets to minimize shear - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A, B, C, E Interventions found to prevent pressure ulcers in critically ill children include nutrition consults, using skin moisturizers, turning the child every 2 hours, and using draw sheets to minimize shear. Dryweave underpads, not underpads with plastic, should be used to reduce moisture. The nurse is preparing to obtain a nasal washing from a child. What equipment should the nurse gather for the procedure? (Select all that apply.) a. Sterile water b. A sterile swab c. Syringe with tubing d. Sterile normal saline e. Tracheal suction catheter - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C, D Nasal washings may be obtained to identify viral pathogens and guide therapy in some respiratory conditions. The child is placed supine, and 1 to 3 ml of sterile normal saline is instilled with a sterile syringe (without a needle) into one nostril. The contents are aspirated with a syringe with 5 cm (2 inches) of 18- to 20-gauge tubing. The saline is quickly instilled and then aspirated to recover the nasal specimen. A tracheal suction catheter would not trap the mucus. Normal saline is used, not sterile water. A sterile swab is used for a throat culture, not for nasal washings. The clinic nurse is teaching parents about when to call the office immediately for a child with a fever. What should the nurse include in the teaching session? (Select all that apply.) a. The child has a stiff neck. b. The fever is over 40.6° C (105° F). c. The child is younger than 2 months. d. The fever has lasted for more than 3 days. e. The fever went away for more than 24 hours and then returned. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A, B, C Parents should call the office immediately if a child has a fever over 40.6° C (105° F), the child is younger than 2 months, or the child has a stiff neck. Parents are to call within 24 hours if the fever went away for more than 24 hours and then returned or the fever has lasted for more than 3 days. What strategies should the nurse implement to assist in feeding a sick child? (Select all that apply.) a. Serve large portions. b. Make mealtimes pleasant. c. Avoid foods that are highly seasoned. d. Provide finger foods for young children. e. Ensure a variety of foods, textures, and colors. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B, C, D, E To assist in feeding a sick child mealtimes should be pleasant; highly seasoned foods should be avoided; finger foods should be provided for young children; and a variety of foods, textures, and colors should be ensured. Small portions, not large, should be served. What disease processes require contact isolation? (Select all that apply.) a. Rotavirus b. Hepatitis A c. Streptococcal pharyngitis d. Mycoplasmal pneumonia e. Respiratory syncytial virus - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A, B, E In addition to Standard Precautions, use contact precautions for patients known or suspected to have serious illnesses easily transmitted by direct patient contact or by contact with items in the patient's environment. Examples of such illnesses include rotavirus, hepatitis A, and respiratory syncytial virus. Streptococcal pharyngitis and mycoplasmal pneumonia require droplet precautions. What disease processes require airborne precautions? (Select all that apply.) a. Measles b. Varicella c. Pertussis d. Meningitis e. Tuberculosis - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A, B, E In addition to Standard Precautions, use airborne precautions for patients known or suspected to have serious illnesses transmitted by airborne droplet nuclei. Examples of such illnesses include measles, varicella (including disseminated zoster), and tuberculosis. Pertussis and meningitis require droplet precautions. What are the advantages of an implanted port (Port-a-Cath)? (Select all that apply.) a. Reduced risk of infection b. Reduced cost for the family c. Placed completely under the skin d. Easy to use for self-administered infusions e. Removal does not require a surgical procedure - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A, B, C The advantages of an implanted port include reduced risk of infection, reduced cost for the family, and placed completely under the skin. Because it is implanted and must be accessed, it is not easy to use for self-administered infusions, and removal does require a surgical procedure. What play activities should the nurse implement to encourage fluid intake for a child? (Select all that apply.) a. Have a tea party. b. Use a crazy straw. c. Cut gelatin into fun shapes. d. Place liquid in large Styrofoam cups. e. Make ice pops using the child's favorite juice. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A, B, C, E Play activities to encourage fluid intake for a child include tea parties, crazy straws, cutting gelatin into fun shapes, and making ice pops using the child's favorite juice. Small cups, not large Styrofoam cups, should be used. A 6 year old child's growth curve shows their length at 6% and their weight at 95%. The large difference in percentiles would prompt the nurse to give anticipatory guidance on which of the following subjects? a. Short stature b. Obesity c. Nutrition d. Both B & C - CORRECT ANSWER d. Both B & C You are caring for a newborn that is being discharged later that day. Which of the following anticipatory guidance topics would be LEAST important to discuss at this time? a. Breast feeding b. What to do if your child has a fever c. car seat safety d. dental care for your infant - CORRECT ANSWER d. dental care for your infant The nurse is using the FLACC scale to rate the pain in a 9-month-old child . Which is the nurse's best response to the father's question of what the FLACC scale is? a. "It estimates a child's level of pain utilizing vital sign information" b. "It estimates a child's level of pain based on parents' perception" c. "It estimates a child's level of pain utilizing behavioral and physical responses" d. "It estimates a child's level of pain utilizing a numeric scale from 0-10" - CORRECT ANSWER c. "It estimates a child's level of pain utilizing behavioral and physical responses" An example of active artificial immunity would be immunity aquired by which of the following? a. Breast feeding b. IVIG c. MMR d. Going to a chicken pox party - CORRECT ANSWER c. MMR Attenuated live vaccinations can't be given in pregnancy due to risk of a modified pathogen crossing the placenta. True or False - CORRECT ANSWER True Parents of a hospitalized toddler as the nurse, "What is meant by family-centered care?" The nurse should respond with which statement? a. Family-centered care reduces the effect of cultural diversity on the family. b. Family-centered care encourages family dependence on the health care system. c. Family-centered care recognizes that the family is the constant in a child's life. d. Family-centered care avoids expecting families to be part of the decision-making process. - CORRECT ANSWER c. Family-centered care recognizes that the family is the constant in a child's life. You are seeing a 10 year old boy with an ACE score of 6 (Adverse Childhood Experinces ACE's). Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for him in adulthood? a. Thyroid Disease b. Addiction c. Obesity d. Depression - CORRECT ANSWER a. Thyroid Disease The nurse is caring postoperatively for an 8-year-old child with multiple fractures and other trauma resulting from a motor vehicle injury. The child is experiencing severe pain. Which of the following is an important consideration in managing the child's pain? a. Give only an opioid analgesic at this time b. Increase the dosage of analgesic until the child is adequately sedated. c. Plan a preventative schedule of pain medication around the clock and include chosen forms of distraction. d. Give - CORRECT ANSWER c. Plan a preventative schedule of pain medication around the clock and include chosen forms of distraction. A 6-year-old boy is hospitalized for intravenous antibiotic therapy. He eats very little on his regular diet trays. He tells the nurse that all he wants to eat is pizza, tacos, and ice cream. What nursing action is the most apporpriate? a. Request these favorite foods for him. b. Identify healthier food choices for him that he might like. c. Explain that he needs fruits and vegetables. d. Reward him with ice cream at the end of every meal that he eats. - CORRECT ANSWER a. Request these favorite foods for him. What is a key indicator of developmental health in an infant? a. length b. weight c. vital signs d. head circumference - CORRECT ANSWER d. head circumference A child who leads a sedentary lifestyle and is only outdoors when he has outdoor recess at school is at a higher risk for all of the following EXCEPT? a. Autism b. Anxiety c. Metabolic Syndrome d. Obesity - CORRECT ANSWER a. Autism A nurse is about to administer the ASQ developmental screening questionnaire (Ages & Stages Questionaire) to a toddler during a routine pediatric visit. The parent asks "What is the ASQ?" How do you respond to this question? a. 'It's a simple intelligence test for young children." b. "It tells us what your child is doing at a particular age." c. "It's a test we give to measure a child's growth." d. "It's an excellent way to see if parents know what their toddlers can do." - CORRECT ANSWER b. "It tells us what your child is doing at a particular age." The nurse is assessing a newborn after a vaginal delivery. Which of the following findings is CONCERNING when observed in a newborn?. a. uneven head shape (moulding) b. respirations are irregular between 30-60 bpm c. (+) moro reflex d. heart rate is 80 beats pm - CORRECT ANSWER d. heart rate is 80 beats pm (normal HR for newborn is 100-205 when awake, 90-160 when at sleep) Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding infants at birth? a. Infants move more air in and out of their lungs compared to adults. b. Infants have limited aveolar surface for gas exchange relative to her height and weight. c. Infants immune system is immature and therefor they should not receive immunizations until they are 2 months old. d. The trachea is shorter and smaller in diameter putting infants at higher risk for tracheal obstruction. - CORRECT ANSWER c. Infants immune system is immature and therefor they should not receive immunizations until they are 2 months old. Which of the following would be helpful word to substitute for the word "shot" when working with a 4-year-old? a. Poke b. Bee sting c. Injection d. Medication under the skin - CORRECT ANSWER a. Poke The nurse is assessing the reflexes of a newborn. Stroking the outer sole of the foot assesses which reflex? a. Grasp b. Babinski c. Perez d. Dance or step - CORRECT ANSWER b. Babinski What advice would you give a parent regarding media use for their 11 year old child? a. Limit time spent on the device outside of school work to 3-4 hours daily. b. Parents should role model healthy habits and media use and limit their own use to 2 hours daily. c. Know what your child is watching & playing on their devices at all times. Children and adolescents need monitoring. d. B & C - CORRECT ANSWER d. B & C Which data should be included in a health history? a. Physical assessment b. Review of systems c. Growth measurements d. Record of vital signs - CORRECT ANSWER b. Review of systems The nurse needs to take the blood pressure of a pre-school boy (3 years old) for the first time. Which action would be best in gaining his cooperation? a. Take his blood pressure even though the parent has stepped out of the room. b. Tell him that this procedure will help him get well faster. c. Explain to him how blood flows through the arm and why the blood pressure is important. d. Permit him to handle equipment and see the dial move before putting the cuff in place. - CORRECT ANSWER d. Permit him to handle equipment and see the dial move before putting the cuff in place. Children who are food insecure are at increased risk for which of the following? a. Obesity b. Anxiety c. Fewer opportunities for physical activity d. All of the above - CORRECT ANSWER d. All of the above What respiratory condition or disease results in both increased compliance and increased resistance? a. Asthma b. Atelectasis c. Surfactant deficiency d. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A Compliance is a measure of the relative ease with which the chest wall expands. Resistance is determined primarily by airway size. Asthma results in increased compliance and increased resistance, both of which increase the work of breathing. Atelectasis and surfactant deficiency both decrease compliance but do not affect resistance. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia increases resistance but does not affect compliance. How much oxygen is contained in ambient air (room air)? a. 15% b. 21% c. 30% d. 42% - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Room air is composed of 21% oxygen, trace amounts of carbon dioxide, and 79% n During a respiratory assessment, the nurse notes a sinking in of soft tissues relative to the cartilaginous and bony thorax. What is the term for this finding? a. Grunting b. Tachypnea c. Retractions d. Nasal flaring - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Retractions are defined as the sinking of soft tissue relative to the cartilaginous or bony thorax. Retractions can be extreme in severe airway obstruction as the work of breathing increases. Grunting can be a sign of pain in older children with respiratory issues. It serves to increase the end-respiratory pressure, which prolongs the period of oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange across the membrane. Tachypnea is an increase in the respiratory rate above the child's baseline. Nasal flaring, the enlargement of the nostrils, helps reduce nasal resistance and maintains airway patency. What test measures the amount of air inhaled and exhaled during any respiratory cycle? a. Tidal volume b. Vital capacity c. Dynamic compliance d. Pulmonary resistance - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A Tidal volume is defined as the amount of air inhaled and exhaled during any respiratory cycle. When it is multiplied by the respiratory rate, the minute volume is obtained. Forced vital capacity is the maximum amount of air that can be expired after maximum inspiration. It is used to monitor individuals with obstructive airway disease. Dynamic compliance is the relationship between the change in volume and pressure difference. Pulmonary resistance measures the changes in pressure with changes in flow on inspiration and expiration. What is the best explanation for using pulse oximetry on young children to determine oxygen saturation? a. Pulse oximetry is noninvasive. b. Pulse oximetry is better than capnography. c. Pulse oximetry is more accurate than arterial blood gases. d. Pulse oximetry provides intermittent measurements of oxygen. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A Pulse oximetry is a noninvasive measure of oxygen saturation of hemoglobin. Capnography measures carbon dioxide inhalation and exhalation. It does not provide information about oxygen saturation. Arterial blood gases provide additional clinical information, including pH, PCO2, bicarbonate, base excess, and PO2. An arterial puncture is required, which can be painful, and continuous monitoring cannot be done without an arterial line. Pulse oximetry can be either intermittent or continuous. It is important to make certain that sensory connectors and oximeters are compatible because incompatible wiring can cause which condition? a. Hyperthermia b. Electrocution c. Pressure necrosis d. Burns under sensors - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D Incompatible wiring can generate considerable heat at the tip of the sensor, resulting in partial- and full-thickness burns. Heat may be generated at the site of the sensor, but it will not result in generalized hyperthermia. Electrocution is not a possibility with oximeters. Pressure necrosis can occur from improperly applied sensors but not from incompatible wiring. What test should the nurse do as a precautionary measure before doing an arterial puncture to obtain an arterial blood sample? a. Allen test b. Smith test c. Venipuncture d. Cold compress - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A The Allen test determines the adequacy of collateral circulation in the extremity distal to the proposed puncture site. If the child does not have satisfactory circulation when the proposed artery is occluded, that extremity is not used. The Smith test, venipuncture, and a cold compress are not done before arterial blood gas sampling. Arterial blood gases have just been drawn on a child. What should the nurse do next? a. Take the sample to the laboratory immediately. b. Pack the sample in ice and take it to the laboratory immediately. c. Place the sample in a brown bag until it can be taken to laboratory. d. Refrigerate the sample until it can be taken to the laboratory. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Arterial blood gases require careful handling for accurate results. Immediately after obtaining the specimen, the nurse packs it in ice to reduce cellular metabolism and takes it to the laboratory. The continuous administration of mist, or aerosolized water, for the treatment of inflammatory conditions of the airways is a common practice that functions in which manner? a. Has no proven benefit b. Decreases the viscosity of mucus c. Decreases bronchoconstriction d. Reduces the inflammation of the lower airways - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A Aerosol therapy or mist therapy with water is not a treatment of choice for inflammatory airway conditions. Some questionable benefit may occur in mild viral croup. The parent and child may experience a reduction in anxiety in a cool, humid environment. Upper airway secretions may be moistened; however, inhaled mist does not affect the viscosity of mucus. Humidity may worsen bronchospasm. Aerosolized medications are able to reduce inflammation of the lower airways, but water does not have this effect. When is bronchial (postural) drainage generally performed? a. Before meals and at bedtime b. Right before all aerosol therapy c. Immediately on arising and at bedtime d. Thirty minutes after meals and at bedtime - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A The therapy should be done at bedtime and before meals or 1 to 1 1/2 hours after meals to avoid stomach upset. Postural drainage is most effective when it is performed after other respiratory therapy interventions, including bronchodilator and nebulizer treatments. Immediately on arising and at bedtime are appropriate times, but postural drainage is usually carried out at least three times each day. Thirty minutes after meals may induce vomiting. What nursing consideration is most important in the care of a child on a mechanical ventilator? a. Humidification is not necessary. b. Respiratory assessment is done by the ventilator. c. Positioning the child for comfort and optimum ventilation is necessary. d. Support and reassurance are not as important because the child is unconscious. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C The ventilator will do the work of breathing, but the nurse must position the child with attention to achieving optimum gas exchange. The reason for mechanical ventilation and the child's comfort are part of the assessment. Mechanical ventilation is usually achieved by intubation or tracheostomy. These routes bypass the humidification that occurs in the upper airway. The ventilator provides some information about the work of breathing, but patient assessment must be done by the nurse. Support and reassurance are always important for both the child and family. Opioids and anxiolytics are often used to decrease the child's anxiety. Careful assessment is indicated. What intervention is necessary when weaning a child from the ventilator? a. Light sedation before scheduled extubation b. No suctioning before scheduled extubation c. Cool mist begun immediately after extubation d. Vigorous chest physiotherapy and suctioning performed immediately after extubation - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C A cool mist or noninvasive oxygen therapy is initiated immediately after extubation. Steroids may be administered to minimize any laryngeal edema. Analgesics may be given, but sedation is not usually indicated. The child is suctioned just before extubation to ensure that the airway is clear. Chest physiotherapy and suctioning are performed before extubation. The nurse must suction a 6-month-old infant with a tracheostomy. What intervention should be included? a. Encourage the child to cough to raise the secretions before suctioning. b. Perform each pass of the suction catheter for no longer than 5 seconds. c. Allow the child to rest after every five times the suction catheter is passed. d. Select a catheter with a diameter three quarters of the diameter of the tracheostomy tube. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Suctioning should require no longer than 5 seconds per pass. Otherwise, the airway may be occluded for too long. An infant would be unable to cooperate with instructions to cough up secretions. The child is allowed to rest for 30 to 60 seconds after each aspiration to allow oxygen tension to return to normal. Then the process is repeated until the trachea is clear. The catheter should have a diameter one half the size of the tracheostomy tube. If it is too large, it might block the child's airway. A 3-year-old child with a tracheostomy will soon be discharged. What recommendation should the nurse share with the family? a. Tub baths cannot be given. b. The child cannot be allowed to play outdoors. c. Avoid exposure to noxious fumes such as paint or varnish. d. Cover the tracheostomy with a plastic bib when exposed to cold air. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C The child with a tracheostomy should not be exposed to noxious fumes such as paint, varnish, or hair spray or to substances such as talc. The parent and child must be cautioned about safety measures around bodies of water. Baths can be taken, but parents must observe the necessary safety precautions. The child may play outdoors with a scarf or other protection that allows air through. The nurse is planning home care for a 2-year-old child with a tracheostomy. What recommendation should be included? a. Sterile technique is essential in home care of the tracheostomy. b. Parents are able to change the tracheostomy tube when needed. c. Play activities must be sedentary such as listening to music and working on puzzles. d. The child must wear a plastic bib when eating or drinking to prevent aspiration into the stoma. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B A plugged, clogged, or obstructed tracheostomy tube is a life-threatening circumstance. Parents are taught the signs and symptoms, how to suction, and how to change the tube. Clean technique and thorough hand washing are sufficient for suctioning, cleaning the tracheostomy site, and changing the tracheostomy tube. The child who is physically able can engage in activities appropriate to age. Young children who may spill food near the stoma should wear a fabric bib without a plastic lining or other device to prevent dribbled food and crumbs from being aspirated. Respiratory failure can result from many causes. What condition is a specific primary cause of inefficient gas transfer? a. Anemia b. Pneumothorax c. Cystic fibrosis d. Laryngospasm - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A Respiratory failure is defined as the inability of the respiratory system to maintain adequate oxygenation of the blood. In primary inefficient gas transfer, there is insufficient alveolar ventilation. Anemia, which is characterized by low hemoglobin levels, results in an inability to adequately oxygenate the blood. Pneumothorax and cystic fibrosis are examples of restrictive lung disease. Laryngospasm is an example of obstructive lung disease. The nurse is caring for a child with a tracheostomy. What clinical manifestation should the nurse recognize as an early sign of impending respiratory distress or failure? a. Cyanosis b. Restlessness c. Audible stridor d. Crowing respiration - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Signs of hypoxemia are initially subtle. Cardinal signs of impending respiratory failure include restlessness, tachypnea, tachycardia, and diaphoresis. Cyanosis is a sign of severe hypoxia. Stridor and crowing respirations are indicative of inflammation. Sternal retractions are an early but less obvious sign. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is begun on a toddler. What pulse is usually palpated because it is the most central and accessible? a. Radial b. Carotid c. Femoral d. Brachial - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B In a toddler, the carotid pulse is palpated. The radial pulse is not considered a central pulse. The femoral pulse is not the most central and accessible. Brachial pulse is felt in infants younger than 1 year of age. What medication is considered to be the most useful in treating cardiac arrest? a. Bretylium tosylate (Bretylium) b. Xylocaine (lidocaine) c. Adrenaline (epinephrine) d. Naloxone (Narcan) - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Epinephrine is considered one of the most useful drugs in treating cardiac arrest. As an adrenergic agent, it acts on both - and -receptors in the heart. Epinephrine is rapidly cleared from the bloodstream. Bretylium is no longer used in pediatric cardiac arrest management. Lidocaine is used for ventricular arrhythmias only. Naloxone is useful only to reverse effects of opioids. Effective cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) on a 5-year-old child should include what technique? a. Provide one breath to every five chest compressions. b. Provide two breaths to every 30 chest compressions. c. Reassess the child every 10 minutes while CPR continues. d. Evaluate the child after 50 cycles of compression and ventilation. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Two breaths to 15 compressions is the standard for infants and children when two rescuers are present. One breath to every five chest compressions is not the appropriate ratio for CPR in this age group. Reassessment of the child should take place after 20 cycles or 1 minute. A series of subdiaphragmatic abdominal thrusts (the Heimlich maneuver) is recommended for airway obstruction in children older than which age? a. 1 year b. 4 years c. 8 years d. 12 years - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A A series of subdiaphragmatic abdominal thrusts (the Heimlich maneuver) is recommended for airway obstruction in children older than 1 year. For children younger than 1 year, back blows and chest thrusts are administered. The mother of a toddler yells to the nurse, "Help! He is choking to death on his food!" The nurse determines that lifesaving measures are necessary based on which finding? a. Gagging b. Coughing c. Pulse over 100 beats/min d. Inability to speak - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D The inability to speak is indicative of a foreign body airway obstruction of the larynx. Abdominal thrusts are needed for treatment of the choking child. Gagging, not obstruction, indicates irritation at the back of the throat. Coughing does not indicate a complete airway obstruction. Tachycardia may be present for many reasons. The nurse is caring for a 4-year-old child who is receiving 2 L of oxygen per nasal cannula. What disadvantage should the nurse consider when planning care for the child? a. The child may need to have high humidity administered with the oxygen. b. The child may not be able to eat and drink comfortably. c. A nasal cannula may cause an accumulation of moisture on the face. d. A nasal cannula may cause abdominal distention. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D All oxygen delivery systems have advantages and disadvantages. One disadvantage of a nasal cannula is possible abdominal distention and discomfort, which could lead to vomiting. The advantages include that the child is able to eat and drink more comfortably, there is no need for a high humidity environment, and there is no accumulation of moisture causing skin irritation. A 5-month-old infant is in respiratory distress. What should the nurse expect to find? a. Nasal flaring b. Bradycardia c. Abdominal breathing d. Capillary refill of 2 seconds - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A Nasal flaring is a sign of respiratory distress and a significant finding in an infant. The enlargement of the nostrils helps reduce nasal resistance and maintains airway patency. Nasal flaring may be intermittent or continuous and should be described as minimum or marked. The infant would have tachycardia, not bradycardia, in respiratory distress. Abdominal breathing and a capillary refill are normal findings in an infant. A child is in uncompensated respiratory acidosis. What should the nurse expect the arterial blood gas to be? a. O2, 95; CO2, 45; pH, 7.40 b. O2, 88; CO2, 55; pH, 7.30 c. O2, 88; CO2, 35; pH, 7.28 d. O2, 92; CO2, 54; pH, 7.35 - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Respiratory acidosis results from diminished or inadequate pulmonary ventilation that causes an elevation in plasma Pco2 and thus an increased concentration of dissolved carbonic acid, which leads to elevated carbonic acid and hydrogen ion concentration. This tends to lower the pH. CO2 of 55 is elevated (normal CO2 is 35-45), and a pH of 7.30 is low (normal pH is 7.35-7.45). A child is in uncompensated respiratory alkalosis. What should the nurse expect the arterial blood gas to be? a. CO2, 30; pH, 7.50 b. CO2, 55; pH, 7.30 c. CO2, 35; pH, 7.28 d. CO2, 54; pH, 7.35 - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A Laboratory findings in respiratory alkalosis include reduced PCO2 (35?9?mm?9?Hg) and elevated plasma pH (>7.45). A child is in uncompensated metabolic alkalosis. What should the nurse expect the arterial blood gas to be? a. HCO3, 24; pH, 7.35 b. HCO3, 28; pH, 7.50 c. HCO3, 20; pH, -7.30 d. HCO3, 26; pH, 7.40 - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B Metabolic alkalosis results in an elevated plasma pH (normal pH is 7.35-7.45) that occurs when there is an excess of bicarbonate (normal HCO3 is 22-26). A child is in uncompensated metabolic acidosis. What should the nurse expect the arterial blood gas to be? a. HCO3, 24; pH, 7.35 b. HCO3, 28; pH, 7.50 c. HCO3, 20; pH, 7.30 d. HCO3, 26; pH, 7.40 - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C Laboratory findings of uncompensated metabolic acidosis include lowered plasma pH (<7.35) and diminished plasma bicarbonate concentration (normal HCO3 is 22-26). A nurse is calculating the correlation of Pao2 with Sao2 according to the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve. What parameter should indicate that the Pao2 is less than 50 to 60 mm Hg? a. Coarse lung sounds b. Temperature of 100° F c. Respiratory rate of 58 d. Pulse oximetry reading of 90% or less - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D The Pao2 can be correlated with the Sao2 by means of the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve, although changes in Pao2 do not cause identical (linear) changes in Sao2. The curve represents the relationship between Pao2 (measured in the blood) and Sao2 (measured by the pulse oximeter). When the Pao2 is 60?9?mm?9?Hg, the Sao2 is 90%. The oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve does not correlate with lung sounds, temperature, or respiratory rate. The nurse is reviewing factors that affect lung development. What factor delays surfactant production and maturation of alveolar cells? a. Thyroxine b. Prolactin c. Glucocorticosteroids d. Excess of endogenous insulin - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D An excess of endogenous insulin can delay surfactant production and delays maturation of alveolar cells. Glucocorticosteroids, thyroxine, and prolactin enhance lung development. The nurse is caring for a child in respiratory distress. What is an early but less obvious sign of respiratory failure? a. Stupor b. Headache c. Bradycardia d. Somnolence - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B An early but less obvious sign of respiratory failure is a headache. Stupor, bradycardia, and somnolence are signs of more severe hypoxia. The nurse is caring for a child on oxygen being delivered by a nasal cannula. What is the advantage of delivering oxygen in this manner? a. It can deliver mist if desired. b. It is less likely to cause abdominal distention. c. The child is able to eat and talk while getting oxygen. d. This method can deliver a higher concentration of oxygen. - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: C An advantage of delivering oxygen by nasal cannula is that the child is able to eat and talk while getting oxygen. This method cannot deliver mist or higher concentrations of oxygen. A disadvantage of this method is that it may cause abdominal distention. The nurse is evaluating arterial blood gas results. What condition can cause an increase in PCO2? a. Hypoxia b. Hyperventilation c. Pulmonary embolism d. Obstructive lung disease - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D Obstructive lung disease causes an increase in PCO2. Hypoxia, hyperventilation, and pulmonary embolism cause a decrease in PCO2. The nurse is evaluating arterial blood gas results. What condition can cause an increase in HCO3? a. Renal failure b. Lactic acidosis c. Diabetic ketoacidosis d. Fluid loss from upper gastrointestinal tract - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D Fluid loss from an upper gastrointestinal tract causes an increase in HCO3. Renal failure, lactic acidosis, and diabetic ketoacidosis cause a decrease in HCO3. The nurse is analyzing an arterial blood gas of pH, 7.30; PCO2, 50; and HCO3, 29. What result should the nurse document for this blood gas? a. Fully compensated respiratory acidosis b. Partially compensated respiratory acidosis c. Fully compensated metabolic acidosis d. Partially compensated metabolic acidosis - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B When the fundamental acid-base ratio is altered for any reason, the body attempts to correct the deviation. In a simple disturbance, a single primary factor affects one component of the acid-base pair and is usually accompanied by a compensatory or secondary change in the component that is not primarily affected. In respiratory acidosis, the pH is low (?6?7.35), and the PCO2 is high (?7?45). When the pH is restored to normal, the disturbance is described as compensated. It is partially compensated because the pH remains abnormal, but the HCO3 is high (?7?26), indicating an attempt at compensation. The nurse is analyzing an arterial blood gas of pH, 7.50; PCO2, 50; and HCO3, 29. What result should the nurse document for this blood gas? a. Fully compensated metabolic alkalosis b. Partially compensated metabolic alkalosis c. Fully compensated respiratory alkalosis d. Partially compensated respiratory alkalosis - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B When the fundamental acid-base ratio is altered for any reason, the body attempts to correct the deviation. In a simple disturbance, a single primary factor affects one component of the acid-base pair and is usually accompanied by a compensatory or secondary change in the component that is not primarily affected. In metabolic alkalosis, the pH is high (?7?7.45), and the HCO3 is high (?7?26). When the pH is restored to normal, the disturbance is described as compensated. It is partially compensated because the pH remains abnormal, but the PCO2 is high (?7?45), indicating an attempt at compensation. The nurse is analyzing an arterial blood gas of pH, 7.29; PCO2, 30; and HCO3, 20. What result should the nurse document for this blood gas? a. Fully compensated respiratory acidosis b. Partially compensated respiratory acidosis c. Fully compensated metabolic acidosis d. Partially compensated metabolic acidosis - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D When the fundamental acid-base ratio is altered for any reason, the body attempts to correct the deviation. In a simple disturbance, a single primary factor affects one component of the acid-base pair and is usually accompanied by a compensatory or secondary change in the component that is not primarily affected. In metabolic acidosis, the pH is low (?6?7.35), and the HCO3 is low (?6?22). When the pH is restored to normal, the disturbance is described as compensated. It is partially compensated because the pH remains abnormal, but the PCO2 is low (?6?35), indicating an attempt at compensation. The nurse is analyzing an arterial blood gas of pH, 7.50; PCO2, 30; and HCO3, 20. What result should the nurse document for this blood gas? a. Fully compensated metabolic alkalosis b. Partially compensated metabolic alkalosis c. Fully compensated respiratory alkalosis d. Partially compensated respiratory alkalosis - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: D When the fundamental acid-base ratio is altered for any reason, the body attempts to correct the deviation. In a simple disturbance, a single primary factor affects one component of the acid-base pair and is usually accompanied by a compensatory or secondary change in the component that is not primarily affected. In respiratory alkalosis, the pH is high (?7?7.45), and the PCO2 is low (?6?35). When the pH is restored to normal, the disturbance is described as compensated. It is partially compensated because the pH remains abnormal, but the HCO3 is low (?6?22), indicating an attempt at compensation. What conditions can produce hyperventilation? (Select all that apply.) a. Hysteria b. Narcotics c. Atelectasis d. Salicylate intoxication e. Mechanical ventilation - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A, D, E Hysteria, salicylate intoxication, and mechanical ventilation can produce hyperventilation. Narcotics and atelectasis produce inadequate gas exchange, not hyperventilation. What condition or disease decreases lung compliance? (Select all that apply.) a. Asthma b. Atelectasis c. Pneumothorax d. Pulmonary edema e. Lobar emphysema - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: B, C, D Atelectasis, pneumothorax, and pulmonary edema decrease lung compliance. Asthma and lobar emphysema increase lung compliance. The nurse is caring for an intubated child on mechanical ventilation. What interventions should the nurse implement to prevent ventilator-assisted pneumonia (VAP)? (Select all that apply.) a. Routine oral hygiene b. Appropriate hand hygiene c. Limit oropharyngeal suctioning of secretions d. Elevating the head of the bed 30 to 45 degrees e. Wearing gloves to handle respiratory secretions - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A, B, D, E Critically ill children on mechanical ventilation are at risk for acquisition of VAP. To prevent VAP, recommendations for nurses working with mechanically ventilated patients include appropriate hand hygiene measures; wearing gloves to handle respiratory secretions or contaminated objects; elevating the head of the bed 30 to 45 degrees; and routine oral hygiene, which includes oropharyngeal suctioning of secretions. The nurse recognizes that oxygen mist tents are rarely used for a child with respiratory distress. What are reasons for not using an oxygen mist tent? (Select all that apply.) a. Poor access to the child b. Cool and wet tent environment c. Oxygen levels fall when tent is entered d. Child may not tolerate it around the crib/bed e. Lower oxygen concentrations cannot be achieved - CORRECT ANSWER ANS: A, B, C, D The disadvantages of using a mist tent include poor access to the child, a cool and wet tent environment, oxygen levels fall when the tent is entered, and the child may not tolerate it around the crib or bed. Lower oxygen concentrations can be achieved in the tent and is an advantage. The nurse is participating in a code blue on a 12-year-old child in a full respiratory arrest. The child weighs 110 lb. The health care provider has ordered an initial dose of epinephrine hydrochloride (1:10,000) given intravenously. Calculate the correct initial dose of epinephrine in mg. - CORRECT ANSWER 110 lb/2.2 kg = 50 kg Initial dose of 1:10,000 epinephrine is 0.01 mg/kg 0.01 mg 50 = *0.5 mg* The nurse is calculating the amount of expected urinary output for a 24-hour period on an intubated young child who weighs 22 lb. The nurse recognizes the formula to be used is 2 ml/kg/hr. What is the expected 24-hour urinary output for this child in milliliters? - CORRECT ANSWER 22/2.2 = 10 kg 10 × 2 × 24 = *480 ml* The nurse is calculating the amount of expected urinary output for a 24-hour period on an intubated young child who weighs 33 lb. The nurse recognizes the formula to be used is 2 ml/kg/hr. What is the expected 24-hour urinary output for this child in milliliters? - CORRECT ANSWER 33/2.2 = 15 kg 15 × 2 × 24 = *720 ml* The gold standard for diagnosing cystic fibrosis is: a. A positive sweat test with chloride > 60 mmol/L b. A child who has a history of intussusception. c. A child with diabetes. d. A child with failure to thrive. - CORRECT ANSWER A Group A Beta-hemolytic streptocci infection is usually a: a. serious infection of the upper airway b. common cause of pharyngitis in children over the age of 15 c. brief illness that leaves a child at risk for serious sequelae if not treated d. disease of the heart, lungs, joints, and central nervous system - CORRECT ANSWER C Of the following which is NOT a factor increasing the risk of asthma exacerbation: a. 2 or more ED/hospital visits in the past year. b. history of intubation. c. Airflow obstruction on inspiration. d. Taking medications as prescribed. - CORRECT ANSWER D A child with cystic fibrosis is admitted to the hospital. The likely reasons for this admission are? a. Growth failure from malabsorption b. Bacterial lung infection accompanied with chronic lung obstruction c. Diabetes symptoms d. all of the above - CORRECT ANSWER D In a child with Cystic Fibrosis there is a direct correlation between a patient with a BMI > 50% for their age and gender and improved lung function. True or False? - CORRECT ANSWER True Tobacco is one of the largest risk factors for treatment failure in children with asthma. True or False? - CORRECT ANSWER True Identify which of the following therapies is NOT usually included in the care of the child or adolescent with cystic fibrosis. a. Administration of NSAID's in high doses. b. Administration of pancreatic enzymes. c. Airway clearance therapy. d. Administration of low dose daily steroids. - CORRECT ANSWER D Most children (children 3-5 years) with croup: a. Require hospitalization. b. Will need to be intubated. c. Can be treated at home with supportive measures. d. Are over 6 years old. - CORRECT ANSWER C Infants are at higher risk for respiratory distress because of all of the following EXCEPT: a. Infants are diaphragmatic breathers. b. Air passing through the infant's trachea is warm and moist. c. Infants have decreased numbers of alveolar sacs for oxygen exchange. d. Infants have a higher risk for contracting RSV. - CORRECT ANSWER B Which of the following is accurate regarding RSV? a. The younger the infant, the greater the likelihood of severe lower respiratory disease. b. Often leads to hospitalization in young infants. c. Often infants have tachypnea, wheezing, and poor air exchange d. all of the above - CORRECT ANSWER D Cystic fibrosis is an exocrine gland dysfunction that: a. Affects the transfer of both sodium and potassium across the cell membranes. b. Increases the release and secretion of pancreatic enzymes. c. Increases the viscosity of the mucous gland secretions. d. None of the above - CORRECT ANSWER C Which of the following statements about inhaled corticosteroids is FALSE? a. They are used to treat inflammation. b. They impair growth. c. They can cause oral thrush so patients are educated to rinse their mouth after use. d. Are used to treat acute asthma exacerbations. - CORRECT ANSWER D The nurse is caring for an infant admitted to the hospital with a respiratory syncytial virus infection. Which of the following assessment findings would be most concerning? a. Heart rate 130 beats per minute. b. Respiratory rate 79 breaths per minute. c. Infant is breastfeeding. d. Respiratory rate 32 breaths per minute. - CORRECT ANSWER B A patient with cystic fibrosis should take the opportunity while in the hospital to meet with other children with cystic fibrosis so they can support each other. True or False? - CORRECT ANSWER False An 8 month old infant is admitted with possible pertussis, the nurse should particularly assess the: a. living conditions of the infant. b. labor and delivery history of the mother. c. immunization status of the infant d. alcohol and drug intake of the mother. - CORRECT ANSWER C Which of the following children is in the greatest need of emergency medical treatment? a. A 3-year-old who has a barky cough, is afebrile, and presenting with stridor this morning. b. An infant with wheezing, tachypnea, tachycardia, and a high fever. c. An 7-year-old who has abrupt onset of mild subcostal retractions, a low grade fever, and a barky cough. d. A 13-year-old with a high fever, stridor but no retractions, and purulent secretions. - CORRECT ANSWER B Vaccines have lead to a significant decrease in the number of INFANTS diagnosed with pneumonia. Which of the following vaccines does NOT decrease risk of pneumonia in INFANTS? a. Meningococcal (Menactra) b. Haemophilus Influenza (HIB) c. Pneumococcus (Prevnar) d. None of the above. - CORRECT ANSWER A The nurse caring for an infant admitted to the hospital with probable RSV would expect: a. The patient is placed in a single room or is co-horted with another child with RSV. b. The patient is on standard precautions. c. The patient is on standard, contact and droplet precautions. d. Both A & C - CORRECT ANSWER D You are instructing the parents of a premature infant . What are the signs and symptoms of respiratory distress and when should they call their primary care provider? You would include all of the following in your education EXCEPT: a. Refusal to breast feed. b. Respiratory rate of 40. c. Fever over 101.5. d. Wheezing and substernal retractions. - CORRECT ANSWER B What substance is released from the posterior pituitary gland and promotes water retention in the renal system? A. Renin B. Aldosterone C. Angiotensin D.Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) - CORRECT ANSWER Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) ADH is released in response to increased osmolality and decreased volume of intravascular fluid; it promotes water retention in the renal system by increasing the permeability of renal tubules to water. Renin release is stimulated by diminished blood flow to the kidneys. Aldosterone is secreted by the adrenal cortex. It enhances sodium reabsorption in renal tubules, promoting osmotic reabsorption of water. Renin reacts with a plasma globulin to generate angiotensin, which is a powerful vasoconstrictor. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone. Nurses should be alert for increased fluid requirements in which circumstance? A. Fever B. Mechanical ventilation C. Congestive heart failure D. Increased intracranial pressure - CORRECT ANSWER Fever Fever leads to great insensible fluid loss in young children because of increased body surface area relative to fluid volume. The mechanically ventilated child has decreased fluid requirements. Congestive heart failure is a case of fluid overload in children. Increased intracranial pressure does not lead to increased fluid requirements in children. What factor predisposes an infant to fluid imbalances? A. Decreased surface area B. Lower metabolic rate C. Immature kidney functioning D. Decreased daily exchange of extracellular fluid - CORRECT ANSWER Immature kidney functioning The infant's kidneys are functionally immature at birth and are inefficient in excreting waste products of metabolism. Infants have a relatively high body surface area (BSA) compared with adults. This allows a higher loss of fluid to the environment. A higher metabolic rate is present as a result of the higher BSA in relation to active metabolic tissue. The higher metabolic rate increases heat production, which results in greater insensible water loss. Infants have a greater exchange of extracellular fluid, leaving them with a reduced fluid reserve in conditions of dehydration. What is the required number of milliliters of fluid needed per day for a 14-kg child? A. 800 B. 1000 C. 1200 D. 1400 - CORRECT ANSWER 1200 For the first 10 kg of body weight, a child requires 100 ml/kg. For each additional kilogram of body weight, an extra 50 ml is needed.10 kg × 100 ml/kg/day = 1000 ml4 kg × 50 ml/kg/day = 200 ml1000 ml + 200 ml = 1200 ml/dayEight hundred to 1000 ml is too little; 1400 ml is too much. An infant is brought to the emergency department with the following clinical manifestations: poor skin turgor, weight loss, lethargy, tachycardia, and tachypnea. This is suggestive of which situation? A. Water excess B. Sodium excess C. Water depletion D. Potassium excess - CORRECT ANSWER Water depletion These clinical manifestations indicate water depletion or dehydration. Edema and weight gain occur with water excess or overhydration. Sodium or potassium excess would not cause these symptoms. Clinical manifestations of sodium excess (hypernatremia) include which signs or symptoms? A. Hyperreflexia B. Abdominal cramps C. Cardiac dysrhythmias D. Dry, sticky mucous membranes - CORRECT ANSWER Dry, sticky mucous membranes Dry, sticky mucous membranes are associated with hypernatremia. Hyperreflexia is associated with hyperkalemia. Abdominal cramps, weakness, dizziness, nausea, and apprehension are associated hyponatremia. Cardiac dysrhythmias are associated with hypokalemia. What laboratory finding should the nurse expect in a child with an excess of water? A. Decreased hematocrit B. High serum osmolality C. High urine specific gravity D. Increased blood urea nitrogen - CORRECT ANSWER Decreased hematocrit The excess water in the circulatory system results in hemodilution. The laboratory results show a falsely decreased hematocrit. Laboratory analysis of blood that is hemodiluted reveals decreased serum osmolality and blood urea nitrogen. The urine specific gravity is variable relative to the child's ability to correct the fluid imbalance. What clinical manifestation(s) is associated with calcium depletion (hypocalcemia)? A. Nausea, vomiting B. Weakness, fatigue C. Muscle hypotonicity D. Neuromuscular irritability - CORRECT ANSWER Neuromuscular irritability Neuromuscular irritability is a clinical manifestation of hypocalcemia. Nausea and vomiting occur with hypercalcemia and hypernatremia. Weakness, fatigue, and muscle hypotonicity are clinical manifestations of hypercalcemia. What type of dehydration occurs when the electrolyte deficit exceeds the water deficit? A. Isotonic dehydration B. Hypotonic dehydration C. Hypertonic dehydration D. Hyperosmotic dehydration - CORRECT ANSWER Hypotonic dehydration Hypotonic dehydration occurs when the electrolyte deficit exceeds the water deficit, leaving the serum hypotonic. Isotonic dehydration occurs in conditions in which electrolyte and water deficits are present in balanced proportion. Hypertonic dehydration results from water loss in excess of electrolyte loss. This is the most dangerous type of dehydration. It is caused by feeding children fluids with high amounts of solute. Hyperosmotic dehydration is another term for hypertonic dehydration. What amount of fluid loss occurs with moderate dehydration? A. <50 ml/kg B. 50 to 90 ml/kg C. <5% total body weight D. >15% total body weight - CORRECT ANSWER 50 to 90 ml/kg Moderate dehydration is defined as a fluid loss of between 50 and 90 ml/kg. Mild dehydration is defined as a fluid loss of less than 50 ml/kg. Weight loss up to 5% is considered mild dehydration. Weight loss over 15% is severe dehydration. Physiologically, the child compensates for fluid volume losses by which mechanism? A. Inhibition of aldosterone secretion B. Hemoconcentration to reduce cardiac workload C. Fluid shift from interstitial space to intravascular space D. Vasodilation of peripheral arterioles to increase perfusion - CORRECT ANSWER Fluid shift from interstitial space to intravascular space Compensatory mechanisms attempt to maintain fluid volume. Initially, interstitial fluid moves into the intravascular compartment to maintain blood volume. Aldosterone is released to promote sodium retention and conserve water in the kidneys. Hemoconcentration results from the fluid volume loss. With less circulating volume, tachycardia results. Vasoconstriction of peripheral arterioles occurs to help maintain blood pressure. Ongoing fluid losses can overwhelm the child's ability to compensate, resulting in shock. What early clinical sign precedes shock? A. Tachycardia B. Slow respirations C. Warm, flushed skin D. Decreased blood pressure - CORRECT ANSWER Tachycardia Shock is preceded by tachycardia and signs of poor tissue perfusion and decreased pulse oximetry values. Respirations are increased as the child attempts to compensate. As a result of the poor peripheral circulation, the child has skin that is cool and mottled with decreased capillary refilling after blanching. In children, lowered blood pressure is a late sign and may accompany the onset of cardiovascular collapse. The presence of which pair of factors is a good predictor of a fluid deficit of at least 5% in an infant? A. Weight loss and decreased heart rate B. Capillary refill of less than 2 seconds and no tears C. Increased skin elasticity and sunken anterior fontanel D. Dry mucous membranes and generally ill appearance - CORRECT ANSWER Dry mucous membranes and generally ill appearance A good predictor of a fluid deficit of at least 5% is any two four factors: capillary refill of more than 2 seconds, absent tears, dry mucous membranes, and ill general appearance. Weight loss is associated with fluid deficit, but the degree needs to be quantified. Heart rate is usually elevated. Skin elasticity is decreased, not increased. The anterior fontanel is depressed. The nurse suspects fluid overload in an infant receiving intravenous fluids. What clinical manifestation is suggestive of water intoxication? A. Oliguria B. Weight loss C. Irritability and seizures D. Muscle weakness and cardiac dysrhythmias - CORRECT ANSWER Irritability and seizures Irritability, somnolence, headache, vomiting, diarrhea, and generalized seizures are manifestations of water intoxication. Urinary output is increased as the child attempts to maintain fluid balance. Weight gain is usually associated with water intoxication. Muscle weakness and cardiac dysrhythmias are not associated with water intoxication. What physiologic state(s) produces the clinical manifestations of nervous system stimulation and excitement, such as overexcitability, nervousness, and tetany? A. Metabolic acidosis B. Respiratory alkalosis C. Metabolic and respiratory acidosis D. Metabolic and respiratory alkalosis - CORRECT ANSWER Metabolic and respiratory alkalosis The major symptoms and signs of alkalosis include nervous system stimulation and excitement, including overexcitability, nervousness, tingling sensations, and tetany that may progress to seizures. Acidosis (both metabolic and respiratory) has clinical signs of depression of the central nervous system, such as lethargy, diminished mental capacity, delirium, stupor, and coma. Respiratory alkalosis has the same symptoms and signs as metabolic alkalosis. What is an approximate method of estimating output for a child who is not toilet trained? A. Have parents estimate output. B. Weigh diapers after each void. C. Place a urine collection device on the child. D. Have the child sit on a potty chair 30 minutes after eating. - CORRECT ANSWER Weigh diapers after each void Weighing diapers will provide an estimate of urinary output. Each 1 g of weight is equivalent to 1 ml of urine. Having parents estimate output would be inaccurate. It is difficult to estimate how much fluid is in a diaper. The urine collection device would irritate the child's skin. It would be difficult for a toddler who is not toilet trained to sit on a potty chair 30 minutes after eating. The nurse is selecting a site to begin an intravenous infusion on a 2-year-old child. The superficial veins on his hand and arm are not readily visible. What intervention should increase the visibility of these veins? A. Gently tap over the site. B. Apply a cold compress to the site. C. Raise the extremity above the level of the body. D. Use a rubber band as a tourniquet for 5 minutes - CORRECT ANSWER Gently tap over the site Gently tapping the site can sometimes cause the veins to be more visible. This is done before the skin is prepared. Warm compresses (not cold) may be useful. The extremity is held in a dependent position. A tourniquet may be helpful, but if too tight, it could cause the vein to burst when punctured. Five minutes is too long. When caring for a child with an intravenous (IV) infusion, what is an appropriate nursing action? A. Change the insertion site every 24 hours. B. Check the insertion site frequently for signs of infiltration. C. Use a macrodropper to facilitate reaching the prescribed flow rate. D. Avoid restraining the child to prevent undue emotional stress. - CORRECT ANSWER Check the insertion site frequently for signs of infiltration The nursing responsibility for IV therapy is to calculate the amount to be infused in a given length of time; set the infusion rate; and monitor the apparatus frequently, at least every 1 to 2 hours, to make certain that the desired rate is maintained, the integrity of the system remains intact, the site remains intact (free of redness, edema, infiltration, or irritation), and the infusion does not stop. Insertion sites do not need to be changed every 24 hours unless a problem is found with the site. This exposes the child to significant trauma. A minidropper (60 drops/ml) is the recommended IV tubing in pediatric patients. Intravenous sites should be protected. This may require soft restraints on the child. The nurse determines that a child's intravenous infusion has infiltrated. The infused solution is a vesicant. What is the most appropriate nursing action? A. Stop the infusion and apply ice. B. End the infusion and notify the practitioner. C. Slow the infusion rate and notify the practitioner. D. Discontinue the infusion and apply warm compresses. - CORRECT ANSWER End the infusion and notify the practitioner A vesicant causes cellular damage when even minute amounts escape into the tissue. The intravenous infusion is immediately stopped, the extremity is elevated, the practitioner is notified, and the treatment protocol is initiated. The applying of heat or ice depends on the fluid that has extravasated. The catheter is left in place until it is no longer needed. Several types of long-term central venous access devices are used. What is a benefit of using an implanted port (e.g., Port-a-Cath)? A. You do not need to pierce the skin for access. B. It is easy to use for self-administered infusions. C. The patient does not need to limit regular physical activity, including swimming. D. The catheter cannot dislodge from the port even if the child "plays" with the port site. - CORRECT ANSWER The patient does not need to limit regular physical activity, including swimming. No limitations on physical activity are needed. The child is able to participate in all regular physical activities, including bathing, showering, and swimming. The skin over the device is pierced with a Huber needle to access. Long-term central venous access devices are difficult to use for self-administration. The port is placed under the skin. If the child manipulates the device and plays with the actual port, the catheter can be dislodged. The nurse is teaching the family of a child with a long-term central venous access device about signs and symptoms of bacteremia. What finding indicates the presence of bacteremia? A. Hypertension B. Pain at the entry site C. Fever and general malaise D. Redness and swelling at the entry site - CORRECT ANSWER Fever and general malaise Fever, chills, general malaise, and an ill appearance can be signs of bacteremia and require immediate intervention. Hypotension would be indicative of sepsis and possible impending cardiovascular collapse. Pain, redness, and swelling at the entry site indicate local infection. What flush solution is recommended for intravenous catheters larger than 24 gauge? A. Saline B. Heparin C. Alteplase D. Heparin and saline combination - CORRECT ANSWER Saline The recommended solution for flushing venous access devices is saline. The turbulent flow flush with saline is effective for catheters larger than 24 gauge. The use of heparin does not increase the longevity of the venous access device. In 24-gauge catheters, heparin may offer an advantage. Alteplase is used for treating catheter-related occlusions in children. The heparin and saline combination does not offer any advantage over saline or heparin individually. The nurse is teaching a parent of a 10-year-old child who will be discharged with a venous access device (VAD). What statement by the parent indicates a correct understanding of the teaching? A. "I should have my child wear a protective vest when my child wants to participate in contact sports." B. "I should apply pressure to the entry site to the vein, not the exit site, if the VAD is accidentally removed." C. "I can expect my child to have feelings of general malaise for 1 week after the VAD i - CORRECT ANSWER "I should apply pressure to the entry site to the vein, not the exit site, if the VAD is accidentally removed." The parents of a child with a VAD should be taught to apply pressure to the entry site to the vein, not the exit site, if the VAD is accidentally removed. The child should not participate in contact sports, even with a protective vest, to prevent the VAD from becoming dislodged. General malaise is a sign of an infection, not an expected finding after insertion of the VAD. The child can shower or take a bath after insertion of the VAD; the child does not need a sponge bath for any length of time. What condition is often associated with severe diarrhea? A. Metabolic acidosis B. Metabolic alkalosis C. Respiratory acidosis D. Respiratory alkalosis - CORRECT ANSWER Metabolic Acidosis Metabolic acidosis results from the increased absorption of short-chain fatty acids produced in the colon. There is an increase in lactic acid from tissue hypoxia secondary to hypovolemia. Bicarbonate is lost through the stool. Ketosis results from fat metabolism when glycogen stores are depleted. Metabolic alkalosis and respiratory alkalosis do not occur from severe diarrhea. What type of diarrhea is associated with an inflammation of the mucosa and submucosa in the ileum and colon caused by infectious agents? A. Osmotic B. Secretory C. Cytotoxic D. Dysenteric - CORRECT ANSWER Dysenteric Dysenteric diarrhea is associated with an inflammation of the mucosa and submucosa in the ileum and colon caused by infectious agents such as Campylobacter, Salmonella, or Shigella organisms. Edema, mucosal bleeding, and leukocyte infiltration occur. Osmotic diarrhea occurs when the intestine cannot absorb nutrients or electrolytes. It is commonly seen in malabsorption syndromes such as lactose intolerance. Secretory diarrhea is usually a result of bacterial enterotoxins that stimulate fluid and electrolyte secretion from the mucosal crypt cells, the principal secretory cells of the small intestine. Cytotoxic diarrhea is characterized by the viral destruction of the villi of the small intestine. This results in a smaller intestinal surface area, with a decreased capacity for fluid and electrolyte absorption. What organism is a parasite that causes acute diarrhea? A. Shigella organisms B. Salmonella organisms C. Giardia lamblia D. Escherichia coli - CORRECT ANSWER Giardia lamblia G. lamblia is a parasite that represents 10% of nondysenteric illness in the United States. Shigella, Salmonella, and E. coli are bacterial pathogens A school-age child with diarrhea has been rehydrated. The nurse is discussing the child's diet with the family. What food or beverage should be tolerated best? A. Clear fluids B. Carbonated drinks C. Applesauce and milk D. Easily digested foods - CORRECT ANSWER Easily digested foods Easily digested foods such as cereals, cooked vegetables, and meats should be provided for the child. Early reintroduction of nutrients is desirable. Continued feeding or reintroduction of a regular diet has no adverse effects and actually lessens the severity and duration of the illness. Clear fluids (e.g., fruit juices and gelatin) and carbonated drinks have high carbohydrate content and few electrolytes. Caffeinated beverages should be avoided because caffeine is a mild diuretic. In some children, lactose intolerance will develop with diarrhea, and cow's milk should be avoided in the recovery stage. A school-age child with acute diarrhea and mild dehydration is being given oral rehydration solutions (ORS). The child's mother calls the clinic nurse because he is also occasionally vomiting. The nurse should recommend which intervention? A. Bring the child to the hospital for intravenous fluids. B. Alternate giving ORS and carbonated drinks. C. Continue to give ORS frequently in small amounts. D. Keep child NPO (nothing by mouth) for 8 hours and resume ORS if vomiting has subsided - CORRECT ANSWER Continue to give ORS frequently in small amounts. Children who are vomiting should be given ORS at frequent intervals and in small amounts. Intravenous fluids are not indicated for mild dehydration. Carbonated beverages are high in carbohydrates and are not recommended for the treatment of diarrhea and vomiting. The child is not kept NPO because this would cause additional fluid losses. A 7-year-old child with acute diarrhea has been rehydrated with oral rehydration solution (ORS). The nurse should recommend that the child's diet be advanced to what kind of diet? A. Regular diet B. Clear liquids C. High carbohydrate diet D. BRAT (bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast or tea) diet - CORRECT ANSWER Regular diet It is appropriate to advance to a regular diet after ORS has been used to rehydrate the child. Clear liquids are not appropriate for hydration or afterward. A high carbohydrate diet may contribute to loose stools because of the low electrolyte content and high osmolality. The BRAT diet has little nutritional value and is high in carbohydrates. What is the most frequent cause of hypovolemic shock in children? A. Sepsis B. Blood loss C. Anaphylaxis D. Heart failure - CORRECT ANSWER Blood loss Blood loss is the most frequent cause of hypovolemic shock in children. Sepsis causes septic shock, which is overwhelming sepsis and circulating bacterial toxins. Anaphylactic shock results from extreme allergy or hypersensitivity to a foreign substance. Heart failure contributes to hypervolemia, not hypovolemia. What type of shock is characterized by a hypersensitivity reaction causing massive vasodilation and capillary leaks, which may occur with drug or latex allergy? A. Neurogenic shock B. Cardiogenic shock C. Hypovolemic shock D. Anaphylactic shock - CORRECT ANSWER Anaphylactic shock Anaphylactic shock results from extreme allergy or hypersensitivity to a foreign substance. Neurogenic shock results from loss of neuronal control, such as the interruption of neuronal transmission after a spinal cord injury. Cardiogenic shock is decreased cardiac output. Hypovolemic shock is a reduction in the size of the vascular compartment, decreasing blood pressure, and low central venous pressure. What clinical manifestation(s) should the nurse expect to see as shock progresses in a child and becomes decompensated shock? A. Thirst B. Irritability C. Apprehension D. Confusion and somnolence - CORRECT ANSWER Confusion and somnolence Confusion and somnolence are beginning signs of decompensated shock. Thirst, irritability, and apprehension are signs of compensated shock. The nurse suspects shock in a child 1 day after surgery. What should be the initial nursing action? A. Place the child on a cardiac monitor. B. Obtain arterial blood gases. C. Provide supplemental oxygen. D. Put the child in the Trendelenburg position. - CORRECT ANSWER Provide supplemental oxygen The initial nursing action for a patient in shock is to establish ventilatory support. Oxygen is provided, and the nurse carefully observes for signs of respiratory failure, which indicates a need for intubation. Cardiac monitoring would be indicated to assess the child's status further, but ventilatory support comes first. Oxygen saturation monitoring should be begun. Arterial blood gases would be indicated if alternative methods of monitoring oxygen therapy were not available. The Trendelenburg position is not indicated and is detrimental to the child. The head-down position increases intracranial pressure and decreases diaphragmatic excursion and lung volume. What explains physiologically the edema formation that occurs with burns? A. Vasoconstriction B. Reduced capillary permeability C. Increased capillary permeability D. Diminished hydrostatic pressure within capillaries - CORRECT ANSWER Increased capillary permeability With a major burn, capillary permeability increases, allowing plasma proteins, fluids, and electrolytes to be lost into the interstitial space, causing edema. Maximum edema in a small wound occurs about 8 to 12 hours after injury. In larger injuries, the maximum edema may not occur until 18 to 24 hours later. Vasodilation occurs, causing an increase in hydrostatic pressure. What is a systemic response to severe burns in a child? A. Metabolic alkalosis B. Decreased metabolic rate C. Increased renal plasma flow D. Abrupt drop in cardiac output - CORRECT ANSWER Abrupt drop in cardiac output The initial physiologic response to a burn injury is a dramatic change in circulation. A precipitous drop in cardiac output precedes any change in circulating blood or plasma volumes. A circulating myocardial depressant factor associated with severe burn injury is thought to be the cause. Metabolic acidosis usually occurs secondary to the disruption of the body's buffering action resulting from fluid shifting to extravascular space. There is a greatly accelerated metabolic rate in burn patients, supported by protein and lipid breakdown. With the loss of circulating volume, there is decreased renal blood flow and depressed glomerular filtration. A child is admitted with extensive burns. The nurse notes burns on the child's lips and singed nasal hairs. The nurse should suspect what condition in the child? A. A chemical burn B. A hot-water scald C. An electrical burn D. An inhalation injury - CORRECT ANSWER An inhalation injury Evidence of an inhalation injury includes burns of the face and lips, singed nasal hairs, and laryngeal edema. Clinical manifestations may be delayed for up to 24 hours. Chemical burns, electrical burns, and burns associated with hot-water scalds would not produce singed nasal hair. What is the most immediate threat to life in children with thermal injuries? A. Shock B. Anemia C. Local infection D. Systemic sepsis - CORRECT ANSWER Shock The immediate threat to life in children with thermal injuries is airway compromise and profound shock. Anemia is not of immediate concern. During the healing phase, local infection or sepsis is the primary complication. After the acute stage and during the healing process, what is the primary complication from burn injury? A. Shock B. Asphyxia C. Infection D. Renal shutdown - CORRECT ANSWER Infection During the healing phase, local infection or sepsis is the primary complication. Respiratory problems, primarily airway compromise, and shock are the primary complications during the acute stage of burn injury. Renal shutdown is not a complication of the burn injury but may be a result of the profound shock. What sign is one of the first to indicate overwhelming sepsis in a child with burn injuries? A. Seizures B. Bradycardia C. Disorientation D. Decreased blood pressure - CORRECT ANSWER Disorientation Disorientation in the burn patient is one of the first signs of overwhelming sepsis and may indicate inadequate hydration. Seizures, bradycardia, and decreased blood pressure are not initial manifestations of overwhelming sepsis. A toddler sustains a minor burn on the hand from hot coffee. What is the first action in treating this burn? A. Apply burn ointment. B. Put ice on the burned area. C. Cover the hand with gauze dressing. D. Hold the hand under cool running water. - CORRECT ANSWER Hold the hand under cool running water In minor burns, the best method to stop the burning process is to hold the burned area under cool running water. Ointments are not applied to a new burn; the ointment will contribute to the burning. Ice is not recommended. Gauze dressings do not stop the burning process. What finding is the most reliable guide to the adequacy of fluid replacement for a small child with burns? A. Absence of thirst B. Falling hematocrit C. Increased seepage from burn wound D. Urinary output of 1 to 2 ml/kg of body weight/hr - CORRECT ANSWER Urinary output of 1 to 2 ml/kg of body weight/hr Replacement fluid therapy is delivered to provide a urinary output of 30 ml/hr in older children or 1 to 2 ml/kg of body weight/hr for children weighing less than 30 kg (66 lb). Thirst is the result of a complex set of interactions and is not a reliable indicator of hydration. Thirst occurs late in dehydration. A falling hematocrit would be indicative of hemodilution. This may reflect fluid shifts and may not accurately represent fluid replacement therapy. Increased seepage from a burn wound would be indicative of increased output, not adequate hydration. What is the purpose of a high-protein diet for a child with major burns? A. Promote growth B. Improve appetite C. Minimize protein breakdown D. Diminish risk of stress-induced hyperglycemia - CORRECT ANSWER Minimize protein breakdown Initially after major burns, there is a hypometabolic phase, which lasts for 2 or 3 days. A hypermetabolic phase follows, characterized by increased body temperature, oxygen and glucose consumption, carbon dioxide production, glycogenolysis, proteolysis, and lipolysis. This response continues for up to 9 months. A diet high in protein and calories is necessary. Healing, not growth, is the primary consideration. Many children have poor appetites, and supplementation is necessary. Hypoglycemia, not hyperglycemia, can occur from the stress of burn injury because the liver glycogen stores are rapidly depleted. Fentanyl and midazolam (Versed) are given before débridement of a child's burn wounds. What is the purpose of using these medications? A. Facilitate healing B. Provide pain relief C. Minimize risk of infection D. Decrease amount of débridement needed - CORRECT ANSWER Provide pain relief Partial-thickness burns require débridement of devitalized tissue to promote healing. The procedure is painful and requires analgesia and sedation before the procedure. Fentanyl and midazolam provide excellent intravenous sedation and analgesia to control procedural pain in children with burns. Hydrotherapy is required to treat a child with extensive partial-thickness burn wounds. What is the purpose of hydrotherapy? A. Provide pain relief B. Débride the wounds C. Destroy bacteria on the skin D. Increase peripheral blood flow - CORRECT ANSWER Debride the wounds Soaking in a tub or showering once or twice a day acts to loosen and remove sloughing tissue, exudate, and topical medications. The hydrotherapy cleanses the wound and the entire body and helps maintain range of motion. Appropriate pain medications are necessary. Dressing changes are extremely painful. The total bacterial count of the skin is reduced by the hydrotherapy, but this is not the primary goal. There may be an increase in peripheral blood flow, but the primary purpose is for wound débridement. What is the nursing action related to the applying of biologic or synthetic skin coverings for a child with partial-thickness burns of both legs? A. Splint the legs to prevent movement. B. Observe wounds for signs of infection. C. Monitor closely for manifestations of shock. D. Examine dressings for indications of bleeding. - CORRECT ANSWER Observe wounds for signs of infection When applied early to a superficial partial-thickness injury, biologic dressings stimulate epithelial growth and faster wound healing. If the dressing covers areas of heavy microbial contamination, infection occurs beneath the dressing. In the case of partial-thickness burns, such infection may convert the wound to a full-thickness injury. Infection is the primary concern when biologic dressings are used. What is an effective strategy to reduce the stress of burn dressing procedures? A. Involve the child and give choices as feasible. B. Explain to the child why analgesics cannot be used. C. Reassure the child that dressing changes are not painful. D. Encourage the child to master stress with controlled passivity. - CORRECT ANSWER Involve the child and give choices as feasible Children who have an understanding of the procedure and some perceived control demonstrate less maladaptive behavior. They respond well to participating in decisions and should be given as many choices as possible. Analgesia and sedation can and should be used. The dressing change procedure is very painful and stressful. Misinformation should not be given to the child. Encouraging the child to master stress with controlled passivity is not a positive coping strategy. What consideration is important for the nurse when changing dressings and applying topical medication to a child's abdomen and leg burns? A. Apply topical medication with clean hands. B. Wash hands and forearms before and after dressing change. C. If dressings have adhered to the wound, soak in hot water before removal. D. Apply dressing so that movement is limited during the healing process. - CORRECT ANSWER Wash hands and forearms before and after dressing change Frequent hand and forearm washing is the single most important element of the infection-control program. Topical medications should be applied with a tongue blade or gloved hand. Dressings that have adhered to the wound can be removed with tepid water or normal saline. Dressings are applied with sufficient tension to remain in place but not so tightly as to impair circulation or limit motion. What is a strategy used to minimize scarring with burn injury in a child? A. Applying of drying agents on skin B. Use of loose-fitting garments over healing areas C. Limitation of period without pressure to areas of scarring D. Immobilization of extremities while healing is occurring - CORRECT ANSWER Limitation of period without pressure to areas of scarring Uniform pressure to the scar decreases the blood supply and forces the collagen into a more normal alignment. When pressure is removed, blood supply to the scar is immediately increased; therefore, periods without pressure should be brief to avoid nourishment of the hypertrophic tissue. Moisturizing agents are used with massage to help stretch tissue and prevent contractures. Compression garments, not loose-fitting garments, are indicated. Range of motion exercises are done to minimize contractures. Prevention of burn injury is important anticipatory guidance. In the infant and toddler period, which mode is the most common cause of burn? A. Matches B. Electrical cords C. Hot liquids in the kitchen D. Microwave-heated foods - CORRECT ANSWER Hot liquids in the kitchen Infants and toddlers are most commonly injured by hot liquids in the kitchen and bathroom. This often occurs as a result of inadequate supervision of this curious and energetic age group. Matches and lighters are seen as toys by young children and should be kept out of reach. Older toddlers and preschool children are at risk of chewing on electrical cords and placing objects in outlets. Microwave-heated fluids and foods can become superheated, resulting in oral burns. The nurse is teaching a group of female adolescents about toxic shock syndrome and the use of tampons. What statement by a participant indicates a need for additional teaching? A. "I can alternate using a tampon and a sanitary napkin." B. "I should wash my hands before inserting a tampon." C. "I can use a super absorbent tampon for more than 6 hours." D. "I should call my health care provider if I suddenly develop a rash that looks like sunburn." - CORRECT ANSWER "I can use a superabsorbent tampon for more than 6 hours." Teaching female adolescents about the association between toxic shock syndrome and the use of tampons is important. The teaching should include not using superabsorbent tampons; not leaving the tampon in for longer than 4 to 6 hours; alternating the use of tampons with sanitary napkins; washing hands before inserting a tampon to decrease the chance of introducing pathogens; and informing a health care provider if a sudden high fever, vomiting, muscle pain, dizziness, or a rash that looks like a sunburn appears. The nurse is caring for an 18-month-old child with rotavirus. What clinical manifestations should the nurse expect to observe? A. Severe abdominal cramping and bloody diarrhea B. Mild fever and vomiting followed by onset of watery stools C. Colicky abdominal pain and vomiting D. High fever, diarrhea, and lethargy - CORRECT ANSWER Mild fever and vomiting followed by onset of watery stools Rotavirus is one of the most common pathogens that cause gastroenteritis in children younger than the age of 2 years. Clinical manifestations include mild to moderate fever and vomiting followed by the onset of watery stools. The fever and vomiting usually abate in 1 or 2 days, but the diarrhea persists for 5 to 7 days. Severe abdominal cramping and bloody diarrhea are seen with Escherichia coli infection; colicky abdominal pain and vomiting are seen with salmonella infection; and high fever, diarrhea, and lethargy are seen with infection by Salmonella typhi. The nurse is preparing a presentation on compensated, decompensated, and irreversible shock in children. What clinical manifestations related to decompensated shock should the nurse include? (Select all that apply.) A. Tachypnea B. Oliguria C. Confusion D. Pale extremities E. Hypotension F. Thready pulse - CORRECT ANSWER A. Tachypnea B. Oliguria C. Confusion D. Pale extremities As shock progresses, perfusion in the microcirculation becomes marginal despite compensatory adjustments, and the signs are more obvious. Signs include tachypnea, oliguria, confusion, and pale extremities, as well as decreased skin turgor and poor capillary filling. Hypotension and a thready pulse are clinical manifestations of irreversible shock. In what condition should the nurse be alert for altered fluid requirements in children? (Select all that apply.) A. Oliguric renal failure B. Increased intracranial pressure C. Mechanical ventilation D. Compensated hypotension E. Tetralogy of Fallot F. Type 1 diabetes mellitus - CORRECT ANSWER A. Oliguric renal failure B. Increased intracranial pressure C. Mechanical ventilation The nurse should recognize that conditions such as oliguric renal failure, increased intracranial pressure, and mechanical ventilation can cause an increase or a decrease in fluid requirements. Conditions such as hypotension, tetralogy of Fallot, and diabetes mellitus (type 1) do not cause an alteration in fluid requirements. What clinical manifestations should be observed in a 2-year-old child with hypotonic dehydration? (Select all that apply.) A. Thick, doughy feel to the skin B. Slightly moist mucous membranes C. Absent tears D. Very rapid pulse E. Hyperirritability - CORRECT ANSWER B. Slightly moist mucous membranes C. Absent tears D. Very rapid pulse Clinical manifestations of hypotonic dehydration include slightly moist mucous membranes, absent tears, and a very rapid pulse. A thick, doughy feel to the skin and hyperirritability are signs of hypertonic dehydration. The nurse is caring for a child with hypokalemia. The nurse evaluates the child for which signs and symptoms of hypokalemia? (Select all that apply.) A. Twitching B. Hypotension C. Hyperreflexia D. Muscle weakness E. Cardiac arrhythmias - CORRECT ANSWER B. Hypotension D. Muscle Weakness E. Cardiac arrhythmias Signs and symptoms of hypokalemia are hypotension, muscle weakness, and cardiac arrhythmias. Twitching and hyperreflexia are signs of hyperkalemia. The nurse is caring for a child with hypercalcemia. The nurse evaluates the child for which signs and symptoms of hypercalcemia? (Select all that apply.) A. Tetany B. Anorexia C. Constipation D. Laryngospasm E. Muscle hypotonicity - CORRECT ANSWER B. Anorexia C. Constipation E. Muscle hypotonicity Signs and symptoms of hypercalcemia are anorexia, constipation, and muscle hypotonicity. Tetany and laryngospasm are signs of hypocalcemia. The nurse is caring for a child with hypernatremia. The nurse evaluates the child for which signs and symptoms of hypernatremia? (Select all that apply.) A. Apathy B. Lethargy C. Oliguria D. Intense thirst E. Dry, sticky mucos - CORRECT ANSWER B. Lethargy C. Oliguria E. Dry, stick mucous membranes Signs and symptoms of hypernatremia are nausea; oliguria; and dry, sticky mucous. Apathy and lethargy are signs of hyponatremia. Match the type of skin graft to its definition: A. Allografts B. Xenografts C. Autografts D. Isografts Defs: a. Tissue obtained from undamaged areas of the patient s own body b. Histocompatible tissue obtained from genetically identical individuals c. Skin that is obtained from genetically different members of the same species who are free of disease d. Skin that is obtained from members of a different species, primarily pigskin - CORRECT ANSWER A - c B - d C - a D - b [Show More]
Last updated: 5 months ago
Preview 1 out of 84 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 08, 2023
Number of pages
84
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 08, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
116






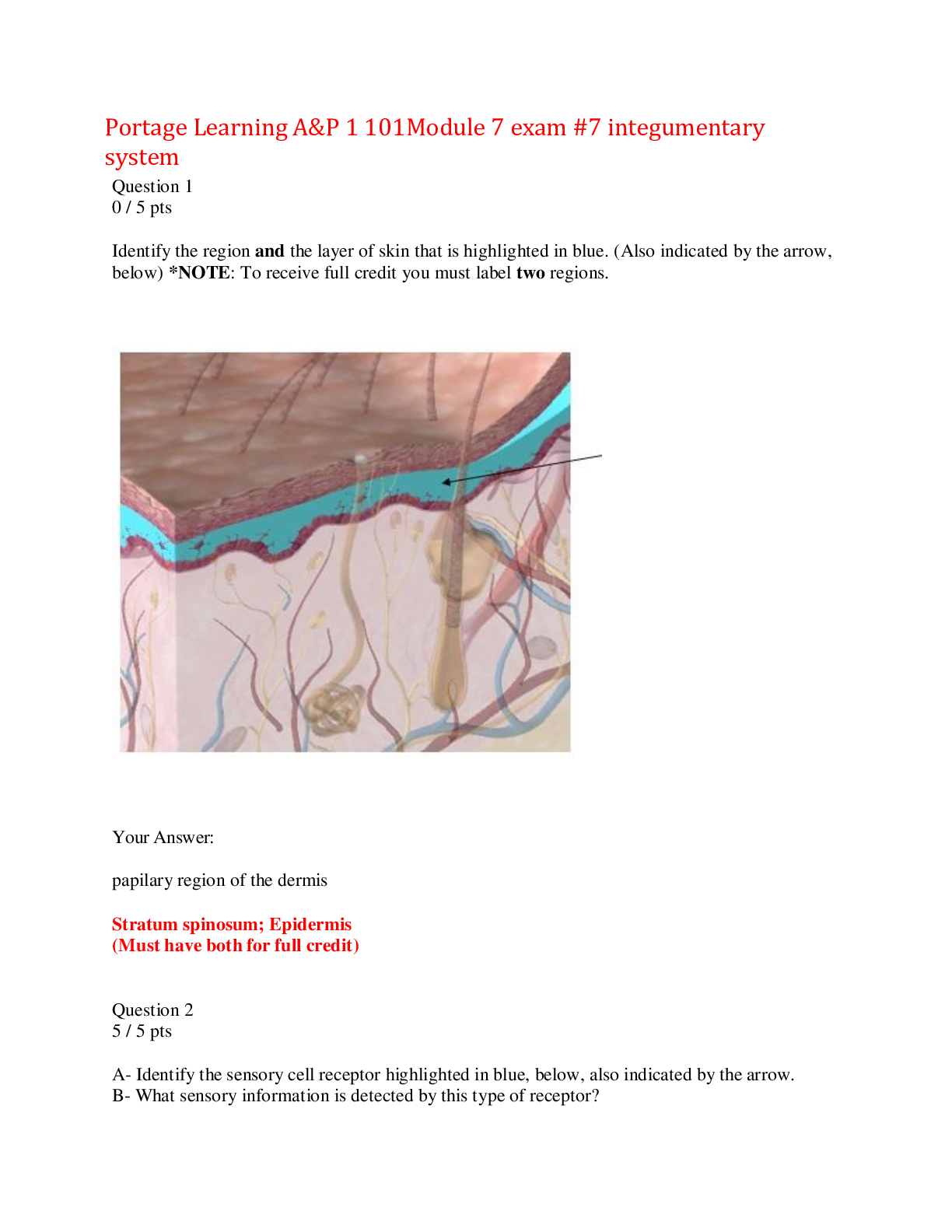





















.png)




