Med Surg NEW EXAM TEST QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Document Content and Description Below
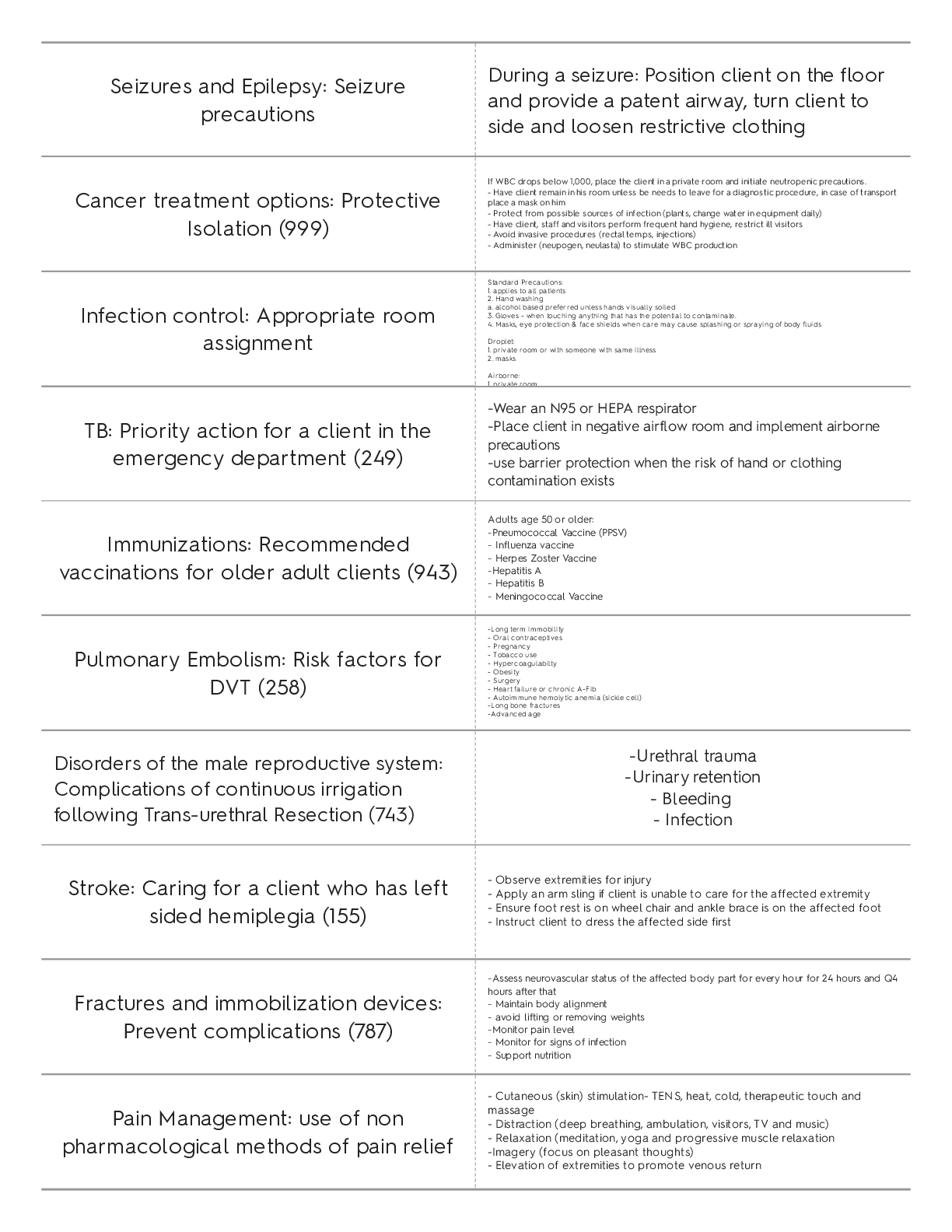
Med Surg NEW EXAM TEST QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Seizures and Epilepsy: Seizure precautions During a seizure: Position client on the floor and provide a patent airway, turn client to side and loosen... restrictive clothing Cancer treatment options: Protective Isolation (999) If WBC drops below 1,000, place the client in a private room and initiate neutropenic precautions. - Have client remain in his room unless be needs to leave for a diagnostic procedure, in case of transport place a mask on him - Protect from possible sources of infection (plants, change water in equipment daily) - Have client, staff and visitors perform frequent hand hygiene, restrict ill visitors - Avoid invasive procedures (rectal temps, injections) - Administer (neupogen, neulasta) to stimulate WBC production Infection control: Appropriate room assignment Standard Precautions: 1. applies to all patients 2. Hand washing a. alcohol based preferred unless hands visually soiled 3. Gloves - when touching anything that has the potential to contaminate. 4. Masks, eye protection & face shields when care may cause splashing or spraying of body fluids Droplet: 1. private room or with someone with same illness 2. masks Airborne: 1 private room TB: Priority action for a client in the emergency department (249) -Wear an N95 or HEPA respirator -Place client in negative airflow room and implement airborne precautions -use barrier protection when the risk of hand or clothing contamination exists Immunizations: Recommended vaccinations for older adult clients (943) Adults age 50 or older: -Pneumococcal Vaccine (PPSV) - Influenza vaccine - Herpes Zoster Vaccine -Hepatitis A - Hepatitis B - Meningococcal Vaccine Pulmonary Embolism: Risk factors for DVT (258) -Long term immobility - Oral contraceptives - Pregnancy - Tobacco use - Hypercoagulabilty - Obesity - Surgery - Heart failure or chronic A-Fib - Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (sickle cell) -Long bone fractures -Advanced age Disorders of the male reproductive system: Complications of continuous irrigation following Trans-urethral Resection (743) -Urethral trauma -Urinary retention - Bleeding - Infection Stroke: Caring for a client who has left sided hemiplegia (155) - Observe extremities for injury - Apply an arm sling if client is unable to care for the affected extremity - Ensure foot rest is on wheel chair and ankle brace is on the affected foot - Instruct client to dress the affected side first Fractures and immobilization devices: Prevent complications (787) -Assess neurovascular status of the affected body part for every hour for 24 hours and Q4 hours after that - Maintain body alignment - avoid lifting or removing weights -Monitor pain level - Monitor for signs of infection - Support nutrition Pain Management: use of non pharmacological methods of pain relief - Cutaneous (skin) stimulation- TENS, heat, cold, therapeutic touch and massage - Distraction (deep breathing, ambulation, visitors, TV and music) - Relaxation (meditation, yoga and progressive muscle relaxation -Imagery (focus on pleasant thoughts) - Elevation of extremities to promote venous return Acute Kidney injury and chronic kidney disease: Evaluating teaching about nutrition -Restrict dietary intake of potassium, phosphate and magnesium during oliguric phase -K and Na is regulated according to stage of kidney injury - high protein diet to replace the high rate of protein breakdown due to the stress from the illness. Possible TPN Heart failure and pulmonary edema: Dietary teaching about sodium restriction Maintain fluid and sodium restriction Increase dietary intake of potassium Pulmonary Embolism: Planning care for a client who is receiving enoxaparin -Assess for contraindications (active bleeding, peptic ulcer disease, history of stroke, recent trauma) -Monitor bleeding times (PT, aPTT and INR) -Monitor for side effects such as thrombocytopenia, anemia and hemmorhage Rheumatoid Arthritis: Reviewing Laboratory Values -Positive Anti- cyclic citrullinated peptide -RF Antibody (Diagnostic level for RA is 1:40-1:60) expected reference range 1:20 - Elevated ESR 20-40 mild inflammation 40-70 moderate 70-150 severe - Positive C-reactive protein - Positive ANA titier - Elevated WBC's Medications affecting coagulation: Heparin Contraindications Avoid NSAIDS while on heparin Antibiotics affecting protein synthesis: Adverse effects of gentamicin -Ototoxicity: cochlear damage (hearing loss) and vestibular damage (loss of balance). -Nephrotoxicity (proteinuria, elevated BUN, creatinine levels). -Hypersensitivity ( rash, pruritis, parathesia of hands and feet, and urticaria). Electrolyte imbalance: manifestations of hypokalemia Weak, irregular pulse, hypotension, respiratory distress Premature ventricular contractions, bradycardia, inverted T waves, ST depression Decreased GI motility, abdominal distension, constipation, n/v, anorexia, polyuria Decreased K (<3.5) ABG: Metabolic alkalosis (pH > 7.45) Electrolyte imbalance: Priority assessment for hypokalemia Assessing for a patent and open airway Blood and blood product transfusions: Administering Fresh Frozen Plasma Initiate a large bore IV access: 20 gauge needle Complete transfusion withing 2-4 hours time frame If reaction occurs: -Stop transfusion immediately - Initiate 0.9% NaCl in a separate line - Save blood bag and blood tubing Cardiovascular Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures: Caring for a client who has a PICC -Assessing site every 8 hours. Note redness, swelling, drainage, tenderness and condition of dressing -Change tube and positive pressure cap per facility protocol -Using 10mL or larger syringe to flush the line -Cleanse with alcohol for 3 seconds before accessing it -Use transparent dressing Cardiovascular Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures: Teaching about a PICC -Advise client not to immerse arm in water, to cover dressing site to avoid water exposure -Avoid BP in the arm with PICC Cardiovascular Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures: PICC care - Apply an initial dressing of gauze and replace with transparent dressing within 24 hours - An initial x-ray should be taken to ensure proper placement Cardiovascular and Hematologic Disorders: teaching client about food interaction with Warfarin -Kale, spinach -Brussels sprouts -collard greens, mustard greens -green tea -grapefruit juice, alcohol Angina and MI: Client teaching about nitroglycerin Nitrogylcerin prevents coronary artery vasospasm and reduces preload and afterload. Used to treat angina and help with BP. - Place nitro under tongue to dissolve - Take up to two more doses of nitro at 5-min intervals - Stop activity and rest Headache is a common side effect Orthostatic hypotension Osteoporosis: Teaching about self administration of Alendronate Take with 8oz water in the early morning before eating Remain upright for 30 minutes after taking medication Diabetes Mellitus Management: teaching about self administration of insulin - Rotate injection sites - Inject at a 90 degree angle. Aspiration is not necessary - Advise client to eat at regular intervals, avoid alcohol intake and adjust insulin to exercise and diet to avoid hypoglycemia - When mixing insulin's, draw up the shorter acting insulin into the syringe first and then the longer acting insulin. IV therapy: Performing Venipuncture on an older adult client a 22-24 gauge catheter is best to use on older adults Tie the tourniquet sparingly and try to avoid veins in the hand Dosage calculations: Calculating IV infusion rate Ex: nurse is preparing to administer dextrose 5% in water 500 mL IV to infuse over 4 hours. The nurse should set the IV infusion pump to deliver how many mL/hr> -Volume (mL)/Time (hr) = X -500 mL/5hr = 125 mL/hr IV therapy: Medication administration Know -Right Patient -Right drug -Right Dose -Right Time -Right Route Arthoplasty: Pain control Analgesics - opiods (epidural, PCA, IV, Oral) NSAIDS Continuous peripheral nerve block Ice or cold therapy to reduce swelling Head of bed slightly elevated and the affected leg in a neutral position. place a pillow or abduction device between the legs when turning to the unaffectedNe side Pain management: PCA Small frequent dosing ensure consistent plasma levels Morphine and Dilaudid Let nurse know if the pump doesn't control the pain Client is the only person to push the button Pain management: Interventions to promote postoperative recovery Managing acute severe pain with short term around the clock administration of opiods parental route is best for immediate short term relief GI therapeutic procedures: D/C TPN therapy Never abruptly stop TPN, gradually decrease (10%) to allow body adjustment. Monitor vital signs q 4-8 hours GI therapeutic procedures: Shortage of TPN Solution Clients receiving TPN frequently need supplemental regular insulin. Keep dextrose 10% in water at the bedside in case the solution runs out. this minimizes the risk of hypoglycemia Nutrition Assessment: Caring for a client with pancreatitis -increased serum glucose -reduce pancreatic stimulation through NPO; NG tube is inserted to suction gastric contents -snacks high in calories in order to maintain weight ECG and Dysrthymia monitoring: Analyzing ECG Watch for manifestations of dysrhythmias (chest pain, decreased LOC, SOB) and hypoxia. Remove leads, print ECG report and notify the provider ECG and Dysrthymia monitoring: Performing 12 lead ECG Prepare client for 12 lead if prescribed - Position client in supine position with chest exposed - wash skin to remove oils - Attach one electrode to each of the clients extremities by applying electrodes to flat surfaces above the wrist and ankles and the other 6 electrodes to the chest, avoiding chest hair. Instruct client to remain still Neurologic Diagnostic Procedures: Preparing for a lumbar puncture -Instruct client to void before procedure and have them stretch over an overbed table if sitting is preferred - Monitor the puncture site for several hours to ensure the site clots and to decrease the risk of post lumbar puncture headaches COPD: Expected ABG results Hypoxemia (decreased PaO2, less than 80) Hypercarbia (increased PaO2, greater than 45) Respiratory acidosis, metabolic alkalosis compensation Hematologic Diagnostic Procedures: Laboratory findings to report RBC: 4.2-5.4 and 4.7-6.1 WBC: 5-10,000 Platelets: 150-400,000 Hgb: 12-16 and 14-18 Hct: 37-47% and 42-52% PT: 11-12.5 sec aPPT: 1.5-2 times normal range of 30-40 INR: 2-3 on warfarin Acid base imbalance: Interpreting ABG results 1) Look at pH <7.35 acidosis >7.45 Alkalosis 2) PaCo2 and HCO3 <35 or >45 PaCO2 is respiratory <22 or >26 is metabolic Diabetes Mellitus Management: Evaluating Glycemic Control Monitor with HbA1c expected reference range is 4-6% acceptable target for clients with diabetes 6.5-8% indicator of average blood glucose for the past 120 days Electrolyte Imabalances: Increasing the risk for digoxin toxicity Hypokalemia and client receiving digoxin increases the risk for digoxin toxicity Respiratory Diagnostic Procedures: Client positioning for thoracentesis Position the client sitting upright with his arms and shoulders raised and supported on pillows and/or on an overbed table and with his feet and legs well supported Hepatitis and Cirrhosis: Client positioning following a biopsy Assist the client into a supine position with the upper right quadrant of the abdomen exposed Cushing Disease/ Syndrome: Priority Actions Daily weights Monitor I&O assess for hypervolemia monitor for skin breakdown Fractures and Immobilization devices: Assessing for complications (795) Fat embolism: Dyspnea, chest pain and decreased oxygen saturation Decreased mental acuity Respiratory distress Tachycardia Tachypnea Fever Osteomyelitis: Constant bone pain Edema Fever Possible elevated sedimentation rate Gastrointestinal Therapeutic Procedures: Ostomy complications Necrosis: pale pink or bluish/purple in color intestinal obstruction: abdominal pain, absent bowel sounds, distention, n/v Burns: Priority action during resuscitation phase Maintain airway and ventilation rapid fluid resuscitation (0.9% NaCl or LR's) Inflammatory Disorders: Assessing a client who has a friction rub Assess lung sounds in all fields Friction rub occurs from -Pericarditis -Myocarditis -Rheumatic endocarditis Diabetes mellitus management: Recognizing Hypoglycemia Confusion Shaking (tremors) Hunger Diaphoresis Tachycardia Meningitis: Assessing for client findings - Constant Headache -Stiff neck - Photophobia - Fever and chills - Nausea and vomiting - Altered LOC - Positive Kernigs and Brudzinski's signs Peripheral Vascular Diseases: Arterial Revascularization used for severe claudication and or limb pain at rest - maintain adequate circulation - check pedal and dorsalis pulse -Note color, temperature, sensation and cap refill Diagnostic and therapeutic procedures for female reproductive disorders: Discharge teaching for abdominal hysterectomy well balanced diet (high in protein) Hormonal therapy restrict activity for as long as 6 weeks avoid use of tampons look for foul smelling drainage and temp > 100F Arthroplasty: Preventing complications following hip arthoplasty Follow position restrictions to avoid dislocation - use elevated seating - straight chairs with arms - abduction pillow or a pillow between client legs - externally rotate toes Cancer disorders: client teaching following partial glossectomy -Client need for alternate communication following surgery -head of bed elevated to reduce edema -report leakage of fluid from the suture line or swallowing difficulty -thicken liquids -frequent oral hygiene Meningitis: Planning interventions for care (53) -Isolate client as soon as meningitis is expected -Implement fever reduction measures -report to public health department -Bed rest with HOB 30 degrees -Provide quiet environment and minimize exposure to bright light -Avoid coughing and sneezing which increased ICP -Maintain safety and seizure precautions Chest tube insertion and monitoring: Maintaining drainage system First Chamber: Drainage collection Second Chamber: Water seal Third Chamber: Suction control Position client in semi-fowlers to high-fowlers position to promote optimal lung expansion - Tidaling with movement is expected in the water seal chamber - Cessation of tidaling in the water seal chamber signals lung reexpansion - Continuous bubbling in the water seal chamber (air leak finding) Diabetes Mellitus Management: Sick Day Management Monitor blood glucose every 3-4 hours Continue to take insulin or oral hypoglycemia agents consume 4oz sugar free liquid every 30 minutes meet carb needs with soft foods Test urine for ketones Head Injury: indications of increased intracranial pressure -Severe headache - Deteriorating LOC - Dilated, pinpoint or asymmetric pupils - Alteration in breathing pattern - Abnormal posturing - cerebrospinal fluid leakage Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis: Intervening for decreased dialysate flow rate -Reposition client -milk tubing -check tubing for kinks or closed clamps -Tell client to avoid constipation by taking stool softeners and consuming a diet high in fiber Respiratory management and mechanical ventilation: caring for a client who has an ET tube Maintain a patent airway -assess the position and placement of tube - Suction oral and tracheal secretions to maintain tube patency - Soft wrist restraints - Maintain cuff pressure below 20mm Hg TB: Discharge teaching about TB -Continue medication therapy for its full duration of 6-12 months -continue with follow-up care for 1 year -Sputum samples every 2-4 weeks, no longer contagious after 3 neg samples -proper hand hygiene -wear N95 Electrolyte imbalances: Treatment of hypokalemia IV potassium supplement Never administer IV bolus Encourage foods high in K Fluid imbalances: Assessment findings Hypo: Increased Hct Increased urine specific gravity increased serum sodium Hyper: Decreased Hct Normal sodium decreased electrolytes, BUN and creatinine Respiratory alkalosis Fluid Imbalances: Clinical manifestations of hypervolemia Tachycardia bounding pulse hypertension muscle weakness headache ascites orthopnea crackeles distended neck veins Fluid Imbalances: Clinical manifestations of Dehydration Hyperthermia tachycardia thready pulse hypotension decreased CVP tachypneic hypoxia dizziness syncope confusion thirst decreased cap refill Hyperthyroidism: Caring for a client following a thyroidectomy Client in high fowlers position, support head and neck with pillow and avoid neck extension check surgical site for excessive bleeding have trach supplies immediately available Hypocalcemia can occur [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 33 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 01, 2021
Number of pages
33
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 01, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
57


.png)




















.png)











